Substitution of Secondary Propargylic Phosphates Using Aryl-Lithium-Based Copper Reagents †
Abstract
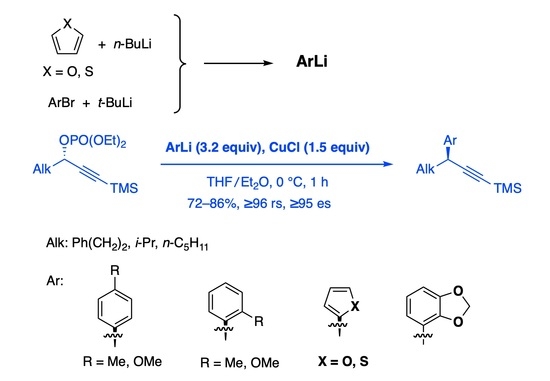
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Representative Procedures of the Coupling Reaction
3.2.1. Method A Using Commercial PhLi (Table 1, Entry 7)
3.2.2. Method B Using PhLi Derived from PhI and t-BuLi (Table 1, Entry 8)
3.2.3. Method C Using PhLi Derived from PhBr and t-BuLi (Table 1, Entry 9)
3.3. Representative Procedure for the Conversion of TMS-Acetylenes to Phenylacetylenes
3.4. Experiments and Characterization of the Products
3.4.1. Synthesis of (S)-(3,5-Diphenylpent-1-yn-1-yl)trimethylsilane [(S)-2aa], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5aa, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.2. Synthesis of (S)-Trimethyl[5-phenyl-3-(p-tolyl)pent-1-yn-1-yl]silane [(S)-2ab], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5ab, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.3. Synthesis of (S)-Trimethyl[5-phenyl-3-(o-tolyl)pent-1-yn-1-yl]silane [(S)-2ac], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5ac, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.4. Synthesis of (S)-[3-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-5-phenylpent-1-yn-1-yl]trimethylsilane [(S)-2ad], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5ad, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.5. Synthesis of (S)-[3-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-5-phenylpent-1-yn-1-yl]trimethylsilane [(S)-2ae], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5ae, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.6. Synthesis of (R)-[3-(Furan-2-yl)-5-phenylpent-1-yn-1-yl]trimethylsilane [(R)-2af], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5af, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.7. Synthesis of (R)-Trimethyl[5-phenyl-3-(thiophen-2-yl)pent-1-yn-1-yl]silane [(R)-2ag], Its Conversion to Ph-Acetylene (S)-5ag, and Chiral HPLC Analysis
3.4.8. Synthesis of Trimethyl(4-methyl-3-phenylpent-1-yn-1-yl)silane (2ba)
3.4.9. Synthesis of [3-(2-Methoxyphenyl)-4-methylpent-1-yn-1-yl]trimethylsilane (2be)
3.4.10. Synthesis of [3-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-4-yl)oct-1-yn-1-yl]trimethylsilane (2ch)
3.4.11. Synthesis of Pent-1-yne-1,3,5-triyltribenzene (5aa)
3.4.12. Synthesis of (R)-[3-(2-Methoxyphenyl)pent-1-yne-1,5-diyl]dibenzene [(R)-5ae]
3.4.13. Synthesis of (S)-Dec-4-yne-1,3-diyldibenzene [(S)-9]
3.5. Synthesis of (1,5-Diphenylpenta-1,2-dien-1-yl)trimethylsilane (3aa) (Table 1, Entry 10)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kobayashi, Y. Alkyl Pyirdinesulfonates and Allylic Pyridinecarboxylates, New Boosters for the Substitution at Secondary Carbons. Heterocycles 2020, 100, 499–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Shimoda, M. Substitution of Allylic Picolinates with Various Copper Reagents and Synthetic Applications. In Cutting-Edge of Organic Synthesis and Chemical Biology of Bioactive Molecules; Kobayashi, Y., Ed.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2019; Chapter 7; pp. 145–169. ISBN 978-981-13-6243-9 for hardcover. Available online: https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9789811362439 (accessed on 14 June 2019).
- Kobayashi, Y. Coupling Reactions on Secondary Allylic, Propargylic, and Alkyl Carbons using Organoborates/Ni and RMgX/Cu Reagents. Catalysts 2023, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.H.; Miller, J.D.; Chan, H.-K.; Delaney, M.O. Scope and Utility of a New Soluble Copper Catalyst [CuBr-LiSPh-LiBr-THF]: A Comparison with Other Copper Catalysts in Their Ability to Couple One Equivalent of a Grignard Reagent with an Alkyl Sulfonate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-T.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Liang, J.; Liu, J.-H.; Lu, X.-Y.; Chen, H.-H.; Liu, L. Copper-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Nonactivated Secondary Alkyl Halides and Tosylates with Secondary Alkyl Grignard Reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11124–11127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Oda, A.; Bobinski, T.; Li, H.; Matsueda, Y.; Negishi, E. Highly Efficient, Convergent, and Enantioselective Synthesis of Phthioceranic Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9319–9322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, R.; Morita, M.; Ogawa, N.; Kobayashi, Y. Use of the 2-Pyridinesulfonyloxy Leaving Group for the Fast Copper-Catalyzed Coupling Reaction at Secondary Alkyl Carbons with Grignard Reagents. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3247–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breit, B.; Schmidt, Y. Directed Reactions of Organocopper Reagents. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2928–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.; Marek, I. Enantioselective synthesis of all-carbon quaternary stereogenic centers in acyclic systems. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4593–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmiya, H.; Sawamura, M. Copper Catalyzed Allylic Substitution and Conjugate Addition with Alkylboranes. J. Synth. Org. Chem. Jpn. 2014, 72, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiyotsuka, Y.; Acharya, H.P.; Katayama, Y.; Hyodo, T.; Kobayashi, Y. Picolinoxy Group, a New Leaving Group for anti SN2′ Selective Allylic Substitution with Aryl Anions Based on Grignard Reagents. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyotsuka, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Acharya, H.P.; Hyodo, T.; Kobayashi, Y. New General Method for Regio- and Stereoselective Allylic Substitution with Aryl and Alkenyl Coppers Derived from Grignard Reagents. J. Org. Chem. 2009, 74, 1939–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, Y.; Kiyotsuka, Y.; Acharya, H.P.; Kobayashi, Y. Construction of a quaternary carbon at the carbonyl carbon of the cyclohexane ring. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5482–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Kobayashi, Y. Allylic Substitution for Construction of a Chiral Quaternary Carbon Possessing an Aryl Group. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 3755–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guisán-Ceinos, M.; Martín-Heras, V.; Tortosa, M. Regio- and Stereospecific Copper-Catalyzed Substitution Reaction of Propargylic Ammonium Salts with Aryl Grignard Reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8448–8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ma, E.; Li, Z. Copper-Catalyzed Selective Cross-Couplings of Propargylic Ethers with Aryl Grignard Reagents. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2019, 8, 1834–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B.M.; Debien, L. Re-orienting coupling of organocuprates with propargyl electrophiles from SN20 to SN2 with stereocontrol. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4985–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.-L.; Wan, X.; Zhang, X. Copper-Catalyzed Highly Stereoselective Trifluoromethylation and Difluoroalkylation of Secondary Propargyl Sulfonates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3187–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Wang, G. Regioselectivity Control by a Ligand Switch in the Coupling Reaction Involving Allenic/Propargylic Palladium Species. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 4215–4217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo-Legarda, P.; Soler-Yanes, R.; Quirós-López, M.T.; Buñuel, E.; Cárdenas, D.J. Iron-Catalyzed Coupling of Propargyl Bromides and Alkyl Grignard Reagents. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 2018, 4900–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjón-Mata, I.; Quirós, M.T.; Buñuel, E.; Cárdenas, D.J. Regioselective Iron-Catalysed Cross-Coupling Reaction of Aryl Propargylic Bromides and Aryl Grignard Reagents. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2020, 362, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, H.; Kawatsura, M. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Propargylic Substitution of Propargylic Alcohol Derivatives Bearing an Internal Alkyne Group. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2020, 9, 1924–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.W.; Fu, G.C. Nickel-Catalyzed Negishi Cross-Couplings of Secondary Nucleophiles with Secondary Propargylic Electrophiles at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 9334–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schley, N.D.; Fu, G.C. Nickel-Catalyzed Negishi Arylations of Propargylic Bromides: A Mechanistic Investigation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16588–16593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oelke, A.J.; Sun, J.; Fu, G.C. Nickel-Catalyzed Enantioselective Cross-Couplings of Racemic Secondary Electrophiles That Bear an Oxygen Leaving Group. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2966–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishibayashi, Y. Development of Asymmetric Propargylic Substitution Reactions Using Transition Metal Catalysts. Chem. Lett. 2021, 50, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakata, K.; Nishibayashi, Y. Mechanism and reactivity of catalytic propargylic substitution reactions via metal–allenylidene intermediates: A theoretical perspective. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuji, J.; Mandai, T. Palladium-Catalyzed Reactions of Propargylic Compounds in Organic Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 34, 2589–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Takashima, Y.; Motoyama, Y.; Isogawa, Y.; Katagiri, K.; Tsuboi, A.; Ogawa, N. α- and γ-Regiocontrol and Enantiospecificity in the Copper-catalyzed Substitution Reaction of Propargylic Phosphates with Grignard Reagents. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 3779–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, N.; Uematsu, C.; Kobayashi, Y. Stereoselective Synthesis of (−)-Heliannuol E by α-Selective Propargyl Substitution. Synlett 2021, 32, 2071–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, Y.; Isogawa, Y.; Tsuboi, A.; Ogawa, N.; Kobayashi, Y. Synthesis of a TNF inhibitor, flurbiprofen and an i-Pr analogue in enantioenriched forms by copper catalyzed propargylic substitution with Grignard reagents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 9906–9909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Hirotsu, T. Synthesis of (S)-Nyasol through the Copper-catalyzed Propargylic Substitution. Synlett 2023, 34, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kiyotsuka, Y.; Sugihara, Y.; Wada, K. Installation of the imidazole ring on chiral substrates via allylic substitution. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 6481–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denmark, S.E.; Vogler, T. Synthesis and Reactivity of Enantiomerically Enriched Thiiranium Ions. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11737–11745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarov, A.S.; Uchuskin, M.G.; Trushkov, I.V. Furan Oxidation Reactions in the Total Synthesis of Natural Products. Synthesis 2018, 50, 3059–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, M.; Kitano, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Sato, F. Preparation of optically active 2-furylcarbinols by kinetic resolution using the Sharpless reagent and their application in organic synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Nakano, M.; Kumar, G.B.; Kishihara, K. Efficient Conditions for Conversion of 2-Substituted Furans into 4-Oxygenated 2-Enoic Acids and Its Application to Synthesis of (+)-Aspicilin, (+)-Patulolide A, and (−)-Pyrenophorin. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 7505–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.S.; Behling, J.R.; Campbell, A.L.; Nguyen, D.; Lipshutz, B. Reactions of higher order cyanocuprates derived from 2-lithiated furans: Scope, limitations, and synthetic utility. Tetrahedron Lett. 1988, 29, 3045–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipshutz, B.H.; Koerner, M.; Parker, D.A. 2-thienyl(cyano)copper lithium. A lower order, “cuprate in a bottle” precursor to higher order reagents. Tetrahedron Lett. 1987, 28, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipshutz, B.H.; Kozlowski, J.A.; Parker, D.A.; Nguyen, S.L.; McCarthy, K.E. More highly mixed, higher order cyanocuprates “RT(2-thienyl)Cu(CN)Li2”. Efficient reagents which promote selective ligand transfer. J. Organomet. Chem. 1985, 285, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Lalitnorasate, P.; Kaneko, Y.; Kiyotsuka, Y.; Endo, Y. Synthesis of ACAT inhibitors through substitution using allylic picolinate and copper reagent. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 6018–6021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.V.; Skattebøl, L. One-pot synthesis of substituted catechols from the corresponding phenols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 3357–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Entry | Ph Reagent | Cu Salt | PhLi 1/Cu Salt | Temp. | Time | 2aa/3aa/1a 2 | Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PhLi | – | – | rt | 6 h | – 3 | – |
| 2 | PhLi | CuCN | 2.5:3 | rt | 17 h | 44:56:0 | nd 4 |
| 3 | PhLi | CuCN | 3:1.5 | rt | 2 h | 94:6:0 | nd 4 |
| 4 | PhLi, MgBr2 5 | CuBr·Me2S | 3:3 | 0 °C | 2 h | 13:87:0 | nd 4 |
| 5 | PhLi | CuBr2 | 3:1.5 | 0 °C | 2 h | 7:45:48 | nd 4 |
| 6 | PhLi | CuCl | 2.5:3 | 0 °C | 7 h | 17:83:0 | nd 4 |
| 7 | PhLi | CuCl | 3:1.5 | 0 °C | 2 h | 98:2:0 | 76% |
| 8 | PhI, t-BuLi 6 | CuCl | 3:1.5 | 0 °C | 1 h | 98:2:0 | 80% |
| 9 | PhBr, t-BuLi 6 | CuCl | 3:1.5 | 0 °C | 2 h | 97:3:0 | 73% |
| 10 | PhLi, MgBr2 5 | Cu(acac)2 | 3.6:2:5 | 0 °C | 4 h | 1:>99:0 | 85% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kobayashi, Y.; Hirotsu, T.; Haimoto, Y.; Ogawa, N. Substitution of Secondary Propargylic Phosphates Using Aryl-Lithium-Based Copper Reagents. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071084
Kobayashi Y, Hirotsu T, Haimoto Y, Ogawa N. Substitution of Secondary Propargylic Phosphates Using Aryl-Lithium-Based Copper Reagents. Catalysts. 2023; 13(7):1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071084
Chicago/Turabian StyleKobayashi, Yuichi, Takayuki Hirotsu, Yosuke Haimoto, and Narihito Ogawa. 2023. "Substitution of Secondary Propargylic Phosphates Using Aryl-Lithium-Based Copper Reagents" Catalysts 13, no. 7: 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071084
APA StyleKobayashi, Y., Hirotsu, T., Haimoto, Y., & Ogawa, N. (2023). Substitution of Secondary Propargylic Phosphates Using Aryl-Lithium-Based Copper Reagents. Catalysts, 13(7), 1084. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071084