The Role of Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer in the Setting of Hip Prosthesis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
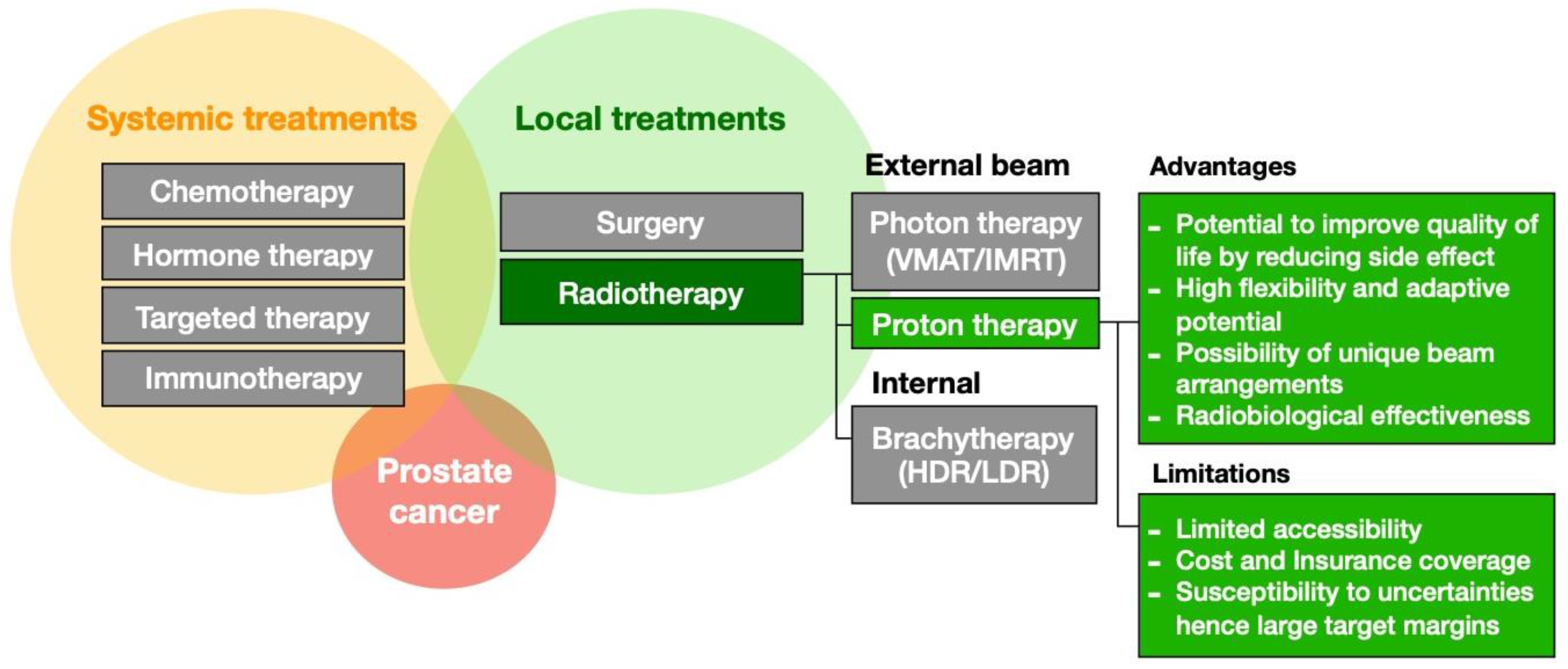
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Treatment Planning and Robustness Evaluation
2.3. LET Modeling
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dosimetric and Outcome Comparison
3.2. Robustness Comparison
3.3. LET-Weighted Dose to Urethra for PArc
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| AoL | Anterior oblique lateral |
| LET | Linear energy transfer |
| LETd | Dose-averaged linear energy transfer |
| MCO | Multicriteria optimization |
| NTCP | Normal tissue complication probability |
| OAR | Organ at risk |
| PArc | Proton arc therapy |
| PSA | Prostate-specific antigen |
| PT | Proton therapy |
| RBE | Relative biological effectiveness |
| RT | Radiation therapy |
| VMAT | Volumetric modulated arc therapy |
References
- American Cancer Society’s (ACS) Publication, Cancer Facts & Figures. 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/annual-cancer-facts-and-figures/2023/2023-cancer-facts-and-figures.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- National Cancer Institute. Prostate Cancer Treatment (PDQ). 2023. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/prostate/hp/prostate-treatment-pdq (accessed on 25 December 2023).
- Meijer, T.W.H.; Scandurra, D.; Langendijk, J.A. Reduced radiation-induced toxicity by using proton therapy for the treatment of oropharyngeal cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musielak, M.; Suchorska, W.M.; Fundowicz, M.; Milecki, P.; Malicki, J. Future Perspectives of Proton Therapy in Minimizing the Toxicity of Breast Cancer Radiotherapy. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, B.C.; Mitra, N.; Harton, J.G.; Xiao, Y.; Wojcieszynski, A.P.; Gabriel, P.E.; Zhong, H.; Geng, H.; Doucette, A.; Wei, J.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Proton vs. Photon Therapy as Part of Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiotto, M.T.; McGovern, S.L.; Gunn, G.B.; Grosshans, D.; McAleer, M.F.; Frank, S.J.; Paulino, A.C. Proton Radiotherapy to Reduce Late Complications in Childhood Head and Neck Cancers. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2021, 8, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstathiou, J. Proton Therapy versus IMRT for Low or Intermediate Risk Prostate Cancer (PARTIQoL). Published 12 June 2012, Updated 9 January 2018. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01617161 (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Kooy, H.M.; Grassberger, C. Intensity modulated proton therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2015, 88, 20150195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, F.; Matter, M.; Nenoff, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lomax, A. Online daily adaptive proton therapy. Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unkelbach, J.; Botas, P.; Giantsoudi, D.; Gorissen, B.L.; Paganetti, H. Reoptimization of Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy Plans Based on Linear Energy Transfer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 96, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabe-Fernandez, A.; Bertolet-Reina, A.; Karagounis, I.; Huynh, K.; Dale, R.G. Is there a role for arcing techniques in proton therapy? Br. J. Radiol. 2020, 93, 20190469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenderfer, E.S.; Sørensen, B.S.; Mazal, A.; Carlson, D.J. The current status of preclinical proton FLASH radiation and future directions. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 2039–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maradit Kremers, H.; Larson, D.R.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Washington, R.E.; Steiner, C.A.; Jiranek, W.A.; Berry, D.J. Prevalence of Total Hip and Knee Replacement in the United States. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2015, 97, 1386–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reft, C.; Alecu, R.; Das, I.J.; Gerbi, B.J.; Keall, P.; Lief, E.; Mijnheer, B.J.; Papanikolaou, N.; Sibata, C.; Van Dyk, J. Dosimetric considerations for patients with HIP prostheses undergoing pelvic irradiation. Report of the AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 63. Med. Phys. 2003, 30, 1162–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, D.; Xhaferllari, I.; Liu, M.; Liang, J.; Knill, C.; Nandalur, S.; Gustafson, G.; Lack, D. Evaluation of VMAT Planning Strategies for Prostate Patients with Bilateral Hip Prosthesis. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211038490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Brunt, J.; Temple, S.; Saipillai, M.; Haridass, A.; Wong, H.; Malik, Z.; Eswar, C. Volumetric modulated arc therapy in prostate cancer patients with metallic hip prostheses in a UK centre. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2015, 20, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, A.M.; Hoskin, P.J. Radiotherapy-induced toxicity in prostate cancer patients with hip prostheses. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, R.; Kumar, M.; Cheruliyil, S.; Jayakumar, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Cramb, J. Volumetric modulated arc therapy for prostate cancer patients with hip prosthesis. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2013, 18, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunishima, N.; Naoi, Y.; Yoda, K. Anatomy-based volumetric modulated arc therapy for a prostate cancer patient with a hip prosthesis. J. Radiat. Res. 2013, 54, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.B.; Pokharel, S. A dosimetric study of volumetric modulated arc therapy planning techniques for treatment of low-risk prostate cancer in patients with bilateral hip prostheses. South. Asian J. Cancer. 2014, 3, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, X.; Qin, A.; Zhou, J.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Krauss, D.; Kabolizdeh, P. Have we reached proton beam therapy dosimetric limitations?—A novel robust, delivery-efficient and continuous spot-scanning proton arc (SPArc) therapy is to improve the dosimetric outcome in treating prostate cancer. Acta Oncol. 2018, 57, 435–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Fan, K.H. Proton therapy for prostate cancer: Current state and future perspectives. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, G.; Janssens, G.; De Wilde, O.; Bossier, V.; Lerot, X.; Pouppez, A.; Yan, D.; Stevens, C.; Kabolizadeh, P.; et al. The first prototype of spot-scanning proton arc treatment delivery. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 137, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rechner, L.A.; Howell, R.M.; Zhang, R.; Etzel, C.; Lee, A.K.; Newhauser, W.D. Risk of radiogenic second cancers following volumetric modulated arc therapy and proton arc therapy for prostate cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2012, 57, 7117–7132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, B.A.; Korevaar, E.W.; Maring, A.; Werkman, C.I.; Scandurra, D.; Janssens, G.; Both, S.; Langendijk, J.A. Proton arc therapy increases the benefit of proton therapy for oropharyngeal cancer patients in the model based clinic. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 184, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Cheng, C.; Zheng, Y.; Hsi, W.; Zeidan, O.; Schreuder, N.; Vargas, C.; Larson, G. Dosimetric study of uniform scanning proton therapy planning for prostate cancer patients with a metal hip prosthesis, and comparison with volumetric-modulated arc therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2014, 15, 4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuaron, J.J.; Harris, A.A.; Chon, B.; Tsai, H.; Larson, G.; Hartsell, W.F.; Hug, E.; Cahlon, O. Anterior-oriented proton beams for prostate cancer: A multi-institutional experience. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polf, J.C.; Chuong, M.; Zhang, B.; Mehta, M. Anteriorly oriented beam arrangements with daily in vivo range verification for proton therapy of prostate cancer: Rectal toxicity rates. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2016, 2, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moteabbed, M.; Trofimov, A.; Sharp, G.C.; Wang, Y.; Zietman, A.L.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Lu, H.M. Proton therapy of prostate cancer by anterior-oblique beams: Implications of setup and anatomy variations. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 1644–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Suzuki, T.; Sugama, Y.; Marino, K.; Sano, N.; Komiyama, T.; Aoki, S.; Maehata, Y.; Yoshizawa, K.; Ashizawa, K.; et al. Comparison of rectal dose reduction by a hydrogel spacer among 3D conformal radiotherapy, volumetric-modulated arc therapy, helical tomotherapy, CyberKnife and proton therapy. J. Radiat. Res. 2020, 61, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadhum, M.; Boman, E.; Rossi, M. The robustness of prostate radiotherapy for patients with hip prosthesis. Med. Dosim. 2021, 46, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccarelli, M.J.; Krafft, S.P.; Briere, T.M.; Svensson, S.; Han, E.Y. Evaluation of RayStation’s delivered dose and accumulated dose features for spine stereotactic radiotherapy. Med. Dosim. 2023, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganetti, H. Relative biological effectiveness (RBE) values for proton beam therapy. Variations as a function of biological endpoint, dose, and linear energy transfer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2014, 59, R419–R472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataria, T.; Gupta, D.; Goyal, S.; Bisht, S.S.; Chaudhary, R.; Narang, K.; Banerjee, S.; Basu, T.; Abhishek, A.; Sambasivam, S.; et al. Simple diagrammatic method to delineate male urethra in prostate cancer radiotherapy: An MRI based approach. Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20160348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.; Savjani, R.R.; Gao, Y.; Cao, M.; Hu, P.; Sheng, K.; Low, D.A.; Steinberg, M.; Kishan, A.U.; Yang, Y. Evaluation of T2-Weighted MRI for Visualization and Sparing of Urethra with MR-Guided Radiation Therapy (MRgRT) On-Board MRI. Cancers. 2021, 13, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Shin, J.; Verburg, J.M.; Bobić, M.; Winey, B.; Schuemann, J.; Paganetti, H. MOQUI: An open-source GPU-based Monte Carlo code for proton dose calculation with efficient data structure. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 174001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The R Project for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 5 August 2023).
- Pedersen, J.; Liang, X.; Bryant, C.; Mendenhall, N.; Li, Z.; Muren, L.P. Normal tissue complication probability models for prospectively scored late rectal and urinary morbidity after proton therapy of prostate cancer. Phys. Imaging Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 20, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, A.L.K.; Knight, K.; Panettieri, V.; Dimmock, M.; Tuan, J.K.L.; Tan, H.Q.; Wright, C. Predictive modelling for late rectal and urinary toxicities after prostate radiotherapy using planned and delivered dose. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1084311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ornelas, M.; Carlo Iorio, G.; Bossart, E.; Ricardi, U.; Seldon, C.; Dal Pra, A.; Butkus, M. Bone marrow sparing in prostate cancer patients treated with Post-operative pelvic nodal radiotherapy—A proton versus photon comparison. Phys. Med. 2023, 112, 102644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, R.C.; Hoppe, B.S.; Ho, M.W.; Martinez, H.; Henderson, R.H.; Marcus, R.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Costa, J.A.; Williams, C.R.; Mendenhall, N.P. Safety of proton therapy treatment for prostate cancer patients with unilateral hip replacements. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29 (Suppl. S7), 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakusagi, Y.; Takayama, Y.; Kusano, Y.; Koge, H.; Kano, K.; Shima, S.; Tsuchida, K.; Mizoguchi, N.; Yoshida, D.; Kamada, T.; et al. Carbon-Ion Radiotherapy Using Metal Artifact Reduction Computed Tomography in a Patient with Prostate Cancer with Bilateral Hip Prostheses: A Case Report. Case Rep. Oncol. 2022, 15, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolstad, K.; Flatabø, S.; Aadnevik, D.; Dalehaug, I.; Vetti, N. Metal artifact reduction in CT, a phantom study: Subjective and objective evaluation of four commercial metal artifact reduction algorithms when used on three different orthopedic metal implants. Acta Radiol. 2018, 59, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieminski, S.; Khandekar, M.; Wang, Y. Assessment of multi-criteria optimization (MCO) for volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) in hippocampal avoidance whole brain radiation therapy (HA-WBRT). J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2018, 19, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| CTV70 V68.8 (%) | CTV50 V49 (%) | Bladder V39 (%) | Bladder V61 (%) | Rectum V35 (%) | Rectum V61 (%) | Femoral Head V39 (%) | Penile Bulb Dmean (Gy) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | 99 | 95 | 50 | 20 | 40 | 15 | 5 | 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moteabbed, M.; Bobić, M.; Paganetti, H.; Efstathiou, J.A. The Role of Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer in the Setting of Hip Prosthesis. Cancers 2024, 16, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020330
Moteabbed M, Bobić M, Paganetti H, Efstathiou JA. The Role of Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer in the Setting of Hip Prosthesis. Cancers. 2024; 16(2):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020330
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoteabbed, Maryam, Mislav Bobić, Harald Paganetti, and Jason A. Efstathiou. 2024. "The Role of Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer in the Setting of Hip Prosthesis" Cancers 16, no. 2: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020330
APA StyleMoteabbed, M., Bobić, M., Paganetti, H., & Efstathiou, J. A. (2024). The Role of Proton Therapy for Prostate Cancer in the Setting of Hip Prosthesis. Cancers, 16(2), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16020330






