Abstract
Electrochemical water splitting is a viable solution for producing clean energy sources. However, the sluggish reaction kinetics and high overpotential restrict their further application in large-scale hydrogen generation. In this work, we prepared NiFeP catalysts by a hydrothermal reaction and phosphorization treatment and studied the effect of the reaction temperature on the morphology and properties of the samples. The prepared NiFeP-140 samples possess a specific surface area of 25.13 m2g−1, which provides many active sites for the electrochemical reaction. They show an overpotential of 93 mV at 10 mA cm−2 for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and 233 mV @ 50 mA cm−2 for oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Also, the samples show Tafel slopes of 79.24 mV dec−1 (HER) and 80.73 mV dec−1 (OER). This facile strategy can be extended to prepare other transition-metal electrocatalysts.
1. Introduction
With the acceleration of industrialization, people face the dual challenges of environmental pollution and energy dilemma [1]. To resolve these issues, it is imperative to design and develop some renewable and clean energy sources, such as solar, hydrogen, tidal and geothermal energy [2,3]. Hydrogen is recognized as a potential sustainable energy option due to its characteristics of high energy density and zero carbon emission [4]. It produces no harmful greenhouse gases or other pollutants during its utilization [5]. Hydrogen possesses a broad application prospect in fuel cells and hydrogen internal combustion engines to provide power for transportation. Also, hydrogen as an energy storage medium can solve the problems of intermittency and instability. In addition, it serves as an industrial raw material in petroleum, chemical, metallurgy, electronics and medical fields [6]. With technological advances and cost reductions, hydrogen is expected to account for a large share of the future energy ratio [7]. Despite hydrogen possessing enormous potential, its large-scale application still encounters some challenges because of its production efficiency.
Hydrogen can be obtained by a variety of routes, including natural gas, coal and water electrolysis and so on [8]. Hydrogen production from electrolyzed water consumes less energy than other routes. Meanwhile, it is widely studied due to its high purity product and lack of carbon emission [9]. Water splitting consists of two half-reactions, the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) at the anode and the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) at the cathode [10]. The OER possesses a complex four-electron transfer process, and the sluggish kinetics affects the efficiency of the reaction [11,12]. At present, IrO2 (313 mV at 50 mA cm−2 for OER) and Pt/C (38.7 mV at 10 mA cm−2 for HER) are the main metal catalysts with significant applications in electrocatalytic fields [13]. They have been widely investigated and utilized for their excellent physicochemical properties [14]. IrO2 can maintain outstanding activity in catalysis process due to its high conductivity and stability [15]. The activity of Pt/C derives from its large specific surface area and favorable electronic conductivity [16]. Carbon carriers provide a conductive platform for uniform dispersion of Pt particles [17]. However, their applications are largely limited by inferior stability and scarce reserves. Also, precious metal catalysts are sensitive to toxic substances such as chlorides and sulfides, which can lead to catalyst degradation or deactivation [18]. Therefore, it is essential to design some low-cost and high-efficiency electrocatalysts.
Compared to precious metals, many transition metals are abundant and low-cost, which facilitates large-scale production. Meanwhile, they possess outstanding thermal and chemical stability which can maintain their catalytic properties in different temperatures and chemical environments. Transition metal compounds such as iron, cobalt [19], nickel and molybdenum [20] possess excellent catalytic activity. Their catalytic capability can be improved by changing their chemical composition, crystal structure and surface properties [21]. In this regard, NiFe-layered double hydroxides (NiFe-LDH) demonstrate excellent OER catalytic capacity in alkaline conditions [22]. However, their lack of activity in the HER process leads to high overpotential for overall water splitting [23]. Phosphorus in transition-metal phosphides is widely regarded as an active site that can improve catalytic performance [24,25]. The interaction between a P atom and metal can change the electronic structure to obtain the desired properties [26]. Therefore, one can improve the HER catalytic performance of NiFe catalysts by phosphide treatment. Many researchers have reported the catalytic properties of nickel–iron phosphides. For example, Hu and his coworkers reported a porous amorphous NiFeOx/NiFeP framework that achieves a current density of 10 mA cm−2 at an overpotential of 319 mV [27]. Chen et al. prepared N, P double-doped FeNiP nanoparticles with an overpotential of 280 mV at 10 mA cm−2 for OER [28]. Yang and colleagues synthesized nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes encapsulated with NiFeP nanoparticles with an overpotential of 180 mV for HER [29]. In previous work, we prepared a bifunctional NiCoP electrocatalyst that demonstrates an overpotential of 84 mV @ 10 mA cm−2 and a Tafel slope of 75.74 mV/dec−1 in HER [30]. Although some progress has been achieved, much work is still required to optimize the catalytic activity of electrocatalysts.
In this work, we designed NiFeP catalysts by a hydrothermal reaction and subsequent phosphating process. The NiFeP-140 samples show an overpotential of 93 mV @10 mA cm−2 with a Tafel slope of 79.24 mV dec−1 for HER. Also, they serve as a catalyst for OER with an overpotential of 233 mV at 50 mA cm−2 and a Tafel slope of 80.73 mV dec−1. In the two-electrode system, the prepared samples obtain a cell voltage of 1.66 V at 50 mA cm−2. Moreover, there is no significant performance degradation after multi-step chronoamperometric characterization.
2. Results and Discussion
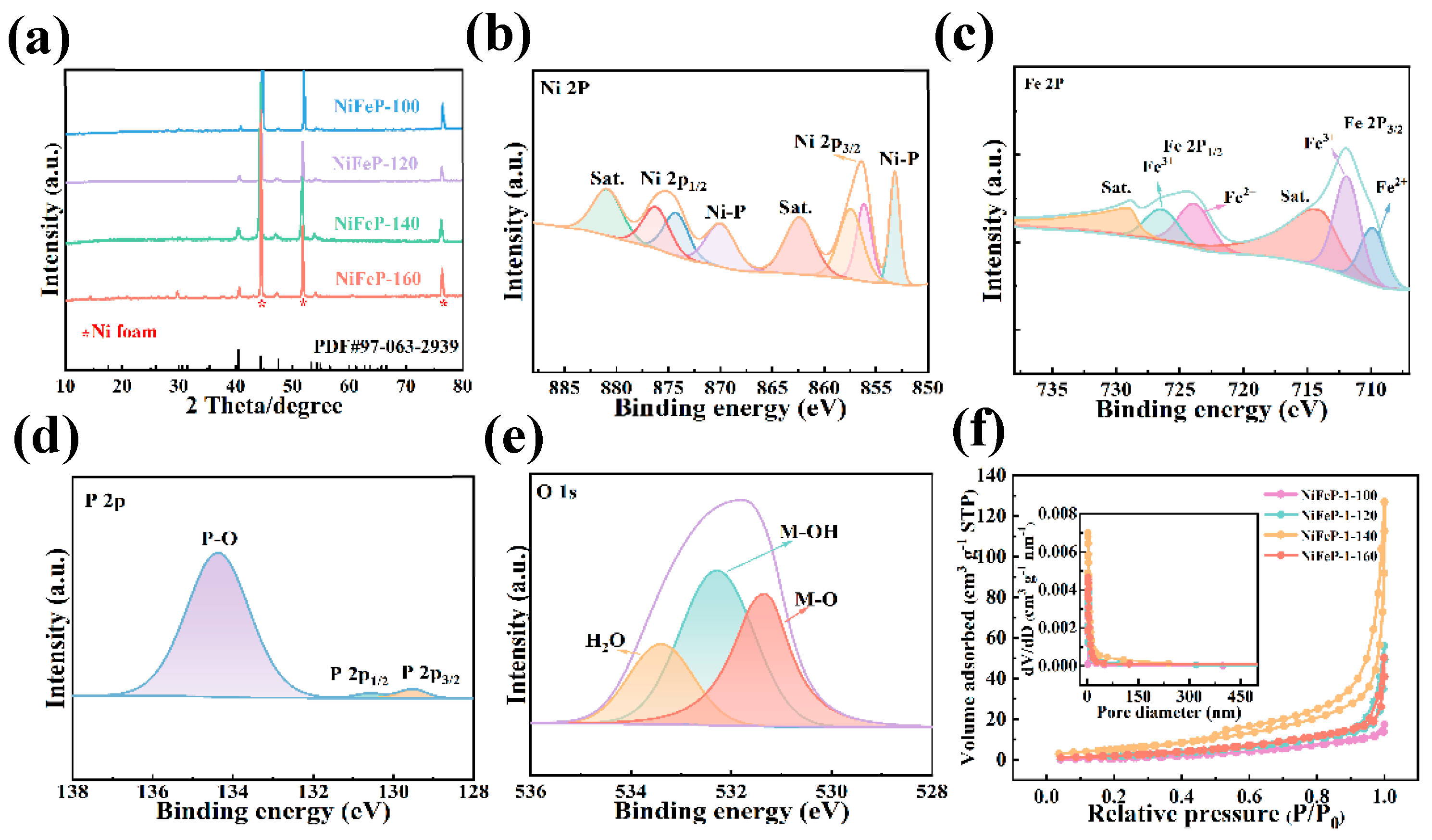
Firstly, we investigated the crystal structure of the samples by X-ray diffraction (XRD). Figure 1a shows that the diffraction peaks at 2θ values of 44.3, 51.6 and 76.1 are indexed to the (111), (200) and (220) crystal faces of nickel foam (NF). The (111), (201) and (210) crystal faces of NiFeP correspond 2θ values of 40.4, 44.4 and 46.9, respectively. Moreover, the NiFeP-140 sample does not exhibit other additional peaks, indicating its high crystallinity. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed to study the element composition and chemical states of the samples. The peaks at 856.4 eV and 875.2 eV binding energies are attributed to Ni 2p3/2 and Ni 2p1/2, respectively [31]. Meanwhile, the peaks at 862.7 eV and 880.9 eV correspond to typical satellite peaks of Ni 2p3/2 and Ni 2p1/2 [32]. Furthermore, the appearance of the peaks at 853.2 eV and 870.1 eV is ascribed to the Ni-P bonds generated by the phosphating treatment (Figure 1b) [2]. By fitting the Ni 2p peak, it can be concluded that Ni atoms possess the valence states of Ni2+ and Ni3+ [33]. In Figure 1c, the peaks of Fe2+ 2p3/2 and Fe2+ 2p1/2 are found at positions 709.9 eV and 723.9 eV [34]. The 711.9 eV and 726.5 eV binding energies are associated with the Fe3+ 2p3/2 and Fe3+ 2p1/2 orbitals [35]. Moreover, the satellite peaks of Fe are assigned to 713.9 eV and 729.1 eV [36]. The characteristic peaks of metal–P bonding occur at 129.5 eV and 130.6 eV (Figure 1d) [25]. In Figure 1e, the binding energy at 531.3 eV, 532.8 eV and 533.4 eV is attributed to the metal–oxygen bond, hydroxides and surface-adsorbed H2O, respectively [23,37]. Figure 1f illustrates the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of the prepared samples. A typical type IV isotherm is observed, indicating that the sample possesses a dense porous structure with wide pore size distribution. The NiFeP-140 catalyst shows a specific surface area of 25.13 m2/g, which is larger than NiFeP-100 (19.41 m2/g), NiFeP-120 (12.49 m2/g) and NiFeP-160 (14.64 m2/g). The NiFeP-140 sample possesses a large total pore volume of 0.206 cm3 g−1 compared to the other samples. The results show that NiFeP-140 samples have more exposed active sites.
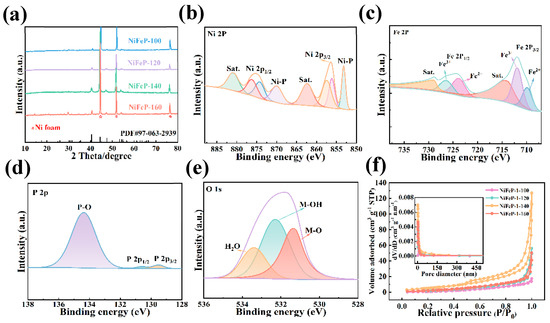
Figure 1.
Structural characterization. (a) XRD patterns. (b) XPS survey spectrum of Ni 2p. (c) Fe 2p. (d) P 2p. (e) O 1s. (f) The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms of the samples. The inset presents the pore size distribution curves.
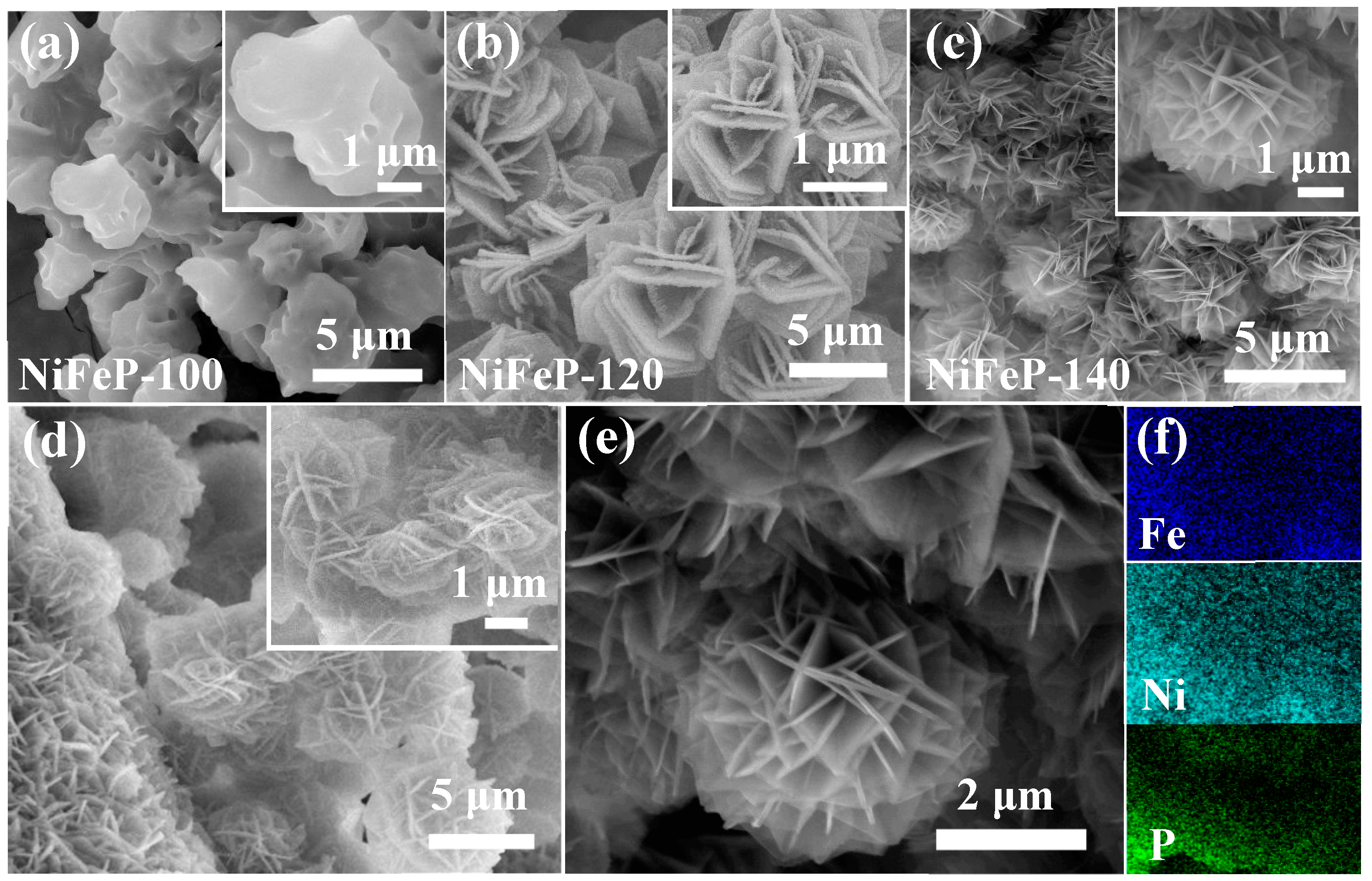
We then studied the growth process of NiFeP samples by controlling the reaction temperature. From Figure 2a–d, when the temperature is from 100 °C to 120 °C, it is observed that the samples present rough, lamellar structures. As the temperature increases to 140 °C, spherical structures are assembled by nanosheets grown on the surface of the NF. This structure facilitates the exposure of active sites in the catalytic process [38]. With the reaction temperature further increasing to 160 °C, the spherical structure collapses owning to the high temperature. Therefore, the morphology of NiFeP materials is closely related to the reaction temperature. Figure 2e shows high-magnification scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of single sphere. The corresponding elemental mappings (Figure 2f) confirm that the three elements (Ni, Fe and P) are uniformly distributed in the sample.

Figure 2.
Morphology characterization. SEM images of the nanospherical structure of (a) NiFe-100; (b) NiFe-120; (c) NiFeP-140; (d) NiFe-160 and (e) NiFeP-140. (f) Corresponding EDX elemental mappings.
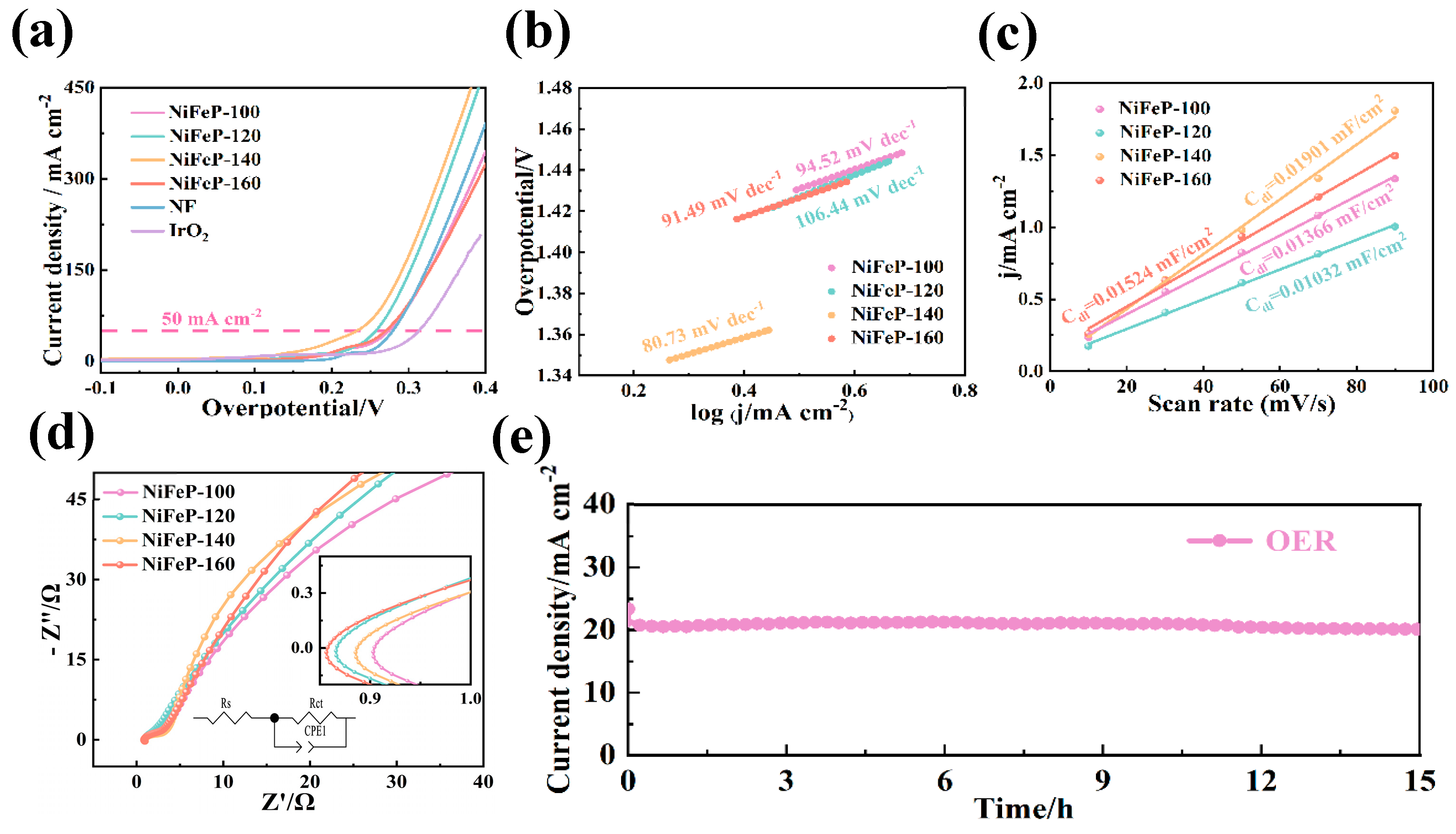
After that, the OER properties of the samples were evaluated by a three-electrode system. From Figure 3a, the overpotential (233 mV @ 50 mA cm−2) of the NiFeP-140 sample is lower than that of NiFeP-100 (274 mV), NiFeP-120 (257 mV) and NiFeP-160 (270 mV) samples. Low overpotential means that the catalyst can promote electrochemical reactions at lower voltages [39]. The Tafel slope is an important metric for electrochemical characterization, it can be divided into four steps as follows in alkaline solution [40]:
* + OH− → OH* + e−
OH* + OH− → O* + e− + H2O
O* + OH− → OOH* + e−
OOH* + OH− → * + O2 + H2O + e−
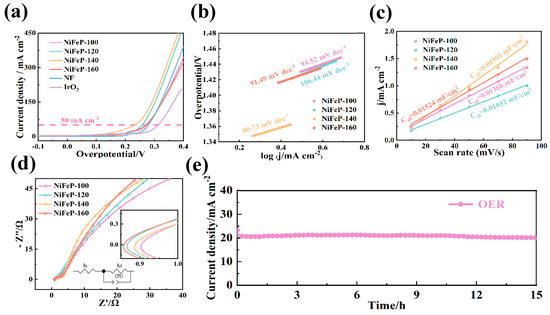
Figure 3.
(a) OER LSV curves. (b) OER Tafel plots. (c) The Cdl at the non-faradaic potential window for OER. (d) Nyquist plots for OER. (e) OER chronoamperometric curves.
Figure 3b shows that NiFeP-140 samples possess a Tafel slope of 80.73 mV dec−1. The small Tafel slope is a direct reflection of the fast reaction kinetics and strong catalytic activity of the electrocatalyst. This indicates that it can achieve efficient charge transfer with a low overpotential in the electrochemical process. The improvement in OER properties is attributed to the synergistic effect between Ni atoms and Fe atoms, which accelerates the conversion from FeP to FeOOH [41].
In addition, the catalytic ability of NiFeP-140 was further explored by EISs. It is obtained by the following formula [42]:
where Rct refers to the charge transfer resistance and Rs represents the internal resistance of the solution. ω is the frequency, and σw represents the Warburg impedance coefficient. It shows the low charge transfer resistance (2.3 Ω) of the catalysts (Figure 3c, Table 1), proving that the NiFeP-140 sample possesses a fast charge transfer rate. Electrochemical double-layer capacitance (Cdl) is imperative in studying active sites of materials. Cdl is determined by the current through the sample (Ic) and the scan rate (v) [43]:
Z = Rs + Rct + σwω−1/2
Ic = ν·Cdl

Table 1.
Charge transfer resistance and solution resistance of the OER for the sample.
Also, we can obtain the electrochemically active surface area (ECSA) from the relationship between Cdl and specific capacitance (Cs), which is observed through the following equation [43]:
ECSA = Cdl/Cs
The NiFeP-140 sample presents a value of 0.03816 mF cm−2 (Figure 3d), which is superior to those of NiFeP-100 (0.03617 mF cm−2), NiFeP-120 (0.01971 mF cm−2) and NiFeP-160 (0.02191 mF cm−2). This demonstrates that the NiFeP material possesses a large specific surface area at the reaction temperature of 140 °C. The large specific surface area increases the density of highly active sites and increases the electrochemical activity on the material surface. From Figure 3e, no significant drop in voltage plateau can be observed after 15 h of cycling, demonstrating the superior stability of the sample.
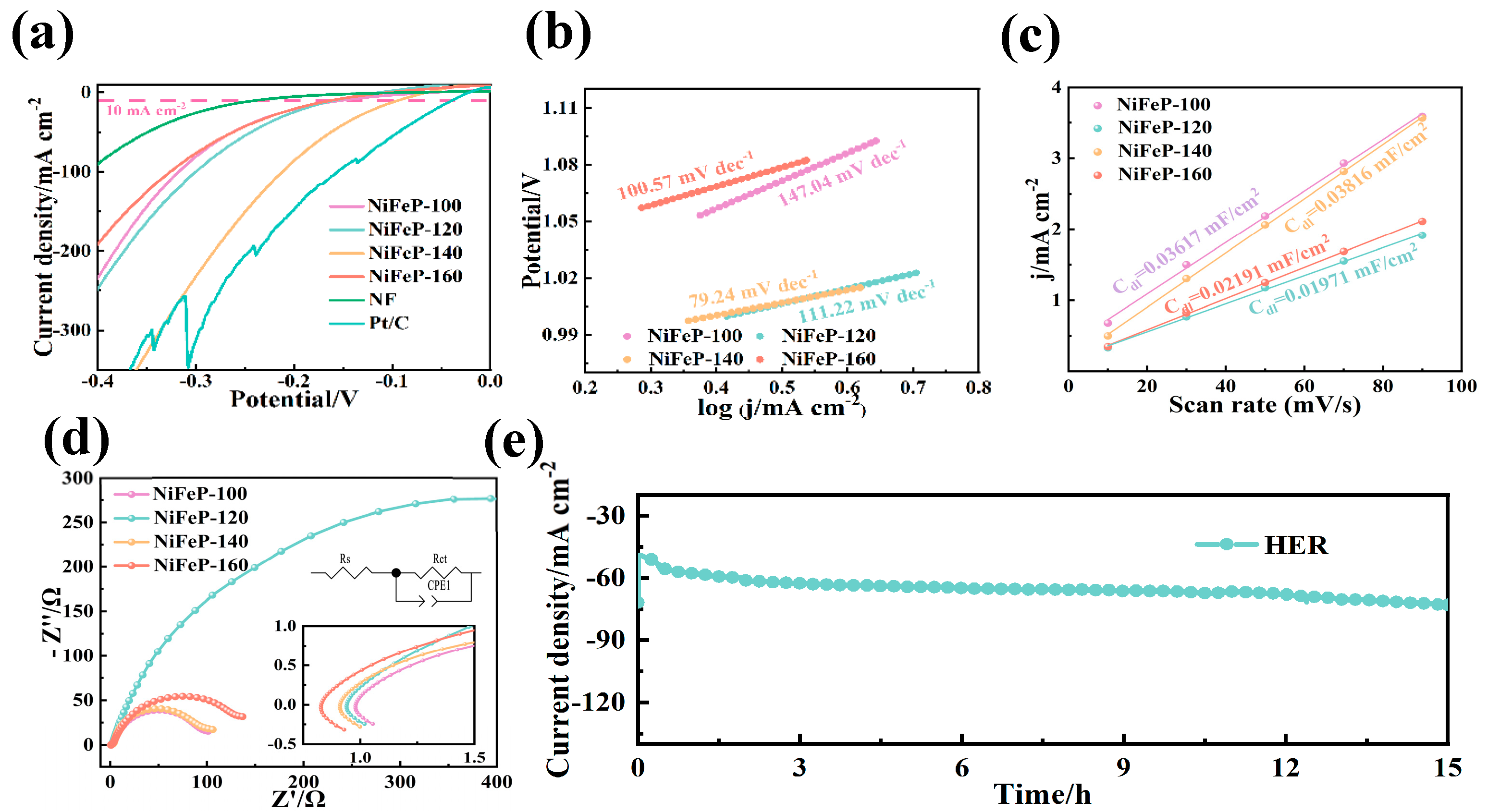
Also, we investigated the HER performance, and Pt/C was selected as the reference. The NiFeP-140 electrode reveals an overpotential of 93 mV at 10 mA cm−2, demonstrating the low potential and the high HER catalytic activity among the prepared catalysts (NiFeP-100 (150 mV), NiFeP-120 (158 mV) and NiFeP-160 (161 mV)) (Figure 4a). The enhancement in HER performance is attributed to the introduction of P, which improves the catalytic ability to capture H protons [25,44]. The HER Tafel slopes are expressed through the following steps [45]:
H2O + e− → Hads + OH−
Hads + H2O + e− → H2 + OH−
H2O + e− → Hads + OH−
Hads + Hads → H2 ↑
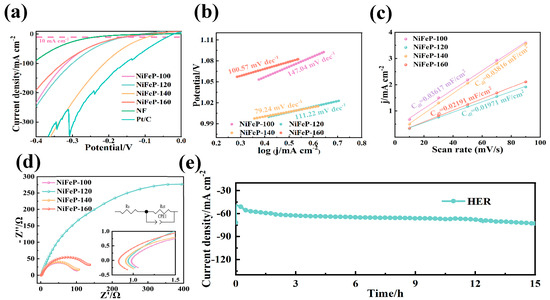
Figure 4.
(a) HER LSV curves. (b) HER Tafel plots. (c) The Cdl at the non-faradaic potential window. (d) Nyquist plots for HER. (e) HER chronoamperometric curves.
Figure 4b shows that NiFeP sample possesses a low Tafel slope (79.24 mV dec−1). The low charge transfer resistance (2.4 Ω, Figure 4c, Table 2) again proves their fast reaction rate during the reaction. The Cdl of HER plotted by CV curves reveals that NiFeP-140 catalysts possess a large active area (Figure 4d). The Cdl reaches 0.01901 mF cm−2, which is higher than that of NiFeP-100 (0.01366 mF cm−2), NiFeP-120 (0.01032 mF cm−2) and NiFeP-160 (0.01524 mF cm−2). The stability of the sample was also studied at a constant voltage for 15 h. Figure 4e shows its stable HER catalytic ability.

Table 2.
Charge transfer resistance and solution resistance of the HER for the sample.
Finally, we investigated the overall water-splitting properties in a two-electrode system in 1 M KOH solution. The overall water-splitting reaction under alkaline conditions can be expressed as the following equations:
2OH− → 1/2 O2 ↑ + H2O + 2e− (Anode)
2H2O + 2e− → H2 ↑ + 2OH− (Cathode)
H2O → H2 ↑ + 1/2 O2 ↑ (Overall)
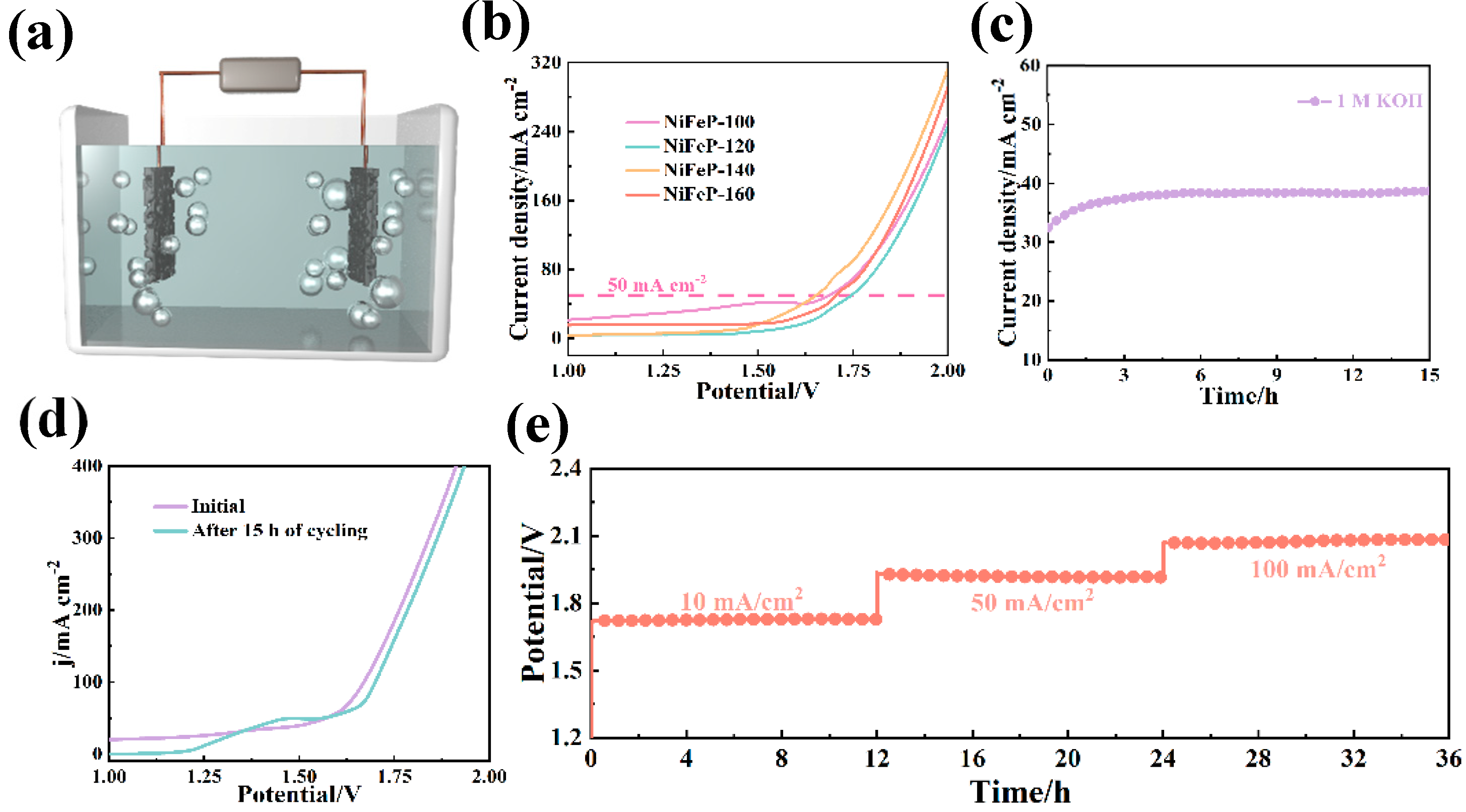
As shown in Figure 5a, O2 is generated from OH− at the anode, while the H2O-to-H2 transition occurs at the cathode [46]. From the polarization curves (Figure 5b), it was found that the NiFeP-140 catalyst provides 1.65 V at 50 mA cm−2 and 1.77 V at 100 mA cm−2. Nickel foam with numerous micropores and charge-transfer channels enable the fast transfer of electrons [47]. It effectively increases the catalytic efficiency of the catalyst. Furthermore, we performed a chronoamperometric test for 15 h in the two-electrode system (Figure 5c). The polarization curves change little after cycling, and it is further shown that the prepared samples possess excellent stability (Figure 5d). Subsequently, the multi-step chronopotentiometry results show that the electrode maintains stable voltage and current platform after 36 h of cycling (Figure 5e).
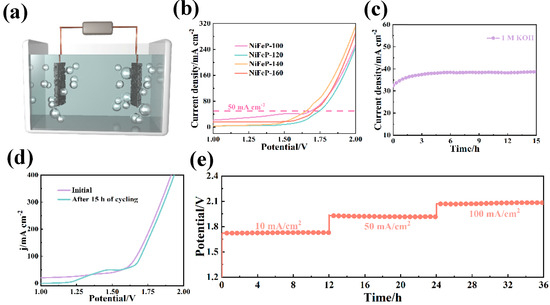
Figure 5.
(a) Schematic of experimental apparatus for overall water splitting (the prepared electrodes are used as cathode and anode). (b) Polarization curves of the overall water splitting. (c) Chronoamperometric curves. (d) Polarization curves before and after cycling. (e) Chronopotentiometry.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
Ethanol (AR, 99.5%) and nickel nitrate hexahydrate (Ni(NO3)2·6H2O) were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Company, Shanghai, China. Ferric nitrate nonahydrate (Fe(NO3)3·9H2O), ammonium fluoride (NH4F) and urea were purchased from Tianjin Damao Chemical Reagent Factory, Tianjin, China. NF with a thickness of 1 mm was obtained from Kunshan Guangshengjia New Material Co., Kunshan, China. Deionized water (DI) was acquired by a self-made ultrapure water instrument. All materials were directly employed without purification.
3.2. Preparation of NiFeP Catalysts
First, a piece of nickel foam (4 cm × 3 cm) was soaked in 1 M HCl solution for 30 min. It was disposed twice in ultrasonic cleaning equipment with DI water and then alcohol. The treated NFs were transferred to a vacuum oven and dried at 60 °C for 30 min. Then, 1 mmol Ni(NO3)2·6H2O, 1 mmol Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, 3 mmol urea and 7.5 mmol NH4F were dissolved in 60 mL DI water. Subsequently, the mixture was stirred for 30 min to completely dissolve the solids. The pretreated NF and the mixed solution were then transferred into 80 mL Teflon-lined autoclave and maintained at 140 °C for 6 h. After cooling to room temperature, the products were washed several times with DI water and alcohol. After that, the NiFe precursor was placed in a tube furnace with NaH2PO2 powder as the phosphorus source and annealed at 350 °C for 2 h with a heating speed of 5 °C min−1 in an argon atmosphere. The synthetic material was named NiFeP-140. Based on the different reaction temperature, several other samples were marked NiFeP-100, NiFeP-120 and NiFeP-160.
3.3. Structural Characterization
The structure and morphology of the materials were investigated through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (Thermo Scientific Kα, Al Kα source, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and X-ray diffraction (Cu Kα radiation, Ultima IV, 40 KV, Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Their morphology was observed by a scanning electron microscope (Gemini 300-71-31, Carl Zeiss AG, Oberkochen, German). The specific surface area and pore size distribution of the samples were determined using the N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms, following the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) analysis.
3.4. Electrochemical Characterization
All electrochemical experiments were performed on an electrochemical workstation (Shanghai Chenhua CHI 660e, Shanghai, China) with a 1 M KOH electrolyte. We chose a Hg/HgO electrode as the reference. The graphite rod and platinum sheet were used as counter electrodes for HER and OER, respectively, whereas the prepared samples were applied as working electrodes. Potential values were calculated by using the reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE) through the following formula [31]:
ERHE = E(Hg/HgO) + 0.098 + 0.591 × pH (1 M KOH pH ~ 13.7)
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) curves were investigated to characterize the double-layer capacitance (Cdl) of the samples by utilizing a three-electrode system. In addition, linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) was collected by a scan rate of 5 mV/s. Then, the Tafel slopes were fitted with a logarithmic form (log j). The electrochemical impedance spectra (EISs) were scanned at frequencies from 0.01 to 105 Hz in an amplitude of 5 mV. Chronopotentiometry and chronoamperometry were adopted to measure the stability properties of materials at fixed voltages and different currents, respectively. All measurements of overall water splitting were performed in a two-electrode system. Furthermore, we measured the polarization curves and stability in overall water splitting. To further investigate the stability, we selected the polarization curves after the water-splitting cycle for comparison.
4. Conclusions
In summary, we synthesized several kinds of NiFeP catalysts by a hydrothermal route and subsequent phosphating treatment. The prepared samples possess small overpotential and Tafel slopes under alkaline conditions. Meanwhile, the electrocatalysts show low charge transfer resistance and large specific surface area, which increases the number of active sites and improves the reaction rate. In addition, the materials present a low cell voltage during overall water splitting. Meanwhile, it is shown that the currents and voltages remain stable after many cycles, demonstrating the remarkable structural stability of the prepared samples. This study provides a feasible synthesis approach for the design of other high-performance electrocatalysts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.L.; methodology, D.L.; software, D.L.; validation, D.L.; formal analysis, D.L.; investigation, D.L.; resources, D.L.; data curation, D.L.; writing—original draft preparation, D.L.; writing—review and editing, X.W.; supervision, X.W.; project administration, X.W.; funding acquisition, X.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 52172218).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lin, Y.; Wang, H.; Peng, C.K.; Bu, L.; Chiang, C.L.; Tian, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.G.; Lee, J.M.; et al. Co-induced electronic optimization of hierarchical NiFe LDH for oxygen evolution. Small 2020, 16, 2002426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L. Nickel-iron phosphides nanorods derived from bimetallic-organic frameworks for hydrogen evolution reaction. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 457, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, X. Metal-organic framework assisted design of ZnVOx cathode for aqueous zinc batteries at extreme work condition. Nano Energy 2024, 127, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Dai, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Wu, X. PPy film anchored on ZnCo2O4 nanowires facilitating efficient bifunctional electrocatalysis. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Li, M.; Ni, Y. Hierarchically porous FeNi3@FeNi layered double hydroxide nanostructures: One-step fast electrodeposition and highly efficient electrocatalytic performances for overall water splitting. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 6306–6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.W.; Fowler, M. Performance evaluation and durability analysis of NiFeCoOx catalysts for alkaline water electrolysis in anion exchange membrane electrolyzers. Catalysts 2024, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Qiu, C.; Ling, X.; Tian, B.; Chen, W.; Su, C. B, N codoped and defect-rich nanocarbon material as a metal-free bifunctional electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction and evolution reactions. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaj, S.; Kundu, S.; Noda, S. “The Fe Effect”: A review unveiling the critical roles of Fe in enhancing OER activity of Ni and Co based catalysts. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.B.; Mei, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hou, P.X.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.M.; Li, J.C. Prussian-blue-analogue-derived ultrathin Co2P-Fe2P nanosheets for universal-pH overall water splitting. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 8331–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, M.E.G.; Floquet, S. Mechanism of oxygen reactions at porous oxide electrodes. Part 2–oxygen evolution at RuO2, IrO2 and IrxRu1−xO2 electrodes in aqueous acid and alkaline solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 5314–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ning, M.; Xing, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, G.; Song, S.; Wang, D.; Yuan, C.; Yu, L.; et al. Boosting oxygen evolution reaction of (Fe,Ni)OOH via defect engineering for anion exchange membrane water electrolysis under industrial conditions. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2306097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Wu, X. Realizing efficient electrochemical overall water electrolysis through hierarchical CoP@NiCo-LDH nanohybrids. Nano Energy 2023, 114, 108681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.c.; Wu, X.; Cho, Y.R. Highly efficient and stable Mo-CoP3@FeOOH electrocatalysts for alkaline seawater splitting. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2301474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Dai, M.; Liu, H.; Duan, Z.; Tan, X.; Wu, X. Bifunctional ZnCo2S4@CoZn13 hybrid electrocatalysts for high efficient overall water splitting. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 69, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, P.; Xue, X.; Wang, D.; Shang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, B. Interface engineering of three-phase nickel–cobalt sulfide/nickel phosphide/iron phosphide heterostructure for enhanced water splitting and urea electrolysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 665, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Wang, T.; Zhang, J.; Liu, P.; Sun, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, M.; Feng, X. Accelerated hydrogen evolution kinetics on NiFe-layered double hydroxide electrocatalysts by tailoring water dissociation active sites. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X. High-efficiency NiCo layered double hydroxide electrocatalyst. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 18535–18542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Zhao, D.; Sun, Y.; Tan, X.; Wu, X. Bifunctional Fe-doped CoP@Ni2P heteroarchitectures for high-efficient water electrocatalysis. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 8865–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, X.F.; Nai, J.; Zang, S.Q.; Lou, X.W. Construction of hierarchical Co-Fe oxyphosphide microtubes for electrocatalytic overall water splitting. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1900576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Xu, Y.; Wang, R.; Shan, A. Enhanced alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction of MoO2/Ni3S2 nanorod arrays by interface engineering. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; He, R.; Pan, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, Y. Lattice distortion induced Ce-doped NiFe-LDH for efficient oxygen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 464, 142669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.-Q.; Kuai, C.-G.; Sokaras, D.; Zheng, X.-L.; Sainio, S.; Lin, F.; Dong, C.-K.; Nordlund, D.; Du, X.-W. Unveiling the critical role of the Mn dopant in a NiFe(OH)2 catalyst for water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17471–17476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dong, L.; Wu, H.B.; Yu, X.-Y. Activating the hydrogen evolution and overall water splitting performance of NiFe LDH by cation doping and plasma reduction. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2020, 266, 118627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Q.; Tao, D.; Yang, H.; Zhan, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, G. Optimizing nanostructure and constructing heterostructure via Mo/W incorporation to improve electrochemical properties of NiCoP for hybrid supercapacitors. Sci. China-Mater. 2022, 65, 1195–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Li, Q.; Xiao, W.; Wang, J.; Dong, B.; Chai, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L. Unique CoP microflower decorated with phosphorous-enriched PtP2 onto nickel foam with interfacial electronic interactions to boost alkaline water-splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Du, X.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, Z.; Kong, Q.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Hydrated eutectic electrolytes with ligand-oriented solvation shells for long-cycling zinc-organic batteries. Joule 2020, 4, 1557–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, X.; Tao, J.; Yang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Peng, Z. Porous amorphous NiFeOx /NiFeP framework with dual electrocatalytic functions for water electrolysis. J. Power Sources 2019, 428, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chang, S.; Yu, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. FeNiP nanoparticle/N, P dual-doped carbon composite as a trifunctional catalyst towards high-performance zinc–air batteries and overall water electrolysis. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 17136–17146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Bin, D.; Tamirat, A.G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, B. Bamboo-like nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes encapsulated with NiFeP nanoparticles and their efficient catalysis in the oxygen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Umar, A.; Wu, X. Enhanced water electrolysis performance of bifunctional NiCoP electrocatalyst in alkaline media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 950, 117888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Huai, X.; Abdukader, A.; Umar, A.; Wu, X. Highly active and durable NiCoP electrocatalyst through Ga ion intercalation strategy for long-lasting water electrolysis. Appl. Surf. Sci 2014, 660, 159972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Ren, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, S. Synergistic effect of multiple vacancies to induce lattice oxygen redox in NiFe-layered double hydroxide OER catalysts. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2023, 323, 122091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Ying, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Fu, N.; Guo, X.; Yu, F.; Huang, H. Engineering NiFe layered double hydroxide by valence control and intermediate stabilization toward the oxygen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 26130–26138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Chen, T.; Xie, F.; Xue, D.; Liu, T.; Chen, L.; Xia, J.; Du, S.; Wang, F.; Xie, F.; et al. NiFeP composites supported on Ni foam as an efficient and robust bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting in alkaline solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, T.; Zhao, G. Electro-fenton oxidation of pesticides with a novel Fe3O4@Fe2O3/activated carbon aerogel cathode: High activity, wide pH range and catalytic mechanism. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2012, 125, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yao, Y.; Sun, S.; Liang, J.; Hong, S.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Carbon oxyanion self-transformation on NiFe oxalates enables long-term ampere-level current density seawater oxidation. Angew. Chem.-Int. Edit. 2023, 63, 2316522. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, C.Z.; Zhang, X.N.; Yin, J.; Zhou, H.W.; Liu, K.; Liu, X. Highly efficient FeS2@FeOOH core-shell water oxidation electrocatalyst formed by surface reconstruction of FeS2 microspheres supported on Ni foam. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2023, 339, 123171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Yu, K.; Li, H.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lei, X.; Fu, H.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, Z. Hollow structured micro/nano MoS2 spheres for high electrocatalytic activity hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 5517–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Fu, S.; Luo, Y.; Peng, C.; Cheng, L.; Jiao, Z. Deciphering the space charge effect of the CoNiLDH/FeOOH n–n heterojunction for efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution. Small 2023, 19, 2305241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.P.; Gong, M.X.; Deng, S.F.; Zhao, T.H.; Shen, T.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.L. Transforming damage into benefit: Corrosion engineering enabled electrocatalysts for water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhai, H.; Chen, L.; Mei, L.; Tan, P.; Yang, K.; Pan, J. Unraveling the synergistic mechanism of bi-functional nickel–iron phosphides catalysts for overall water splitting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2302621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhao, D.; Wu, X. NiCo layered double hydroxide nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, A.C.; Antos, J.; Masar, M.; Michal, U.; Michal, M.; Ivo, K. Comprehensive evaluation of photoelectrochemical performance dependence on geometric features of ZnO nanorod electrodes. Nanoscale Adv. 2023, 11, 3091–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Sun, S.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; Kim, M.G.; Lian, J.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.; et al. In situ phosphating of Zn-doped bimetallic skeletons as a versatile electrocatalyst for water splitting. Energy Environ. Sci. 2022, 15, 2425–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.; Zheng, L.; Ying, X.; Yang, Y.W. IrMo nanocluster-doped porous carbon electrocatalysts derived from cucurbituril boost efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2023, 145, 16548–16556. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Q.; Brocks, G.; Bieberle-Hütter, A. Oxygen evolution reaction (OER) mechanism under alkaline and acidic conditions. J. Phys. A Energy 2021, 3, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Liu, H.; Tan, X.; Umar, A.; Wu, X. Bifunctional CoP electrocatalysts for overall water splitting. Catal. Commun. 2022, 162, 106379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).