Roles of Annexin A1 Expression in Small Cell Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
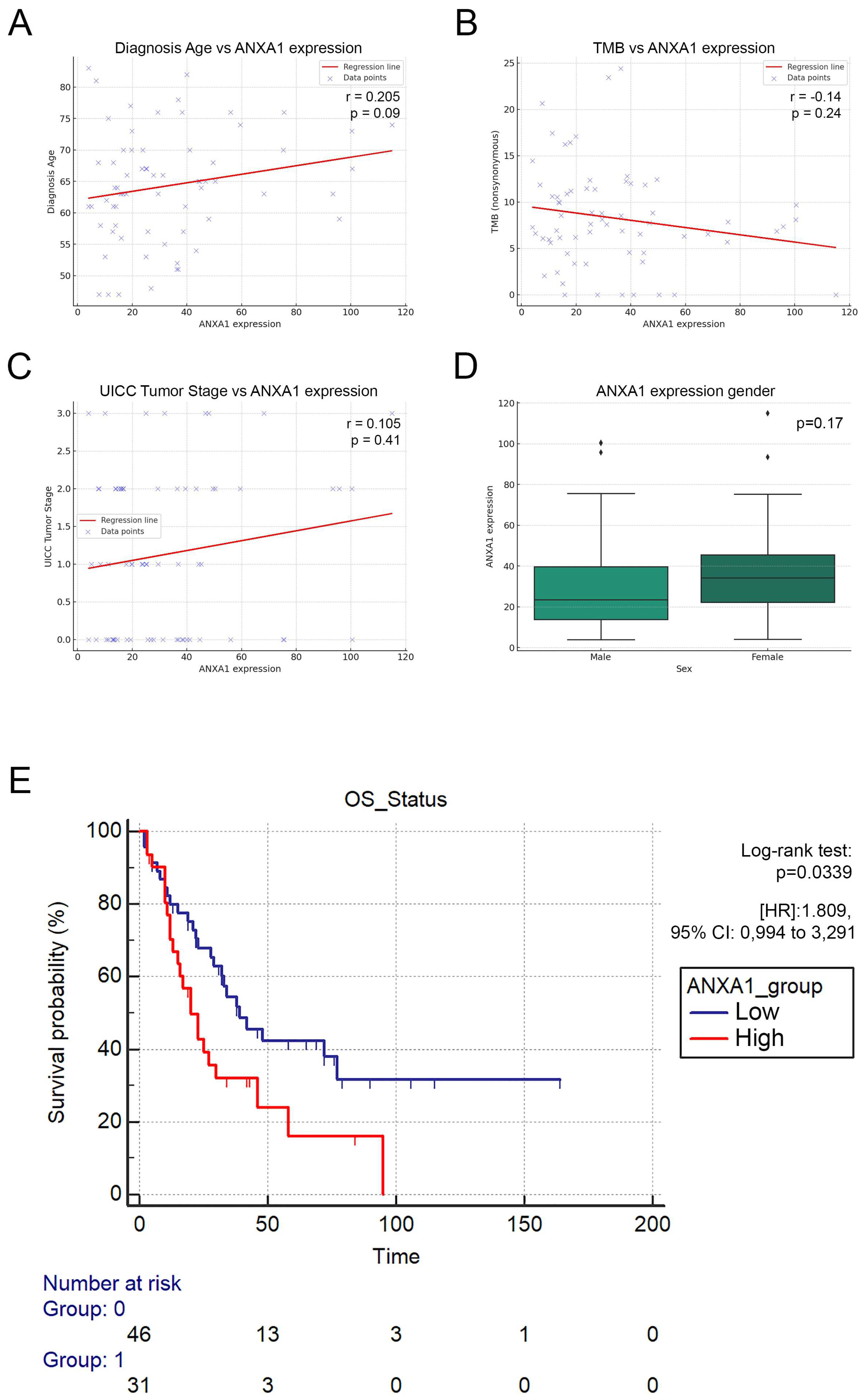
2.1. Predictive Algorithms and RNA-Seq Dataset
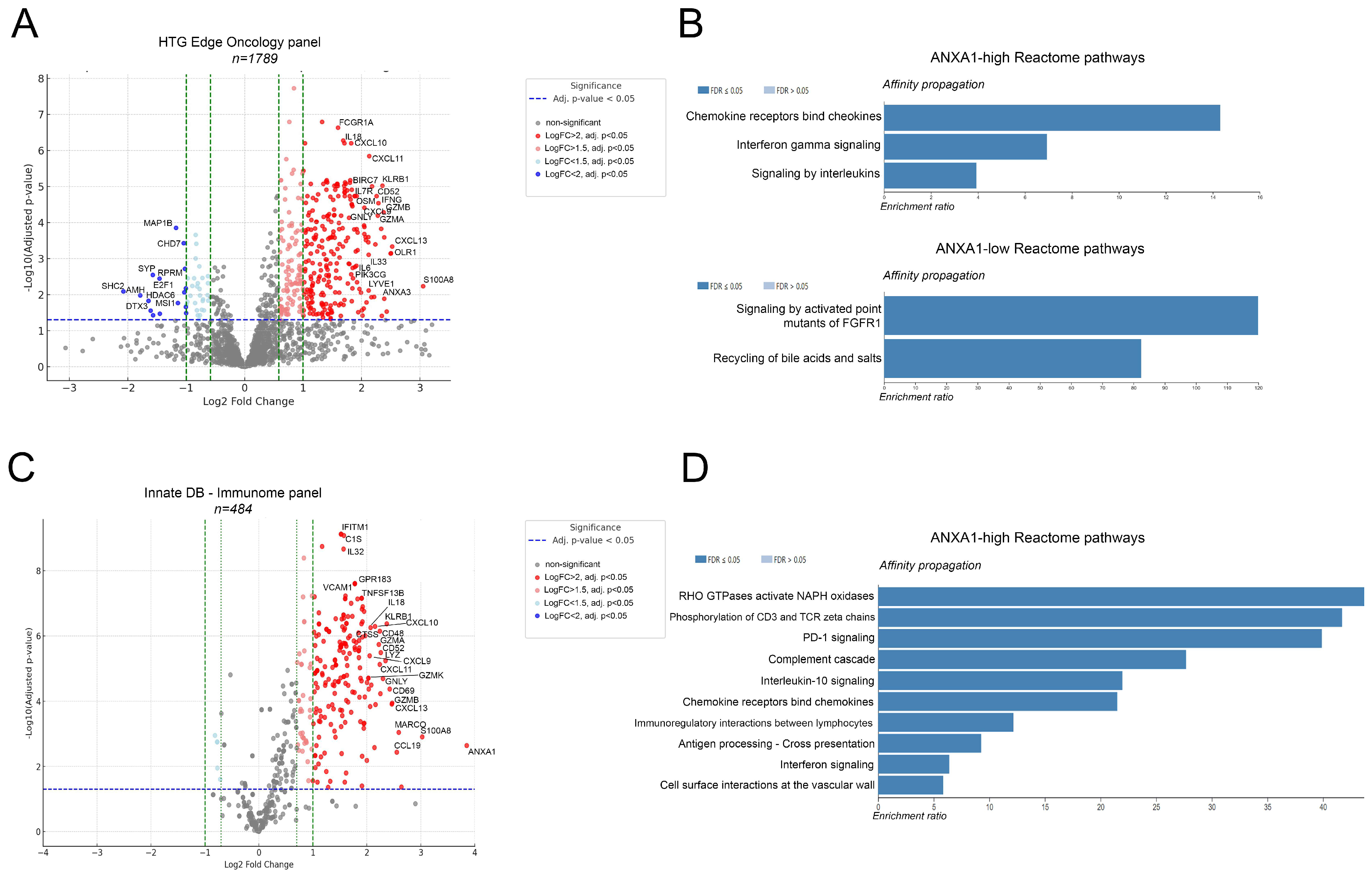
2.2. Differential Expression and Pathway Analyses
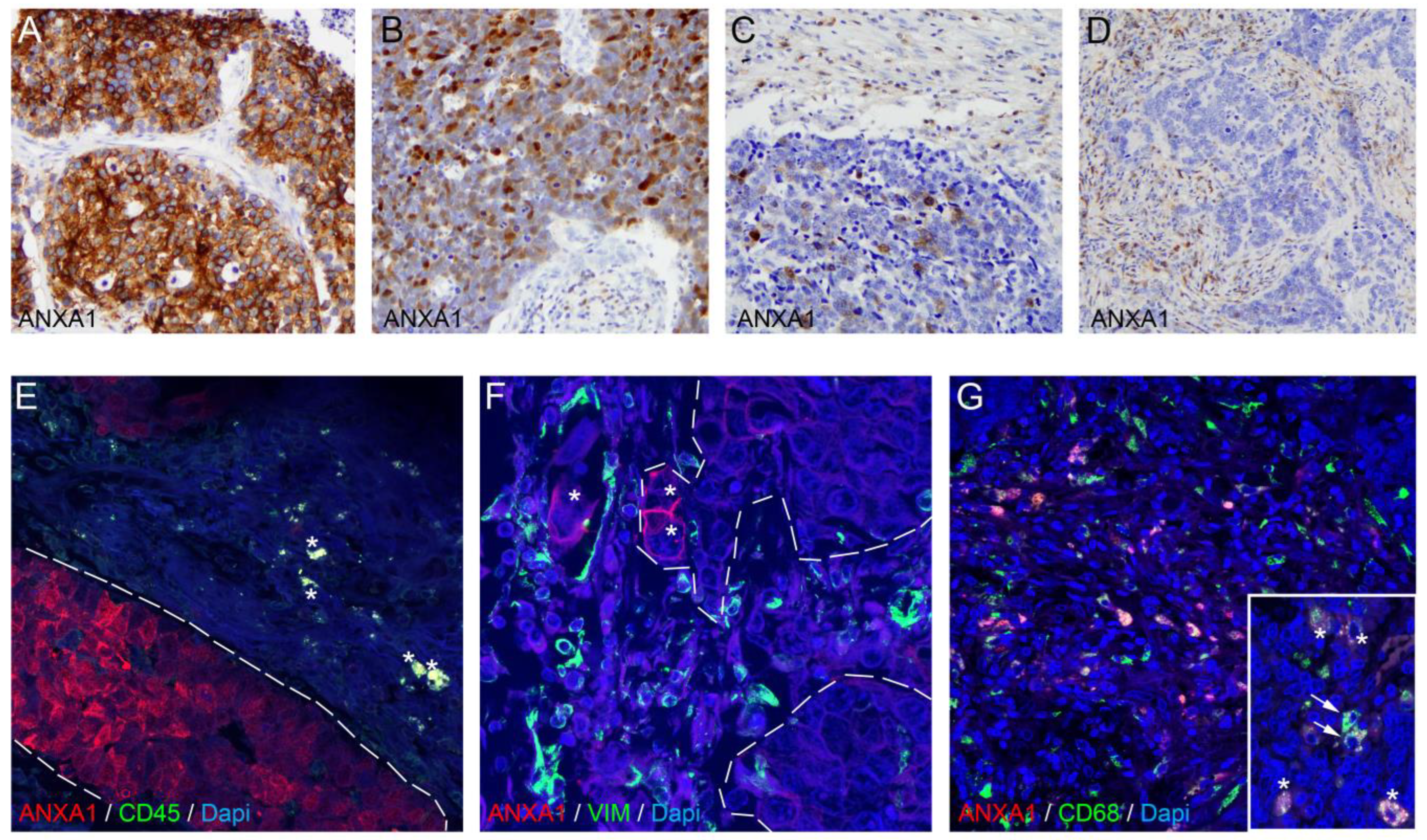
2.3. Tumor Samples, Immunohistochemistry, and Immunofluorescence
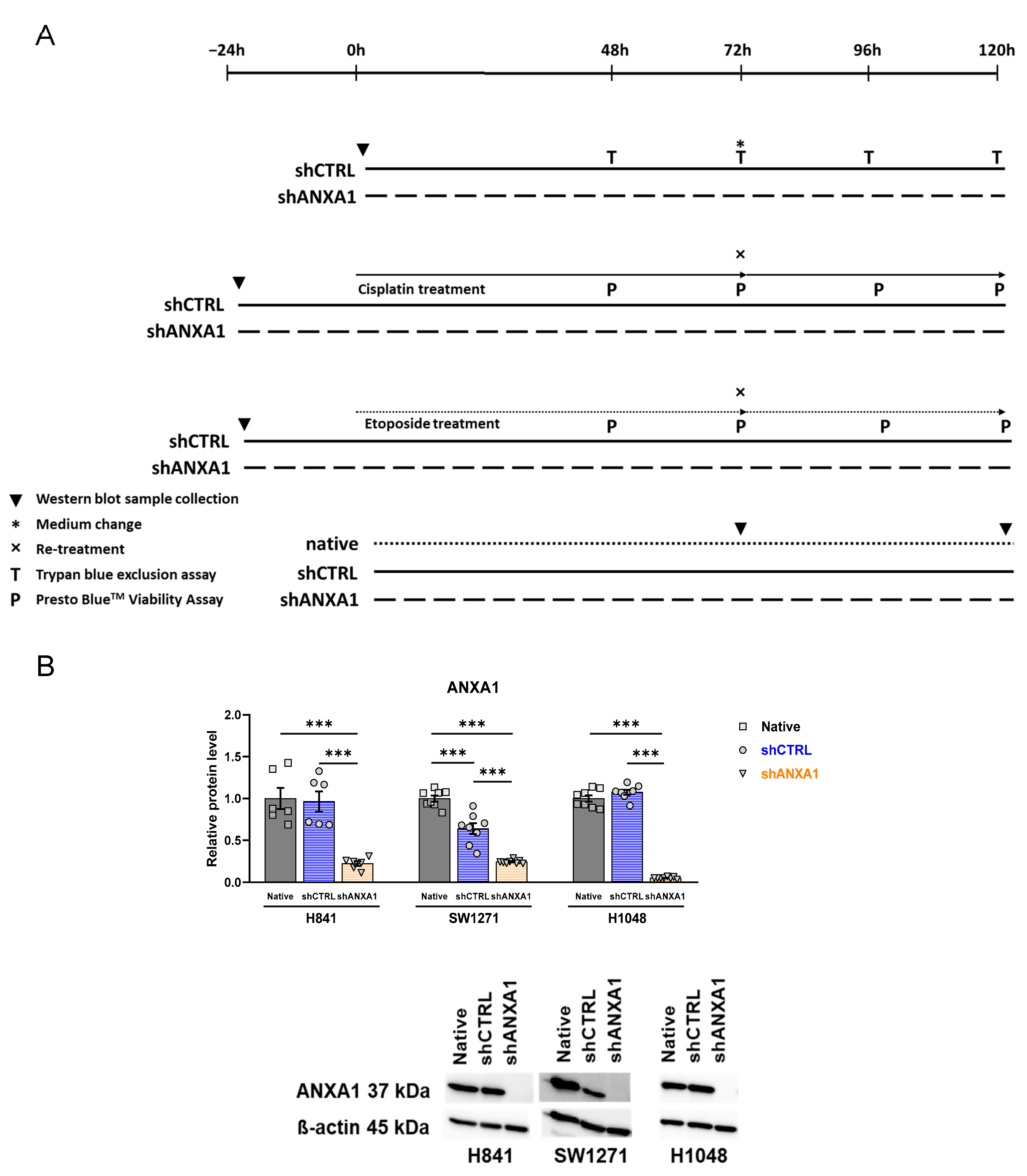
2.4. Cell Lines, Transfection, and Culture Conditions
2.5. Trypan Blue Exclusion Growth Rate Assay
2.6. Assessment of Chemosensitivity and Growth Rate with Presto Blue Viability AssayTM
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. High ANXA1 Expression Is Associated with Increased Immune Infiltrates and Stromality
3.2. ANXA1-High Tumors Differentially Express Immune-Related Genes and Pathways of Active Immunosuppression
3.3. ANXA1-High Patients Exhibit Significantly Decreased Overall Survival
3.4. ANXA1 Protein Is Expressed on Tumor Cells and Macrophages in SCLC Tumor Samples
3.5. Annexin A1 Expression Is Stably Silenced in shANXA1 Transfected Cells
3.6. Effects of ANXA1 Silencing on Growth Rate
3.7. Effects of ANXA1 Silencing on Cisplatin and Etoposide Chemosensitivity
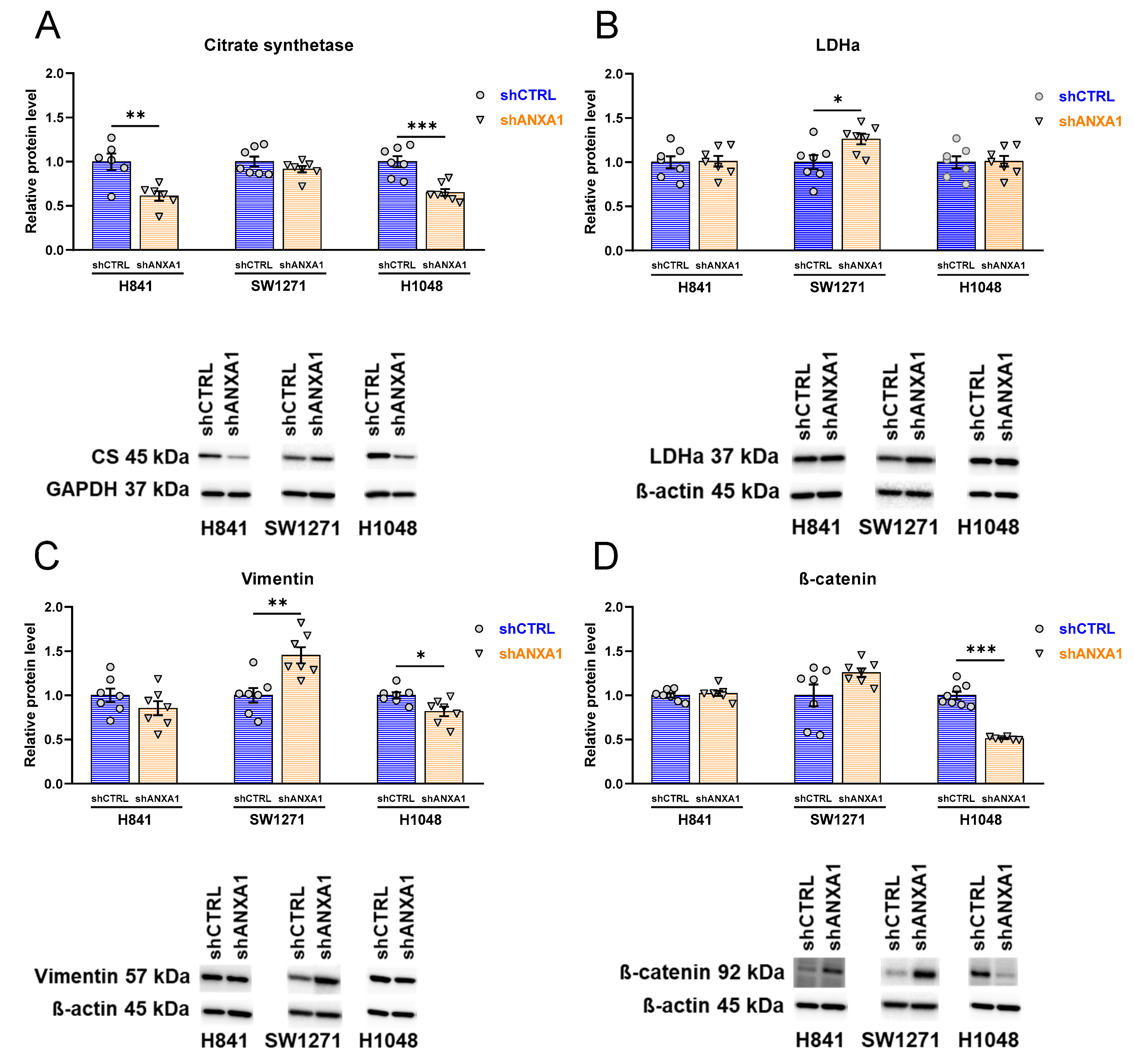
3.8. Effects of ANXA1 Silencing on Expression of Metabolic and Mesenchymal Markers
3.9. Effects of ANXA1 Silencing on Expression of Dominant Transcriptional Drivers and Immune-Relevant Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANXA1 | annexin A1 |
| CD | cluster of differentiation |
| CS | citrate synthetase |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| OS | overall survival |
| PD-L1 | programmed cell death ligand 1 |
| POU2F3 | POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 3 |
| SCLC | small cell lung cancer |
| YAP1 | yes-associated protein 1 |
References
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretic, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araghi, M.; Mannani, R.; Heidarnejad Maleki, A.; Hamidi, A.; Rostami, S.; Safa, S.H.; Faramarzi, F.; Khorasani, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Recent advances in non-small cell lung cancer targeted therapy; an update review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Lai, Q.; Gou, L.; Feng, J.; Yang, J. Opportunities and obstacles of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in small cell lung cancer. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.V.; Mok, T.S.K.; Nabet, B.Y.; Mansfield, A.S.; De Boer, R.; Losonczy, G.; Sugawara, S.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Krzakowski, M.; Smolin, A.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of long-term survivors with extensive-stage small cell lung cancer treated with first-line atezolizumab plus carboplatin and etoposide. Lung Cancer 2023, 186, 107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Ozguroglu, M.; Ji, J.H.; Garassino, M.C.; et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: 3-year overall survival update from CASPIAN. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganti, A.K.P.; Loo, B.W.; Bassetti, M.; Blakely, C.; Chiang, A.; D’Amico, T.A.; D’Avella, C.; Dowlati, A.; Downey, R.J.; Edelman, M.; et al. Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 19, 1441–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remon, J.; Aldea, M.; Besse, B.; Planchard, D.; Reck, M.; Giaccone, G.; Soria, J.C. Small cell lung cancer: A slightly less orphan disease after immunotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fur, G.M.; Nemes, K.; Mago, E.; Beno, A.A.; Topolcsanyi, P.; Moldvay, J.; Pongor, L.S. Applied models and molecular characteristics of small cell lung cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2024, 30, 1611743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Poirier, J.T.; Byers, L.A.; Dive, C.; Dowlati, A.; George, J.; Heymach, J.V.; Johnson, J.E.; Lehman, J.M.; MacPherson, D.; et al. Molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer: A synthesis of human and mouse model data. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.; Takahashi, N.; Kumar, R.; Nichols, S.; Malin, J.; Hunt, A.; Schultz, C.; Cao, Y.; Tillo, D.; Nousome, D.; et al. Microenvironment shapes small-cell lung cancer neuroendocrine states and presents therapeutic opportunities. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ireland, A.S.; Micinski, A.M.; Kastner, D.W.; Guo, B.; Wait, S.J.; Spainhower, K.B.; Conley, C.C.; Chen, O.S.; Guthrie, M.R.; Soltero, D.; et al. MYC Drives Temporal Evolution of Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes by Reprogramming Neuroendocrine Fate. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 60–78.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dora, D.; Rivard, C.; Yu, H.; Bunn, P.; Suda, K.; Ren, S.; Lueke Pickard, S.; Laszlo, V.; Harko, T.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; et al. Neuroendocrine subtypes of small cell lung cancer differ in terms of immune microenvironment and checkpoint molecule distribution. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1947–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dora, D.; Rivard, C.; Yu, H.; Pickard, S.L.; Laszlo, V.; Harko, T.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; Dinya, E.; Gerdan, C.; Szegvari, G.; et al. Characterization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages and the Immune Microenvironment in Limited-Stage Neuroendocrine-High and -Low Small Cell Lung Cancer. Biology 2021, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, L.; McGrath, S.; Rodgers, L.; McCall, K.; Tulunay Virlan, A.; Dempsey, F.; Crichton, S.; Goodyear, C.S. Annexin-A1: The culprit or the solution? Immunology 2022, 166, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, L.; Liu, L.; Yu, R.; Li, X.; Luo, Z. Knockdown of Annexin-A1 Inhibits Growth, Migration and Invasion of Glioma Cells by Suppressing the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. ASN Neuro 2021, 13, 17590914211001218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elakad, O.; Li, Y.; Gieser, N.; Yao, S.; Kuffer, S.; Hinterthaner, M.; Danner, B.C.; von Hammerstein-Equord, A.; Strobel, P.; Bohnenberger, H. Role of Annexin A1 in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer Progression. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 5520832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ali, H.N.; Crichton, S.J.; Fabian, C.; Pepper, C.; Butcher, D.R.; Dempsey, F.C.; Parris, C.N. A therapeutic antibody targeting annexin-A1 inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2024, 43, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Min, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Tan, G.; Zhang, F. Annexin A1 is a potential biomarker of bone metastasis in small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Wu, P.F.; Li, Q.; Dai, W.M.; Yuan, S.; Xu, Z.H.; Liu, T.T.; Miao, Z.W.; Fang, W.G.; et al. Brain microvascular endothelium induced-annexin A1 secretion contributes to small cell lung cancer brain metastasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 66, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martinez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Trevino, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Racle, J.; Gfeller, D. EPIC: A Tool to Estimate the Proportions of Different Cell Types from Bulk Gene Expression Data. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2120, 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, J.; Pujar, S.; Loveland, J.E.; Astashyn, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Cox, E.; Davidson, C.; Ermolaeva, O.; Farrell, C.M.; et al. A joint NCBI and EMBL-EBI transcript set for clinical genomics and research. Nature 2022, 604, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voros, I.; Onodi, Z.; Toth, V.E.; Gergely, T.G.; Saghy, E.; Gorbe, A.; Kemeny, A.; Leszek, P.; Helyes, Z.; Ferdinandy, P.; et al. Saxagliptin Cardiotoxicity in Chronic Heart Failure: The Role of DPP4 in the Regulation of Neuropeptide Tone. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, L.A.; Kar, S.; Foo, S.L.; Gu, T.; Toh, Y.Q.; Ampomah, P.B.; Sachaphibulkij, K.; Yap, G.; Zharkova, O.; Lukman, H.M.; et al. Annexin-A1 enhances breast cancer growth and migration by promoting alternative macrophage polarization in the tumour microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Multhoff, G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: Historical dogma versus current understanding. J. Physiol. 2021, 599, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, S.L.; Yap, G.; Cui, J.; Lim, L.H.K. Annexin-A1—A Blessing or a Curse in Cancer? Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graauw, M.; van Miltenburg, M.H.; Schmidt, M.K.; Pont, C.; Lalai, R.; Kartopawiro, J.; Pardali, E.; Le Devedec, S.E.; Smit, V.T.; van der Wal, A.; et al. Annexin A1 regulates TGF-beta signaling and promotes metastasis formation of basal-like breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6340–6345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, L.A.; Ampomah, P.B.; Lim, L.H.K. Annexin A1 in inflammation and breast cancer: A new axis in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Adh Migr. 2018, 12, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Zeng, T.; Zhu, W.; Yu, Z.Z.; Huang, W.; Yi, H.; Lu, S.S.; Feng, J.; Feng, X.P.; Wu, D.; et al. ANXA1 Promotes Tumor Immune Evasion by Binding PARP1 and Upregulating Stat3-Induced Expression of PD-L1 in Multiple Cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 1367–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkenburg, K.C.; de Groot, A.E.; Pienta, K.J. Targeting the tumour stroma to improve cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 366–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Wang, C.; Gong, W.; Yoshimura, T.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.M. Cell surface receptor FPR2 promotes antitumor host defense by limiting M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bist, P.; Shu, S.; Lee, H.; Arora, S.; Nair, S.; Lim, J.Y.; Dayalan, J.; Gasser, S.; Biswas, S.K.; Fairhurst, A.M.; et al. Annexin-A1 regulates TLR-mediated IFN-beta production through an interaction with TANK-binding kinase 1. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 4375–4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, M.; Wu, M.; Wu, F.; Zhou, F.; Du, Y.; et al. Natural Coevolution of Tumor and Immunoenvironment in Glioblastoma. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2820–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, F.; Zhang, P.; Fu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Q.; Li, D.; Li, B.; Wu, K. Targeting ANXA1 abrogates Treg-mediated immune suppression in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radomir, L.; Kramer, M.P.; Perpinial, M.; Schottlender, N.; Rabani, S.; David, K.; Wiener, A.; Lewinsky, H.; Becker-Herman, S.; Aharoni, R.; et al. The survival and function of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells are negatively controlled by SLAMF5. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Qian, H.; Zhuang, Q. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: From basic science to anticancer therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.I.; Griendling, K.K. Nox proteins in signal transduction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1239–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.H. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: Physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Al-Haidari, A.; Sun, J.; Kazi, J.U. T cell receptor (TCR) signaling in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A. Cytokines in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2018, 10, a028472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, D.; Angell, H.K.; Galon, J. The immune contexture and Immunoscore in cancer prognosis and therapeutic efficacy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 662–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Su, L.; Han, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, W.; Wang, Y.; Xue, X. ANXA1: An Important Independent Prognostic Factor and Molecular Target in Glioma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 851505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Zhang, P.F.; Li, M.Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Chen, Z.C. Identification of annexin A1 as a proinvasive and prognostic factor for lung adenocarcinoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.F.; Ni, X.G.; Zhao, P.; Liu, S.M.; Wang, H.X.; Guo, B.; Zhou, L.P.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.S.; Wang, K.; et al. Overexpression of annexin 1 in pancreatic cancer and its clinical significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.Y.; Wu, M.S.; Lin, J.T.; Lin, M.T.; Shun, C.T.; Huang, H.Y.; Hua, K.T.; Kuo, M.L. Annexin A1 is associated with gastric cancer survival and promotes gastric cancer cell invasiveness through the formyl peptide receptor/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/integrin beta-1-binding protein 1 pathway. Cancer 2012, 118, 5757–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manai, M.; Doghri, R.; Finetti, P.; Mrad, K.; Bouabsa, R.; Manai, M.; Birnbaum, D.; Bertucci, F.; Charfi, L.; Driss, M. Overexpression of Annexin A1 Is an Independent Predictor of Longer Overall Survival in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. In Vivo 2020, 34, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Guan, X.; Cai, T.; Long, J.; Wang, H.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y. Knockdown of ANXA1 suppresses the biological behavior of human NSCLC cells in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3858–3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shi, G.; Lu, J.; Qian, X.; Wang, D. Potential regulatory mechanism of TNF-alpha/TNFR1/ANXA1 in glioma cells and its role in glioma cell proliferation. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, W.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Li, H.; He, F. ANXA1 enhances tumor proliferation and migration by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway in papillary thyroid carcinoma. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.M.; Tian, J.; Qi, L.; Liu, L.M.; Xu, N. ANXA1 affects cell proliferation, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 5214–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Wen, S.; Gao, X.; Liu, L. ANXA1-GSK3beta interaction and its involvement in NSCLC metastasis. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Li, X.; Luo, S.; Zhao, L. An overview of the regulatory role of annexin A1 in the tumor microenvironment and its prospective clinical application (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Acunto, C.W.; Gbelcova, H.; Festa, M.; Ruml, T. The complex understanding of Annexin A1 phosphorylation. Cell Signal 2014, 26, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlier, C.; Kintz, P.; Dubois, N.; Plomteux, G. Fatal overdosage with cisplatin. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2004, 28, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Minami, H.; Saka, H.; Ando, M.; Sakai, S.; Shimokata, K. Therapeutic drug monitoring of etoposide in a 14-day infusion for non-small-cell lung cancer. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1996, 87, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, D.R.; Davis, M. Clinically Relevant Concentrations of Anticancer Drugs: A Guide for Nonclinical Studies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 3489–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S.; Andresen, H.; Schmoldt, A. Therapeutic and toxic blood concentrations of nearly 1,000 drugs and other xenobiotics. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Jiang, P.; Yan, L.; Mo, D.; Tang, X.; Yan, F. DCST1-AS1 Promotes TGF-beta-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Enhances Chemoresistance in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via ANXA1. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Hu, Z.; Niu, G.; Xia, J.; Wang, X.; Hong, R.; Gu, J.; Wang, D.; Ke, C. Annexin A1 induces oxaliplatin resistance of gastric cancer through autophagy by targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Li, Y.W.; Zhao, C.; Jia, N.; Li, R.L.; Cao, S.S.; Cui, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Y.; et al. Regulatory mechanisms of annexin-induced chemotherapy resistance in cisplatin resistant lung adenocarcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 3191–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Meng, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhang, M. Correlation of ANXA1 expression with drug resistance and relapse in bladder cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 5538–5548. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, Y.; Kumamoto, K.; Saito, K.; Okayama, H.; Hayase, S.; Kofunato, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakamura, I.; Ohki, S.; Koyama, Y.; et al. Up-regulated Annexin A1 expression in gastrointestinal cancer is associated with cancer invasion and lymph node metastasis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011, 2, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, L.D.; Vishwanatha, J.K. Prognostic impact of AnxA1 and AnxA2 gene expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 2697–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschler, S.; Gebeshuber, C.A.; Wiedemann, E.M.; Alacakaptan, M.; Schreiber, M.; Custic, I.; Beug, H. Annexin A1 attenuates EMT and metastatic potential in breast cancer. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermes, A.; Gatzemeier, U.; Waschki, B.; Reck, M. Lactate dehydrogenase as prognostic factor in limited and extensive disease stage small cell lung cancer—A retrospective single institution analysis. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 1937–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Peng, G. Targeting citrate as a novel therapeutic strategy in cancer treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2020, 1873, 188332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberti, M.V.; Locasale, J.W. Correction to: ‘The Warburg Effect: How Does it Benefit Cancer Cells?’: [Trends in Biochemical Sciences, 41 (2016) 211]. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 287. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, L.; Alesi, G.N.; Kang, S. Glutaminolysis as a target for cancer therapy. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Tenjin, Y.; Yamada, T.; Kudoh, S.; Kudo, N.; Sanada, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsuo, A.; Orita, Y.; Ito, T. The role of YAP1 in small cell lung cancer. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McColl, K.; Wildey, G.; Sakre, N.; Lipka, M.B.; Behtaj, M.; Kresak, A.; Chen, Y.; Yang, M.; Velcheti, V.; Fu, P.; et al. Reciprocal expression of INSM1 and YAP1 defines subgroups in small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73745–73756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavan, A.; Attili, I.; Pasello, G.; Guarneri, V.; Conte, P.F.; Bonanno, L. Immunotherapy in small-cell lung cancer: From molecular promises to clinical challenges. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, Y.; Wise, R.; Zolkiewska, A. Proteolytic processing of PD-L1 by ADAM proteases in breast cancer cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.; Feulner, L.; Santos Rubenich, D.; Heimer, S.; Rohrmuller, S.; Reinders, Y.; Falchetti, M.; Wetzel, M.; Braganhol, E.; Lummertz da Rocha, E.; et al. Subcellular localization of PD-L1 and cell-cycle-dependent expression of nuclear PD-L1 variants: Implications for head and neck cancer cell functions and therapeutic efficacy. Mol. Oncol. 2024, 18, 431–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Xun, Y.; You, H. The landscape overview of CD47-based immunotherapy for hematological malignancies. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosi, A.; Lorenzi, M.; Del Bianco, P.; Roma, A.; Pavan, A.; Scapinello, A.; Resi, M.V.; Bonanno, L.; Frega, S.; Calabrese, F.; et al. Extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer in patients receiving atezolizumab plus carboplatin-etoposide: Stratification of outcome based on a composite score that combines gene expression profiling and immune characterization of microenvironment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, N.; Morabito, A.; La Rocca, A.; De Luca, G.; De Cecio, R.; Botti, G.; Totaro, G.; Muto, P.; Picone, C.; Esposito, G.; et al. Surgery in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, K.; Ploski, J.E. RISC-y Business: Limitations of Short Hairpin RNA-Mediated Gene Silencing in the Brain and a Discussion of CRISPR/Cas-Based Alternatives. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 914430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C.; Rossi, J.J. RNA-based therapeutics: Current progress and future prospects. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.T.; On, K.F.; Tsang, Y.H.; Poon, R.Y. An inducible system for expression and validation of the specificity of short hairpin RNA in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.B.; Guthrie, E.H.; Huang, M.T.; Taxman, D.J. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA): Design, delivery, and assessment of gene knockdown. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 629, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Covariate | b | SE | Wald | P | HR | 95% CI of HR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANXA1_group = 1 | 0.7161 | 0.2968 | 5.8199 | 0.0158 | 2.0463 | 1.1471 to 3.6504 |
| Sex = 1 | −1.0178 | 0.3953 | 6.6306 | 0.0100 | 0.3614 | 0.1672 to 0.7811 |
| Stage_group = 1 | 0.5630 | 0.2991 | 3.5443 | 0.0598 | 1.7560 | 0.9801 to 3.1462 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paál, Á.; Dora, D.; Takács, Á.; Rivard, C.; Pickard, S.L.; Hirsch, F.R.; Roskó, B.; Kiraly, P.; Ferdinandy, P.; Varga, Z.V.; et al. Roles of Annexin A1 Expression in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091407
Paál Á, Dora D, Takács Á, Rivard C, Pickard SL, Hirsch FR, Roskó B, Kiraly P, Ferdinandy P, Varga ZV, et al. Roles of Annexin A1 Expression in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(9):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091407
Chicago/Turabian StylePaál, Ágnes, David Dora, Ákos Takács, Christopher Rivard, Shivaun Lueke Pickard, Fred R. Hirsch, Brigitta Roskó, Peter Kiraly, Péter Ferdinandy, Zoltán V. Varga, and et al. 2025. "Roles of Annexin A1 Expression in Small Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 9: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091407
APA StylePaál, Á., Dora, D., Takács, Á., Rivard, C., Pickard, S. L., Hirsch, F. R., Roskó, B., Kiraly, P., Ferdinandy, P., Varga, Z. V., Lohinai, Z., & Görbe, A. (2025). Roles of Annexin A1 Expression in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 17(9), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17091407







