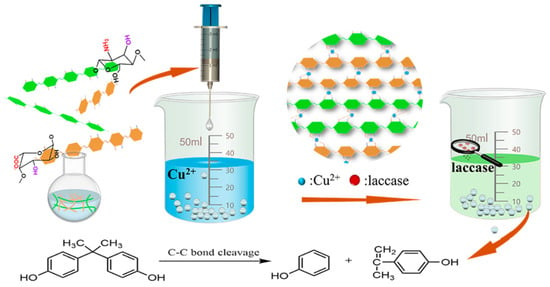
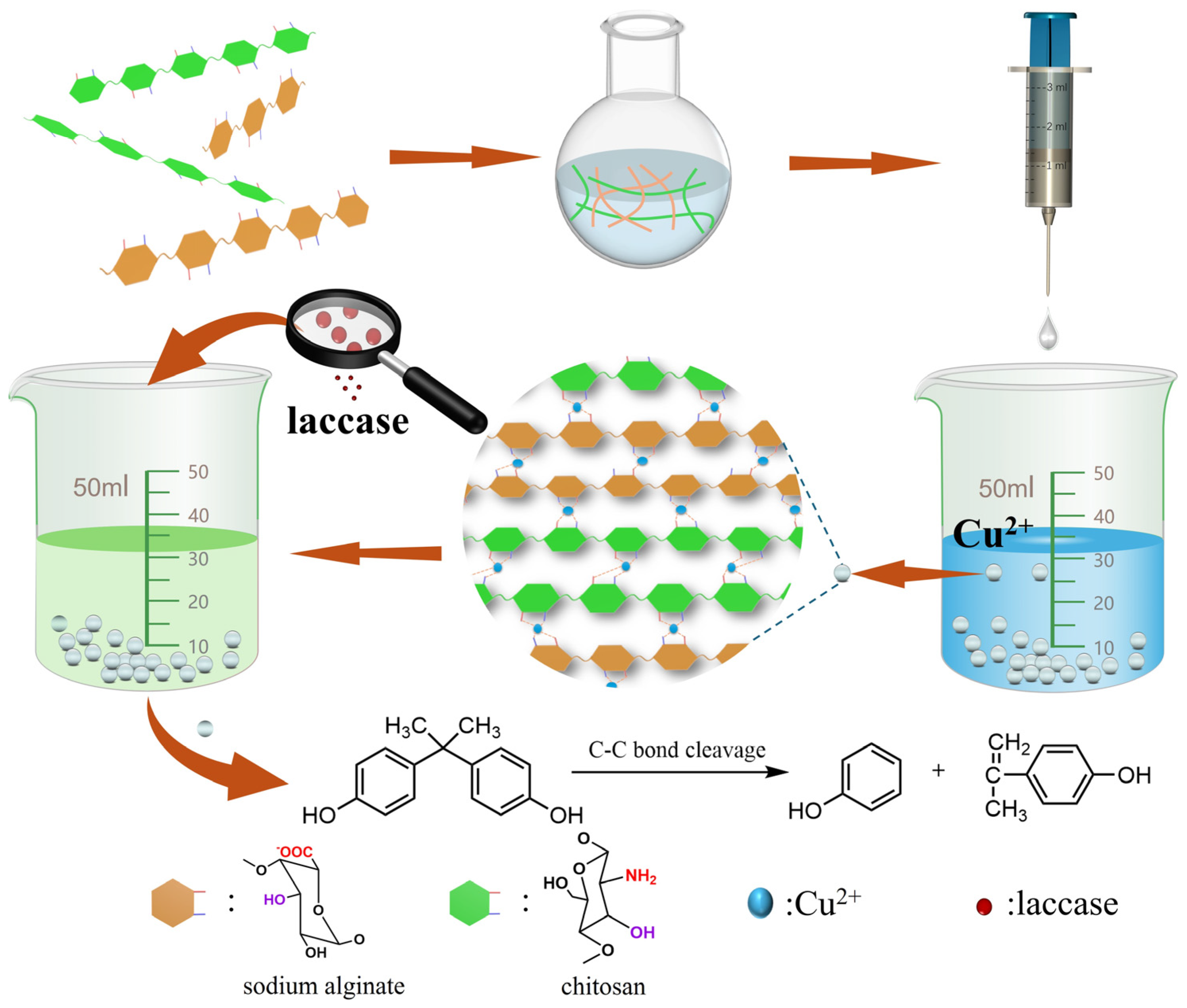
Functionalized Chitosan and Alginate Composite Hydrogel-Immobilized Laccase with Sustainable Biocatalysts for the Effective Removal of Organic Pollutant Bisphenol A
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
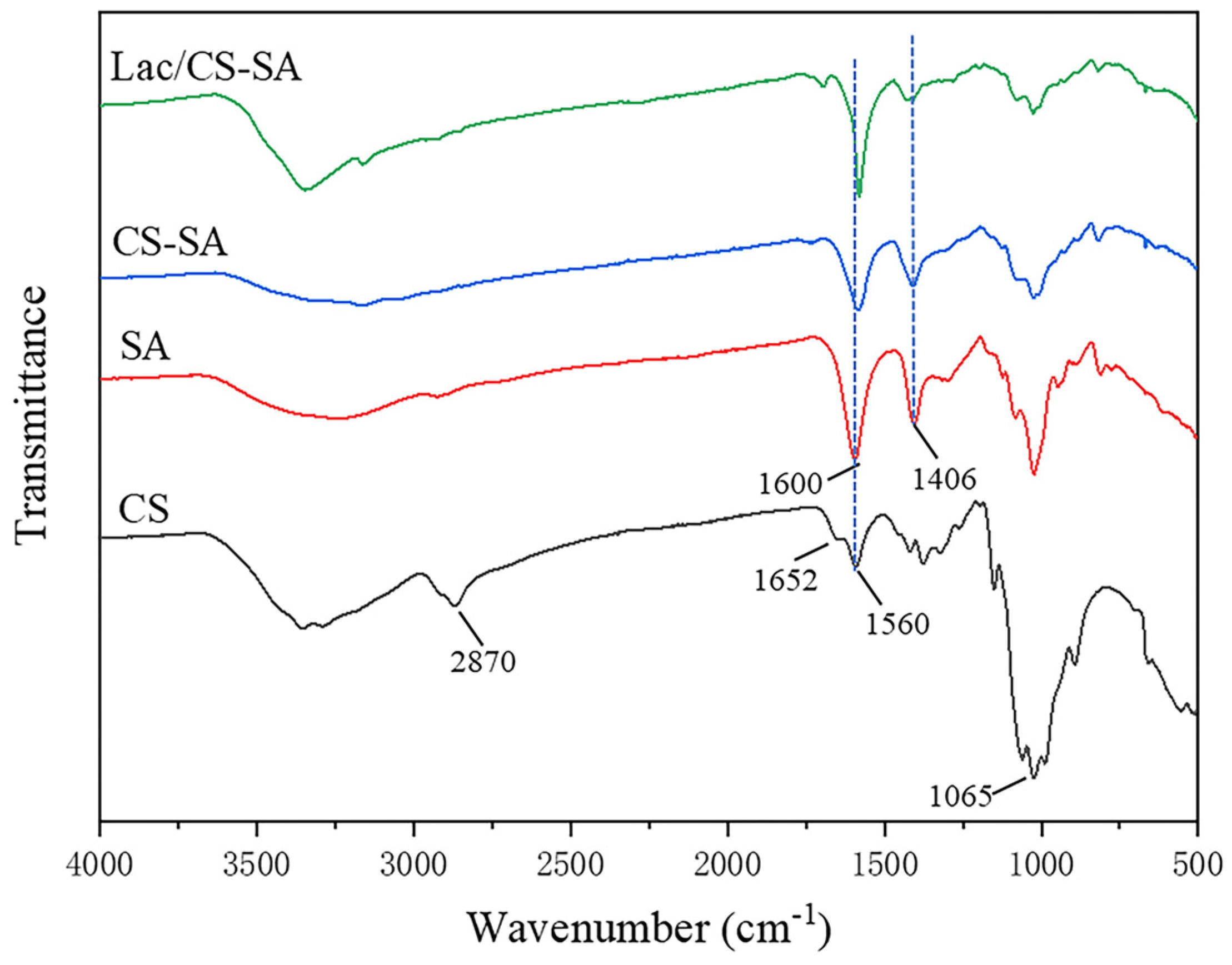
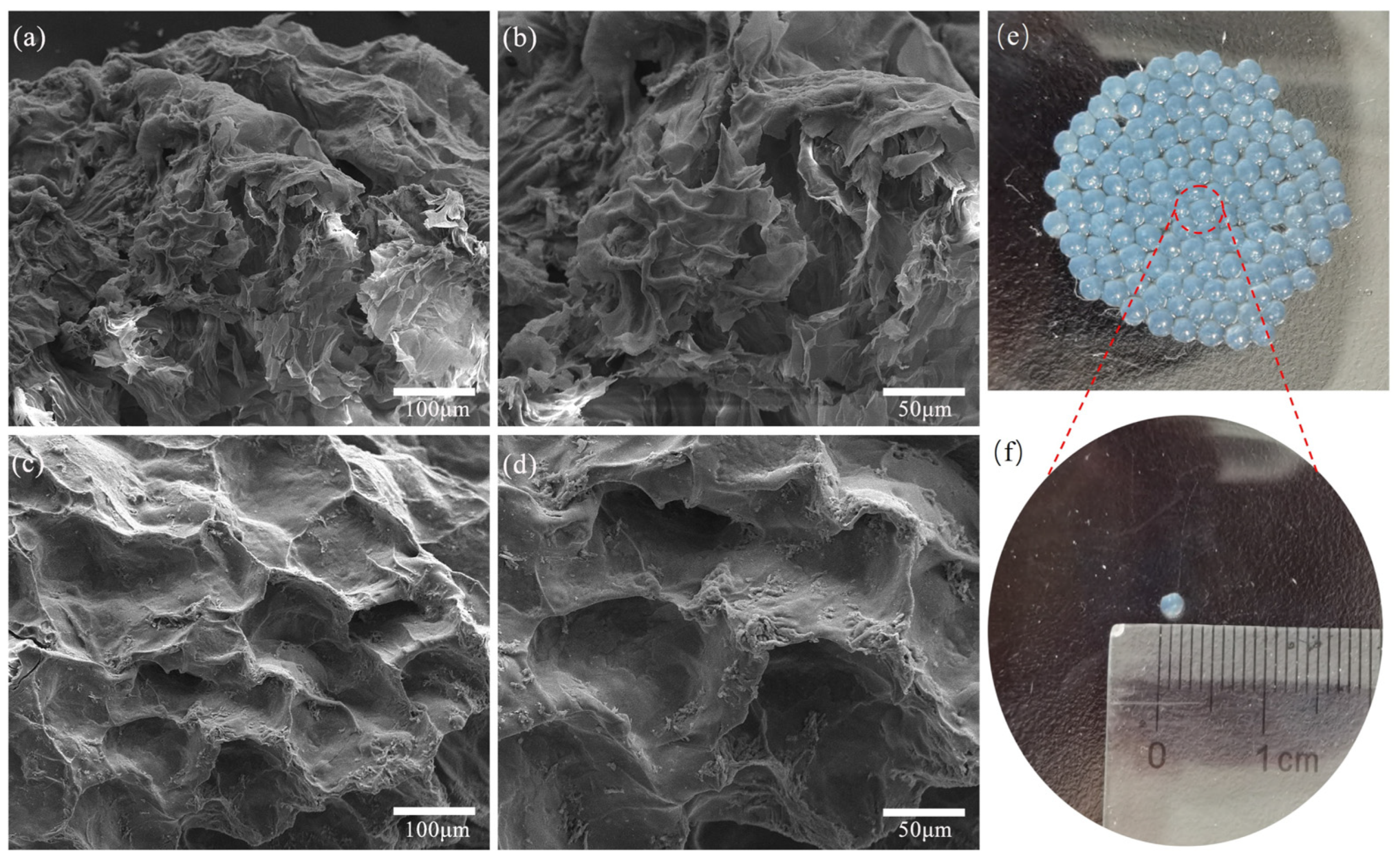
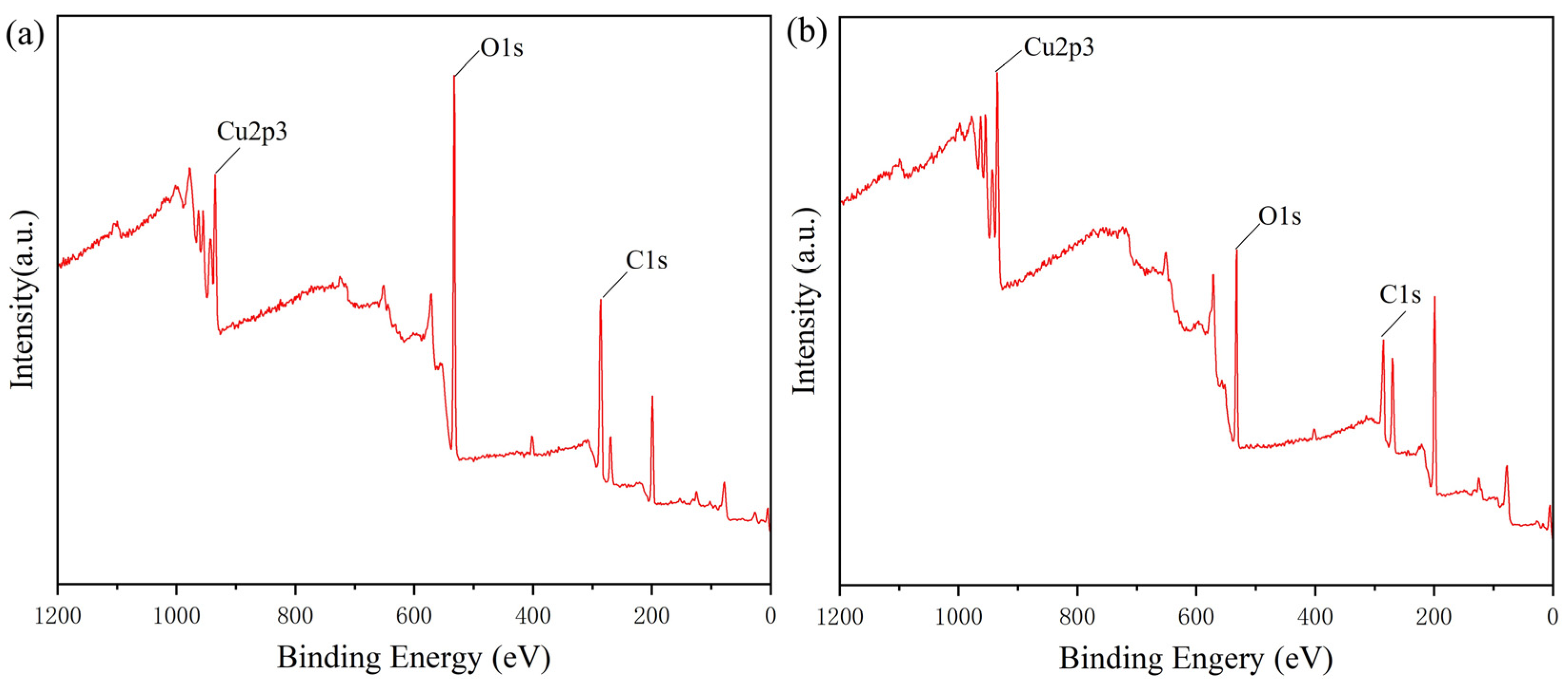
2.1. Characterization of CS-SA Beads and Lac/CS-SA Beads
2.2. Effect of Initial Concentration of Enzyme on Laccase Immobilization Process
2.3. Michaelis–Menten Kinetics Analysis
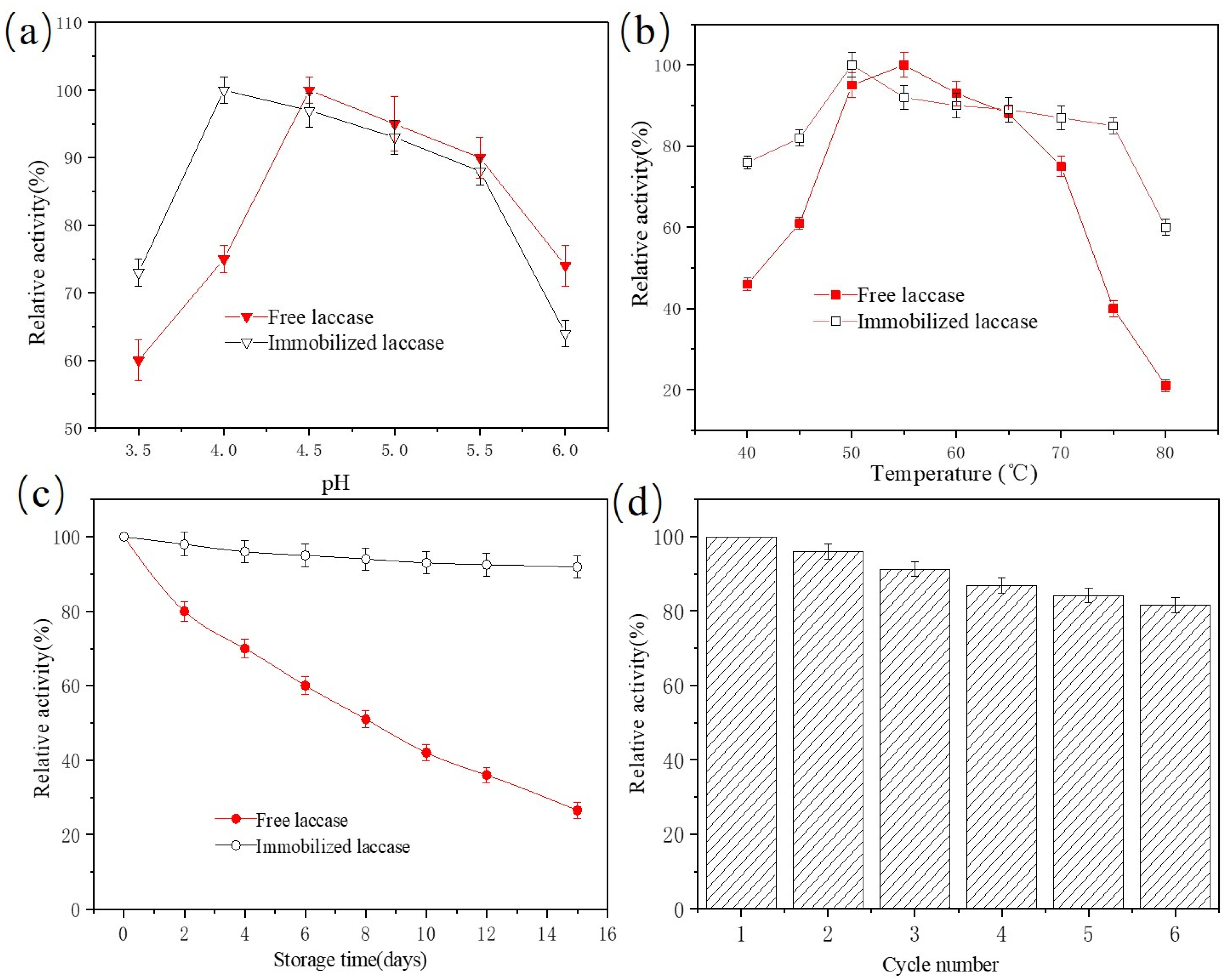
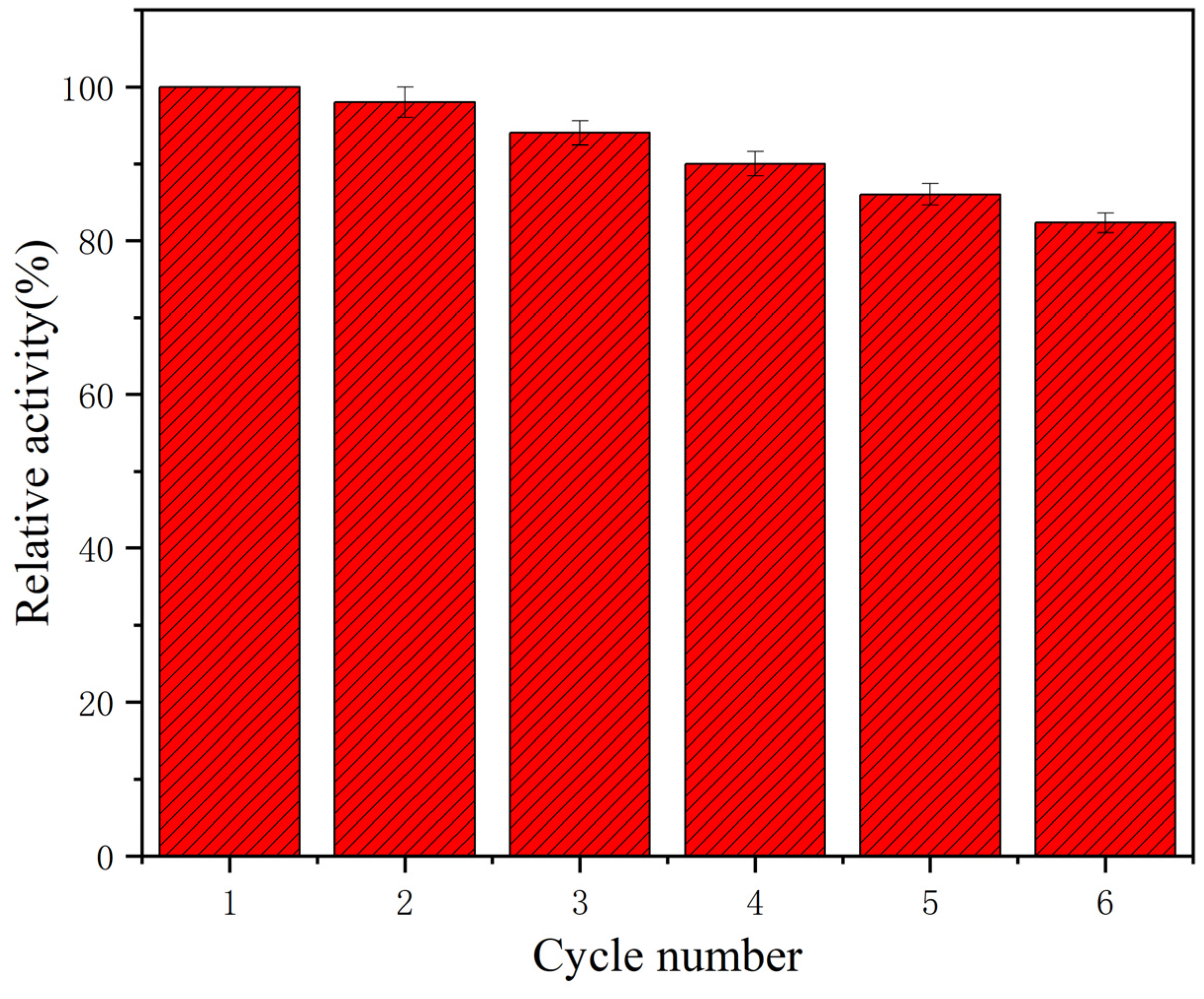
2.4. Stability and Reusability of Immobilized Laccase
2.5. Effects of pH, Temperature, and Initial Concentration on BPA Removal
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Lac/CS-SA Hydrogel Beads
3.3. Characterization of CS-SA Hydrogel Beads and Lac/CS-SA Hydrogel Beads
3.4. Measurements of Free and Immobilized Enzyme Activities and Kinetic Parameters
3.5. pH, Thermal and Storage Stability, and Reusability of Free and Immobilized Laccases
3.6. Removal of Environmental Pollutant Bisphenol A
3.7. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Z.-M.; Oh, W.-D.; Yap, P.-S. Recent advances in the utilization of immobilized laccase for the degradation of phenolic compounds in aqueous solutions: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135824–135847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios-Estrada, C.; Rostro-Alanis, M.-D.J.; Parra, A.-L.; Belleville, M.-P.; Sanchez-Marcano, J.; Iqbal, H.-M.-N.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Potentialities of active membranes with immobilized laccase for Bisphenol A degradation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tan, L.-R.; Hagedoorn, P.-L.; Wang, R.-Q.; Wen, L.; Wu, S.-W.; Tan, X.-M.; Xu, H.; Zhou, X. Micro-nano bubbles assisted laccase for biocatalytic degradation of bisphenols. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 48, 102880–102896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, J.-Z.; Huang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.-B.; Bi, L.; Ma, C.-Y.; Song, M.-Y.; Jiang, G.-B. Spatial nanopores promote laccase degradation of bisphenol A and its analogs. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166429–166445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-B.; Yuan, F.; Jia, S.-G.; Zhang, X.-K.; Xing, W.-H. Laccase encapsulation immobilized in mesoporous ZIF-8 for enhancement bisphenol A degradation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130460–130489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, M.-Y.; Zou, D.-L.; Yang, Y.-S.; Ren, X.-H.; Qin, C.-Y.; Piao, Y.-X. Multi-Functional Laccase Immobilized Hydrogel Microparticles for Efficient Removal of Bisphenol A. Materials. 2019, 12, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.-T.; Zhang, W.-X.; Cai, Y.-P. Laccase Immobilization for Water Purification: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 403, 126272–126296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Veena, R.; Samuel, M.-S.; Selvarajan, E. Immobilization of laccases and applications for the detection and remediation of pollutants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 19, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Yu, Z.-J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.-J.; Jiang, L.; Xu, C.; Xian, M. Application of Laccase Catalysis in Bond Formation and Breakage: A Review. Catalysts 2023, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, H.; Penninckx, M.; Frédéric, D. Product formation from phenolic compounds removal by laccases: A review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.; Meyer, L.-E.; Kara, S. Enzyme immobilization in hydrogels: A perfect liaison for efficient and sustainable biocatalysis. Eng. Life. Sci. 2021, 22, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santis, P.-D.; Meyer, L.-K.; Kara, S. The rise of continuous flow biocatalysis–fundamentals, very recent developments and future perspectives. React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 5, 2155–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, L.-E.; Horváth, D.; Vaupel, S.; Meyer, J.; Alcalde, M.; Kara, S. A 3D printable synthetic hydrogel as an immobilization matrix for continuous synthesis with fungal peroxygenases. React. Chem. Eng. 2023, 8, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraj, B.; Solomon, P.-R. Immobilization of Lipases—A Review. Part I: Enzyme Immobilization. ChemBioEng Rev. 2019, 6, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-P.; Xiong, L.-K.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Yuan, X.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.-Y. Bio-functional electrospun nanomaterials: From topology design to biological applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 91, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahdev, A.-K.; Raorane, C.-J.; Shastri, D.; Raj, V.; Singh, A.; Kim, S.-C. Update on modified chitosan frameworks and their applications for food, wastewater, toxic heavy metals, dyes treatment and cancer drug delivery. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108656–108669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliadi, E.; Xenakis, A.; Zoumpanioti, M. Chitosan hydrogels: A new and simple matrix for lipase catalysed biosynthesis. Mol. Catal. 2018, 445, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, J.; Zhong, L.; Du, Y.-M. Immobilization of a protease on modified chitosan beads for the depolymerization of chitosan. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2697–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, F.; Ariaeenejad, S.; Ghollasi, M.; Motamedi, E. Synthesis of two novel bio-based hydrogels using sodium alginate and chitosan and their proficiency in physical immobilization of enzymes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2072–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia, P.; Bernal, C.; Wilson, L.; Illanes, A. Use of chitosan heterofunctionality for enzyme immobilization: β-galactosidase immobilization for galacto-oligosaccharide synthesis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 116, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, M.; Ayad, D.-M.; Wei, Y.; Sarhan, A.-A. Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase on modified chitosan beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 46, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Jing, Z.-X.; Ma, R.; Wan, X.-W.; Liu, J.; Huang, W.-T. A critical review of enzymes immobilized on chitosan composites: Characterization and applications. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2023, 46, 1539–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.-B.; Xu, Y.; Yu, X.-W. Formation lipase cross-linked enzyme aggregates on octyl-modified mesocellular foams with oxidized sodium alginate. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110501–110518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurayama, F.; Bahadur, N.-M.; Furusawa, T.; Sato, M.; Suzuki, N. Facile preparation of aminosilane-alginate hybrid beads for enzyme immobilization: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 150, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Xiao, W.-Q.; Gao, Z.-M.; Hu, B.; Jiang, W.-X.; Li, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Ni, X.-W. Modulating in vitro fecal fermentation behavior of sodium alginate by Ca2+ cross-linking. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113552–113560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Fang, Y.-R.; Chen, K.-Z.; Wu, M.; Zhang, W.-C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, D.-W.; Gao, J.-Q.; Li, H.-G.; Lv, J.-H.; et al. Tudy of double network hydrogels based on sodium methacrylate alginate and carboxymethyl chitosan. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 194, 112137–112146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.-M.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.-P. Advances on methods and easy separated support materials for enzymes immobilization. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 102, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, A.-M.; Quattrocchi, L.; Scuto, F.-R. Silica-chitosan hybrid support for laccase immobilization. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 318, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Chi, C.; Li, F.; Zhang, B. Laccase-polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous membrane: Highly immobilized, stable, reusable, andefficacious for 2,4,6-trichlorophenol removal. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 12554–12560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Li, W.; Hu, Y. Laccase immobilized on magnetic nanoparticles modified by amino-functionalized ionicliquid via dialdehyde starch for phenolic compounds biodegradation. Chem Eng. J. 2020, 391, 123564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Coronel, L.-A.; Cobas, M.; Rostro-Alanis, M.-D.J.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Hernandez-Luna, C.; Pazos, M.; Sanromán, M.-Á. Immobilization of laccase of Pycnoporus sanguineus CS43. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, A.-A.; Jang, J.; Jee, S.-C.; Sung, J.-S.; Lee, D.-S. Chitosan-functionalized supermagnetic halloysite nanotubes for covalent laccase immobilization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 194, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Q.; Chen, T.-H.; Xu, L.; Lin, J. Immobilization of laccase on magnetic nanoparticles for enhanced polymerization of phenols. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2024, 172, 110331–110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.-K.-S.; Kalia, V.-C.; Lee, J.-K. Laccase Immobilization on Copper-Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Bisphenol Degradation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.-H.; Xue, P.; Jia, F.; Shi, K. Co-immobilization of laccase and ABTS onto novel dual-functionalized cellulose beads for highly improved biodegradation of indole. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 118–124. [Google Scholar]

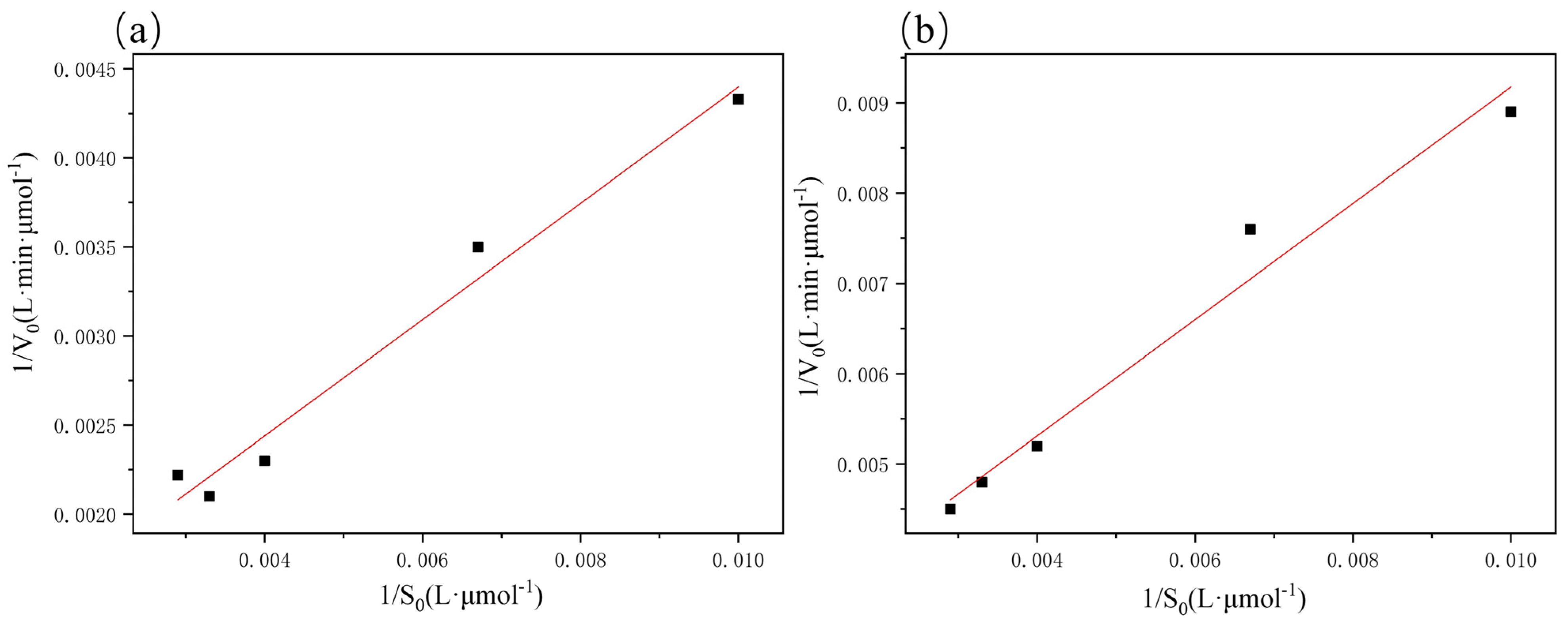

| Samples | R2 | kcat (s−1) | Km (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free laccase | 0.9697 | 0.589 | 288.85 |
| Immobilized laccase | 0.9643 | 0.243 | 234.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Zeng, X.; Ren, B. Functionalized Chitosan and Alginate Composite Hydrogel-Immobilized Laccase with Sustainable Biocatalysts for the Effective Removal of Organic Pollutant Bisphenol A. Catalysts 2024, 14, 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14050304
Zhang H, Zhang X, Wang L, Wang B, Zeng X, Ren B. Functionalized Chitosan and Alginate Composite Hydrogel-Immobilized Laccase with Sustainable Biocatalysts for the Effective Removal of Organic Pollutant Bisphenol A. Catalysts. 2024; 14(5):304. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14050304
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hong, Xin Zhang, Lei Wang, Bo Wang, Xu Zeng, and Bo Ren. 2024. "Functionalized Chitosan and Alginate Composite Hydrogel-Immobilized Laccase with Sustainable Biocatalysts for the Effective Removal of Organic Pollutant Bisphenol A" Catalysts 14, no. 5: 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14050304
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhang, X., Wang, L., Wang, B., Zeng, X., & Ren, B. (2024). Functionalized Chitosan and Alginate Composite Hydrogel-Immobilized Laccase with Sustainable Biocatalysts for the Effective Removal of Organic Pollutant Bisphenol A. Catalysts, 14(5), 304. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal14050304