Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1/Metadherin (AEG-1/MTDH): A Promising Molecular Marker and Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Epidemiology and Risk Factors
1.2. HCC: Treatment Strategy
1.3. HCC: Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers
2. Regulation of Expression and Function and Structural Motifs in AEG-1
2.1. AEG-1 Gene and Its Regulation of Expression in Cancer
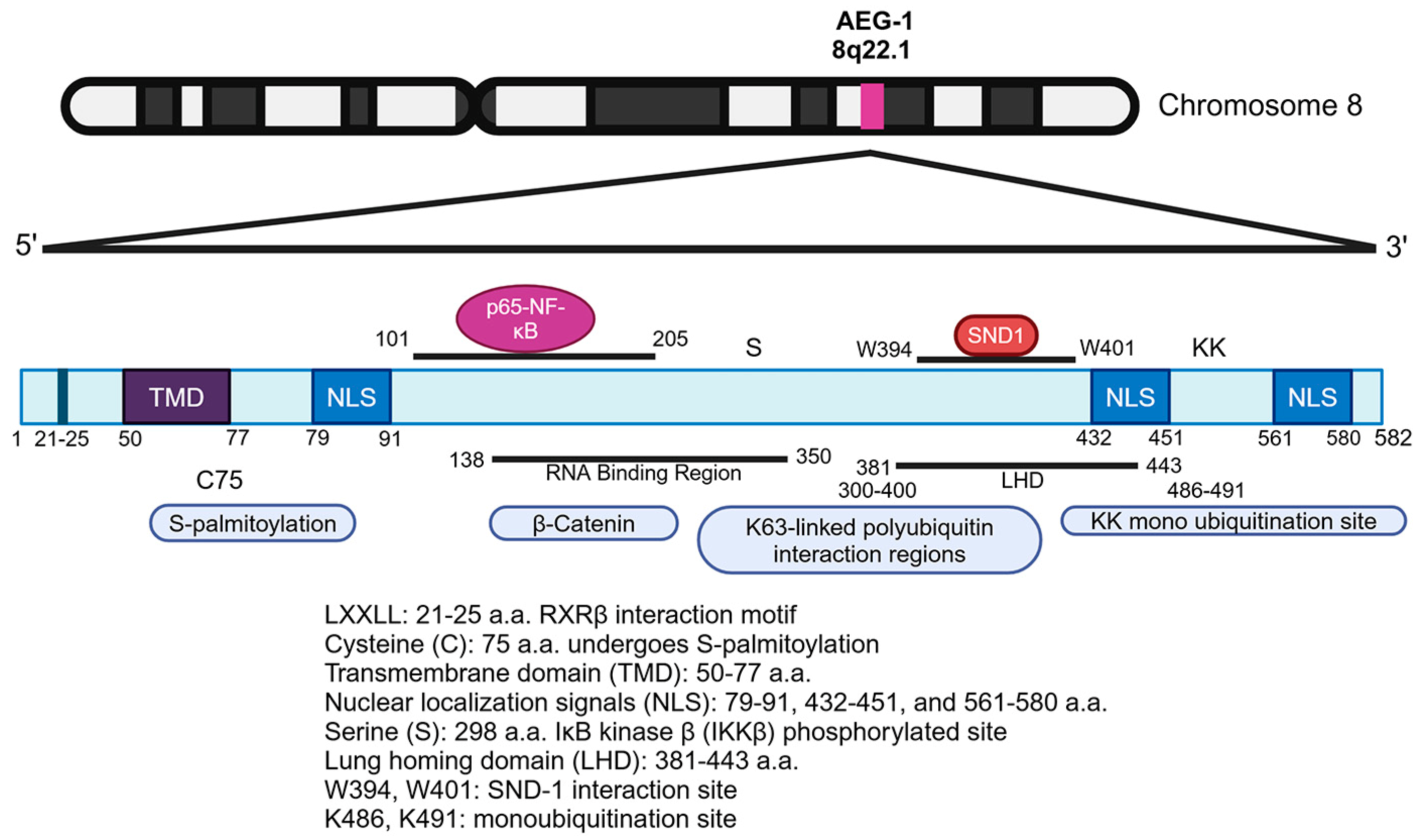
2.2. AEG-1 Protein: Structure, Motifs, and Key Residues
3. AEG-1 Function in Normal Physiology
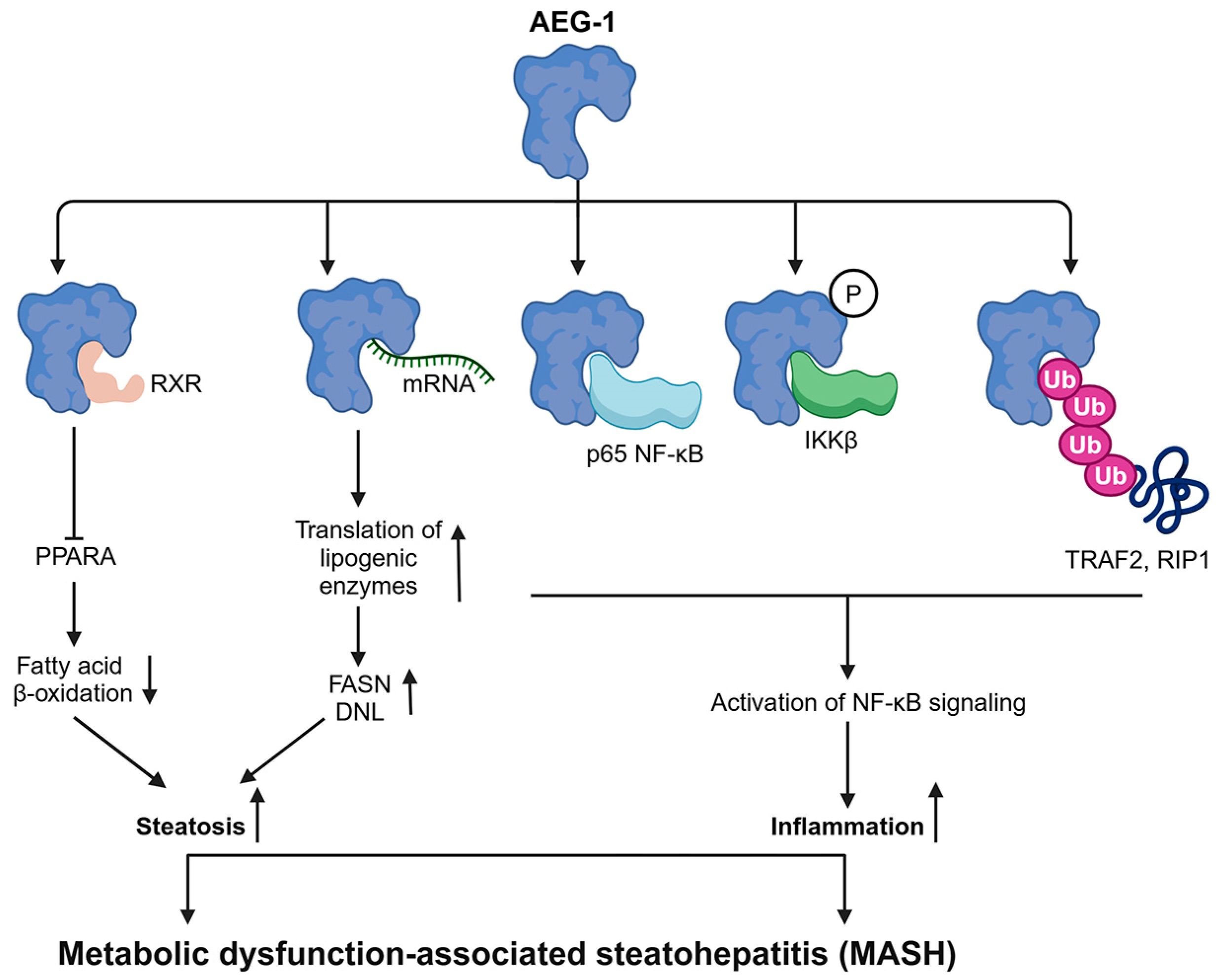
4. Role of AEG-1 in Regulating MASH: A Precursor to HCC
5. Oncogenic Role of AEG-1
5.1. Interaction and Cooperation of AEG-1 with Other Proteins and RNAs
5.1.1. Interaction with SND1: A Key Mechanism Mediating AEG-1′s Oncogenic Functions
5.1.2. Cooperation of AEG-1 and MYC
5.1.3. Implication of AEG-1/RXR Interaction for HCC
5.1.4. Interaction of AEG-1 with RNAs
5.1.5. Additional AEG-1-Interacting Proteins Relevant to HCC
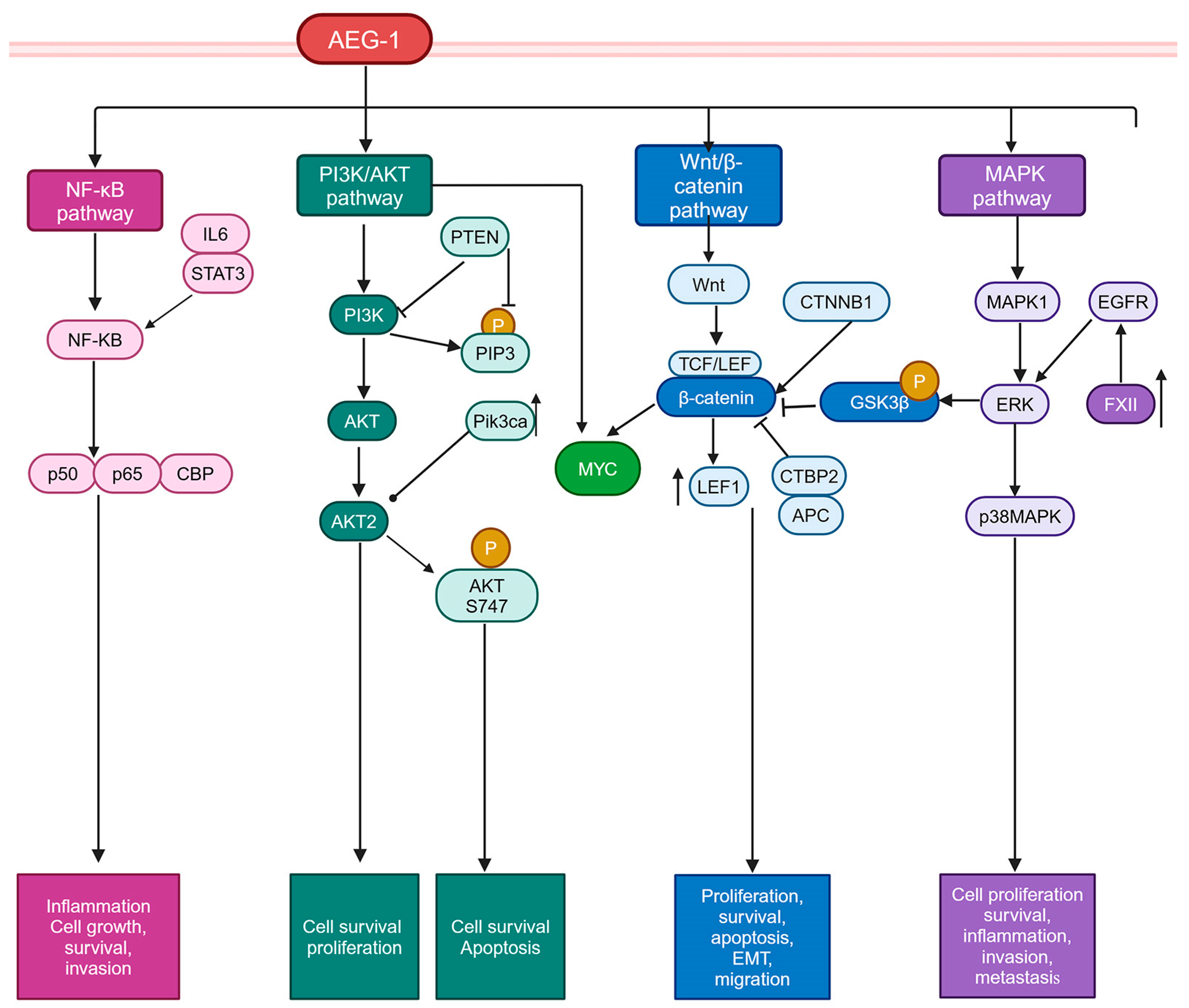
5.2. Signaling Pathways Activated by AEG-1
5.2.1. PI3K/AKT Pathway
5.2.2. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway
5.2.3. MAPK Pathway
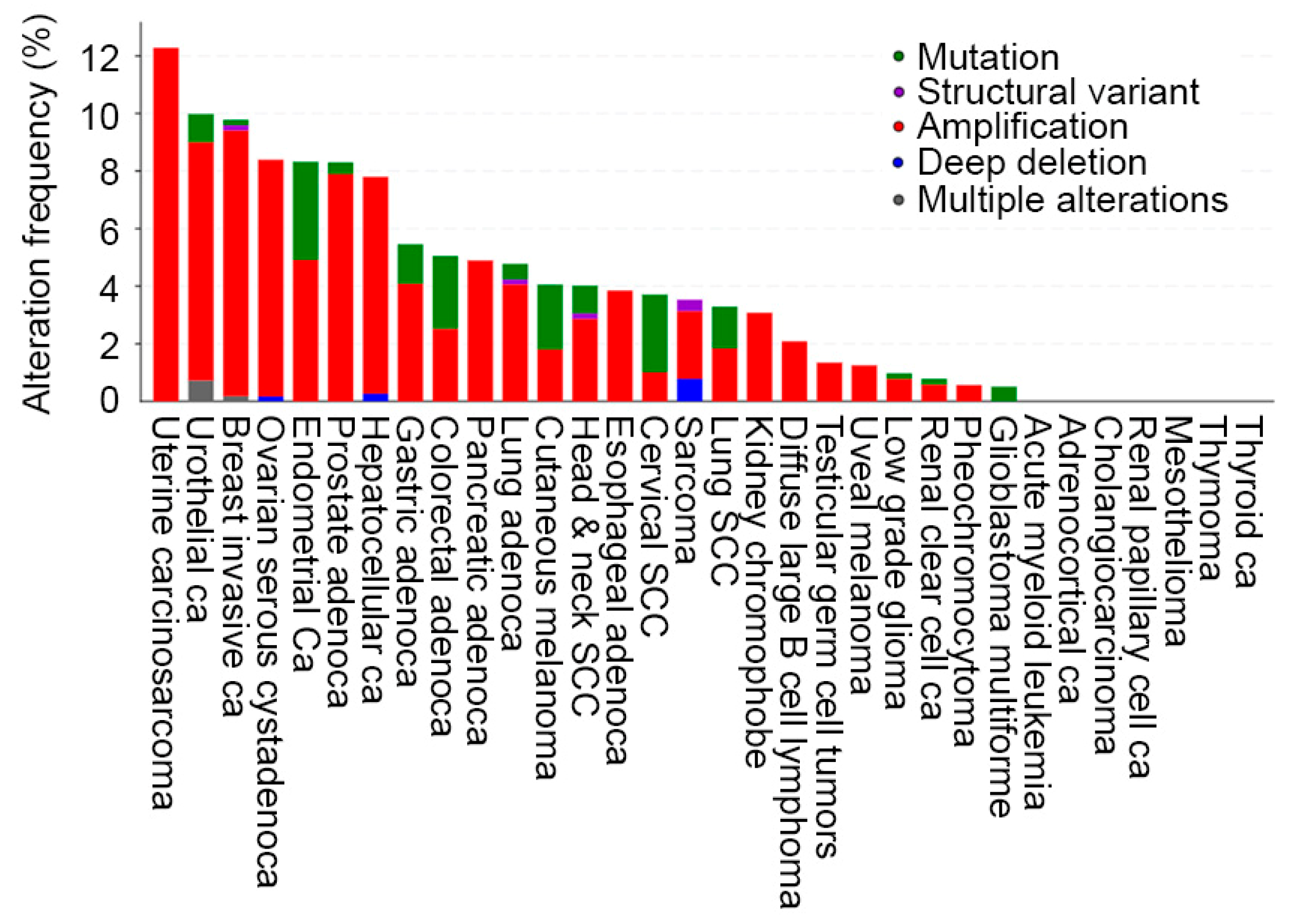
6. Clinical Correlation, and Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of AEG-1 in HCC
7. Therapeutic Targeting of AEG-1
7.1. Gene Silencing Strategies for Targeting AEG-1
7.2. Inhibition of AEG-1/SND1 Interaction
7.3. Synergy with Existing Therapies in HCC
7.4. Challenges in AEG-1-Targeting Therapy and Potential Solutions
8. Current Challenges and Knowledge Gaps
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAT | α1-antitrypsin |
| AEG-1 | Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 |
| AFP | Alpha-Fetoprotein |
| AFP-L3 | Lens culinaris agglutinin reactive Alpha-Fetoprotein |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| ALB | Albumin |
| APC | Adenomatous Polyposis Coli |
| ASO | Antisense Oligonucleotide |
| ATG5 | Autophagy Related 5 |
| ATRA | All-Trans Retinoic Acid |
| BCL2 | B Cell Lymphoma 2 |
| CAR | Constitutive Androstane Receptor |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A |
| CM | Conditioned Media |
| co-IP | Co-Immunoprecipitation |
| CREBBP | CREB Binding Protein |
| CTBP2 | C-terminal Binding Protein 2 |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte-Associated Protein 4 |
| CTNNB1 | Catenin Beta-1 (β-catenin) |
| CPEB1/CPEB3 | Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 1/3 |
| ctDNA | Circulating Tumor DNA |
| DEN | N-nitrosodiethylamine |
| DDX17 | DEAD-box Helicase 17 |
| DIO1 | Type I 5′-Deiodinase |
| DNL | De Novo Lipogenesis |
| Dox | Doxorubicin |
| DCP | Des-γ-carboxy Prothrombin |
| DSS | Dextran Sodium Sulfate |
| DPYD | Dihydropyrimidine Dehydrogenase |
| EAAT2 | Excitatory Amino Acid Transporter 2 |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ER | Endoplasmic Reticulum |
| ERG | ETS-Related Gene |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FAO | Fatty Acid β-Oxidation |
| FASN | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| FXR | Farnesoid X Receptor |
| GPC3 | Glypican-3 |
| GSK3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus |
| HCQ | Hydroxychloroquine |
| HFD | High Fat Diet |
| HITS-CLIP | High-Throughput Sequencing of RNA Isolated by Crosslinking Immunoprecipitation |
| HSC | Hepatic Stellate Cells |
| ICC | Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IKK | IκB Kinase |
| IL1B | Interleukin 1 Beta |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 |
| K63 | Lysine 63 |
| lncRNA | Long Non-Coding RNA |
| LNA | Locked Nucleic Acid |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LSF/TFCP2 | Late SV40 Factor/Transcription Factor CP2 |
| LXR | Liver X Receptor |
| MAFLD | Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| Miat | Myocardial Infarction Associated Transcript |
| Miz1 | Myc-Interacting Zinc Finger Protein 1(ZBTB17) |
| mRNA | Messenger RNA |
| MTDH | Metadherin |
| MDR1/ABCB1 | Multidrug Resistance Protein 1/ATP-Binding Cassette Sub-Family B Member 1 |
| MYC | Myelocytomatosis Oncogene |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells |
| ncRNA | Non-Coding RNA |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio |
| NLS | Nuclear Localization Signal |
| NTIS | Non-Thyroidal Illness Syndrome |
| NR1H3/LXR | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group H Member 3/Liver X Receptor |
| NR1H4/FXR | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group H Member 4/Farnesoid X Receptor |
| NR1I2/PXR | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group I Member 2/Pregnane X Receptor |
| NR1I3/CAR | Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 1 Group I Member 3/Constitutive Androstane Receptor |
| PAX | Paired Box Gene Family |
| PAR-CLIP | Photoactivatable Ribonucleoside-Enhanced Crosslinking and Immunoprecipitation |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Death-Ligand 1 |
| PEG | Polyethylene Glycol |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase |
| PIP3 | Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-Triphosphate |
| PIVKA-II | Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence-II |
| PRMT5 | Protein Arginine Methyltransferase 5 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog |
| PXR | Pregnane X Receptor |
| RAR | Retinoic Acid Receptor |
| RASSF1A | Ras Association Domain Family Member 1 |
| RBP | RNA-Binding Protein |
| RIPK1 | Receptor Interacting Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 |
| RISC | RNA-Induced Silencing Complex |
| RNA-seq | RNA Sequencing |
| RXR | Retinoid X Receptor |
| ScFv | Single-Chain Variable Fragment |
| SEPTIN9 | Septin 9 |
| SND1 | Staphylococcal Nuclease and Tudor Domain Containing 1 |
| SN | Staphylococcal Nuclease |
| SRC-1 | Steroid Receptor Coactivator 1 |
| ST | Spatial Transcriptomics |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| TACE | Transarterial Chemoembolization |
| TCF/LE | T Cell Factor/Lymphoid Enhancer-Binding Factor |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| TKI | Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor |
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| TR | Thyroid Hormone Receptor |
| TRAF2 | TNF Receptor-Associated Factor 2 |
| TS | Thymidylate Synthase |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| VEGFR2 | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| VDR | Vitamin D Receptor |
| Y2H | Yeast Two-Hybrid |
| YB1 | Y-box Binding Protein 1 |
| ZBTB16 | Zinc Finger and BTB Domain Containing 16 |
| ZBTB17 | Zinc Finger and BTB Domain Containing 17 |
| ZDHHC6 | Zinc Finger DHHC-Type Palmitoyltransferase 6 |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajdu, S.I. A note from history: Landmarks in history of cancer, part 1. Cancer 2011, 117, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdu, S.I. Greco-Roman thought about cancer. Cancer 2004, 100, 2048–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, D.; Villanueva, A.; Friedman, S.L.; Llovet, J.M. Liver Cancer Cell of Origin, Molecular Class, and Effects on Patient Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 745–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology of viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1264–1273 e1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; Singal, A.G.; Kono, Y.; Tan, D.J.H.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Changing global epidemiology of liver cancer from 2010 to 2019: NASH is the fastest growing cause of liver cancer. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 969–977.e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty, S.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, etiology and molecular classification. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 1–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serag, H.B.; Rudolph, K.L. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2557–2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarchoan, M.; Agarwal, P.; Villanueva, A.; Rao, S.; Dawson, L.A.; Llovet, J.M.; Finn, R.S.; Groopman, J.D.; El-Serag, H.B.; Monga, S.P.; et al. Recent Developments and Therapeutic Strategies against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4326–4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fabrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, A.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Pinyol, R.; Kelley, R.K.; El-Khoueiry, A.; Reeves, H.L.; Wang, X.W.; Gores, G.J.; Villanueva, A. Molecular pathogenesis and systemic therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 386–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Numata, K.; Stein, S.; Verret, W.; Hack, S.P.; Spahn, J.; Liu, B.; Abdullah, H.; et al. Atezolizumab with or without bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (GO30140): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casak, S.J.; Donoghue, M.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.; Jiang, X.; Rodriguez, L.; Shen, Y.L.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Advanced Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.H.; Brewer, J.R.; Fan, J.; Cheng, J.; Shen, Y.L.; Xiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lemery, S.J.; Pazdur, R.; Kluetz, P.G.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Tremelimumab in Combination with Durvalumab for the Treatment of Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, Y.H.; Lee, Y.T.; Tseng, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; You, S.; Agopian, V.G.; Yang, J.D. Alpha-fetoprotein: Past, present, and future. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Sterling, R.K.; Chung, R.T.; Everhart, J.E.; Dienstag, J.L.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Wright, E.C.; Everson, G.T.; Lindsay, K.L.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with advanced hepatitis C: Results from the HALT-C Trial. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leerapun, A.; Suravarapu, S.V.; Bida, J.P.; Clark, R.J.; Sanders, E.L.; Mettler, T.A.; Stadheim, L.M.; Aderca, I.; Moser, C.D.; Nagorney, D.M.; et al. The utility of Lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive alpha-fetoprotein in the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: Evaluation in a United States referral population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 394–402; quiz 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebman, H.A.; Furie, B.C.; Tong, M.J.; Blanchard, R.A.; Lo, K.J.; Lee, S.D.; Coleman, M.S.; Furie, B. Des-gamma-carboxy (abnormal) prothrombin as a serum marker of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 310, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, H.; Suzuki, H.; Shimomura, M.; Kojima, M.; Gotohda, N.; Takahashi, S.; Nakagohri, T.; Konishi, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Kinoshita, T.; et al. Glypican-3 expression is correlated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.S.; Yu, W.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Han, F.; Huang, T. Increased expression of miR-21 predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7234–7238. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, S.Y.; Yu, J.I.; Choi, C.; Kang, S.Y.; Joh, J.W.; Paik, S.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.; Park, H.C.; Park, C.K. Prognostic significance of miR-122 expression after curative resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, K.; Zhang, F.; Lu, S.; Chen, R.; Ren, Z.; Yin, X. The prognostic significance of microRNA-221 in hepatocellular carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2021, 36, 17246008211032689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, L.P.; Meng, Z.Q. Serum miR-224 reflects stage of hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts survival. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 731781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Li, C.J.; Huang, Y.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Chu, P.Y.; Lin, H.Y. New Insights into the Role of miR-29a in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Implications in Mechanisms and Theragnostics. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopystecka, A.; Patryn, R.; Lesniewska, M.; Budzynska, J.; Koziol, I. The Use of ctDNA in the Diagnosis and Monitoring of Hepatocellular Carcinoma-Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Debes, J.D.; Boonstra, A. DNA methylation markers in the detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 191, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.Y.; She, W.H.; Dai, W.C.; Tsang, S.H.Y.; Chok, K.S.H.; Chan, A.C.Y.; Fung, J.; Lo, C.M.; Cheung, T.T. Prognostic value of preoperative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level in patients receiving curative hepatectomy- an analysis of 1182 patients in Hong Kong. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J. Prognostic value of des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with transarterial chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.S.; Niu, X.J.; Wang, W.H. Genetic alterations in hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 9069–9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Jin, T.; Zhu, Y.; Dai, C. Immune checkpoint therapy in liver cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, G.J.; Charles, K.A.; Roxburgh, C.S.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. The systemic inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in patients with cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 88, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gingold, J.A.; Su, X. Immunomodulatory TGF-beta Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 1010–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampat, K.R.; O’Neil, B. Antiangiogenic therapies for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2013, 18, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Z.Z.; Kang, D.C.; Chen, Y.; Pekarskaya, O.; Chao, W.; Volsky, D.J.; Fisher, P.B. Identification and cloning of human astrocyte genes displaying elevated expression after infection with HIV-1 or exposure to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein by rapid subtraction hybridization, RaSH. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3592–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.C.; Su, Z.Z.; Sarkar, D.; Emdad, L.; Volsky, D.J.; Fisher, P.B. Cloning and characterization of HIV-1-inducible astrocyte elevated gene-1, AEG-1. Gene 2005, 353, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Ruoslahti, E. Metadherin, a cell surface protein in breast tumors that mediates lung metastasis. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britt, D.E.; Yang, D.F.; Yang, D.Q.; Flanagan, D.; Callanan, H.; Lim, Y.P.; Lin, S.H.; Hixson, D.C. Identification of a novel protein, LYRIC, localized to tight junctions of polarized epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 300, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, H.G.; Lam, Y.W.; Briers, S.; Lamond, A.I.; Bickmore, W.A. 3D3/lyric: A novel transmembrane protein of the endoplasmic reticulum and nuclear envelope, which is also present in the nucleolus. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 294, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdad, L.; Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Jeon, H.Y.; Boukerche, H.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) functions as an oncogene and regulates angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21300–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnosa, S.; Ticha, I.; Haapaniemi, S.; Sun, X.F. MTDH genetic variants in colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Chong, R.A.; Yang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Blanco, M.A.; Li, F.; Reiss, M.; Au, J.L.; Haffty, B.G.; Kang, Y. MTDH activation by 8q22 genomic gain promotes chemoresistance and metastasis of poor-prognosis breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.K.; Emdad, L.; Su, Z.Z.; Villanueva, A.; Chiang, D.Y.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Mills, A.S.; Waxman, S.; Fisher, R.A.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is a target gene of oncogenic Ha-ras requiring phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and c-Myc. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17390–17395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartak-Sharma, N.; Gelman, B.B.; Joshi, C.; Borgamann, K.; Ghorpade, A. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel modulator of HIV-1-associated neuroinflammation via regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB signaling and excitatory amino acid transporter-2 repression. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 19599–19612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuda, I.I.; Koide, N.; Noman, A.S.; Dagvadorj, J.; Tumurkhuu, G.; Naiki, Y.; Komatsu, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yokochi, T. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is induced by lipopolysaccharide as toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) ligand and regulates TLR4 signalling. Immunology 2009, 128, e700–e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Robertson, C.L.; Ebeid, K.; Dozmorov, M.; Rajasekaran, D.; Mendoza, R.; Siddiq, A.; Akiel, M.A.; Jariwala, N.; Shen, X.N.; et al. A novel role of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) in regulating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Hepatology 2017, 66, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.F.; Dai, H.; Ou, Q.; Zuo, G.Q.; Liu, C.A. Overexpression of microRNA-30a-5p inhibits liver cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting MTDH/PTEN/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5885–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Lin, J.S.; He, X.X.; Huang, H.J. miR-195 inhibits cell proliferation via targeting AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3118–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Pan, Q.; Jia, L.Q.; Dai, Z.; Ke, A.W.; Zeng, H.Y.; Tang, Z.Y.; Fan, J.; Zhou, J. MiR-302c inhibits tumor growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing the endothelial-mesenchymal transition of endothelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.X.; Chang, Y.; Meng, F.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Xie, Q.H.; Tang, F.; Li, P.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Lin, J.S. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.J.; Zhang, Y.N.; Liao, J.Z.; Ke, K.P.; Chang, Y.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, J.S.; He, X.X. MiR-497 suppresses angiogenesis and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting VEGFA and AEG-1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29527–29542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malayaperumal, S.; Sriramulu, S.; Jothimani, G.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S. A Review on AEG-1 oncogene regulating MicroRNA expression in Colon Cancer progression. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2020, 21, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, T.; Zhang, D.; Sun, X.; Zhang, X. The long non-coding RNA HCG18 promotes the growth and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through sponging miR-1271 and upregulating MTDH/Wnt/beta-catenin. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2020, 47, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Shan, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D.; Jin, W.; Ren, T. Long noncoding RNA SNHG1 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression by up-regulating MTDH via sponging miR-145-5p. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3957–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Fu, Y.; Zeng, N.; Yin, J.; Li, Q. LncRNA FAM83H-AS1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer progression by regulating the miR-136-5p/metadherin axis. Aging 2020, 12, 3594–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, L.; Liu, S.; Yang, L.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Zhao, H.; Song, Z. LncRNA DDX11-AS1 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting the miR-30c-5p/MTDH axis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirkettle, H.J.; Girling, J.; Warren, A.Y.; Mills, I.G.; Sahadevan, K.; Leung, H.; Hamdy, F.; Whitaker, H.C.; Neal, D.E. LYRIC/AEG-1 is targeted to different subcellular compartments by ubiquitinylation and intrinsic nuclear localization signals. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3003–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanek, D.M.; Wells, D.G. CPEB1 Regulates the Expression of MTDH/AEG-1 and Glioblastoma Cell Migration. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zou, C.; Qiu, Z.; E, F.; Li, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, D.; Tan, Q.; Yin, W.; Matunda, C.; et al. CPEB3-mediated MTDH mRNA translational suppression restrains hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, D.; Desalle, R.; Fisher, P.B. Evolution of MDA-5/RIG-I-dependent innate immunity: Independent evolution by domain grafting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17040–17045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.C.; Reid, D.W.; Hoffman, A.M.; Sarkar, D.; Nicchitta, C.V. Oncoprotein AEG-1 is an Endoplasmic Reticulum RNA Binding Protein Whose Interactome is Enriched In Organelle Resident Protein-Encoding mRNAs. RNA 2018, 5, 688–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexia, C.; Poalas, K.; Carvalho, G.; Zemirli, N.; Dwyer, J.; Dubois, S.M.; Hatchi, E.M.; Cordeiro, N.; Smith, S.S.; Castanier, C.; et al. The endoplasmic reticulum acts as a platform for ubiquitylated components of nuclear factor kappaB signaling. Sci. Signal 2013, 6, ra79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Robertson, C.L.; Rajasekaran, D.; Gredler, R.; Siddiq, A.; Emdad, L.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Ghosh, S.; Hylemon, P.B.; Gil, G.; et al. AEG-1 Regulates Retinoid X Receptor and Inhibits Retinoid Signaling. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4364–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luxton, H.J.; Barnouin, K.; Kelly, G.; Hanrahan, S.; Totty, N.; Neal, D.E.; Whitaker, H.C. Regulation of the localisation and function of the oncogene LYRIC/AEG-1 by ubiquitination at K486 and K491. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Su, Z.Z.; Randolph, A.; Boukerche, H.; Valerie, K.; Fisher, P.B. Activation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway by astrocyte elevated gene-1: Implications for tumor progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1509–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Park, E.S.; Emdad, L.; Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Fisher, P.B. Molecular basis of nuclear factor-kappaB activation by astrocyte elevated gene-1. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heery, D.M.; Kalkhoven, E.; Hoare, S.; Parker, M.G. A signature motif in transcriptional co-activators mediates binding to nuclear receptors. Nature 1997, 387, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komaniecki, G.; Camarena, M.D.C.; Gelsleichter, E.; Mendoza, R.; Subler, M.; Windle, J.J.; Dozmorov, M.G.; Lai, Z.; Sarkar, D.; Lin, H. Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 Cys75 S-Palmitoylation by ZDHHC6 Regulates Its Biological Activity. Biochemistry 2023, 62, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, R.K.; Nolte, H.; Sun, T.; Kaur, H.; Sreenivasan, K.; Looso, M.; Offermanns, S.; Kruger, M.; Swiercz, J.M. Quantitative analysis of the TNF-alpha-induced phosphoproteome reveals AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC as an IKKbeta substrate. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.K.; Santhekadur, P.K.; Gredler, R.; Chen, D.; Emdad, L.; Bhutia, S.K.; Pannell, L.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Increased RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) activity contributes to hepatocelllular carcinoma. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1538–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.A.; Aleckovic, M.; Hua, Y.; Li, T.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Z.; Cristea, I.M.; Kang, Y. Identification of staphylococcal nuclease domain-containing 1 (SND1) as a Metadherin-interacting protein with metastasis-promoting functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19982–19992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Wan, L.; Zheng, A.; Stanevich, V.; Wei, Y.; Satyshur, K.A.; Shen, M.; Lee, W.; Kang, Y.; Xing, Y. Structural Insights into the Tumor-Promoting Function of the MTDH-SND1 Complex. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Smith, H.A.; Wei, Y.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, N.; Rowicki, M.; Tang, Y.; Hang, X.; Wu, S.; et al. Pharmacological disruption of the MTDH-SND1 complex enhances tumor antigen presentation and synergizes with anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Wei, Y.; Kim, H.; Wan, L.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Hang, X.; Raba, M.; Remiszewski, S.; Rowicki, M.; Wu, C.G.; et al. Small-molecule inhibitors that disrupt the MTDH-SND1 complex suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Ding, J.; Ji, J.; Hu, L.; Min, W.; Hou, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Discovery of Novel Small-Molecule Inhibitors Disrupting the MTDH-SND1 Protein-Protein Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 68, 1844–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Goodfellow, R.X.; Jia, Y.; Thiel, K.W.; Reyes, H.D.; Yang, B.; Leslie, K.K. Genetic Deficiency of Mtdh in Mice Causes Male Infertility via Impaired Spermatogenesis and Alterations in the Expression of Small Non-coding RNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 11853–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.L.; Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Gredler, R.; Emdad, L.; Rajasekaran, D.; Akiel, M.; Shen, X.N.; Corwin, F.; Sundaresan, G.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) regulates lipid homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18227–18236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.L.; Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Gredler, R.; Emdad, L.; Rajasekaran, D.; Akiel, M.; Shen, X.N.; Guo, C.; Giashuddin, S.; et al. Genetic deletion of AEG-1 prevents hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6184–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, C.L.; Mendoza, R.G.; Jariwala, N.; Dozmorov, M.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.J.; Lai, Z.; Fisher, P.B.; Ghosh, S.; et al. Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 Regulates Macrophage Activation in Hepatocellular Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6436–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, K.; Kegelman, T.P.; Dash, R.; Das, S.K.; Choi, J.K.; Emdad, L.; Howlett, E.L.; Jeon, H.Y.; Su, Z.Z.; et al. Oncogene AEG-1 promotes glioma-induced neurodegeneration by increasing glutamate excitotoxicity. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6514–6523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.M.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Nuclear Receptors, RXR, and the Big Bang. Cell 2014, 157, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, R.S.; Weindruch, R. Oxidative stress, caloric restriction, and aging. Science 1996, 273, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, T.; Fujita, T.; Usuda, N.; Cook, W.; Qi, C.; Peters, J.M.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Yeldandi, A.V.; Rao, M.S.; Reddy, J.K. Peroxisomal and mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation in mice nullizygous for both peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha and peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase. Genotype correlation with fatty liver phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19228–19236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, N.; Han, D.; Su, P.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, G.; Yang, Q. MTDH Promotes Intestinal Inflammation by Positively Regulating TLR Signalling. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 2103–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Emdad, L.; Santhekadur, P.; Chen, D.; Gredler, R.; Shen, X.-N.; Robertson, C.L.; Dumur, C.I.; Hylemon, P.B.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis: Novel insights from a mouse model. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Su, Z.Z.; Emdad, L.; Sarkar, D.; Franke, T.F.; Fisher, P.B. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 activates cell survival pathways through PI3K-Akt signaling. Oncogene 2008, 27, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutia, S.K.; Kegelman, T.P.; Das, S.K.; Azab, B.; Su, Z.Z.; Lee, S.G.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 induces protective autophagy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22243–22248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, Y.Z.; Li, A.D.; Ma, J.J.; Hao, H.Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Ji, C.G.; Qi, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Knockdown of Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 Inhibits Activation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2016, 61, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, Y.; Reghupaty, S.C.; Mendoza, R.G.; Manna, D.; Banerjee, I.; Subler, M.A.; Weldon, K.; Lai, Z.; Giashuddin, S.; Fisher, P.B.; et al. Dissecting the Balance Between Metabolic and Oncogenic Functions of Astrocyte-Elevated Gene-1/Metadherin. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, L.H.; Shipston, M.J. The physiology of protein S-acylation. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 341–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Aramsangtienchai, P.; Tong, Z.; Lin, H. Protein Lipidation: Occurrence, Mechanisms, Biological Functions, and Enabling Technologies. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 919–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, X.; Kong, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Shao, X.; Liu, Z.; Song, H.; et al. The palmitoylation of AEG-1 dynamically modulates the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6898–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, F.; Andersson, A.; Saarenpaa, S.; Larsson, L.; Van Hul, N.; Kanatani, S.; Masek, J.; Ellis, E.; Barragan, A.; Mollbrink, A.; et al. Spatial Transcriptomics to define transcriptional patterns of zonation and structural components in the mouse liver. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saverino, A.; Qu, X.; Mendoza, R.G.; Raha, S.; Manna, D.; Ermi, A.G.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.J.; Liu, J.; Sarkar, D. Spatial transcriptomics unravels palmitoylation and zonation-dependent gene regulation by AEG-1 in mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Ojha, R.; Noguera-Ortega, E.; Rebecca, V.W.; Attanasio, J.; Liu, S.; Piao, S.; Lee, J.J.; Nicastri, M.C.; Harper, S.L.; et al. PPT1 inhibition enhances the antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 antibody in melanoma. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e133225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.R.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Yang, W.Z.; Chen, Y.P.; Yuan, H.S. Structural and functional insights into human Tudor-SN, a key component linking RNA interference and editing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 3579–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Aittomaki, S.; Pesu, M.; Carter, K.; Saarinen, J.; Kalkkinen, N.; Kieff, E.; Silvennoinen, O. Identification of p100 as a coactivator for STAT6 that bridges STAT6 with RNA polymerase II. Embo J. 2002, 21, 4950–4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Valineva, T.; Hong, J.; Bu, T.; Yao, Z.; Jensen, O.N.; Frilander, M.J.; Silvennoinen, O. Transcriptional co-activator protein p100 interacts with snRNP proteins and facilitates the assembly of the spliceosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 4485–4494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudy, A.A.; Ketting, R.F.; Hammond, S.M.; Denli, A.M.; Bathoorn, A.M.; Tops, B.B.; Silva, J.M.; Myers, M.M.; Hannon, G.J.; Plasterk, R.H. A micrococcal nuclease homologue in RNAi effector complexes. Nature 2003, 425, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scadden, A.D. The RISC subunit Tudor-SN binds to hyper-edited double-stranded RNA and promotes its cleavage. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005, 12, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jariwala, N.; Rajasekaran, D.; Mendoza, R.G.; Shen, X.N.; Siddiq, A.; Akiel, M.A.; Robertson, C.L.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.J.; Fisher, P.B.; et al. Oncogenic Role of SND1 in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhekadur, P.K.; Das, S.K.; Gredler, R.; Chen, D.; Srivastava, J.; Robertson, C.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Multifunction Protein Staphylococcal Nuclease Domain Containing 1 (SND1) Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Novel Pathway That Involves Nuclear Factor kappaB and miR-221. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 13952–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Lu, X.; Yuan, S.; Wei, Y.; Guo, F.; Shen, M.; Yuan, M.; Chakrabarti, R.; Hua, Y.; Smith, H.A.; et al. MTDH-SND1 interaction is crucial for expansion and activity of tumor-initiating cells in diverse oncogene- and carcinogen-induced mammary tumors. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; He, S.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, L. MTDH promotes metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by activating SND1-mediated ERK signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Aging 2020, 12, 1465–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.Y.; Rudoy, D.; Frank, S.B.; Phan, L.T.; Klezovitch, O.; Kwan, J.; Coleman, I.; Haffner, M.C.; Li, D.; Nelson, P.S.; et al. SND1 binds to ERG and promotes tumor growth in genetic mouse models of prostate cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulouarn, C.; Gomez-Quiroz, L.E.; Lee, J.S.; Kaposi-Novak, P.; Conner, E.A.; Goldina, T.A.; Onishchenko, G.E.; Factor, V.M.; Thorgeirsson, S.S. Oncogene-specific gene expression signatures at preneoplastic stage in mice define distinct mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirkettle, H.J.; Mills, I.G.; Whitaker, H.C.; Neal, D.E. Nuclear LYRIC/AEG-1 interacts with PLZF and relieves PLZF-mediated repression. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3663–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Siddiq, A.; Gredler, R.; Shen, X.N.; Rajasekaran, D.; Robertson, C.L.; Subler, M.A.; Windle, J.J.; Dumur, C.I.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 and c-Myc cooperate to promote hepatocarcinogenesis in mice. Hepatology 2015, 61, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altucci, L.; Gronemeyer, H. The promise of retinoids to fight against cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, M.H.; Beckett, G.J. Mechanisms behind the non-thyroidal illness syndrome: An update. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 205, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, J.; Robertson, C.L.; Gredler, R.; Siddiq, A.; Rajasekaran, D.; Akiel, M.A.; Emdad, L.; Mas, V.; Mukhopadhyay, N.D.; Fisher, P.B.; et al. Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 (AEG-1) Contributes to Non-thyroidal Illness Syndrome (NTIS) Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15549–15558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, A.; Fischer, B.; Eichelbaum, K.; Horos, R.; Beckmann, B.M.; Strein, C.; Davey, N.E.; Humphreys, D.T.; Preiss, T.; Steinmetz, L.M.; et al. Insights into RNA biology from an atlas of mammalian mRNA-binding proteins. Cell 2012, 149, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, A.G.; Munschauer, M.; Schwanhausser, B.; Vasile, A.; Murakawa, Y.; Schueler, M.; Youngs, N.; Penfold-Brown, D.; Drew, K.; Milek, M.; et al. The mRNA-bound proteome and its global occupancy profile on protein-coding transcripts. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, S.C.; Yi, H.; Eichelbaum, K.; Fohr, S.; Fischer, B.; You, K.T.; Castello, A.; Krijgsveld, J.; Hentze, M.W.; Kim, V.N. The RNA-binding protein repertoire of embryonic stem cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Jagannathan, S.; Reid, D.W.; Zheng, T.; Nicchitta, C.V. Hierarchical regulation of mRNA partitioning between the cytoplasm and the endoplasmic reticulum of mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 2646–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.K.; Chen, D.; Su, Z.-Z.; Gredler, R.; Yoo, J.; Shah, K.; Fisher, P.B.; Sarkar, D. Molecular mechanism of chemoresistance by Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 (AEG-1). Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3249–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, K.L.; Vasudevan, H.N.; Lockney, D.T.; Baum, R.; Hendrickson, R.C.; Raleigh, D.R.; Schmitt, A.M. Miat and interacting protein Metadherin maintain a stem-like niche to promote medulloblastoma tumorigenesis and treatment resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2203738119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Han-Hua, D.; Qiu-Meng, L.; Deng, N.; Peng-Chen, D.; Jie, M.; Lei, X.; Xue-Wu, Z.; Hui-Fang, L.; Yan, C.; et al. MTDH-stabilized DDX17 promotes tumor initiation and progression through interacting with YB1 to induce EGFR transcription in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncogene 2023, 42, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhangyuan, G.; Wang, F.; Jin, K.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, W.; et al. The zinc finger protein Miz1 suppresses liver tumorigenesis by restricting hepatocyte-driven macrophage activation and inflammation. Immunity 2021, 54, 1168–1185 e1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Peng, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhan, H.; Yang, L.; Gao, Q.; Jia, H.; Luo, R.; Dai, Z.; Tang, Z.; et al. Metadherin-PRMT5 complex enhances the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through the WNT-beta-catenin signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis 2020, 41, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lezana, T.; Lopez-Canovas, J.L.; Villanueva, A. Signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Adv. Cancer Res. 2021, 149, 63–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.H.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, P.R.; Chang, H.W.; Ger, L.P.; Lin, Y.W.; Changchien, C.S.; Lee, C.M.; Tai, M.H. Expression and prognostic role of tumor suppressor gene PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2003, 97, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Kataoka, E.; Sasaki, T.; Hamada, K.; Sasaki, J.; Mizuno, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Kishimoto, H.; Iizuka, M.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific Pten deficiency results in steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinomas. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1774–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Tateishi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Mohri, D.; Isomura, Y.; Seto, M.; Nakagawa, H.; Asaoka, Y.; et al. Altered composition of fatty acids exacerbates hepatotumorigenesis during activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1400–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavens, K.F.; Easton, R.M.; Shulman, G.I.; Previs, S.F.; Birnbaum, M.J. Akt2 is required for hepatic lipid accumulation in models of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Blenis, J.; Yuan, J. Activation of PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways regulates Myc-mediated transcription by phosphorylating and promoting the degradation of Mad1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6584–6589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Emdad, L.; Bacolod, M.D.; Kegelman, T.P.; Shen, X.N.; Alzubi, M.A.; Das, S.K.; Sarkar, D.; Fisher, P.B. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) interacts with Akt isoform 2 to control glioma growth, survival and pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7321–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Deng, H.; Yan, W.; Luo, M.; Tu, W.; Xia, Y.; He, J.; Han, P.; Fu, Y.; Tian, D. AEG-1 promotes anoikis resistance and orientation chemotaxis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugorria, M.J.; Olaizola, P.; Labiano, I.; Esparza-Baquer, A.; Marzioni, M.; Marin, J.J.G.; Bujanda, L.; Banales, J.M. Wnt-beta-catenin signalling in liver development, health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouissou, S.; Franconi, A.; Calderaro, J.; Letouze, E.; Imbeaud, S.; Pilati, C.; Nault, J.C.; Couchy, G.; Laurent, A.; Balabaud, C.; et al. Genotype-phenotype correlation of CTNNB1 mutations reveals different ss-catenin activity associated with liver tumor progression. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikarsky, E.; Porat, R.M.; Stein, I.; Abramovitch, R.; Amit, S.; Kasem, S.; Gutkovich-Pyest, E.; Urieli-Shoval, S.; Galun, E.; Ben-Neriah, Y. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature 2004, 431, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haybaeck, J.; Zeller, N.; Wolf, M.J.; Weber, A.; Wagner, U.; Kurrer, M.O.; Bremer, J.; Iezzi, G.; Graf, R.; Clavien, P.A.; et al. A lymphotoxin-driven pathway to hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Karin, M. NF-kappaB and STAT3—Key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, H.; Peng, J.; Song, W.; Chen, C.; Cai, S.; He, Y.; et al. Uncontrolled inflammation induced by AEG-1 promotes gastric cancer and poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5541–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.; Wang, K.; Shi, H. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 promotes inflammation and invasion of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Cell 2017, 49, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, S.; Gong, W.; Chen, T.; Sun, L.; Zheng, C.; Yin, B.; et al. Micheliolide ameliorates diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting Mtdh-mediated renal inflammation in type 2 diabetic db/db mice. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Dai, Z.; Pan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, G.H.; Yu, L.; Ding, Z.B.; Shi, G.M.; Ke, A.W.; Yang, X.R.; et al. Metadherin Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis through Induction of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7294–7302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.I.; Ahn, T.; Bae, S.H.; Chung, J.C.; Kim, H.; Chin, S.; Jeong, D.; Cho, H.D.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, H.C.; et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 overexpression in hepatocellular carcinoma: An independent prognostic factor. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2015, 88, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Gao, L.; Ma, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, S.; Yang, L.; Feng, Z.; Dang, Y.; Chen, G. The essential role of MTDH in the progression of HCC: A study with immunohistochemistry, TCGA, meta-analysis and in vitro investigation. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1561–1579. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Liu, W.; You, N.; Wang, T.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Zhao, G.; Yang, P.; Wang, D.; Dou, K. Prognostic significance of metadherin overexpression in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 2073–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cao, W.; Sharma, M.; Imam, R.; Yu, J. Study on Diagnostic Values of Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1) and Glypican 3 (GPC-3) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 152, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Dong, K.; Long, M.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Wei, J.; Ren, J.; Zhang, H. Serum anti-AEG-1 auto-antibody is a potential novel biomarker for malignant tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2012, 4, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, D.; Srivastava, J.; Ebeid, K.; Gredler, R.; Akiel, M.; Jariwala, N.; Robertson, C.; Shen, X.N.; Siddiq, A.; Fisher, P.; et al. Combination of nanoparticle-delivered siRNA for Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) and all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA): An effective therapeutic strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Bioconjugate Chem. 2015, 26, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.L.; Wang, B.; Wu, M.L.; Li, J.; Gong, R.M.; Song, L.N.; Zhang, H.S.; Zhu, G.Q.; Chen, S.P.; Cai, J.L.; et al. MTDH antisense oligonucleotides reshape the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment to sensitize Hepatocellular Carcinoma to immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Cancer Lett. 2022, 541, 215750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Andresen, J.L.; Manan, R.S.; Langer, R. Nucleic acid delivery for therapeutic applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 178, 113834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; LoRusso, P.M.; Cervantes, A.; Schwartz, G.K.; Weiss, G.J.; Paz-Ares, L.; Cho, D.C.; Infante, J.R.; Alsina, M.; et al. First-in-humans trial of an RNA interference therapeutic targeting VEGF and KSP in cancer patients with liver involvement. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Xie, S.; Rowicki, M.; Michel, S.; Wei, Y.; Hang, X.; Wan, L.; Lu, X.; Yuan, M.; Jin, J.F.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of Metadherin Suppresses Colorectal and Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020, 81, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhan, M.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Shen, M.; Yang, F.; Kang, Y.; Yin, F.; Li, Z. Structure-Based Design, Optimization, and Evaluation of Potent Stabilized Peptide Inhibitors Disrupting MTDH and SND1 Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 12188–12199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, D.; Sarkar, D. Multifunctional Role of Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1 (AEG-1) in Cancer: Focus on Drug Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.K.; Gredler, R.; Vozhilla, N.; Su, Z.Z.; Chen, D.; Forcier, T.; Shah, K.; Saxena, U.; Hansen, U.; Fisher, P.B.; et al. Identification of genes conferring resistance to 5-fluorouracil. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12938–12943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.P.; Liao, J.Z.; Lu, Y.Q.; Tian, D.A.; Ye, F.; Zhao, P.X.; Xiang, G.Y.; Tang, W.X.; He, X.X. MiR-375 and Doxorubicin Co-delivered by Liposomes for Combination Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 7, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, M.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Dong, K. Adenovirus-mediated anti-AEG-1 ScFv expression driven by stathmin promoter inhibits tumor growth in cervical cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittrup, A.; Lieberman, J. Knocking down disease: A progress report on siRNA therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2015, 16, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, A.L.; Linsley, P.S. Recognizing and avoiding siRNA off-target effects for target identification and therapeutic application. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Ma, X.; Gao, F.; Guo, Y. Off-target effects in CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1143157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Al-Megrin, W.A.I.; Aljamaan, A.N.; Rahmani, A.H.; Khan, A.A. Recent Advances in Genome-Editing Technology with CRISPR/Cas9 Variants and Stimuli-Responsive Targeting Approaches within Tumor Cells: A Future Perspective of Cancer Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High, K.A.; Roncarolo, M.G. Gene Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Almotairy, A.R.Z.; Henidi, H.; Alshehri, O.Y.; Aldughaim, M.S. Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Systems: A Review of the Implication of Nanoparticles’ Physicochemical Properties on Responses in Biological Systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reghupaty, S.C.; Sarkar, D. Current Status of Gene Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinal, C.J.; Tohkin, M.; Miyata, M.; Ward, J.M.; Lambert, G.; Gonzalez, F.J. Targeted disruption of the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR impairs bile acid and lipid homeostasis. Cell 2000, 102, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, X.; Yi, T.; Yen, Y.; Moore, D.D.; Huang, W. Spontaneous development of liver tumors in the absence of the bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Choi, K.M.; Bang, G.; Park, S.G.; Kim, E.B.; Choi, J.W.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, E.; et al. Identification of Nucleolin as a Novel AEG-1-Interacting Protein in Breast Cancer via Interactome Profiling. Cancers 2021, 13, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhu, D.; Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Brachova, P.; Leslie, K.K. Cytoplasmic Metadherin (MTDH) provides survival advantage under conditions of stress by acting as RNA-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4485–4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Jain, A.D.; Truica, M.I.; Izquierdo-Ferrer, J.; Anker, J.F.; Lysy, B.; Sagar, V.; Luan, Y.; Chalmers, Z.R.; Unno, K.; et al. Small-Molecule MYC Inhibitors Suppress Tumor Growth and Enhance Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 483–497 e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1300–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Molecule | Location of Interaction | Consequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SND1 | Cytoplasm | 1. Stabilization of SND1 2. Augmented RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) activity resulting in increased degradation of tumor suppressor mRNAs | [73,74] |
| RXR | Nucleus | 1. Inhibition of RXR-dependent gene transcription 2. Contributes to metabolic dysfunction-induced steatohepatitis (MASH) 3. Contributes to non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS) | [48,66,116] |
| DDX17 | Nucleus | 1. Stabilization of DDX17 2. Increased EGFR and MEK/ERK signaling | [123] |
| ZBTB17/Miz1 | Cytoplasm | 1. Sequestration of AEG-1 resulting in inhibition of NF-κB activation 2. Inhibition of macrophage activation and inflammation | [124] |
| mRNAs encoding endomembrane proteins | ER membrane | 1. Increased protein translation 2. Chemoresistance 3. MASH | [48,63,121] |
| Strategy | Application | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| IHC | Correlation between AEG-1 levels with overall survival and recurrence as a measure of prognosis | [142] |
| IHC | Combination of AEG-1 and GPC3 levels as diagnostic markers for HCC biopsy samples | [146] |
| ELISA | Serum AEG-1 antibody levels as a diagnostic marker for HCC | [147] |
| Targeted nanoparticle-delivered AEG-1 siRNA | Treatment of HCC in combination with ATRA; Prevention of MASH | [48,148] |
| Locked nucleic acid-modified (LNA) antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) for AEG-1 | Treatment of HCC in combination with anti-PD-1 antibody | [149] |
| Small molecules (C26-A6 and C19) inhibiting AEG-1/SND1 interaction | Treatment of HCC | [76,77,78] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davis, E.; Ermi, A.G.; Sarkar, D. Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1/Metadherin (AEG-1/MTDH): A Promising Molecular Marker and Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081375
Davis E, Ermi AG, Sarkar D. Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1/Metadherin (AEG-1/MTDH): A Promising Molecular Marker and Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(8):1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081375
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavis, Eva, Ali Gawi Ermi, and Devanand Sarkar. 2025. "Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1/Metadherin (AEG-1/MTDH): A Promising Molecular Marker and Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 8: 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081375
APA StyleDavis, E., Ermi, A. G., & Sarkar, D. (2025). Astrocyte Elevated Gene-1/Metadherin (AEG-1/MTDH): A Promising Molecular Marker and Therapeutic Target for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(8), 1375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17081375






