Research Progress on Metal Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Main Reactions of the NH3-SCR System
3. SCR Catalysts
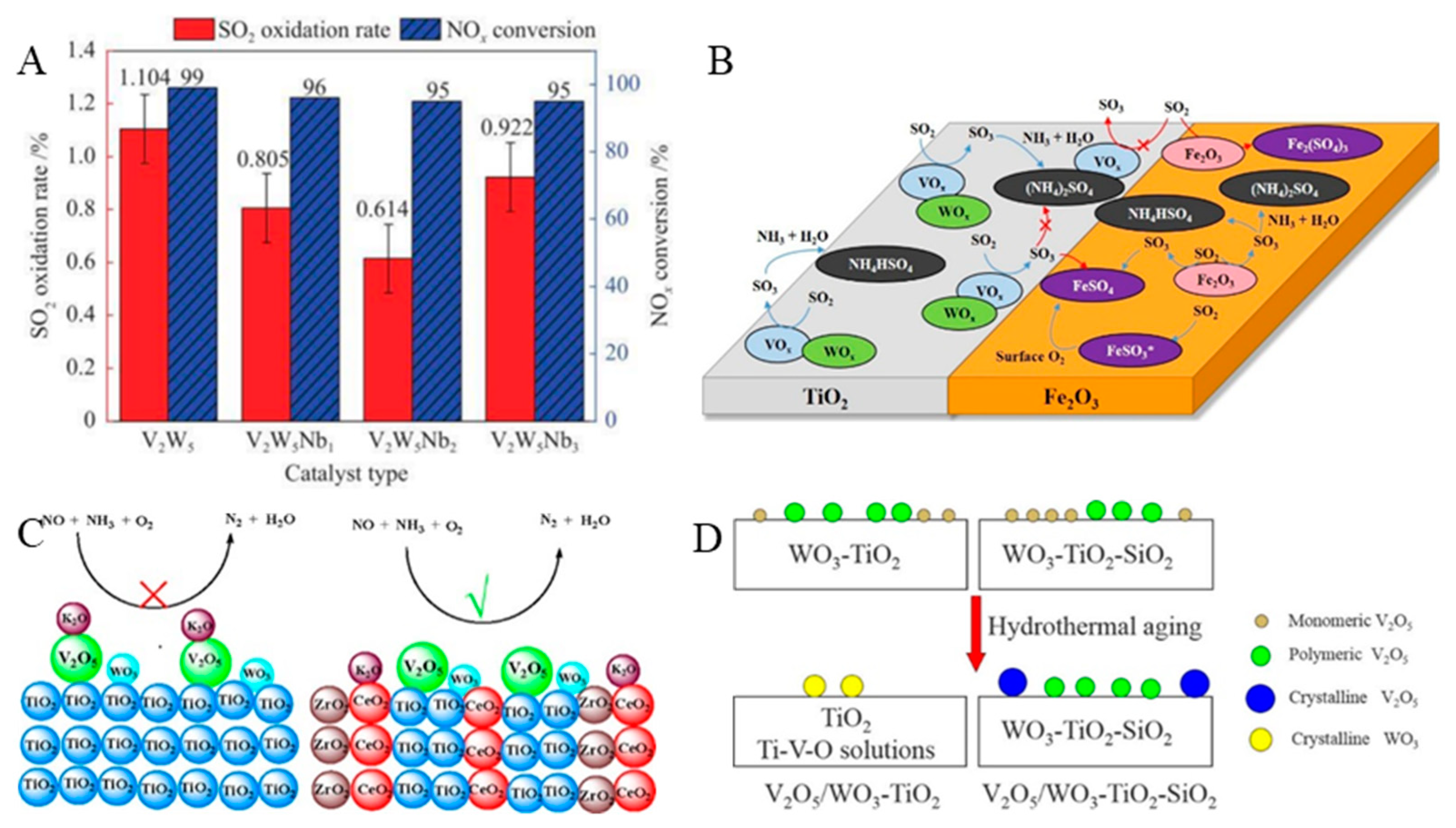
3.1. V-Based Catalysts
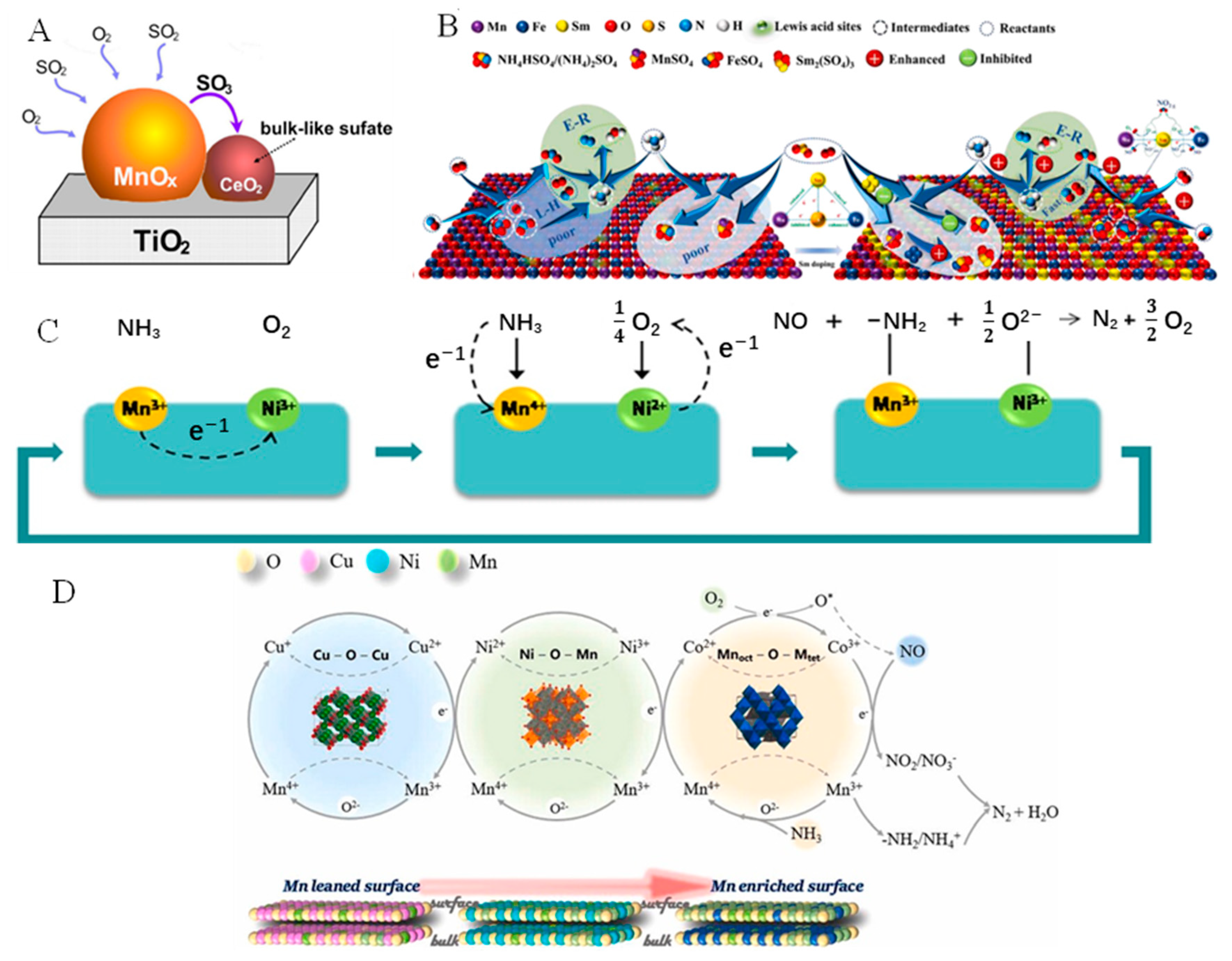
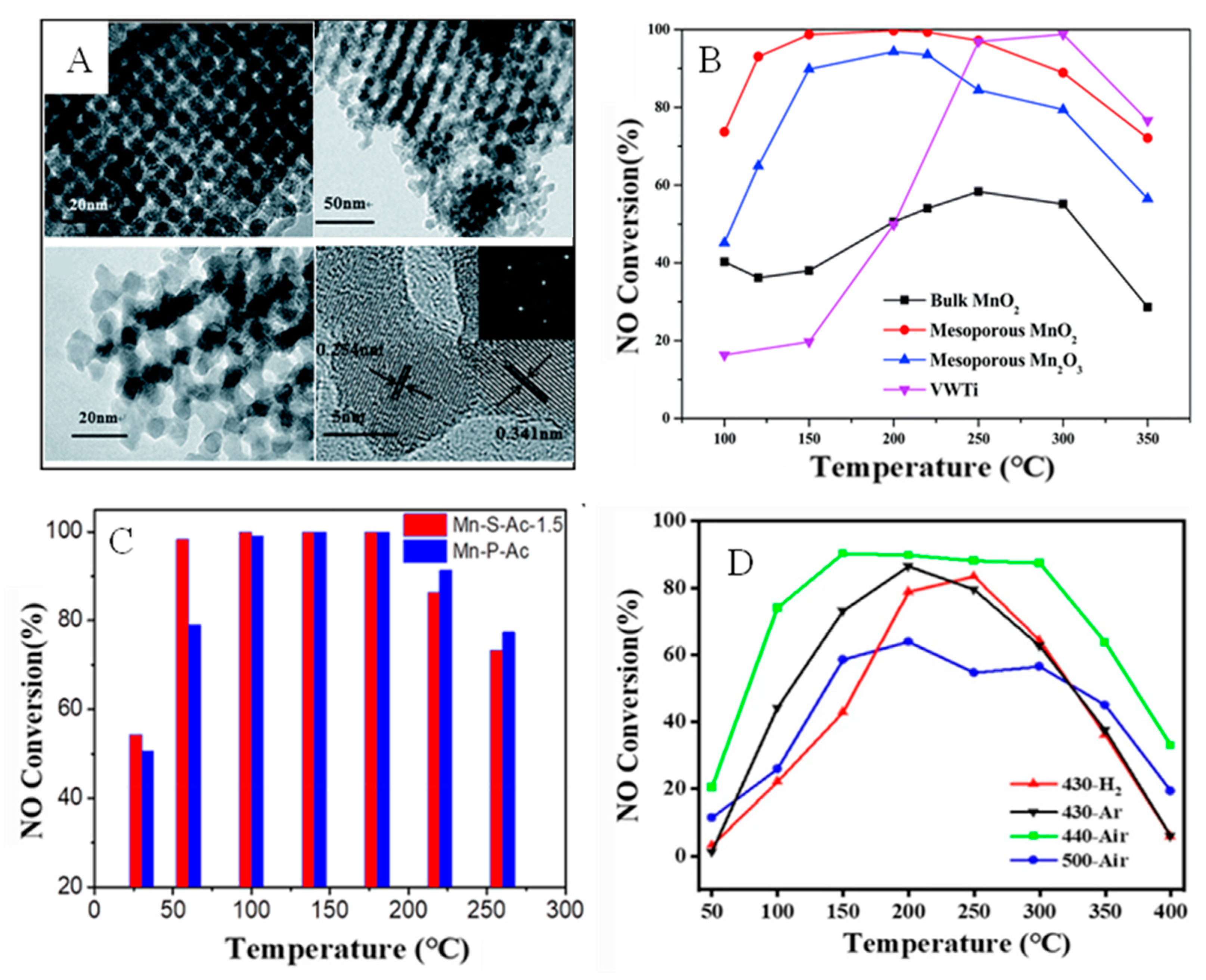
3.2. Mn-Based Catalyst
| Catalysts | Feed Composition | GHSV (h−1) | Conversion (Corresponding Temperature Window) | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO (ppm) | NH3 (ppm) | O2 (vol%) | SO2 (ppm) | H2O (vol%) | ||||
| MnO2 Mn2O3 Mn3O4 | 500 | 500 | 11 | 36,000 | 100% (150 °C) 100% (250 °C) 100% (200 °C) | [48] | ||
| Mn–Ni/TiO2 (Ni/Mn = 0.4) | 400 | 400 | 2 | - | -- | 50,000 | 100% (200 °C) | [49] |
| α-MnO2 γ-MnO2 β-MnO2 | 500 | 500 | 19 | - | - | 36,000 | 100% (120 °C) 100% (120 °C) 40% (120 °C) | [50] |
| mesoporous MnO2 | 500 | 500 | 3 | - | - | 28,000 | 100% (150–250 °C) | [56] |
| Mn3CeW0.3Ox | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 100,000 | >70% (100–275 °C) | [59] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 5 | >72% (150–300 °C) | ||||
| Cr(0.4)–MnOx | 1000 | 1000 | 3 | - | - | 30,000 | >98% (120–220 °C) | [61] |
| 1000 | 1000 | 3 | 100 | 85% (120 °C) | ||||
| CeO2@α-MnO2 | 500 | 500 | 11 | - | - | 36,000 | 100% (75–250 °C) | [66] |
| SmMnFe-0.1 | 500 | 500 | 5 | 60,000 | 100% (75–200 °C) | [70] | ||
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 100 | 5 | 90% (200 °C) | |||
| Ni(0.4)-MnOx | 500 | 500 | 5 | 64,000 | 100% (150–240 °C) | [72] | ||
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 100 | 87% (230 °C) | ||||
| Co-MnOx | 500 | 500 | 5 | 200 | 10 | 32,000 | 86% (200 °C) | [73] |
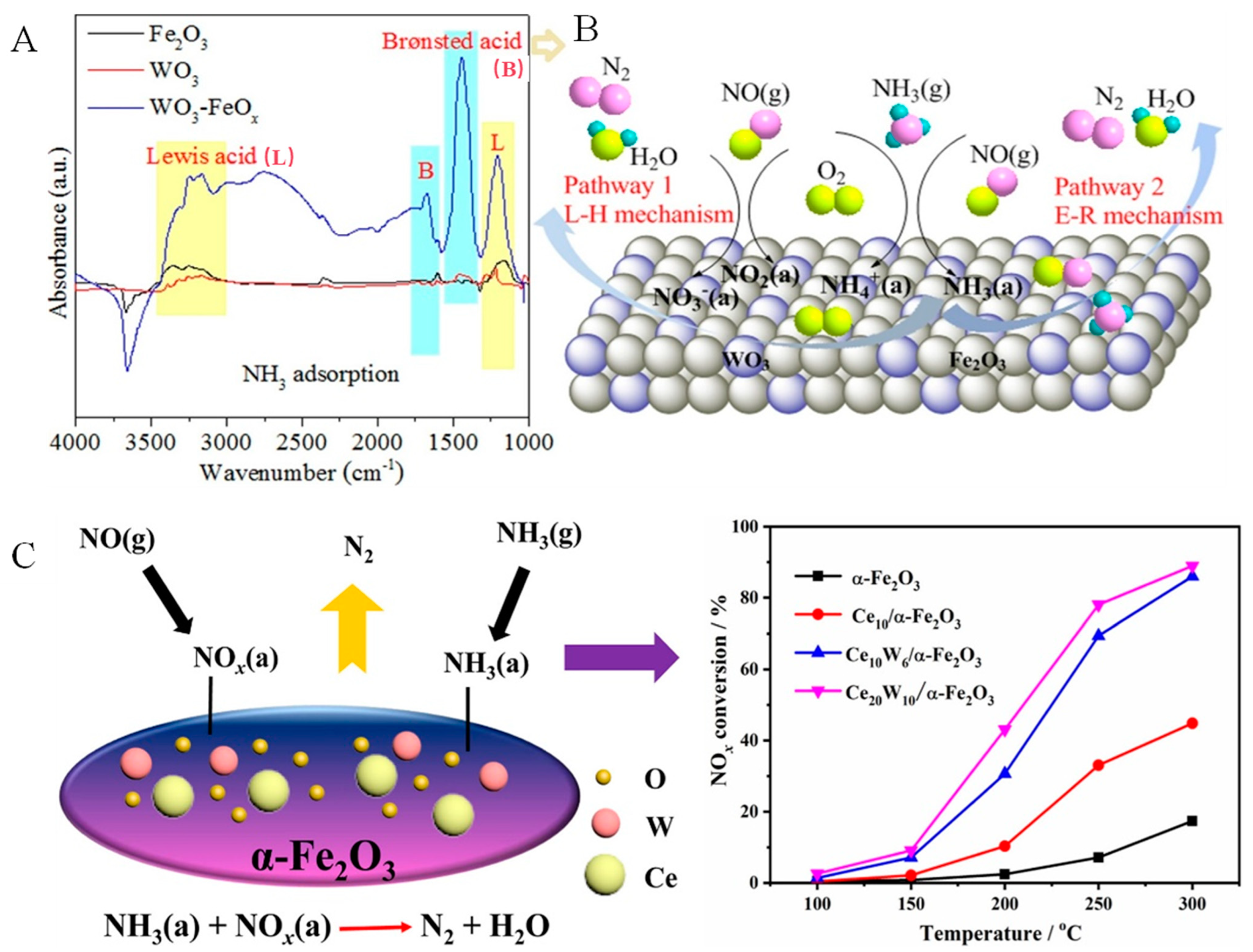
3.3. Fe-Based Catalysts
3.4. Ce-Based Catalyst
3.5. Cu-Based Catalyst
4. The Stability of the SCR Catalyst
5. Conclusions and Outlook
- (1)
- The metal oxide catalysts have disadvantages, such as narrow operating temperature windows basically within the low or medium–low temperature range and poor N2 selectivity. Therefore, modifying catalysts to enhance their NH3-SCR catalytic performance is the main focus of future research.
- (2)
- The presence of H2O and SO2 are definite in diesel vehicle exhaust and metal oxides can easily react with them to deactivate the catalyst, therefore, improving the hydrothermal stability and SO2 tolerance of the catalyst remains the major factor of the SCR technology.
- (3)
- Further research needs to be focused on the reaction mechanisms of sulfur dioxide and water poisoning processes for catalysts. The studies of catalyst poisoning mechanisms cannot determine the process of catalyst poisoning only through in situ characterization technology. The synchrotron-radiation, theoretical calculations, and isotopic tracer techniques should also be considered to fully explain the mechanisms of the catalyst poisoning process.
- (4)
- The injection of NH3 is a major component of the SCR device, but there may be blockages in the NH3 injection on occasion and the NH3 amount is imprecise. Therefore, optimizing the injection way and accurately controlling the injection amount will be one of the important goals.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiaqiang, E.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Han, D.; Chen, J.; Wei, K.; Gong, J.; Yin, Z. Effect analysis on cold starting performance enhancement of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel fuel based on an improved thermodynamic model. Appl. Energy 2019, 243, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Zhao, D.; Wang, B.; Li, J.W.; Guan, Y.H. NOx emission and thermal performances studies on premixed ammonia-oxygen combustion in a CO2-free micro-planar combustor. Fuel 2020, 280, 118554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jiaqiang, E.; Chen, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, B.; Deng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Yin, Z. Effects of boiling heat transfer on the performance enhancement of a medium speed diesel engine fueled with diesel and rapeseed methyl ester. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2020, 169, 114984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Gao, X.; Hatakeyama, S.; Hwang, J.; Tsai, C.J. Overview of the Special Issue “PM2.5 in Asia” for 2015 Asian Aerosol Conference. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadidi, L.A.; Aldosary, A.S.; Al-Matar, A.K.; Mudallah, O.A. An optimization model to improve gas emission mitigation in oil refineries. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 118, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, T.S.; Guo, Y.Q.; Wang, J.W.; Wei, J.X.; Yu, Q.J. Recent advances in simultaneous removal of SO2 and NOx from exhaust gases: Removal process, mechanism and kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayeva, N.O.; Mamiyev, Z. Chapter 5—Integrated processes involving adsorption, photolysis, and photocatalysis. In Hybrid and Combined Processes for Air Pollution Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 117–153. [Google Scholar]
- Khanal, V.; Balayeva, N.O.; Günnemann, C.G.; Mamiyev, Z.; Dillert, R.; Bahnemann, D.W.; Subramanian, V. Photocatalytic NOx removal using tantalum oxide nanoparticles: A benign pathway. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 291, 119974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Ren, Y.; Yu, X.H.; Peng, C.; Yu, D.; Zhong, C.M.; Hou, J.; Yin, C.Y.; Fan, X.Q.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Novel preparation method, catalytic performance and reaction mechanisms of PrxMn1-xOδ/3DOM ZSM-5 catalysts for the simultaneous removal of soot and NOx. J. Catal. 2023, 417, 226–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Wang, Q.; Pan, J.F. Novel process on simultaneous removal of nitric oxide and sulfur dioxide using vacuum ultraviolet (VUV)-activated O2/H2O/H2O2 system in a wet VUV-spraying reactor. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12966–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, U.; Rafiq, S.; Anwar, A.; Iqbal, T.; Ahmed, A.; Jamil, F.; Khurram, M.S.; Akbar, G.; Farooq, A.; Shah, N.S.; et al. Review on the progress in emission control technologies for the abatement of CO2, SOx and NOx from fuel combustion. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.T.; Louis, B.; O’Hare, D.; Wang, Q. Fabrication of lithium silicates as highly efficient high-temperature CO2 sorbents from SBA-15 precursor. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 7821–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Li, T.Y.; Wey, M.Y. Preferred enhancement of fast-SCR by Mn/CeSiOx catalyst: Study on Ce/Si promotion and shape dependence. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Yu, X.H.; Wei, Y.C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Z. Research advances of rare earth catalysts for catalytic purification of vehicle exhausts. J. Rare Earths 2021, 39, 1151–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boningari, T.; Pappas, D.K.; Smirniotis, P.G. Metal oxide-confined interweaved titania nanotubes M/TNT (M = Mn, Cu, Ce, Fe, V, Cr, and Co) for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx in the presence of excess oxygen. J. Catal. 2018, 365, 320–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.P.; Cai, S.X.; Gao, M.; Hasegawa, J.Y.; Wang, P.L.; Zhang, J.P.; Shi, L.Y.; Zhang, D.S. Selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 by using novel catalysts: State of the art and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10916–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.W.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, M.; Bae, W.B.; Shin, H.; Hazlett, M.J.; Kang, D.; Tesfaye, B.; Park, P.W.; Kang, S.B. High N2 selectivity of Pt-V-W/TiO2 oxidation catalyst for simultaneous control of NH3 and CO emissions. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 444, 136517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Herreros, J.M.; Tsolakis, A.; York, A.P.E. Increased NO2 concentration in the diesel engine exhaust for improved Ag/Al2O3 catalyst NH3-SCR activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillot, S.; Tricot, G.; Vezin, H.; Dacquin, J.P.; Dujardin, C.; Granger, P. Induced effect of tungsten incorporation on the catalytic properties of CeVO4 systems for the selective reduction of NOx by ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 234, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Fan, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, M.; Gan, G.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, D. Inductive effect boosting catalytic performance of advanced Fe1−xVxOδ catalysts in Low-temperature NH3 selective catalytic reduction: Insight into the structure, interaction, and mechanisms. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 6760–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, X.; Meng, H.; Qu, L.; Wu, X. Fabrication of high-silica Cu/ZSM-5 with confinement encapsulated Cu-based active species for NH3-SCR. Catal. Commun. 2020, 138, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, S.K.; Kaisare, N.; Kummari, S.K.; Aghalayam, P. Low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO over robust RuNi/Al-SBA-15 catalysts: Effect of Ru loading. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Huang, B.C.; Yu, C.L.; Lu, M.J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.L. Research progress, challenges and perspectives on the sulfur and water resistance of catalysts for low temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Appl. Catal. A 2019, 588, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Fu, Y.; Shan, Y.L.; Du, J.P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Gao, M.; Shi, X.Y.; He, G.Z.; Xue, S.; Han, X.W.; et al. Si/Al ratio determines the SCR performance of Cu-SSZ-13 catalysts in the presence of NO2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 17946–17954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendrich, M.; Scheuer, A.; Hayes, R.E.; Votsmeier, M. Unified mechanistic model for standard SCR, fast SCR, and NO2-SCR over a copper chabazite catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 222, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andana, T.; Rapp’e, K.J.; Ga, F.; Szanyi, J.; Pereira-Hernandez, X.; Wang, Y. Recent advances in hybrid metal oxide–zeolite catalysts for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by ammonia. Appl. Catal. B 2021, 291, 120054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; He, H.; Chu, B.W. Microkinetic study of NO oxidation, standard and fast NH3-SCR on CeWOx at low temperatures. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 130128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens, T.V.W.; Falsig, H.; Lundegaard, L.F.; Vennestrøm, P.N.R.; Rasmussen, S.B.; Moses, P.G.; Giordanino, F.; Borfecchia, E.; Lomachenko, K.A.; Lamberti, C.; et al. A consistent reaction scheme for the selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with ammonia. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2832–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Peng, Q.; Jiaqiang, E.; Xie, B.; Wei, J.; Yin, R.; Fu, G. Mechanism, performance and modification methods for NH3-SCR catalysts: A review. Fuel 2023, 331, 125885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Qu, R.; Song, H.; Gao, X.; Luo, Z.; Ni, M.; Cen, K. New Insights into the Various Decomposition and Reactivity Behaviors of NH4HSO4 with NO on V2O5/TiO2 Catalyst Surfaces. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Chen, J.L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.B.; Zhao, H.R.; Wu, X.Q. Research progress of hydrothermal stability of metal-based zeolite catalysts in NH3-SCR reaction. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2020, 48, 1193–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.Y.; Ma, L.; Li, Z.H.; Qu, Z.; Yan, N.Q.; Li, J.H. Review of sulfur promotion effects on metal oxide catalysts for NOx emission control. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13119–13139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.F.; Wu, X.D.; Gao, Y.X.; Lin, Q.W.; Hu, J.F.; Weng, D. Comparative study on sulfur poisoning of V2O5-Sb2O3/TiO2 and V2O5-WO3/TiO2 monolithic catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR. Catal. Commun. 2017, 93, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bian, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, S.Q.; Shen, B.X. Modification of the V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst with Nb to reduce its activity for SO2 oxidation during the selective catalytic reduction of NOx. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2022, 50, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Cha, J.S.; Kim, B.S. Characteristics of deactivation and thermal regeneration of Nb-doped V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalyst for NH3–SCR reaction. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, A.; Wang, X.; Yu, T.; Shen, M. The Effect of Zirconia additive on the activity and structure stability of V2O5/WO3-TiO2 ammonia SCR catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 106, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.H.; Youn, S.; Kim, D.H. Improved catalytic performance and resistance to SO2 over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst physically mixed with Fe2O3 for low-temperature NH3-SCR. Catal. Today 2021, 376, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.W.; Song, I.; Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Byun, Y.; Koh, D.J.; Kim, D.H. Enhanced SO2 resistance of V2O5/WO3-TiO2 catalyst physically mixed with alumina for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.W.; Peng, Y.W.; Dai, G.Y.; Zhao, H.W.; Huang, Z.W.; Wu, X.M.; Jing, G.H.; Feng, W.; Yuan, Y. Ceria accelerates ammonium bisulfate decomposition for improved SO2 resistance on a V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst in low-temperature NH3-SCR. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 140, 104555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Chao, J.; Fang, Y.; He, H.; Li, J.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, G. Promotion of ceria for decomposition of ammonia bisulfate over V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 303, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yi, W.; Yu, J.; Zeng, J.; Chang, H. Novel methods for assessing the SO2 poisoning effect and thermal regeneration possibility of MOx−WO3/TiO2 (M = Fe, Mn, Cu, and V) catalysts for NH3-SCR. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 12612–12620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Kumar, P.A.; Maqbool, M.S.; Rao, K.N.; Song, K.H.; Ha, H.P. Ceria added Sb-V2O5/TiO2 catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR: Physico-Chemical properties and catalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 2013, 142–143, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yao, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Fu, M.; Tang, C.; Dong, L. Improving the deNOx performance and K-poisoning resistance of the V2O5-WO3/TiO2 catalyst by Ce4+ and Zr4+ co-doping. Chin. J. Catal. 2019, 40, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Wang, B.D.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.L.; Xu, W.Q.; Li, J.H. New insights into the promotional effects of Cu and Fe over V2O5-WO3/TiO2 NH3-SCR catalysts towards oxidation of Hg0. Catal. Commun. 2017, 100, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Xu, T.; Weng, D.; Si, Z.; Ran, R. Effects of silica additive on the NH3-SCR activity and thermal stability of a V2O5/WO3-TiO2 catalyst. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Yuan, M.L.; Yang, J.; Zhan, W.C.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G.Z. Thermal stability of Si-doped V2O5/WO3–TiO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Rare Metals 2019, 38, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, T.S.; Jiang, L.J.; Long, H.M.; Guo, F.Q.; Kong, M. Role of cerium in improving NO reduction with NH3 over Mn-Ce/ASC catalyst in low-temperature flue gas. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, S.; Zhou, Y.H.; Su, Z.H.; Yao, L.; Cao, J.; Jiang, L.J.; Hu, J.; Kong, M.; Yang, J.; et al. In situ IR comparative study on N2O formation pathways over different valence states manganese oxides catalysts during NH3–SCR of NO. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirupathi, B.; Smirniotis, P.G. Nickel-doped Mn/TiO2 as an efficient catalyst for the low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3: Catalytic evaluation and characterizations. J. Catal. 2012, 288, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ren, S.; Su, B.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, G.; Jiang, L.; Cao, J.; Liu, W.; Yao, L.; Kong, M.; et al. Insight into N2O formation over different crystal phases of MnO2 during low-temperature NH3−SCR of NO. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151, 2964–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.J.; Gao, C.; Zhang, Z.R.; Wang, B.; Xuan, Y.; Tong, K.B.; Wang, Y.Z.; Yun, Y.; Wang, D.; Peng, Y. Modulation of paired acid centers for the α-, β-, γ- and δ-MnO2 for the NH3-SCR: A comparative density functional theory (DFT) study. Mol. Catal. 2023, 546, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Xie, J.L.; Hu, H.; Yang, H.; He, F.; Fu, Z.B. Identification of MnOx species and Mn valence states in MnOx/TiO2 catalysts for low temperature SCR. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 271, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.Z.; Gao, M.; Peng, Y.; Yu, Y.B.; Shan, W.P.; He, H. Superior oxidative dehydrogenation performance toward NH3 determines the excellent low-temperature NH3 -SCR activity of Mn-based catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 6995–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, J.L.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, M.H. Effect of promoters on the catalytic performance and SO2/H2O resistance of α-MnO2 catalysts for low temperature NH3-SCR. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Jin, B.; Liu, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, K.; Su, F. Abundant oxygen vacancies induced by the mechanochemical process boost the low-temperature catalytic performance of MnO2 in NH3-SCR. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, S.H.; Zhu, D.D.; Qiu, M.Y.; Yu, H.B.; Li, Y. Highly efficient removal of NO with ordered mesoporous manganese oxide at low temperature. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29353–29361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wei, Y.J.; Li, P.Z.; Zhang, P.P.; Su, W.; Sun, Y.; Zou, R.Q.; Zhao, Y.L. Experimental and theoretical investigation of mesoporous MnO2 nanosheets with oxygen vacancies for high-efficiency catalytic deNOx. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.Y.; Li, J.Q.; Chen, C.Y.; Ning, D.Y.; Yang, J.; Chu, Z.Y.; Mao, X.S.; Lan, Y.P. Low-temperature NOx selective catalytic reduction activity evaluation of hollow-spherical manganese oxides. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 2022, 48, 3007–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Shan, W.; Liu, F.; Yang, S. Adjustment of operation temperature window of Mn-Ce oxide catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 405, 124223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Hou, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Yang, Y.T.; Huang, Z.G. Confinement of MnOx@Fe2O3 core-shell catalyst with titania nanotubes: Enhanced N2 selectivity and SO2 tolerance in NH3- SCR process. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2022, 608, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Chi, T.S. Cr–MnOx mixed-oxide catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 at low temperature. J. Catal. 2010, 276, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Zou, R.Q.; Wang, X.D. Toward an atomic-level understanding of the catalytic mechanism of selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 14347–14375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cen, W.L.; Wu, Z.B.; Wang, H.Q.; Weng, X.L. The role of cerium in the improved SO2 tolerance for NO reduction with NH3 over Mn-Ce/TiO2 catalyst at low temperature. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 148–149, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.W.; Gong, J.; Wang, X.; Bao, Z.H.; Guo, Y.B.; Wu, Z.L. A Review on the impact of SO2 on the oxidation of NO, hydrocarbons, and CO in diesel emission control catalysis. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12446–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Chen, B.B.; Zhao, Q.; Crocker, M.; Li, Y.J.; Shi, C. Metal-support interaction induced atomic dispersion and redispersion of Pd on CeO2 for passive NOx adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 11, 144080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, S.; Xing, X.D.; Yang, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.C. Effect of MnO2 crystal types on CeO2@MnO2 oxides catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Ren, S.; Xing, X.D.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Li, X.D. Catalytic performance of CeO2-NPs and α-MnO2 mixed oxides catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NO. J. Energy Inst. 2022, 103, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.J.; Chen, K.A.; Xie, S.Z.; Li, L.L.; Ou, X.M.; Wei, X.L.; Luo, X.T.; Dong, L.H.; Li, B. Enhanced SO2 and H2O resistance of MnTiSnOy composite oxide for NH3-SCR through Sm modification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 583, 152478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.M.; Zhan, W.C.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Lu, G.Z. A highly effective catalyst of Sm-MnOx for the NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperature: Promotional role of Sm and its catalytic performance. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5973–5983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.C.; Ren, S.; Wang, M.M.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.Z.; Liu, Q.C.; Su, B.X. Insights into samarium doping effects on catalytic activity and SO2 tolerance of MnFeOx catalyst for low-temperature NH3-SCR reaction. Fuel 2022, 321, 124113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Jin, L.Y.; Zhang, A.C.; Sun, Z.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhu, Q.F.; Yang, C.Z.; Zhang, S.B. Investigation of Co-doped Mn oxide catalyst for NH3-SCR activity and SO2/H2O resistance. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2022, 50, 1404–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.P.; Zhao, W.R.; Tang, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, H.J.; Cui, Y.L.; Gu, J.L.; Li, Y.S.; Shi, J.L. Ni-Mn bi-metal oxide catalysts for the low temperature SCR removal of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 148–149, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.R.; Yi, H.H.; Gao, F.Y.; Zhao, S.Z.; Xie, Z.L.; Tang, X.L. Evolution mechanism of transition metal in NH3-SCR reaction over Mn-based bimetallic oxide catalysts: Structure-activity relationships. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.S.; Shi, X.Y.; Yan, Z.D.; Shan, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Y.B.; He, H. Design of high-performance iron–niobium composite oxide catalysts for NH3-SCR: Insights into the interaction between Fe and Nb. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 9825–9836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, M.X.; Zhang, Z.X.; Shangguan, W.F. Efficient Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst with wide active temperature window for NH3 selective catalytic reduction of NO: Synergistic effect of isolated Fe3+ and Fe2O3. J. Catal. 2019, 378, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Y.F.; Yu, T.T.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.K.; Douthwaite, M.; Liu, J.Y.; Albilali, R.; He, C. In-depth understanding of the morphology effect of a-Fe2O3 on catalytic ethane destruction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.Z.; Li, W.H.; Liu, Z.M. Significantly enhanced catalytic performance of Fe2(SO4)3/CeO2 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 15472–15478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Chen, C.; Ma, M.; Douthwaite, M.; He, C.; Miao, J.; Chen, J.; Li, C. SO2 Promoted in situ recovery of thermally deactivated Fe2(SO4)3/TiO2 NH3-SCR catalysts: From experimental work to theoretical study. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 361, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Peng, X.B.; Yang, L.L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Y.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Au, C.T.; Jiang, L.L. Effects of cerium and tungsten addition on acid–base properties of spindle-like α-Fe2O3 in low-temperature SCR of NOx with NH3. J. Rare Earth. 2022, 40, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, S.; Liu, H.; Huang, F.; Shao, Q.H.; Liu, L.; Sun, J.; Sun, C.; Chen, D.; Dong, L. Single-atom Ce-modified α-Fe2O3 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10442–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husnain, N.; Wang, E.; Fareed, S.; Anwar, M.T. Comparision on the low-temperature NH3-SCR performance of γ-Fe2O3 catalysts prepared by two ddifferent methods. Catalysts 2019, 9, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mou, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Wei, X.; Su, D.S.; Shen, W. Rod-shaped Fe2O3 as an efficient catalyst for the selective reduction of nitrogen oxide by ammonia. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Tan, W.; An, D.; Wang, X.; Liu, A.; Zou, W.; Tang, C.; Ge, C.; Tong, Q.; Sun, J.; et al. Insight into the SO2 resistance mechanism on γ-Fe2O3 catalyst in NH3-SCR reaction: A collaborated experimental and DFT study. Appl. Catal. B 2021, 281, 119544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.F.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Ge, C.Y.; Tang, C.J.; Wan, H.Q.; Dong, L. Comparative study of different doped metal cations on the reduction, acidity, and activity of Fe9M1Ox (M = Ti4+, Ce4+/3+, Al3+) catalysts for NH3-SCR reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12101–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.X.; Lu, M.X.; Ying, T.T.; Deng, B.H.; Dai, W.L.; Luo, X.B.; Zou, J.P.; Luo, S.L. Enhancing SO2-shielding effect and Lewis acid sites for high efficiency in low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3: Reinforced electron-deficient extent of Fe3+ enabled by Ti4+ in Fe2O3. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 311, 123272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Chen, W.; Jia, X.X.; Liu, A.N.; Gao, F.; Feng, S.; Dong, L. Comprehensive understanding of the superior performance of Sm-modified Fe2O3 catalysts with regard to NO conversion and H2O/SO2 resistance in the NH3-SCR reaction. Chin. J. Catal. 2021, 42, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Xion, Z.B.; Yang, Q.G.; Zhou, F.; Lu, W.; Shi, H.C. Influence of copper doping on the low-medium NH3-SCR activity of magnetic W/Fe2O3 catalyst: Its synergetic effect of glucose dosage. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wang, R. Low-temperature NH3-SCR reaction over 3D Cu/Fe-TiO2-rGO composite catalyst synthesized by photoreduction method. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.M.; Su, H.; Chen, B.H.; Li, J.H.; Woo, S.I. Activity enhancement of WO3 modified Fe2O3 catalyst for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 299, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Ning, P.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Ma, Y.P.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhang, Q.L. Highly efficient WO3-FeOx catalysts synthesized using a novel solvent-free method for NH3-SCR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Han, L.P.; He, J.B.; Li, H.R.; Yan, T.T.; Chen, G.R.; Zhang, J.P.; Shi, L.Y.; Zhang, D.S. Improved NOx reduction in the presence of SO2 by using Fe2O3-promoted halloysite-supported CeO2–WO3 catalysts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Z.H.; Shan, W.P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; He, H. Morphology-Dependent catalytic performance of NbOx/CeO2 catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 12736–12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.L.; Zhang, S.G.; Liu, B. Effect of oxygen vacancies on ceria catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 529, 147068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Feng, X.; Li, J.L.; Liu, W.Z.; Ren, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.C. In situ deposition of 0D CeO2 quantum dots on Fe2O3-containing solid waste NH3-SCR catalyst: Enhancing redox and NH3 adsorption ability. Waste Manage. 2022, 149, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Ren, S.; Rang, J.; Liu, W.Z.; Su, Z.H.; Chen, Z.C.; Wang, M.M.; Chen, L. NH3 treatment of CeO2 nanorods catalyst for improving NH3-SCR of NO. J. Energy Inst. 2021, 98, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Seo, C.Y.; Nahata, M.; Chen, X.Y.; Li, J.H.; Schwank, J.W. Shape dependence and sulfate promotion of CeO2 for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Appl. Catal. B 2018, 232, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.; Singh, S.; Quang, M.N.; Ngo, A.B.; Brückner, A.; Armbruster, U. Insight into the properties of MnO2-Co3O4-CeO2 catalyst series for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx by C3H6 and NH3. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 784, 147394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Lin, Q.; Hu, J.; Ran, R.; Weng, D. SO2 promoted V2O5-MoO3/TiO2 catalyst for NH3-SCR of NOx at low temperatures. Appl. Catal. A 2019, 570, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.L.; Li, S.J.; Zhang, S.H.; Li, W. Phosphate on ceria with controlled active sites distribution for wide temperature NH3-SCR. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 427, 128148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Ye, J.; Yi, Z.; Luo, Z.; Cen, K. The activity and characterization of CeO2-TiO2 catalysts prepared by the sol-gel method for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 174, 734–739. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wenren, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Harding, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Tu, X.; Zhang, X.M. Plasma-enhanced low temperature NH3-SCR of NOx over a Cu-Mn/SAPO-34 catalyst under oxygen-rich conditions. Appl. Catal. B 2021, 286, 119886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Zhang, T.J.; Song, Z.X.; Liu, W.; Xing, Y. Effect of sulfate species on the performance of Ce-Fe-O catalysts in the selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2021, 49, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Li, W. NO oxidation to NO2 over manganese-cerium mixed oxides. Catal. Today 2015, 258, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Yang, R.T. Performance and kinetics study for low-temperature SCR of NO with NH3 over MnOx–CeO2 catalyst. J. Catal. 2003, 217, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Shi, J.W.; Liu, C.; Gao, C.; Fan, Z.Y.; Niu, C.M. Mn/CeO2 catalysts for SCR of NOx with NH3: Comparative study on the effect of supports on low-temperature catalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 411, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Fu, P.; Lv, D.F.; Chen, Y.; Fan, M.L.; Wu, J.L.; Meshram, A.; Mu, B.; Li, X.; Xia, Q.B. Unusual positive effect of SO2 on Mn-Ce mixed-oxide catalyst for the SCR reaction of NOx with NH3. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 127071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.X.; Wang, J.T.; Jia, X.F.; Ma, C.; Qiao, W.M.; Ling, L.C. Low-Temperature Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3 over Mn–Ce Composites Synthesized by Polymer-Assisted Deposition. ACS Omega. 2021, 6, 12801–12812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Wang, Q.L.; Zhang, J.C.; Jin, J.; Lu, S.Y.; Yan, J.H. Mechanism and Kinetics Study on Low-Temperature NH3-SCR Over Manganese–Cerium Composite Oxide Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 22763–22770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Q.; Hu, F.; Li, J.; Crittenden, J. NH3-SCR performance of WO3 blanketed CeO2 with different morphology: Balance of surface reducibility and acidity. Catal. Today 2019, 332, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Ma, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y. Excellent low-temperature NH3 -SCR of NO activity and resistance to H2O and SO2 over WaCex (a = 0.06, 0.12, 0.18, 0.24) catalysts: Key role of acidity derived from tungsten addition. Appl. Catal. A 2021, 627, 118374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Cao, J.; Yang, F.; Tan, W.; Dong, L. Morphology and Crystal-Plane Effects of CeO2 on TiO2/CeO2 Catalysts During NH3-SCR Reaction. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 12407–12419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
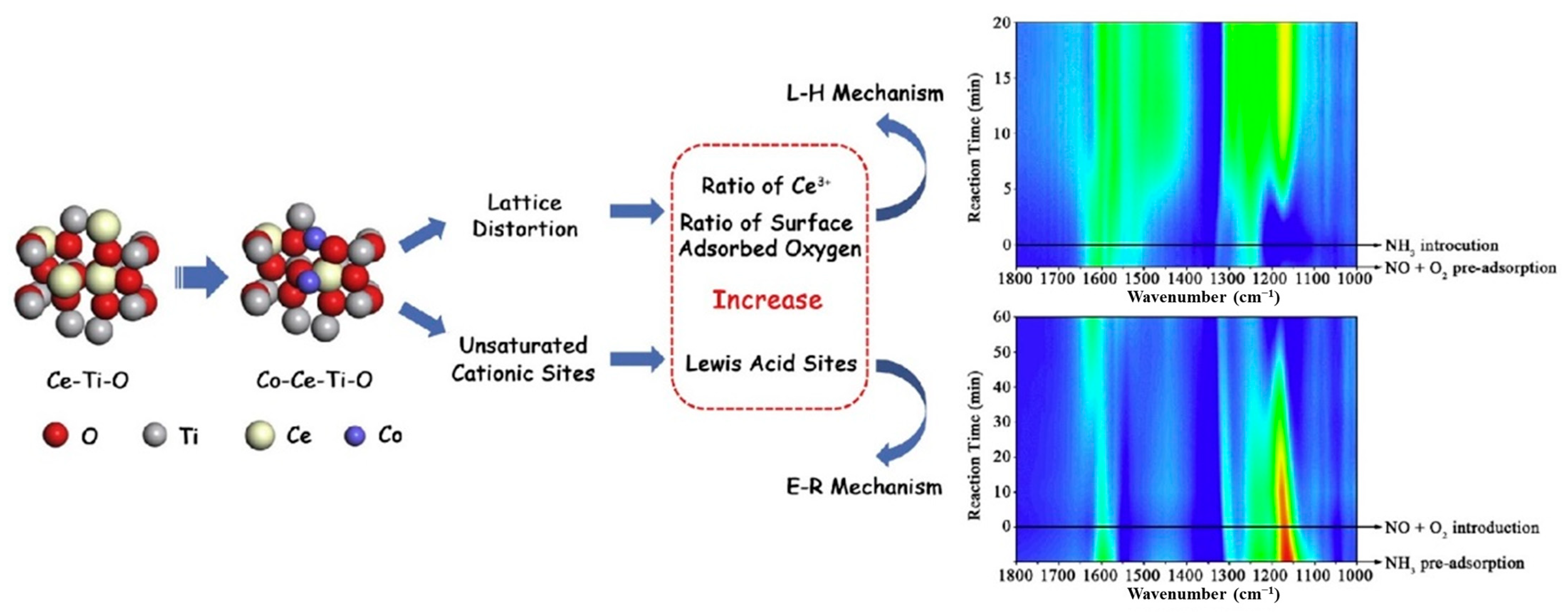
- Liu, J.; Li, X.Y.; Zhao, Q.D.; Ke, J.; Xiao, H.N.; Lv, X.J.; Liu, S.M.; Tadé, M.; Wang, S.B. Mechanistic investigation of the enhanced NH3-SCR on cobalt-decorated Ce-Ti mixed oxide: In situ FTIR analysis for structure-activity correlation. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 200, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andana, T.; Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Veyre, L.; Thieuleux, C.; Russo, N.; Fino, D.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Pirone, R. CuO nanoparticles supported by ceria for NOx-assisted soot oxidation: Insight into catalytic activity and sintering. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 216, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Wu, X.; Weng, D. Effect of barium loading on CuOx–CeO2 catalysts: NOx storage capacity, NO oxidation ability and soot oxidation activity. Catal. Today 2011, 175, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piumetti, M.; Bensaid, S.; Andana, T.; Russo, N.; Pirone, R.; Fino, D. Cerium-copper oxides prepared by solution combustion synthesis for total oxidation reactions: From powder catalysts to structured reactors. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 205, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papavasiliou, J.; Rawski, M.; Vakros, J.; Avgouropoulos, G. A novel post-synthesis modification of CuO-CeO2 catalysts: Effect on their activity for selective CO oxidation. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konsolakis, M. The role of copper–ceria interactions in catalysis science: Recent theoretical and experimental advances. Appl. Catal. B. 2016, 198, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Han, W.L.; Lu, G.X.; Lu, J.Y.; Tang, Z.C.; Zhen, X.P. Promotion of redox and stability features of doped Ce–W–Ti for NH3-SCR reaction over a wide temperature range. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 379, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.P.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.R.; Niu, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J. Effects of Nb-modified CeVO4 to form surface Ce-O-Nb bonds on improving low-temperature NH3-SCR deNOx activity and resistance to SO2 & H2O. Fuel 2023, 331, 125799. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Guo, R.T.; Li, C.F.; You, Y.H.; Pan, W.G. Recent advances in core-shell structured catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR of NOx. Chemosphere 2023, 333, 138942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, R. A CuO-V2O5/TiO2 Catalyst for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2015, 187, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Guo, R. The promotion effect of copper doping on the potassium resistance of V/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem. Pap. 2017, 71, 2253–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Shan, W.P.; Lian, Z.H.; Zhu, T.Y. Revealing the Ca resistance enhancement mechanism for the NH3−SCR reaction over VTi catalyst by CuO modification. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2022, 637, 118606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, S.; Alphin, M.S.; Sivachandiran, L.; Singh, P.; Damma, D.; Smirniotis, P.G. TiO2 -carbon nanotubes composite supported MnOx-CuO catalyst for low-temperature NH3 -SCR of NO: Investigation of SO2 and H2O tolerance. Fuel 2022, 307, 121886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, T.; Qiao, Y.J.; Dong, S.C.; Qu, Z.P. Investigation of the promotion effect of Mo doped CuO catalysts for the low-temperature performance of NH3-SCR reaction. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 5223–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.K.; Miao, J.F.; Wang, J.X.; He, C.; Chen, J.S. Facile synthesis of CuSO4/TiO2 catalysts with superior activity and SO2 tolerance for NH3-SCR: Physicochemical properties and reaction mechanism. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.M.; Ye, S.; Qu, H.X.; Guo, L.; Zhong, Q. Synergistic effect of Cu2+ doping and sulfation in Cu-Ce-S, tolerance to H2O and SO2 and decomposition behaviors of ammonia salts. Mol. Catal. 2018, 459, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.K.; Chen, C.W.; He, C.; Miao, J.F.; Chen, J.S. In situ growth synthesis of CuO@Cu-MOFs core-shell materials as novel low-temperature NH3-SCR catalysts. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zheng, R.Z.; Jia, Y.; Guo, L.N.; Huang, M.Y.; Hu, J.; Xia, Y.J. Investigation of SO2 and H2O poisoning over Cu-HPMo/TiO2 catalyst for Low temperature SCR: An experimental and DFT study. Mol. Catal. 2020, 493, 111044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, Z.M.; Shen, B.X.; Yuan, P.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Kong, W.W. An overview of the deactivation mechanism and modification methods of the SCR catalysts for denitration from marine engine exhaust. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Jin, Q.J.; Tao, X.J.; Pan, Y.C.; Gu, S.S.; Shen, Y.S. Novel W-Zr-Ox/TiO2 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 at high temperature. Catal. Today 2020, 358, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Li, Z.M.; Shen, B.X.; Yuan, P.; Wang, B.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Ma, J.; Kong, W.W. High activity of NH3-SCR at high temperature over W-Zr/ZSM-5 in the exhaust gas of diesel engine. Fuel 2022, 323, 124337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.J.; Shen, Y.S.; Ma, L.; Pan, Y.C.; Zhu, S.M.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W.; Wei, X.F.; Li, X.J. Novel TiO2 catalyst carriers with high thermostability for selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3. Catal. Today 2019, 327, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Removal Technologies of NOx | Representative Catalysts and Their Performance |
|---|---|
| SCR | V2O3-WO3/TiO2 catalysts exhibit the satisfactory catalytic performance in the medium temperature range |
| SNCR | - |
| Activated carbon adsorption | Activated carbon adsorbs low concentration NOx at temperatures below 300 °C |
| Photocatalytic degradation | Commercially available TiO2 has the excellent NO removal effect |
| Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) ozone oxidation | Al2O3 catalyst has the higher oxidation efficiency and longer lifespan |
| Catalysts | Feed Composition | GHSV (h−1) | Conversion (Corresponding Temperature Window) | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO (ppm) | NH3 (ppm) | O2 (vol%) | SO2 (ppm) | H2O (vol%) | ||||
| V2O5-Sb2O3/TiO2 monolithic catalyst | 1000 | 1000 | 5 | 1000 | 10 | 5000 | >90% (225–375 °C) | [33] |
| V1WT | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 120,000 | >90% (300–500 °C) | [36] |
| VW/Ti + Fe | 1200 | 1200 | 13 | 5%CO2 | 5.2 | 120,000 | >95% (300–400 °C) | [37] |
| 7Ce-VW/Ti | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 160,000 | 100% (250–400 °C) | [39] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 200 | 5.5 | 65% (250 °C) | |||
| 3V6Mo10CeTi | 1000 | 1000 | 8 | - | - | 30,000 | 97% (200 °C) | [40] |
| SbV10Ce/TiO2 | 800 | 800 | 3 | - | - | 60,000 | >90% (220–450 °C) | [42] |
| 800 | 800 | 3 | 800 | 6 | >85% (220–500 °C) | |||
| VWTCZ | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 60,000 | >97% (300–400 °C) | [43] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 100 | 5 | 75% (350 °C) | |||
| VWTS | 500 | 500 | 5 | 10 | 100,000 | >80% (350–550 °C) | [45] | |
| VWTSi10-550 °C | 500 | 500 | 5 | 300 mL min−1 | >80% (205–520 °C) | [46] | ||
| Catalysts | Feed Composition | GHSV (h−1) | Conversion (Corresponding Temperature Window) | Ref. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO (ppm) | NH3 (ppm) | O2 (vol%) | SO2 (ppm) | H2O (vol%) | ||||
| 6FeSCe | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 118,000 | >90% (300–450 °C) | [77] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 50 | 5 | 85% (300 °C) | |||
| FeTi | 500 | 500 | 4 | 60,000 | >90% (350–450 °C) | [78] | ||
| Fe0.93Ce0.07Ox | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 90,000 | >95% (175–325 °C) | [80] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 200 | 5 | 93% (250 °C) | |||
| γ-Fe2O3-FM | 500 | 500 | 3 | - | - | 30,000 | 96% (230 °C) | [81] |
| 500 | 500 | 3 | 300 | 79% (230 °C) | ||||
| Fe9Ti1Ox | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 60,000 | >80% (150–350 °C) | [84] |
| Fe0.94Sm0.06Ox | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 60,000 | >95% (175–325 °C) | [86] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 200 | 5 | 85% (250 °C) | |||
| 10W/Fe | 500 | 500 | 5 | - | - | 100,000 | >90% (275–425 °C) | [89] |
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 50 | 5 | 90% (350 °C) | |||
| 0.3W-Fe | 600 | 600 | 5 | 60,000 | 100% (250–500 °C) | [90] | ||
| 600 | 600 | 5 | 100 | 10 | 90% (250 °C) | |||
| Fe(4)@CeW/H | 500 | 500 | 5 | 40,000 | >96% (270–420 °C) | [91] | ||
| 500 | 500 | 5 | 100 | 8 | 82% (300 °C) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhou, S.; You, M.; Yu, D.; Zhang, C.; Gao, S.; Yu, X.; Zhao, Z. Research Progress on Metal Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071086
Wang L, Zhou S, You M, Yu D, Zhang C, Gao S, Yu X, Zhao Z. Research Progress on Metal Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia. Catalysts. 2023; 13(7):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071086
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lanyi, Shengran Zhou, Mengxia You, Di Yu, Chunlei Zhang, Siyu Gao, Xuehua Yu, and Zhen Zhao. 2023. "Research Progress on Metal Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia" Catalysts 13, no. 7: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071086
APA StyleWang, L., Zhou, S., You, M., Yu, D., Zhang, C., Gao, S., Yu, X., & Zhao, Z. (2023). Research Progress on Metal Oxides for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with Ammonia. Catalysts, 13(7), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13071086









