Advanced External Beam Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Skull Base Reirradiation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. External Beam Radiation Delivery Systems
2.2. Radiation Treatment Planning Systems
2.3. Patients and Treatment Plan Generation
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iannalfi, A.; Riva, G.; Ciccone, L.; Orlandi, E. The role of particle radiotherapy in the treatment of skull base tumors. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1161752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, F.Y.; Chung, C. Radiation for skull base meningiomas: Review of the literature on the approach to radiotherapy. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6 (Suppl. S1), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, J.D.; Gamez, M.E.; Ranta, K.; Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Peterson, J.L.; Blakaj, D.M.; Prevedello, D.; Carrau, R.; Mahajan, A.; Chaichana, K.L.; et al. Radiation therapy strategies for skull-base malignancies. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2020, 150, 445–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, M.; Choucha, A.; Dannhoff, G.; Kong, D.S.; Zoia, C.; Iaconetta, G. Treating Trigeminal Schwannoma through a Transorbital Approach: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, M.; Conti, V.; Palermo, G.; De Maria, L.; Iaconetta, G. Advancements in Glioma Care: Focus on Emerging Neurosurgical Techniques. Biomedicines 2023, 12, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin-Alamer, O.; Mallela, A.N.; Palmisciano, P.; Gersey, Z.C.; Elarjani, T.; Labib, M.A.; Zenonos, G.A.; Dehdashti, A.R.; Sheehan, J.P.; Couldwell, W.T.; et al. Adjuvant stereotactic radiosurgery with or without postoperative fractionated radiation therapy in adults with skull base chordomas: A systematic review. Neurosurg. Focus 2022, 53, E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choucha, A.; Troude, L.; Morin, L.; Fernandes, S.; Baucher, G.; De Simone, M.; Lihi, A.; Mazen, K.; Alseirihi, M.; Passeri, T.; et al. Management of large Trigeminal Schwannoma: Long-term oncologic and functional outcome from a multicentric retrospective cohort. Acta Neurochir. 2024, 166, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krengli, M.; Apicella, G.; Deantonio, L.; Paolini, M.; Masini, L. Stereotactic radiation therapy for skull base recurrences: Is a salvage approach still possible? Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2015, 20, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, I.; Karam, I.; El-Sehemy, A.; Abu-Gheida, I.; Al-Ibraheem, A.; Al-Assaf, H.; Aldehaim, M.; Alghamdi, M.; Alotain, I.; Ashour, M.; et al. The Evolving Role of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Head and Neck Cancer: Where Do We Stand? Cancers 2023, 15, 5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Kida, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Mizumatsu, S.; Hatano, M. Stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy for malignant skull base tumors. Cureus 2020, 12, e8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Phan, J. Reirradiation of Skull Base Tumors With Advanced Highly Conformal Techniques. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 19, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.P.; Wang, H.; Pollard, C., 3rd; Nguyen, T.; Bahig, H.; Fuller, C.D.; Gunn, G.B.; Garden, A.S.; Reddy, J.P.; Morrison, W.H.; et al. Patient Outcomes after Reirradiation of Small Skull Base Tumors using Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy, Intensity Modulated Radiotherapy, or Proton Therapy. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2020, 81, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Lunsford, D.; Kondziolka, D. Gamma knife radiosurgery for skull base chordomas: A 13 year review from a single institution. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2002, 54, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, R.; Rich, K.M. Therapeutic Role of Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery in Neuro-Oncology. Mo. Med. 2020, 117, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, Y.; Long, Y.; Du, L.; Chen, R.; Hu, T.; Guo, Q.; Liao, G.; Huang, J. Is the CyberKnife® radiosurgery system effective and safe for patients? An umbrella review of the evidence. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, B.; Supe, S.S.; Ramachandra, A. Cyberknife: A double edged sword? Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2010, 15, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J.S.; Yu, C.; Petrovich, Z.; Apuzzo, M.L.J. The CyberKnife Stereotactic Radiosurgery System: Description, Installation, and an Initial Evaluation of Use and Functionality. Neurosurgery 2003, 53, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biston, M.C.; Dupuis, P.; Gassa, F.; Grégoire, V. Do all the linear accelerators comply with the ICRU 91’s constraints for stereotactic body radiation therapy treatments? Cancer/Radiothérapie 2019, 23, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Rong, Y.; Burmeister, J.W.; Chao, E.H.; Corradini, N.A.; Followill, D.S.; Li, X.A.; Liu, A.; Qi, X.S.; Shi, H.; et al. AAPM Task Group Report 306: Quality control and assurance for tomotherapy: An update to Task Group Report 148. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, e25–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Welsh, J.S. Dosimetric and clinical review of helical tomotherapy. Expert. Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2011, 11, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, M.A.; Chhabra, A.M.; Lin, L.; Simone, C.B., 2nd. First Ever Use of Proton Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Delivered with Curative Intent to Bilateral Synchronous Primary Renal Cell Carcinomas. Cureus 2017, 9, e1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, C.B.; Lin, L. Proton SBRT is ready to move past uncertainties and towards improved clinical outcomes. J. Radiosurg SBRT 2023, 9, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J. Impact of dose calculation algorithm on radiation therapy. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, W.; Primeßnig, A.; Nenoff, L.; Wesolowska, P.; Izewska, J.; Georg, D. The influence of errors in small field dosimetry on the dosimetric accuracy of treatment plans. Acta Oncol. 2020, 59, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malicki, J. The importance of accurate treatment planning, delivery, and dose verification. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2012, 17, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, K.; Nguyen, T.P.; Moreno, A.C.; Reddy, J.P.; Garden, A.S.; Wang, C.H.; Tung, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.A.; Rosenthal, D.I.; et al. Stereotactic body ablative radiotherapy for reirradiation of small volume head and neck cancers is associated with prolonged survival: Large, single-institution, modern cohort study. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3331–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogineni, E.; Zhang, I.; Rana, Z.; Marrero, M.; Gill, G.; Sharma, A.; Riegel, A.C.; Teckie, S.; Ghaly, M. Quality of Life Outcomes Following Organ-Sparing SBRT in Previously Irradiated Recurrent Head and Neck Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddick, I.; Lippitz, B. A simple dose gradient measurement tool to complement the conformity index. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 105, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggar, W.N.; Morris, B.; Fatemi, A.; Bonds, J.; He, R.; Kanakamedala, M.; Rey-Dios, R.; Vijayakumar, S.; Yang, C. Gamma Knife(®) icon CBCT offers improved localization workflow for frame-based treatment. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, T.J.C.; Cheng, S.K.; Elliston, C.D.; Savacool, M.K.; Dona Lemus, O.; Sisti, M.B.; Wuu, C.S. Performance of the cone beam computed tomography-based patient positioning system on the Gamma Knife Icon™. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 4333–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elekta, A.B. High Definition Motion Management—Enabling stereotactic Gamma Knife® Radiosurgery with Non-Rigid Patient Fixations. Elekta White Paper 2015, Stockholm, Sweden. Available online: https://www.elekta.com/medical-affairs/bibliographies/High%20Definition%20Motion%20Management%20-%20enabling%20stereotactic%20Gamma%20Knife%C2%AE%20radiosurgery%20with%20non-rigid%20patient%20fixations%20white%20paper.pdf (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Knutson, N.C.; Hawkins, B.J.; Bollinger, D.; Goddu, S.M.; Kavanaugh, J.A.; Santanam, L.; Mitchell, T.J.; Zoberi, J.E.; Tsien, C.; Huang, J.; et al. Characterization and validation of an intra-fraction motion management system for masked-based radiosurgery. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akino, Y.; Sumida, I.; Shiomi, H.; Higashinaka, N.; Murashima, Y.; Hayashida, M.; Mabuchi, N.; Ogawa, K. Evaluation of the accuracy of the CyberKnife Synchrony™ Respiratory Tracking System using a plastic scintillator. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petti, P.L.; Rivard, M.J.; Alvarez, P.E.; Bednarz, G.; Daniel Bourland, J.; DeWerd, L.A.; Drzymala, R.E.; Johansson, J.; Kunugi, K.; Ma, L.; et al. Recommendations on the practice of calibration, dosimetry, and quality assurance for gamma stereotactic radiosurgery: Report of AAPM Task Group 178. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, e733–e770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-H.; Hickling, S.V.; Qian, J.; Blackwell, C.R.; McLemore, L.B.; Tryggestad, E.J. Characterization and commissioning of a Leksell Gamma Knife ICON system for framed and frameless stereotactic radiosurgery. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.C.; Ott, J.T.; Williams, J.B.; Dickow, D. Commissioning and acceptance testing of a CyberKnife linear accelerator. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2007, 8, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, S.; Cavedon, C.; Chuang, C.F.; Cohen, A.B.; Garrett, J.A.; Lee, C.L.; Lowenstein, J.R.; d’Souza, M.F.; Taylor, D.D., Jr.; Wu, X.; et al. Report of AAPM TG 135: Quality assurance for robotic radiosurgery. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 2914–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.E.; Hanley, J.; Bayouth, J.; Yin, F.F.; Simon, W.; Dresser, S.; Serago, C.; Aguirre, F.; Ma, L.; Arjomandy, B.; et al. Task Group 142 report: Quality assurance of medical accelerators. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 4197–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J.; Dresser, S.; Simon, W.; Flynn, R.; Klein, E.E.; Letourneau, D.; Liu, C.; Yin, F.F.; Arjomandy, B.; Ma, L.; et al. AAPM Task Group 198 Report: An implementation guide for TG 142 quality assurance of medical accelerators. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, e830–e885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandy, B.; Taylor, P.; Ainsley, C.; Safai, S.; Sahoo, N.; Pankuch, M.; Farr, J.B.; Yong Park, S.; Klein, E.; Flanz, J.; et al. AAPM task group 224: Comprehensive proton therapy machine quality assurance. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e678–e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farr, J.B.; Moyers, M.F.; Allgower, C.E.; Bues, M.; Hsi, W.C.; Jin, H.; Mihailidis, D.N.; Lu, H.M.; Newhauser, W.D.; Sahoo, N.; et al. Clinical commissioning of intensity-modulated proton therapy systems: Report of AAPM Task Group 185. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, e1–e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madle, N. Versatility is the key for the future of radiotherapy linear accelerators. J. Radiother. Pract. 2007, 6, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorsak, E.B. Treatment machines for external beam radiotherapy. In Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers and Students; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2005; pp. 103–132. [Google Scholar]
- Da Silva Mendes, V.; Reiner, M.; Huang, L.; Reitz, D.; Straub, K.; Corradini, S.; Niyazi, M.; Belka, C.; Kurz, C.; Landry, G.; et al. ExacTrac Dynamic workflow evaluation: Combined surface optical/thermal imaging and X-ray positioning. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2022, 23, e13754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrett, B.; Ukath, J.; Horgan, E.; Noble, C.; Ramachandran, P. A Framework for Exactrac Dynamic Commissioning for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy. J. Med. Phys. 2022, 47, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, A.; Sarkar, V.; Price, R.G.; St. James, S.; Dial, C.; Poppe, M.M.; Salter, B.J. CT-on-Rails Utilization for Image Guidance and Plan Adaptation at a Single-Room Proton Therapy Center. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 117, e704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.; Farah, J.; Barbet, N.; Khodri, M. Commissioning and performance testing of the first prototype of AlignRT InBore™ a Halcyon™ and Ethos™-dedicated surface guided radiation therapy platform. Phys. Medica 2020, 80, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sanchis, A.; Brualla-González, L.; Fuster-Diana, C.; Gordo-Partearroyo, J.C.; Piñeiro-Vidal, T.; García-Hernandez, T.; López-Torrecilla, J.L. Surface-guided radiation therapy for breast cancer: More precise positioning. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hallaq, H.A.; Cerviño, L.; Gutierrez, A.N.; Havnen-Smith, A.; Higgins, S.A.; Kügele, M.; Padilla, L.; Pawlicki, T.; Remmes, N.; Smith, K.; et al. AAPM task group report 302: Surface-guided radiotherapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, e82–e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Yin, Y. Clinical application of MR-Linac in tumor radiotherapy: A systematic review. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Lee, A.; Phan, J.; Lim, T.Y.; Fuller, C.D.; Han, E.Y.; Rhee, D.J.; Salzillo, T.; Zhao, Y.; et al. MR-guided stereotactic radiation therapy for head and neck cancers. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2024, 46, 100760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirvani, S.M.; Huntzinger, C.J.; Melcher, T.; Olcott, P.D.; Voronenko, Y.; Bartlett-Roberto, J.; Mazin, S. Biology-guided radiotherapy: Redefining the role of radiotherapy in metastatic cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20200873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surucu, M.; Ashraf, M.R.; Romero, I.O.; Zalavari, L.T.; Pham, D.; Vitzthum, L.K.; Gensheimer, M.F.; Yang, Y.; Xing, L.; Kovalchuk, N.; et al. Commissioning of a novel PET-Linac for biology-guided radiotherapy (BgRT). Med. Phys. 2024, 51, 4389–4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, T.; Nie, K.; Zhu, J.; Danish, S.; Weiner, J.; Chundury, A.; Ohri, N.; Zhang, Y.; Vergalasova, I.; Yue, N.; et al. Clinical Evaluation of the Inverse Planning System Utilized in Gamma Knife Lightning. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 832656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, D.J.; Kotecha, R.; Hall, M.D.; Tom, M.C.; Davis, S.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; McDermott, M.W.; Mehta, M.P.; Gutierrez, A.N.; Tolakanahalli, R. Systematic evaluation and plan quality assessment of the Leksell® gamma knife® lightning dose optimizer. Med. Dosim. 2022, 47, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schüler, E.; Lo, A.; Chuang, C.F.; Soltys, S.G.; Pollom, E.L.; Wang, L. Clinical impact of the VOLO optimizer on treatment plan quality and clinical treatment efficiency for CyberKnife. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2020, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paddick, I. A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Technical note. J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. S3), 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuvret, L.; Noël, G.; Mazeron, J.-J.; Bey, P. Conformity index: A review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2006, 64, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-S.; Huang, H.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Hsu, S.-M. Utilizing collimated aperture with proton pencil beam scanning (PBS) for stereotactic radiotherapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med Phys. 2024, 25, e14362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Holmes, J.M.; Vora, S.A.; Stoker, J.B.; Bues, M.; Wong, W.W.; Sio, T.S.; Foote, R.L.; Patel, S.H.; Shen, J.; et al. Modelling small block aperture in an in-house developed GPU-accelerated Monte Carlo-based dose engine for pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2024, 69, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickling, S.V.; Corner, S.; Kruse, J.J.; Deisher, A.J. Design and characterization of an aperture system and spot configuration for ocular treatments with a gantry-based spot scanning proton beam. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 4521–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.; Shen, J.; Shan, J.; Patrick, C.L.; Wong, W.W.; Foote, R.L.; Patel, S.H.; Bues, M.; Liu, W. Technical note: Evaluation and second check of a commercial Monte Carlo dose engine for small-field apertures in pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 3497–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, J.N.; Zhang, X.D.; Li, J.; Frank, S.J.; Zhao, Z.X.; Luo, D.S.; Zhu, X.R.; Wang, C.J.; Tung, S.; et al. Treatment-Plan Comparison of Three Advanced Radiation Treatment Modalities for Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy to the Head and Neck. Int. J. Med. Phys. Clin. Eng. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 8, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, H.; Soleimani, A.; Gharehaghaji, N.; Mesbahi, A.; Manouchehri, F.; Shekarchi, B.; Dormanesh, B.; Dadgar, H.A. An overview on small-field dosimetry in photon beam radiotherapy: Developments and challenges. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2017, 13, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracchiolla, F.; Engwall, E.; Janson, M.; Tamm, F.; Lorentini, S.; Fellin, F.; Bertolini, M.; Algranati, C.; Righetto, R.; Farace, P.; et al. Clinical validation of a GPU-based Monte Carlo dose engine of a commercial treatment planning system for pencil beam scanning proton therapy. Phys. Med. 2021, 88, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Feng, H.; Morales, D.H.; Patel, S.H.; Wong, W.W.; Fatyga, M.; Bues, M.; Schild, S.E.; Foote, R.L.; Liu, W. Virtual particle Monte Carlo: A new concept to avoid simulating secondary particles in proton therapy dose calculation. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 6666–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosse, C.; Narayanasamy, G.; Saenz, D.; Myers, P.; Kirby, N.; Rasmussen, K.; Mavroidis, P.; Papanikolaou, N.; Stathakis, S. Dose Calculation Comparisons between Three Modern Treatment Planning Systems. J. Med. Phys. 2020, 45, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, F.; Clemente, S.; Graeff, C.; Palma, G.; Cella, L. Dose Calculation Algorithms for External Radiation Therapy: An Overview for Practitioners. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco, L.; Vega, K.; Maffei, N.; Gutierrez, M.V.; Cenacchi, E.; Bernabei, A.; Bruni, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Meduri, B.; Lohr, F.; et al. Validation of RayStation Monte Carlo dose calculation algorithm for multiple LINACs. Phys. Med. 2023, 109, 102588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantelis, E.; Logothetis, A.; Zoros, E.; Pappas, E.P.; Papagiannis, P.; Paddick, I.; Nordström, H.; Kollias, G.; Karaiskos, P. Dosimetric accuracy of the Convolution algorithm for Leksell Gamma Plan radiosurgery treatment planning: Evaluation in the presence of clinically relevant inhomogeneities. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2023, 24, e13903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, D.; Blanck, O.; Gauer, T.; Fix, M.K.; Brunner, T.B.; Fleckenstein, J.; Loutfi-Krauss, B.; Manser, P.; Werner, R.; Wilhelm, M.L.; et al. Technological quality requirements for stereotactic radiotherapy: Expert review group consensus from the DGMP Working Group for Physics and Technology in Stereotactic Radiotherapy. Strahlenther. Onkol. 2020, 196, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesko, S.; Wang, H.; Tung, S.; Wang, C.; Pasalic, D.; Chapman, B.V.; Moreno, A.C.; Reddy, J.P.; Garden, A.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; et al. Estimating PTV Margins in Head and Neck Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy (SABR) Through Target Site Analysis of Positioning and Intrafractional Accuracy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 106, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younkin, J.E.; Morales, D.H.; Shen, J.; Ding, X.; Stoker, J.B.; Yu, N.Y.; Sio, T.T.; Daniels, T.B.; Bues, M.; Fatyga, M.; et al. Technical Note: Multiple energy extraction techniques for synchrotron-based proton delivery systems may exacerbate motion interplay effects in lung cancer treatments. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 4812–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diwanji, T.P.; Mohindra, P.; Vyfhuis, M.; Snider, J.W., 3rd; Kalavagunta, C.; Mossahebi, S.; Yu, J.; Feigenberg, S.; Badiyan, S.N. Advances in radiotherapy techniques and delivery for non-small cell lung cancer: Benefits of intensity-modulated radiation therapy, proton therapy, and stereotactic body radiation therapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, S.M.; Lai, Y.C.; Jeng, C.C.; Tseng, C.Y. Dosimetric comparison of different treatment modalities for stereotactic radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 12, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.S.; Hall, L.; Li, X.; Downes, L.; Shearer, A.; Shelton, B.J.; Gerring, S.; McGarry, R.C. Comparison of outcomes of stereotactic body radiation therapy delivered with three different technologies to the lung. J. Radiosurg SBRT 2018, 5, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aljabab, S.; Vellayappan, B.; Vandervoort, E.; Bahm, J.; Zohr, R.; Sinclair, J.; Caudrelier, J.M.; Szanto, J.; Malone, S. Comparison of four techniques for spine stereotactic body radiotherapy: Dosimetric and efficiency analysis. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2018, 19, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Kwong, T.; Danish, S.F.; Weiner, J.; Wang, X.; Yue, N.; Dai, Z.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Dosimetric comparisons of different hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy techniques in treating intracranial tumors > 3 cm in longest diameter. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 132, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, J.; Suilamo, S.; Tenhunen, M.; Sailas, L.; Virsunen, H.; Kaleva, E.; Keyriläinen, J. Dosimetric Comparison and Evaluation of 4 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Techniques for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, J.; Pollard, C.; Brown, P.D.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; Garden, A.S.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Fuller, C.D.; Frank, S.J.; Gunn, G.B.; Morrison, W.H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal pain secondary to recurrent malignant skull base tumors. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 812–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrends, C.; Bäumer, C.; Verbeek, N.G.; Wulff, J.; Timmermann, B. Optimization of proton pencil beam positioning in collimated fields. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 2540–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

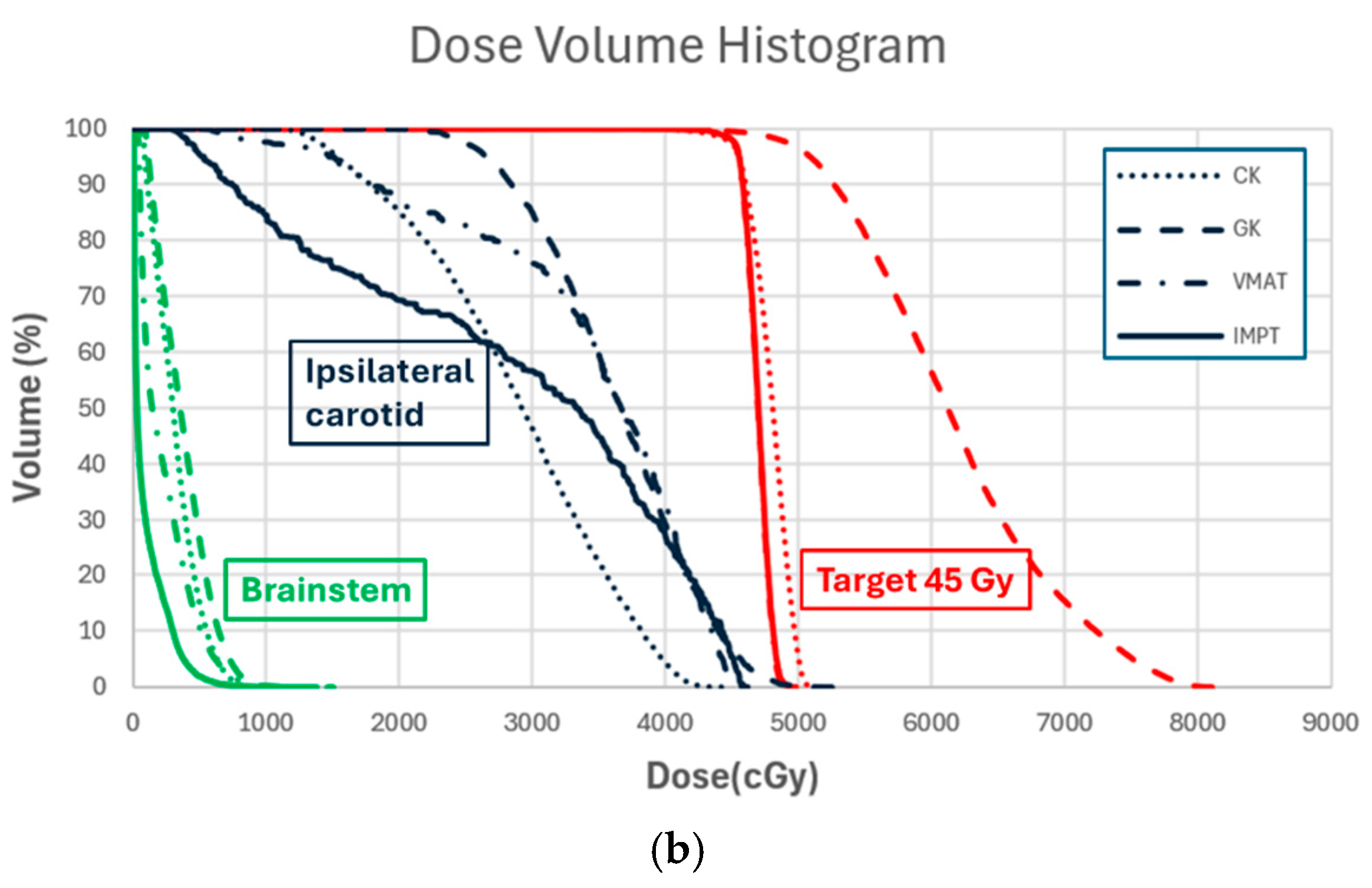

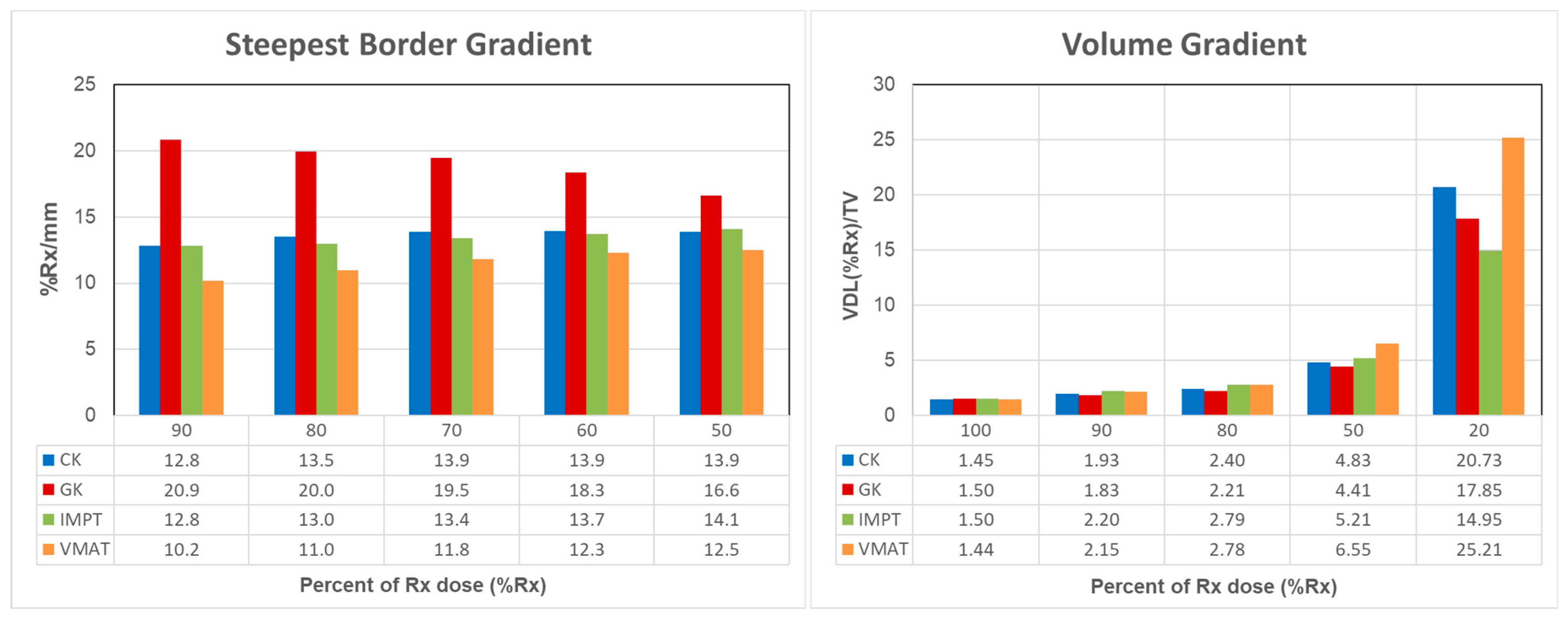

| Modalities and Models | Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion/ICONTM | CyberKnife M6/S7 | TrueBeam STx | Proton ProBeat-FR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturers | Elekta | Accuray | Varian | Hitachi |
| Radiation source/energy | 192 sealed Co-60 sources (1.17 MeV and 1.33 MeV) | 6 MeV photons on robotic arm | 6 MeV, 10 MeV, 6 MeV FFF, 10 MeV FFF Photon on C arm | 72.5 MeV–221.8 MeV proton |
| Mechanical and radiation accuracy | Sub-millimeter | Sub-millimeter | Sub-millimeter | Sub-millimeter |
| Collimation | Eight-sector crown-shaped collimator | Fixed cone, Iris collimator, InCise MLC | Jaw, high-definition MLC | Aperture, focused collimator |
| Maximum field size | 1.6 cm (shot size) | Fixed cone, Iris collimator: 6 cm MLC: 12 cm × 10 cm | Jaw: 40 cm × 40 cm MLC: 22 cm × 40 cm | 30 cm × 40 cm |
| Beam delivery | Combination of 4, 8, and 16 mm beams (shots) | Beamlets from hundreds of unique angles | Fixed-angle IMRT beams, VMAT | Passive scattering, Spot scanning (IMPT, spot size ~0.5 cm) |
| Dose rate | 2.0 Gy/min (before source change)—3.6 Gy/min (new source) | 400–1000 MU/min | 400–600 MU/min (6 MeV, 10 MeV photon), 1400 MU/min (6 MeV FFF), 2400 MU/min (10 MeV FFF photon) | 480 MU/min ** |
| Onboard imaging * | CBCT (ICON) [29,30] | kV imagers | 2D kV/MV and CBCT, 4D CBCT | 2D KV and CBCT |
| Motion management | ICON: high-definition motion management [31,32] | Synchrony respiratory tracking system [33] | External gating system | External gating system |
| 6 DoF setup/motion correction | 6 DoF treatment plan adaptation | 6 DoF delivery arm | 6 DoF couch | 6 DoF couch |
| Commissioning and quality assurance | Petti 2021 (TG 178) [34], Hu 2022 [35] | Sharma 2007 (TG 135) [36], Dieterich 2011 [37] | Klein 2009 (TG 142) [38], Hanley 2021 (TG 198) [39] | Arjomandy 2019 (TG 185) [40], Farr 2021 [41] |
| Treatment Planning Systems | Leksell GammaPlan | Accuray Precision | RayStation—IMRT/VMAT | RayStation—Proton |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturers | Elekta | Accuray | RaySearch | RaySearch |
| Planning image | CT (pre-RT), MRI | CT | CT | CT |
| Isocenter(s) per prescription | Non-isocentric | Non-isocentric | Isocentric | Isocentric |
| Dose calculation engine | TMR10, convolution | Ray Tracing, FSPB (MLC), Monte Carlo (MLC) | CC Convolution, Monte Carlo | Monte Carlo |
| inhomogeneity correction | Yes, in convolution when using CT and tumor < 2 cm distance from skin | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Optimization | Traditional inverse planning, LDO optimizer [54,55] | VOLO optimizer [56] | DMPO, MCO, robust optimization | DMPO, MCO, robust optimization |
| Adaptative planning | No | Yes, through PreciseART | Yes | Yes |
| Patient | Site | Anatomical/Clinical Region | Target Volume (cm3) | Prescription (Gy) | Number of Fractions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Petroclival Occiput | Posterior Cranial Fossa | 36.4 | 45 | 5 |
| 2 | Petroclival Occiput | Posterior Cranial Fossa | 36.4 | 24 | 3 |
| 3 | Petroclival Occiput | Posterior Cranial Fossa | 29.8 | 21 | 3 |
| 4 | V3/Ovale | Central Skull Base | 29.6 | 45 | 5 |
| 5 | Clivus | Central Skull Base | 26.1 | 45 | 5 |
| 6 | Ethmoid/Cribiform | Anterior Cranial Fossa | 25.7 | 45 | 5 |
| 7 | Nasopharynx | Retropharynx | 21.6 | 45 | 5 |
| 8 | Cavernous Sinus | Central Skull Base | 20.7 | 45 | 5 |
| 9 | Retropharyngeal Node | Retropharynx | 16.3 | 45 | 5 |
| 10 | Cavernous Sinus | Central Skull Base | 15 | 27 | 3 |
| 11 | Cavernous Sinus | Central Skull Base | 10.5 | 21 | 3 |
| 12 | Petroclival | Posterior Cranial Fossa | 9.2 | 24 | 3 |
| 13 | Retropharyngeal | Retropharynx | 9 | 45 | 5 |
| 14 | Retropharyngeal | Retropharynx | 7.4 | 45 | 5 |
| 15 | Dura | Intracranial | 2.6 | 24 | 3 |
| 16 | Petroclival | Posterior Cranial Fossa | 2.1 | 21 | 3 |
| Structures | Clinical Goals/Dose Constraints | |
|---|---|---|
| PTVs | V100% > 95% | |
| Dmax < 120% | ||
| OARs | No hot spot if in target, as low as reasonably achievable if outside of or away from target | |
| 21–27 Gy/3 fractions | 40–45 Gy/5 fractions | |
| Brainstem | Dmax < 10 Gy | Dmax < 13 Gy |
| Spinal cord | Dmax < 9 Gy | Dmax < 12 Gy |
| Optic apparatus | Dmax < 9 Gy | Dmax < 12 Gy |
| Carotids | Dmax < 20 Gy | Dmax < 30 Gy |
| Cochlea | Dmax < 21 Gy | Dmax < 21 Gy |
| Temporal lobe | Dmax < 18 Gy V12 Gy < 3 cm3 | Dmax < 27 Gy V18 Gy < 3 cm3 |
| Technique | Primary Target Coverage (%) | PCI | HI | Beam-on-Time (min) | Delivery Time (min) | SBG @90%Rx (%/mm) | SBG @50%Rx (%/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 98 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 24.3 * | 24.3 | 12.8 | 13.9 |
| GK | 96.8 | 0.64 | 0.56 | 71.3 * | 71.3 | 20.9 | 16.6 |
| IMPT | 97.9 | 0.65 | 0.09 | 2.2 | 12.1 | 12.8 | 14.1 |
| VMAT | 98.1 | 0.69 | 0.08 | 4.4 | 6.1 | 10.2 | 12.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Alsanea, F.M.; Rhee, D.J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Williamson, T.D.; Hunter, R.A.; et al. Advanced External Beam Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Skull Base Reirradiation. Cancers 2025, 17, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030540
Wang H, Alsanea FM, Rhee DJ, Zhang X, Liu W, Yang J, Wen Z, Zhao Y, Williamson TD, Hunter RA, et al. Advanced External Beam Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Skull Base Reirradiation. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030540
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, He, Fahed M. Alsanea, Dong Joo Rhee, Xiaodong Zhang, Wei Liu, Jinzhong Yang, Zhifei Wen, Yao Zhao, Tyler D. Williamson, Rachel A. Hunter, and et al. 2025. "Advanced External Beam Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Skull Base Reirradiation" Cancers 17, no. 3: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030540
APA StyleWang, H., Alsanea, F. M., Rhee, D. J., Zhang, X., Liu, W., Yang, J., Wen, Z., Zhao, Y., Williamson, T. D., Hunter, R. A., Balter, P. A., Briere, T. M., Zhu, R. X., Lee, A., Moreno, A. C., Reddy, J. P., Garden, A. S., Rosenthal, D. I., Gunn, G. B., & Phan, J. (2025). Advanced External Beam Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Skull Base Reirradiation. Cancers, 17(3), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030540








