Updates on the Treatment of Richter’s Syndrome, Including Novel Combination Approaches
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
3. Pathogenesis
4. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis
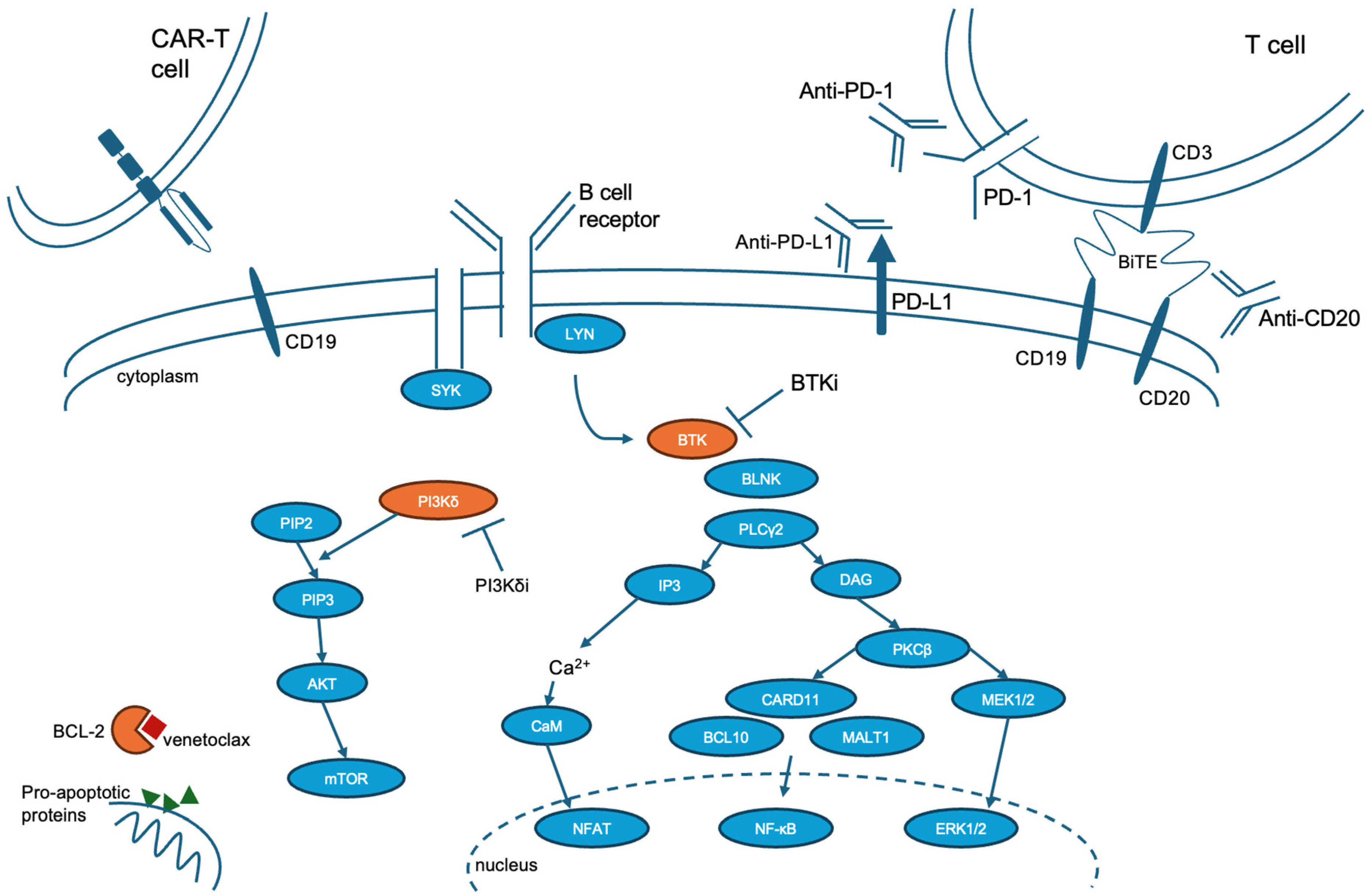
5. Treatment
5.1. Chemotherapy and Chemoimmunotherapy
5.2. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
5.3. Small Molecule Targeted Therapy
5.4. Protein Degrader Therapy
5.5. Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy
5.6. Bispecific Antibodies/Bispecific T Cell Engager Therapy
5.7. Chimeric Antigen T Cell Therapy
5.8. Potential New Therapeutic Agents
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RS | Richter’s syndrome |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| CLL | Chronic lymphocytic leukemia |
| CIT | Chemoimmunotherapy |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| CAR-T | Chimeric antigen receptor T cell |
| BsAb | Bispecific antibody |
References
- Richter, M.N. Generalized Reticular Cell Sarcoma of Lymph Nodes Associated with Lymphatic Leukemia. Am. J. Pathol. 1928, 4, 285–292.7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Petrackova, A.; Turcsanyi, P.; Papajik, T.; Kriegova, E. Revisiting Richter transformation in the era of novel CLL agents. Blood Rev. 2021, 49, 100824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, S.A.; Rabe, K.G.; Call, T.G.; Zent, C.S.; Habermann, T.M.; Ding, W.; Leis, J.F.; Schwager, S.M.; Hanson, C.A.; Macon, W.R.; et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Richter syndrome) in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL): A cohort study of newly diagnosed patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 162, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Keating, M.J. Richter syndrome: Biology, incidence, and therapeutic strategies. Cancer 2005, 103, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Robrecht, S.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Cramer, P.; Tresckow, J.V.; Lange, E.; Kiehl, M.; Dreyling, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)—A pooled analysis of German CLL Study Group (GCLLSG) front line treatment trials. Leukemia 2021, 35, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Cerri, M.; Capello, D.; Deambrogi, C.; Rossi, F.M.; Zucchetto, A.; De Paoli, L.; Cresta, S.; Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; et al. Biological and clinical risk factors of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 142, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, W. Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of novel agents. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 18, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Parikh, S.A.; Shanafelt, T.D. Risk factors for Richter syndrome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2014, 9, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villamor, N.; Conde, L.; Martinez-Trillos, A.; Cazorla, M.; Navarro, A.; Bea, S.; Lopez, C.; Colomer, D.; Pinyol, M.; Aymerich, M.; et al. NOTCH1 mutations identify a genetic subgroup of chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients with high risk of transformation and poor outcome. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, S.; Rossi, D.; Bergui, L.; D’Arena, G.; Ferrero, E.; Bonello, L.; Omede, P.; Novero, D.; Morabito, F.; Carbone, A.; et al. CD38 gene polymorphism and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A role in transformation to Richter syndrome? Blood 2008, 111, 5646–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rasi, S.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Vaisitti, T.; Tripodo, C.; Forconi, F.; De Paoli, L.; Fangazio, M.; Sozzi, E.; Cencini, E.; et al. A variant of the LRP4 gene affects the risk of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia transformation to Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 152, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.E.; Farooqui, M.Z.H.; Tian, X.; Valdez, J.; Sun, C.; Soto, S.; Lotter, J.; Housel, S.; Stetler-Stevenson, M.; Yuan, C.M.; et al. Depth and durability of response to ibrutinib in CLL: 5-year follow-up of a phase 2 study. Blood 2018, 131, 2357–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Hillmen, P.; Ghia, P.; Kater, A.P.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Furman, R.R.; O’Brien, S.; Yenerel, M.N.; Illés, A.; Kay, N.; et al. Acalabrutinib Versus Ibrutinib in Previously Treated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results of the First Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3441–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morabito, F.; Tripepi, G.; Del Poeta, G.; Mauro, F.R.; Reda, G.; Sportoletti, P.; Laurenti, L.; Coscia, M.; Herishanu, Y.; Bossio, S.; et al. Comparison of ibrutinib and idelalisib plus rituximab in real-life relapsed/resistant chronic lymphocytic leukemia cases. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.F.; D’Rozario, J.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; de la Serna, J.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Enduring undetectable MRD and updated outcomes in relapsed/refractory CLL after fixed-duration venetoclax-rituximab. Blood 2022, 140, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, P.J.; Rabe, K.G.; Wang, Y.; Hwang, S.R.; Kenderian, S.S.; Muchtar, E.; Leis, J.F.; Koehler, A.; Tsang, M.; Parrondo, R.; et al. Incidence of Richter Transformation in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SLL): A Cohort Study Evaluating Different Therapeutic Eras. Blood 2023, 142, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Bahlo, J.; Fink, A.M.; Goede, V.; Herling, C.D.; Cramer, P.; Langerbeins, P.; von Tresckow, J.; Engelke, A.; Maurer, C.; et al. Long-term remissions after FCR chemoimmunotherapy in previously untreated patients with CLL: Updated results of the CLL8 trial. Blood 2016, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; Jones, J.A.; Zhao, W.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Three-year follow-up of treatment-naive and previously treated patients with CLL and SLL receiving single-agent ibrutinib. Blood 2015, 125, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Keating, M.; Wierda, W.; Estrov, Z.; Ferrajoli, A.; Jain, N.; George, B.; James, D.; Kantarjian, H.; Burger, J.; et al. Outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia after discontinuing ibrutinib. Blood 2015, 125, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddocks, K.J.; Ruppert, A.S.; Lozanski, G.; Heerema, N.A.; Zhao, W.; Abruzzo, L.; Lozanski, A.; Davis, M.; Gordon, A.; Smith, L.L.; et al. Etiology of Ibrutinib Therapy Discontinuation and Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. JAMA Oncol. 2015, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.R.; Ruppert, A.S.; Heerema, N.A.; Maddocks, K.J.; Labanowska, J.; Breidenbach, H.; Lozanski, G.; Zhao, W.; Gordon, A.L.; Jones, J.A.; et al. Near-tetraploidy is associated with Richter transformation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients receiving ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Davids, M.S.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Puvvada, S.D.; Gerecitano, J.F.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Brown, J.R.; Gressick, L.; et al. Targeting BCL2 with Venetoclax in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Gaidano, G. Biology and treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2018, 131, 2761–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soilleux, E.J.; Wotherspoon, A.; Eyre, T.A.; Clifford, R.; Cabes, M.; Schuh, A.H. Diagnostic dilemmas of high-grade transformation (Richter’s syndrome) of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: Results of the phase II National Cancer Research Institute CHOP-OR clinical trial specialist haemato-pathology central review. Histopathology 2016, 69, 1066–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H. (Ed.) WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gine, E.; Martinez, A.; Villamor, N.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Camos, M.; Martinez, D.; Esteve, J.; Calvo, X.; Muntanola, A.; Abrisqueta, P.; et al. Expanded and highly active proliferation centers identify a histological subtype of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (“accelerated” chronic lymphocytic leukemia) with aggressive clinical behavior. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordone, I.; Matutes, E.; Catovsky, D. Monoclonal antibody Ki-67 identifies B and T cells in cycle in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Correlation with disease activity. Leukemia 1992, 6, 902–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Raffeld, M.; Richter, M.; Krugmann, J.; Burek, C.; Hartmann, E.; Rudiger, T.; Jaffe, E.S.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; et al. IgVH mutational status and clonality analysis of Richter’s transformation: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Hodgkin lymphoma in association with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) represent 2 different pathways of disease evolution. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Spina, V.; Deambrogi, C.; Rasi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Arcaini, L.; Lucioni, M.; Rocque, G.B.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; et al. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Blood 2011, 117, 3391–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigrinova, E.; Rinaldi, A.; Kwee, I.; Rossi, D.; Rancoita, P.M.; Strefford, J.C.; Oscier, D.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Papadaki, T.; Berger, F.; et al. Two main genetic pathways lead to the transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia to Richter syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, G.; Khiabanian, H.; Holmes, A.B.; Wang, J.; Messina, M.; Mullighan, C.G.; Pasqualucci, L.; Rabadan, R.; Dalla-Favera, R. Genetic lesions associated with chronic lymphocytic leukemia transformation to Richter syndrome. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2273–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Barchino, M.J.; Sarasquete, M.E.; Panizo, C.; Morscio, J.; Martinez, A.; Alcoceba, M.; Fresquet, V.; Gonzalez-Farre, B.; Paiva, B.; Young, K.H.; et al. Richter transformation driven by Epstein-Barr virus reactivation during therapy-related immunosuppression in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. J. Pathol. 2018, 245, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdad, A.; Griffin, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ma, S.; Kelemen, K.; Lu, X.; Chen, Q.C. PD-1 is highly expressed by neoplastic B-cells in Richter transformation. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, D.; Camoni, L.; Rodella, C.; Giubbini, R.; Bertagna, F. 2-[(18)F]-FDG PET/CT Role in Detecting Richter Transformation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Predicting Overall Survival. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, e277–e283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michallet, A.-S.; Sesques, P.; Rabe, K.G.; Itti, E.; Tordot, J.; Tychyj-Pinel, C.; Baseggio, L.; Subtil, F.; Salles, G.; Dupuis, J.M.; et al. An 18F-FDG-PET maximum standardized uptake value > 10 represents a novel valid marker for discerning Richter’s Syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 1474–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchi, L.; Keating, M.J.; Marom, E.M.; Truong, M.T.; Schlette, E.J.; Sargent, R.L.; Trinh, L.; Wang, X.; Smith, S.C.; Jain, N.; et al. Correlation between FDG/PET, histology, characteristics, and survival in 332 patients with chronic lymphoid leukemia. Blood 2014, 123, 2783–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaja, B.S.; O’Brien, S.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E.; Thomas, D.A.; Albitar, M.; Schlette, E.S.; Faderl, S.; Sarris, A.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin (daunoXome), and dexamethasone (hyperCVXD) regimen in Richter’s syndrome. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 42, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.; Thomas, D.A.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Verstovsek, S.; Ferrajoli, A.; Wierda, W.; Alvarado, Y.; et al. Fractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, liposomal daunorubicin, and dexamethasone plus rituximab and granulocyte-macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) alternating with methotrexate and cytarabine plus rituximab and GM-CSF in patients with Richter syndrome or fludarabine-refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer 2003, 97, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wierda, W.G.; Wen, S.; Plunkett, W.; O’Brien, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Jones, J.A.; Badoux, X.; Kantarjian, H.; Keating, M.J.; et al. Phase I-II clinical trial of oxaliplatin, fludarabine, cytarabine, and rituximab therapy in aggressive relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or Richter syndrome. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2013, 13, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langerbeins, P.; Busch, R.; Anheier, N.; Durig, J.; Bergmann, M.; Goebeler, M.E.; Hurtz, H.J.; Stauch, M.B.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Dohner, H.; et al. Poor efficacy and tolerability of R-CHOP in relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter transformation. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, E239–E243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Clifford, R.; Bloor, A.; Boyle, L.; Roberts, C.; Cabes, M.; Collins, G.P.; Devereux, S.; Follows, G.; Fox, C.P.; et al. NCRI phase II study of CHOP in combination with ofatumumab in induction and maintenance in newly diagnosed Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, K.A.; Huang, Y.; Ruppert, A.S.; Salem, G.; Stephens, D.M.; Heerema, N.A.; Andritsos, L.A.; Awan, F.T.; Byrd, J.C.; Flynn, J.M.; et al. A single-institution retrospective cohort study of first-line R-EPOCH chemoimmunotherapy for Richter syndrome demonstrating complex chronic lymphocytic leukaemia karyotype as an adverse prognostic factor. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durot, E.; Michallet, A.S.; Lepretre, S.; Le, Q.H.; Leblond, V.; Delmer, A. Platinum and high-dose cytarabine-based regimens are efficient in ultra high/high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia and Richter’s syndrome: Results of a French retrospective multicenter study. Eur. J. Haematol. 2015, 95, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsimberidou, A.M.; O’Brien, S.; Khouri, I.; Giles, F.J.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Champlin, R.; Wen, S.; Do, K.A.; Smith, S.C.; Lerner, S.; et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with Richter’s syndrome treated with chemotherapy or chemoimmunotherapy with or without stem-cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwynarski, K.; van Biezen, A.; de Wreede, L.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Bunjes, D.; Metzner, B.; Koza, V.; Mohty, M.; Remes, K.; Russell, N.; et al. Autologous and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for transformed chronic lymphocytic leukemia (Richter’s syndrome): A retrospective analysis from the chronic lymphocytic leukemia subcommittee of the chronic leukemia working party and lymphoma working party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guieze, R.; Eikema, D.J.; Koster, L.; Schetelig, J.; Sengeloev, H.; Passweg, J.; Finke, J.; Arat, M.; Broers, A.E.C.; Stolzel, F.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for patients with Richter transformation: A retrospective study on behalf of the Chronic Malignancies Working Party of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024, 59, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.F.; Ahn, K.W.; Litovich, C.; Chen, Y.; Assal, A.; Bashir, Q.; Bayer, R.L.; Coleman, M.; DeFilipp, Z.; Farhadfar, N.; et al. Autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-type Richter syndrome. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3528–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.T.; Baker, P.O.; Parry, E.; Davids, M.; Alyea, E.P.; Ho, V.T.; Cutler, C.; Koreth, J.; Gooptu, M.; Romee, R.; et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in patients with Richter’s transformation. Haematologica 2021, 106, 3219–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puckrin, R.; Owen, C.; Fontaine, A.; Peters, A.; Stewart, D.; Shafey, M. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia: An intention-to-transplant analysis. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2023, 58, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, M.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Call, T.G.; Ding, W.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Leis, J.F.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Bowen, D.; Conte, M.; Schwager, S.M.; et al. The efficacy of ibrutinib in the treatment of Richter syndrome. Blood 2015, 125, 1676–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Schuh, A.; Eyre, T.A.; Pagel, J.M.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Allan, J.N.; Wierda, W.; Hamdy, A.; Huang, J.; et al. Acalabrutinib Monotherapy in Patients with Richter Transformation from the Phase 1/2 ACE-CL-001 Clinical Study. Blood 2016, 128, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, T.A.; Schuh, A.; Wierda, W.G.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Pagel, J.M.; Furman, R.R.; Cheung, J.; Hamdy, A.; Izumi, R.; et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ACE-CL-001): Analysis of the Richter transformation cohort of an open-label, single-arm, phase 1-2 study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e912–e921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.; Munoz, J.; Cull, G.; Opat, S.; Allewelt, H.; Zhang, X.; Stern, J.C.; Hilger, J.; By, K.; Cohen, A.; et al. Zanubrutinib, Alone and in Combination with Tislelizumab, for the Treatment of Richter Transformation of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierda, W.G.; Shah, N.N.; Cheah, C.Y.; Lewis, D.; Hoffmann, M.S.; Coombs, C.C.; Lamanna, N.; Ma, S.; Jagadeesh, D.; Munir, T.; et al. Pirtobrutinib, a highly selective, non-covalent (reversible) BTK inhibitor in patients with B-cell malignancies: Analysis of the Richter transformation subgroup from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 BRUIN study. Lancet Haematol. 2024, 11, e682–e692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia/Small Lymphocytic Leukemia. 2025. Volume 1.2025. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/cll.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Davids, M.S.; Roberts, A.W.; Seymour, J.F.; Pagel, J.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Wierda, W.G.; Puvvada, S.; Kipps, T.J.; Anderson, M.A.; Salem, A.H.; et al. Phase I First-in-Human Study of Venetoclax in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Rogers, K.A.; Tyekucheva, S.; Wang, Z.; Pazienza, S.; Renner, S.K.; Montegaard, J.; Ihuoma, U.; Lehmberg, T.Z.; Parry, E.M.; et al. Venetoclax plus dose-adjusted R-EPOCH for Richter syndrome. Blood 2022, 139, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, P.J.; Swaminathan, M.; Rogers, K.A.; Parry, E.M.; Burger, J.A.; Davids, M.S.; Ding, W.; Ferrajoli, A.; Hyak, J.M.; Jain, N.; et al. A multicenter study of venetoclax-based treatment for patients with Richter transformation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 2342–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visentin, A.; Imbergamo, S.; Scomazzon, E.; Pravato, S.; Frezzato, F.; Bonaldi, L.; Pizzi, M.; Vio, S.; Gregianin, M.; Burei, M.; et al. BCR kinase inhibitors, idelalisib and ibrutinib, are active and effective in Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, J.F.; Cheah, C.Y.; Parrondo, R.; Thompson, M.C.; Stevens, D.A.; Lasica, M.; Wang, M.L.; Kumar, A.; Trotman, J.; Alwan, M.; et al. First Results from a Phase 1, First-in-Human Study of the Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Degrader Bgb-16673 in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) B-Cell Malignancies (BGB-16673-101). Blood 2023, 142, 4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencker, K. BeiGene’s BGB-16673 Receives U.S. FDA Fast Track Designation for CLL/SLL. Available online: https://ir.beigene.com/news/beigene-s-bgb-16673-receives-u-s-fda-fast-track-designation-for-cll-sll/ed433e34-61fd-4d89-b243-9e79381811df/ (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Reynolds, A. Nurix Therapeutics Presents New Positive Data from Phase 1a/1b Clinical Trial of NX-5948 in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia at the 66th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting. Available online: https://ir.nurixtx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/nurix-therapeutics-presents-new-positive-data-phase-1a1b (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Ding, W.; LaPlant, B.R.; Call, T.G.; Parikh, S.A.; Leis, J.F.; He, R.; Shanafelt, T.D.; Sinha, S.; Le-Rademacher, J.; Feldman, A.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood 2017, 129, 3419–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Murawski, N.; Molin, D.; Zain, J.; Eichhorst, B.; Gulbas, Z.; Hawkes, E.A.; Pagel, J.M.; Phillips, T.; Ribrag, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Richter syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e117–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Brody, J.; Carpio, C.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Ben-Yehuda, D.; Ferhanoglu, B.; Nagler, A.; Ozcan, M.; Avivi, I.; Bosch, F.; et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: A phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e67–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Senapati, J.; Thakral, B.; Ferrajoli, A.; Thompson, P.; Burger, J.; Basu, S.; Kadia, T.; Daver, N.; Borthakur, G.; et al. A phase 2 study of nivolumab combined with ibrutinib in patients with diffuse large B-cell Richter transformation of CLL. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Ligtvoet, R.; Robrecht, S.; Stumpf, J.; Fink, A.M.; Tausch, E.; Schneider, C.; Böttcher, S.; Mikusko, M.; Ritgen, M.; et al. Tislelizumab Plus Zanubrutinib in Patients with Richter Transformation: Primary Endpoint Analysis of the Prospective, Multi-Center, Phase-II RT1 Trial of the German CLL Study Group. Blood 2023, 142, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, B.T.; Ma, S.; Zent, C.S.; Baran, A.M.; Wallace, D.S.; Advani, A.; Winter, A.; Winter, J.; Gordan, L.; Karmali, R.; et al. Response-adapted, time-limited venetoclax, umbralisib, and ublituximab for relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.; Ferrajoli, A.; Thompson, P.A.; Konopleva, M.; Green, M.R.; Sampath, D.; Neelapu, S.S.; Takahashi, K.; Strati, P.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Venetoclax, Obinutuzumab and Atezolizumab (PD-L1 Checkpoint Inhibitor) for Treatment for Patients with Richter Transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, A.; Frustaci, A.M.; Condoluci, A.; Coscia, M.; Chiarle, R.; Zinzani, P.L.; Motta, M.; Gaidano, G.; Quaresmini, G.; Scarfo, L.; et al. Atezolizumab, venetoclax, and obinutuzumab combination in Richter transformation diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (MOLTO): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, A.R.; Svoboda, J.; Luning Prak, E.T.; Schuster, S.J.; Tsao, P.; Dorsey, C.; Becker, P.S.; Brander, D.M.; Dwivedy Nasta, S.; Landsburg, D.J.; et al. Phase I/II Study of Umbralisib (TGR-1202) in Combination with Ublituximab (TG-1101) and Pembrolizumab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory CLL and Richter’s Transformation. Blood 2018, 132, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, B.M.; Choi, M.Y.; Kipps, T.J. Obinutuzumab, High-Dose Methylprednisolone (HDMP), and Lenalidomide for the Treatment of Patients with Richter’s Syndrome. Cancers 2022, 14, 6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.; Morschhauser, F.; Iacoboni, G.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Offner, F.C.; Sureda, A.; Salles, G.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Crump, M.; Thomas, D.N.; et al. Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Jiang, X.; Banerjee, P.; Basar, R.; Garg, N.; Chen, K.; Kaplan, M.; Nandivada, V.; Cortes, A.K.N.; Ferrajoli, A.; et al. A phase two study of high dose blinatumomab in Richter’s syndrome. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2228–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guièze, R.; Ysebaert, L.; Roos-Weil, D.; Fornecker, L.-M.; Ferrant, E.; Molina, L.; Aurran, T.; Clavert, A.; de Guibert, S.; Michallet, A.-S.; et al. Blinatumomab after R-CHOP bridging therapy for patients with Richter transformation: A phase 2 multicentre trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kater, A.P.; Janssens, A.; Eradat, H.; Offner, F.; Sandoval-Sus, J.D.; Shadman, M.; Bjørn Poulsen, C.; Haaber Christensen, J.; Thompson, M.C.; Rios, M.; et al. CLL-280 Epcoritamab Induces Deep Responses in Patients with Richter Transformation (RT): Primary Results from the EPCORE CLL-1 Trial. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2024, 24, S350–S351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittai, A.S.; Bond, D.A.; William, B.; Saad, A.; Penza, S.; Efebera, Y.; Larkin, K.; Wall, S.A.; Choe, H.K.; Bhatnagar, B.; et al. Clinical activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in adult patients with Richter syndrome. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4648–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.M.; Bharadwaj, S.; Herrera, A.F.; Iragavarapu, C.; Mirza, S.; Palomba, M.L.; Patel, S.S.; Gharibo, M.M.; Bernasconi, D.; Krimmel, T.; et al. Real-world outcomes of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients (pt) with Richter transformation (RT) from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittai, A.S.; Bond, D.; Huang, Y.; Bhat, S.A.; Blyth, E.; Byrd, J.C.; Chavez, J.C.; Davids, M.S.; Dela Cruz, J.P.; Dowling, M.R.; et al. Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Richter Transformation: An International, Multicenter, Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, O.; Fried, S.; Shouval, R.; Flynn, J.R.; Beyar-Katz, O.; Leslie, L.A.; Zucherman, T.; Yerushalmi, R.; Shem-Tov, N.; Palomba, M.L.; et al. Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy has less efficacy in Richter transformation than in de novo large B-cell lymphoma and transformed low-grade B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3566–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Marin, D.; Banerjee, P.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Thompson, P.; Basar, R.; Nassif Kerbauy, L.; Overman, B.; Thall, P.; Kaplan, M.; et al. Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Martines, C.; Porro, F.; Fortunati, I.; Bonato, A.; Dimishkovska, M.; Piazza, S.; Yadav, B.S.; Innocenti, I.; Fazio, R.; et al. B-cell receptor signaling and genetic lesions in TP53 and CDKN2A/CDKN2B cooperate in Richter transformation. Blood 2021, 138, 1053–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Lin, T.S.; Dalton, J.T.; Wu, D.; Phelps, M.A.; Fischer, B.; Moran, M.; Blum, K.A.; Rovin, B.; Brooker-McEldowney, M.; et al. Flavopiridol administered using a pharmacologically derived schedule is associated with marked clinical efficacy in refractory, genetically high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Fabbro, D.; Bauer, M.; Murone, M.; Lehal, R. Notch Inhibition in Cancer: Challenges and Opportunities. Chimia 2020, 74, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casulo, C.; Ruan, J.; Dang, N.H.; Gore, L.; Diefenbach, C.; Beaven, A.W.; Castro, J.E.; Porcu, P.; Faoro, L.; Dupont, J.; et al. Safety and Preliminary Efficacy Results of a Phase I First-in-Human Study of the Novel Notch-1 Targeting Antibody Brontictuzumab (OMP-52M51) Administered Intravenously to Patients with Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2016, 128, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massard, C.; Azaro, A.; Soria, J.C.; Lassen, U.; Le Tourneau, C.; Sarker, D.; Smith, C.; Ohnmacht, U.; Oakley, G.; Patel, B.K.R.; et al. First-in-human study of LY3039478, an oral Notch signaling inhibitor in advanced or metastatic cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Tornel, S.; Chen-Liang, T.H.; Zurdo, M.; Puiggros, A.; Gómez-Llonín, A.; García-Malo, M.-D.; Cuenca, E.J.; Ortuño, F.J.; Hurtado López, A.M.; Espinet, B.; et al. NOTCH1 Mutation in CLL Enhances Cell Cycle G1/S Transition through Specific Cyclin Overexpression: Preclinical Ground for CDK4/6 Targeted Inhibition. Blood 2021, 138, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Barrientos, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.M.; Choi, M.Y.; de Vos, S.; Kallam, A.; Patel, K.; Kipps, T.J.; et al. Zilovertamab Vedotin Targeting of ROR1 as Therapy for Lymphoid Cancers. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patients with CLL (n) | Rate of Development Richter’s Syndrome | Median Time to Onset/ Cumulative Incidence Rate from Diagnosis | Study Dates | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1641 | 37/1641 (2.3%) | 1 year 0.5% | 2000–2011 | Parikh 2013 [3] |
| 84 | 4/84 (4.8%) | NR | 2011–2017 | Ahn 2018 [12] |
| 2975 | 103/2975 (3.5%) | NR | 1999–2016 | Al-Sawaf 2021 [5] |
| 533 | 23/533 (4.3%) total study population 10/268 (3.7%) in acalabrutinib arm 13/265 (4.9%) in ibrutinib arm | 7.1 months in acalabrutinib arm/11.5 months in ibrutinib arm | 2015–2020 | Byrd 2021 [13] |
| 675 | 28/675 (4.2%) total study population 26/563 (4.6%) in ibrutinib arm 2/112 (1.8%) in idelalisib+ rituximab arm | NR | - | Morabito 2021 [14] |
| 382 | 13/382 (3.4%) | NR | 2014–2020 | Seymour 2022 [15] |
| 3347 | 82/3347 (2.4%) | 1 year 0.6%, 5 year 1.8%, 10 year 3.0% | 2000–2023 | Hampel 2023 [16] |
| Treatment | Patients (n) | ORR/CRR (%) | Median PFS (months) | Median OS (months) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib | 4 | 75%/25% | 6.1 | NR | Tsang 2015 [51] |
| Acalabrutinib | 25 29 | 40%/8% 38%/14% | 3.2 | NR | Eyre 2021 [53] Hillmen 2016 [52] |
| Zanubrutinib | 13 | 61.5%/15.4% | 17.3 | 29.3 | Tam 2023 [54] |
| Pirtobrutinib | 82 | 50%/13% | 3.7 | 12.5 | Wierda 2024 [55] |
| Venetoclax | 7 | 43%/0% | NR | NR | Davids 2017 [57] |
| Venetoclax + DA R-EPOCH | 26 | 62%/50% | 10.1 | 19.6 | Davids 2022 [58] |
| Venetoclax + BTKi | 28 | 36%/25% | 4.9 | 14.3 | Hampel 2024 [59] |
| Venetoclax + R-CHOP | 13 | 54%/46% | 14.9 | Not reached | Hempel 2024 [59] |
| Idelalisib | 4 | 75%/25% | NR | NR | Visentin 2019 [60] |
| Pembrolizumab | 9 23 | 44%/11% 13%/0% | 5.4 1.6 | 10.7 3.8 | Ding 2017 [64] Armand 2020 [65] |
| Nivolumab + ibrutinib | 20 24 | 65%/10% 42%/33% | 5.0 NR | 10.3 13 | Younes 2019 [66] Jain 2023 [67] |
| Tislelizumab + zanubrutinib | 48 | 58.3%/18.8% | 10 | NR | Al-Sawaf 2023 [68] |
| Umbralisib + ublituximab + venetoclax | 5 | 40%/40% | NR | NR | Hill 2024 [69] |
| Atezolizumab + obinutuzumab + venetoclax | 7 28 | 100%/71% 67.9%/28.6% | NR NR | NR NR | Jain 2021 [70] Tedeschi 2024 [71] |
| Pembrolizumab + umbralisib + ublituximab | 8 | 37.5%/25% | NR | NR | Mato 2018 [72] |
| Obinutuzumab + high-dose methylprednisolone + lenalidomide | 7 | 43%/29% | 5 | 17 | Heyman 2022 [73] |
| Glofitamab | 10 | 83%/50% | 2.9 (all aggressive NHL) | NR | Hutchings 2021 [74] |
| Blinatumomab | 9 25 | 22%/11% 46%/20% | 1.9 3.8 | 10.3 9.1 | Thompson 2022 [75] Guieze 2024 [76] |
| Epcoritamab | 35 | 50%/35% | NR | NR | Kater 2024 [77] |
| Axicabtagene ciloleucel | 8 | 100%/62.5% | NR | NR | Kittai 2020 [78] |
| Lisocabtagene maraleucel | 30 | 76%/66% | NR | NR | Winter 2024 [79] |
| CD19 CAR-T cell | 69 | 63%/46% | 4.7 | 8.5 | Kittai 2024 [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, T.; Heyman, B. Updates on the Treatment of Richter’s Syndrome, Including Novel Combination Approaches. Cancers 2025, 17, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060943
Jain T, Heyman B. Updates on the Treatment of Richter’s Syndrome, Including Novel Combination Approaches. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060943
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Tanim, and Benjamin Heyman. 2025. "Updates on the Treatment of Richter’s Syndrome, Including Novel Combination Approaches" Cancers 17, no. 6: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060943
APA StyleJain, T., & Heyman, B. (2025). Updates on the Treatment of Richter’s Syndrome, Including Novel Combination Approaches. Cancers, 17(6), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060943






