Transfer Learning-Based Integration of Dual Imaging Modalities for Enhanced Classification Accuracy in Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
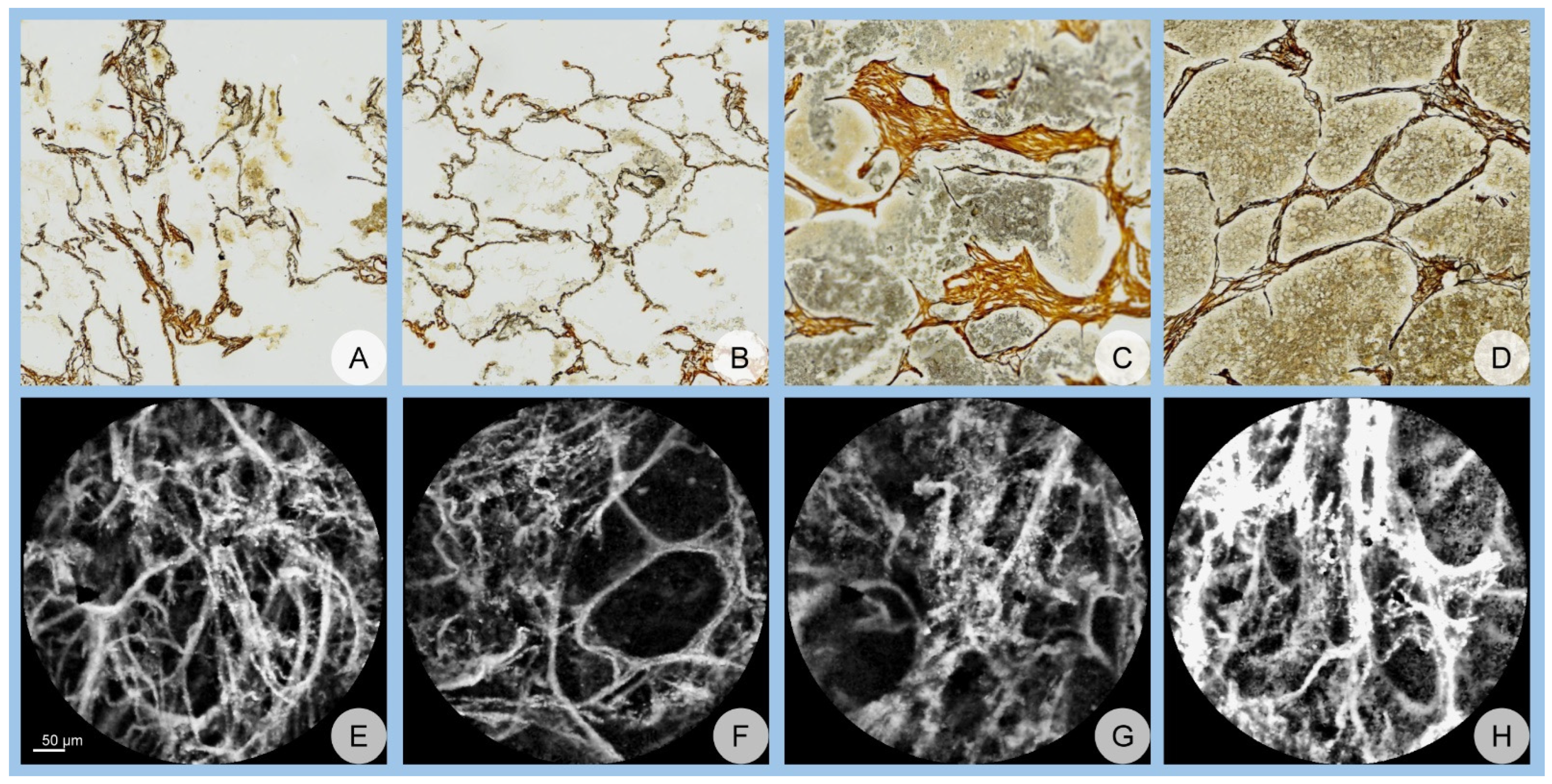
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Network Performance
3.1.1. Accuracy Assessment
3.1.2. AUC Assessment
| Accuracy, Mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) | AlexNet | GoogLeNet | ResNet | ANOVA, p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual TL scenario | 94.97 ± 1.76 | 91.43 ± 2.17 | 89.87 ± 2.15 | <0.001 |
| Confocal TL scenario | 90.14 ± 2.13 | 85.71 ± 2.55 | 84.65 ± 1.84 | <0.001 |
| Student’s t-test, p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| AUC, Mean ± Standard Deviation (SD) | AlexNet | GoogLeNet | ResNet | ANOVA, p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dual TL scenario | 0.98 ± 0.01 | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.96 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Confocal TL scenario | 0.97 ± 0.01 | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 0.94 ± 0.01 | <0.001 |
| Student’s t-test, p | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
3.2. Confusion Matrix Analysis
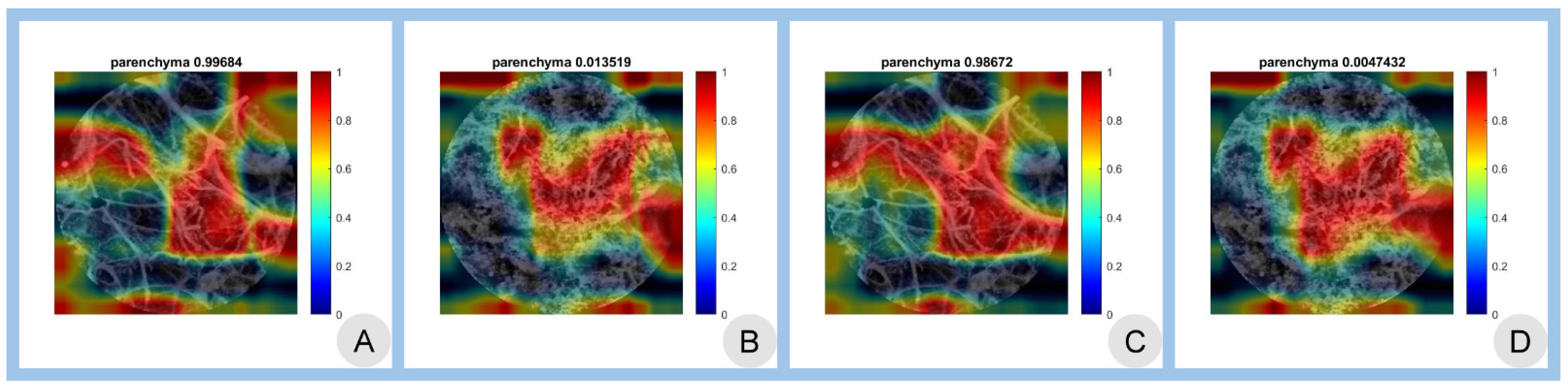
3.3. Class Activation Mapping
3.4. Summary of Performance Metrics
3.5. Statistical Significance
3.6. Overall Performance
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
4.2. Wrap-Up and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| CAM | class activation mapping |
| CNN | convolutional neural network |
| DL | deep learning |
| LDCT | low-dose computed tomography |
| pCLE | confocal laser endomicroscopy |
| TL | transfer learning |
References
- Cai, W.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Xu, Y. Interpretation of global lung cancer statistics. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 562–569. [Google Scholar]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.G.; Haines, C.; Perkel, R.; Enck, R.E. Lung cancer: Diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 2007, 75, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, J.; Malvezzi, M.; Negri, E.; La Vecchia, C.; Boffetta, P. Risk factors for lung cancer worldwide. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 48, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipfert, F.W.; Wyzga, R.E. Longitudinal relationships between lung cancer mortality and air pollution. Risk Anal. 2019, 39, 1646–1664. [Google Scholar]
- Maisonneuve, P.; Rampinelli, C.; Bertolotti, R.; Melloni, G.; Pelosi, G.; de Braud, F.; Spaggiari, L.; Pastorino, U. Low-dose computed tomography screening for lung cancer in smokers. JAMA 2019, 322, 584–594. [Google Scholar]
- Gouvinhas, C.; De Mello, R.A.; Oliveira, D.; Castro-Lopes, J.M.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Dos Santos, R.S.; Hespanhol, V.; Pozza, D.H. Lung cancer: A brief review of epidemiology and screening strategies. Future Oncol. 2018, 14, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, A.; Dubey, A.; Saini, D.; Singh, M.; Prasad, C.P.; Roy, S.; Mandal, C.; Bhandari, S.; Kumar, S.; Lathwal, A.; et al. Environ-mental and occupational determinants of lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8 (Suppl. S1), S31–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, W.G. Integrating prevention and screening for lung cancer into clinical practice. Chest 2013, 143, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar]
- D’Urso, D.; Doneddu, G.; Lojacono, M.; Tanda, F.; Serra, M.; Marras, V.; Cossu, A.; Corda, S.; Piredda, S.; Deidda, M.; et al. Sputum analysis for non-invasive early lung cancer detection. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrett, M.B.; Crosbie, P.A. Targeting lung cancer screening to individuals at highest risk. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 226–228. [Google Scholar]
- Takemura, S.; Kurimoto, N.; Miyazawa, T.; Ohta, K.; Hino, H.; Murata, Y.; Takai, Y.; Kaneko, Y.; Maekura, R. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy for rapid diagnosis of pulmonary nodules. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudoir, B.R.; Brandi, C.; McGill, S.; Smith, R.A.; Wilson, J.; Park, G.; Klein, C. Frontier in pathology: Comparison of pCLE and biopsy. J. Thorac. Dis. 2014, 6, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Wellikoff, A.S.; Holladay, R.C.; Downie, G.H. Comparison of in vivo probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy with biopsy. Respiration 2015, 90, 205–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yserbyt, J.; Dooms, C.; Ninane, V. Perspectives using probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Respiration 2013, 85, 304–310. [Google Scholar]
- Danilevskaya, O.V.; Sazonov, D.V.; Zabozlaev, F.G.; Averyanov, A.V.; Sorokina, A.; Sotnikova, A.G.; Urazovsky, N.; Kuzovlev, O.P.; Shablovsky, O.R. Confocal laser endomicroscopy in diagnosis of solitary and multiple pulmonary nodular infiltrates. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 660. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiek, H.; Fiorentino, F.; Larici, A.; Ravaglia, C.; Poletti, V.; Tognini, G.; Roviaro, G.; Fanti, S.; Neri, E.; Fiume, D. Usefulness of bron-choscopic probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in pneumonia. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Yserbyt, J.; Dooms, C.; Verleden, G.M.; Vanaudenaerde, B.M.; Vos, R.; Weynand, B.; Decramer, M.; Verleden, S.E. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in acute lung rejection. Am. J. Transplant. 2011, 11, 2466–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Salaün, M.; Guisier, F.; Lena, H.; Thiberville, L. In vivo probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy in pulmonary pathology. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 225. [Google Scholar]
- Buchner, A.M.; Gómez, V.; Heckman, M.G.; Shah, R.J.; Schueler, B.A.; Ghabril, M.S.; Raimondo, M.; Krishna, M.; Wallace, M.B. The learning curve of in vivo probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Endoscopy 2009, 41, 902–908. [Google Scholar]
- Nóbrega, R.V.M.; Peixoto, S.A.; Silva, S.P.; Filho, P.P. Lung nodule classification via deep transfer learning in CT Lung Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 31st International Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems (CBMS), Karlstad, Sweden, 18–21 June 2018; pp. 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhani, P.; Sundaram, B. Deep learning at chest radiography: Automated classification of tuberculosis. Radiology 2017, 284, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z. Interpretability study of pretrained models via transfer learning for lung cancer prediction. Proc. SPIE Med. Imaging 2022, 12451, 124514X. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z. The transferability of transfer learning model based on ImageNet for medical image classification tasks. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2023, 18, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmani, N.; Rezayi, S.; Esmaeeli, E.; Karimi, A. Transfer learning from non-medical images to medical images. Front. Health Inform. 2024, 13, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.; Interian, Y.; Solberg, T.; Valdes, G. Targeted transfer learning for small medical datasets. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar]
- Bungărdean, R.M.; Şerbănescu, M.-S.; Streba, C.T.; Crişan, M. Deep learning with transfer learning in pathology. Case study: Classification of basal cell carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022, 62, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, Y.; Talo, M.; Yıldırım, Ö.; Karabatak, M.; Acharya, U.R. Automated invasive ductal carcinoma detection using deep transfer learning. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2020, 133, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anusha, M.; Reddy, D.S. Enhancing lung and colon cancer diagnosis using ImageNet-trained transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2024 Tenth International Conference on Bio Signals, Images, and Instrumentation (ICBSII), Chennai, India, 20–22 March 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Said, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Sumon, M.S.I.; Vranić, S.; Al Saady, R.M.; Alqahtani, A.; Chowdhury, M.; Pedersen, S. Innovative deep learning for lung and colon cancer classification. Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft. Comput. 2024, 2024, 5562890. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, R.; Tang, Y.; Xu, K.; Kammer, M.; Antic, S.; Deppen, S.; Sandler, K.; Massion, P.; Huo, Y.; Landman, B.A. Deep multi-path network integrating incomplete biomarker and chest CT data. Proc. SPIE Med. Imaging 2020, 11596, 115961E. [Google Scholar]
- MathWorks. AlexNet. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/deeplearning/ref/alexnet.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- MathWorks. GoogLeNet. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/deeplearning/ref/googlenet.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- MathWorks. ResNet-18. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/help/deeplearning/ref/resnet18.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- ImageNet. Available online: http://www.image-net.org/ (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Nica, R.-E.; Șerbănescu, M.-S.; Florescu, L.-M.; Camen, G.-C.; Streba, C.T.; Gheonea, I.-A. Deep Learning: A Promising Method for Histological Class Prediction of Breast Tumors in Mammography. J. Digit. Imaging 2021, 34, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convo-lutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tortora, M.; Cordelli, E.; Sicilia, R.; Nibid, L.; Ippolito, E.; Perrone, G.; Ramella, S.; Soda, P. RadioPathomics: Multimodal Learning in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.12423. [Google Scholar]
- Mercuţ, R.; Ciurea, M.E.; Traşcă, E.T.; Ionescu, M.; Mercuţ, M.F.; Rădulescu, P.M.; Călăraşu, C.; Streba, L.; Ionescu, A.G.; Rădulescu, D. Applying Neural Networks to Analyse Inflammatory, Sociodemographic, and Psychological Factors in Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer and Colon Cancer: A Statistical and Artificial Intelligence Approach. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, D.; Calafeteanu, D.M.; Radulescu, P.-M.; Boldea, G.-J.; Mercut, R.; Ciupeanu-Calugaru, E.D.; Georgescu, E.-F.; Boldea, A.M.; Georgescu, I.; Caluianu, E.-I.; et al. Enhancing the Understanding of Abdominal Trauma During the COVID-19 Pandemic Through Co-Occurrence Analysis and Machine Learning. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şerbănescu, M.-S.; Manea, N.C.; Streba, L.; Belciug, S.; Pleşea, I.E.; Pirici, I.; Bungărdean, R.M.; Pleşea, R.M. Automated Gleason grading of prostate cancer using transfer learning from general-purpose deep-learning networks. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şerbănescu, M.-S.; Oancea, C.-N.; Streba, C.T.; Pleşea, I.E.; Pirici, D.; Streba, L.; Pleşea, R.M. Agreement of two pre-trained deep-learning neural networks built with transfer learning with six pathologists on 6000 patches of prostate cancer from Gleason2019 Challenge. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2020, 61, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șerbănescu, M.-S.; Bungărdean, R.M.; Georgiu, C.; Crișan, M. Nodular and Micronodular Basal Cell Carcinoma Subtypes Are Different Tumors Based on Their Morphological Architecture and Their Interaction with the Surrounding Stroma. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungărdean, R.-M.; Şerbănescu, M.-S.; Colosi, H.A.; Crişan, M. High-frequency ultrasound: An essential non-invasive tool for the pre-therapeutic assessment of basal cell carcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2022, 62, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitroi, G.; Pleşea, R.M.; Pop, O.T.; Ciovică, D.V.; Şerbănescu, M.S.; Alexandru, D.O.; Stoiculescu, A.; Pleşea, I.E. Correlations between intratumoral interstitial fibrillary network and vascular network in Srigley patterns of prostate adenocarcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56, 1319–1328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pleşea, I.E.; Stoiculescu, A.; Serbănescu, M.; Alexandru, D.O.; Man, M.; Pop, O.T.; Pleşea, R.M. Correlations between intratumoral vascular network and tumoral architecture in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2013, 54, 299–308. [Google Scholar]
- Stoiculescu, A.; Plesea, I.E.; Pop, O.T.; Alexandru, D.O.; Man, M.; Serbanescu, M.; Plesea, R.M. Correlations between intratumoral in-terstitial fibrillary network and tumoral architecture in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2012, 53, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plesea, R.M.; Serbanescu, M.-S.; Ciovica, D.V.; Rosu, G.-C.; Moldovan, V.T.; Bungardean, R.M.; Popescu, N.A.; Plesea, I.E. The study of tumor architecture components in prostate adenocarcinoma using fractal dimension analysis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2019, 60, 501–519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.A.A.; Sayed, M.S.; Abdalla, M.I.; Rashwan, M.A. Breast cancer masses classification using deep convolutional neural networks and transfer learning. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 30735–30768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, X. Breast cancer histopathological image classification using convolutional neural networks with small SE-ResNet modules. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazo, C.; Bernal, J.; Trujillo, M.; Alegre, E. Transfer learning for classification of cardiovascular tissues in histological images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 165, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neamah, K.; Mohamed, F.; Waheed, S.R.; Kurdi, W.H.M.; Taha, A.Y.; Kadhim, K.A. Utilizing Deep Improved ResNet-50 for Brain Tumor Classification Based on MRI. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2024, 5, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, L.; Zhang, L. Medical Image Classification Using Transfer Learning and Network Pruning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 1–4 October 2023; pp. 1932–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Anusha, M.; Reddy, D.S. Enhancing Lung and Colon Cancer Diagnosis: An ImageNet-Trained Transfer Learning Approach for Histopathological Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2024 Tenth International Conference on Bio Signals, Images, and Instrumentation (ICBSII), Chennai, India, 20–22 March 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Boumaraf, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Ferkous, C. A new transfer learning-based approach to magnification dependent and independent classification of breast cancer in histopathological images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2021, 63, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, K.H.; Rowe, S.P.; Sadaghiani, M.S.; Leal, J.P.; Mena, E.; Choyke, P.L.; Du, Y.; Pomper, M.G. Deep Semisupervised Transfer Learning for Fully Automated Whole-Body Tumor Quantification and Prognosis of Cancer on PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2024, 65, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Whitney, H.M.; Giger, M.L. A deep learning methodology for improved breast cancer diagnosis using multiparametric MRI. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.-B.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lai, M.; Chang, E.I.-C. Large scale tissue histopathology image classification, segmentation, and visualization via deep convolutional activation features. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 19, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, A.H.; Khan, T.; Khan, S.A. Deep Transfer Learning Techniques-Based Automated Classification and Detection of Pulmonary Fibrosis from Chest CT Images. Processes 2023, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Hao, H.; Zhao, M.; Feng, Y.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Suzuki, K. A deep CNN-based transfer learning method for false positive reduction. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, Z.; Tong, R.; Lin, L. A deep 3D residual CNN for false-positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. Med. Phys. 2018, 45, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noaman, N.F.; Kanber, B.M.; Al Smadi, A.; Jiao, L.; Alsmadi, M.K. Advancing Oncology Diagnostics: AI-Enabled Early Detection of Lung Cancer Through Hybrid Histological Image Analysis. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 64396–64415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setio, A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Litjens, G.J.; Gerke, P.K.; Jacobs, C.; Riel, S.J.; Wille, M.M.; Naqibullah, M.; Sánchez, C.I.; Ginneken, B.V. Pulmonary Nodule Detection in CT Images: False Positive Reduction Using Multi-View Convolutional Networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaunzwa, T.L.; Hosny, A.; Xu, Y.; Shafer, A.; Diao, N.; Lanuti, M.; Christiani, D.C.; Mak, R.H.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Deep learning classification of lung cancer histology using CT images. Eur. J. Radiol. 2021, 145, 110013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şerbănescu, M.S.; Pleşea, I.E. A hardware approach for histological and histopathological digital image stain normalization. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56 (Suppl. S2), 735–741. [Google Scholar]

| AlexNet | GoogLeNet | ResNet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | Malignant | Benign | Malignant | Benign | Malignant | |||
| Actual class | Confocal TL scenario | Benign | 395 | 43 | 366 | 46 | 341 | 32 |
| Malignant | 5 | 357 | 34 | 354 | 59 | 368 | ||
| Dual TL scenario | Benign | 394 | 24 | 387 | 58 | 341 | 27 | |
| Malignant | 6 | 376 | 13 | 342 | 59 | 373 | ||
| Predicted class | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Șerbănescu, M.-S.; Streba, L.; Demetrian, A.D.; Gheorghe, A.-G.; Mămuleanu, M.; Pirici, D.-N.; Streba, C.-T. Transfer Learning-Based Integration of Dual Imaging Modalities for Enhanced Classification Accuracy in Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040611
Șerbănescu M-S, Streba L, Demetrian AD, Gheorghe A-G, Mămuleanu M, Pirici D-N, Streba C-T. Transfer Learning-Based Integration of Dual Imaging Modalities for Enhanced Classification Accuracy in Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(4):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040611
Chicago/Turabian StyleȘerbănescu, Mircea-Sebastian, Liliana Streba, Alin Dragoș Demetrian, Andreea-Georgiana Gheorghe, Mădălin Mămuleanu, Daniel-Nicolae Pirici, and Costin-Teodor Streba. 2025. "Transfer Learning-Based Integration of Dual Imaging Modalities for Enhanced Classification Accuracy in Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of Lung Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 4: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040611
APA StyleȘerbănescu, M.-S., Streba, L., Demetrian, A. D., Gheorghe, A.-G., Mămuleanu, M., Pirici, D.-N., & Streba, C.-T. (2025). Transfer Learning-Based Integration of Dual Imaging Modalities for Enhanced Classification Accuracy in Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy of Lung Cancer. Cancers, 17(4), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17040611







