Abstract
Replacing homogeneous acids with heterogeneous acids provides an appealing approach for biodiesel production due to their reusability and easy recycling. The physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids have a significant influence on catalytic activity and reusability. Herein, the influence of physicochemical properties (i.e., acid density, acid strength, acid type, wettability, thermal sensitivity, and magnetism) on catalytic activity and recyclability is elaborately discussed. Characterization techniques for identifying physicochemical properties are elaborated. Methods for regulating physicochemical properties are summarized. Finally, the opportunities and challenges of heterogeneous acid use for biodiesel production are discussed. This review provides theoretical guidance for developing efficient and stable heterogeneous acid catalysts for biodiesel production by adjusting their physicochemical properties.
1. Introduction
The excessive consumption of fossil resources has caused serious environmental pollution and energy security issues [1]. To alleviate this global concern, developing clean and renewable energy sources to replace fossil resources is a hot topic for researchers. Among these sources, biodiesel (fatty acid methyl esters, FAMEs) is regarded as a promising substitute or supplement to conventional diesel, owing to its unique advantages such as renewability, environmental friendliness, fuel properties similar to those of petrochemical diesel, and excellent lubricity for decelerating engine wear and tear [2,3]. As a result, replacing fossil diesel with biodiesel has become a global consensus to promote society towards green and sustainable development [4].
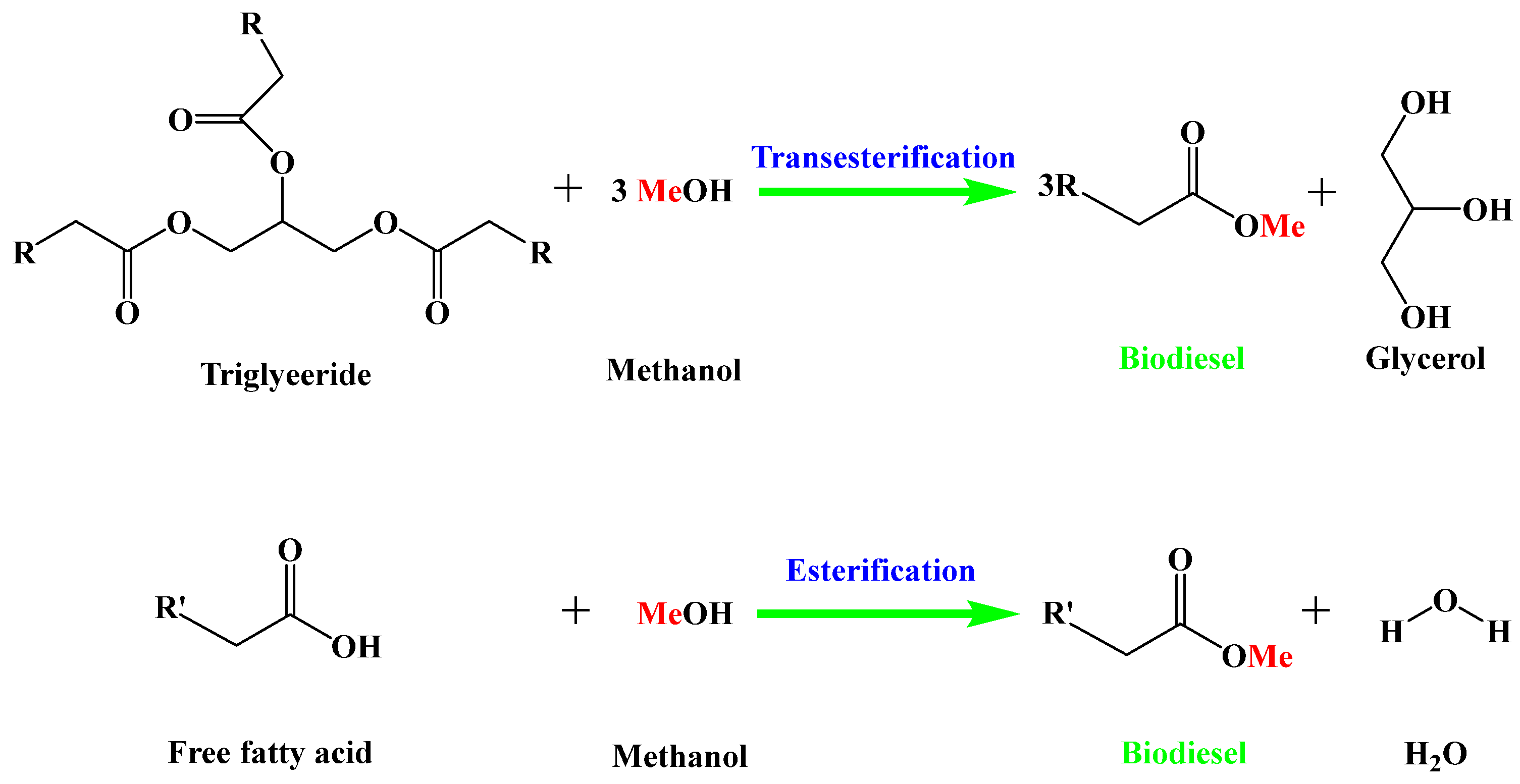
Biodiesel is mainly produced from vegetable oil, animal oil, and waste cooking oils via the esterification of free fatty acids or/and transesterification of triglycerides with methanol (Figure 1). Compared with edible oils, the utilization of non-edible oils as feedstocks for biodiesel production not only greatly reduces the biodiesel cost, but also avoids competition with human food [5,6]. Nevertheless, these non-edible oils usually contain a large amount of free fatty acids [7]. The base-catalyzed transesterification method cannot be directly used to convert these non-edible oils into biodiesel because the base catalyst is poisoned by free fatty acids through the saponification reaction [8]. On the contrary, acid catalysis is an effective strategy for the conversion of non-edible oils with a high acid value into biodiesel, because an acid catalyst can simultaneously catalyze both the esterification of free fatty acids and the transesterification of triglycerides without saponification [9]. According to the phase state of acid catalysts in the reaction system, acid catalysts can be divided into homogeneous acid catalysts and heterogeneous acid catalysts.
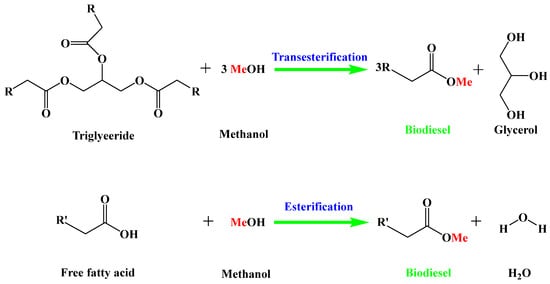
Figure 1.
Production of biodiesel from non-edible oils through esterification and transesterification reactions.
Homogeneous acid catalysts, such as H2SO4, benzene sulfonic acid, HCl, and AlCl3, have been widely explored for the catalytic production of biodiesel, owing to their merits of a low cost and satisfactory catalytic activity [10]. The acidic sites of homogeneous acidic catalysts are in the same phase as reactants and can contact effectively with reaction substrates [11]. Nevertheless, homogeneous acid catalysts generally suffer from severe equipment corrosion and difficulty in recycling and reuse, resulting in the tedious purification of biodiesel and generating a large amount of wastewater (Table 1). This inevitably increases the production cost of biodiesel and pollutes the environment. On the contrary, heterogeneous acid catalysts are easy to recycle from the reaction mixture by simple centrifugation or filtration and lead to low equipment corrosion [12]. The green and efficient production of biodiesel is an inevitable trend for sustainable development. Thus, heterogeneous catalysts as a promising alternative to homogeneous catalysts have attracted tremendous attention for biodiesel production. The development of efficient and stable heterogeneous catalysts is one of the key requirements to achieve this goal. Nevertheless, the development of efficient and stable heterogeneous catalysts is still a challenge because heterogeneous catalysts typically have lower catalytic activity and are easier to deactivate compared with homogeneous catalysts.

Table 1.
Comparison of homogeneous acid and heterogeneous acid catalysts.
Given their unique advantages, various heterogeneous acids have attracted tremendous research interest as excellent alternatives to homogeneous acids for biodiesel production [13]. A growing number of studies on heterogeneous catalytic biodiesel production have been reported. Various heterogeneous acids, such as mixed oxides [14], catalysts with sulfonic acid groups [15], heteropoly acid-based catalysts [16], and zeolites [17], have been explored for the catalytic production of biodiesel. It has been found that the physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids possess a critical influence on their catalytic activity and recyclability. For instance, a high acid density and strong acid strength are beneficial for promoting the activation of fatty acids and triglycerides, improving the biodiesel yield [18,19]. Meanwhile, the acid site types of Brønsted and Lewis can affect the catalytic reaction mechanism of esterification and transesterification [20,21]. The wettability of heterogeneous acids for reaction substrates facilitates the contact efficiency of acidic sites with these substrates, resulting in the high catalytic activity of heterogeneous acids [22,23]. In recent years, substantial progress has been witnessed in understanding the impact of the physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acid on their catalytic activity. Nevertheless, a comprehensive commentary on the influence of the physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids on the activity of catalytic biodiesel production has not been reported.
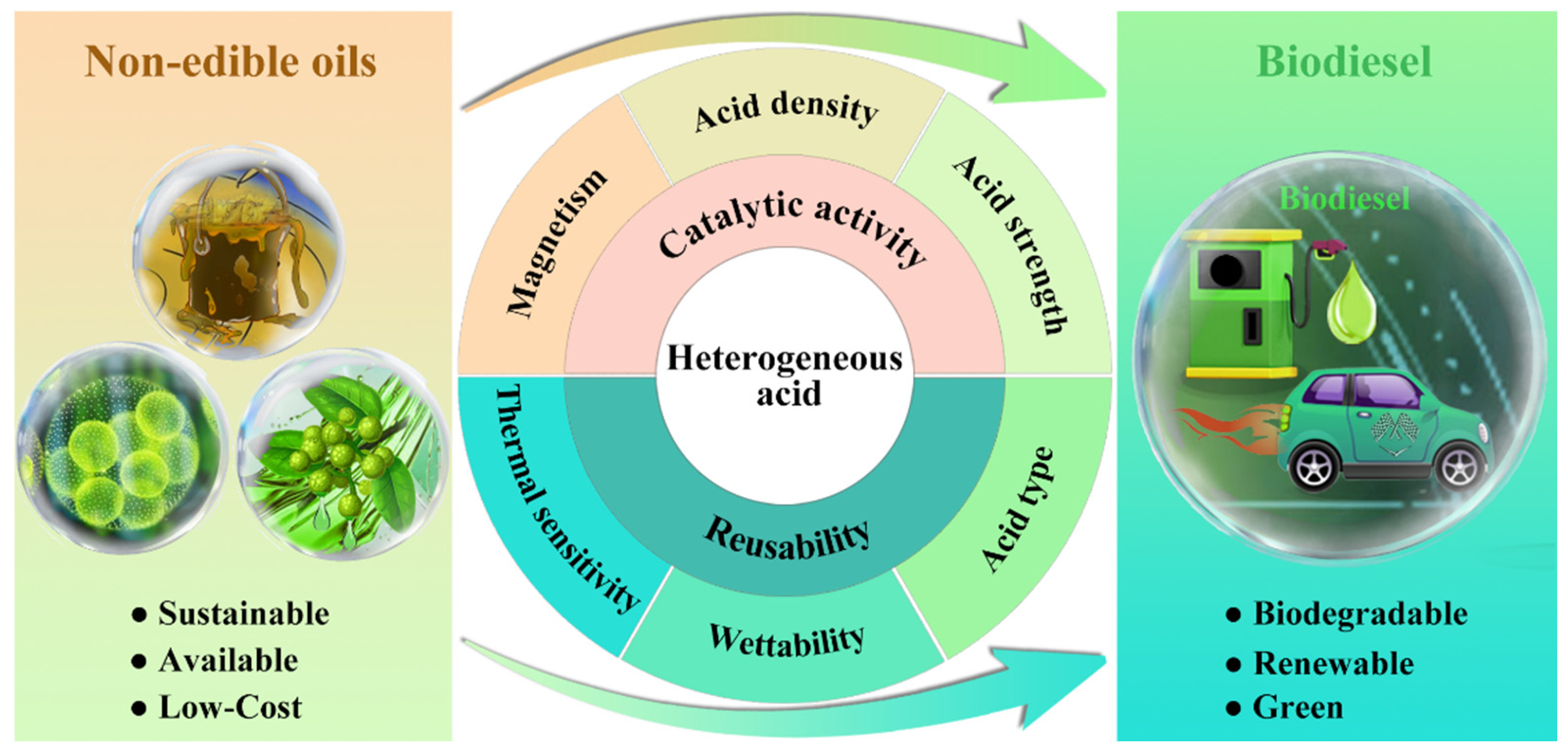
Herein, this review commits to providing a comprehensive commentary on the influence of the physicochemical properties (i.e., acid density, acid strength, acid type, wettability, thermal sensitivity, and magnetism) of heterogeneous acids on their catalytic activity and recyclability (Figure 2). Characterization techniques for identifying the physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids are elaborated. Methods for regulating the physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids also are summarized. Meanwhile, the effect of physicochemical properties on catalytic activity and reusability is elaborately discussed. The influencing mechanisms of physicochemical properties on catalytic activity and repeatability are also reviewed. In the end, a summary and perspective on the opportunities and challenges of heterogeneous-acid-catalyzed biodiesel production are given. Future directions for the development of efficient and robust heterogeneous acid are also presented by regulating physicochemical properties.
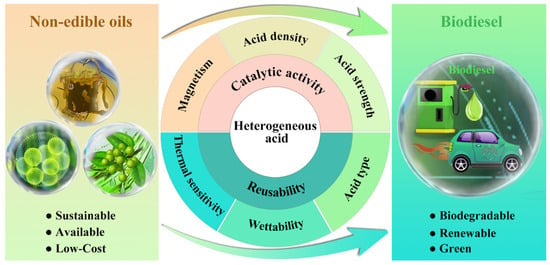
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of catalytic conversion of non-edible oils into biodiesel over heterogeneous acid catalyst and physicochemical properties affecting the catalytic activity and reusability of heterogeneous acid.
2. Effect of Acid Density on Catalytic Activity
Acid density is an important parameter for evaluating the number of acid sites in a solid acid and is usually expressed as the millimolar amount of acidic sites per gram of solid acid (mmol H+/gsolid acid) [24]. It is mainly determined by the two methods of acid–base neutralization titration and temperature-programmed desorption using ammonia molecules (NH3-TPD) [25,26]. For the acid–base neutralization titration method, acid density is measured by the acid–base neutralization reaction between the acid sites of a solid acid and standard alkaline solution, where strong alkali hydroxide (e.g., NaOH and KOH) or carbonate (e.g., Na2CO3 and K2CO3) are commonly used as standard alkaline solutions [27,28]. NH3-TPD is another commonly used technique for determining the acid density of a solid acid. Acid density is obtained by measuring the amount of desorbed NH3 captured by the solid acid through the neutralization reaction of NH3 and the acid sites of the solid acid [29]. Due to the poor thermal stability of organic solid acids, the NH3-TPD method is ineffective for testing their acid densities [30]. In such cases, the acid–base neutralization titration method demonstrates the advantage of low requirements for the thermal stability of solid acids [31]. Nevertheless, acid–base titration is more suitable for determining the amount of Brønsted acid sites, while it is inaccurate for measuring the amount of Lewis acid sites because of the vague reaction equivalent between Lewis acid sites and standard alkali solution. For sulfonic acid-based solid acids, measuring the sulfur element content of a solid acid is also an effective method for determining its acid density [32].
The influence of acid density on catalytic activity was investigated through the esterification of palm fatty acid distillate with methanol for biodiesel production using solid acids with different acid densities as catalysts [33]. Carbon-based solid acids with different acid densities were synthesized by the incomplete carbonization of biomass-based glucose (ICG), followed by the sulfonation of the obtained carbon material with concentrated sulfuric acid (H2SO4). The acid densities of the carbon-based solid acids were adjusted by controlling the sulfonation time. The acid densities of the prepared catalysts were determined by NH3-TPD technology. As listed in Table 2, the carbon material ICG without sulfonation treatment exhibited neglected catalytic activity (Scheme 1). After the sulfonation of the ICG, the catalytic activity was significantly improved, indicating that sulfonic acid groups were the main active sites. Acid density gradually increased with the prolongation of sulfonation time. As the acid density of the catalyst increased, the conversion rate of palm fatty acid (PFA) gradually increased. This may be attributed to catalysts with a high acid density offering abundant catalytic active sites, resulting in a high PFA conversion rate.

Table 2.
Catalytic activities of carbon-based acid catalysts with different acid densities [33].
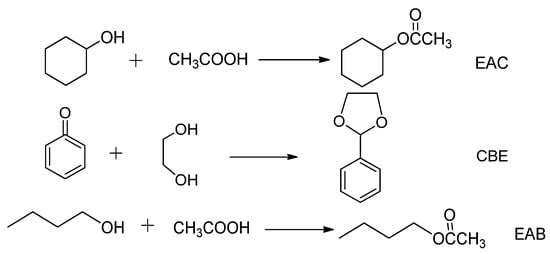
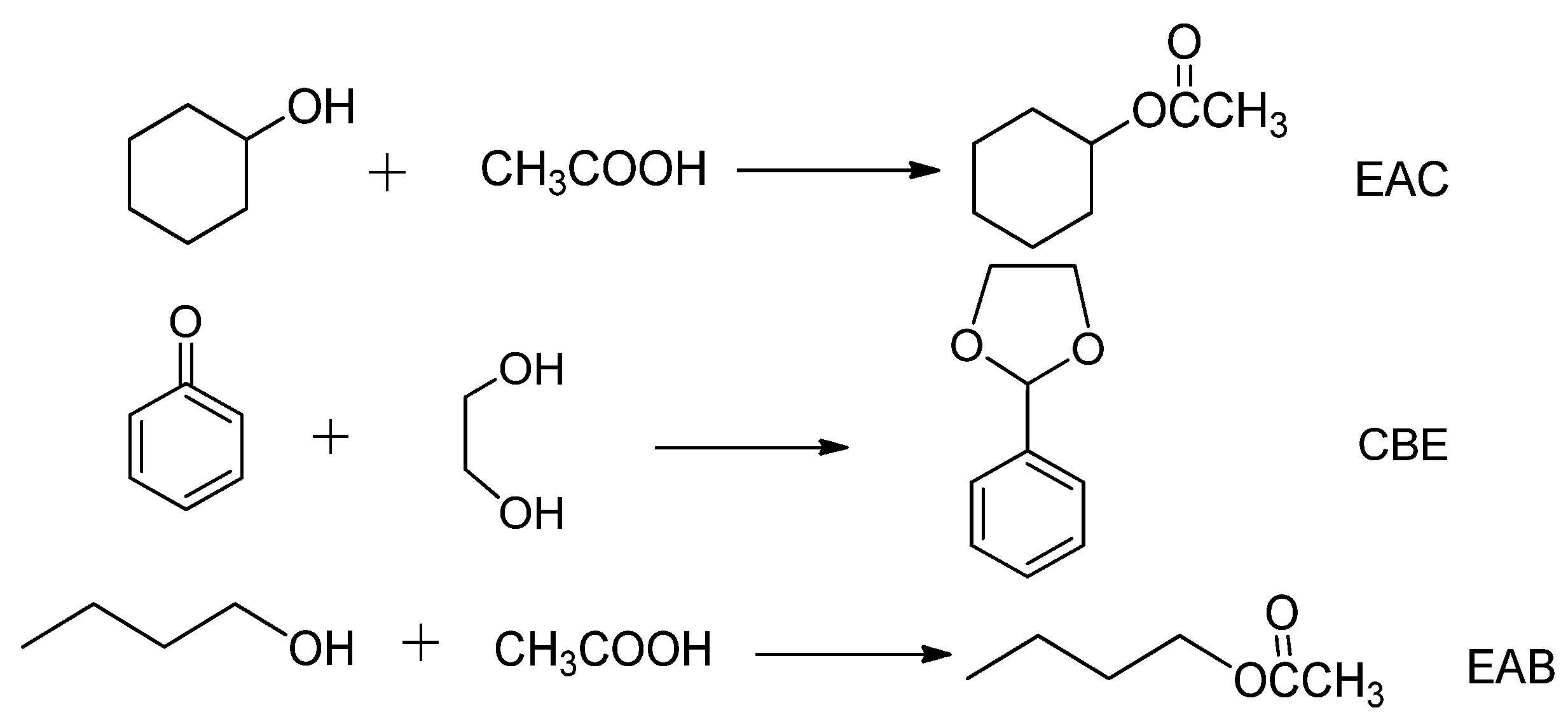
Scheme 1.
Reaction routes of EAC, CBE, and EAB reactions.
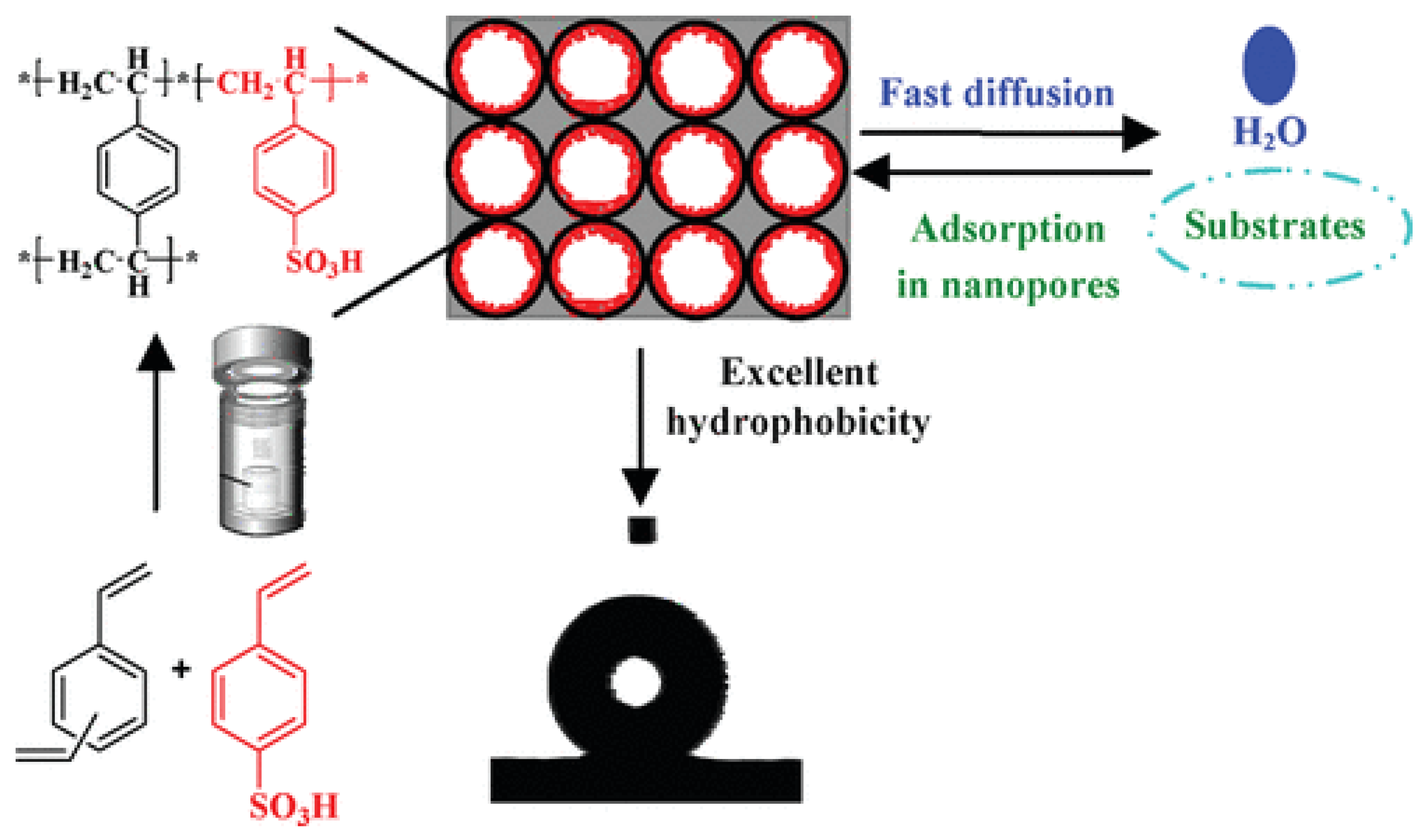
Mesoporous polymer solid acid catalysts were solvothermally synthesized from the copolymerization of sodium p-vinylbenzene sulfonate and diethylbenzene and subsequent ion exchange with sulfuric acid (Figure 3) [30]. By adjusting different molar ratios of sodium p-vinylbenzene sulfonate and diethylbenzene, the acid densities of polymer solid acids can be regulated. As listed in Table 3, catalytic activity increased with an increase in acid density. However, an excessive acid density resulted in a decrease in catalytic activity, which may be attributed to the excessive loading of sulfonic acid reducing the hydrophobicity of the catalyst.
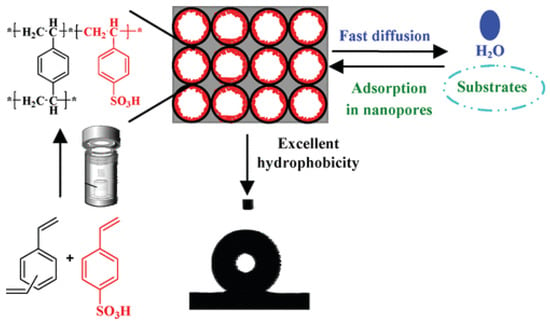
Figure 3.
Synthesis of mesoporous polymer solid acid with adjustable acid density and excellent hydrophobicity [30]. Copyright 2012 American Chemical Society. * Indicates the meaning of polymer.

Table 3.
Catalytic activity of mesoporous polymer acid catalysts with different acid densities [30].
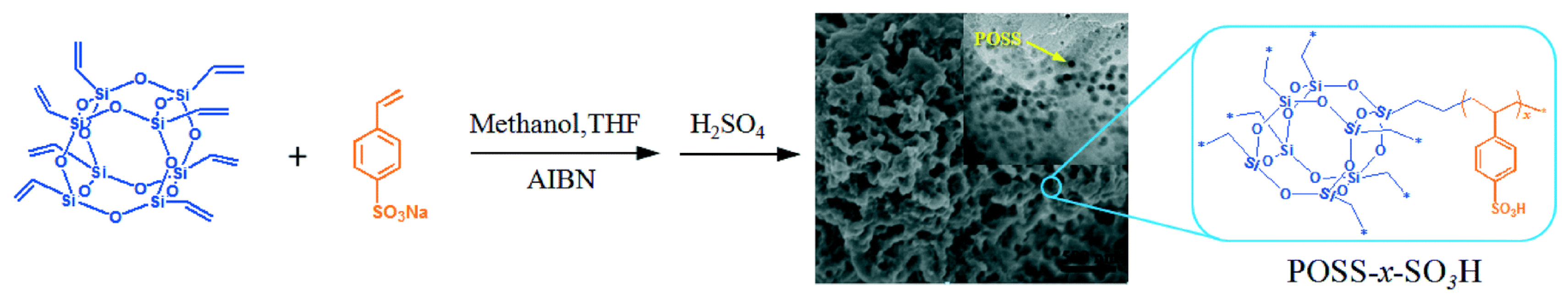
The effect of acid density on the catalytic esterification reaction was investigated by Leng et al. using organic–inorganic composites as catalysts [34]. Catalysts with tunable acid densities were prepared by free radical copolymerization with different molar ratios of sodium p-vinylbenzene sulfonate and vinyl siloxane, then subsequently treated with sulfuric acid (Figure 4). As the molar ratio of benzenesulfonic acid increased, catalytic activity gradually improved, however, an excessive content of benzenesulfonic acid led to a decrease in catalytic activity. This reduced catalytic activity may be attributed to the excessive content of benzenesulfonic acid causing a decrease in the specific surface area of the catalyst.
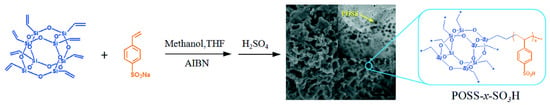
Figure 4.
Synthesis of mesoporous composite solid acid via copolymerization of p-vinylbenzenesulfonic acid and vinyl siloxane [34]. Copyright 2016 Elsevier.
3. Effect of Acid Types on Catalytic Activity
Acid types can be classified into Brønsted (B) acid sites and Lewis (L) acid sites. B and L acid sites are defined as giving proton (H+) sites and accepting electron sites, respectively. Pyridine-adsorbed Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR) spectra are a commonly used characterization technique for identifying the type of acid site [35]. Characteristic peaks at 1449 cm−1 and 1600 cm−1 indicate the presence of L acidic sites, while peaks at 1540 cm−1 and 1550 cm−1 demonstrate the presence of B acidic sites [36]. Meanwhile, a peak at 1498 cm−1 implies the coexistence of B and L acid sites.
Due to their unique characteristics of a negligible volatility, outstanding solubility, adjustable structure, and remarkable thermal stability, acidic ionic liquids have aroused increasing attention as catalysts for the production of biodiesel [37]. To investigate the influence of acid site types on catalytic activity, acidic ionic liquids with B acid and L acid sites were prepared by introducing metal chloride (MnCln) into commercial acidic ionic liquids ([BMIm] [TS]) (Table 4) [38]. The catalytic activities of acidic ionic liquids were evaluated through the esterification of oleic acid with methanol and the simultaneous esterification and transesterification of high-acid-value Jatropha curcas seed oil. The [BMIm] [TS] with only B acid sites showed low catalytic activity. After introducing metal chloride into the B acid site, the catalytic activities of [BMIm] [TS] were significantly improved. This indicates that synergistic effects of B and L acid sites promoted the catalytic production of biodiesel.

Table 4.
Catalytic activities of different chloride ionic liquids with B acid and L acid [38].
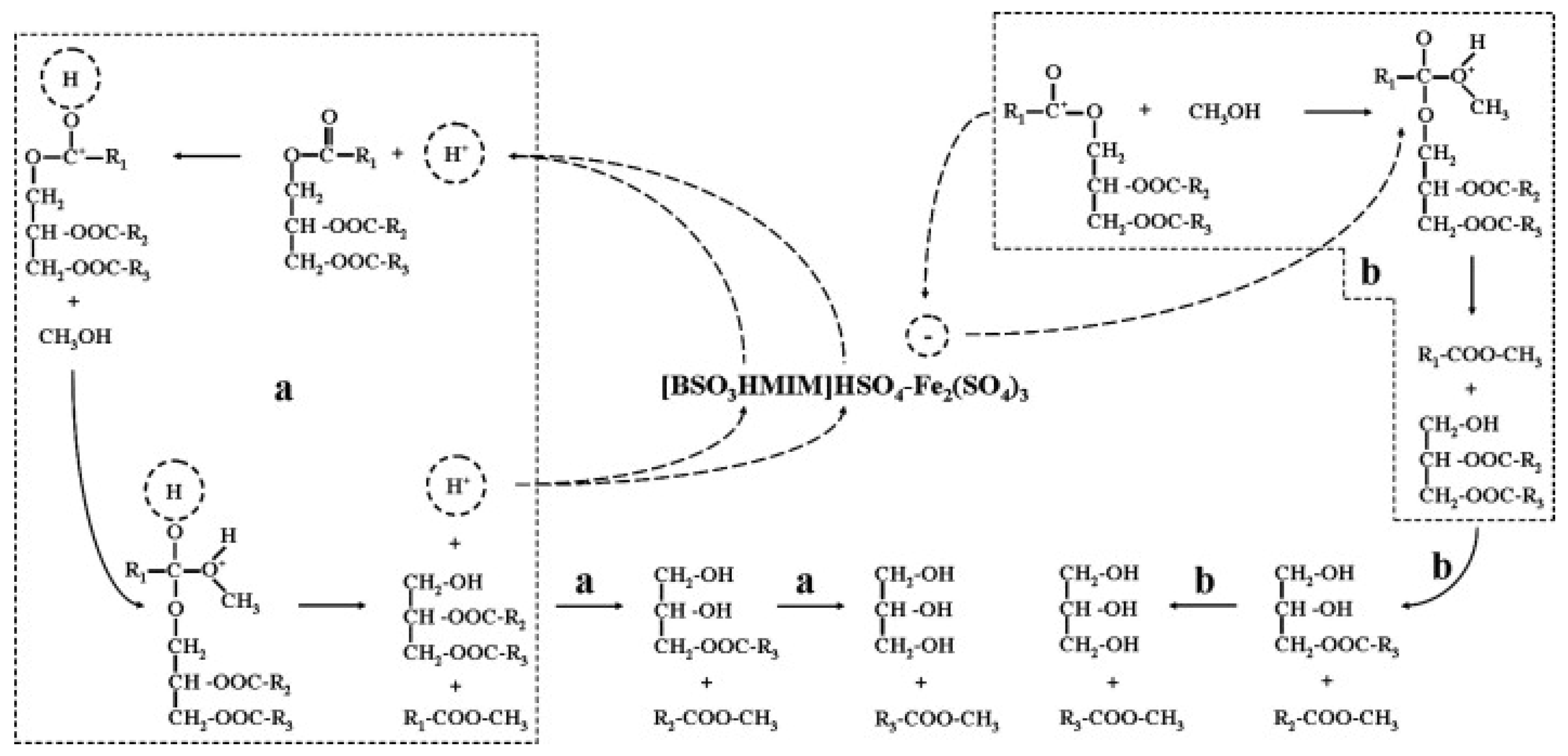
Acidic ionic liquids with B and L acidic sites were synthesized by introducing various metal sulfates (i.e., MgSO4, CaSO4, CuSO4, ZnSO4, and Fe2(SO4)3) into an acidic ionic liquid of [BSO3HMIM]HSO4 [39]. They were used for the microwave-assisted conversion of Camptotheca acuminata seed oil with a high acid value into biodiesel. It was found that [BSO3HMIM]HSO4-Fe2(SO4)3 exhibited the optimal catalytic activity with a biodiesel yield of 86.2% due to the synergistic effects of strong B acidic sites of [BSO3HMIM]HSO4 and strong L acidic sites of Fe2(SO4)3 (Figure 5). B acidic sites originating from H+ and L acidic sites originating from Fe3+ can effectively activate the carbonyl groups of triglycerides and promote transesterification reactions for the production of biodiesel.
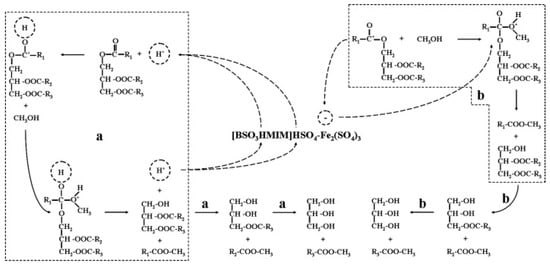
Figure 5.
The synergistic catalytic mechanism of B and L acidic sites for production of biodiesel from Camptotheca acuminata seed oil with high acid value [39]. Copyright 2014 Elsevier B.V. a denotes the reaction path through the B acid site, and b denotes the reaction path through the L acid site.
A solid acid catalyst (IL/Fe-SBA-15) with B and L acid sites was synthesized by the immobilization of acidic ionic liquids on Fe-doped mesoporous silica (Fe-SBA-15) for the production of biodiesel via the esterification of oleic acid with methanol [40]. The B and L acid sites of IL/Fe-SBA-15 originated from the acidic ionic liquid and Fe-SBA-15, respectively, which was identified by pyridine-adsorbed FT-IR spectra characterization. The characteristic peak at 1544 cm−1 corresponded to B acid sites and the peak at 1488 cm−1 indicated the coexistence of B and L acid sites. It was found that IL/Fe-SBA-15 with B acid and L acid had a higher catalytic activity than IL with only B acid sites and Fe-SBA-15 with only L acid sites.
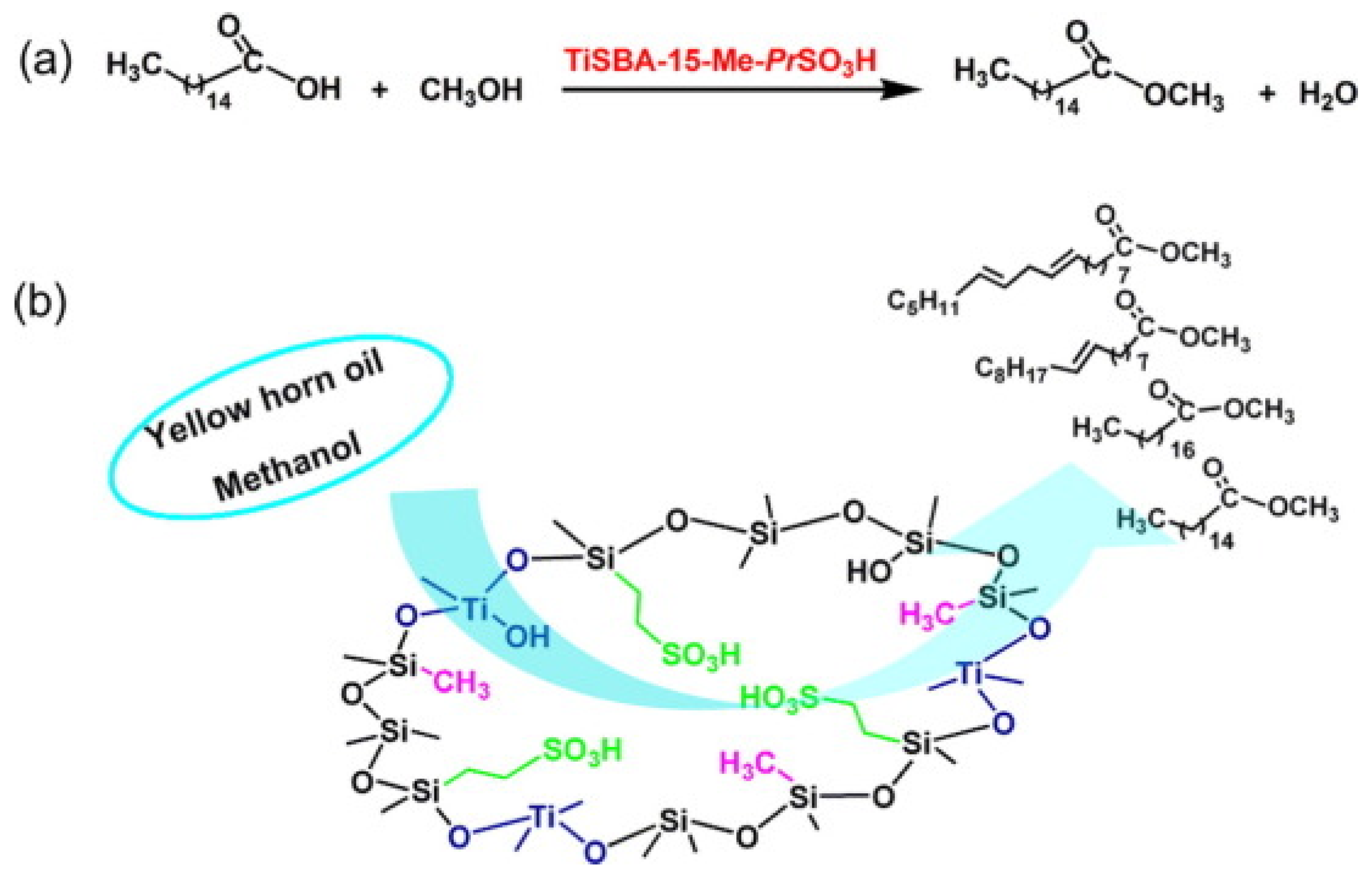
A TiSBA-15-Me-PrSO3H solid acid catalyst was prepared using the low-temperature thermal solvent method, where propanesulfonic acid provided B acid sites and Ti sites provided L acid sites (Figure 6) [41]. The catalytic activities of SBA-15 with neglected acid sites, SBA-15-Me-PrSO3H with only B acid sites, and TiSBA-15-Me-PrSO3H with B and L acid sites were compared by the esterification reaction of palmitic acid and the transesterification of yellow horn oil. Owing to its neglected acid sites, SBA-15 showed a low catalytic activity. Due to the synergistic catalysis of B and L acid sites, TiSBA-15-Me-PrSO3H exhibited the optimal catalytic activity, which was superior to that of SBA-15, TiSBA-15 and SBA-15-PrSO3H. Meanwhile, the methyl groups in TiSBA-15-Me-PrSO3H provided its surface hydrophobicity. The prominent catalytic performances of TiSBA-15-Me-PrSO3H were explained by the contribution of its outstanding physicochemical properties.
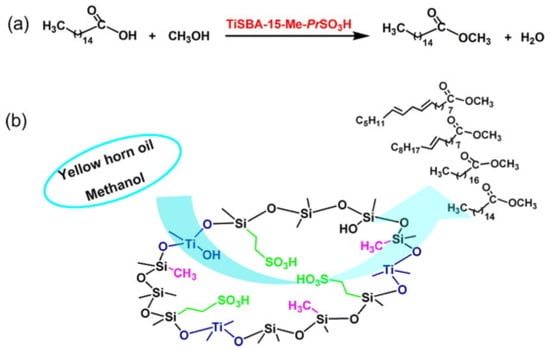
Figure 6.
TiSBA-15-Me-PrSO3H solid acid for catalytic production of biodiesel via esterification reaction (a) and transesterification reaction (b) [41]. Copyright 2015 Elsevier.
4. Effect of Acid Strength on Catalytic Activity
The acid strength of a solid acid mainly exhibits the ability of providing protons for B acid sites or accepting electron pairs for L acid sites [42,43]. Acid strength can be characterized by the Hammett indicator method, NH3-temperature programmed desorption (NH3-TPD) method, and [31] P NMR probe technique [44]. Sulfonic-acid-functionalized ionic liquids with different anions (i.e., HSO4−, p-CH3C6H4SO3−, H2PO4−, and COOCF3−) were synthesized for the transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel [45]. The acid strength of these ionic liquids was characterized using the Hammett indicator method with 4-nitroaniline as a basic indicator. It was found that the order of activity for the anions in the IL was [HSO4−] > [p-CH3C6H4SO3−] > [H2PO4−] > [CF3COO−]. This order of activity was consistent with the order of acid strength. This implies that the high acid strength of IL promotes its catalytic activity, while the low acid strength of IL is detrimental to its catalytic activity.
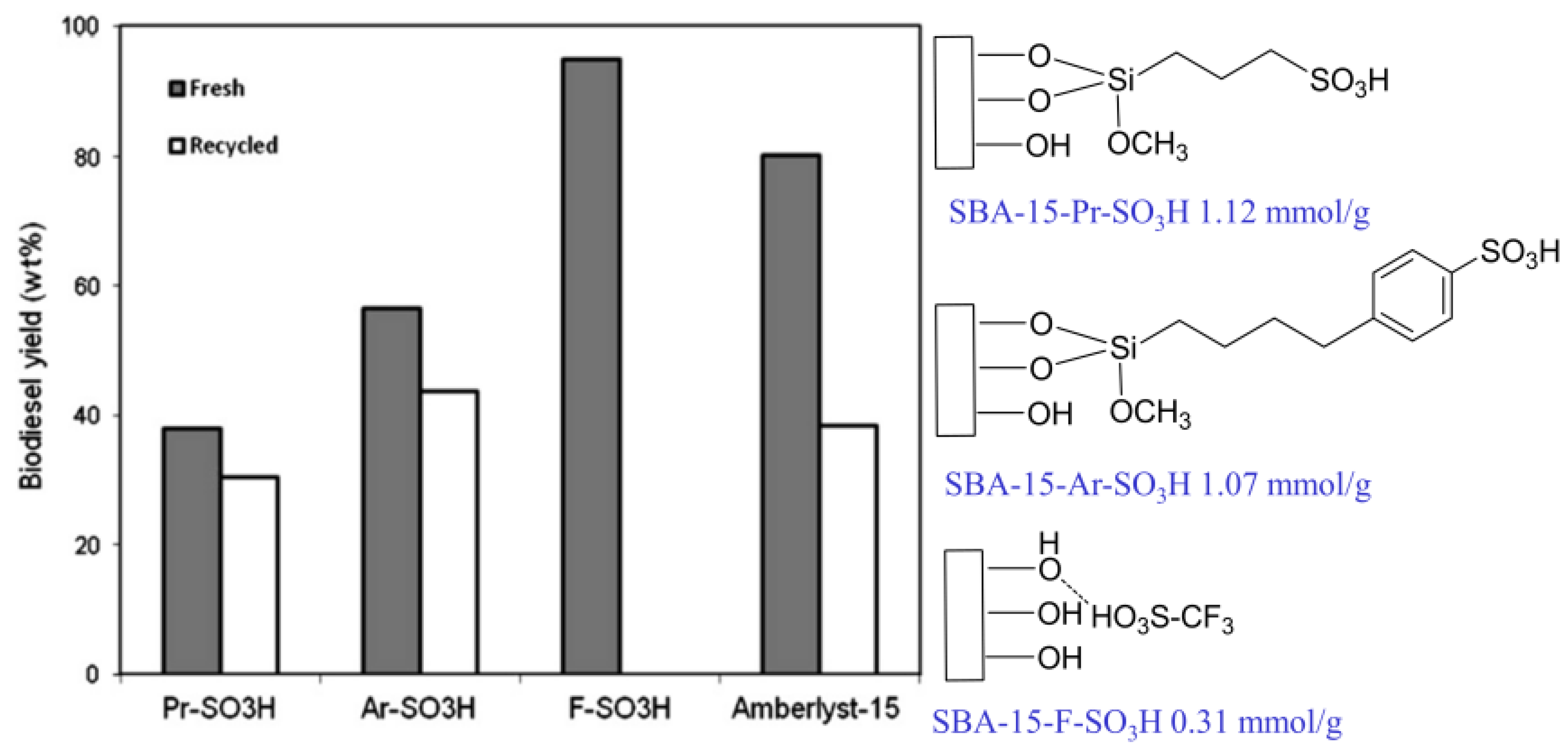
To investigate the effect of acid strength on the transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel, acidic ionic liquids with different acid strengths were immobilized on mesoporous SBA-15 [46]. Although SBA-15-F-SO3H exhibited a lower acid density, its catalytic activity was higher than that of SBA-15-Pr-SO3H and SBA-15-Ar-SO3H (Figure 7). This is mainly attributed to SBA-15-F-SO3H showing a higher acid strength than that of SBA-15-Pr-SO3H and SBA-15-Ar-SO3H. This indicates that the strong acid strength of the catalyst could even compensate for the shortcoming of its low acid density.
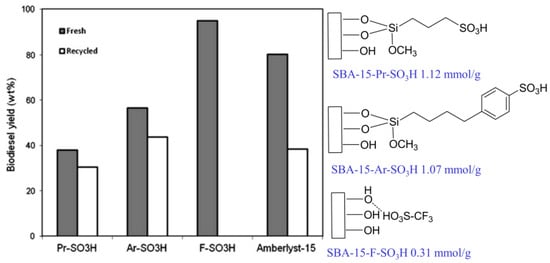
Figure 7.
Comparison of acid catalytic activity of SBA-15 loaded with different acid strength (Reaction conditions: 3.0 g soybean oil, 1.53 g n-butanol, catalyst dosage = 5 wt.%, reaction time = 15 min, reaction temperature = 190 °C) [46]. Copyright 2013 Elsevier.
5. Effect of Wettability on Catalytic Activity
Although heterogeneous acid catalysts have many advantages compared with homogeneous acid catalysts, most heterogeneous acid catalysts cannot perform as well as their homogeneous counterparts [47,48]. Compared to homogeneous acids, the acid sites of heterogeneous solid acids lack mobility, resulting in a limited accessibility between the acid sites and reaction substrates [49]. This greatly limits the catalytic activity of heterogeneous acids. The heterogeneous catalytic reaction mainly occurs on the surface of such catalysts. An ideal catalyst surface should have a good affinity for reactants and strong repulsion for products, which will be beneficial for improving its catalytic activity, especially for reversible reactions [50,51]. For reversible esterification and transesterification reactions, water and glycerol are by-products, respectively. A desirable heterogeneous acid surface for the production of biodiesel is supposed to selectively adsorb reaction substrates (fatty acids or/and triglycerides) but expel water and glycerol, so as to weaken the reverse reaction. Contact angle characterization can measure the contact angles of various liquids with solids and evaluate the wettability of liquids with solids based on the size of the contact angle [52]. Ionic liquids functionalized on superhydrophobic mesoporous polymer were developed for the production of biodiesel via the transesterification of tripalmitin with methanol [53]. The prepared PDVB-[C1vim][SO3CF3] showed higher activities than the corresponding homogeneous ionic liquids. This excellent catalytic activity can mainly be attributed to its superhydrophobicity, which indicated superwettability for methanol and tripalmitin and strong repulsion towards water.
A mesoporous core–shell solid acid was prepared by using mesoporous silica-coated magnetic Fe3O4 as a carrier for loading sulfonic acid sites [54]. Due to the hydrophilicity of silica, the catalytic activity of the catalyst was unsatisfactory. After introducing hydrophobic phenyl functional groups onto the surface of the solid acid, the catalyst exhibited obvious hydrophobicity. It was found that the catalyst with phenyl functional groups had a higher catalytic activity than that without phenyl functional groups.
Water, as a by-product of the esterification reaction, easily adsorbs on the hydrophilic surface of a catalyst, which hinders the contact between the catalyst and the organic substrate [55,56]. This greatly reduces the contact efficiency between acidic sites and substrates, resulting in a decrease in the catalytic activity of the catalyst [57]. The effect of catalyst hydrophobicity on the esterification reaction was investigated [58]. The results showed that the hydrophobicity of the catalyst promoted its activity and reusability.
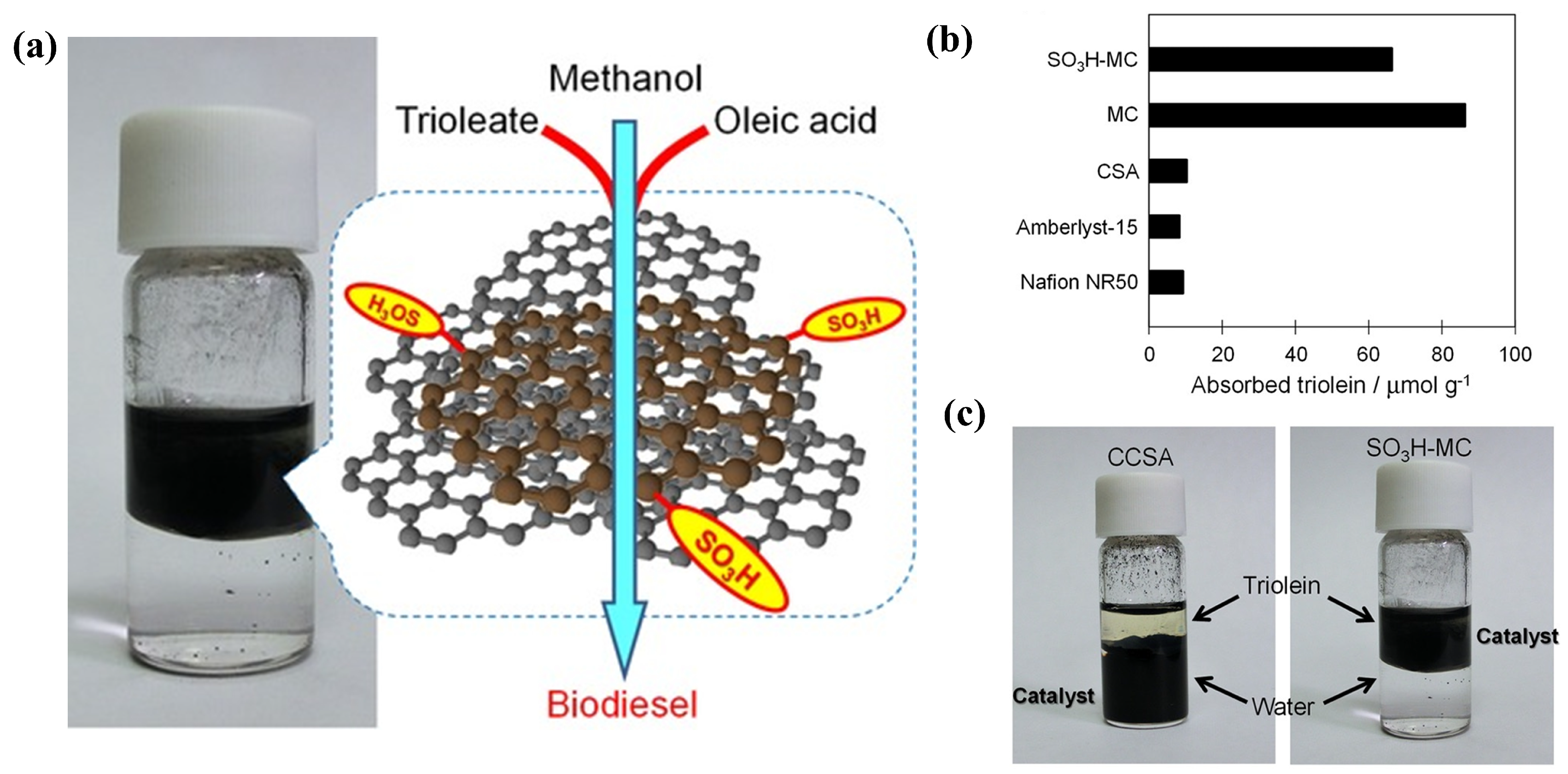
A carbon-based solid acid with an acid density of 0.5 mmol g−1 was synthesized using biomass-based furfuryl alcohol as a carbon source, followed by sulfonation with chlorosulfuric acid (Figure 8) [59]. The effect of catalyst hydrophobicity on the adsorption capacity of substrate triglycerides was investigated. Hydrophobic catalysts showed a high adsorption capacity for substrates of triglyceride and oleic acid, facilitating contact between the acidic site and the substrates (Figure 8b,c). Due to its excellent hydrophobicity and high specific surface area (about 2000 m2 g−1), the catalytic activity of the carbon-based solid acid was higher than those of commercial polymers of Amberlyst-15 and Nafion NR50.
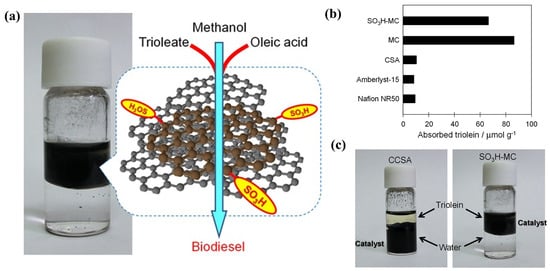
Figure 8.
(a) Production of biodiesel from triglyceride and oleic acid over the hydrophobic carbon-based solid acid catalyst. (b) Comparison of triolein adsorption capacity (c) Triolein−water mixture with CCSA or SO3H−MC [59]. Copyright 2015 Wiley.
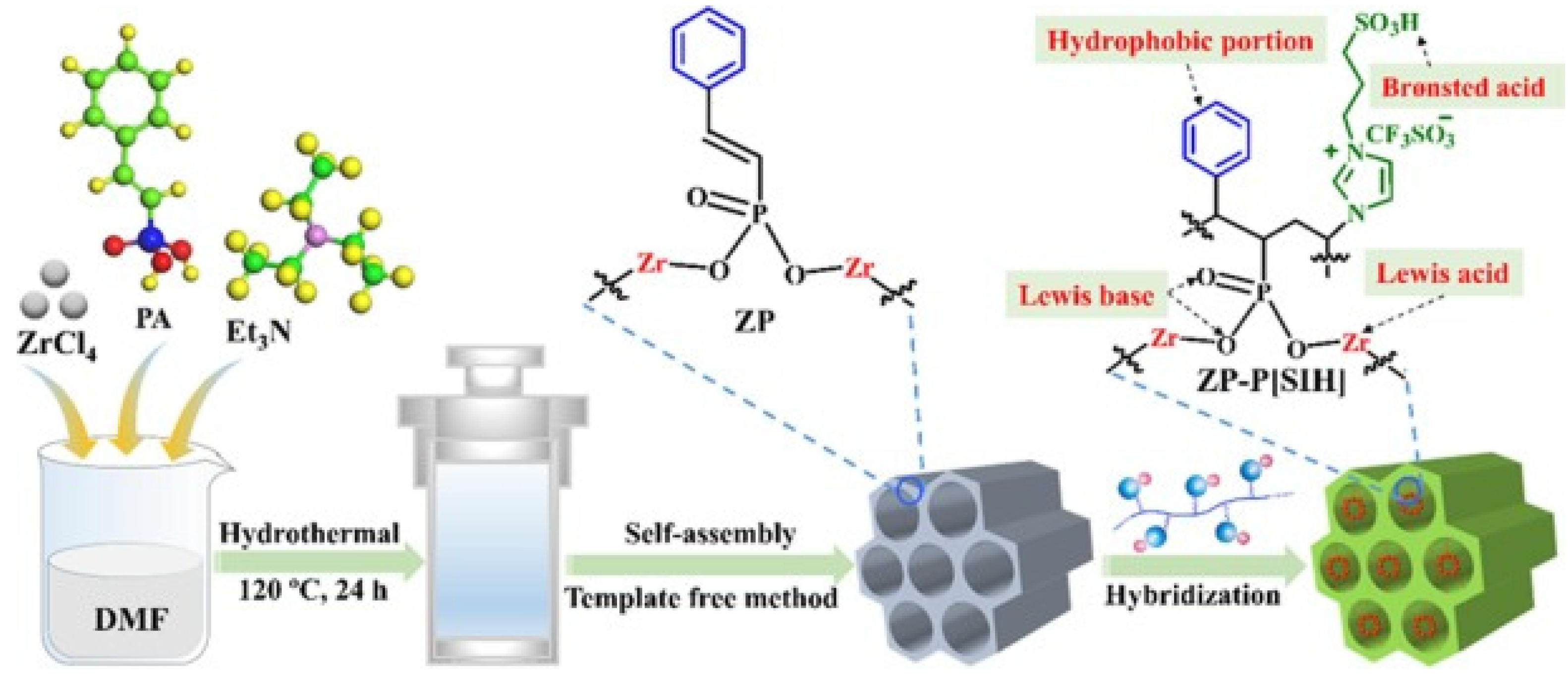
Pan et al. [60]. designed multifunctional mesoporous composite materials for catalytic biodiesel production from crude Euphorbia lathyris L. oil with an acid value of 26.1 mg KOH/g (Figure 9). Owing to its excellent hydrophobicity and wettability for oil and methanol, the prepared ZP-P[SIH]-2 exhibited a 93% biodiesel yield under the conditions of an 8 wt.% catalyst dosage and 40:1 ratio of methanol to oil at 150 °C for 8 h, which surpassed those of single P[SIH] and ZP. Meanwhile, its catalytic activity did significantly decrease over four cycles. The excellent hydrophobicity and wettability of ZP-P[SIH]-2 were attributed to the introduction of hydrophobic phenyl functional groups into the framework.
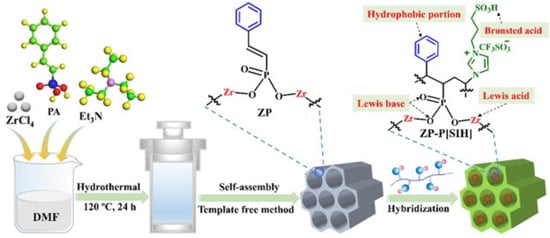
Figure 9.
Synthetic route of ZP and ZP-P[SIH] [60]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V.
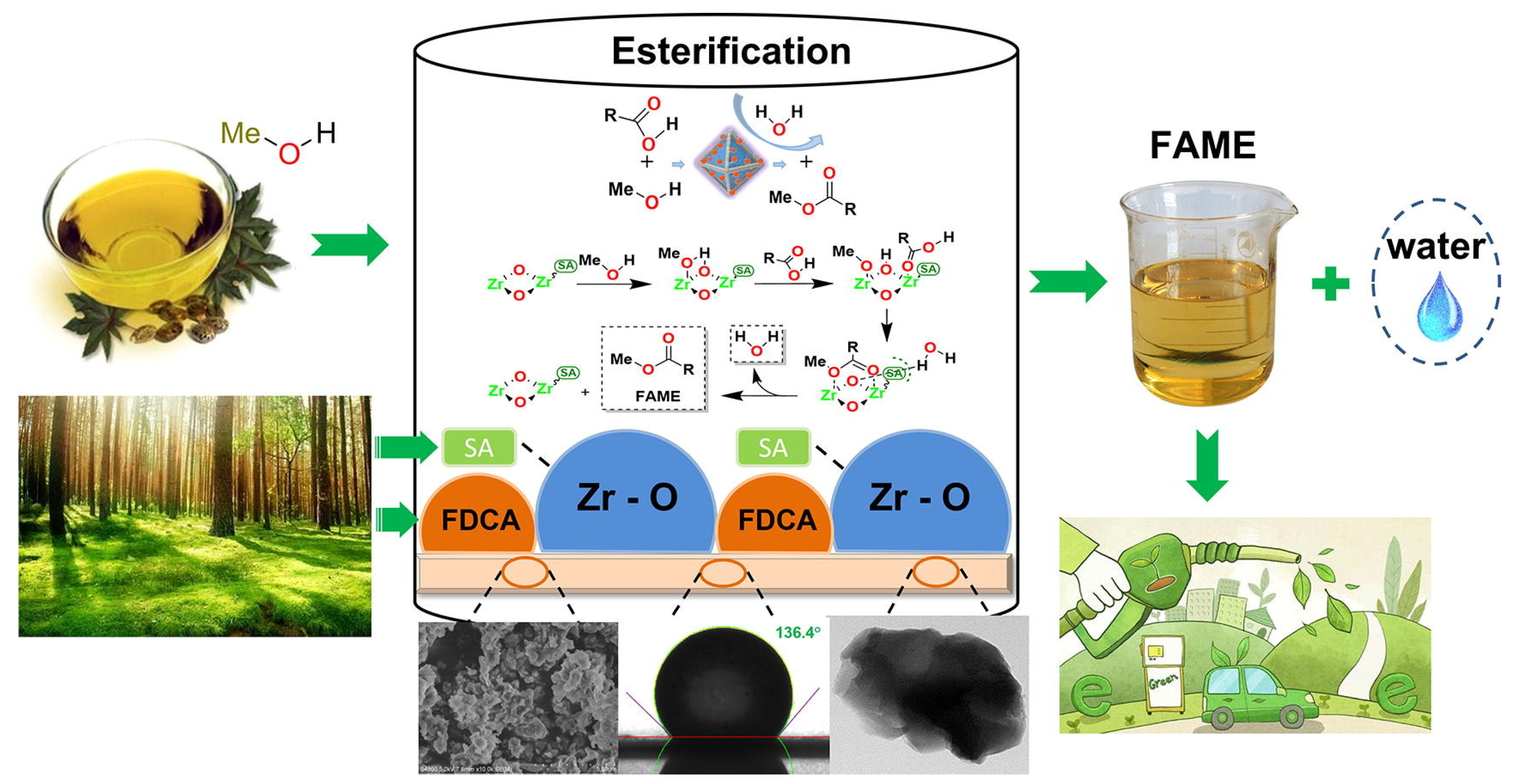
A hydrophobic polymeric solid acid was synthesized using biomass-derived stearic acid and 2,5-furandicarboxylicacid as a hydrophobic ligand and green organic linker, respectively [61]. The prepared hydrophobic acid catalyst showed a highly hydrophobic network with a water contact angle of 136.4 °C, which was beneficial for the adsorption of lipophilic acid and the desorption of water (Figure 10). The hydrophobic acid catalyst exhibited a 98.4% biodiesel yield from oleic acid via esterification under the reaction conditions of a 6.1 wt.% catalyst dosage and 39:1 ratio of methanol to oil at 60.2 °C for 24.5 h, which was superior to the corresponding catalyst without hydrophobicity. The biodiesel yield still reached above 90% after six recycles.
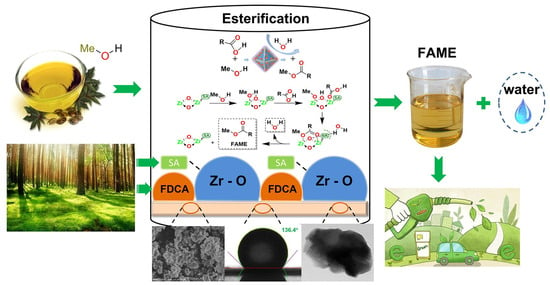
Figure 10.
Biomass-derived hydrophobic polymeric solid acid for production of biodiesel via esterification of oleic acid and methanol [61]. Copyright 2022 Elsevier B.V.
6. Effect of Specific Surface Area on Catalytic Activity
The limited contact efficiency between acidic sites and substrates greatly restricts the catalytic activity of solid acids. To overcome this issue, increasing the specific surface area of solid acids is an effective strategy [62]. Nitrogen adsorption characterization is a commonly used method for testing specific surface area [63]. Solid acids possess porous structures, which is a common method to increase the specific surface area. According to the size of the porous diameter, the pore structure is divided into micropores (<2 nm), mesopores (2–50 nm), and macropores (>50 nm) [64]. Because the size of long-chain fatty acids and their triglycerides is greater than 2 nanometers, microporous solid acids are not suitable for catalyzing the preparation of biodiesel. Substrates of >2 nm cannot enter micropores and contact with the acid sites within them, resulting in a poor catalytic activity of microporous solid acids [65]. The development of mesoporous solid acids has gained tremendous interest in biodiesel production [66]. In addition to porous acid catalysts, nanocatalysts are another attractive alternative to conventional catalysts for improving the contact efficiency between active sites and substrates [67]. Nano acid catalysts are a type of nano-sized functional material with a large surface-to-volume ratio, resulting in an enhanced accessibility of acid sites to reaction substrates [68]. Nano acid catalysts not only have the merits of recoverability and recyclability, but also exhibit a similar activity to homogeneous acid catalysts [69]. An MIPHPW solid acid was fabricated by the ion exchange of a mesoporous ionic covalent polymer (MICP) with H3PW12O40 (HPW), where the MICP was synthesized using an easy solvothermal method [70]. The MIPHPW solid acid exhibited a rich mesoporous structure with strong acid sites, which endowed a 98% conversion rate of oleic acid esterification under the reaction conditions of a 10 wt.% catalyst dosage and a methanol to oil molar ratio of 20:1 at 80 °C for 5 h.
7. Magnetic Catalyst Is Beneficial to Recovery
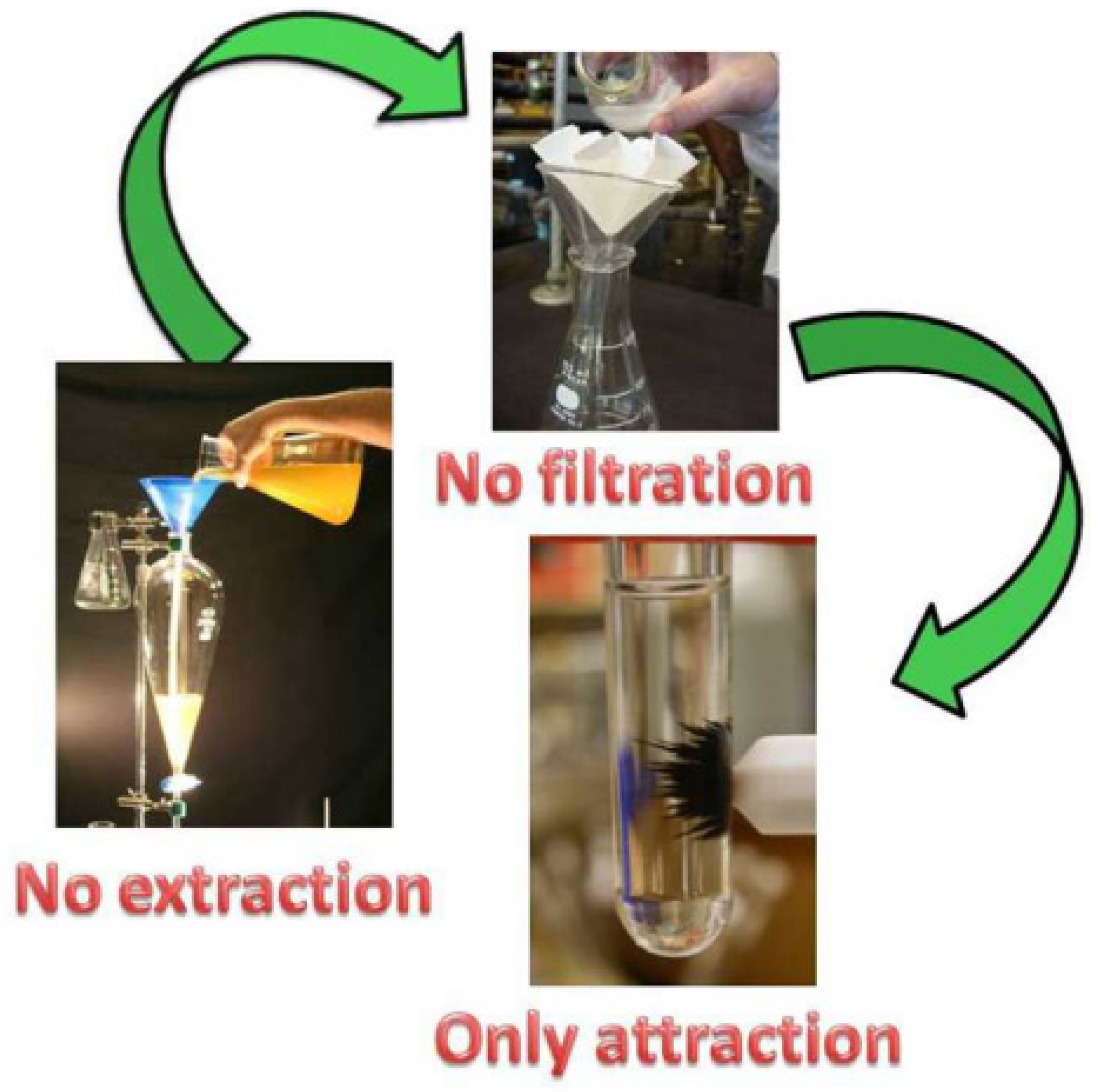
The separation of catalysts after a catalytic reaction is an essential process for reducing costs and environmental pollution. Catalyst recovery and reusability are the two vital features for evaluating the practicality of catalysts [71]. Nevertheless, the isolation and recovery of catalysts from a reaction mixture are not so easy, especially the separation of nanocatalysts [72]. Filtration, centrifugation, and extraction are common methods for separating catalysts (Figure 11) [73]. These methods are usually inefficient and energy-consuming, which hampers the economics and sustainability of heterogeneous catalysis [74]. To address these issues, the development of magnetic nanocatalysts is considered to be an effective strategy, because their insoluble and paramagnetic nature allows them to be easily and effectively recovered from reaction mixtures with an external magnet [75]. Meanwhile, magnetic nanoparticles exhibit a high surface area-to-volume ratio, allowing for loading a large number of active sites, which is beneficial for improving catalytic activity [76]. The magnetic properties of magnetic catalysts are measured using vibrating-sample magnetometry [77].
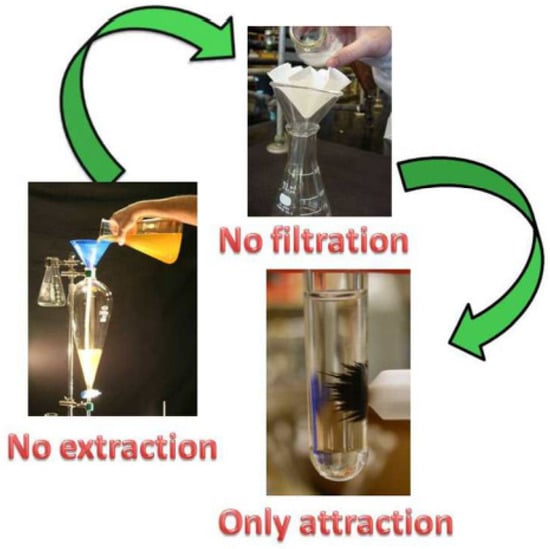
Figure 11.
Magnetic catalysts are conducive to recovery compared with extraction and filtration [73]. Copyright 2013 Elsevier Ltd.
The production of biodiesel from cottonseed oil usually requires the following six steps: cottonseed drying, cottonseed grinding, oil extraction, oil purification, esterification pretreatment, and the transesterification reaction for generating biodiesel. Utilizing the easy separation of magnetic catalysts, the production process of biodiesel from cottonseed oil can be simplified into cottonseed drying, cottonseed grinding, and the catalytic production of biodiesel, which is beneficial for reducing the production costs of biodiesel and improving production efficiency [78]. In this simplified process, a magnetic solid acid S2O8/ZrO2-TiO2-Fe3O4 was utilized as a catalyst for simultaneously catalyzing the esterification and transesterification reactions. Meanwhile, methyl acetate as a substitute for methanol acted in the in situ reactive extraction of cottonseeds. Under the conditions of a 50 °C reaction temperature, 21.3 wt.% catalytic amount, 13.8 milliliters of methyl acetate per gram of cottonseeds, and 10.8 h reaction time, the biodiesel yield achieved 98.5%. In addition, the S2O8/ZrO2-TiO2-Fe3O4 catalyst was easily recycled under a magnetic field and showed a biodiesel yield of 87.4%in the eighth reaction cycle.
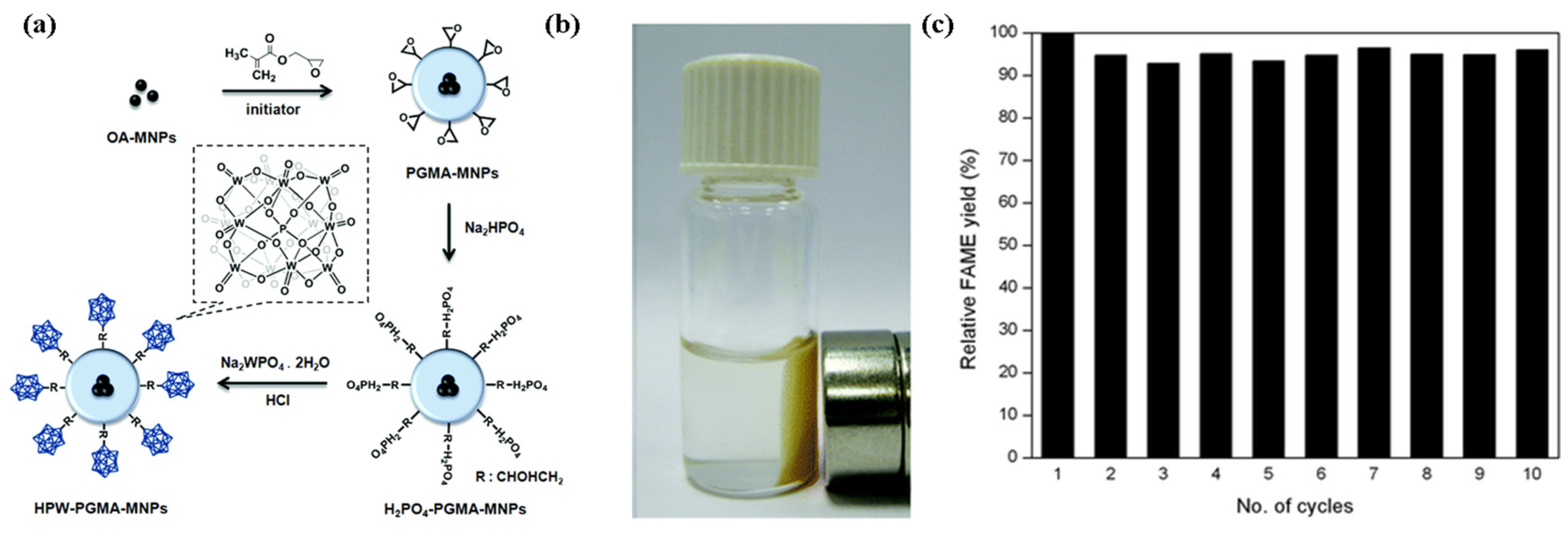
A magnetic nano acid catalyst (HPW-PGMA-MNPs) was synthesized by immobilizing phosphotungstic acid (HPW) on core–shell-structured magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), which were composed of iron oxide MNPs as the core and poly(glycidyl methacrylate) (PGMA) as the shell (Figure 12) [79]. HPW-PGMA-MNPs catalysts were used for the conversion of waste grease oil (21.3% wt.% FFA) into biodiesel via simultaneous esterification and transesterification in one pot. A 98% yield was achieved under the conditions of a methanol to oil molar ratio of 33:1, catalyst amount of 4 wt.%, temperature of 122 °C, and duration of 24 h. The catalyst was easy to recover under the condition of an external magnetic field. The catalyst testing was repeated 10 times and its activity was slightly reduced in the tenth reaction cycle.
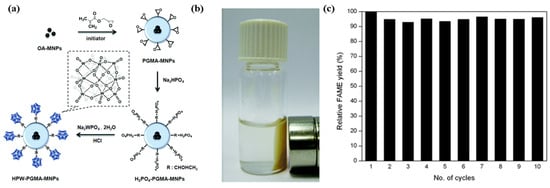
Figure 12.
(a) Synthesis route of magnetic supported heteropoly acid catalyst. (b) Under the external magnetic field, the magnetic catalyst is easy to recover. (c) Reusability of catalyst (Reaction conditions: molar ratio of methanol to oil = 33:1, catalyst dosage = 4 wt.%, reaction time = 24 h, reaction temperature = 122 °C) [79]. Copyright 2014 Royal Society of Chemistry.
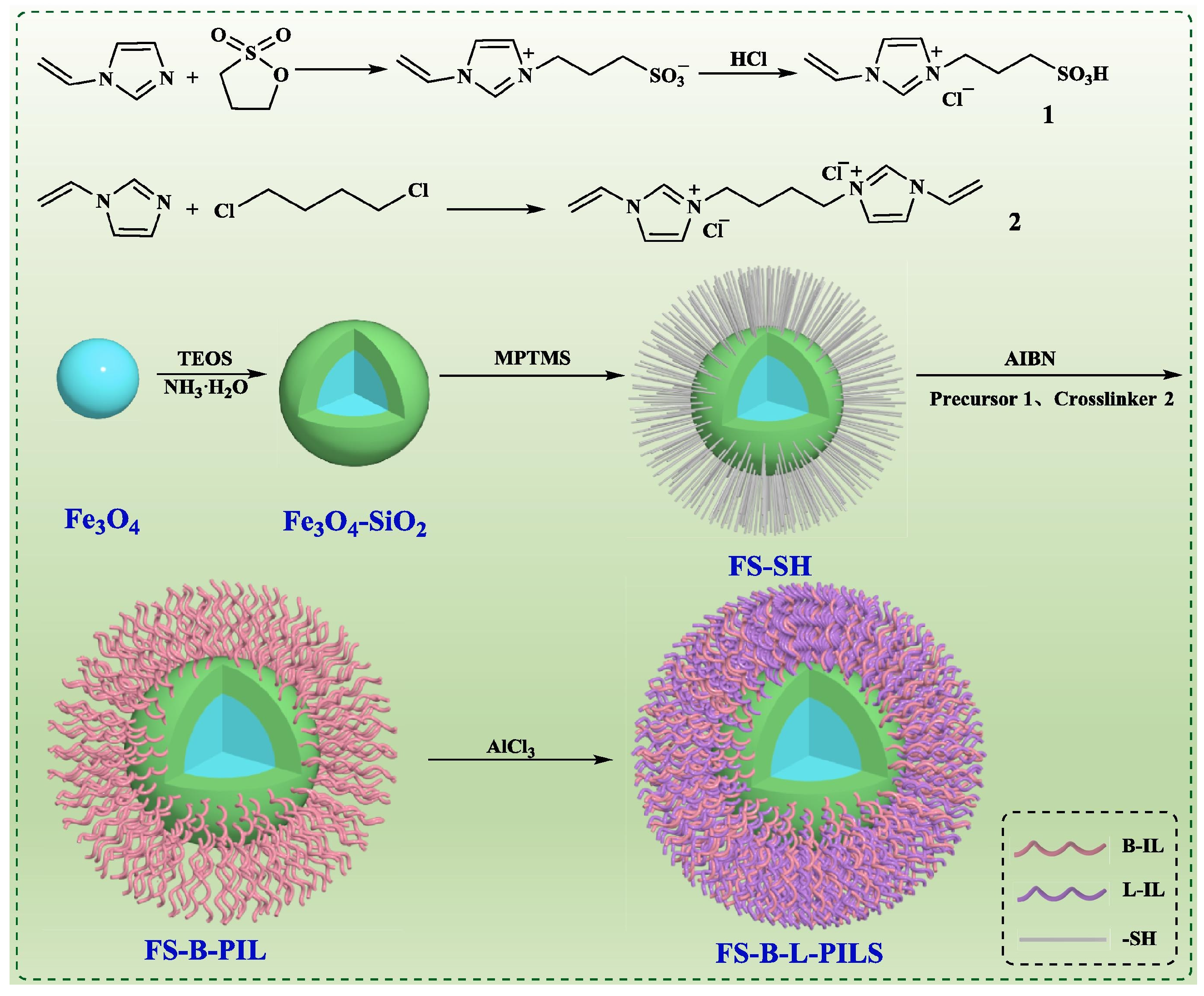
Acidic nanocatalysts (FS-BL-PILS) were synthesized by loading poly (acidic ionic liquid) onto silica-coated iron oxide as a carrier (Figure 13) [80]. The FS-B-L-PILS (2) nanocatalyst exhibited hydrophobicity (81.9°), strong superparamagnetic magnetization, and B and L acid sites. A biodiesel yield of 98.1% was achieved from Euphorbia lathyris L. oil with a high acid value of 25.60 mg KOH/g. The FS-B-L-PILS (2) nanocatalyst was facilely separated by magnetic force, with the biodiesel yield still reaching 91.2% in the fifth recycle.
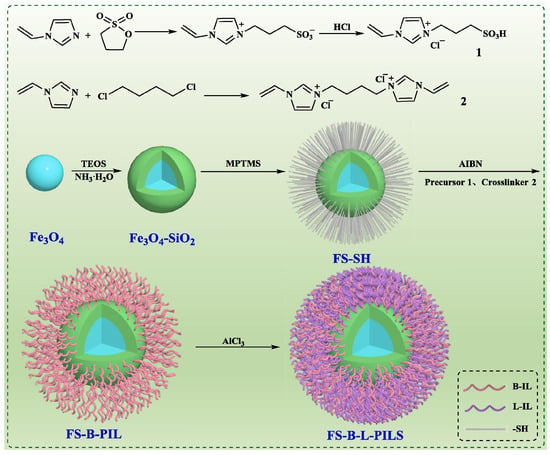
Figure 13.
Synthesis route of acidic nanocatalysts (FS-BL-PILS) [80]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier Ltd.
8. Thermosensitive Catalyst
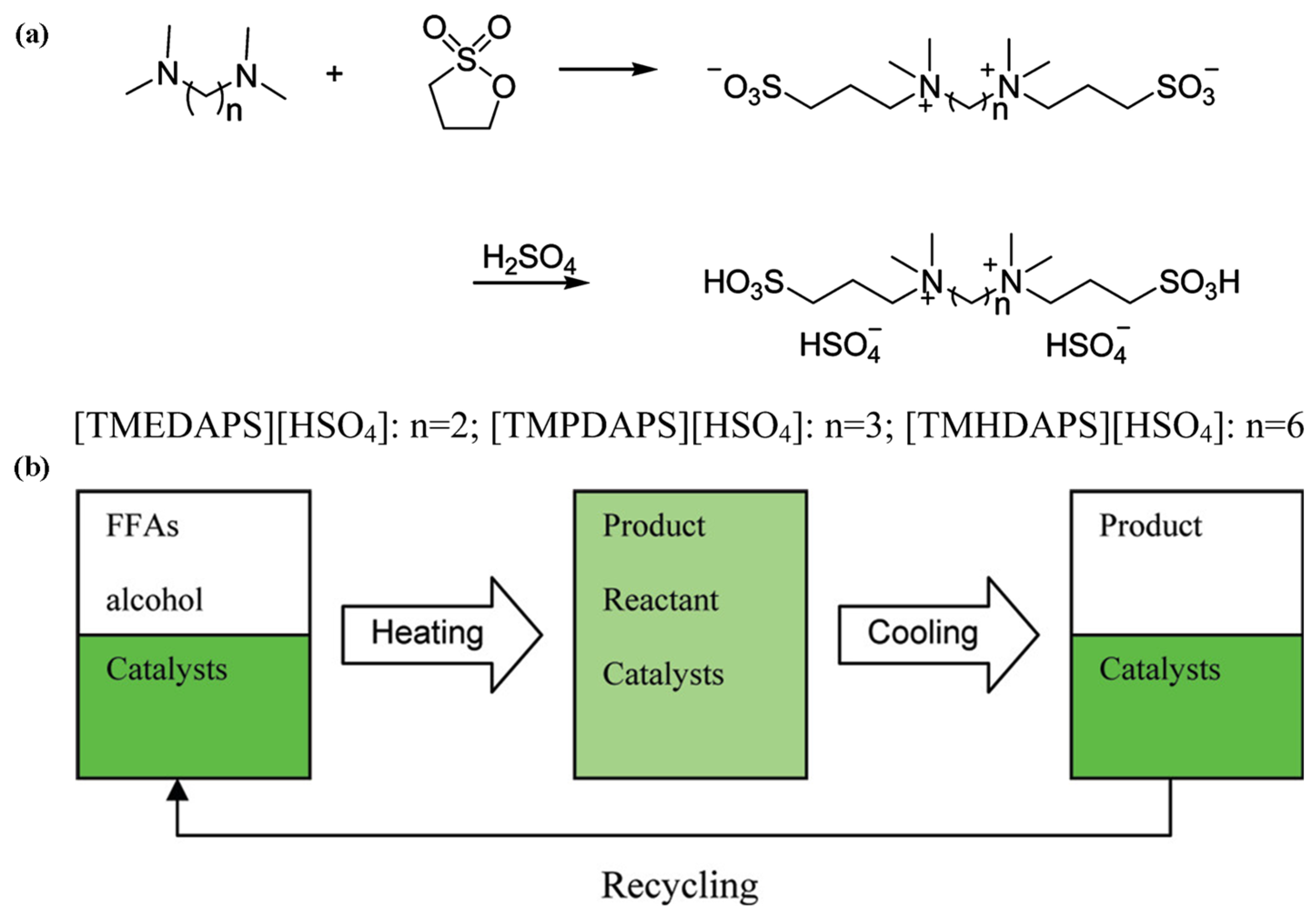
The replacement of homogeneous liquid catalysts with heterogeneous solid catalysts has become a trend in the development of green and sustainable chemical industry due to the convenient operation and recovery of heterogeneous solid catalysts [81]. However, the catalytic activity of heterogeneous solid catalysts is generally lower than that of homogeneous catalysts owing to the lower exposure degree of catalytic active sites to reaction substrates [82]. To address these issues, temperature-dependent IL–liquid biphasic catalytic systems have been developed [83]. In this catalytic system, the catalyst and substrate system are two-phase before the catalytic reaction, but they become homogeneous phase when the catalytic system is heated during the catalytic reaction process, because the catalyst is nearly insoluble in the catalytic system at room temperature, but miscible at a high temperature [84]. When the catalytic reaction is completed and cooled to room temperature, the final reaction mixture forms two phases and the catalyst is separated through a simple liquid separation operation [85]. Thermosensitive catalysts have the advantages of both homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts [86].
Some dicationic acidic ionic liquids were prepared as catalysts for the production of biodiesel from long-chain fatty acids with alcohols (Figure 14) [87]. They can form temperature-regulated reversible biphasic catalytic systems. The reaction systems were monophase at the reaction temperature, while two phases were formed after being cooled to room temperature. The ionic liquid catalyst was separated readily by the liquid/liquid separation of decantation. The conversion rate of oleic acid reached 95% at 70 °C for 6 h and was reduced by about 3% after six cycles.
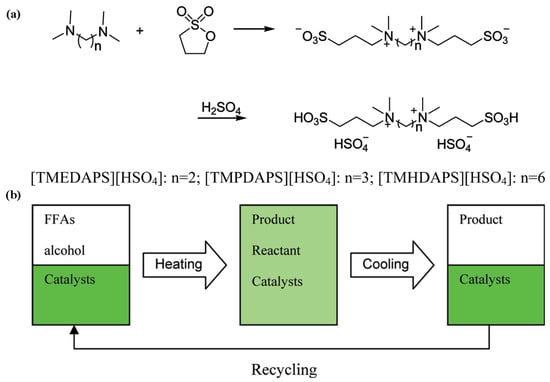
Figure 14.
(a) The synthetic pathway of ionic liquids. (b) Temperature-dependent catalytic system for production of biodiesel [87]. Copyright 2011 American Chemical Society.
9. Conclusions and Perspectives
Given the development demands of a green and sustainable society, the development of green and sustainable fuels has aroused tremendous interest. Biodiesel, as one green-biomass-based liquid fuel, has been deemed as a promising alternative to petrochemical diesel. Various countries have explored biodiesel raw feedstocks that are suitable for their own national conditions. The utilization of non-edible oils with a high acid value as raw feedstocks for biodiesel production is desired universally because it is beneficial for reducing the cost of biodiesel and avoids competition with human food. Acid catalysts are suitable for the production of biodiesel from high-acid-value oils because they can catalyze the esterification and transesterification reactions simultaneously in one pot. The replacement of homogeneous catalysts with heterogeneous catalysts has received considerable research interest due to the easy separation and high recyclability of these catalysts. Nevertheless, the catalytic activities of heterogeneous catalysts are usually lower than those of homogeneous catalysts. The physicochemical properties of heterogeneous catalysts have a significant impact on their catalytic activity and recyclability. Herein, various physical and chemical properties of such catalysts, such as acid density, acid types, acid strength, specific surface area, wettability, magnetism, and thermosensitivity, were elaborately discussed, with an emphasis on the effect of catalytic activity and reusability. Further, characterization techniques for identifying the physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids were introduced. Methods for regulating physicochemical properties of heterogeneous acids were also summarized. The influencing mechanisms of physicochemical properties on catalytic activity and repeatability were also reviewed.
Based on this commentary, the following guidelines for the development of efficient and stable heterogeneous acid catalysts are recommended for biodiesel production:
- (1)
- Acid density is an important parameter reflecting the number of acidic sites in a catalyst. A high acid density is beneficial for improving the catalytic activity of a catalyst due to the provision of abundant acidic sites for activating reaction substrates.
- (2)
- B acidic sites are conducive to facilitate esterification reaction, while L acidic sites are beneficial for promoting the transesterification reaction. The synergy of B and L acidic sites is helpful for the conversion of high-acid-value oil into biodiesel in one pot via catalyzing the esterification and transesterification reactions simultaneously.
- (3)
- The strength of acidic sites in catalysts has a significant impact on their catalytic activity. Super strong acid sites have a strong ability to activate reaction substrates, resulting in a high catalytic activity. The development of efficient and stable solid superacids is highly desirable for the production of biodiesel.
- (4)
- Catalysts with a high specific surface area are beneficial for facilitating contact efficiency between acidic sites and reaction substrates, improving the yield of biodiesel. Making a catalyst with a porous or nanoscale structure is an effective strategy to increase the specific surface area of the catalyst. A catalyst with a microporous structure is futile for improving catalytic activity due to oil molecules being larger than two nanometers, leading to difficulty in achieving contact between oil molecules and acid sites in the micropore channel.
- (5)
- A desirable heterogeneous acid surface for the production of biodiesel is supposed to selectively adsorb reaction substrates (methanol, fatty acids, or/and triglycerides) but expel water and glycerol as by-products, so as to weaken the reverse reaction.
- (6)
- Catalyst recycling is tedious, especially for homogeneous catalysts and nanocatalysts. Magnetic catalysts are easily and effectively recovered from reaction mixtures with an external magnet.
- (7)
- By designing temperature-sensitive acidic ionic liquids (ILs), temperature-dependent ILs–liquid biphasic catalytic systems can be developed. These exhibit the dual advantages of homogeneous catalysts with an excellent catalytic activity and heterogeneous catalysts with convenient recycling.
The combination of multiple excellent characteristics, such as a high acid density with B and L acid sites, strong acidity, large surface area, superhydrophobicity, and magnetism, in a solid acid catalyst is desirable but challenging. For instance, a high acid density inevitably reduces the hydrophobicity and specific surface area of the catalyst. How to reasonably coordinate the various properties of catalysts is the key to achieving a high catalytic activity. Nevertheless, considering the extraordinary complexity of this topic, joint efforts by chemists, materials scientists, physicists, and so forth are believed to be very beneficial for combatting this challenge.
Author Contributions
The contributions of the authors for the manuscript are the following: writing—original draft, J.H.; writing—review, J.H.; conceptualization, J.H.; editing, M.J.; conceptualization, H.P. and Q.X.; funding acquisition, H.P. and Q.X.; investigation, P.J. and Z.Y.; visualization, L.J. and J.Z.; supervision, Pan, H., and Q.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LQ22B060008) and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Jiaxing City (2024AD10053).
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financials support from the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Jiaxing City.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pan, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Qiu, L.; Zhou, B. Solar-Driven Biomass Reforming for Hydrogen Generation: Principles, Advances, and Challenges. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2402651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Xu, C.C.; Yang, S. Heterogeneously Chemo/Enzyme-Functionalized Porous Polymeric Catalysts of High-Performance for Efficient Biodiesel Production. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10990–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Sudarsanam, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Functionalized magnetic nanosized materials for efficient biodiesel synthesis via acid-base/enzyme catalysis. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 2977–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xia, Q.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Huang, H.; Ge, Z.; Li, X.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; et al. Recent advances in biodiesel production using functional carbon materials as acid/base catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 237, 107421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Rao, K.T.V.; Xu, C.C.; Yang, S. Advances in production of bio-based ester fuels with heterogeneous bifunctional catalysts. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2019, 114, 109296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, N.; Rao, P.K.; Sarkar, A.; Kubavat, J.; Vadivel, S.; Manwar, N.R.; Paul, B. Advancements in sustainable biodiesel production: A comprehensive review of bio-waste derived catalysts. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2024, 318, 118884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Yang, S. Functional nanomaterials-catalyzed production of biodiesel. Curr. Nanosci. 2020, 16, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Delbari, S.A.; Namini, A.S.; Van Le, Q.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Varma, R.S.; Jang, H.W.; T-Raissi, A.; Shokouhimehr, M.; et al. Recent developments in solid acid catalysts for biodiesel production. Mol. Catal. 2023, 547, 113362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Li, J. Magnetic solid catalysts for sustainable and cleaner biodiesel production: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2023, 171, 113017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Jin, D.; Yang, S. Effective production of biodiesel from non-edible oil using facile synthesis of imidazolium salts-based Brønsted-Lewis solid acid and co-solvent. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2018, 166, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Chen, L.; He, L.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, S. Facile synthesis of chitosan-derived sulfonated solid acid catalysts for realizing highly effective production of biodiesel. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 210, 118058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruatpuia, J.V.; Changmai, B.; Pathak, A.; Alghamdi, L.A.; Kress, T.; Halder, G.; Wheatley, A.E.; Rokhum, S.L. Green biodiesel production from Jatropha curcas oil using a carbon-based solid acid catalyst: A process optimization study. Renew. Energ. 2023, 206, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Gao, M.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H. Reduced surface sulphonic acid concentration Alleviates carbon-based solid acid catalysts deactivation in biodiesel production. Energy 2023, 271, 127079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, H.; Liu, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Xue, W.; Yang, S. Solid mixed-metal-oxide catalysts for biodiesel production: A review. Energy Technol. Ger. 2014, 2, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sudarsanam, P.; Tan, J.; Wang, A.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Sulfonic acid-functionalized heterogeneous catalytic materials for efficient biodiesel production: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huth, D.; Rose, M. Selective catalytic synthesis of short chain oxymethylene ethers by a heteropoly acid-a reaction parameter and kinetic study. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alismaeel, Z.T.; Al-Jadir, T.M.; Albayati, T.M.; Abbas, A.S.; Doyle, A.M. Modification of FAU zeolite as an active heterogeneous catalyst for biodiesel production and theoretical considerations for kinetic modeling. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkhoda, A.M.; West, A.H.; Ellis, N. Biochar based solid acid catalyst for biodiesel production. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2010, 382, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, N.; Yadav, G.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. Biomass-derived sulfonated polycyclic aromatic carbon catalysts for biodiesel production by esterification reaction. Biofuel. Bioprod. Bior. 2023, 17, 1343–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Pan, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, K.; Huang, S.; Yang, S. Efficient production of biodiesel with promising fuel properties from Koelreuteria integrifoliola oil using a magnetically recyclable acidic ionic liquid. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2017, 138, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istadi, I.; Riyanto, T.; Buchori, L.; Anggoro, D.D.; Gilbert, G.; Meiranti, K.A.; Khofiyanida, E. Enhancing Brønsted and Lewis acid sites of the utilized spent RFCC catalyst waste for the continuous cracking process of palm oil to biofuels. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 9459–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, S.; Saidi, M. Application of nano hydrophobic sulfated mordenite as a novel catalyst for biodiesel production from neem seed-derived oil by electrochemical method. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2024, 299, 117886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, K.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Biomass-derived hydrophobic metal-organic frameworks solid acid for green efficient catalytic esterification of oleic acid at low temperatures. Fuel Process. Technol. 2023, 239, 107558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, S.P.; Ngaosuwan, K.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Selvaraj, M.; Halder, G.; Rokhum, S.L. Microwave assisted biodiesel production using sulfonic acid-functionalized metal-organic frameworks UiO-66 as a heterogeneous catalyst. Renew. Energ. 2022, 197, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakason, K.; Sumrannit, P.; Youngjan, S.; Wanmolee, W.; Kraithong, W.; Khemthong, P.; Kanokkantapong, V.; Panyapinyopol, B. Environmental impact of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural production from cellulosic sugars using biochar-based acid catalyst. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 287, 119729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Yan, X.; Mao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guan, W.; Chen, Y. High-efficient microwave-assisted conversion of fructose to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural over rice straw-derived sulfonated porous carbonaceous catalyst. Fuel 2024, 373, 132348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfa, M.; Duval, J.F.; Marsac, R.; Dia, A.; Pinheiro, J.P. Absolute and Relative Positioning of Natural Organic Matter Acid-Base Potentiometric Titration Curves: Implications for the Evaluation of the Density of Charged Reactive Sites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 10494–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.Y.; Chandler, B.D. Surface hydroxyl chemistry of titania-and alumina-based supports: Quantitative titration and temperature dependence of surface Brønsted acid-base parameters. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2023, 15, 6868–6876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Bian, Y.; Dai, W. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of Brønsted and Lewis acid sites in zeolites: A combined probe-assisted 1H MAS NMR and NH3-TPD investigation. Chin. J. Struc. Chem. 2024, 43, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Kong, W.; Qi, C.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, F.S. Design and synthesis of mesoporous polymer-based solid acid catalysts with excellent hydrophobicity and extraordinary catalytic activity. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busca, G.; Gervasini, A. Solid acids, surface acidity and heterogeneous acid catalysis. Adv. Catal. 2020, 67, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Li, H.; Liu, X.F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, K.L.; Huang, S.; Yang, S. Mesoporous polymeric solid acid as efficient catalyst for (trans) esterification of crude Jatropha curcas oil. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 150, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokman, I.M.; Rashid, U.; Taufiq-Yap, Y.H.; Yunus, R. Methyl ester production from palm fatty acid distillate using sulfonated glucose-derived acid catalyst. Renew. Energ. 2015, 81, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, P.; Lu, D. POSS-derived solid acid catalysts with excellent hydrophobicity for highly efficient transformations of glycerol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun Kumar, M.; Kamali, M.; Putla, S.B.; Subha, P.; Sudarsanam, P. Nb2O5/Ce1–x NbxO2−δ Nanorod Catalyst for Selective Oxidative Coupling of Aromatic Alcohols and Amines. ACS Appl. Nano. Mater. 2024, 7, 5899–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Liu, H.; Cui, H.; Tian, Y.; Yang, H. Efficient and high para-selective conversion of toluene with NO2 to para-nitrotoluene in an O2–Ac2O–HβD4 composite catalytic system. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 1854–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; ChenYang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cai, R.; Han, B. Biodiesel synthesis through soybean oil transesterification using choline-based amino acid ionic liquids as catalysts. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 208, 117869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Fang, Z.; Tian, X.F.; Long, Y.D.; Jiang, L.Q. One-step production of biodiesel from Jatropha oil with high-acid value in ionic liquids. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 140, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, X.; Luo, M.; Zhao, C.J.; Gu, C.B.; Zu, Y.G.; Fu, Y.J. Biodiesel production from Camptotheca acuminata seed oil catalyzed by novel Brönsted-Lewis acidic ionic liquid. Appl. Energ. 2014, 115, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, L.; Wan, H.; Guan, G. Biodiesel Production by Esterification of Oleic Acid over Brønsted Acidic Ionic Liquid Supported onto Fe-Incorporated SBA-15. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 16590–16596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léon, C.I.S.; Song, D.; Su, F.; An, S.; Liu, H.; Gao, J.; Guo, Y.; Leng, J. Propylsulfonic acid and methyl bifunctionalized TiSBA-15 silica as an efficient heterogeneous acid catalyst for esterification and transesterification. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2015, 204, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trickett, C.A.; Osborn Popp, T.M.; Su, J.; Yan, C.; Weisberg, J.; Huq, A.; Urban, P.; Jiang, J.; Kalmutzki, M.J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Identification of the strong Brønsted acid site in a metal–organic framework solid acid catalyst. Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macht, J.; Carr, R.T.; Iglesia, E. Functional assessment of the strength of solid acid catalysts. J. Catal. 2009, 264, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuhara, T. Water-tolerant solid acid catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 3641–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, L. Transesterification of soybean oil to biodiesel by brønsted-type ionic liquid acid catalysts. Catal. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2013, 36, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.; Lane, J.; Culy, D.; Schultz, M.; Pullar, A.; Waxman, M. Sulfonic acid functionalized mesoporous SBA-15 catalysts for biodiesel production. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 129, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lotero, E.; Goodwin, J.G., Jr. A comparison of the esterification of acetic acid with methanol using heterogeneous versus homogeneous acid catalysis. J. Catal. 2006, 242, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, A.; Saqib, S.; Lin, H.; Shah, M.U.H.; Ullah, S.; Younas, M.; Rezakazemi, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Mahmood, A.; Asif, S.; et al. Current status and challenges in the heterogeneous catalysis for biodiesel production. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2022, 157, 112012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Guo, G.; Pan, J.; Gao, L.; Huo, Y. Polystyrene sulfonate threaded in MIL-101Cr (III) as stable and efficient acid catalysts. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 18084–18088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Zeng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, J.J.; Xie, J. Superhydrophobic and superacid magnetic catalyst induced highly selective aldol condensation and alkylation for high-density biofuels. Fuel 2024, 378, 132930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Aguila, B.; Verma, G.; Liu, X.; Dai, Z.; Deng, F.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F.; Ma, S. Superhydrophobicity: Constructing homogeneous catalysts into superhydrophobic porous frameworks to protect them from hydrolytic degradation. Chem 2016, 1, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, A.; Noshadi, I.; Xiao, F. Design and synthesis of hydrophobic and stable mesoporous polymeric solid acid with ultra strong acid strength and excellent catalytic activities for biomass transformation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2013, 136, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, L.; Meng, X.; Xiao, F. Transesterification catalyzed by ionic liquids on superhydrophobic mesoporous polymers: Heterogeneous catalysts that are faster than homogeneous catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 16948–16950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wu, X.; Liang, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, H. Highly active, water-compatible and easily separable magnetic mesoporous Lewis acid catalyst for the Mukaiyama–Aldol reaction in water. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 3768–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, Z. Design of Water-Tolerant Solid Acids: A Trade-Off Between Hydrophobicity and Acid Strength and their Catalytic Performance in Esterification. Catal. Surv. Asia 2021, 25, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchy, A.S.; Rashed, M.N.; Huang, M.; Toyao, T.; Shimizu, K.I.; Siddiki, S.H. Lewis acid promoted sustainable transformation of triglycerides to fatty acids using a water-tolerant Nb2O5 catalyst. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11791–11799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos-Durndell, V.C.; Durndell, L.J.; Isaacs, M.A.; Lee, A.F.; Wilson, K. WOX/ZrOX functionalised periodic mesoporous organosilicas as water-tolerant catalysts for carboxylic acid esterification. Sustain. Energ. Fuels 2023, 7, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobaraki, A.; Movassagh, B.; Karimi, B. Hydrophobicity-enhanced magnetic solid sulfonic acid: A simple approach to improve the mass transfer of reaction partners on the surface of the heterogeneous catalyst in water-generating reactions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 472, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuhara, K.; Nakajima, K.; Kitano, M.; Hayashi, S.; Hara, M. Transesterification of Triolein over hydrophobic microporous carbon with SO3H groups. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 3945–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xia, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Zhou, Z. Direct production of biodiesel from crude Euphorbia lathyris L. Oil catalyzed by multifunctional mesoporous composite materials. Fuel 2022, 309, 122172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Green synthesis of heterogeneous polymeric bio-based acid decorated with hydrophobic regulator for efficient catalytic production of biodiesel at low temperatures. Fuel 2022, 329, 125467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Wan, F. Immobilization of polyoxometalate-based sulfonated ionic liquids on UiO-66-2COOH metal-organic frameworks for biodiesel production via one-pot transesterification-esterification of acidic vegetable oils. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 365, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Niu, S. Preparation of carbon-based solid acid with large surface area to catalyze esterification for biodiesel production. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 69, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, H.; Tang, D.; Mathews, J.P.; Li, S.; Tao, S. A comparative evaluation of coal specific surface area by CO2 and N2 adsorption and its influence on CH4 adsorption capacity at different pore sizes. Fuel 2016, 183, 420–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, K.M.; Tahir, K.; Khan, A.U.; Nazir, S.; Almarhoon, Z.M.; Alanazi, A.A.; Althagafi, T.M.; Al-Saeedi, S.I.; Hassan, H.M.; Zaki, M.E. Catalytic conversion of triglycerides to biodiesel using ZnO/SnTiO4/SBA-15 nanostructures. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 325, 129694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, I.; Fadillah, G.; Sagadevan, S.; Oh, W.-C.; Ameta, K.L. Mesoporous silica-based catalysts for biodiesel production: A review. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.I.; Ramlee, N.N.; da Silva Duarte, J.L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Selvasembian, R.; Amir, F.; de Oliveira, L.H.; Azelee, N.I.W.; Meili, L.; Rangasamy, G. A comprehensive review on nanocatalysts and nanobiocatalysts for biodiesel production in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brazil and USA. Chemosphere 2023, 319, 138003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardy, J.; Rehan, M.; Hassanpour, A.; Lai, X.; Nizami, A.S. Advances in nano-catalysts based biodiesel production from non-food feedstocks. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 249, 109316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, K.; Devanand, J.; Kumar, P.S.; Soundarajan, K.; Sivasubramanian, V.; Sindhu, J.; Vo, D.V.N. A review on nano-catalysts and biochar-based catalysts for biofuel production. Fuel 2021, 306, 121632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, H.; Guo, L.; Li, H.; Jiang, L.; Yang, S. Synergetic combination of a mesoporous polymeric acid and a base enables highly efficient heterogeneous catalytic one-pot conversion of crude Jatropha oil into biodiesel. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 1698–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, S.; Esmaeili, H.; Moghadas, B.K. Performance of functionalized magnetic nanocatalysts and feedstocks on biodiesel production: A review study. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 305, 127200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.A. Nanocatalysts for biodiesel production. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, R.N.; Varma, R.S. Magnetically retrievable catalysts for organic synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 752–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawlid, O.A.; Abdelhady, H.H.; El-Deab, M.S. Boosted biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using novel SrO/MgFe2O4 magnetic nanocatalyst at low temperature: Optimization process. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2022, 273, 116435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, S.A.; Villarreal, J.S.; Acosta, P.I.; Noboa, J.F.; Gallo-Cordova, A.; Mora, J.R. Designing an efficient and recoverable magnetic nanocatalyst based on Ca, Fe and pectin for biodiesel production. Fuel 2022, 310, 122456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; Rashid, U.; Hazmi, B.; Moser, B.R.; Alharthi, F.A.; Rokhum, S.L.; Ngamcharussrivichai, C. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using magnetic bifunctional calcium and iron oxide nanocatalysts derived from empty fruit bunch. Fuel 2022, 317, 123525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changmai, B.; Wheatley, A.E.; Rano, R.; Halder, G.; Selvaraj, M.; Rashid, U.; Rokhum, S.L. A magnetically separable acid-functionalized nanocatalyst for biodiesel production. Fuel 2021, 305, 121576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. In situ reactive extraction of cottonseeds with methyl acetate for biodiesel production using magnetic solid acid catalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 174, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngu, T.A.; Li, Z. Phosphotungstic acid-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles as an efficient and recyclable catalyst for the one-pot production of biodiesel from grease via esterification and transesterification. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 1202–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Yan, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, H. Superparamagnetic nanospheres with efficient bifunctional acidic sites enable sustainable production of biodiesel from budget non-edible oils. Energ. Convers. Manag. 2023, 297, 117758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Ramli, A.; Subbarao, D. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using bifunctional heterogeneous solid catalysts. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 59, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaera, F. Designing sites in heterogeneous catalysis: Are we reaching selectivities competitive with those of homogeneous catalysts? Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 8594–8757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Yang, J.M.; Zhang, H.B.; Jiao, C.M. Synthesis of 4H-pyrans catalyzed by thermol-regulated PEG1000-based ionic liquid/EM. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2011, 17, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, N.; Gao, Y.; Lin, W.; Li, C. Thermosensitive polymer stabilized core-shell AuNR@Ag nanostructures as “smart” recyclable catalyst. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ge, Y.; Turner, A.P. A catalytic and positively thermosensitive molecularly imprinted polymer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, K.; Yang, J.; He, F.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Fan, L. Unlocking the Full Potential of Green Catalysis: A Novel Thermosensitive Catalytic System for Ultrasonic-microwave Liquefaction of Woody Biomass. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2024, 215, 118678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Yang, J.; Jiao, C. Dicationic ionic liquids as environmentally benign catalysts for biodiesel synthesis. ACS Catal. 2021, 1, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).