Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Transactivate Glycosylated Cytokine Receptors on Cancer Cells to Induce Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition to the Metastatic Phenotype
Simple Summary
Abstract
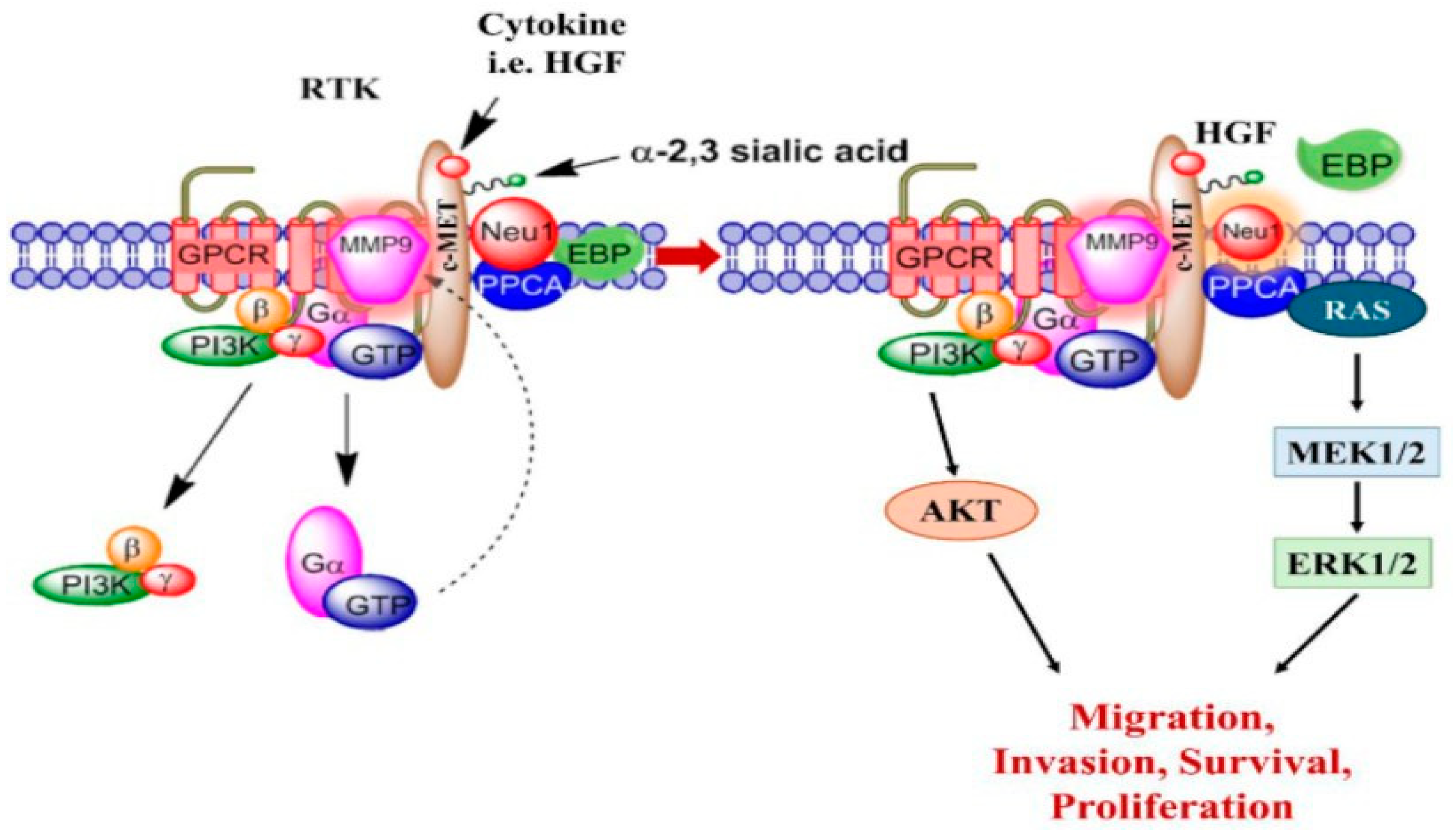
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Cytokines
2.3. Antibodies
2.3.1. Immunofluorescence
2.3.2. Colocalization
2.4. Inhibitors
2.5. Immunofluorescence Protocol
2.6. Colocalization Protocol
2.7. Sialidase Activity Assay
2.8. AlamarBlue Viability Assay and Metabolic Activity
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
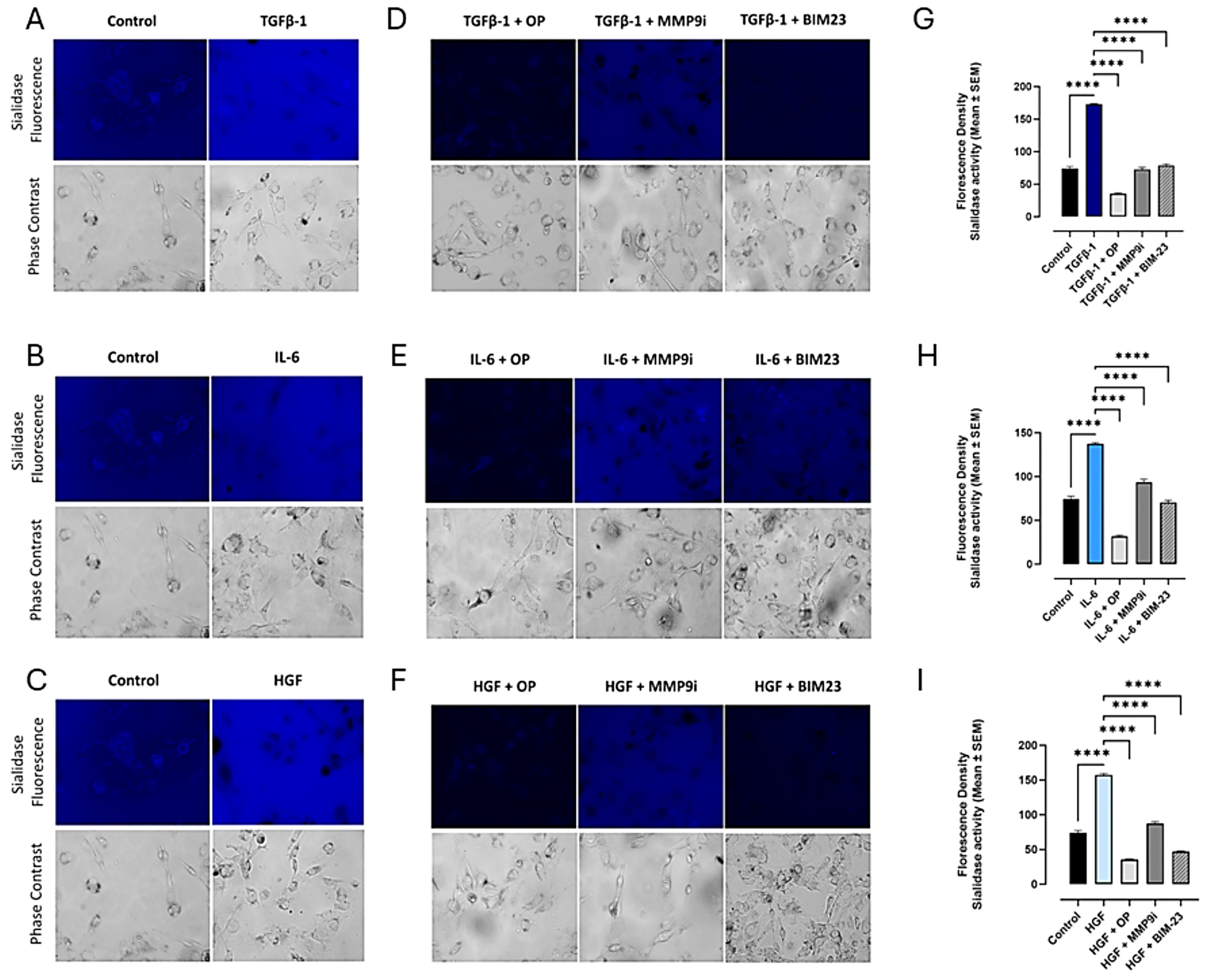
3.1. TGFβ-1, IL-6, and HGF Binding Respective Cytokine Receptors Induce Sialidase Activity
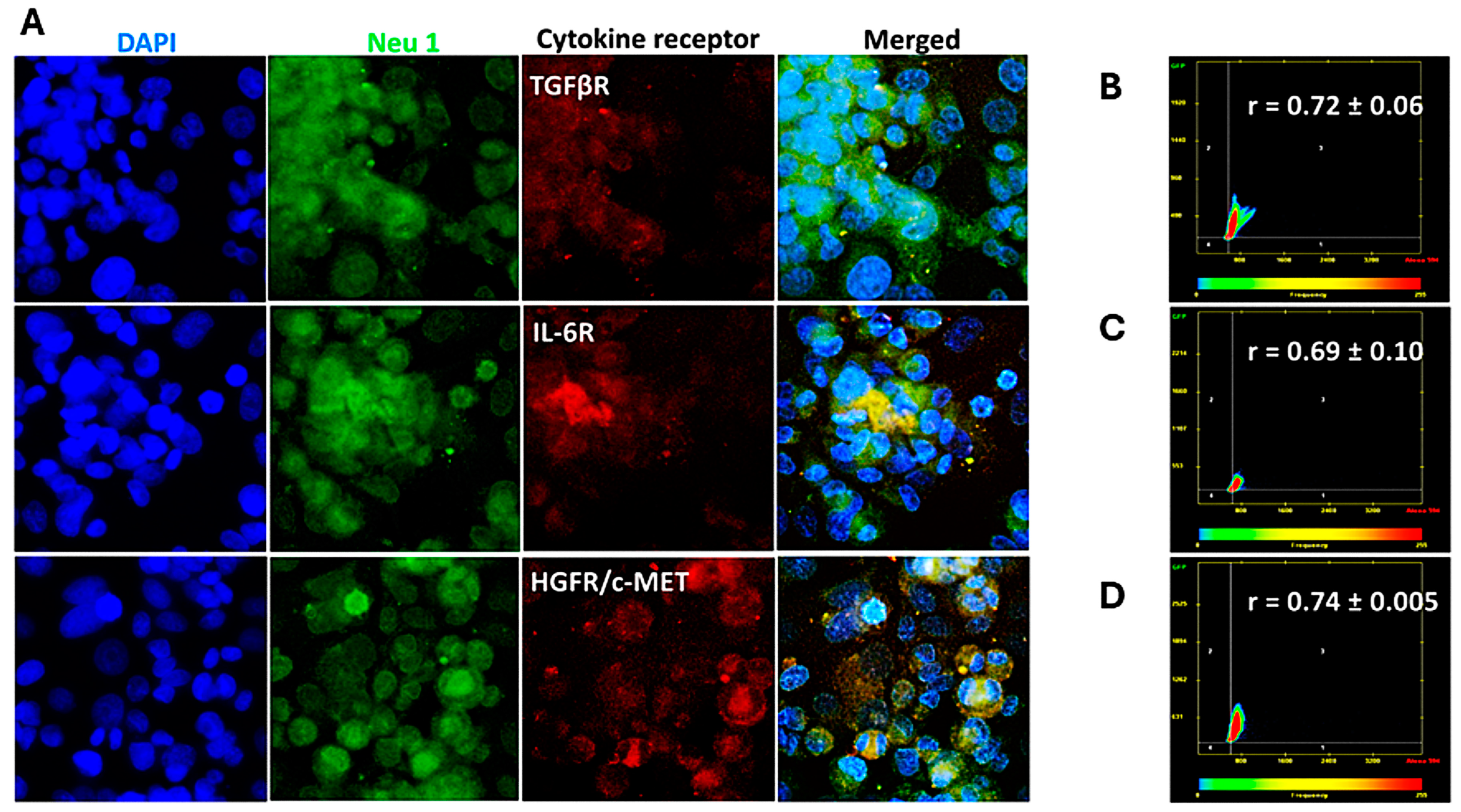
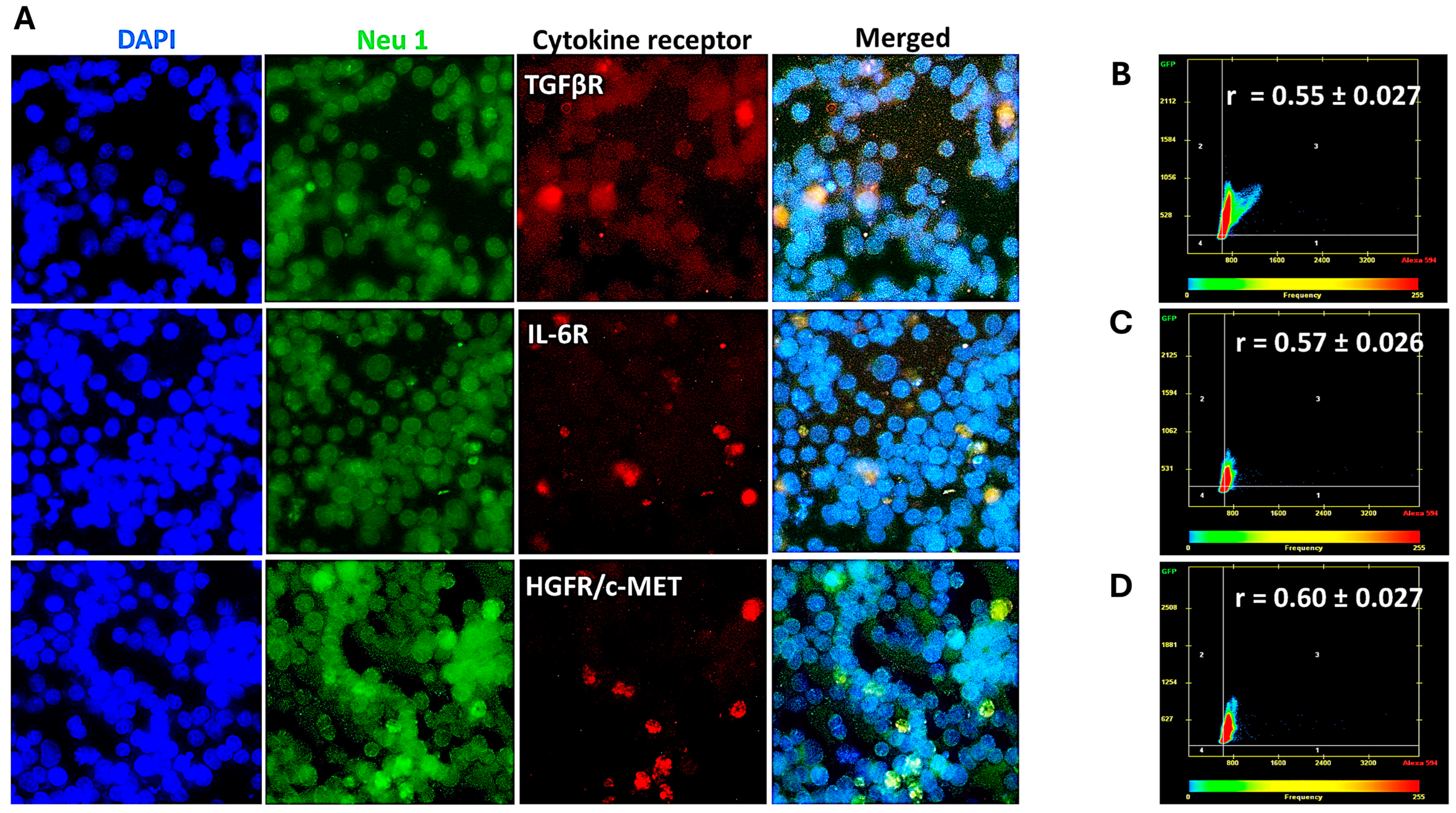
3.2. Cytokine Receptors Colocalize with Neu1 on the Cell Surface of Naïve Unstimulated PANC-1, SW-620, and MCF7 Cells
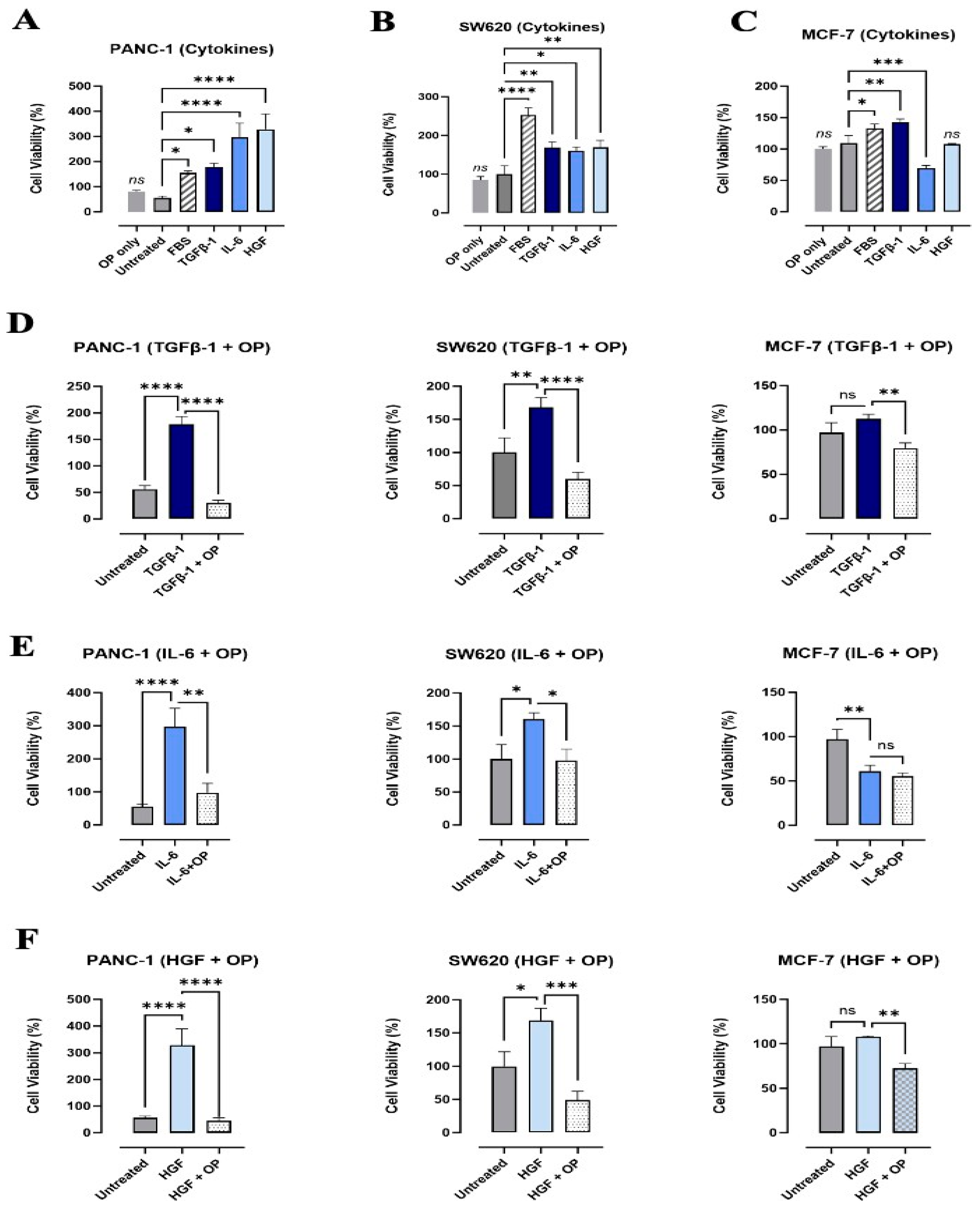
3.3. Effects of TGFβ-1, IL-6, and HGF on the Viability and Metabolic Activity of PANC-1, SW620, and MCF-7 Cancer Cells
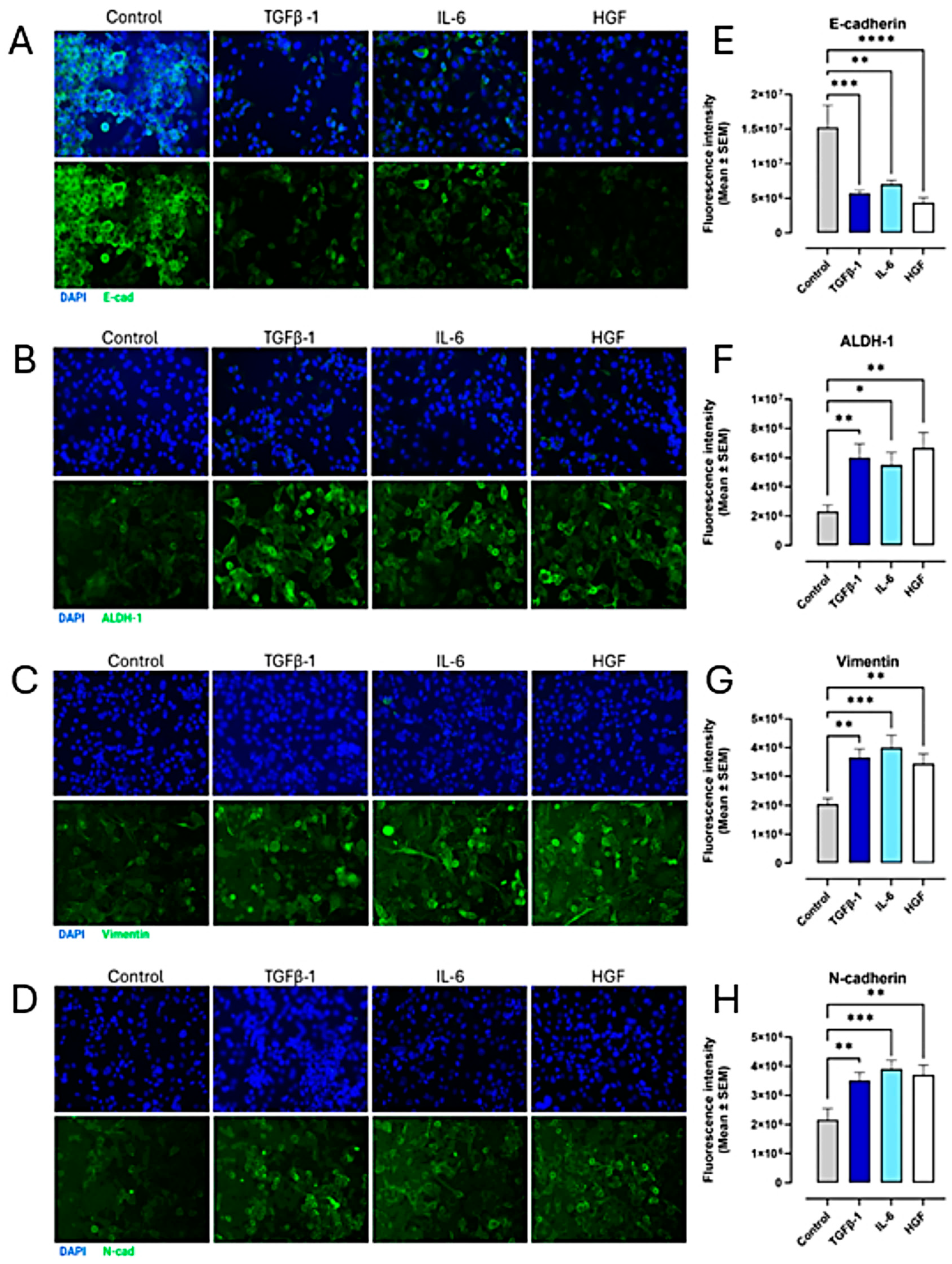
3.4. TGFβ-1, IL-6, and HGF Induce the EMT Phenotype in PANC-1, SW620, and MCF-7 Cancer Cells
3.5. The Effect of TGFβ-1, IL-6, and HGF on CD44 and CD24 as Markers for Identifying and Characterizing Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) to Metastasize
3.6. Cells Do Not Express Markers of EMT Treated with Co-Combination of OP and Cytokines
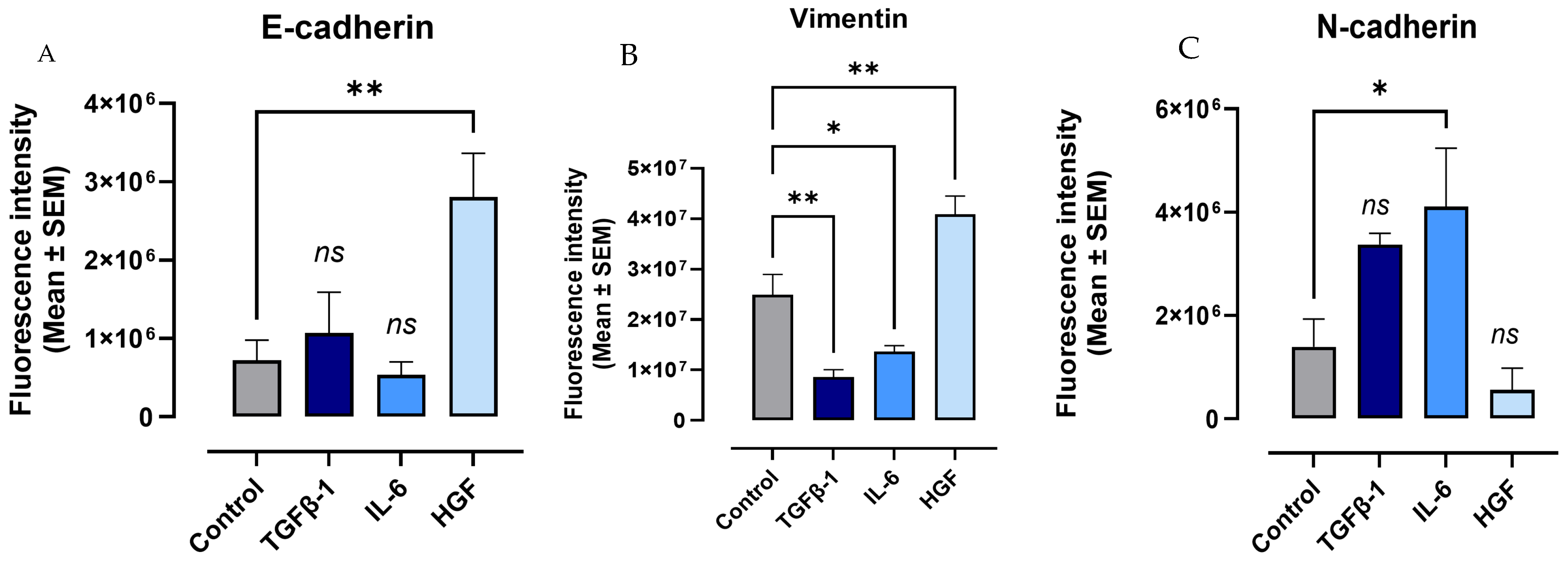
3.7. Macrophage Cells Express a Hybrid of EMT Markers When Treated with Cytokines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
7. Clinical Trials USFDA
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Liu, C.; Chu, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; George, J.; Young, H.A.; Liu, G. Cytokines: From clinical significance to quantification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2004433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, K.C.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in the treatment of cancer. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 6–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.A.; Punt, J.; Stranford, S.A.; Jones, P.P.; Kuby, J. Kuby Immunology, 7th ed.; W.H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, L.; Kaufmann, A.M. The significance of cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in metastasis and anti-cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Karin, M. Inflammation and oncogenesis: A vicious connection. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2010, 20, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kang, Y. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derynck, R.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT and Cancer: More Than Meets the Eye. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.H.; Moustakas, A. Signaling Receptors for TGF-β Family Members. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a022053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, D.K.; Poluri, K.M. Molecular insights into kinase-mediated signaling pathways of chemokines and their cognate G protein-coupled receptors. Front. Biosci.-Landmark 2020, 25, 1361–1385. [Google Scholar]
- Harless, W.W. Revisiting perioperative chemotherapy: The critical importance of targeting residual cancer prior to wound healing. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baghaie, L.; Haxho, F.; Leroy, F.; Lewis, B.; Wawer, A.; Minhas, S.; Harless, W.W.; Szewczuk, M.R. Contemporaneous Perioperative Inflammatory and Angiogenic Cytokine Profiles of Surgical Breast, Colorectal, and Prostate Cancer Patients: Clinical Implications. Cells 2023, 12, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillehoj, E.P.; Hyun, S.W.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, A.; Guang, W.; Nguyen, C.; Luzina, I.G.; Atamas, S.P.; Passaniti, A.; et al. NEU1 sialidase expressed in human airway epithelia regulates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and MUC1 protein signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8214–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haxho, F.; Neufeld, R.J.; Szewczuk, M.R. Neuraminidase-1: A novel therapeutic target in multistage tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qorri, B.; Mokhtari, R.B.; Harless, W.W.; Szewczuk, M.R. Next generation of cancer drug repurposing: Therapeutic combination of aspirin and oseltamivir phosphate potentiates gemcitabine to disable key survival pathways critical for pancreatic cancer progression. Cancers 2022, 14, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, M.; Wei, H.; Li, C.; Hu, D.; Zheng, L.; Wang, D.W. Neuraminidase inhibitor treatment is associated with decreased mortality in COVID-19 patients: A retrospective analysis. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2022, 8, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengez, B.; Carr, B.I.; Alotaibi, H. EMT and Inflammation: Crossroads in HCC. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2023, 54, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Chung, I.; Wong, W.F.; Masamune, A.; Sim, M.S.; Looi, C.Y. Paracrine IL-6 signaling mediates the effects of pancreatic stellate cells on epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Stat3/Nrf2 pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.E.; Stuelten, C.H. Alternative splicing in EMT and TGF-β signaling during cancer progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 101, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, I.; Michael, A.; Meira, L.B.; Ellis, P.E. The Role of Cytokines in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Gynaecological Cancers: A Systematic Review. Cells 2023, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.T.; Wu, K.J. Epigenetic regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Focusing on hypoxia and TGF-β signaling. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuhwerk, H.; Brabletz, T. Mutual regulation of TGFβ-induced oncogenic EMT, cell cycle progression and the DDR. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 97, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, L.K.; Abdulkhalek, S.; Allison, S.; Neufeld, R.J.; Szewczuk, M.R. Therapeutic targeting of Neu1 sialidase with oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu®) disables cancer cell survival in human pancreatic cancer with acquired chemoresistance. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Loh, C.Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skapinker, E.; Aucoin, E.B.; Kombargi, H.L.; Yaish, A.M.; Li, Y.; Baghaie, L.; Szewczuk, M.R. Contemporaneous Inflammatory, Angiogenic, Fibrogenic, and Angiostatic Cytokine Profiles of the Time-to-Tumor Development by Cancer Cells to Orchestrate Tumor Neovascularization, Progression, and Metastasis. Cells 2024, 13, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhalek, S.; Geen, O.D.; Brodhagen, L.; Haxho, F.; Alghamdi, F.; Allison, S.; Simmons, D.J.; O’Shea, L.K.; Neufeld, R.J.; Szewczuk, M.R. Transcriptional factor snail controls tumor neovascularization, growth and metastasis in a mouse model of human ovarian carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2014, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa-Gonçalves, M.; Bragança, B.; Martins-Dias, E.; Correia-de-Sá, P.; Fontes-Sousa, A.P. Is the adenosine A(2B) ‘biased’ receptor a valuable target for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension? Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, W.; Song, W.; Li, Z. Mutual regulation between glycosylation and transforming growth factor-β isoforms signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effendi, W.I.; Nagano, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, Y. Focusing on Adenosine Receptors as a Potential Targeted Therapy in Human Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkhalek, S.; Hrynyk, M.; Szewczuk, M. A novel G-protein-coupled receptor-signaling platform and its targeted translation in human disease. Res. Rep. Biochem. 2013, 3, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Oka, M.; Murase, K.; Soda, H.; Isomoto, H.; Takeshima, F.; Mizuta, Y.; Murata, I.; Kohno, S. Expression of interleukin 6 and its receptor in human gastric and colorectal cancers. J. Int. Med. Res. 2003, 31, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yu, J.; Wong, C.C. Metabolic rewiring in the promotion of cancer metastasis: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6139–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Fendt, S.-M. The metabolism of cancer cells during metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karno, B.; Edwards, D.N.; Chen, J. Metabolic control of cancer metastasis: Role of amino acids at secondary organ sites. Oncogene 2023, 42, 3447–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, F.C.E.; Chaves-Filho, A.B.; Schulze, A. Lipids as mediators of cancer progression and metastasis. Nat. Cancer 2024, 5, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.; Kundu, A.; Kundu, C.N. The cytokines in tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation-elongation-progression to metastatic outgrowth. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 196, 104311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lu, Z. Metabolic features of cancer cells. Cancer Commun 2018, 38, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampersad, S.N. Multiple applications of Alamar Blue as an indicator of metabolic function and cellular health in cell viability bioassays. Sensors 2012, 12, 12347–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, S.; Waseem, N.H.; Nguyen, T.K.N.; Mohsin, S.; Jamal, A.; Teh, M.T.; Waseem, A. Vimentin Is at the Heart of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Mediated Metastasis. Cancers 2021, 13, 4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, N.; Vp, S.; Parvathy, K.; Sneha, A.S.; Maliekal, T.T. ALDH1A1 as a marker for metastasis initiating cells: A mechanistic insight. Exp. Cell Res. 2024, 442, 114213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chute, J.P.; Muramoto, G.G.; Whitesides, J.; Colvin, M.; Safi, R.; Chao, N.J.; McDonnell, D.P. inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase and retinoid signaling induces the expansion of human hematopoietic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11707–11712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamer-Azzabi, A.; Ndozangue-Touriguine, O.; Bréard, J. Metastatic SW620 colon cancer cells are primed for death when detached and can be sensitized to anoikis by the BH3-mimetic ABT-737. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Lin, H.H.; Tang, M.J.; Wang, Y.K. Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal adhesion maturation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15966–15983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Unraveling the roles of CD44/CD24 and ALDH1 as cancer stem cell markers in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero Mendez, L.; Srinivasan, M.; Hamouda, R.K.; Ambedkar, B.; Arzoun, H.; Sahib, I.; Fondeur, J.; Mohammed, L. Evaluation of CD44+/CD24- and Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Enzyme Markers in Cancer Stem Cells as Prognostic Indicators for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cureus 2022, 14, e28056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, D.; Saha, P.; Samanta, A.; Bishayee, A. Emerging Concepts of Hybrid Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Progression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.; Tabor, V.; Wikell, A.; Jalkanen, S.; Fuxe, J. TGF-β1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition promotes monocyte/macrophage properties in breast cancer cells. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Moustakas, A.; Heldin, C.-H. Mechanisms of TGFβ-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.; Georgoudaki, A.; Lambut, L.; Johansson, J.; Tabor, V.; Hagikura, K.; Jin, Y.; Jansson, M.; Alexander, J.; Nelson, C.M. TGF-β1-induced EMT promotes targeted migration of breast cancer cells through the lymphatic system by the activation of CCR7/CCL21-mediated chemotaxis. Oncogene 2016, 35, 748–760. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, B.; Datta, J.; Teknos, T.N.; Kumar, P. IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial–mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, X.; Cao, S.; Zhou, Y. Paracrine HGF promotes EMT and mediates the effects of PSC on chemoresistance by activating c-Met/PI3K/Akt signaling in pancreatic cancer in vitro. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118523. [Google Scholar]
- Qorri, B.; Harless, W.; Szewczuk, M.R. Novel Molecular Mechanism of Aspirin and Celecoxib Targeting Mammalian Neuraminidase-1 Impedes Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis and Induces Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 2020, 14, 4149–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martling, A.; Lindberg, J.; Hed Myrberg, I.; Nilbert, M.; Mayrhofer, M.; Gronberg, H.; Bengt Glimelius ALASCCA Trial Study Group. Low-dose aspirin to reduce recurrence rate in colorectal cancer patients with PI3K pathway alterations: 3-year results from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, LBA125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qorri, B.; Mokhtari, R.B.; Harless, W.W.; Szewczuk, M.R. Repositioning of Old Drugs for Novel Cancer Therapies: Continuous Therapeutic Perfusion of Aspirin and Oseltamivir Phosphate with Gemcitabine Treatment Disables Tumor Progression, Chemoresistance, and Metastases. Cancers 2022, 14, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarique, A.A.; Logan, J.; Thomas, E.; Holt, P.G.; Sly, P.D.; Fantino, E. Phenotypic, functional, and plasticity features of classical and alternatively activated human macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 676–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, M.; Rees, A.; Cronin, J.G.; Nair, M.; Jones, N.; Thornton, C.A. Macrophage plasticity in reproduction and environmental influences on their function. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 607328. [Google Scholar]
- Martinelli, E.; Morgillo, F.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F. Cancer resistance to therapies against the EGFR-RAS-RAF pathway: The role of MEK. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 53, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Jiang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Bu, X.; Cai, S. TGF-β induces M2-like macrophage polarization via SNAIL-mediated suppression of a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Laoui, D.; Naessens, T.; Smits, H.H.; Hokke, C.H.; Stijlemans, B.; Grooten, J.; De Baetselier, P.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. E-cadherin expression in macrophages dampens their inflammatory responsiveness in vitro, but does not modulate M2-regulated pathologies in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baghaie, L.; Bunsick, D.A.; Aucoin, E.B.; Skapinker, E.; Yaish, A.M.; Li, Y.; Harless, W.W.; Szewczuk, M.R. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Transactivate Glycosylated Cytokine Receptors on Cancer Cells to Induce Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition to the Metastatic Phenotype. Cancers 2025, 17, 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071234
Baghaie L, Bunsick DA, Aucoin EB, Skapinker E, Yaish AM, Li Y, Harless WW, Szewczuk MR. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Transactivate Glycosylated Cytokine Receptors on Cancer Cells to Induce Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition to the Metastatic Phenotype. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071234
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaghaie, Leili, David A. Bunsick, Emilyn B. Aucoin, Elizabeth Skapinker, Abdulrahman M. Yaish, Yunfan Li, William W. Harless, and Myron R. Szewczuk. 2025. "Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Transactivate Glycosylated Cytokine Receptors on Cancer Cells to Induce Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition to the Metastatic Phenotype" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071234
APA StyleBaghaie, L., Bunsick, D. A., Aucoin, E. B., Skapinker, E., Yaish, A. M., Li, Y., Harless, W. W., & Szewczuk, M. R. (2025). Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Transactivate Glycosylated Cytokine Receptors on Cancer Cells to Induce Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition to the Metastatic Phenotype. Cancers, 17(7), 1234. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071234






