Radiomic Fingerprinting of the Peritumoral Edema in Brain Tumors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
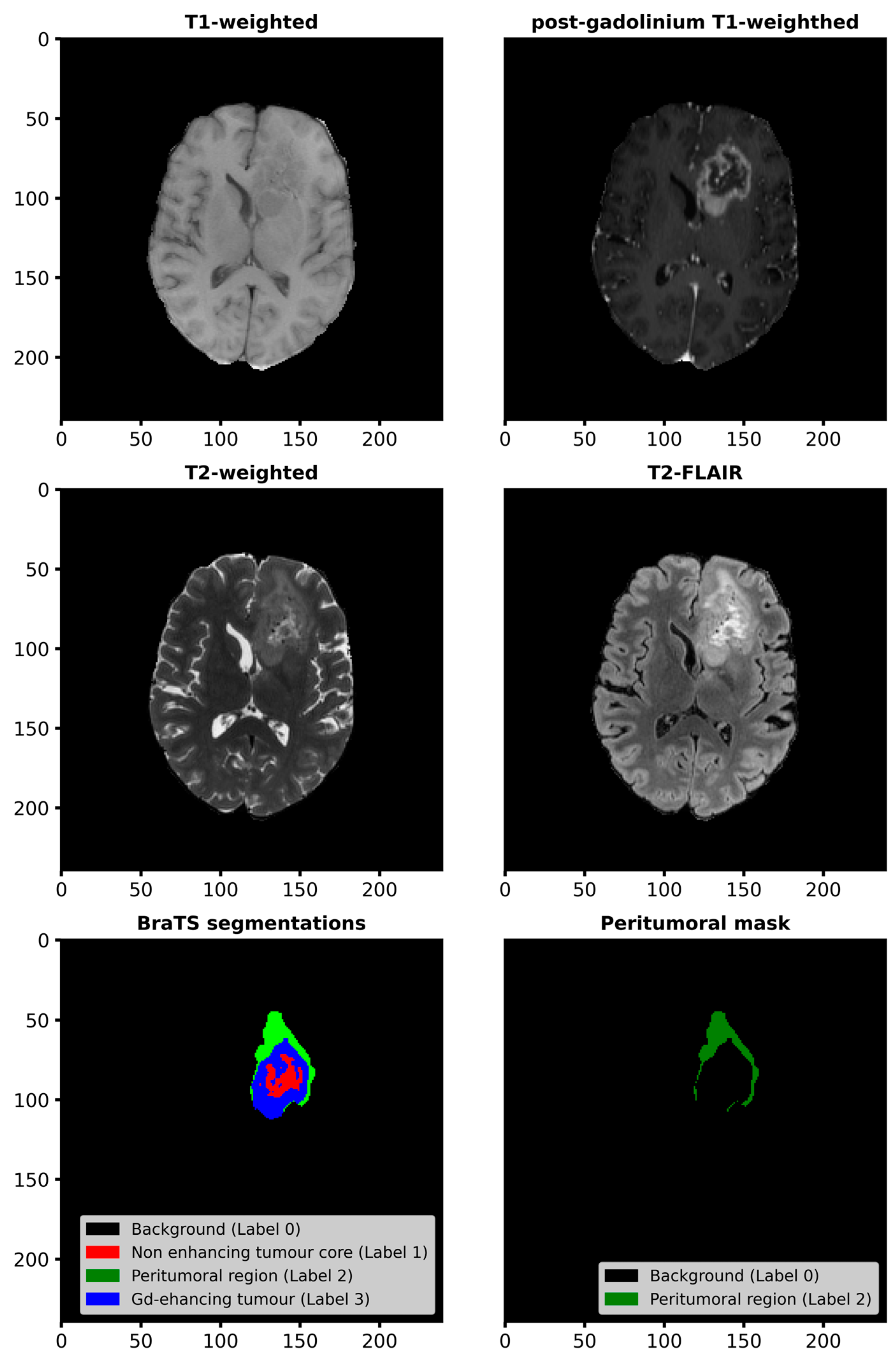
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
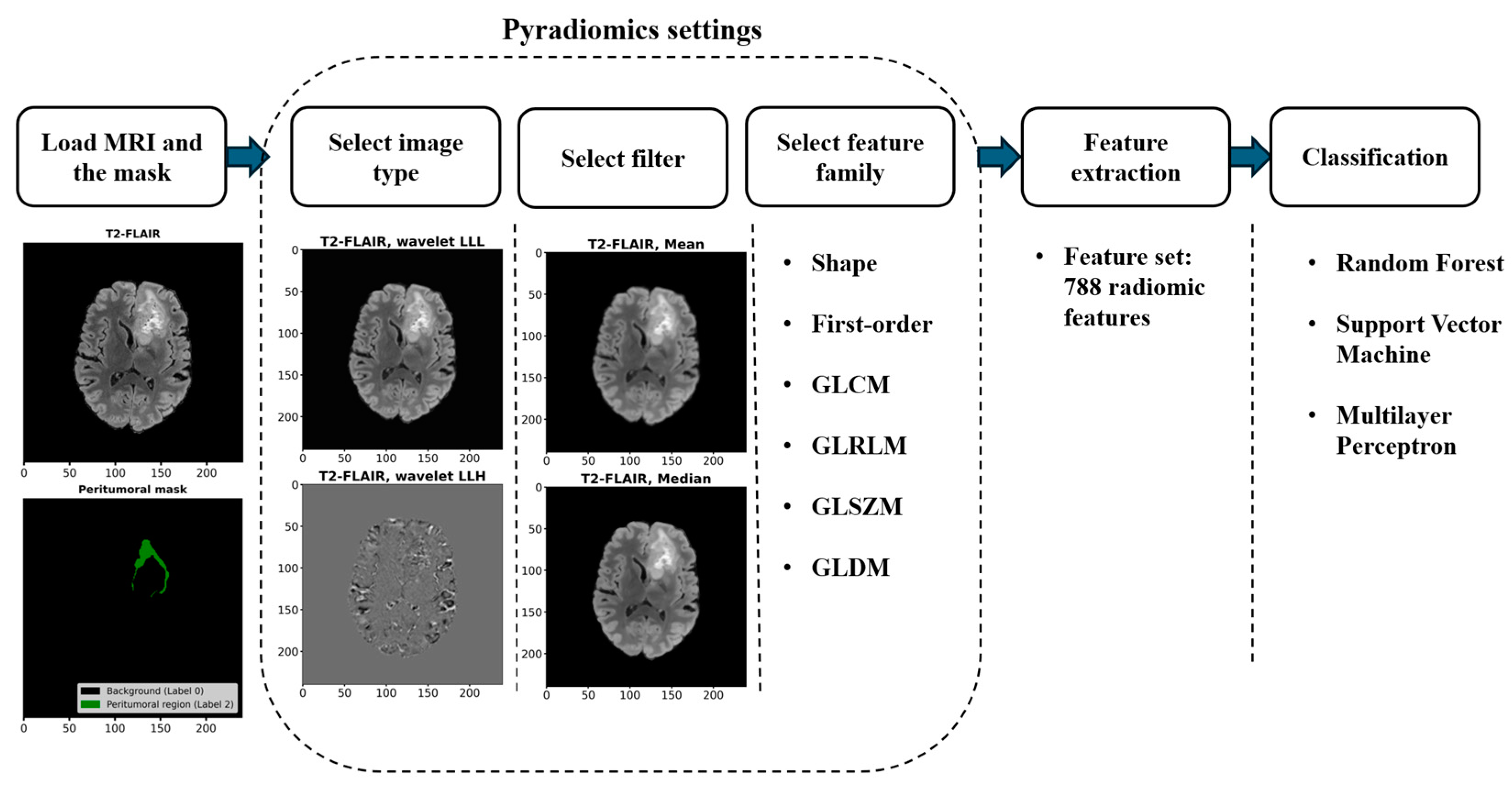
2.2.1. Workflow for Radiomic Feature Extraction and Tumor Classification
2.2.2. Radiomic Feature Extraction
2.2.3. Feature Normalization, Data Imbalance Handling, and Feature Selection
2.2.4. Classification and Performance Evaluation
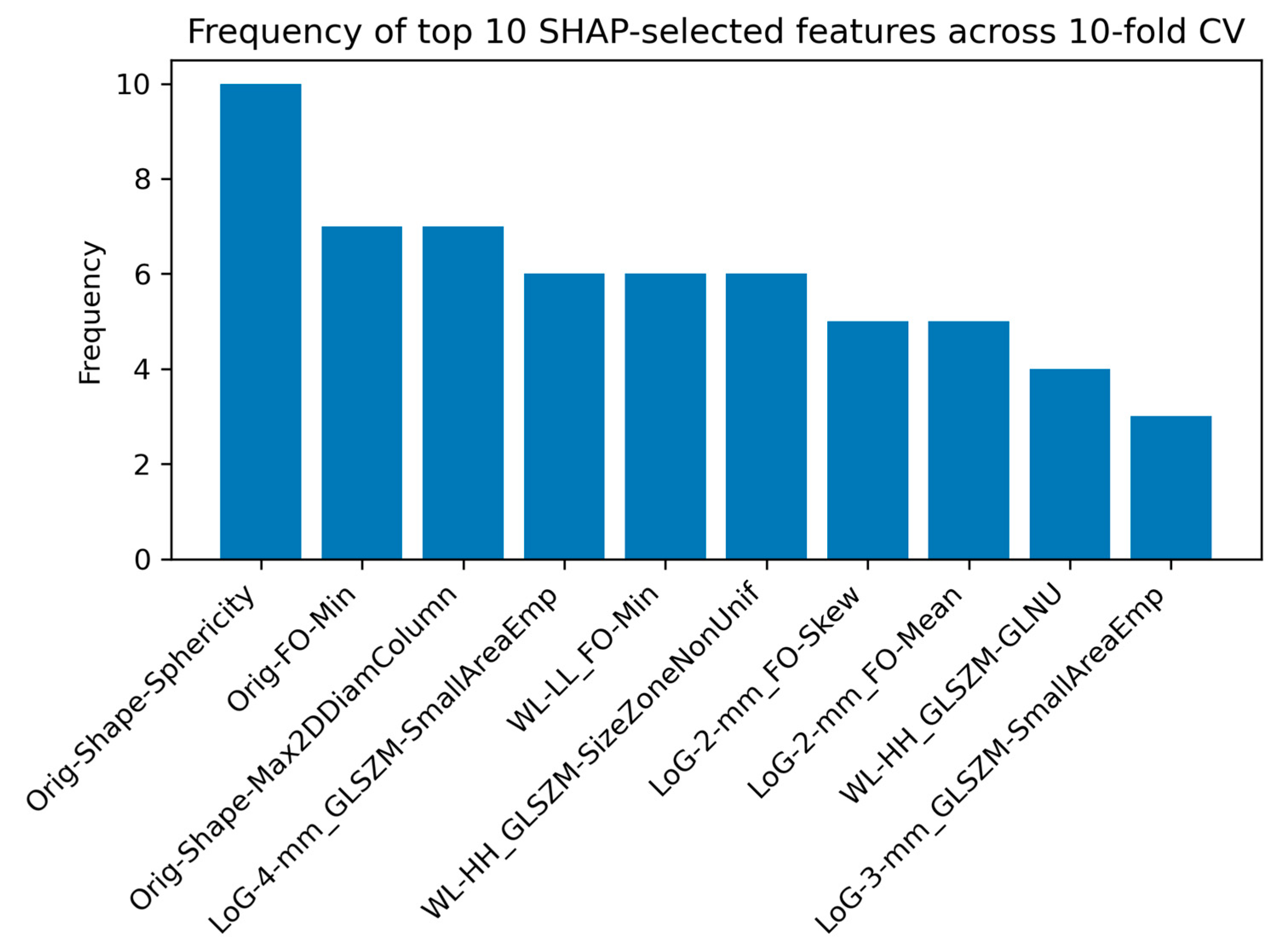
2.2.5. SHAP Analysis for Feature Interpretability
3. Results
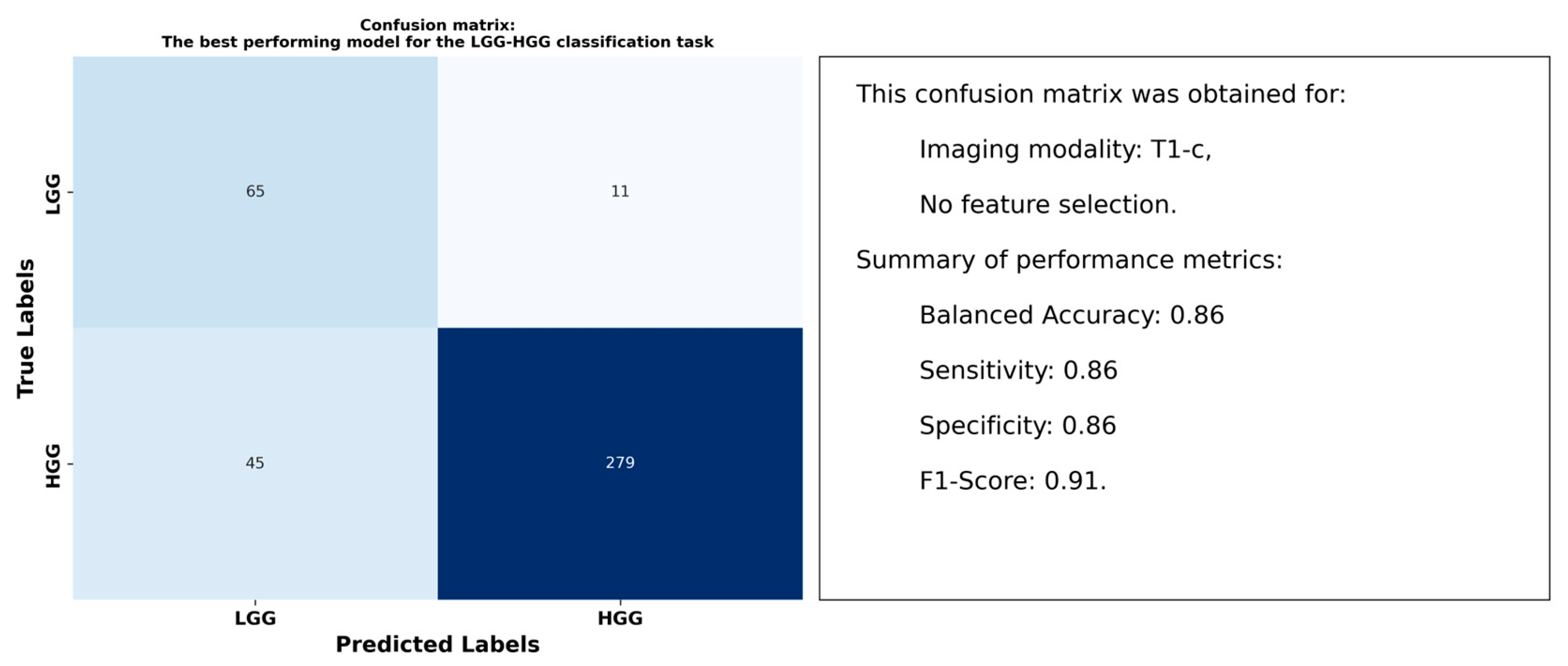
3.1. Results for the LGG-HGG Classification Task
3.2. Results for the GLI-MEN-MET Classification Task
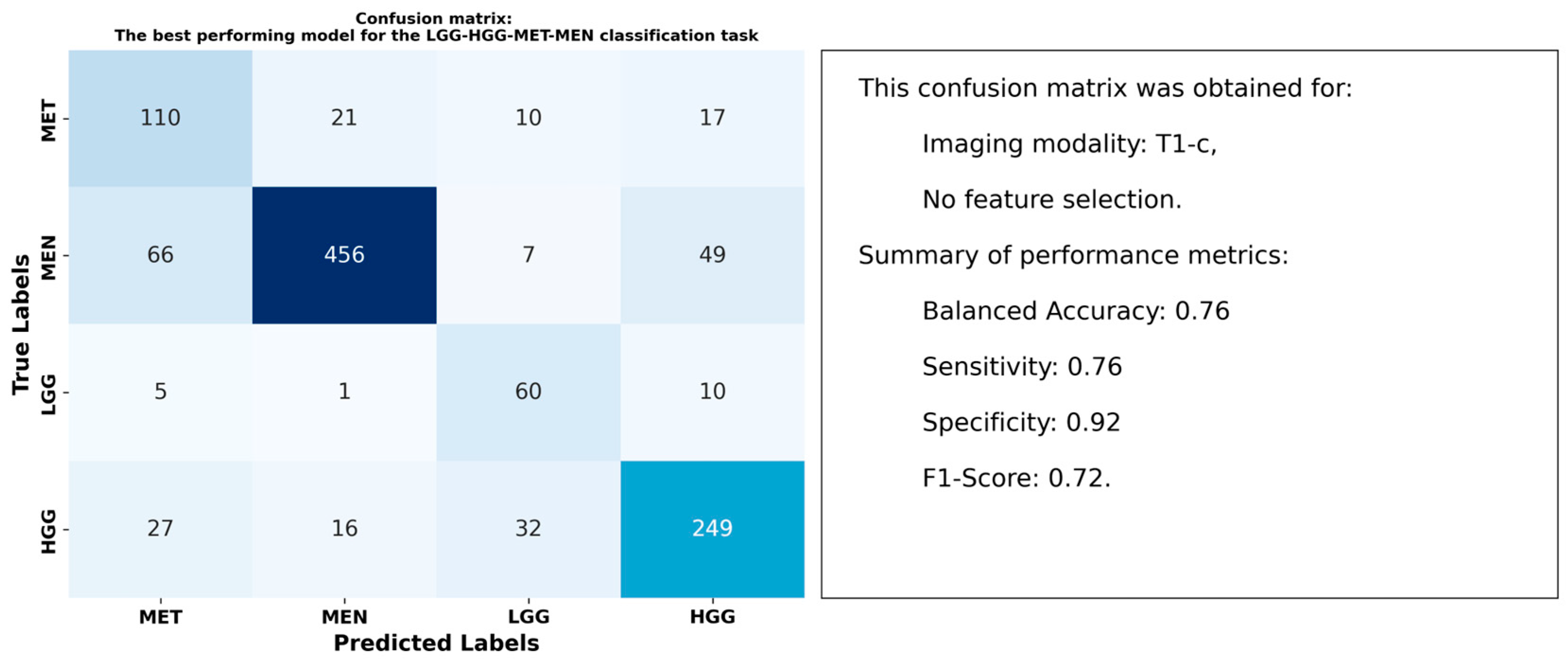
3.3. Results for the LGG-HGG-MET-MEN Classification Task
4. Discussion
4.1. Distinct Radiomic Signatures of Peritumoral Edema
4.2. Optimal Models and Superior Performance of T1-c Features
4.3. Impact of Data Balancing and Feature Selection Techniques
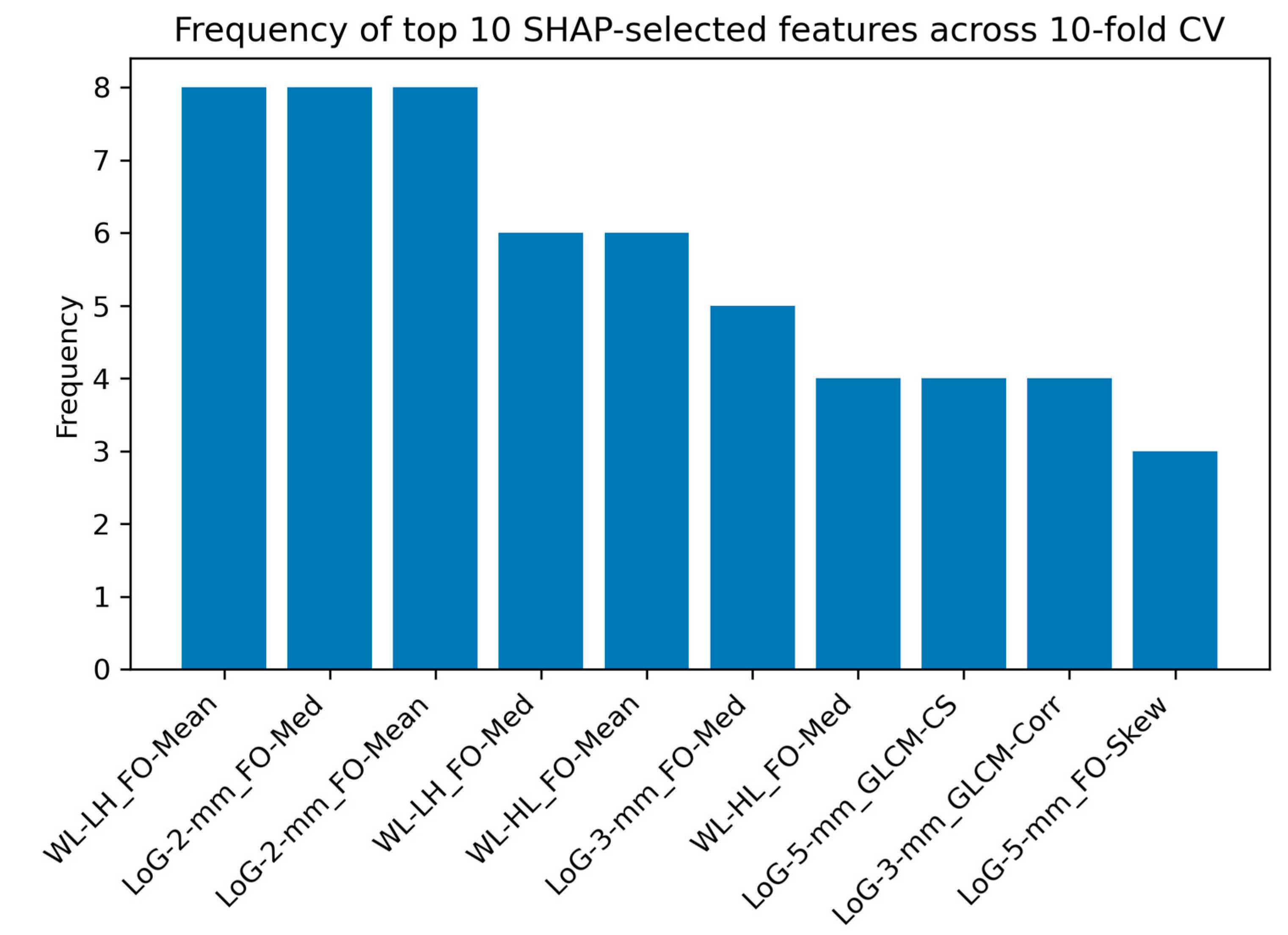
4.4. Interpretation of Radiomic Features Using SHAP Analysis
4.5. Future Directions in Peritumoral Radiomics and Clinical Applications
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| FO | First-order |
| GLCM | Gray-level co-occurrence matrix |
| GLDM | Gray-level dependence matrix |
| GLI | Glioma |
| GLRLM | Gray-level run length matrix |
| GLSZM | Gray-level size zone matrix |
| HGG | High-grade glioma |
| LGG | Low-grade glioma |
| LoG | Laplacian of Gaussian |
| MEN | Meningioma |
| MET | Metastasis |
| MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRS | Magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| NaN | Not a number |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| RF | Random forest |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| RUS | Random under sampling |
| SMOTE | Synthetic minority over-sampling technique |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| WL | Wavelet |
References
- Yip, S.S.F.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150–R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beig, N.; Bera, K.; Tiwari, P. Introduction to radiomics and radiogenomics in neuro-oncology: Implications and challenges. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, iv3–iv14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, S.P.; Burtness, B.; Yarbrough, W.G.; Payabvash, S. Applications of radiomics in precision diagnosis, prognostication and treatment planning of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Cancers Head Neck 2020, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Z.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y. Radiomics model based on dual-energy CT can determine the source of thrombus in strokes with middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neuroradiology 2024, 66, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Kong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, Y.; et al. Conventional magnetic resonance imaging–based radiomic signature predicts telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation status in grade II and III gliomas. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasanna, P.; Patel, J.; Partovi, S.; Madabhushi, A.; Tiwari, P. Radiomic features from the peritumoral brain parenchyma on treatment-naïve multi-parametric MR imaging predict long versus short-term survival in glioblastoma multiforme: Preliminary findings. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 27, 4188–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, A.; Liu, S.; Di Ieva, A. Artificial Intelligence for Survival Prediction in Brain Tumors on Neuroimaging. Neurosurgery 2022, 91, 8–26, [Online]. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/neurosurgery/fulltext/2022/07000/artificial_intelligence_for_survival_prediction_in.2.aspx (accessed on 29 January 2025). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Luo, Y.; Gu, F.; Tian, B.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, G.; Nie, X.; Yu, J.; Tong, J.; Liao, X. Artificial intelligence-based MRI radiomics and radiogenomics in glioma. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aichholzer, M.; Rauch, P.; Kastler, L.; Pichler, J.; Aufschnaiter-Hiessböck, K.; Ruiz-Navarro, F.; Aspalter, S.; Hartl, S.; Schimetta, W.; Böhm, P.; et al. Tailored Intraoperative MRI Strategies in High-Grade Glioma Surgery: A Machine Learning–Based Radiomics Model Highlights Selective Benefits. Oper. Neurosurg. 2023, 26, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ren, W.; He, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tan, Y.; Mao, L.; Ouyang, W.; Lu, N.; Ouyang, J.; Chen, K.; et al. Machine learning radiomics of magnetic resonance imaging predicts recurrence-free survival after surgery and correlation of LncRNAs in patients with breast cancer: A multicenter cohort study. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Li, B.; Teng, X.-Z.; Zhang, J.; Lam, S.; Zhou, T.; Ma, Z.-R.; Sheng, J.-B.; et al. Artificial intelligence-driven radiomics study in cancer: The role of feature engineering and modeling. Mil. Med. Res. 2023, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Ren, X.; Xu, M.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Bu, Y.; Zhou, C. Magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics was used to evaluate the level of prognosis-related immune cell infiltration in breast cancer tumor microenvironment. BMC Med. Imaging 2024, 24, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ak, M.; Toll, S.; Hein, K.; Colen, R.; Khatua, S. Evolving Role and Translation of Radiomics and Radiogenomics in Adult and Pediatric Neuro-Oncology. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 43, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, B.S.; Mathur, P.; McGuinness, G.; Dillon, H.; Lee, E.H.; Yeom, K.W.; Lawlor, A.; Killeen, R.P. A Radiomic “Warning Sign” of Progression on Brain MRI in Individuals with MS. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2024, 45, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Grzegorzek, M.; Sun, H. Habitat radiomics analysis of pet/ct imaging in high-grade serous ovarian cancer: Application to Ki-67 status and progression-free survival. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 948767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lyu, Z.; Xu, P.; Gu, W.; Tian, L.; Fu, P. Using tumor habitat-derived radiomic analysis during pretreatment 18F-FDG PET for predicting KRAS/NRAS/BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Shen, H.; Zheng, F.; Zang, Y.; Chen, X. Machine learning-based analysis of magnetic resonance radiomics for the classification of gliosarcoma and glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 699789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, N.; Geraghty, B.; Dasgupta, A.; Maralani, P.J.; Sandhu, M.; Detsky, J.; Tseng, C.-L.; Soliman, H.; Myrehaug, S.; Husain, Z.; et al. MRI radiomics to differentiate between low grade glioma and glioblastoma peritumoral region. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 155, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, F.-Y.; Yen, Y. Efficient Radiomics-Based Classification of Multi-Parametric MR Images to Identify Volumetric Habitats and Signatures in Glioblastoma: A Machine Learning Approach. Cancers 2022, 14, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Sui, C.; Wang, C.; Zhu, T. MRI-based intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for preoperative prediction of glioma grade: A multicenter study. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1401977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, M.; Al Suman, A.; Molina, E.S.; Pan, E.; Di Ieva, A.; Liu, S. Radiomics and Machine Learning in Brain Tumors and Their Habitat: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2023, 15, 3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.; Russo, C.; Di Ieva, A. Radiomics in gliomas: Clinical implications of computational modeling and fractal-based analysis. Neuroradiology 2020, 62, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Zhou, Q.; Xi, H.; Zhou, J. Radiomics: A review of current applications and possibilities in the assessment of tumor microenvironment. Diagn. Interv. Imaging 2022, 104, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Qiu, X.; Luo, Y.; Luo, J.; Liu, Y.; Xi, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Z. Application of radiomics-based multiomics combinations in the tumor microenvironment and cancer prognosis. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Wang, X.; Ye, H.; Cao, W. Radiomic Models Predict Tumor Microenvironment Using Artificial Intelligence—The Novel Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Immune Microenvironment. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231218227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logotheti, S.; Georgakilas, A.G. More than Meets the Eye: Integration of Radiomics with Transcriptomics for Reconstructing the Tumor Microenvironment and Predicting Response to Therapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiani, B.; Jarrah, R.; Bhandarkar, A.R.; De Stefano, F.; Amare, A.; Aljameey, U.A.; Reardon, T. Peritumoral edema in meningiomas: Pathophysiology, predictors, and principles for treatment. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 25, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, P.; Ranjbar, S.; Curtin, L.; Bond, K.; Singleton, K.; Hawkins-Daarud, A.; Li, J.; Canoll, P.; Hu, L.; Tran, N.; et al. NIMG-19. Image-based modeling map of edema is correlated with multiple blood-brain-barrier permeability relevant transcriptomic markers in brain tumor patients. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, vii165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.S. Peritumoral Edema. In Meningiomas; Lee, J.H., Ed.; Springer: London, UK, 2009; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Long, H.; Zhang, P.; Bi, Y.; Yang, C.; Wu, M.; He, D.; Huang, S.; Yang, K.; Qi, S.; Wang, J. MRI radiomic features of peritumoral edema may predict the recurrence sites of glioblastoma multiforme. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1042498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, E.Y.; Jung, M.R.; Cha, J.H.; Shin, H.J.; Choi, W.J.; Kim, H.H. A predictive model using MRI and clinicopathologic features for breast cancer recurrence in young women treated with upfront surgery. Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 7092–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Shin, J.; Min, J.H.; Jeong, W.K.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.-Y.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, K. Preoperative prediction of early recurrence in resectable pancreatic cancer integrating clinical, radiologic, and CT radiomics features. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaggle. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/bkb2024/brats-2023-training (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. (In English) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lang, J.; Zuo, J.Z.; Dong, Y.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Wong, S.T.C.; et al. The radiomic-clinical model using the SHAP method for assessing the treatment response of whole-brain radiotherapy: A multicentric study. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 8737–8747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, N.E.; John, A.; Amma, C.U.D. Classification of Glioma by Exploring Wavelet-based Radiomic Features and Machine Learning Techniques using Brats Dataset. In Proceedings of the 2023 Third International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Computing, Communication and Sustainable Technologies (ICAECT), Bhilai, India, 5–6 January 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, F.; Liu, Z.; Fang, W.; Niu, L.; Chu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, R.; Yang, G. MRI radiomics for brain metastasis sub-pathology classification from non-small cell lung cancer: A machine learning, multicenter study. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2023, 46, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Ji, C.; Xia, W.; Qi, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.; et al. MRI-derived radiomics assessing tumor-infiltrating macrophages enable prediction of immune-phenotype, immunotherapy response and survival in glioma. Biomark. Res. 2024, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Lin, C.; Jiang, Y.; Xin, E.; Xu, F.; Gan, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Lou, K.; et al. Radiomics model based on intratumoral and peritumoral features for predicting major pathological response in non-small cell lung cancer receiving neoadjuvant immunochemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1348678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Cheng, M.; Du, B.; Li, L.-M.; Huang, W.-P.; Gao, J.-B. Use of radiomics containing an effective peritumoral area to predict early recurrence of solitary hepatocellular carcinoma ≤5 cm in diameter. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1032115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lyu, D.; Yu, D.; Hu, S.; Ma, Y.; Huang, W.; Duan, S.; Zhou, T.; Tu, W.; Zhou, X.; et al. Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics combined with computed tomography features for predicting the invasiveness of lung adenocarcinoma presenting as a subpleural ground-glass nodule with a consolidation-to-tumor ratio ≤50%. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 5122–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, W.; Cao, X.; Luo, J. Effect of multiple peritumoral regions of interest ranges based on computed tomography radiomics for the prediction of early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 6668–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, S.; Katz, S.; Kontos, D.; Roshkovan, L. State of the art: Radiomics and radiomics-related artificial intelligence on the road to clinical translation. BJR|Open 2023, 6, tzad004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Chen, F.; Lei, J.; Li, R.; Xi, L.; Guo, S. Intra- and peritumoral radiomics features based on multicenter automatic breast volume scanner for noninvasive and preoperative prediction of HER2 status in breast cancer: A model ensemble research. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Group | Total Subjects | Excluded Subjects | Subjects in Study | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Segmentations | No Label 2 | Feature Extraction Issues | |||
| MET | 165 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 158 |
| GLI | 1251 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1248 |
| HGG | 325 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 324 |
| LGG | 77 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 76 |
| MEN | 1000 | 22 | 335 | 65 | 578 |
| Total | 2818 | 22 | 341 | 71 | 2384 |
| Classifier | Parameter | Distribution/Value |
|---|---|---|
| RF | n_estimators | randint(100, 500) |
| max_depth | [None] + list(randint(10, 50).rvs(size = 4)) | |
| criterion | [‘entropy’, ‘gini’, ‘log_loss’] | |
| min_samples_split | [2, 3, 4, 5] | |
| max_features | [‘sqrt’, ‘log2’, None, 0.5, 0.7] | |
| MLP | hidden_layer_sizes | [(5, 3), (5,), (5, 5), (10,), (10, 10)] |
| activation | [‘relu’, ‘logistic’, ‘tanh] | |
| alpha | uniform(0.0001, 0.1) | |
| solver | [‘adam’, ‘sgd’] | |
| SVM | C | uniform(0.1, 100) |
| gamma | [‘scale’, ‘auto’, 0.1, 0.01] | |
| kernel | [‘linear’, ‘rbf’, ‘poly’, ‘sigmoid’] | |
| degree | randint(2, 5) | |
| coef0 | uniform(0.0, 10.0) |
| Imaging Modality | Feature Selection Method | Balanced Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | None | 0.74 |
| PCA | 0.67 | |
| T1-c | None | 0.86 |
| PCA | 0.83 | |
| T2 | None | 0.71 |
| PCA | 0.70 | |
| T2-FLAIR | None | 0.65 |
| PCA | 0.62 |
| Imaging Modality | Feature Selection Method | Balanced Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | None | 0.74 |
| PCA | 0.75 | |
| T1-c | None | 0.81 |
| PCA | 0.80 | |
| T2 | None | 0.76 |
| PCA | 0.76 | |
| T2-FLAIR | None | 0.79 |
| PCA | 0.77 |
| Imaging Modality | Feature Selection Method | Balanced Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| T1 | None | 0.65 |
| PCA | 0.60 | |
| T1-c | None | 0.76 |
| PCA | 0.73 | |
| T2 | None | 0.67 |
| PCA | 0.64 | |
| T2-FLAIR | None | 0.63 |
| PCA | 0.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azemi, G.; Di Ieva, A. Radiomic Fingerprinting of the Peritumoral Edema in Brain Tumors. Cancers 2025, 17, 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030478
Azemi G, Di Ieva A. Radiomic Fingerprinting of the Peritumoral Edema in Brain Tumors. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030478
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzemi, Ghasem, and Antonio Di Ieva. 2025. "Radiomic Fingerprinting of the Peritumoral Edema in Brain Tumors" Cancers 17, no. 3: 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030478
APA StyleAzemi, G., & Di Ieva, A. (2025). Radiomic Fingerprinting of the Peritumoral Edema in Brain Tumors. Cancers, 17(3), 478. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030478






