Abstract
Today, the theme of environmental preservation plays an important role within the activities of the scientific community and influences the choices of politics and the common population. In this context, the use of non-fossil substances should be promoted for different reasons: to avoid the depletion and damage of the areas involved in the fossil fuel extraction, decrease the impact of emissions/by-products related to the industrial transformation of fossil-based products and possibly exploit residual biomasses as sources of carbon. This latter aspect also can be viewed as a way to revalorize lignocellulose waste, generally destined to dump as putrescible matter or to be incinerated. In this review, we are aiming to present a concise overview of the multiple functions of lignocellulose biomass in the broad field of catalysis for a sustainable development. The originality of the approach is considering the lignocellulose-derived matter in three different aspects: (i) as a precursor to convert into platform molecules, (ii) as an active material (i.e., humic-like substances as photosensitizers) and (iii) as a green support for catalytic applications. We find that this perspective can widen the awareness level of scientists involved in the catalysis field for the exploitation of residual biomass as a valuable and complementary resource.
1. Introduction
“Skolstrejk för klimatet”: with this sentence pronounced in 2018, the young activist Greta Thunberg promoted a global movement, focused on a wide sensitization about climate and environmental changes [1]. Indeed, according to the report of National Center for Climate Restoration [2], the worst outlined scenario forecasts that, if the policymakers fail the fulfilment of the Paris Agreement and the restraint of greenhouse emissions, by 2050, the temperature will rise, provoking a progressive aridity/desertification and the melting of permafrost, which will increase the sea level [2,3]. In the meanwhile, exacerbated atmospheric phenomena will be able to devastate several ecosystems [2], with other direct consequences such as higher social disequilibria [2] and significant economic costs [4].
One of the most impacting factors on the environment is represented by the wide employment of non-renewable fossil resources (i.e., coal, gas and petroleum) [5], used to produce fuels, energy and chemicals, in turn transformed into consumables [6]. These latter ones comprise macro-categories such as plastics and rubber resins, organic solvents, pesticides, coatings, inks, adhesives, cleaning and personal care products [7]. The fossil fuel footprints on the environment are individuated in emissions of volatile organic compounds [7] and greenhouse gases mostly CO2 (76%), CH4, N2O, fluorinated gases [8,9] which are mainly generated by electricity and heat production, transformation industries and transportation [8]. Global emissions increased from 2 billion tons of carbon dioxide in 1900 to over 36 billion tons in 2017, whose 88% is generated by Asia, North America and Europe [9]. Even the extraction of fossil resources exerts great effects on the environment and human health, changing the equilibrium of the so-called hydrogeological conditions (in terms of soil and surface/underground water contamination), producing polluting gaseous emissions and intensifying the seismicity [10].
Additionally, an underestimated aspect of fossil resources withdrawal are the risks taken by workers involved in extraction, transportation and processing [10].
As already outlined, considering the sources of water depletion by the fossil fuel chain and the climate changes, an equal supply of clean water is another of the hardest challenges of the contemporary world. Water is necessary for human consumption, agriculture, industry as well as recreation [11]; thus, when the access to drinking water and the sanitation conditions are inadequate, health and social problems arise [12,13].
Beside biological pathogens, water is contaminated by substances of geological or anthropogenic origin [11]. Groundwater moving through sedimentary rocks and soils may pick up a wide range of compounds, based on Mg, Ca, Fe and/or chlorides, arsenates, fluorides and nitrates, with potential polluting effects [11]. Man-made contaminants are mainly by-products of industry and agriculture, including heavy metals, dyes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nitrogen, phosphorous, and pesticides [14]. When the infrastructures are available, the wastewater depuration is a multistep procedure, briefly described in Table 1 [15]. Nevertheless, new kinds of not commonly monitored pollutants (Contaminants of Emerging Concern, CECs, as pharmaceuticals and personal care products [16]) detected at trace/sub-trace level in water bodies and often not removed by traditional depuration processes, represent a further hurdle to the achievement of high-quality water standards [14,17].

Table 1.
Wastewater treatment levels [15,17].
The replacement of fossil feedstock and the remediation of compromised ecosystems, whose importance and interconnections have been above underlined, represent the framework in which this overview is articulated.
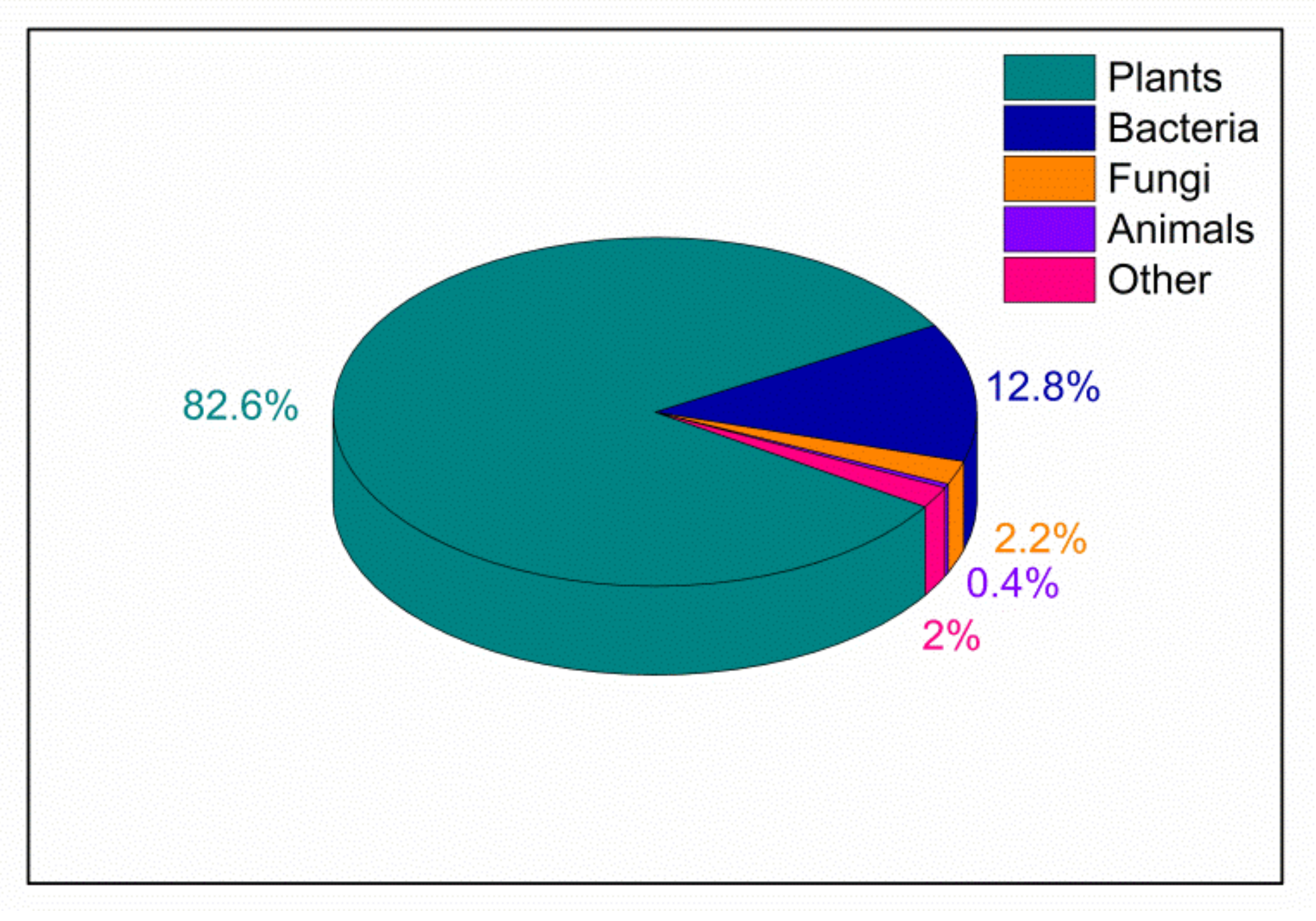
In particular, lignocellulosic biomass (LCB) has favorable characteristics to be exploited as a tool in different fields correlated to green chemistry and sustainable catalysis. LCB is a biopolymer, mainly composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin (see details in Section 2) and represents one of the most abundant materials on the earth, since it is a fundamental component of plants (see Figure 1) [18,19]. LCB fulfills the requirements of sustainability since it is a stable, renewable, biocompatible, biodegradable, low-cost and low-impact material [20].
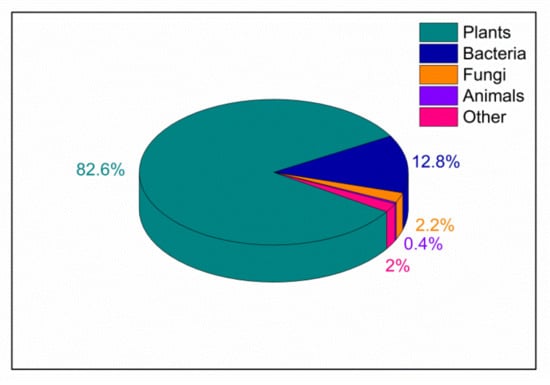
Figure 1.
Biomass distribution for abundant taxonomic groups according to Bar-on et al. [18]; the category labelled as “Other” includes Archaea, Protists and Viruses.
Lignocellulosic materials have historically provided energy through ignition (i.e., wood) and by the 19th century, they have been the core of pulp and paper industry [21,22]. Since the late 20th century, such biomass, due to its composition, has been considered to be transformed and adopted in lieu of fossil feedstock, within the so-called Bio-refinery [22,23,24]. Indeed, LCB is a unique sustainable source of organic carbon and an equivalent of fossil resources for the production of fuels and fine chemicals with net zero carbon emission [25]. In the fields of green and material chemistry, recent research showed the versatility of LCB, which have found other outlets as an adsorbent for aqueous pollutant removal [26,27], as a substrate in biocatalysis promoted by microorganisms for the production of commodity chemicals [28,29], as a precursor of biochar with multi-purpose applications [30] and reinforcing agent for plastics [31] and construction materials [32]. Moreover, the contemporary challenge is the exploitation of lignocellulose-based waste, instead of virgin plants: an example is the transition of the first-generation bio-refinery (which exploited ad hoc food crops) to the second-generation bio-refinery that treats residues and non-edible crops [33,34]. Indeed, the lignocellulose is at the base of nature, but can represent an environmental problem when is in the form of agricultural/domestic/industrial scrap and indiscriminately disposed [35,36]. For instance, the biodegradable fraction (kitchen refuses and green waste from gardens and parks) accounts for 30–50% of municipal solid waste in Europe [36] and the data concerning food waste reveal that every year 89 million tons are generated, whose 39% derives from food manufacturing process [37]. The biomass disposal in landfill is considered a bad practice due to the environmental and safety risks related to the generation of greenhouse gases (i.e., CH4), space usage and leachate [36], containing high values of solids, organic matter, recalcitrant organic pollutants, ammonium and sulphur compounds, and heavy metals, which eventually escape into soil and groundwater [38]. The incineration is another method to get rid of such biowaste, but it cannot be considered advantageous due to the high water content, low calorific value (1.8–4 GJ/ton for food waste) and gaseous emissions [36,39]. Alternatively, biomass waste can be biologically treated by (an-)aerobic digestion, operated by different microorganisms. In aerobic composting, the waste is aerated by air flowing and the biomass is oxo-degraded, to form complex three-dimensional organic polymers, very similar to humic substances naturally present in soils [40,41]. The final product is named compost and can be used as soil improver in both gardening and agriculture [42]. Anaerobic digestion is carried out in an oxygen-deprived chamber, forming gases, particularly methane, which can be used to produce electricity [41,43].
The environmental concerns related to a non-correct end of lignocellulosic waste can be faced through the principle of “closing the loop”, which is a perspective where all residues and wastes re-enter into production chain, creating high value (economic, social and environmental) [35,44], as corroborated by several Life Cycle Assessments (LCA) [24,45,46,47].
In the present overview, a focus on the potential contribution of LCB and waste-LCB in actual technological fields related to catalysis will be given. After the presentation of the chemical features, LCB will be described in three distinct sections on the basis of its applications: (i) as a feedstock for valuable chemicals; (ii) as a precursor of photoactive humic-like substances for water depollution; (iii) as a green support for a sustainable catalysis.
2. Chemistry of Lignocellulose Biomass
As other types of biomass, lignocellulosic matter derives from available atmospheric CO2, water and sunlight through biological photosynthesis.
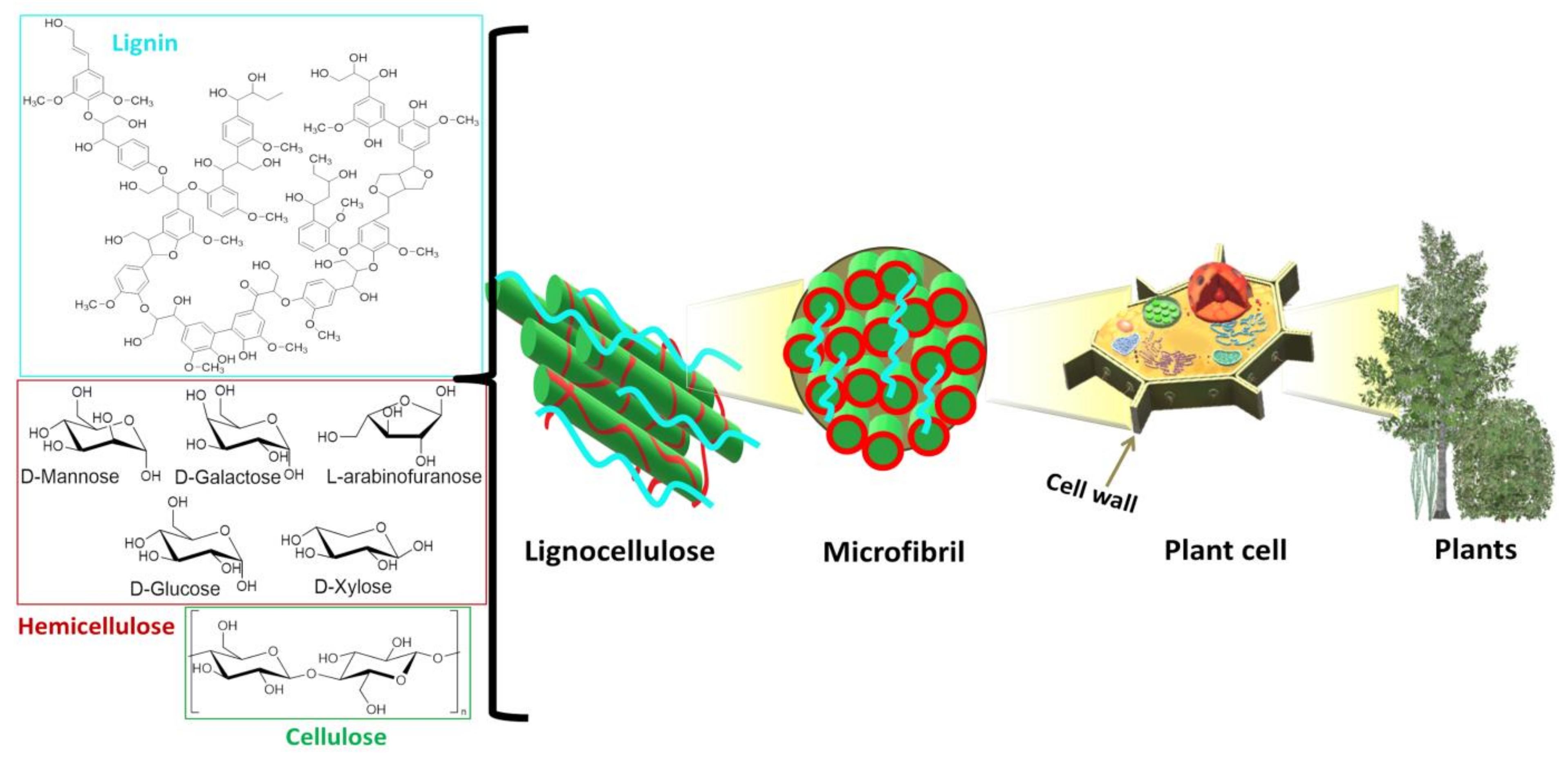
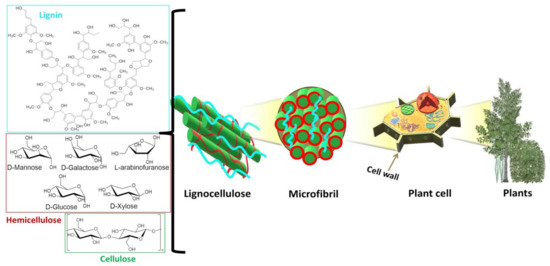
In Scheme 1, the structure of lignocellulose from plant cell walls is reported: its main components are cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin in different ratios and with different organization patterns depending on the plant origin [25] (see some examples in Table 2).
Scheme 1.
Lignocellulosic biomass from plant cell wall and its biopolymers, namely cellulose, lignin and the carbohydrates constituting hemicellulose.

Table 2.
Cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin percentages in different lignocellulosic biomasses.
Cellulose in cell walls is constituted by repeating units of cellobiose [48] in a stretched chain conformation [49], which is composed of one glucose molecule rotating 180° in relation to the next glucose, forming β (1–4)-linked residues [50]. Cellulose is present in the form of crystalline fibrils [48] alternated by amorphous regions [51]; the intramolecular hydrogen bonds within the cellulose chains are responsible for its rigidity and stability [50]. The shape, size, and crystallinity of these fibrils are important structural parameters that influence mechanical properties of the cell wall and are determinant in cellulose conversion processes [51]. Hemicellulose is the second most abundant polymer and, unlike cellulose, has a random and amorphous structure, which is composed of several heteropolymers (i.e., xylan, galactomannan, glucuronoxylan, arabinoxylan, glucomannan and xyloglucan) [25], branched and decorated by functionalities such as acetyl and methyl groups, cinnamic, glucuronic and galacturonic acids [49]. The amorphous hemicellulose covers the surface of rigid cellulose fibrils, stuck together by non-covalent bonds [49]. Moreover, hemicellulose hydrophobic moieties such as acetyl and methyl groups increase the affinity towards lignin, favoring the cohesion between the three lignocellulosic polymeric components [49]. Indeed, lignin is a complex and recalcitrant macromolecule composed of phenylpropanoic units linked by non-hydrolysable C-O-C and C-C bonds [52,53], that plays an important role in the growth and development of plants, improving the rigidity of plant cell wall, hydrophobic and transport properties, in addition to its function as barrier against pests and pathogens [54]. LCB also possesses a small content of pectins, inorganic compounds, proteins, waxes and lipids [49].
The reactivity of LCB in different applications is strictly correlated with the chemical features of the three main constituting macromolecules; for instance, the molecular weight and the availability of multiple functional moieties [19,35]. Likewise, LCB physical characteristics (surface morphology, specific surface area and porosity, mechanical stability, crystallinity) make this complex material very versatile [19,31]. Depending on the final application, a separation among cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin can be necessary. This generally occurs by chemical methods (i.e., hydrolysis, fractionation with ionic liquids, organosolv technique, etc.) and/or by an enzymatic approach [61,62,63].
3. Conversion of LCB into Valuable Chemicals
The transformation of LCB for the achievement of valuable bio-chemicals (Scheme 2) is considerably studied by different research groups since it represents an important issue of green chemistry in terms of eco-sustainability and environmental impact. Actually, the use of LCB, as a renewable commodity, can replace the fossil feedstock for chemicals and, being carbon-neutral, represents a promising strategy to support the green transition. Moreover, if the biomass conversion processes were also economically competitive, they would make LCB an industrial alternative to reduce the petroleum dependence [24].
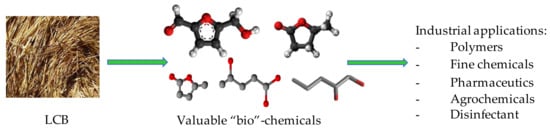
Scheme 2.
Conversion of LCB into industrial valuable chemicals.
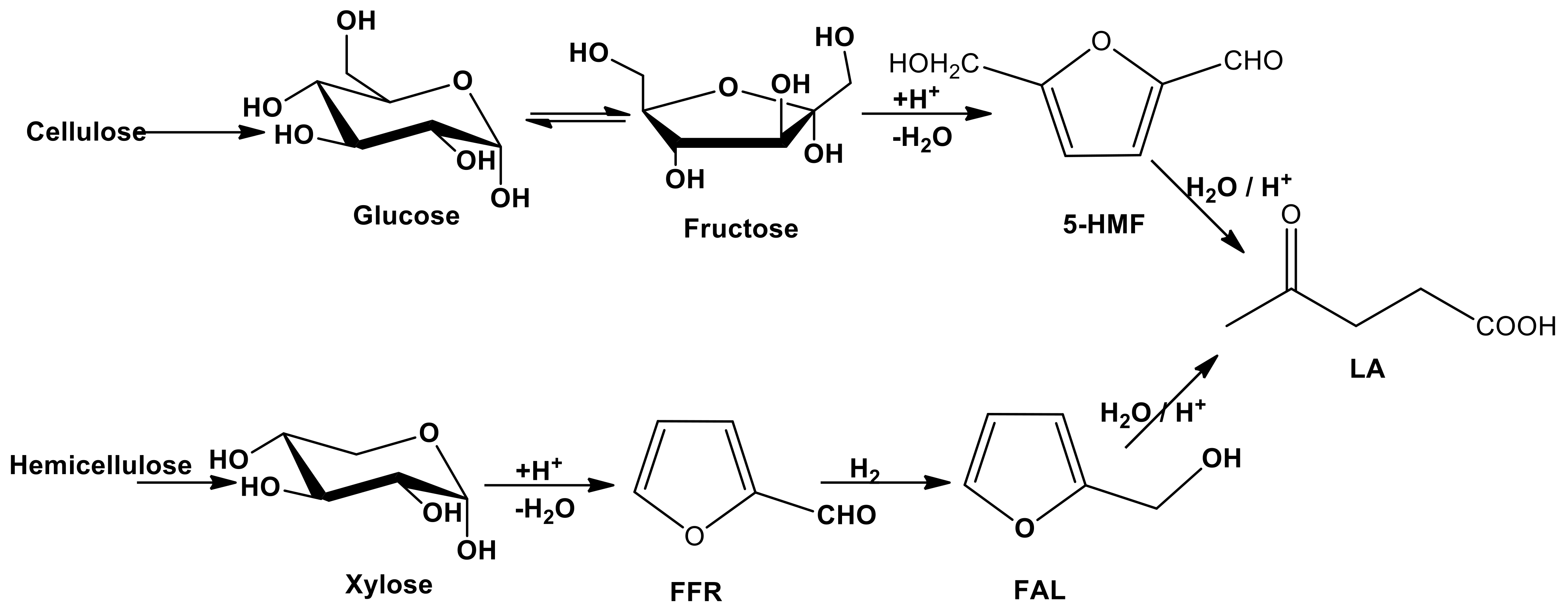
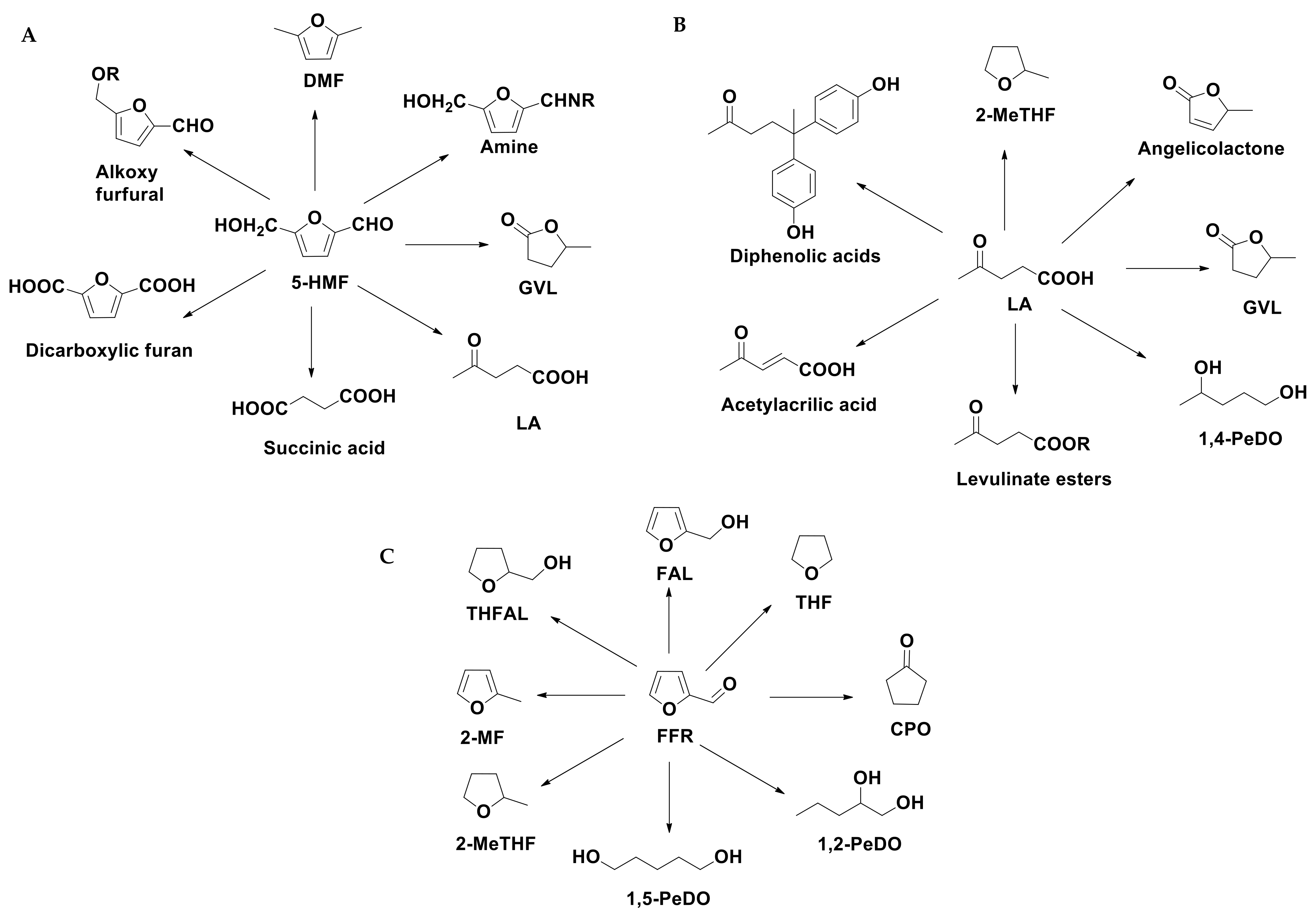
In order to extend the concept of sustainability into the entire lifecycle of chemical products, particular attention is paid to the circular chemistry whose principles include the use of waste as starting materials, the optimization of process efficiency, the use of non-toxic reagents, the assessment of sustainability and the ladder of circularity. Most of these concepts are applied in several processes that use LCB and its derivatives as starting materials for obtaining platform molecules and biofuels. The concept of bio-based platform molecules emerged in the late twentieth century when it was envisaged that simple, small molecules derivable from biomass could be utilized as building blocks for higher-value chemicals and materials [64]. From the hydrolysis of cellulose and hemicellulose components, it is possible to obtain sugars (fructose, glucose or xylose) whose catalytic conversion can lead to the formation of platform chemicals as 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (5-HMF), levulinic acid (LA) and furfural (FFR) (see Scheme 3) [65]. Different types of approaches, as thermal, biological and chemo-catalytic processes are usually employed to achieve this goal. In this section, we focused the attention on the chemo-catalysis and, in particular, on the heterogeneous catalysis that can lead to the development of sustainable procedures, due to the possibility of an easy recovery, regeneration and reutilization of the catalyst and the decrease in the processing costs. The point of view for the description of the LCB conversion processes will be the choice of catalysts and the crucial operating parameters.
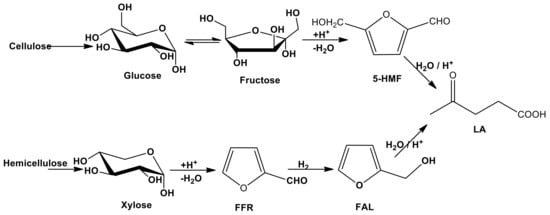
Scheme 3.
Cascade reactions of the conversion of LCB into platform molecules.
Among the reactions involved in the synthesis of added-value products, the most common are acid-catalyzed (i.e., hydrolysis) or metal-catalyzed (i.e., hydrogenation).
5-HMF, FFR and LA can be considered starting molecules for a wide number of compounds applied as industrial feedstock (Scheme 4). 5-HMF and its derivatives can be applied as biomass-based alternatives for fuel components or polymers, pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, flavors and fragrances [66]. FFR can be selectively transformed into different furanic compounds and polyols, which find a wide range of applications in polymer industries for the production of polyesters and polyurethanes [67], as well as for the synthesis of fungicides, disinfectants and fine chemicals. LA is classified among the 12 main platform molecules [65] and is recognized as a building block for different bio-derived chemicals. Due to their properties, methyltetrahydrofurans and levulinate esters are addressed towards the fuel markets as gasoline and biodiesel additives. Tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol (THFAL) is an environmentally acceptable industrial solvent due to its biodegradable nature. Both furfuryl alcohol (FAL) and γ-valerolactone (GVL) are extremely important platform molecules, used in food industry as food additives [68], as intermediate for the production of chemicals (lysine, vitamin C) as well as a sustainable liquid, [69] fuel additive [70]. GVL can be also used as a green solvent due to its inertness toward oxygen and water, high boiling- and flashpoint, low melting point and vapor pressure [71].
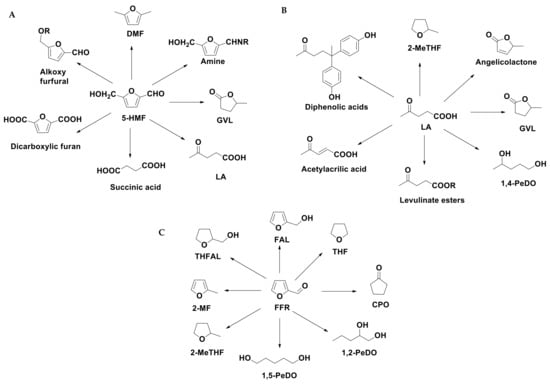
Scheme 4.
Conversion of 5-HMF (A), LA (B) and FFR (C) into valuable chemicals.
As already mentioned, one of the first steps for the achievement of valuable products is the acid- catalyzed hydrolysis of LCB. It is well established that the use of homogenous mineral acids is not environmentally friendly due to the corrosion phenomena of industrial equipment, the difficult recovery of the homogeneous catalyst and the production of acidic waste. Another important drawback is the presence of free acids that induces many side reactions. The literature on the conversion of LCB into chemicals is extremely extensive and, recently, several reviews were published [66,72,73,74,75]. A large number of heterogeneous solid acid catalysts, including ion-exchange resins [76], sulfonic carbon-based materials [74], Fe3O4 magnetic Brønsted catalysts [74] have been studied. Just to streamline this overview, we focused the study only on a few types of solid acid catalysts, such as Amberlyst® resins [72], modified zeolite [77], heteropolyacids [78] and acidic silica-based materials [79]. Table 3 shows some comparative studies of selected solid acid catalyst activity under different reaction conditions. Since the focus is on the sustainable processes, most of the considered studies were performed in aqueous media.

Table 3.
Comparative studies on hydrolysis cellulose based materials of selected solid acid catalysts activity under different reaction conditions.
Amberlyst® found a widespread application in this type of reaction. In fact, due to the high acidity of the material, it can be used both for the transformation of LCB into sugars [76] or directly with cascade reactions to 5-HMF or LA [72]. This is shown in the Table 3, where several types of LCB were used as starting materials and, in almost all cases, the presence of Amberlyst® led to the formation of LA or 5-HMF as final products with high yields. In general, a high acidity of solid acid catalysts, as Amberlyst®, can represent not only an advantage for the achievement of added-value products, but, at the same time, an important disadvantage. In particular, the selective hydrolysis of cellulose into glucose or other monosaccharides (like fructose) by the hydrolytic cleavage of β-1,4 glycosidic bond is a crucial step in the conversion of biomass into valuable chemicals. This means that a high acid catalyst can catalyze most of the reactions of the cascade, losing the selectivity towards the single intermediate. For this reason, the research is oriented to the design and synthesis of selective heterogeneous catalysts addressed to obtain the products of the single reaction steps. Apart from the intrinsic characteristics of the chosen material, its activity is also influenced by the reaction conditions in which the solvent plays an important role for the formation of the desired products. In the case of Amberlyst®, the presence of water led to the formation of LA as a principal product and, in order to stop the cascade reactions, organic solvents such as ionic liquids or dioxane were necessary to obtain sugars (entry 1) or 5-HMF (entry 2), respectively. This behavior was confirmed also in the case of heteropolyacids and zeolites. In particular, when heteropolyacids were used in the conversion of microcrystalline cellulose, it was possible to isolate 5-HMF with a high yield (75%) only by adding of a biphasic solvent (entry 7), otherwise, the reaction was shifted towards the formation of LA (63%) (entry 8). In similar reaction conditions, zeolite-based catalysts (entry 11) were more efficient than heteropolyacids, achieving LA with a very high yield (91%). Analogously, the use of organic solvents in the presence of zeolites favored the isolation of the intermediates as sugars (27%, entry 9) and 5-HMF (10%, entry 10). In their experiments (entries 3 and 10), Ordomsky et al. [81] found that the activities of both Amberlyst® and Mordenite (MOR)-zeolites were strongly influenced by the Lewis and Brønsted acidities of the corresponding materials. In particular, the Brønsted acidity increased the selectivity towards the formation of 5-HMF and, at the same time, Lewis acidity had the opposite effect, inducing side reactions with the consequent formation of carbonaceous species and humins.
Sulfonic silica-based materials demonstrated to convert cellulose into sugars, 5-HMF and LA [72] maintaining water as a solvent. In particular, mesoporous sulfonic materials were able to catalyze the conversion of rice straw-LCB to monosaccharide by hydrolysis at 180 °C within 1-h reaction [79]. Sulfonated mesoporous MCM-41 [90], prepared by H2SO4 impregnation, induced an almost complete fructose conversion and a 77% 5-HMF selectivity at 190 °C. When the high surface area catalyst SO3H-SBA was used at 150–180 °C in water (entries 18–19) [88], it was possible to isolate LA (18–53%) as a final product. In the same study, Lai et al. [88] improved the efficiency of the catalyst by the synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4-SBA-SO3H, that could be easily separated from the reaction mixture, avoiding the energy-consuming process needed to isolate the solid phase. Moreover, this catalyst effectively hydrolyzed β-1,4-glucan, producing a glucose yield of up to 96% from cellobiose, while a 50% yield of glucose could be obtained from the amorphous cellulose. Acid silica-based materials gained particular attention due to their high surface area and large pores, which allowed a more efficient contact between the reagents and the catalytic sites of the materials, together with a good thermal stability. These materials showed a versatile use in the achievement of different valuable chemicals, but their main drawback, in a view of industrial application, is the leaching of the sulfonic groups. For this reason, it is necessary to improve their chemical stability for several cycles: for instance, the use of microwaves as source of energy, instead of thermal one, can provide an enhanced stability of the sulfonic groups. This was confirmed in recent studies on the glycerol etherification [93,94], where, after several cycles, no leaching of the sulfonic group was found, maintaining unchanged both the acidity and the activity of the solid catalyst. Analogously, sulfonic titania was prepared and tested in the conversion of fructose into 5-HMF (entries 16 and 17). When the reaction was carried out in an organic solvent as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (entry 16), the yield of 5-HMF reached 79%, that decreased when water was used as solvent, due to the further decomposition of 5-HMF (entry 17). Testa et al. [92] found that TiO2-SO3H catalyzed a complete conversion (99%) of 1.1 M fructose to 5-HMF at 165 °C, showing a selectivity and a yield of 50% per each parameter. An important improvement of the 5-HMF selectivity (71%) was achieved when the reaction was carried out by using a lower fructose concentration (0.1 M) and a lower temperature (140 °C).
From catalytic conversion of the hemicellulose portion of LCB (see Scheme 3), it is possible to produce Furfural (FFR) that represents another important C5-based molecule for the production of bio-chemicals (see Scheme 4C). It was found that over 80 chemicals directly or indirectly derive from the conversion of FFR, making it a strategic building block. Through the catalytic reactions that involve the aromatic ring or the aldehyde group, it is possible to synthesize useful products such as furfuryl alcohol (FAL), tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol (THFAL), 2-methylfuran (2-MF), and 2-methyl tetrahydrofuran (2-MTHF). FFR can be selectively transformed in polyols [95], which have a wide range of commercial and industrial applications [67,96]. The chemical approach to produce polyols implies the break of C-O bond of the aromatic ring to obtain open chain compounds as alcohols or diols (see Scheme 4C). The sequence takes place in several steps through the formation of FAL and LA, thus different types of mechanisms, such as acid-catalyzed reactions, hydrogenations and breaking of C-O enlaces occur. Therefore, the research is now oriented towards new green strategies with multifunctional catalysts acting by one-pot reaction.
FFR is produced in bio-refineries starting from renewable materials rich in hemicellulose such as wood waste or sugar cane bagasse. The acid catalyzed process generally occurs by homogenous reagents such as acetic acid [66]. Due to the undesired side reactions, such as the decomposition of FFR and the condensation or resinification of by-products (which leads to the formation of solid humin), the reaction was carried out at <200 °C with poor yields (<50%) [66]. Efforts have to be made for the implementation of efficient heterogeneous acid catalysts operating in ecofriendly reaction conditions, in terms of solvent choice and temperature. The use of water as a solvent is not so common in the literature, due to the low solubility of both hemicellulose and FFR, but also due to the increase in side reactions that cause the deposition of bulky species on the surface of catalyst, leading to its poisoning. For this reason, most of the studies report the use of a biphasic system to carry out the conversion of hemicellulose into FFR and its derivatives, in which the organic solvent is able to isolate the chemicals, shifting the reaction towards the increase in the final products. On the contrary, water alone is often used as a reaction medium when homogenous acid catalysts (H2SO4, HCl, HCOOH) are employed [66]. The type of the chosen organic solvent is a fundamental parameter not only for its role on the solubility of the platform molecules but also because, in some cases, it participates in the reaction as H-donor. Table 4 reports some examples of acid catalysts (in pristine or metal-doped form) for the conversion of LCB to FFR or its derivatives (FAL, GVL).

Table 4.
Comparative studies on the conversion of hemicellulose-based materials to FFR and its derivatives under different reaction conditions.
As already mentioned, Amberlyst® is a very high acid solid catalyst with thermal and chemical stability. Amberlyst®-70 and Al-Amberlyst®-15 (entries 1 and 2) were tested in the conversion of xylose achieving 60% and 46% of FFR, respectively [97,98]. The Al-doping of the solid catalyst allowed to carry out the reaction at lower temperature (100 °C) and time reaction (8 h). Nevertheless, in both cases a relevant drawback was represented by the use of toluene and dimethylformamide that are not sustainable solvents.
Zeolites and sulfonic silica-based materials, whose activity is ascribable to both their high acidity and favorable structure, have been widely investigated for the production of FFR and its derivatives. Zeolites showed a high selectivity, thanks to their intrinsic structure and well-defined pore size (5–13 Å) that allowed xylose (used as biomass precursor) to go inside the pores and react with the catalytic functionalities with the formation of FFR (or FAL), avoiding any side reaction of condensation and resinification. Analogously, it was found [111] that the use of catalysts with small pores did not allow the sugar to enter in the pores, causing its accumulation on the surface of the solid material with the consequent formation of carbonaceous by-products and the poisoning of the catalyst surface. Regarding the solvent influence, in the literature, various authors [107,112] claimed that the presence of water had a negative effect on dehydration of xylose during the formation of FFR catalyzed by zeolites. This was evidenced also by O’Neil et al. [101] that carried out the conversion of xylose by using H-ZMS-5 in water at high temperature (200 °C), obtaining FFR with only 46% of yield (entry 5). In other two studies (entry 3 and 4), β-zeolites, in the bare form or Al-doped, were tested in the conversion of arabinose and corncob [99,100], showing significant differences. A higher FFR yield (73%) was achieved when H-β-Zeolite was used in milder reaction conditions (entry 3), namely lower temperature (160 °C) and less time (40 min). The corresponding Al-doped zeolite induced the formation of a lower FFR yield (20%) after 1.5 h at 185 °C. In this case, FAL (37%) was the main product due to the hydrogenation reaction of FFR to FAL, promoted by the metal-doped zeolite.
Due to the high versatility, given the possibility of their functionalization, sulfonic silica-based materials were extensively used for the reactions under examination. Dias et al. [104] studied the conversion of xylose into FFR, catalyzed by SO3H-MCM41 in different solvents (entries 8 and 9). When water was used as solvent, only 47% of FFR was achieved, whereas the addition of toluene as co-solvent allowed the FFR yield to rise up to 96%. To avoid the leaching of sulfonic groups, different studies were aimed to improve the hydrothermal stability of the catalyst by the grafting of organic linkers. Methylpropyl sulfonic MCM41 was prepared and tested in xylose conversion, at 155 °C during only 2 h reaction, achieving a very high yield (93%) of FFR (entry 10). Agirrezabal-Telleria et al. tested the propylsulfonic SBA-15 [113] and the corresponding arenesulfonic SBA-15 [97] (entry 11) in a biphasic system toluene/water 1:1. In both studies, FFR yields were almost similar (82%), but the arenesulfonic derivative reached a higher stability during 4-cycle reaction. The presence of a higher amount of water caused the deactivation of these types of catalysts due to the loss of sulfonic groups, but, as previously described [93,94], changing the reaction conditions, it is possible to improve the stability of SO3H silica-based materials.
Since FAL or GVL can be produced by both the acid-catalyzed and hydrogenation reactions (see Scheme 3), the catalytic materials should be prepared in order to be active in a multi-step sequence. The introduction of metal nanoparticles in the solid acid catalysts and the use of an alcohol as propanol/isopropanol/butanol as (co)-solvent for the conversion of xylose are suitable strategies to fulfil these requirements. For instance, when the acidic β-Zeolite was used in the presence of isopropanol, it catalyzed the dehydration of xylose to produce FFR and also the hydrogenation into FAL (75%) thanks to the isopropanol action as H-donor (entry 6). The doping of β-Zeolite with Zr and Al promoted the conversion of FFR into GVL, through the formation of FAL, LA, 4-hydroxypentanoate in one-pot catalytic conversion (entry 7) [103]. Additionally, in this case, isopropanol was essential as a solvent and H-donor, participating to the reaction mechanism. Moreover, Song et al. [103] found that a small amount of water (5%) improved the formation of GVL up to 95%, but a higher presence (10–15%) decreased the selectivity towards GVL, with the formation of other intermediates. When sulfonic SBA-15 materials were doped with Cu [106] and Pt [107], it was possible to achieve FAL (63 and 83%, respectively) by using xylose as starting molecule. Platinum-doped material was more efficient since a lower amount of organic solvent was used in similar reaction conditions (entries 12 and 13).
Finally, zirconia-based materials were used in the conversion of xylose and FFR to FAL and GVL. In all cases, isopropanol was used as H-donor. Due to its intrinsic characteristic, Pt-doped sulphated zirconia (entry 14) [108] was able to convert xylose to FAL (27%) in only 1h-reaction. When zirconia was associated to SBA or ZMS-5 (entries 15 and 16), 47 and 80% of GVL was obtained, respectively [109,110].
4. Photoactive Humic-Like Substances for Water Remediation
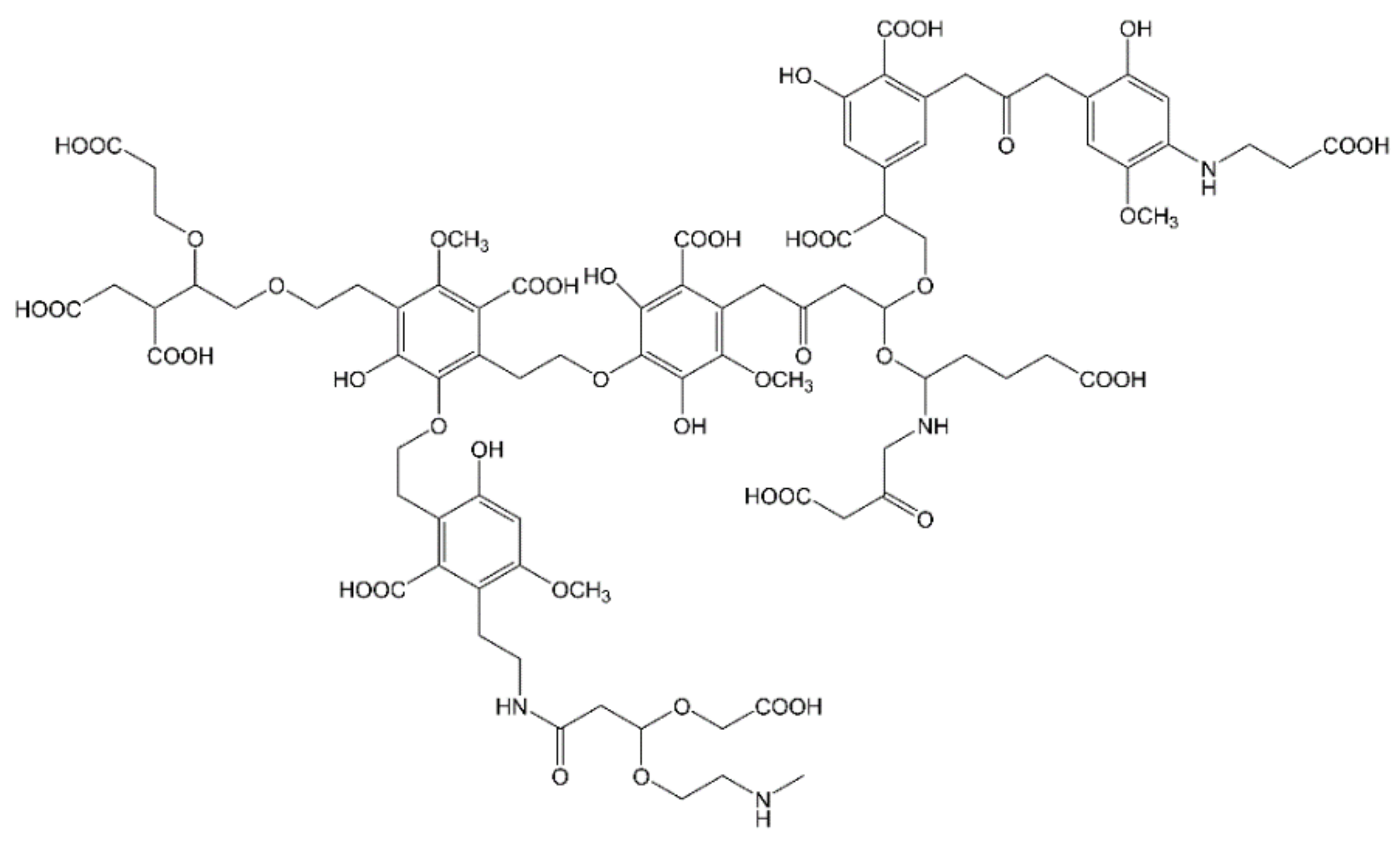
The fate of dead plants in nature is their degradation by microorganisms, whose metabolism induces the transformation of the constituted lignocellulose into the so-called humic substances (HS) [114]. Such substances regulate the global carbon and nitrogen cycles, act as nutrients/fertilizers and take part to soil and water depollution from xenobiotics by multiple mechanisms, i.e., redox reactions, sorption, complexation or photosensitization (if light-activated) [114]. HS persistency in the natural environment derives from the preservation of lignin-like structure, originated by LCB, that confer a high recalcitrance to enzymatic attack [115,116]. In general, HS chemical composition is characterized by aliphatic chains substituted by aromatic rings and multiple functionalities (carboxylic, phenolic, alcoholic, quinone, amino and amido groups), that represent the memory of the initial bio-organic matter (see Figure 2) [117,118]. Three are the fractions of humic substances, distinguished on the basis of water solubility and oxygen content: fulvic acids (FAs), soluble in water under all pH conditions, humic acids (HAs), insoluble in acidic water (pH < 2) but soluble at higher pH values and humin, insoluble in water at any pH value [114].
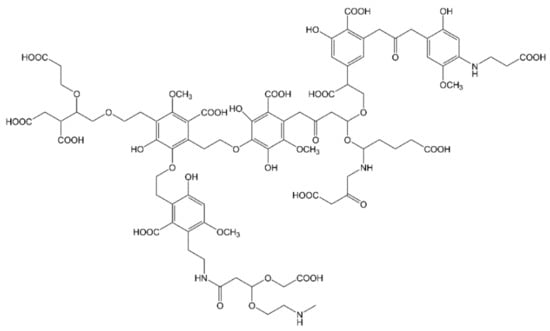
Figure 2.
HS molecular fragment, inspired by Deganello et al. [121].
A convenient way to obtain humic-like substances is using biowaste sources after a proper transformation, promoted by microorganisms; for instance, this happens in waste treatment plants, where biowaste undergoes aerobic/anaerobic digestions, as anticipated in Section 1. In general, the process starts by selecting the biowaste fractions, i.e., humid, green (gardening and agricultural trimming residues), sewage sludge, which are eventually mixed and then digested [42,119]. To isolate HS, the obtained biomass is subjected to basic and acid treatments, followed by separation and purification steps [118]. The final product maintains analogous physical-chemical features with respect to natural HS [120], although it brings along the footprints of original heterogeneous waste [121,122,123]. For these similarities, waste-derived HS find a commercial employment for soil amendment and fertilization (compost) [119].
In this review, different kinds of humic substances (mainly from natural sources or LCB-derived green waste) will be considered in terms of their photosensitizing capability for water depollution purposes, inspired by HS behavior in nature [114]. Photosensitization can be conceptually associated to photocatalysis. Photocatalysis is defined as a “change in the rate of a chemical reaction or its initiation under the action of ultraviolet, visible, or infrared radiation in the presence of a substance—the photocatalyst—that absorbs light and is involved in the chemical transformation of the reaction partners” [124]. On the other hand, a photosensitizer is defined as an agent that absorbs light and subsequently initiates a photochemical or photophysical alteration in the system [124]. Sensitizers absorb light and transfer their electronic excitation energy at a lower level to a substrate [125].
Humic substances show strong absorbance in the UV–visible region, due to the presence of aromatic chromophores and/or other organic compounds; the absorbance around 260-280 nm is commonly used to determine the relative abundance of aromatic C-C content because of the π–π* transitions in substituted benzenes or polyphenols [126,127]. When the HS act as photosensitizers and the target substrates are pollutants, the system works according to the following reaction mechanisms (Equations (1)–(7)).
HS + hν → 3HS*
HS + hν → HS+● + e−aq
3HS* + H-Substrate → HS● + Substrate●
HSH● + O2 → HS + HOO●
e−aq + O2 → O2●−
O2●− + HOO● → H2O2
e−aq + H2O2 → OH● + OH−
The proposed mechanism (Equations (1) and (2)) is the production of excited triplet states (3HS*) and solvated electrons (e−aq) [128]. Excited triplet state can react with organic substrate by two main mechanisms: hydrogen-transfer and energy-transfer [129,130]. The first hypothesis assumes that 3HS* extracts a hydrogen atom from donor organic substrate (Equation (3)). In the presence of oxygen and of the photogenerated electrons, the production of various Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), such as hydroxyl radicals (●OH), anion superoxide (O2●−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroperoxyl radical (HOO●) and singlet oxygen (1O2) can take place (Equations (4)–(7)) [130,131]. ROS may initiate radical chain mechanisms that promote the substrate degradation. Therefore, HS photosensitizers can be conveniently applied in tertiary water treatments [132], and also for the challenging removal of CECs [133,134], within the so-called Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) [135,136,137].
Several studies have been carried out using different types of HS in homogeneous conditions or in heterogeneous systems after a proper immobilization on solid supports [138]. In Table 5, some examples of HS-based systems degrading aqueous pollutants are listed, together with the specifications of operating conditions. For the sake of brevity, photo-activated reactions mediated by other substances, as peroxymonosulfate, iodide, H2O2, Fe(III) or Mn(III), are not taken into account, although they can represent useful pathways to pursue water decontamination in presence of HS, as widely demonstrated by the literature [139,140,141,142,143].

Table 5.
Different HS-based systems for the degradation of water pollutants. The experimental conditions and main results are indicated.
As it possible to observe in Table 5, HS photosensitizer efficiency is variable depending on the substrates and the conditions and does not reach the level of other well-known heterogeneous photocatalysts (i.e., TiO2, ZnO [144]). The main reasons are the light screen operated by colored HS molecules and the scavenging or quenching of ROS, causing a competition between HS themselves and the substrate [145]. Another critical point is related to the selection of specific HS fractions to optimize the photosensitizing performance. For instance, Brahmia and Boulkamh [146] irradiated different humic substances (humic and fulvic acids) extracted from four soils of different geographic origin (central Europe) and from three peats to degrade 1-naphthol [146]. They individuated three main factors influencing the photoinductive capacity: the raw material (soil or peat), its geographical locality and the fraction (humic or fulvic) [146]. Indeed, it has been already assessed that coal-related resources are made up of a higher amount of HS than regular soils and rivers, because of the dense plant-derived carbon materials from which coal is originated [116]. The ratio of humic to fulvic acids is also affected by soil type. In grasslands, humic acids are found at higher levels than fulvic acids; this may be due to the use of the land for stock farming, which involves different mechanisms by which plant materials decay [116]. In this regard, different chemical moieties identify humic and fulvic fractions: more carboxyl/hydroxyl groups and chromophores were detected in fulvic acid than those of humic acid, whereas humic acid molecule has a higher degree of humification (reflected in high ring condensation [147]) and a larger average molecular weight [148]. Moreover, variations of molecular compositions and aliphatic/aromatic ratios were characteristic of specific HS, extracted in different environments and by different methods [116]. All these structural and chemical factors influence the photoactivity: according to Brahmia and Boulkamh [146], a major role was attributed to O-C content, whose increment significantly reduced the half-life time of substrate disappearance for FA and, more pronouncedly, for HA, denoting the high impact of the carbon structure on the photoinductive capacity [146]. On the contrary, the aromatic component seemed to adversely influence the photoactivity: the explanation proposed was correlated to the antioxidant properties of a certain phenolic fraction of HS [146], also in accordance with other studies [149,150]. Such moieties within HS inhibited the substrate degradation by favoring the back-reduction of partially oxidized species [149]. Furthermore, as reported by Calza et al., the low-molecular weight fractions of HS should show a higher ability to form excited triplet states, whereas supra-molecular aggregates of smaller compounds are characterized by charge-transfer interactions that favor internal conversion at the expense of photophysical and photochemical reactivity [149]. Similarly, some fractions more than others resulted to lead to a shielding on light, due to particular functional groups as quinones [151].
Despite some drawbacks and variability of the mechanism, the exploitation of HS should be promoted due to their eco-sustainability and easy recovery from natural sources and, more conveniently, from biowaste. HS possess additional characteristics, as adsorptive and surfactant ones (given by multiple functionalities and amphiphilic nature, respectively), that have been revealed as complementary properties, useful for environmental remediation [14,138]. In particular, the heterogeneous form of HS (i.e., immobilized onto oxides) is highly desirable, even though the available literature is more limited. The main advantages of heterogeneous (photo-) catalysis are broadly recognized: easy and cost-effective separation and reutilization of the solid material, that make the process more sustainable, although at the expenses of higher activity and selectivity [152].
A novel frontier for humic substances is their exploitation in energy devices, as already reported by Vekariya et al., that explored humic acids as photosensitizers to include in dye-sensitized solar cells [153].
5. LCB as a Support for a Sustainable Catalysis
In the previous paragraphs, LCB has been described both as a substrate to be transformed (see Section 3) and as an active photocatalyst (see Section 4). In this section, LCB is presented as unconventional green support of the catalytic process. It is worth underlining that the following applications will be mainly focused on the cellulosic portion, since the modification of lignin has two main drawbacks: the lignin structure heterogeneity and the high reactivity of its functional groups under most of the extraction conditions, which make difficult to maintain the lignin intact during isolation procedures [174].
Most of the studies accounting for LCB as a coadjutant in catalysis concern the more or less complex functionalization with metal or metal-based compounds [175,176], for a wide range of reactions, some examples of which are detailed here. Morshed et al. developed titania-loaded cellulose nanowhiskers (CN) as functional hybrid nanomaterials for photocatalytic degradation of aqueous methylene blue dye [177]. The authors claimed the formation of metal-organic functional core-shell catalyst where cellulose nanowhiskers were effective green carriers, which prevented the leaching of active TiO2 and resulted in a good durability and reusability [177]. CN are non-toxic, easily available and low-cost materials, since they can derive from natural and renewable origins; they are also highly crystalline with a great surface area and good mechanical properties [177].
Zero-Valent Metal Nanoparticles (ZV-MNPs) based on Cu, Co, Ag, and Ni were supported on empty fruit bunch biomass residue (EFB) [178]. Among ZV-MNPs/EFB, Cu/EFB catalyst showed superior catalytic performance in the degradation of target model organic pollutants: dyes (methyl orange, congo red, methylene blue, acridine orange) and 4-nitrophenol, using NaBH4 as a source of hydrogen and electrons [178]. Analogously, the reduction of nitrophenols has been the objective of several works employing cellulose-supported catalysts: Ag- and Au-MNP on cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) (supported by nucleation via solid-state synthesis in the presence of ascorbic acid) [179]; Au-, Ag-, Ni-MNP on electrospun nanofibers of cellulose [180]; Ag-MNP anchored onto the CNCs coated with mussel-inspired polydopamine and further bonded to β-ciclodextrin [181]; Ag-doped cellulose microgels (obtained from paper cellulose treated with NaOH-urea solution) [182]. A strategy to reduce nitrobenzene to N-phenylhydroxylamine was proposed by Li et al. [183], who reported the performances of perfluoroalkyl-modified cellulose supported ultra-small Pd-MNPs, synthesized by a solid-state method. The obtained Pd-catalyst exhibited excellent reductive activity and selectivity under mild conditions, due to the controlled regulation of surface hydrophilicity (given by cellulose) and hydrophobicity (given by F-containing groups) [183].
Cellulose-based catalysts were employed for oxidation reactions, as well. Poly(ionic liquid)/polyoxometalate hybrids resulted to be efficient catalysts for oxidative desulfurization of fuels [184], achieving a complete conversion (for different cycles) of dibenzothiophene in model diesel, under mild condition in the presence of O2 contained in air [184]. Other oxidation reactions catalyzed by metal-cellulose hybrids have been recently summarized by a comprehensive review [185]: glucose, dyes, sulfides, thiols, aldehydes, ethylbenzene and different alcohols have been subjected to oxidation.
Kempasiddaiah et al. immobilized palladium nanoparticles on cellulose fibers, isolated from waste banana pseudostem, as a dip catalyst for Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling reaction between arylhalides and phenylboronic acid [186]. The isolated cellulose fibers from waste banana pseudostem showed some specific properties like water absorption ability, high Young’s modulus and high tensile strength [186]. Additionally, in this case, the positive effect of cellulose support was assessed, due to the bonding between palladium nanoparticles and cellulose surface hydroxyl groups, that acted as stabilizing agents and prevented the aggregation of metal nanoparticles [186]. The same cross-coupling reaction effectively proceeded also in the presence of ferrocene tethered N-heterocyclic carbene-Pd complex anchored on cellulose, whose activity was attributed to the straightforward control of steric properties, given by the arrangement of ferrocenyl group [187]. Similarly, the Heck cross-coupling reaction was conducted by waste corn-cob cellulose-supported poly(amidoxime) Pd(II) complex, which showed a high stability and a remarkable catalytic activity (up to 97% yield). The material was repeatedly used up to seven times without any significant decrease in performance [188]. In most of the cases described, the excellent performances of such hybrid catalysts were attributed to the favorable characteristics of the surface support (area, porosity, exposed functionalities) that led to a stable and homogenous dispersion of the metal-based active phase.
Further modifications were conducted to establish catalytically active functionalities, directly on LCB, avoiding the use of metals and metal oxides. One example is represented by sugarcane bagasse, used to prepare lignocellulose-based AOPs catalyst, introducing acidic functionalities from citric acid [189]. The catalyst, assisted by H2O2, was successfully employed for oxidative degradation of the organics in waste sulphuric acid, to recover high-quality products [189]. A similar approach was adopted by Shaabani et al. [190]: in their work, a cellulose supported sulfuric acid was prepared by the dropwise addition of chlorosulfonic acid to cellulose in CHCl3 at 0 °C. The prepared material was used to catalyze the selective oxidation of sulfides to sulfoxides and thiols to disulfides using hydrogen peroxide as an oxidant [190]. Surface amination was also proposed in different studies [191,192]; for instance, ethylenediamine functionalized-cellulose was applied as a catalyst to synthesize nitroalkenes and 1,3-dinitroalkanes from aromatic aldehydes and nitromethane [193].
As already underlined, the sustainability of a catalytic process can be evaluated by the possibility to easily recover and reuse the catalyst. Although all the above-described materials are intrinsically employed in heterogeneous conditions, further modifications can favor the catalyst recycling, i.e., imparting magnetic properties. For instance, a magnetic system for Michael-type addition was developed [194]. This type of catalyzed reaction is a conjugate addiction, which generally occurs in presence of strong acids—bases as well as stoichiometric amounts of Lewis acids [194]. However, in recent decades, under the impulse of green chemistry, ionic liquids have been employed as reaction media, due to their peculiar chemical and physical properties. According to Beiky et al. [194], a core-shell structure of γ-Fe2O3 supported onto cellulose was modified with epichlorohydrin, hexamethylenetetramine and polytungstophosphate, to produce an immobilized ionic liquid on a magnetic cellulose substrate. The results of Michael-type addition of aniline, phenol, and thiophenol to vinyl pyridine showed a very high yield (up to 95%) within 2 h reaction time at moderate temperature, with a good recyclability level [194]. El-Nahas et al. [195] fabricated nanocomposites from functionalized cellulose (from rice straw) and magnetite, via adsorption. The functionalization was carried out using different organic groups (acetate or succinate) and inorganic groups (phosphorylate or sulfonate), exploiting the availability of cellulose hydroxyl moieties [195]. The catalytic activity of the functionalized nanocellulose and cellulose-magnetite nanocomposites was evaluated towards the esterification of oleic acid with methanol for the production of methyl oleate (biodiesel) [195]. The sulfonated cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite showed the highest catalytic activity toward the esterification reaction (96%) due to the high dispersion of the Lewis acid sites resulted from the impregnation of magnetite in addition to the already presented Brønsted acid sites in the surface of the nanocellulose [195]. Another multicomponent catalyst, a copper (I) iodide supported on NH2-cellulose-based nanomagnetite, was used as a biodegradable catalyst for the synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles, demonstrating improved yields and regioselectivity [196]. The magnetic catalyst was recovered and reused at least four successive runs under the optimal reaction conditions, without appreciable loss of its activity [196].
More and more complex efforts to exploit LCB within high technological fields have been carried out, concretized in form of lignocellulosic micro/nano-reactor [197,198] and cellulose nanocrystal nanomotors [199]. Micro/nano-reactor technology implies the design of size-controlled microfluidic reactors with large surface-area-to-volume ratio to induce diffusion mixing of the reagents and fast dissipation of heat. The benefits are identifiable in terms of reaction selectivity, yield, sustainability, scalability, reproducibility and low-cost production [197]. For instance, Santos de Sa et al. fabricated lignocellulose-based microreactors in form of hydrophilic microsized channels of bamboo, that were doped with copper to run Cu-catalyzed 1,3-dipolar cycloadditions for the continuous-flow synthesis of model 1,2,3-triazole derivatives in aqueous medium [197]. Other nanoreactors were developed from polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimer-grafted cellulose nanocrystals (CNC−PAMAM) as supports for gold nanoparticles. Actually, PAMAM dendrimers were grafted onto oxidized CNCs and were able to act as reducing agents in the formation of the gold nanoparticles from the precursor gold chloride [198]. The immobilized gold nanoparticles displayed superior catalytic properties toward the reduction of 4-nitrophenol to 4-aminophenol, due to the improved dispersity and accessibility of gold nanoparticles within the PAMAM dendrimer domain [198]. On the other hand, nanomotors are molecular machines that use chemical energy to generate physical movement of molecules, triggered by different mechanisms. Most of the nanomotors reported are based on organic/inorganic or bimetallic materials, which have environmental issues related to toxicity, sustainability and lifetime. In this context, cellulose nanocrystals are valid candidates for such application. Beside their sustainability, they possess interesting physico-chemical properties such as high anisotropic elastic modulus, high surface-area, hydroxyl functionality, tunable optical birefringence properties and biocompatibility [199]. Dhar et al. produced cellulose nanocrystals derived from bamboo, decorated with catalytically active, magneto-responsive nanomaterials (Fe2O3/Pd nanoparticles) to remove methylene blue [199]. The so-prepared nanomotors showed an improved motion, together with capability to in situ degrade pollutants and generate local heat through hyperthermia (in presence of alternating magnetic fields), enhancing the rate of degradation process in real time [199]. The hydrophilic nature of cellulose and its high hydroxyl functionality gave enhanced surface wettability characteristics, which fulfilled the requirement for nanomotor stabilization and a uniform dispersion of iron oxides and palladium. Therefore, the utilization of cellulose nanocrystals as substrates for fabrication of nanomotors with simultaneous self-propulsion and dye degradation capability provided an added value to traditional cellulose-based materials aimed to water purification [199].
6. Conclusions
Since the procrastination of effective measures to mitigate the environmental damages caused by human activities is no longer possible, we thought to this review as a vademecum to explore the multiple uses of lignocellulosic biomass for a sustainable catalysis. We also included food for thought for not deepened topics, since LCB is involved in a very complex scenario, due to its ubiquity and potentialities in several research fields. In particular, we strongly highlighted the importance of the valorization of waste LCB, which often represents a biohazard if not properly disposed. LCB and waste-LCB are inexpensive, easy-available and green raw materials. Despite of the variability among different lignocellulose biomasses, in general, they present convenient chemical-physical features that make them multipurpose compounds. LCB can be the “object” of the green catalysis, when their constituting macromolecules (cellulose and hemicellulose) are catalytically transformed into platform molecules and strategic building blocks, which can substitute some petroleum derivatives for the production of biochemicals and biofuels. Herein, we focused our attention on sustainable conditions, as the use of heterogeneous catalysts capable to catalyze one or multi-step sequences, as well as the choice of solvent that, in most of the cases, plays a significant role for the reaction outcome. Then, we analyzed the role of humic-like substances, derived from LCB and waste-LCB, as photo-catalytically active compounds, able to remove water contaminants under light irradiation, through the production of excited species. We reported several examples of degradation studies, carried out in presence of various humic-like compounds, whose activity was intimately correlated by their origin and their chemical structure. Lastly, LCB was considered as a support for metal catalysts and in other high-technological applications (nanomotors and micro/nano-reactors).
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fridays for Future Webpage. Available online: https://fridaysforfuture.org/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Spratt, D.; Dunlop, I. Existential climate-related security risk: A scenario approach. Discuss. Pap. 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Ramanathan, V. Well below 2 °C: Mitigation strategies for avoiding dangerous to catastrophic climate changes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10315–10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanemann, N.; Willner, S.N.; Levermann, A. Paris climate agreement passes the cost-benefit test. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGlade, C.; Ekins, P. The geographical distribution of fossil fuels unused when limiting global warming to 2 °C. Nature 2015, 517, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, P.G.; Cullen, J.M. Mapping global flows of chemicals: From fossil fuel feedstocks to chemical products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, B.C.; De Gouw, J.A.; Gilman, J.B.; Jathar, S.H.; Akherati, A.; Cappa, C.D.; Jimenez, J.L.; Lee-Taylor, J.; Hayes, P.L.; McKeen, S.A.; et al. Volatile chemical products emerging as largest petrochemical source of urban organic emissions. Science 2018, 359, 760–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/ghgemissions/global-greenhouse-gas-emissions-data (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. CO2 and Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/co2-and-other-greenhouse-gas-emissions (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Govorushko, S. Environmental problems of extraction, transportation, and use of fossil fuels. In Fossil Fuels; Kumar, R., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–84. ISBN 978-1-62808-412-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1043–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, S.J.; Clair-Caliot, G.; Taing, L.; Bamwenda, J.T.; Kanyesigye, C.; Rwendeire, N.E.; Kemerink-Seyoum, J.S.; Kansiime, F.; Batega, D.W.; Ferrero, G. Water supply and sanitation services in small towns in rural–urban transition zones: The case of Bushenyi-Ishaka Municipality, Uganda. NPJ Clean Water 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF: Drinking Water Report. Available online: https://data.unicef.org/topic/water-and-sanitation/drinking-water/ (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Tummino, M.L.; Testa, M.L.; Malandrino, M.; Gamberini, R.; Prevot, A.B.; Magnacca, G.; Laurenti, E. Green waste-derived substances immobilized on SBA-15 silica: Surface properties, adsorbing and photosensitizing activities towards organic and inorganic substrates. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englande, A.J.; Krenkel, P.; Shamas, J. Wastewater treatment &water reclamation. In Reference Module in Earth Systems and Environmental Sciences; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–32. ISBN 9780124095489. [Google Scholar]
- Contaminants of Emerging Concern Including Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/wqc/contaminants-emerging-concern-including-pharmaceuticals-and-personal-care-products (accessed on 5 January 2021).
- Tummino, M.L.; Nisticò, R.; Riedo, C.; Fabbri, D.; Cerruti, M.; Magnacca, G. Waste cleaning waste: Combining alginate with biowaste-derived substances in hydrogels and films for water cleanup. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-On, Y.M.; Phillips, R.; Milo, R. The biomass distribution on Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 6506–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoghlami, A.; Paës, G. Lignocellulosic biomass: Understanding recalcitrance and predicting hydrolysis. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Ching, Y.; Chuah, C. Applications of lignocellulosic fibers and lignin in bioplastics: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillman, D.A.; Duong, D.N.B.; Harding, N.S. Blending coal with biomass. In Solid Fuel Blending; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 125–200. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkola, J.; Sklavounos, E.; King, A.W.T.; Virtanen, P. The biorefinery and green chemistry. In Ionic Liquids in the Biorefinery Concept: Challenges and Perspectives; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 1–37. ISBN 9781782622598. [Google Scholar]
- Kamm, B.; Kamm, M. Principles of biorefineries. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 64, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubando, A.T.; Felix, C.B.; Chen, W.H. Biorefineries in circular bioeconomy: A comprehensive review. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isikgor, F.H.; Becer, C.R. Lignocellulosic biomass: A sustainable platform for the production of bio-based chemicals and polymers. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 4497–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Nagpal, G.; Agrawal, S. Rachna water purification by using adsorbents: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 11, 187–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renu; Agarwal, M.; Singh, K. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: A review. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2017, 7, 387–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adsul, M.G.; Singhvi, M.S.; Gaikaiwari, S.A.; Gokhale, D.V. Development of biocatalysts for production of commodity chemicals from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 4304–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govil, T.; Wang, J.; Samanta, D.; David, A.; Tripathi, A.; Rauniyar, S.; Salem, D.R.; Sani, R.K. Lignocellulosic feedstock: A review of a sustainable platform for cleaner production of nature’s plastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 270, 122521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xing, B.; Ding, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, S. A critical review of the production and advanced utilization of biochar via selective pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 312, 123614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, V.K.; Kate, K.H.; Satyavolu, J.; Singh, P.; Tadimeti, J.G.D. Additive manufacturing of natural fiber reinforced polymer composites: Processing and prospects. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 174, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cai, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Yu, H. Laboratory Investigation of lignocellulosic biomass as performance improver for bituminous materials. Polymers 2019, 11, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamil, M.; Ramadan, K.; Ghenai, C.; Olabi, A.G.; Nazzal, I.T. Emissions from combustion of second-generation biodiesel produced from seeds of date palm fruit (Phoenix dactylifera L.). Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, J.; Tamayo, J.A.; Cardona, C.A. Integrating first, second, and third generation biorefineries: Incorporating microalgae into the sugarcane biorefinery. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 118, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummino, M.L.; Tolardo, V.; Malandrino, M.; Sadraei, R.; Magnacca, G.; Laurenti, E. A way to close the loop: Physicochemical and adsorbing properties of soybean hulls recovered after soybean peroxidase extraction. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saveyn, H.; Eder, P. End-of-Waste Criteria for Biodegradable Waste Subjected to Biological Treatment (Compost & Digestate): Technical Proposals; European Commission, Joint Research Centre: Sevilla, Spain, 2014; ISBN 9789279350627. [Google Scholar]
- Gaur, V.K.; Sharma, P.; Sirohi, R.; Awasthi, M.K.; Dussap, C.G.; Pandey, A. Assessing the impact of industrial waste on environment and mitigation strategies: A comprehensive review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 123019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hashim, M.A.; Gupta, B. Sen contemporary environmental issues of landfill leachate: Assessment and remedies. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 472–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlas, M.; Dvořáček, J.; Pitschke, T.; Peche, R. Biowaste Treatment and Waste-To-Energy—Environmental Benefits. Energies 2020, 13, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pognani, M.; Barrena, R.; Font, X.; Sánchez, A. A complete mass balance of a complex combined anaerobic/aerobic municipal source-separated waste treatment plant. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.C.; Sinha, R.K.; Wang, W. Emission of greenhouse gases from home aerobic composting, anaerobic digestion and vermicomposting of household wastes in Brisbane (Australia). Waste Manag. Res. 2011, 29, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabasso, S.; Berto, S.; Rosato, R.; Marinos, J.A.T.; Ginepro, M.; Zelano, V.; Daniele, P.G.; Montoneri, E. Chemical modeling of acid-base properties of soluble biopolymers derived from municipal waste treatment materials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 3405–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouallagui, H.; Touhami, Y.; Ben Cheikh, R.; Hamdi, M. Bioreactor performance in anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable wastes. Process Biochem. 2005, 40, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmani, Z.; Sharma, M.; Karpichev, Y.; Pandey, A.; Chandra Kuhad, R.; Bhat, R.; Punia, R.; Aghbashlo, M.; Tabatabaei, M.; Gupta, V.K. Advancement in valorization technologies to improve utilization of bio-based waste in bioeconomy context. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 109965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuel, P.; Rieker, C.; Bursche, J. Comparative life-cycle-assessment of pretreatment processes for the production of biofuels from lignocellulosic residues. Int. Energy Sustain. Conf. IESC 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, S.; Anoopkumar, A.N.; Aneesh, E.M.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Pandey, A. Sustainability and life cycle assessments of lignocellulosic and algal pretreatments. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Singh, A.; Korres, N.E.; Rathore, D.; Sevda, S.; Pant, D. Sustainable utilization of crop residues for energy generation: A life cycle assessment (LCA) perspective. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 303, 122964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, N.; Kodama, Y.; Numata, K. Revealing the architecture of the cell wall in living plant cells by bioimaging and enzymatic degradation. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.; Gräsvik, J.; Hallett, J.P.; Welton, T. Deconstruction of lignocellulosic biomass with ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2013, 15, 550–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, S.S.; Mohammadi, K.; Ji, K.S. Characterization of cellulose synthesis in plant cells. Sci. World J. 2016, 2016, 8641373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongpipi, S.; Ye, D.; Gomez, E.D.; Gomez, E.W. Progress and opportunities in the characterization of cellulose—An important regulator of cell wall growth and mechanics. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuna, E.; Behling, R.; Valange, S.; Chatel, G.; Colmenares, J.C. Sonocatalysis: A potential sustainable pathway for the valorization of lignocellulosic biomass and derivatives. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 41, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, K.M.; Guggenberger, G. Organic matter | Genesis and formation. In Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment; Hillel, D., Ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2005; pp. 93–101. ISBN 978-0-12-348530-4. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Zheng, L. Lignins: Biosynthesis and biological functions in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Panwar, D.; Kaira, G.S. Bioprocesses for enzyme production using agro-industrial wastes: Technical challenges and commercialization potential. In Agro-Industrial Wastes as Feedstock for Enzyme Production: Apply and Exploit the Emerging and Valuable Use Options of Waste Biomass; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 61–93. ISBN 9780128026120. [Google Scholar]
- Guilherme, A.A.; Dantas, P.V.F.; Santos, E.S.; Fernandes, F.A.N.; Macedo, G.R. Evaluation of composition, characterization and enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated sugar cane bagasse. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybarczyk, M.K.; Peng, H.J.; Tang, C.; Lieder, M.; Zhang, Q.; Titirici, M.M. Porous carbon derived from rice husks as sustainable bioresources: Insights into the role of micro-/mesoporous hierarchy in hosting active species for lithium-sulphur batteries. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 5169–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.D.; Mandavgane, S.A.; Kulkarni, B.D. Fruit peel waste: Characterization and its potential uses. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queirós, C.S.G.P.; Cardoso, S.; Lourenço, A.; Ferreira, J.; Miranda, I.; Lourenço, M.J.V.; Pereira, H. Characterization of walnut, almond, and pine nut shells regarding chemical composition and extract composition. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2020, 10, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusanen, A.; Lappalainen, K.; Kärkkäinen, J.; Tuuttila, T.; Mikola, M.; Lassi, U. Selective hemicellulose hydrolysis of Scots pine sawdust. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2019, 9, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushammala, H.; Mao, J. A review on the partial and complete dissolution and fractionation of wood and lignocelluloses using imidazolium ionic liquids. Polymers 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Hu, H.Q.; Xie, F.J.; Wei, X.Y.; Fan, X. Structural characterization of lignin and its degradation products with spectroscopic methods. J. Spectrosc. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.V.; Hamid, S.B.A.; Zain, S.K. Conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to nanocellulose: Structure and chemical process. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gürbüz, E.; Bond, J.Q.; Dumesic, J.A.; Román-Leshkov, Y. Role of Acid Catalysis in the Conversion of Lignocellulosic Biomass to Fuels and Chemicals. In The Role of Catalysis for the Sustainable Production of Bio-Fuels and Bio-Chemicals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 261–288. ISBN 9780444563309. [Google Scholar]
- Werpy, T.; Petersen, G. Top value added chemicals from biomass volume I. US Natl. Renew. Energy Lab. 2004, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mika, L.T.; Cséfalvay, E.; Németh, Á. Catalytic conversion of carbohydrates to initial platform chemicals: Chemistry and sustainability. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 505–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Tomishige, K. Production of 1,5-pentanediol from biomass via furfural and tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol. Catal. Today 2012, 195, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, I.T.; Mehdi, H.; Fábos, V.; Boda, L.; Mika, L.T. γ-Valerolactone—A sustainable liquid for energy and carbon-based chemicals. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, W.R.H.; Palkovits, R. Development of heterogeneous catalysts for the conversion of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, M.L.; Corbel-Demailly, L.; La Parola, V.; Venezia, A.M.; Pinel, C. Effect of Au on Pd supported over HMS and Ti doped HMS as catalysts for the hydrogenation of levulinic acid to γ-valerolactone. Catal. Today 2015, 257, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhomme, C.; Schaper, L.A.; Zhang-Preße, M.; Raudaschl-Sieber, G.; Weuster-Botz, D.; Kühn, F.E. Catalytic hydrogenation of levulinic acid in aqueous phase. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 724, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzediegwu, E.; Dumont, M.J. Chemo-catalytic transformation of cellulose and cellulosic-derived waste materials into platform chemicals. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.J.; Corma, A.; Iborra, S. Converting carbohydrates to bulk chemicals and fine chemicals over heterogeneous catalysts. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 520–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Maneerung, T.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, C.H. Valorization of biomass to hydroxymethylfurfural, levulinic acid, and fatty acid methyl ester by heterogeneous catalysts. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 246–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawes, G.J.S.; Scott, E.L.; Le Nôtre, J.; Sanders, J.P.M.; Bitter, J.H. Deoxygenation of biobased molecules by decarboxylation and decarbonylation—A review on the role of heterogeneous, homogeneous and bio-catalysis. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3231–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, R.; Palkovits, R.; Schüth, F. Depolymerization of cellulose using solid catalysts in ionic liquids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 8047–8050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, M.; Liu, J.; Fu, W.; Tang, T.; Wu, D. Improved activity for cellulose conversion to levulinic acid through hierarchization of ETS-10 zeolite. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5800–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imteyaz Alam, M.; De, S.; Dutta, S.; Saha, B. Solid-acid and ionic-liquid catalyzed one-pot transformation of biorenewable substrates into a platform chemical and a promising biofuel. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 6890–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Qian, E.W.; Shibata, T.; Hosomi, M. Catalytic hydrothermal saccharification of rice straw using mesoporous silica-based solid acid catalysts. J. Jpn. Pet. Inst. 2012, 55, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Antonyraj, C.A.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.; Lee, K.Y.; Cho, J.K. Commercially attractive process for production of 5-hydroxymethyl-2-furfural from high fructose corn syrup. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2013, 19, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordomsky, V.V.; Van Der Schaaf, J.; Schouten, J.C.; Nijhuis, T.A. Fructose dehydration to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over solid acid catalysts in a biphasic system. ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 1812–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, R.; Conner, W.C.; Huber, G.W. Production of levulinic acid from cellulose by hydrothermal decomposition combined with aqueous phase dehydration with a solid acid catalyst. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 7559–7574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Wang, L.; Yu, I.K.M.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Hunt, A.J.; Jérôme, F.; Zhang, S.; Ok, Y.S.; Poon, C.S. Valorization of lignocellulosic fibres of paper waste into levulinic acid using solid and aqueous BrØnsted acid. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.M.; Gallo, J.M.R.; Mellmer, M.A.; Wettstein, S.G.; Dumesic, J.A. Direct conversion of cellulose to levulinic acid and gamma-valerolactone using solid acid catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 927–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Z.; Xue, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z. Highly efficient preparation of HMF from cellulose using temperature-responsive heteropolyacid catalysts in cascade reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 196, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Cheng, M.; Li, H.; Shi, T.; Yuan, M.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z. One-pot depolymerization of cellulose into glucose and levulinic acid by heteropolyacid ionic liquid catalysis. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9058–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramli, N.A.S.; Amin, N.A.S. Catalytic hydrolysis of cellulose and oil palm biomass in ionic liquid to reducing sugar for levulinic acid production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 128, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.M.; Deng, L.; Guo, Q.X.; Fu, Y. Hydrolysis of biomass by magnetic solid acid. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3552–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, X.; Fan, H.; Xu, N.; Li, G. Selective conversion of cotton cellulose to glucose and 5-hydroxymethyl furfural with SO42-/MxOysolid superacid catalyst. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chao, P.Y.; Cheng, T.Y.; Ho, Y.; Lin, C.T.; Hsu, H.Y.; Wong, J.J.; Tsai, T.C. Design of sulfonated mesoporous silica catalyst for fructose dehydration guided by difructose anhydride intermediate incorporated reaction network. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Du, W.; Gao, Z.; Sun, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Q.; Hu, X. Sulfated TiO2 nanosheets catalyzing conversion of biomass derivatives: Influences of the sulfation on distribution of Brønsted and Lewis acidic sites. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, M.L.; Miroddi, G.; Russo, M.; La Parola, V.; Marcì, G. Dehydration of fructose to 5-HMF over acidic TiO2 catalysts. Materials 2020, 13, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, C.; Liotta, L.F.; La Parola, V.; Testa, M.L.; Nicolosi, G. One-pot microwave assisted catalytic transformation of vegetable oil into glycerol-free biodiesel. Fuel 2013, 113, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado-Deblas, L.; Estevez, R.; Russo, M.; La Parola, V.; Bautista, F.M.; Testa, M.L. Microwave-assisted glycerol etherification over sulfonic acid catalysts. Materials 2020, 13, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, N.S.; La Parola, V.; Rode, C.V.; Testa, M.L. Ti-doped Pd-Au catalysts for one-pot hydrogenation and ring opening of furfural. Catalysts 2018, 8, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koso, S.; Furikado, I.; Shimao, A.; Miyazawa, T.; Kunimori, K.; Tomishige, K. Chemoselective hydrogenolysis of tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol to 1,5-pentanediol. Chem. Commun. 2009, 2035–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirrezabal-Telleria, I.; Requies, J.; Güemez, M.B.; Arias, P.L. Dehydration of d-xylose to furfural using selective and hydrothermally stable arenesulfonic SBA-15 catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 145, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirotori, M.; Nishimura, S.; Ebitani, K. One-pot synthesis of furfural from xylose using Al2 O3 –Ni-Al layered double hydroxide acid-base bi-functional catalyst and sulfonated resin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 45, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, J.M.R.; Alonso, D.M.; Mellmer, M.A.; Yeap, J.H.; Wong, H.C.; Dumesic, J.A. Production of furfural from lignocellulosic biomass using beta zeolite and biomass-derived solvent. Top. Catal. 2013, 56, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xi, G.; Yu, K.; Yu, H.; Wang, X. Furfural production from biomass–derived carbohydrates and lignocellulosic residues via heterogeneous acid catalysts. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 98, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, R.; Ahmad, M.N.; Vanoye, L.; Aiouache, F. Kinetics of aqueous phase dehydration of xylose into furfural catalyzed by ZSM-5 zeolite. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 4300–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, P.N.; Perez, R.F.; Figueiredo, N.G.; Fraga, M.A. Tandem dehydration-transfer hydrogenation reactions of xylose to furfuryl alcohol over zeolite catalysts. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 3759–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Di, L.; Wu, G.; Dai, W.; Guan, N.; Li, L. Meso-Zr-Al-beta zeolite as a robust catalyst for cascade reactions in biomass valorization. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 205, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.S.; Pillinger, M.; Valente, A.A. Dehydration of xylose into furfural over micro-mesoporous sulfonic acid catalysts. J. Catal. 2005, 229, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiprommarat, S.; Kongparakul, S.; Reubroycharoen, P.; Guan, G.; Samart, C. Highly efficient sulfonic MCM-41 catalyst for furfural production: Furan-based biofuel agent. Fuel 2016, 174, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Xu, G.; Fu, Y. One-pot cascade conversion of xylose to furfuryl alcohol over a bifunctional Cu/SBA-15-SO3H catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2020, 41, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canhaci, S.J.; Perez, R.F.; Borges, L.E.P.; Fraga, M.A. Direct conversion of xylose to furfuryl alcohol on single organic–inorganic hybrid mesoporous silica-supported catalysts. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 207, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, R.F.; Canhaci, S.J.; Borges, L.E.P.; Fraga, M.A. One-step conversion of xylose to furfuryl alcohol on sulfated zirconia-supported Pt catalyst—Balance between acid and metal sites. Catal. Today 2017, 289, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, J.; Melero, J.A.; Morales, G.; Paniagua, M.; Hernández, B.; Osatiashtiani, A.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. ZrO2-SBA-15 catalysts for the one-pot cascade synthesis of GVL from furfural. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xue, Y.; Guo, J.; Cen, Y.; Wang, J.; Fan, W. Integrated conversion of hemicellulose and furfural into γ-valerolactone over Au/ZrO2 Catalyst Combined with ZSM-5. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirrezabal-Telleria, I.; Gandarias, I.; Arias, P.L. Heterogeneous acid-catalysts for the production of furan-derived compounds (furfural and hydroxymethylfurfural) from renewable carbohydrates: A review. Catal. Today 2014, 234, 42–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millán, G.G.; Sixta, H. Towards the green synthesis of furfuryl alcohol in a one-pot system from xylose: A review. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agirrezabal-Telleria, I.; Requies, J.; Güemez, M.B.; Arias, P.L. Pore size tuning of functionalized SBA-15 catalysts for the selective production of furfural from xylose. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115–116, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipczynska-Kochany, E. Humic substances, their microbial interactions and effects on biological transformations of organic pollutants in water and soil: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 202, 420–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adani, F.; Spagnol, M.; Nierop, K.G.J. Biochemical origin and refractory properties of humic acid extracted from maize plants: The contribution of lignin. Biogeochemistry 2007, 82, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Yoon, H.Y.; Cha, J.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Kim, P.J.; Jeon, J.R. Artificial humification of lignin architecture: Top-down and bottom-up approaches. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zingaretti, D.; Lombardi, F.; Baciocchi, R. Soluble organic substances extracted from compost as amendments for Fenton-like oxidation of contaminated sites. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikowska, D.; Gusiatin, Z.M.; Bulkowska, K.; Kierklo, K. Humic substances from sewage sludge compost as washing agent effectively remove Cu and Cd from soil. Chemosphere 2015, 136, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.X.; Liu, H.T.; Wu, S.B. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyheraguibel, B.; Silvestre, J.; Morard, P. Effects of humic substances derived from organic waste enhancement on the growth and mineral nutrition of maize. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4206–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deganello, F.; Tummino, M.L.; Calabrese, C.; Testa, M.L.; Avetta, P.; Fabbri, D.; Prevot, A.B.; Montoneri, E.; Magnacca, G. A new, sustainable LaFeO3 material prepared from biowaste-sourced soluble substances. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winarso, S.; Pandutama, M.H.; Purwanto, L.D. Effectivity of humic substance extracted from palm oil compost as liquid fertilizer and heavy metal bioremediation. Agric. Agric. Sci. Procedia 2016, 9, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kałuza-Haładyn, A.; Jamroz, E.; Bekier, J. Humic substances of differently matured composts produced from municipal solid wastes and biomass of energetic plants. Soil Sci. Annu. 2019, 70, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaught, A.D.; Wilkinson, A. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, the Gold Book, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Michelin, C.; Hoffmann, N. Photosensitization and photocatalysis—Perspectives in organic synthesis. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 12046–12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Xue, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J. Dissolved organic matter-mediated photodegradation of anthracene and pyrene in water. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummino, M.L.; Magnacca, G.; Cimino, D.; Laurenti, E.; Nisticò, R. The innovation comes from the sea: Chitosan and alginate hybrid gels and films as sustainable materials for wastewater remediation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce, V.B.; Mucci, C.R.; Fernández Solarte, A.M.; Torres Sánchez, R.M.; Mártire, D.O. Application of novel fulvic acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for CO2-Mediated Photoreduction of Cr(VI). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, M.; Yang, X.; Xian, Q.; Kong, L. Photosensitized degradation of bisphenol A involving reactive oxygen species in the presence of humic substances. Chemosphere 2006, 63, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguer, J.P.; Richard, C. Influence of the excitation wavelength on the photoiductive properties of humic substances. Chemosphere 1999, 38, 2293–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco Prevot, A.; Fabbri, D.; Pramauro, E.; Baiocchi, C.; Medana, C.; Montoneri, E.; Boffa, V. Sensitizing effect of bio-based chemicals from urban wastes on the photodegradation of azo-dyes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 209, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabeu, A.; Vercher, R.F.; Santos-Juanes, L.; Simón, P.J.; Lardín, C.; Martínez, M.A.; Vicente, J.A.; González, R.; Llosá, C.; Arques, A.; et al. Solar photocatalysis as a tertiary treatment to remove emerging pollutants from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Catal. Today 2011, 161, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, L.; Mártire, D.O.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Gomis, J.; Bernabeu, A.; Amat, A.M.; Arques, A. Photochemical fate of a mixture of emerging pollutants in the presence of humic substances. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, J.; Bianco Prevot, A.; Montoneri, E.; González, M.C.; Amat, A.M.; Mártire, D.O.; Arques, A.; Carlos, L. Waste sourced bio-based substances for solar-driven wastewater remediation: Photodegradation of emerging pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 235, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewil, R.; Mantzavinos, D.; Poulios, I.; Rodrigo, M.A. New perspectives for advanced oxidation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 195, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farkas, J.; Náfrádi, M.; Hlogyik, T.; Cora Pravda, B.; Schrantz, K.; Hernádi, K.; Alapi, T. Comparison of advanced oxidation processes in the decomposition of diuron and monuron-efficiency, intermediates, electrical energy per order and the effect of various matrices. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foszpańczyk, M.; Bilińska, L.; Gmurek, M.; Ledakowicz, S. Heterogeneous oxidation of phenolic compounds with photosensitizing catalysts incorporated into chitosan. Catalysts 2019, 9, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, M.L.; Tummino, M.L.; Agostini, S.; Avetta, P.; Deganello, F.; Montoneri, E.; Magnacca, G.; Prevot, A.B. Synthesis, characterization and environmental application of silica grafted photoactive substances isolated from urban biowaste. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47920–47927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Liu, D.; Tian, J.; Wang, W.; Ni, J.; Wang, X. Visible-light-excited humic acid for peroxymonosulfate activation to degrade bisphenol A. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caram, B.; García-Ballesteros, S.; Santos-Juanes, L.; Arques, A.; García-Einschlag, F.S. Humic like substances for the treatment of scarcely soluble pollutants by mild photo-Fenton process. Chemosphere 2018, 198, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco Prevot, A.; Baino, F.; Fabbri, D.; Franzoso, F.; Magnacca, G.; Nisticò, R.; Arques, A. Urban biowaste-derived sensitizing materials for caffeine photodegradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 12599–12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Qu, R.; Ge, J.; Wang, Z.; Gu, C. Enhanced removal of chlorophene and 17β-estradiol by Mn(III) in a mixture solution with humic acid: Investigation of reaction kinetics and formation of co-oligomerization products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 13222–13230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Q.; Hoffmann, M.R. Synergistic impact of humic acid on the photo-reductive decomposition of perfluorooctanoic acid. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwińska-Stefańska, K.; Kubiak, A.; Piasecki, A.; Goscianska, J.; Nowaczyk, G.; Jurga, S.; Jesionowski, T. TiO2-ZnO binary oxide systems: Comprehensive characterization and tests of photocatalytic activity. Materials 2018, 11, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, J.; Liang, J.; Wu, B.; Zuo, J.; Zuo, Y. Role of humic substances in the photodegradation of naproxen under simulated sunlight. Chemosphere 2017, 187, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmia, O.; Boulkamh, A. The influence of the structure of humic substances extracted from different soils and peats on their capacity to photosensitize 1-naphthol. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2016, 7, 310–318. [Google Scholar]
- Rigobello, E.S.; Campos, S.X.; Azevedo, E.R.D.; Dantas, A.D.B.; Vieira, E.M. Comparative characterization of humic substances extracted from freshwater and peat of different apparent molecular sizes. Ambient. E Agua Interdiscip. J. Appl. Sci. 2017, 12, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Niu, H.; Yang, H.; Tong, L.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y. Spectral study of humic substance extract from pressurized oxidizing slag of Carlin-typed gold deposit. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1347, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, P.; Vione, D.; Minero, C. The role of humic and fulvic acids in the phototransformation of phenolic compounds in seawater. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeschbacher, M.; Graf, C.; Schwarzenbach, R.P.; Sander, M. Antioxidant properties of humic substances. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 4916–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Han, X.; Geng, H. Molecular characteristics of leonardite humic acid and the effect of its fractionations on sulfamethoxazole photodegradation. Chemosphere 2020, 246, 125642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranga, S. Comparative analysis of homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis. Int. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. Res. 2017, 4, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Vekariya, R.L.; Sonigara, K.K.; Fadadu, K.B.; Vaghasiya, J.V.; Soni, S.S. Humic acid as a sensitizer in highly stable dye solar cells: Energy from an abundant natural polymer soil component. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, J.; Bedoya, C.; Silva-Agredo, J.; Santamaría, A.; Fernández, J.J.; Torres-Palma, R.A. Role of humic substances in the degradation pathways and residual antibacterial activity during the photodecomposition of the antibiotic ciprofloxacin in water. Water Res. 2016, 94, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, J.; Fernández, J.J.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Richard, C. Humic substances enhance chlorothalonil phototransformation via photoreduction and energy transfer. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.H.; Gong, J.; Seo, S.; Yoon, H.; Chang, Y.S. Photosensitized diastereoisomer-specific degradation of hexabromocyclododecane (HBCD) in the presence of humic acid in aquatic systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 369, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.K.; Yamasaki, T.; Yamada, K. ichi Photodecomposition of tetrabromobisphenol A in aqueous humic acid suspension by irradiation with light of various wavelengths. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipe, O.M.S.; Santos, E.B.H.; Otero, M.; Gonçalves, E.A.C.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S. Photodegradation of metoprolol in the presence of aquatic fulvic acids. Kinetic studies, degradation pathways and role of singlet oxygen, OH radicals and fulvic acids triplet states. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Huang, B.; Yang, B.; Chen, F.; Pan, X.; Dionysiou, D.D. Photobleaching alters the photochemical and biological reactivity of humic acid towards 17α-ethynylestradiol. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, D.; Ren, Z.; Chen, F.; Wang, B.; Huang, B. Predictive role of spectral slope ratio towards 17 α-ethynylestradiol photodegradation sensitized by humic acids. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 112959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskoi, O.A.; Patsaeva, S.V.; Trubetskaya, O.E. Photochemical degradation of organic pollutants in solutions of soil humic acids. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2019, 52, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minella, M.; Merlo, M.P.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Vione, D. Transformation of 2,4,6-trimethylphenol and furfuryl alcohol, photosensitised by Aldrich humic acids subject to different filtration procedures. Chemosphere 2013, 90, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.P.; Lima, D.L.D.; Groth, M.B.; Otero, M.; Esteves, V.I. Effect of natural aquatic humic substances on the photodegradation of estrone. Chemosphere 2016, 145, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuan, R.; Wang, J. Degradation of diclofenac in aqueous solution by ionizing radiation in the presence of humic acid. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 234, 116079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoke, H.; Song, W.; Cooper, W.J.; Peake, B.M. Advanced oxidation treatment and photochemical fate of selected antidepressant pharmaceuticals in solutions of Suwannee River humic acid. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217–218, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koumaki, E.; Mamais, D.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Nika, M.C.; Bletsou, A.A.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Eftaxias, A.; Stratogianni, G. Degradation of emerging contaminants from water under natural sunlight: The effect of season, pH, humic acids and nitrate and identification of photodegradation by-products. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amine-Khodja, A.; Trubetskaya, O.; Trubetskoj, O.; Cavani, L.; Ciavatta, C.; Guyot, G.; Richard, C. Humic-like substances extracted from composts can promote the photodegradation of Irgarol 1051 in solar light. Chemosphere 2006, 62, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozdnyakov, I.P.; Tyutereva, Y.E.; Parkhats, M.V.; Grivin, V.P.; Fang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wan, D.; Luo, F.; Chen, Y. Mechanistic investigation of humic substances assisted photodegradation of imipramine under simulated sunlight. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avetta, P.; Bianco Prevot, A.; Fabbri, D.; Montoneri, E.; Tomasso, L. Photodegradation of naphthalene sulfonic compounds in the presence of a bio-waste derived sensitizer. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 197, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avetta, P.; Bella, F.; Bianco Prevot, A.; Laurenti, E.; Montoneri, E.; Arques, A.; Carlos, L. Waste cleaning waste: Photodegradation of monochlorophenols in the presence of waste-derived photosensitizer. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, F.; Escalada, J.P.; De Gerónimo, E.; Aparicio, V.C.; Einschlag, F.S.G.; Magnacca, G.; Carlos, L.; Mártire, D.O. Carbamazepine degradation mediated by light in the presence of humic substances-coated magnetite nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calza, P.; Di Sarro, J.; Magnacca, G.; Bianco Prevot, A.; Laurenti, E. Low-cost magnetic materials containing waste derivatives as catalyst for removal of organic pollutants: Insights into the reaction mechanism and odd aspects. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Sustainable Solid Waste Management, Naxos Island, Greece, 13–16 June 2018; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nisticò, R.; Prevot, A.B.; Magnacca, G.; Canone, L.; García-Ballesteros, S.; Arques, A. Sustainable magnetic materials (From chitosan and municipal biowaste) for the removal of diclofenac from water. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertella, S.; Luterbacher, J.S. Lignin functionalization for the production of novel materials. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 440–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel-Peña, V.; Guccini, V.; Kumar, S.; Salazar-Alvarez, G.; Rodríguez De San Miguel, E.; De Gyves, J. Hybrids based on borate-functionalized cellulose nanofibers and noble-metal nanoparticles as sustainable catalysts for environmental applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 12460–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, Y.; Deng, X.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, W.; Jia, Q.; Shan, S. Cellulosic Cr(salen) complex as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for copolymerization of SO2 with epoxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morshed, M.N.; Al Azad, S.; Deb, H.; Shaun, B.B.; Shen, X.L. Titania-loaded cellulose-based functional hybrid nanomaterial for photocatalytic degradation of toxic aromatic dye in water. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, K.; Ali, F.; Sohni, S.; Kamal, T.; Asiri, A.M.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Khan, S.B. Lignocellulosic biomass supported metal nanoparticles for the catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisa, W.H.; Abdelgawad, A.M.; Rojas, O.J. Solid-state synthesis of metal nanoparticles supported on cellulose nanocrystals and their catalytic activity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopiraman, M.; Deng, D.; Saravanamoorthy, S.; Chung, I.M.; Kim, I.S. Gold, silver and nickel nanoparticle anchored cellulose nanofiber composites as highly active catalysts for the rapid and selective reduction of nitrophenols in water. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 3014–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Shi, Z.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Mussel-inspired green metallization of silver nanoparticles on cellulose nanocrystals and their enhanced catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol in the presence of β-cyclodextrin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lu, C. Reductant-free synthesis of silver nanoparticles-doped cellulose microgels for catalyzing and product separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6322–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Lu, G.P.; Cai, C. Modified cellulose with tunable surface hydrophilicity/hydrophobicity as a novel catalyst support for selective reduction of nitrobenzene. Catal. Commun. 2020, 137, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Bai, L.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; et al. Cellulose nanocrystal shelled with poly(ionic liquid)/polyoxometalate hybrid as efficient catalyst for aerobic oxidative desulfurization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 554, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Shafiei, N.; Nezafat, Z.; Soheili Bidgoli, N.S.; Soleimani, F. Recent progresses in the application of cellulose, starch, alginate, gum, pectin, chitin and chitosan based (nano)catalysts in sustainable and selective oxidation reactions: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 241, 116353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempasiddaiah, M.; Kandathil, V.; Dateer, R.B.; Sasidhar, B.S.; Patil, S.A.; Patil, S.A. Immobilizing biogenically synthesized palladium nanoparticles on cellulose support as a green and sustainable dip catalyst for cross-coupling reaction. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3335–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, D.; Rashinkar, G.; Kumbhar, A.; Salunkhe, R. Facile Suzuki-Miyaura cross coupling using ferrocene tethered N-heterocyclic carbene-Pd complex anchored on cellulose. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 116, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Rahman, M.L.; Yusoff, M.M.; Sarkar, S.M. Highly active bio-waste cellulose supported poly(amidoxime) palladium(II) complex for Heck reactions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gan, T.; Hu, H.; Cai, X.; Huang, Z.; Liang, X.; Yin, Y.; Qin, Y.; Feng, Z. Effective treatment and utilization of hazardous waste sulfuric acid generated from alkylation by lignocellulose ester-catalyzed oxidative degradation of organic pollutants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 380, 120892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaabani, A.; Ganji, N.; Seyyedhamzeh, M.; Mofakham, H. Cellulose sulfuric acid: As an efficient bio polymer based catalyst for the selective oxidation of sulfides and thiols by hydrogen peroxide. Iran. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 33, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Córdova, A.; Afewerki, S.; Alimohammadzadeh, R.; Sanhueza, I.; Tai, C.W.; Osong, S.H.; Engstrand, P.; Ibrahem, I. A sustainable strategy for production and functionalization of nanocelluloses. Pure Appl. Chem. 2019, 91, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abouzeid, R.E.; Khiari, R.; El-Wakil, N.; Dufresne, A. Current state and new trends in the use of cellulose nanomaterials for wastewater treatment. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 573–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Lai, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, M.; Xue, F.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Y. Design and synthesis of amine-functionalized cellulose with multiple binding sites and their application in C–C bond forming reactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyki, M.H.; Ghasemi, M.H. Quaternized γ-Fe2O3@cellulose ionomer: An efficient recyclable catalyst for Michael-type addition reaction. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nahas, A.M.; Salaheldin, T.A.; Zaki, T.; El-Maghrabi, H.H.; Marie, A.M.; Morsy, S.M.; Allam, N.K. Functionalized cellulose-magnetite nanocomposite catalysts for efficient biodiesel production. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 322, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaqian, S.; Nemati, F.; Heravi, M.M.; Nahzomi, H.T. Copper(I) iodide supported on modified cellulose-based nano-magnetite composite as a biodegradable catalyst for the synthesis of 1,2,3-triazoles. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sá, D.S.; De Andrade Bustamante, R.; Rodrigues Rocha, C.E.; Da Silva, V.D.; Da Rocha Rodrigues, E.J.; Djenne Buarque Müller, C.; Ghavami, K.; Massi, A.; Ginoble Pandoli, O. Fabrication of lignocellulose-based microreactors: Copper-functionalized bamboo for continuous-flow CuAAC click reactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 3267–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, W.; Quinlan, P.J.; Berry, R.M.; Tam, K.C. Sustainable catalysts from gold-loaded polyamidoamine dendrimer-cellulose nanocrystals. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Narendren, S.; Gaur, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Katiyar, V. Self-propelled cellulose nanocrystal based catalytic nanomotors for targeted hyperthermia and pollutant remediation applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).