The Applications of Machine Learning in the Management of Patients Undergoing Stem Cell Transplantation: Are We Ready?
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Hematopoietic Stem Cells Transplantation: Background
1.2. Current Challenges in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
1.3. The Emerging Role of Machine Learning in Medicine
2. Machine Learning Overview
3. Machine Learning Applied to HSCT
3.1. Decision Support
3.1.1. Diagnosis
3.1.2. Donor Selection
3.2. Mortality/Relapse Prediction
3.3. Post-HSCT Complications
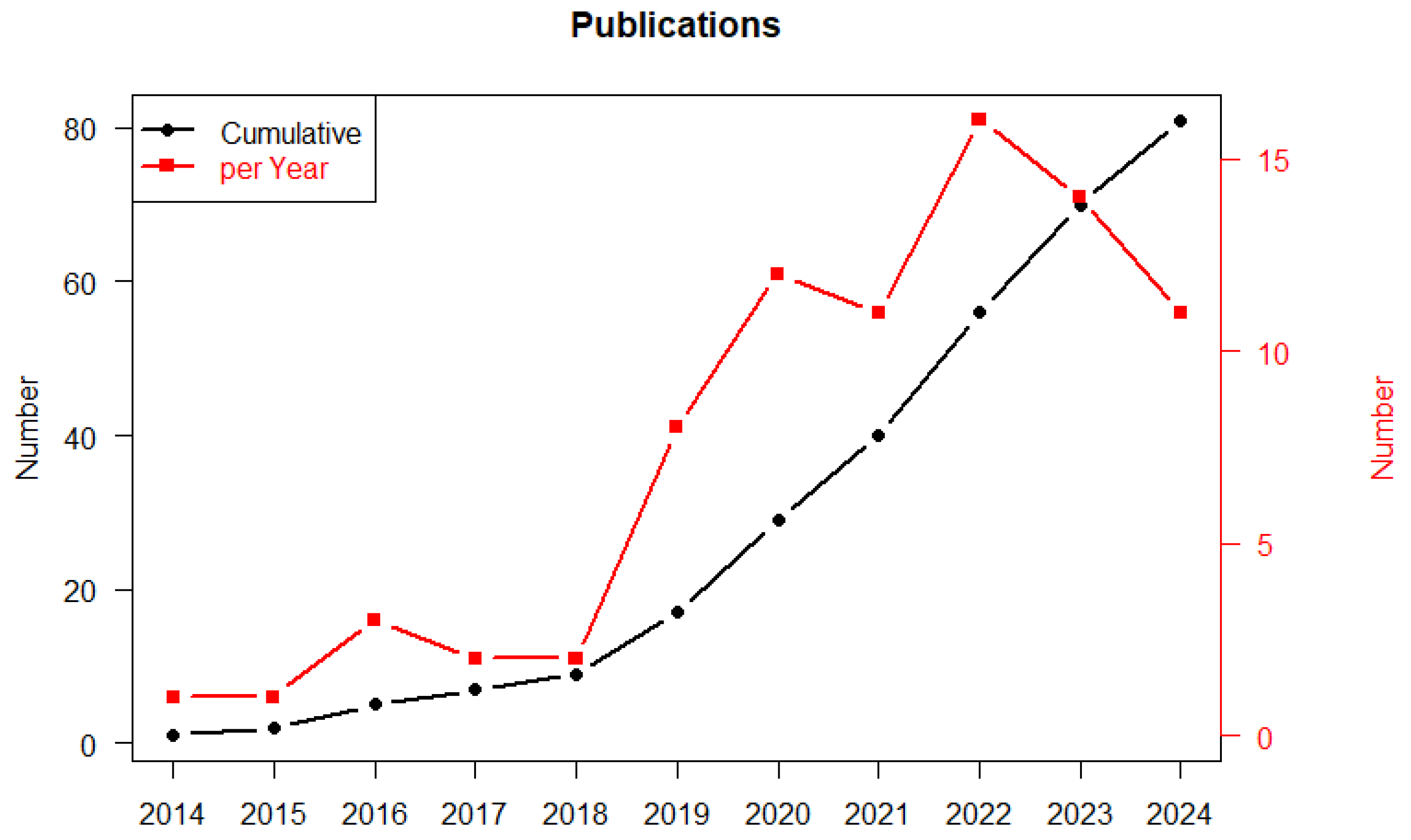
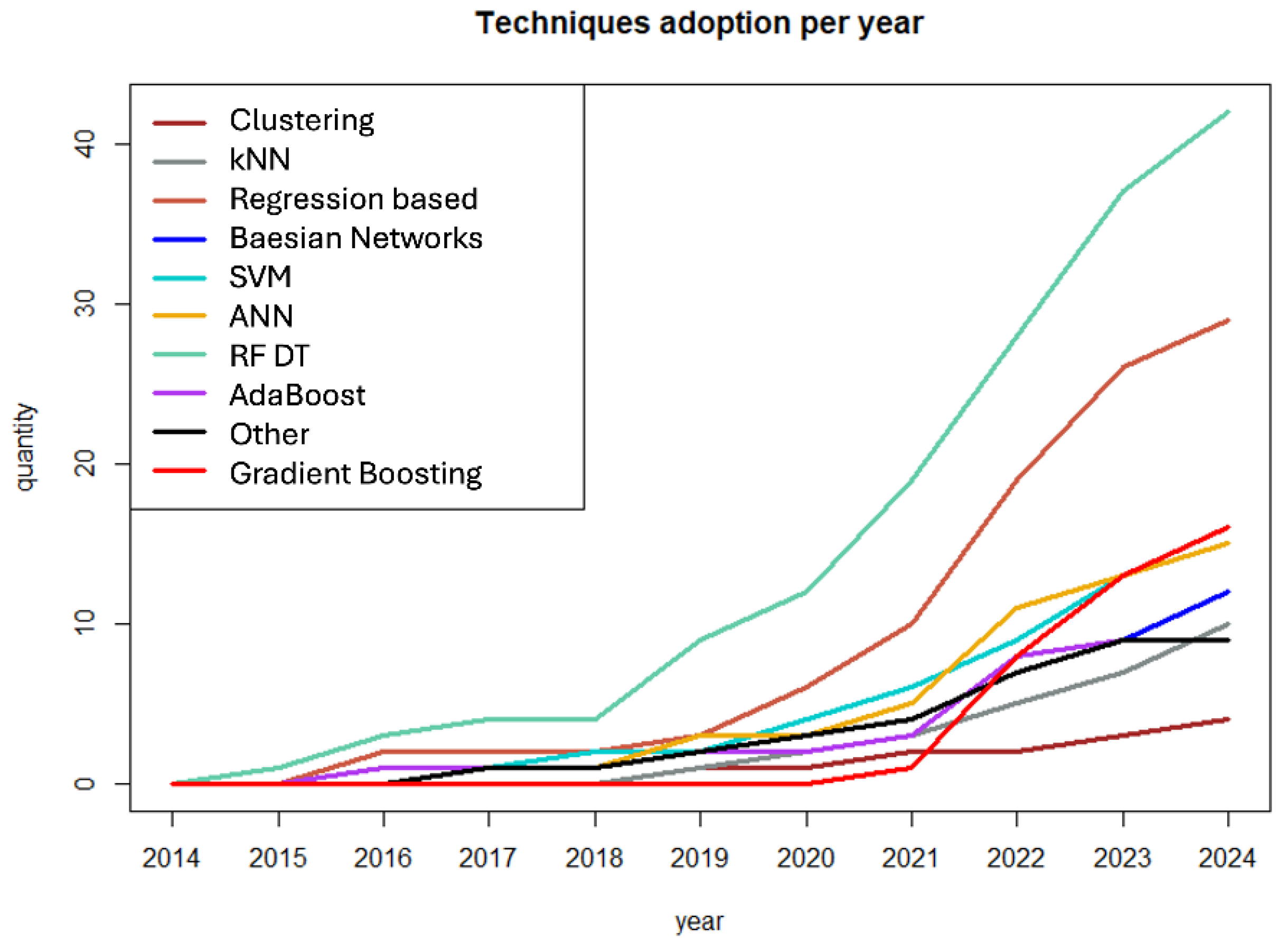
3.4. Evolution of ML Application and Techniques During the Time Period
4. Challenges and Limitations
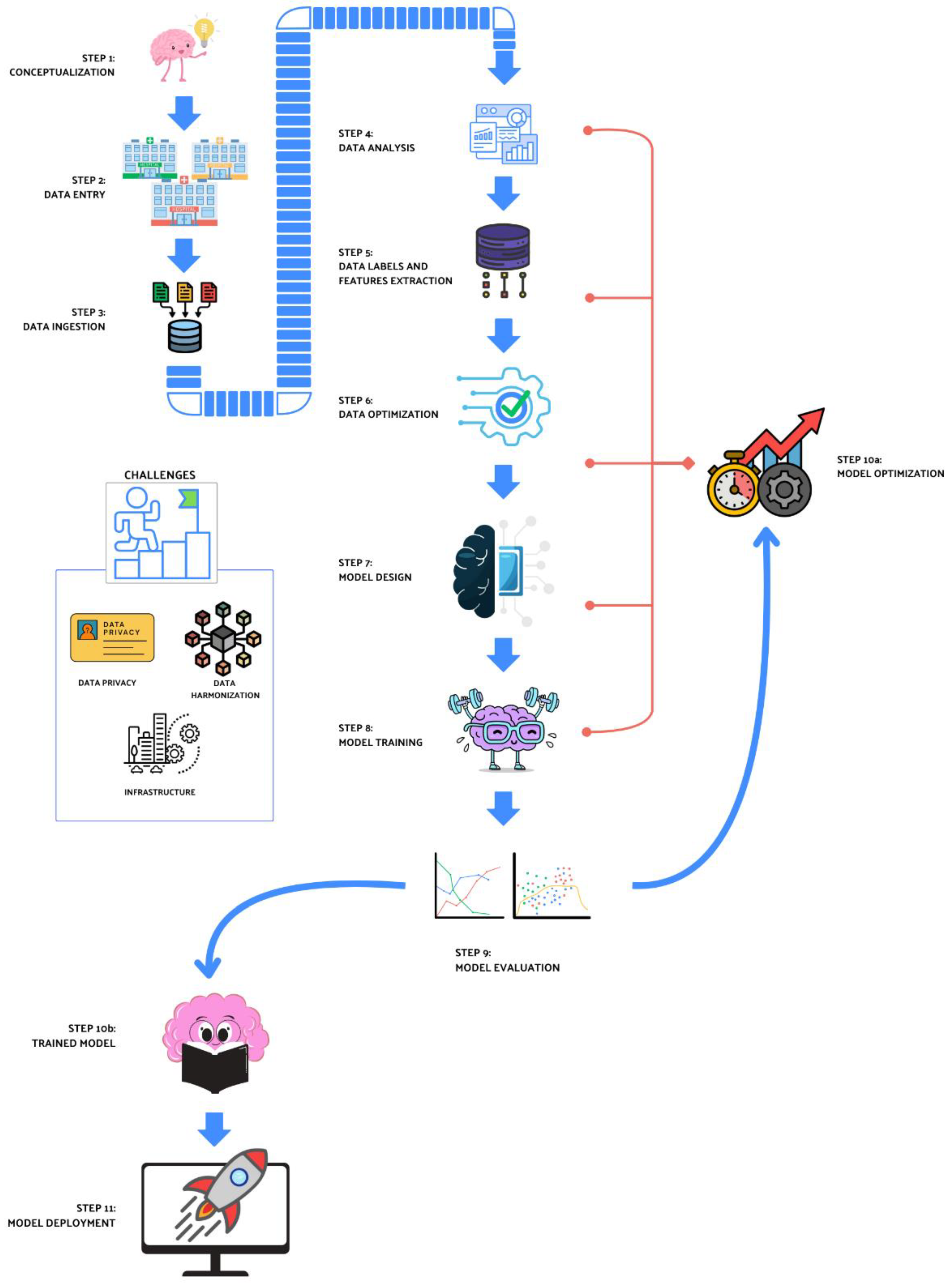
5. Not Only Models: Infrastructures, Legal Issues, and Data Harmonization
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, T.; Greco, R. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapies for autoimmune diseases: Overview and future considerations from the Autoimmune Diseases Working Party (ADWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022, 57, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polverelli, N.; Farina, M.; D’Adda, M.; Damiani, E.; Grazioli, L.; Leoni, A.; Malagola, M.; Bernardi, S.; Russo, D. How We Manage Myelofibrosis Candidates for Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cells 2022, 11, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lougaris, V.; Malagola, M.; Baronio, M.; Morello, E.; Gazzurelli, L.; Benvenuto, A.; Palumbo, L.; Moratto, D.; Girelli, M.F.; Chiarini, M.; et al. Successful hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for complete CTLA-4 haploinsufficiency due to a de novo monoallelic 2q33.2-2q33.3 deletion. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 220, 108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, R.G.; Ramezani, A.; Hawley, T.S. Hematopoietic stem cells. Methods Enzym. 2006, 419, 149–179. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A. Pattern of bone marrow regeneration following chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. J. Med. 1987, 18, 108–122. [Google Scholar]
- Copelan, E.A. Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipovich, A.H.; Weisdorf, D.; Pavletic, S.; Socie, G.; Wingard, J.R.; Lee, S.J.; Martin, P.; Chien, J.; Przepiorka, D.; Couriel, D.; et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2005, 11, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justiz Vaillant, A.A.; Modi, P.M.O. Graft-Versus-Host Disease; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538235/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Luo, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lai, X.; Zheng, W.; Shi, J.; Zheng, G.; Huang, H. Clinical Outcomes of Haploidentical Donor Compared with Unrelated and HLA-Matched Related Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2012, 120, 4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrack, B.; Saccardi, R.; Alexander, T.; Badoglio, M.; Burman, J.; Farge, D.; Greco, R.; Jessop, H.; Kazmi, M.; Kirgizov, K.; et al. Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation and other cellular therapy in multiple sclerosis and immune-mediated neurological diseases: Updated guidelines and recommendations from the EBMT Autoimmune Diseases Working Party (ADWP) and the Joint Acc. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 283–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurkocza, B.; Sandmaier, B.M. Conditioning regimens for hematopoietic cell transplantation: One size does not fit all. Blood 2014, 124, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Labopin, M.; Bondi, O.; Mishan-Shamay, H.; Shimoni, A.; Ciceri, F.; Esteve, J.; Giebel, S.; Gorin, N.C.; Schmid, C.; et al. Prediction of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Mortality 100 Days After Transplantation Using a Machine Learning Algorithm: A European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Acute Leukemia Working Party Retrospective Data Mining Stud. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3144–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, S.; Vallati, M.; Gatta, R. Artificial Intelligence-Based Management of Adult Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Where Are We and Where Are We Going? Cancers 2024, 16, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schork, N.J. Artificial Intelligence and Personalized Medicine. Cancer Treat. Res. 2019, 178, 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.; Braun, T.M.; Chowdhury, M.; Tewari, M.; Choi, S.W. A Systematic Review of Machine Learning Techniques in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT). Sensors 2020, 20, 6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.I.; Celik, S.; Logsdon, B.A.; Lundberg, S.M.; Martins, T.J.; Oehler, V.G.; Estey, E.H.; Miller, C.P.; Chien, S.; Dai, J.; et al. A machine learning approach to integrate big data for precision medicine in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.M. Introduction to Probability and Statistics for Engineers and Scientists; Press, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Russel, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach; Pearson and M. Education Limited: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Özesmi, S.L.; Özesmi, U. An artificial neural network approach to spatial habitat modelling with interspecific interaction. Ecol. Modell. 1999, 116, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, O.K.; Porwit, A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Foucar, K.; Duncavage, E.J.; Arber, D.A. The International Consensus Classification of acute myeloid leukemia. Virchows Arch. 2023, 482, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandradevan, R.; Aljudi, A.A.; Drumheller, B.R.; Kunananthaseelan, N.; Amgad, M.; Gutman, D.A.; Cooper, L.A.D.; Jaye, D.L. Machine-based detection and classification for bone marrow aspirate differential counts: Initial development focusing on nonneoplastic cells. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, S.J.; Locker, J.; Oliveri, D.R.; Shekhter-Levin, S.; Redner, R.L.; Penchansky, L.; Gollin, S.M. A non-classical translocation involving 17q12 (retinoic acid receptor alpha) in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APML) with atypical features. Leukemia 1994, 8, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Tsuzuki, S.; Tsuzuki, M.; Handa, K.; Inaguma, Y.; Emi, N. BCOR as a novel fusion partner of retinoic acid receptor alpha in a t(X;17)(p11;q12) variant of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood 2010, 116, 4274–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najfeld, V.; Scalise, A.; Troy, K. A new variant translocation 11;17 in a patient with acute promyelocytic leukemia together with t(7;12). Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1989, 43, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, P.; Sharma, S.; Sreedharanunni, S.; Sharma, P.; Sachdeva, M.U.S.; Jain, R.; Naseem, S.; Trehan, A.; Varma, N. Myeloperoxidase Deficient Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia: Report of Two Cases. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2018, 34, 372–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheli, E.; Chevalier, S.; Kosmider, O.; Eveillard, M.; Chapuis, N.; Plesa, A.; Heiblig, M.; Andre, L.; Pouget, J.; Mossuz, P.; et al. Diagnosis of acute promyelocytic leukemia based on routine biological parameters using machine learning. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, R.G.; Esserman, D.; Beste, L.A.; Ong, S.Y.; Colomb, D.G.; Bhargava, A.; Wadia, R.; Rose, M.G. A Machine Learning Model to Successfully Predict Future Diagnosis of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia with Retrospective Electronic Health Records Data. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 156, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Aberdeen, A.; Theissen, H.; Sousos, N.; Psaila, B.; Mead, A.J.; Turner, G.D.H.; Rees, G.; Rittscher, J.; Royston, D. Artificial intelligence-based morphological fingerprinting of megakaryocytes: A new tool for assessing disease in MPN patients. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Ai, T.; Horiuchi, Y.; Matsuzaki, A.; Nishibe, K.; Marutani, S.; Saito, K.; Kaniyu, K.; Takehara, I.; Uchihashi, K.; et al. Automated diagnostic support system with deep learning algorithms for distinction of Philadelphia chromosome-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms using peripheral blood specimen. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, T.M.; Allen, T.D.; Lajtha, L.G. Conditions controlling the proliferation of haemopoietic stem cells in vitro. J. Cell Physiol. 1977, 91, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, B.I.; Testa, N.G.; Hendry, J.H. The relative spatial distributions of CFUs and CFUc in the normal mouse femur. Blood 1975, 46, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.K. Endosteal marrow: A rich source of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 1978, 199, 1443–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahata, T.; Ogawa, M. Hemopoietic colony-forming cells in umbilical cord blood with extensive capability to generate mono- and multipotential hemopoietic progenitors. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 70, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.S.; Horvath, J.D.C.; Pereira, M.P.; David, C.N.; Vargas, D.F.; Rigoni, L.D.C.; Sartor, I.T.S.; Kern, L.B.; da Silva, P.O.; Paz, A.A.; et al. Impact of waitlist time on post-HSCT survival: A cohort study at a hospital in southern Brazil. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2024, 46, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passweg, J.R.; Baldomero, H.; Ciceri, F.; Corbacioglu, S.; de la Cámara, R.; Dolstra, H.; Glass, B.; Greco, R.; McLornan, D.P.; Neven, B.; et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation and cellular therapies in Europe 2021. The second year of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. A Report from the EBMT Activity Survey. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2023, 58, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atsuta, Y.; Baldomero, H.; Neumann, D.; Sureda, A.; DeVos, J.D.; Iida, M.; Karduss, A.; Purtill, D.; Elhaddad, A.M.; Bazuaye, N.G.; et al. Continuous and differential improvement in worldwide access to hematopoietic cell transplantation: Activity has doubled in a decade with a notable increase in unrelated and non-identical related donors. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3282–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, M.M.; Gale, R.P.; Sondel, P.M.; Goldman, J.M.; Kersey, J.; Kolb, H.J.; Rimm, A.A.; Ringdén, O.; Rozman, C.; Speck, B. Graft-versus-leukemia reactions after bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1990, 75, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Polverelli, N.; Malagola, M.; Farina, M.; Leoni, A.; Bernardi, S.; Mammoliti, S.; Sacchi, N.; Martino, M.; Ciceri, F.; et al. Changes in Stem Cell Transplant activity and procedures during SARS-CoV2 pandemic in Italy: An Italian Bone Marrow Transplant Group (GITMO) nationwide analysis (TransCOVID-19 Survey). Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021, 56, 2272–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagola, M.; Polverelli, N.; Gandolfi, L.; Zollner, T.; Bernardi, S.; Zanaglio, C.; Re, F.; Morello, E.; Turra, A.; Isidori, A.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Pandemia: Facts and Perspectives in a Bone Marrow Transplant Unit. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, N.; Zabelina, T.; de Wreede, L.; Berger, J.; Alchalby, H.; van Biezen, A.; Milpied, N.; Volin, L.; Mohty, M.; Leblond, V.; et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation for older advanced MDS patients: Improved survival with young unrelated donor in comparison with HLA-identical siblings. Leukemia 2013, 27, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guru Murthy, G.S.; Kim, S.; Hu, Z.H.; Estrada-Merly, N.; Abid, M.B.; Aljurf, M.; Bacher, U.; Badawy, S.M.; Beitinjaneh, A.; Bredeson, C.; et al. Relapse and Disease-Free Survival in Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Using Older Matched Sibling Donors vs Younger Matched Unrelated Donors. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israeli, S.; Maiers, M.; Louzoun, Y. Limited Contribution of Donor Characteristics to One-Year Survival After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Transpl. Cell Ther. 2022, 28, 843.e1–843.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.S. Secondary recurrent miscarriage and H-Y immunity. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2011, 17, 558–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungman, P.; Brand, R.; Hoek, J.; de la Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Einsele, H.; Styczynski, J.; Ward, K.N.; Cesaro, S.; Transplantation, I.D.W.P. of the E.G. for B.; et al. Donor cytomegalovirus status influences the outcome of allogeneic stem cell transplant: A study by the European group for blood and marrow transplantation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, A.; Williamson, T.; Daly, A.; Savoie, M.L.; Stewart, D.A.; Khan, F.; Storek, J. Impact of Donor and Recipient Cytomegalovirus Serostatus on Outcomes of Antithymocyte Globulin-Conditioned Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2016, 22, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, M.; Bernardi, S.; Gandolfi, L.; Zanaglio, C.; Morello, E.; Turra, A.; Zollner, T.; Gramegna, D.; Rambaldi, B.; Cattina, F.; et al. Case Report: Late Onset of Myelodysplastic Syndrome From Donor Progenitor Cells After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Which Lessons Can We Draw From the Reported Case? Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 564521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattina, F.; Bernardi, S.; Mantovani, V.; Toffoletti, E.; Santoro, A.; Pastore, D.; Martino, B.; Console, G.; Martinelli, G.; Malagola, M. Single step multiple genotyping by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry, for evaluation of minor histocompatibility antigens in patients submitted to allogeneic stem cell transplantation from HLA-matched related and unrelated donor. Hematol. Rep. 2017, 9, 7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadsworth, K.; Albrecht, M.; Fonstad, R.; Spellman, S.; Maiers, M.; Dehn, J. Unrelated donor search prognostic score to support early HLA consultation and clinical decisions. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016, 51, 1476–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan, B.R.; Maiers, M.J.; Sparapani, R.A.; Laud, P.W.; Spellman, S.R.; McCulloch, R.E.; Shaw, B.E. Optimal Donor Selection for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Using Bayesian Machine Learning. JCO Clin. Cancer Inf. 2021, 5, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buturovic, L.; Shelton, J.; Spellman, S.R.; Wang, T.; Friedman, L.; Loftus, D.; Hesterberg, L.; Woodring, T.; Fleischhauer, K.; Hsu, K.C.; et al. Evaluation of a Machine Learning-Based Prognostic Model for Unrelated Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Donor Selection. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2018, 24, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, Y.; Komukai, S.; Kitamura, T.; Sobue, T.; Kurosawa, S.; Doki, N.; Katayama, Y.; Ozawa, Y.; Matsuoka, K.I.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Identifying the optimal conditioning intensity for stem cell transplantation in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: A machine learning analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2023, 58, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Kim, H.T.; Logan, B.R.; Wang, Z.; Alyea, E.P.; Kalaycio, M.E.; Maziarz, R.T.; Antin, J.H.; Soiffer, R.J.; Weisdorf, D.J.; et al. Validation and refinement of the Disease Risk Index for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2014, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Bonifazi, F.; Fein, J.; Boschini, C.; Oldani, E.; Labopin, M.; Raimondi, R.; Sacchi, N.; Dabash, O.; Unger, R.; et al. Validation of the acute leukemia-EBMT score for prediction of mortality following allogeneic stem cell transplantation in a multi-center GITMO cohort. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuse, K.; Uemura, S.; Tamura, S.; Suwabe, T.; Katagiri, T.; Tanaka, T.; Ushiki, T.; Shibasaki, Y.; Sato, N.; Yano, T.; et al. Patient-based prediction algorithm of relapse after allo-HSCT for acute Leukemia and its usefulness in the decision-making process using a machine learning approach. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5058–5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouval, R.; Labopin, M.; Unger, R.; Giebel, S.; Ciceri, F.; Schmid, C.; Esteve, J.; Baron, F.; Gorin, N.C.; Savani, B.; et al. Prediction of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Related Mortality- Lessons Learned from the In-Silico Approach: A European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Acute Leukemia Working Party Data Mining Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, S.R.; Lee, S.M.; Binkowski, T.A.; Wang, T.; Haagenson, M.; Wang, H.L.; Maiers, M.; Spellman, S.; van Besien, K.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Identification of high-risk amino-acid substitutions in hematopoietic cell transplantation: A challenging task. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016, 51, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritari, J.; Hyvärinen, K.; Koskela, S.; Itälä-Remes, M.; Niittyvuopio, R.; Nihtinen, A.; Salmenniemi, U.; Putkonen, M.; Volin, L.; Kwan, T.; et al. Genomic prediction of relapse in recipients of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Leukemia 2019, 33, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazha, A.; Komrokji, R.; Meggendorfer, M.; Jia, X.; Radakovich, N.; Shreve, J.; Hilton, C.B.; Nagata, Y.; Hamilton, B.K.; Mukherjee, S.; et al. Personalized Prediction Model to Risk Stratify Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3737–3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera Orgueira, A.; Perez Encinas, M.M.; Diaz Varela, N.A.; Mora, E.; Díaz-Beyá, M.; Montoro, M.J.; Pomares, H.; Ramos, F.; Tormo, M.; Jerez, A.; et al. Machine Learning Improves Risk Stratification in Myelodysplastic Neoplasms: An Analysis of the Spanish Group of Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, C.; Poonia, S.; Kumar, L.; Sengupta, D. Staging System to Predict the Risk of Relapse in Multiple Myeloma Patients Undergoing Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandelman, J.S.; Byrne, M.T.; Mistry, A.M.; Polikowsky, H.G.; Diggins, K.E.; Chen, H.; Lee, S.J.; Arora, M.; Cutler, C.; Flowers, M.; et al. Machine learning reveals chronic graft-versus-host disease phenotypes and stratifies survival after stem cell transplant for hematologic malignancies. Haematologica 2019, 104, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabyarmohammadi, S.; Leo, P.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Janowczyk, A.; Corredor, G.; Fu, P.; Meyerson, H.; Metheny, L.; Madabhushi, A. Machine Learning to Predict Risk of Relapse Using Cytologic Image Markers in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Posthematopoietic Cell Transplantation. JCO Clin. Cancer Inf. 2022, 6, e2100156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.C.; Li, J.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Ko, B.S.; Tang, J.L.; Lee, C.C. A BLSTM with Attention Network for Predicting Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient’s Prognosis using Comprehensive Clinical Parameters. Annu. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2019, 2019, 2455–2458. [Google Scholar]
- Driessen, J.; Zwezerijnen, G.J.C.; Schöder, H.; Kersten, M.J.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Moskowitz, C.H.; Eertink, J.J.; Heymans, M.W.; Boellaard, R.; Zijlstra, J.M. Prognostic model using 18F-FDG PET radiomics predicts progression-free survival in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 6732–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, M.; Kanda, J.; Arai, Y.; Kondo, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Ueda, Y.; Imada, K.; Akasaka, T.; Yonezawa, A.; Yago, K.; et al. Establishment of a predictive model for GVHD-free, relapse-free survival after allogeneic HSCT using ensemble learning. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2618–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCurdy, S.R.; Radojcic, V.; Tsai, H.L.; Vulic, A.; Thompson, E.; Ivcevic, S.; Kanakry, C.G.; Powell, J.D.; Lohman, B.; Adom, D.; et al. Signatures of GVHD and relapse after posttransplant cyclophosphamide revealed by immune profiling and machine learning. Blood 2022, 139, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehnasab, C.; Hajifathali, A.; Asadi, F.; Parkhideh, S.; Kazemi, A.; Roshanpoor, A.; Mehdizadeh, M.; Tavakoli-Ardakani, M.; Roshandel, E. An Intelligent Clinical Decision Support System for Predicting Acute Graft-versus-host Disease (aGvHD) following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Biomed. Phys. Eng. 2021, 11, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, G.; Wang, J.; Siirtola, P.; Röning, J. Leveraging machine learning for predicting acute graft-versus-host disease grades in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for T-cell prolymphocytic leukaemia. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2024, 24, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, Y.; Kondo, T.; Fuse, K.; Shibasaki, Y.; Masuko, M.; Sugita, J.; Teshima, T.; Uchida, N.; Fukuda, T.; Kakihana, K.; et al. Using a machine learning algorithm to predict acute graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic transplantation. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3626–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Arai, Y.; Kanda, J.; Kondo, T.; Ikegame, K.; Uchida, N.; Doki, N.; Fukuda, T.; Ozawa, Y.; Tanaka, M.; et al. A convolutional neural network-based model that predicts acute graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Commun. Med. 2023, 3, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, S.D.; Gunning, T.S.; Pelliccia, M.; Della Pia, A.; Lee, A.; Behrmann, J.; Bangolo, A.; Jandir, P.; Zhang, H.; Kaur, S.; et al. Using Targeted Transcriptome and Machine Learning of Pre- and Post-Transplant Bone Marrow Samples to Predict Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease and Overall Survival after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2024, 16, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, A.; Gao, F.; Fredricks, D.N.; Pergam, S.A.; Mielcarek, M.; Milano, F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Lee, S.J. Analysis of Antibiotic Exposure and Development of Acute Graft-vs-Host Disease Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2317188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvelier, G.D.E.; Ng, B.; Abdossamadi, S.; Nemecek, E.R.; Melton, A.; Kitko, C.L.; Lewis, V.A.; Schechter, T.; Jacobsohn, D.A.; Harris, A.C.; et al. A diagnostic classifier for pediatric chronic graft-versus-host disease: Results of the ABLE/PBMTC 1202 study. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 3612–3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-López, J.; Fernández, J.L.; Lumbreras, E.; Serrano, J.; Martínez-Losada, C.; Martín, C.; Hernández-Rivas, J.M.; Sánchez-García, J. Machine learning applied to gene expression analysis of T-lymphocytes in patients with cGVHD. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 1668–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partanen, J.; Hyvärinen, K.; Bickeböller, H.; Bogunia-Kubik, K.; Crossland, R.E.; Ivanova, M.; Perutelli, F.; Dressel, R. Review of Genetic Variation as a Predictive Biomarker for Chronic Graft-Versus-Host-Disease After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Liu, Y.; Logan, B.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, Y. Learning the Dynamic Treatment Regimes from Medical Registry Data through Deep Q-network. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Combining serum microRNAs and machine learning algorithms for diagnosing infectious fever after HSCT. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiał, K.; Stojanowski, J.; Miśkiewicz-Bujna, J.; Kałwak, K.; Ussowicz, M. KIM-1, IL-18, and NGAL, in the Machine Learning Prediction of Kidney Injury among Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation-A Pilot Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiał, K.; Stojanowski, J.; Augustynowicz, M.; Miśkiewicz-Migoń, I.; Kałwak, K.; Ussowicz, M. Assessment of Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury with Machine Learning Tools in Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, E.; Park, S.S.; Park, M.S.; Jung, J.; Min, G.J.; Park, S.; Lee, S.E.; Cho, B.S.; Eom, K.S.; et al. Prediction and recommendation by machine learning through repetitive internal validation for hepatic veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome and early death after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022, 57, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.X.; Zhu, X.L.; Zhang, A.B.; He, Y.; Fu, H.X.; Wang, F.R.; Mo, X.D.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. Machine learning algorithm as a prognostic tool for venous thromboembolism in allogeneic transplant patients. Transpl. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 57.e1–57.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Hsu, T.C.; Kuo, C.C.; Liu, M.A.; Abdelfattah, A.M.; Chang, C.N.; Yao, M.; Li, C.C.; Wu, K.H.; Chen, T.C.; et al. Validation of a Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder Risk Prediction Score and Derivation of a New Prediction Score Using a National Bone Marrow Transplant Registry Database. Oncologist 2021, 26, e2034–e2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagola, M.; Rambaldi, B.; Ravizzola, G.; Cattaneo, C.; Borlenghi, E.; Polverelli, N.; Turra, A.; Morello, E.; Skert, C.; Cancelli, V.; et al. Bacterial Blood Stream Infections Negatively Impact on Outcome of Patients Treated with Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: 6 Years Single-Centre Experience. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, e2017036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, L.; Brossette, C.; Rauch, J.; Grandjean, A.; Ottinger, H.; Rissland, J.; Schwarz, U.; Graf, N.; Beelen, D.W.; Kiefer, S.; et al. Time-dependent prediction of mortality and cytomegalovirus reactivation after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation using machine learning. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1309–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Hong, H.Y.; Dong, X.Y.; Xu, L.P.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Yan, C.H.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.H.; Han, W.; et al. Machine learning algorithm as a prognostic tool for Epstein-Barr virus reactivation after haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood Sci. 2023, 5, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, M.L.; Mooney, S.J.; Carone, M.; Althouse, B.M.; Liu, C.; Evans, L.E.; Patel, K.; Vo, P.T.; Pergam, S.A.; Phipps, A.I. Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model to Estimate Bacterial Sepsis Among Immunocompromised Recipients of Stem Cell Transplant. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e214514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montassier, E.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Ward, T.; Corvec, S.; Gastinne, T.; Potel, G.; Moreau, P.; de la Cochetiere, M.F.; Batard, E.; Knights, D. Pretreatment gut microbiome predicts chemotherapy-related bloodstream infection. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Roelofs, E.; Reymen, B.; Velazquez, E.R.; Buijsen, J.; Zegers, C.M.; Carvalho, S.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Nalbantov, G.; Oberije, C.; et al. “Rapid Learning health care in oncology”—An approach towards decision support systems enabling customised radiotherapy’. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 109, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, A.; Vallati, M.; Gatta, R.; Dinapoli, N.; Jochems, A.; Deist, T.; van Soest, J.; Dekker, A.; Valentini, V. Distributed Learning to Protect Privacy in Multi-Centric Clinical Studies BT—Artificial Intelligence in Medicine; Holmes, J.H., Bellazzi, R., Sacchi, L., Peek, N., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi, E.; van Soest, J.; Alitto, A.R.; Autorino, R.; Dinapoli, N.; Dekker, A.; Gambacorta, M.A.; Gatta, R.; Tagliaferri, L.; Damiani, A.; et al. VATE: VAlidation of high TEchnology based on large database analysis by learning machine. Color. Cancer 2014, 3, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardelli, B.; Gatta, R.; Nucciarelli, L.; Tudor, A.M.; Tavazzi, E.; Vallati, M.; Orini, S.; Di Giorgi, N.; Damiani, A. GEN-RWD Sandbox: Bridging the gap between hospital data privacy and external research insights with distributed analytics. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nab, L.; Schaffer, A.L.; Hulme, W.; DeVito, N.J.; Dillingham, I.; Wiedemann, M.; Andrews, C.D.; Curtis, H.; Fisher, L.; Green, A.; et al. OpenSAFELY: A platform for analysing electronic health records designed for reproducible research. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2024, 33, e5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada-Torres, A.; Martin, F.; Sieswerda, M.; Van Soest, J.; Geleijnse, G. VANTAGE6: An open source priVAcy preserviNg federaTed leArninG infrastructurE for Secure Insight eXchange. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2020, 2020, 870–877. [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini, G.; Labopin, M.; Beohou, E.; Dalissier, A.; Dalle, J.H.; Cornish, J.; Zecca, M.; Samarasinghe, S.; Gibson, B.; Locatelli, F.; et al. Impact of Conditioning Regimen on Outcomes for Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Undergoing Transplantation in First Complete Remission. An Analysis on Behalf of the Pediatric Disease Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplanta. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2017, 23, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beelen, D.W.; Trenschel, R.; Stelljes, M.; Groth, C.; Masszi, T.; Reményi, P.; Wagner-Drouet, E.M.; Hauptrock, B.; Dreger, P.; Luft, T.; et al. Treosulfan or busulfan plus fludarabine as conditioning treatment before allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukaemia or myelodysplastic syndrome (MC-FludT.14/L): A randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e28–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, E.; Brambilla, G.; Bernardi, S.; Villanacci, V.; Carlessi, M.; Farina, M.; Radici, V.; Samarani, E.; Pellizzeri, S.; Polverelli, N.; et al. Nutritional intervention with TGF-beta enriched food for special medical purposes (TGF-FSMP) is associated with a reduction of malnutrition, acute GVHD, pneumonia and may improve overall survival in patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic stem transp. Transpl. Immunol. 2023, 81, 101954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, E.; Guarinoni, M.G.; Arena, F.; Andreoli, M.; Bernardi, S.; Malagola, M.; Turra, A.; Polverelli, N.; Russo, D. A Systematic Review of the Literature and Perspectives on the Role of Biomarkers in the Management of Malnutrition After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 535890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, E.; Malagola, M.; Bernardi, S.; Pristipino, C.; Russo, D. The role of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in the four P medicine era. Blood Res. 2018, 53, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
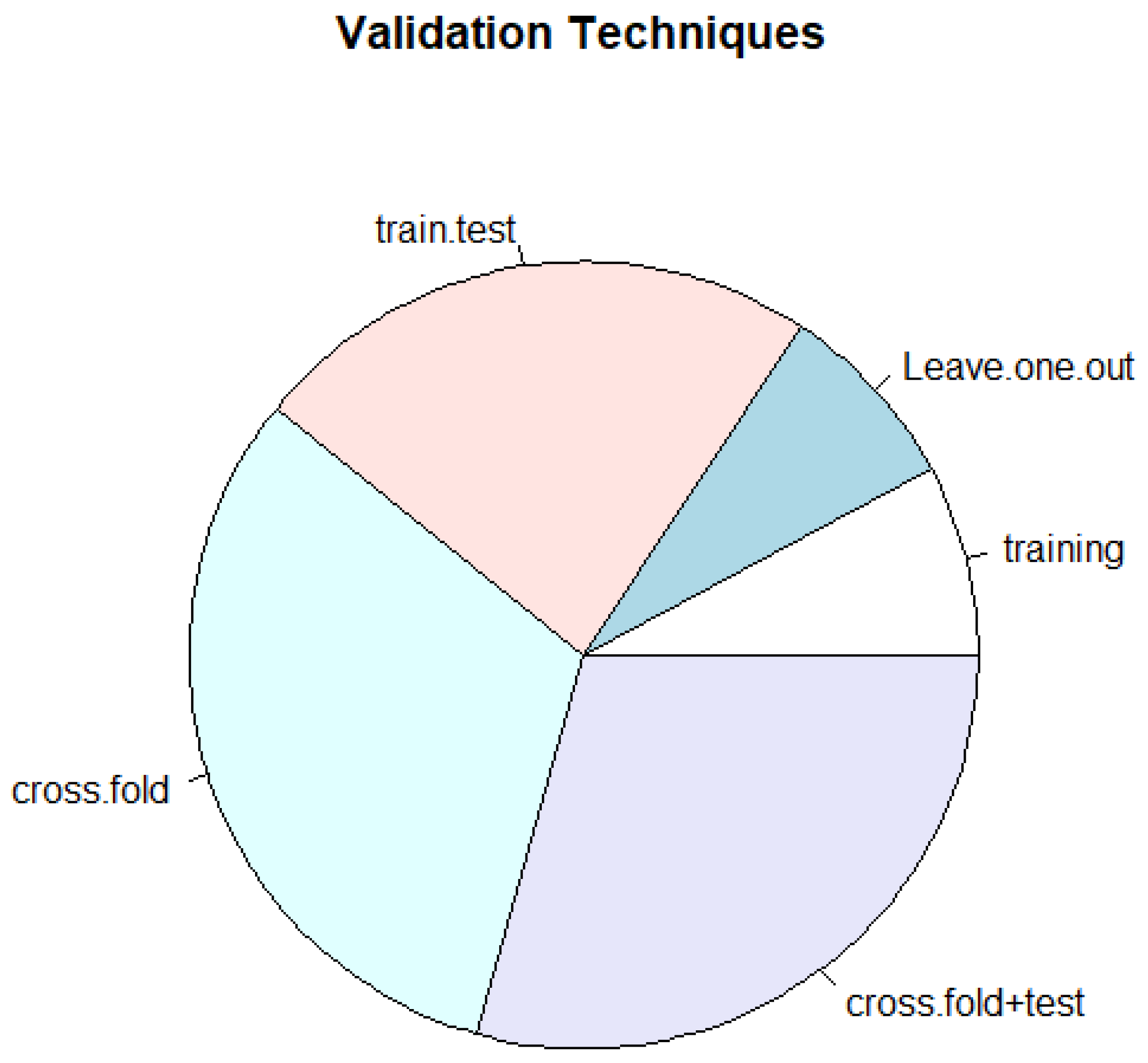
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) | The k-Nearest Neighbors (kNN) algorithm is a simple, non-parametric machine learning method used for classification and regression. It predicts the output for a given input based on the majority class or average of its closest k training samples in the feature space. |
| Linear regression (LR)-based techniques | They are a family of ML learning techniques where a linear regressor is trained and can be used, by a threshold, as a classifier. In this family we have the linear regression, logistic regression, LASSO, etc. |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | They are supervised machine learning algorithms used for classification and regression. They work by finding the optimal hyperplane that maximizes the margin between data points of different classes, often using kernel functions to handle non-linear separations. |
| Bayesian Network (BN) | Bayesian networks are probabilistic graphical models that represent relationships among variables using nodes and directed edges. They encode conditional dependencies and allow for reasoning under uncertainty by applying Bayes’ theorem to update beliefs based on new evidence. |
| Decision Trees (DTs) and Random Forest (RF) | DT is an algorithm used for classification and regression that splits data into branches based on feature values. It works by recursively partitioning the input space to create a tree structure, where each node represents a decision and each leaf a final prediction. RF is an ensemble learning approach exploiting many DTs (often more than 500), differently trained, to estimate the most probable result. |
| Artificial Neural Network (ANN) | An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a machine learning model inspired by the structure of the human brain, consisting of interconnected layers of nodes (neurons). It processes input data through weighted connections and activation functions to learn complex patterns for tasks like classification, regression, and more. |
| Gradient Boosting and Adaboost | They are ensemble learning algorithms that combine multiple weak classifiers, often decision trees, to create a strong classifier. Each new model corrects the errors of the previous ones by optimizing a loss function, resulting in a strong predictive model. During the learning, Adaboost emphasizes reweighting samples, while Gradient Boost emphasizes reducing residual errors through gradient optimization. |
| Clustering | Clustering is an unsupervised machine learning technique that groups similar data points into clusters based on their features. The goal is to identify inherent structures in the data without predefined labels, enabling pattern recognition and data segmentation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garuffo, L.; Leoni, A.; Gatta, R.; Bernardi, S. The Applications of Machine Learning in the Management of Patients Undergoing Stem Cell Transplantation: Are We Ready? Cancers 2025, 17, 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030395
Garuffo L, Leoni A, Gatta R, Bernardi S. The Applications of Machine Learning in the Management of Patients Undergoing Stem Cell Transplantation: Are We Ready? Cancers. 2025; 17(3):395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030395
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaruffo, Luca, Alessandro Leoni, Roberto Gatta, and Simona Bernardi. 2025. "The Applications of Machine Learning in the Management of Patients Undergoing Stem Cell Transplantation: Are We Ready?" Cancers 17, no. 3: 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030395
APA StyleGaruffo, L., Leoni, A., Gatta, R., & Bernardi, S. (2025). The Applications of Machine Learning in the Management of Patients Undergoing Stem Cell Transplantation: Are We Ready? Cancers, 17(3), 395. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030395








