Abstract
The dry reforming of methane (DRM) and the combined steam–CO2 reforming of methane (CSCRM) are promising routes for syngas production while simultaneously utilizing two major greenhouse gases—CO2 and CH4. In this study, a series of Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts with varying Mg/Al molar ratios (Ni/MgAl(x), x = 0.5–0.9), along with Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3, were synthesized, characterized, and evaluated in both the DRM and CSCRM. Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3 exhibited a lower activity due to fewer active sites and a poor CH4/CO2 activation balance. In contrast, Ni/MgAl(0.6), Ni/MgAl(0.7), and Ni/MgAl(0.8) showed an enhanced activity, attributed to more abundant active sites and a more balanced activation of CH4 and CO2. Ni/MgAl(0.7) delivered the best DRM performance, whereas Ni/MgAl(0.8) was optimal for the CSCRM, likely due to its greater number of strong basic sites promoting CO2 and H2O adsorption. At 750 °C and 0.1 MPa over 100 h, Ni/MgAl(0.7) maintained a stable DRM performance (77% CH4 and 86% CO2 conversion; H2/CO = 0.9) at 120 L/(gcat·h), while Ni/MgAl(0.8) achieved a stable CSCRM performance (80% CH4 and 62% CO2 conversion; H2/CO = 2.1) at 132 L/(gcat·h). This study provides valuable insights into designing efficient Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts for targeted syngas production.
1. Introduction
CO2 and CH4 are major greenhouse gases that significantly contribute to global climate change [1]. The dry reforming of methane (DRM, Equation (1)) and the combined steam–CO2 reforming of methane (CSCRM, Equation (2)) convert CO2 and CH4 into valuable syngas while simultaneously mitigating both gases, attracting considerable interest from academic and industrial communities. A key distinction between the DRM and CSCRM lies in the H2/CO molar ratio of the produced syngas: the DRM yields a ratio of approximately one, suitable for dimethyl ether synthesis and higher alcohol production [2,3], whereas the CSCRM generates syngas with a H2/CO ratio of around two, which is preferred for methanol synthesis and the Fischer–Tropsch conversion to liquid fuels [4,5].
Nickel-based catalysts are widely used in reforming reactions due to their low cost and high catalytic activity. However, they are prone to sintering and coke deposition under high-temperature conditions, leading to catalyst deactivation [6,7,8]. Therefore, developing nickel-based catalysts with an enhanced sintering resistance and coke inhibition capabilities is critical for advancing reforming technologies. The choice of support materials plays a crucial role in promoting Ni particle dispersion and improving the catalytic performance of Ni-based catalysts in CH4 reforming reactions. Among various supports, the magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) spinel is a promising candidate due to its excellent thermal stability (melting point of 2135 °C [9]), high mechanical strength, and chemical inertness. Guo et al. [10] reported that Ni/MgAl2O4 exhibited a high DRM activity and stability owing to the high sintering resistance and low acidity of MgAl2O4 as well as its ability to promote Ni dispersion. Similarly, Hadian et al. [11,12] demonstrated that nanocrystalline MgAl2O4-supported Ni catalysts showed a high catalytic activity in both the DRM and the combined dry reforming and partial oxidation of methane. Additionally, Kim et al. [13] found that Ni/MgAl2O4 subjected to an inert-annealing treatment exhibited improved structural properties, leading to a high CH4 conversion and the enhanced durability in the steam reforming of methane (SRM). Yu et al. [14] further demonstrated that Ni supported on sol–gel-derived MgAl2O4 showed a high activity and stability for the CSCRM.
Unfortunately, MgAl2O4 alone lacks sufficient basic sites for effective CO2 adsorption [15,16]. In contrast, MgO exhibits a strong Lewis basicity and is often incorporated to enhance the basicity, resistance to coking, and overall catalytic performance of catalysts [17,18]. As a result, catalyst supports containing MgAl2O4 and MgO have garnered increasing attention. Fang et al. [19] reported that Ni/MgO-Al2O3 with excess MgO possessed a higher number of surface basic sites than Ni/MgAl2O4 without MgO, leading to the improved adsorption and activation of CO2 and CH4 and thereby enhancing the DRM activity. Similarly, Park et al. [20] demonstrated that the Mg/Al ratio influenced not only the basicity of Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts but also their Ni dispersion and reducibility. The optimal catalyst with a Mg/Al ratio of 0.55 exhibited the highest number of Ni active sites, the greatest basicity, and the best DRM performance. More recently, Tao et al. [21] found that the coordination configuration of Ni in MgAl2O4, which depended on the Mg content, affected the metal–support interaction, the crystallinity of deposited carbon species, and the thermal stability of Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts. The effect of the Mg/Al ratio has also been explored in the CSCRM. Schiaroli et al. [22] observed that increasing the Mg/Al ratio improved the activity of Ni-Rh/MgO-Al2O3 by enhancing the CO2 adsorption on the catalyst surface. Koo et al. [23] noted that both low and high MgO contents promoted coke formation—the former due to inactive NiAl2O4 and surface acid sites and the latter owing to the agglomeration of free Ni species. They further reported that a Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalyst with a Mg/Al ratio of 0.5 exhibited an optimal catalytic activity in the CSCRM [24].
The literature survey indicates that Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts are promising for both the DRM and CSCRM, with the Mg/Al ratio being a key factor influencing the catalytic performance. However, its effect may differ between these two distinct processes, suggesting that the optimal Mg/Al ratio could vary accordingly. Although many studies have investigated the DRM and CSCRM individually, making direct comparisons between their findings is challenging due to differences in catalyst preparation methods and reaction conditions. For example, Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts prepared using home-made MgO-Al2O3 were evaluated for the DRM at 800 °C under a high gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 1,500,000 h−1 [20], whereas those derived from commercial MgO-Al2O3 were tested for the CSCRM at 650–750 °C with a GHSV of 530 L/(gcat·h) [24]. To develop high-performance Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts tailored to specific reforming routes—the DRM for higher alcohols and the CSCRM for liquid fuels—a direct comparison of the two processes under similar conditions is crucial. This approach would enable an accurate assessment of the effect of the Mg/Al ratio on the DRM and CSCRM. However, to the best of our knowledge, no such comparative study has been reported to date.
To bridge this gap, a series of Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts with Mg/Al molar ratios ranging from 0.5 to 0.9 were prepared, characterized, and evaluated in this study. Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3 were also included as reference catalysts. To ensure a meaningful comparison, both DRM and CSCRM were conducted under identical temperature and pressure conditions with comparable GHSV values, differing only in the feed composition. The structure–performance relationships of the catalysts were investigated to elucidate the influence of the Mg/Al ratio on each process. Finally, the most effective catalysts for the DRM and CSCRM were subjected to long-term stability tests over 100 h.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalytic Performance
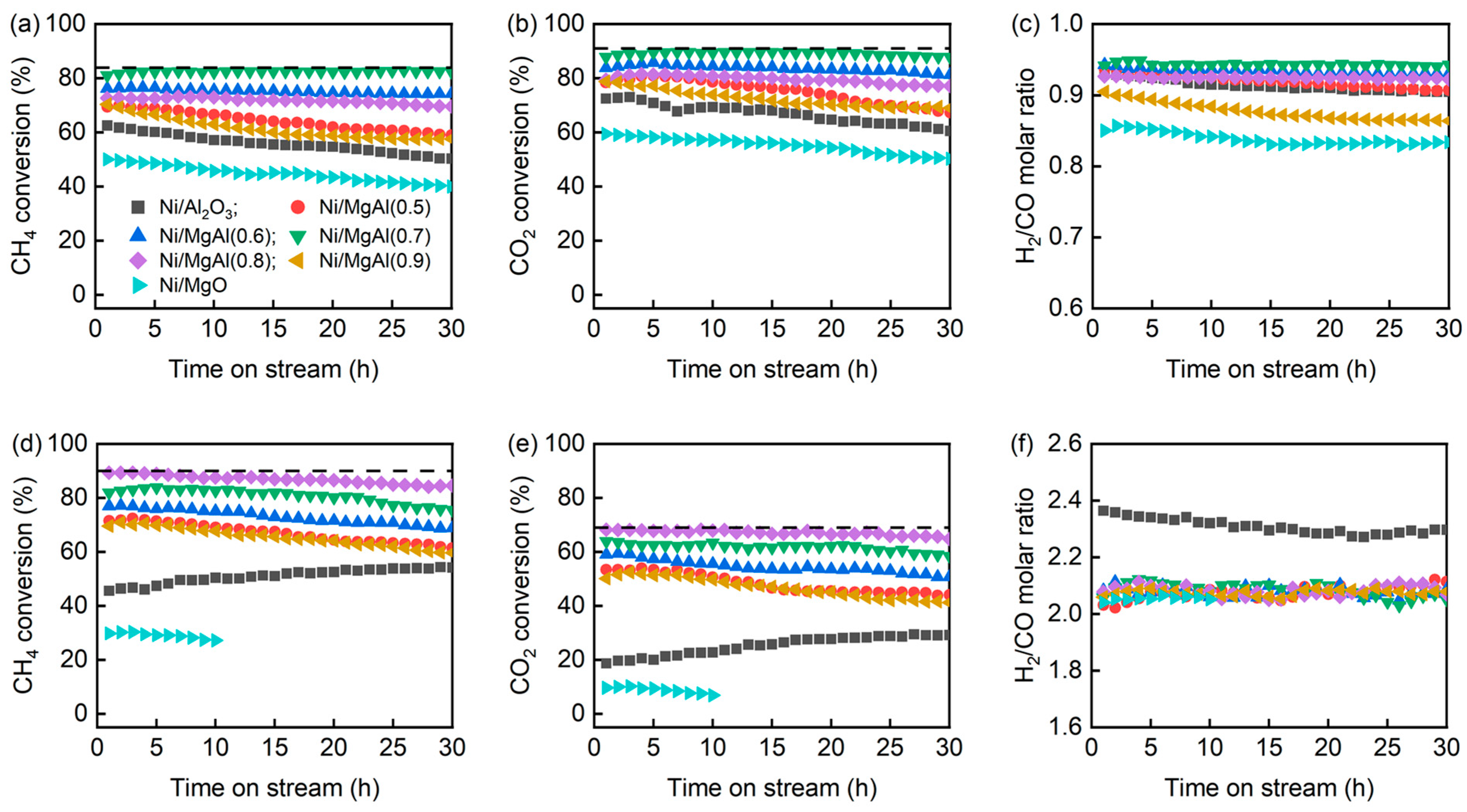
Figure 1 presents the catalytic performances of the Ni/Al2O3, Ni/MgO, and Ni/MgAl(x) catalysts in the DRM and CSCRM as a function of the time on stream (TOS). The equilibrium conversions of CH4 and CO2, calculated using the ASPEN Plus® simulator, are 83.8% and 90.6% for the DRM and 89.9% and 68.5% for the CSCRM, respectively. For Ni/Al2O3 in the DRM, the initial CH4 and CO2 conversions at TOS = 1 h are 62.6% and 72.5%, respectively. However, these values gradually decrease to 50.3% and 60.6% after 30 h of reaction, suggesting a catalyst deactivation. In contrast, under CSCRM conditions, the CH4 and CO2 conversions of Ni/Al2O3 show an opposite trend, increasing from 45.6% and 18.7% at TOS = 1 h to 54.2% and 29.2% after 30 h, respectively, which implies a catalyst reactivation. Compared to Ni/Al2O3, Ni/MgO demonstrates a lower catalytic activity, particularly in the CSCRM. Due to the significantly low activity of Ni/MgO in the CSCRM, only 10 h of TOS testing was conducted.
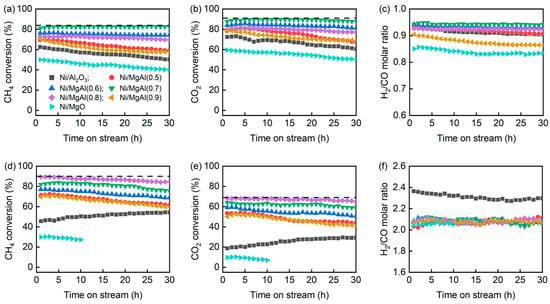
Figure 1.
(a–c) DRM and (d–f) CSCRM performances of various catalysts (Reaction conditions: (a–c) CH4/CO2 = 1/1, GHSV = 120 L/(g‧h), temperature = 750 °C; (d–f) CH4/H2O/CO2 = 2.5/2/1, GHSV = 132 L/(g‧h), and temperature = 750 °C. The dashed lines correspond to the equilibrium conversion data of CH4 and CO2).
The catalytic activities of Ni/MgAl(x) in both the DRM and CSCRM are superior to those of Ni/Al2O3 and Ni/MgO, highlighting the promoting effect of MgO and Al2O3 mixed oxides. In general, the activity of Ni/MgAl(x) initially increases with the increasing x, reaches a maximum, and then declines. However, the optimal catalysts for the DRM and CSCRM differ. For the DRM, Ni/MgAl(0.7) shows the best performance, maintaining a high and stable CH4 conversion (81.0–82.3%) and CO2 conversion (87.9–89.6%) over 30 h. In contrast, for the CSCRM, Ni/MgAl(0.8) is the most effective catalyst, with the CH4 conversion slightly decreasing from 89.4% to 84.5% and the CO2 conversion decreasing from 68.2% to 64.8% over the same period.
For the DRM process, the CO2 conversions over all catalysts are consistently higher than the corresponding CH4 conversions, which can be attributed to the reverse water–gas shift (RWGS) reaction [25,26,27]. This leads to the H2/CO molar ratios below one. Notably, Ni/MgO exhibits the lowest H2/CO ratio (0.83–0.85), followed by Ni/MgAl(0.9) (0.86–0.9) and the other catalysts (0.9–0.95). In contrast, for the CSCRM, the CH4 conversions exceed the CO2 conversions, likely due to the CH4 decomposition [14,28] and the WGS reaction [29]. As a result, the H2/CO ratios are larger than two. Interestingly, the H2/CO ratio over Ni/Al2O3 (2.27–2.36) is much higher than those of the other catalysts (2.02–2.12). It is anticipated that the different behaviors of the catalysts for the DRM and CSCRM are linked to their physicochemical properties. Therefore, in the following section, the properties of both fresh and spent catalysts will be explored in detail.
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of Catalysts
2.2.1. Fresh Catalysts
The N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms and pore size distribution curves of the supports and catalysts are presented in Figures S1 and S2, with the textural data (specific surface area, pore volume, and average pore diameter) summarized in Table 1. All supports and catalysts exhibit IV hysteresis loops and unimodal mesoporous structures [30]. The specific surface area and pore volume of Al2O3 are significantly higher than those of MgO. For the mixed oxide supports, as the Mg/Al ratio increases from 0.5 to 0.9, the surface area and pore volume initially increase and then decrease, with MgAl (0.8) showing the highest values. This suggests that the textural properties of the supports can be tuned by adjusting the Mg/Al ratio. After the Ni loading on the support, the specific surface area of each catalyst, except for Ni/MgO, decreases as expected compared to the support. However, the surface area of Ni/MgO is nearly twice that of MgO, likely due to the formation of smaller particles.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of different catalysts.
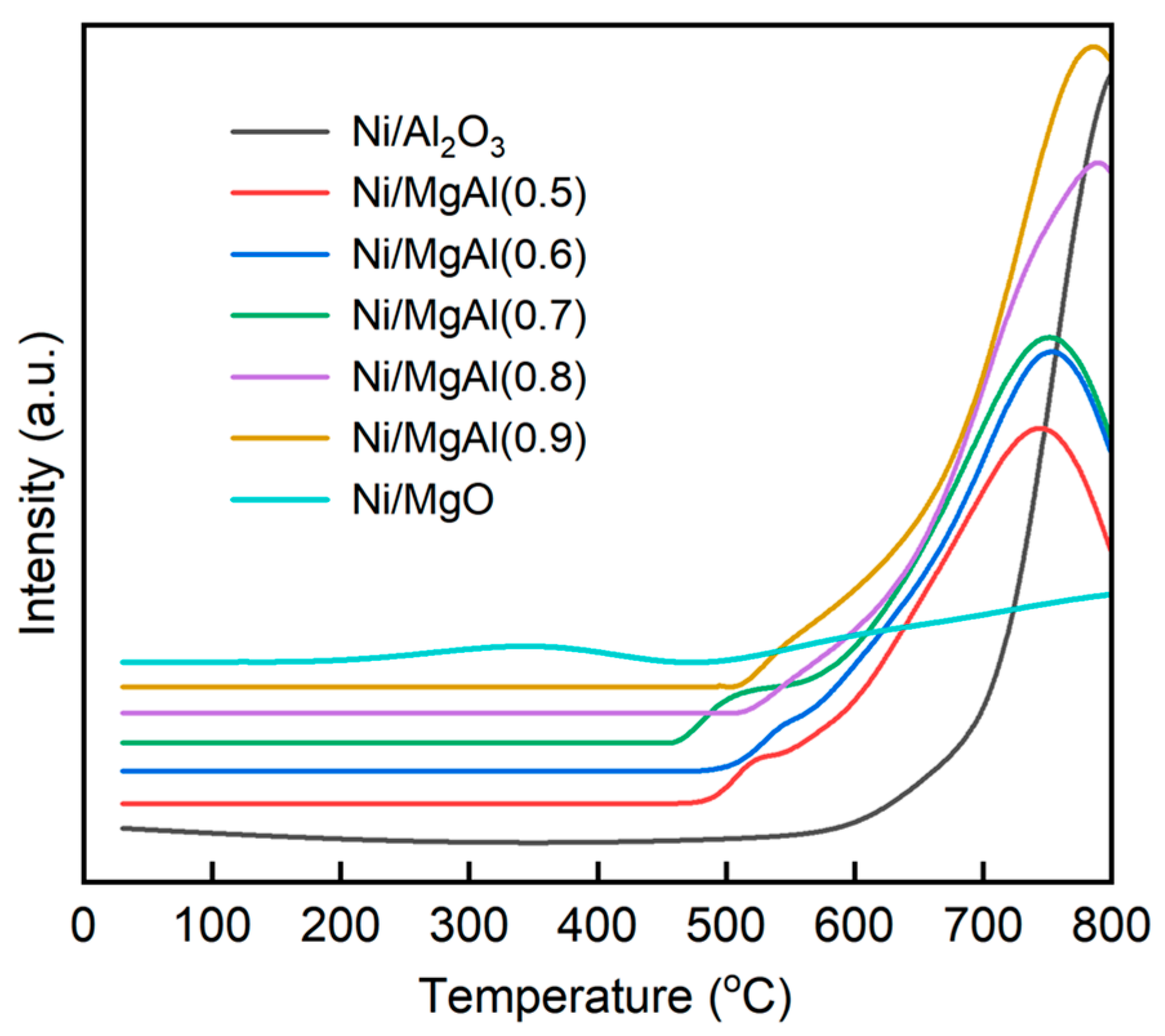
Figure 2 shows the H2-TPR profiles of Ni/Al2O3, Ni/MgO, and Ni/MgAl(x), with the maximum temperature limited to 800 °C due to instrument constraints. All catalysts except Ni/MgO exhibit a prominent high-temperature reduction peak centered between 700 and 800 °C, which is indicative of strong metal–support interactions [31]. In contrast, Ni/MgO shows no distinct peak but instead displays a gradually increasing H2 consumption curve up to 800 °C, suggesting that the Ni species in this catalyst are extremely difficult to reduce. This behavior is attributed to the formation of a MgO-NiO solid solution, facilitated by the shared face-centered cubic structure of NiO and MgO, which significantly impedes the reduction [32]. Compared to Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3, the Ni/MgAl(x) catalysts show a relatively easier reduction. As the value of x increases from 0.5 to 0.9, the reduction peak temperature gradually rises from 740 to 780 °C, implying that the reducibility of Ni/MgAl(x) is dependent on the Mg/Al ratio. Similar findings have been reported by other researchers [21,33,34]. Tao et al. [21] demonstrated that excessive Mg occupies the octahedral sites in the nonstoichiometric Ni-doped MgAl2O4 spinel, thereby impeding the reduction of Ni species. It should be noted that the supports (Al2O3, MgO, and MgAl(x)) themselves display no reduction peaks, confirming the absence of reducible species in the support materials.
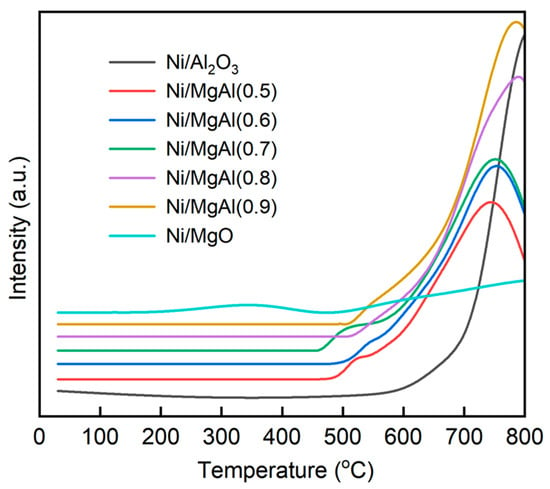
Figure 2.
H2-TPR profiles of various catalysts (signal intensity shown as raw output).
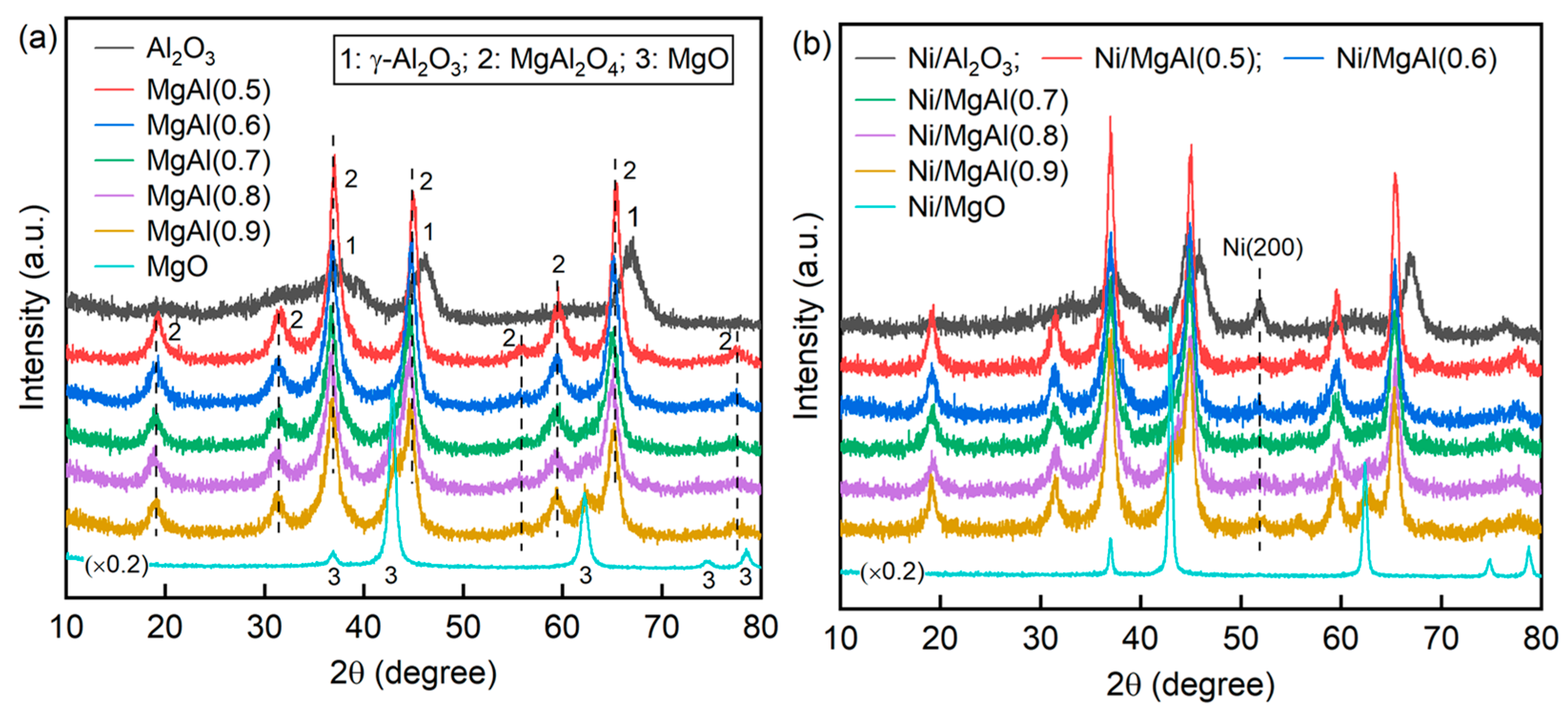
Figure 3 presents the XRD patterns of supports and reduced catalysts. Both Al2O3 and Ni/Al2O3 exhibit characteristic diffraction peaks indexed to γ-Al2O3 (JCPDS #10-0425). In the case of Ni/Al2O3, the Ni(200) diffraction peak (JCPDS #04-0850) is clearly detected, indicating the presence of face-centered cubic Ni. In contrast, no Ni-related peaks are identified in Ni/MgO, where only MgO diffraction peaks (JCPDS #45-0946) appear. The absence of Ni peaks is probably attributed to the low abundance of Ni particles, as supported by the H2-TPR analysis. Further evidence is provided by the much lower H2 uptake of Ni/MgO (3.4 μmol/g, Table 1), which is an order of magnitude lower than that of other catalysts (14.4–24.8 μmol/g). The low H2 uptake suggests a limited number of metal active sites, which likely explains the poor catalytic activity of Ni/MgO in both the DRM and CSCRM processes (Figure 1). For MgAl(x) and Ni/MgAl(x), the peaks corresponding to the MgAl2O4 spinel (JCPDS #21-1152) are observed. In samples with x = 0.8 and 0.9, MgO is faintly detected. Given the high calcination temperature (830 °C), the formation of NiAl2O4 in Ni/Al2O3 is feasible [35,36]. However, identifying NiAl2O4 in the XRD pattern is challenging due to the peak overlap with γ-Al2O3. Based on the reactivation behavior of Ni/Al2O3 observed during the CSCRM process, it can be inferred that a portion of the Ni species remains in the form of NiAl2O4 even after the reduction treatment. The in situ reduction of Ni from NiAl2O4 during the reaction is probably responsible for the observed reactivation phenomenon of Ni/Al2O3.
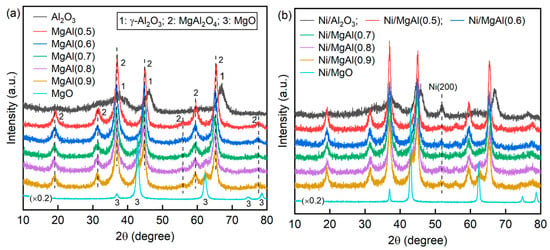
Figure 3.
XRD patterns of (a) supports and (b) fresh reduced catalysts (the intensities for MgO and Ni/MgO are scaled by a factor of 0.2 for a clear comparison).
Based on the Ni(200) peak of the reduced catalysts (except Ni/MgO), the Ni crystallite size can be estimated using the Scherrer equation. As presented in Table 1, Ni/Al2O3 shows an average Ni particle size of 6.9 nm, which is smaller than that of Ni/MgAl(x). This is probably owing to its high reduction temperature, which originates from the reduction of Ni2+ in the NiAl2O4 spinel. For Ni/MgAl(x), as x increases from 0.5 to 0.8, the Ni particle size decreases from 10.3 to 7.9 nm; however, for Ni/MgAl(0.9), it increases to 11.4 nm. This trend generally correlates with the specific surface area of the MgAl(x) support, where a larger surface area promotes metal dispersion, leading to smaller Ni particles. Table 2 shows the lattice parameters of MgAl2O4 for both MgAl(x) and Ni/MgAl(x). These parameters are calculated through cell refinement using Jade 6.5 software. The lattice parameters of the fresh catalysts are consistently smaller than those of their corresponding supports. This reduction implies that Ni is incorporated into the MgAl2O4 lattice, as the ionic radius of Ni2+ (0.55 Å) is smaller than that of Mg2+ (0.57 Å) [37].

Table 2.
Lattice parameters of MgAl2O4 in MgAl(x) and Ni/MgAl(x).
Figure 4 illustrates the morphologies of the supports and catalysts, the microstructures of the catalysts, as well as the elemental distribution across the catalysts. As shown in the FESEM images, Ni/Al2O3 and Ni/MgAl(x) exhibit bulk granular morphologies similar to their respective supports. In contrast, Ni/MgO displays smaller particles compared to MgO, which is consistent with the larger specific surface area of Ni/MgO relative to MgO. The HRTEM analysis reveals distinct microstructural differences in Ni/MgAl(x). For Ni/MgAl(0.5), Ni nanoparticles (dark spots) are dispersed on plate-like particles. However, for Ni/MgAl(x) (x = 0.6–0.9), needle-like particles appear, and their quantity increases with x. The lattice fringe analysis (Figure S3) confirms that the plate-like particles correspond to MgAl2O4, while the needle-like particles are attributed to MgO. This is consistent with the composition of MgAl(0.5), which matches the stoichiometric MgAl2O4, whereas MgAl(x) (x = 0.6–0.9) contains excess MgO beyond the stoichiometric ratio.
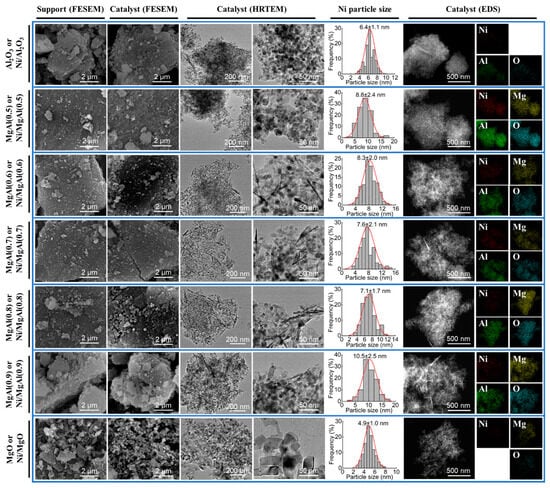
Figure 4.
FESEM images of supports and fresh catalysts, along with HRTEM images, Ni particle size distributions, and EDS mapping of fresh catalysts.
For all catalysts, Ni particles are well dispersed on the supports, as indicated by the EDS mapping analysis. From the HRTEM images, the average Ni particle sizes of the catalysts can be determined. Ni/MgO exhibits the smallest Ni particle size (4.9 nm), followed by Ni/Al2O3 (6.4 nm) and Ni/MgAl(x) (7.1–10.5 nm). This trend is likely associated with the reducibility of the catalysts, as the Ni species in the NiO-MgO solid solutions and NiAl2O4 spinel are more difficult to reduce, resulting in smaller Ni particles [38,39,40]. Notably, Ni/MgO contains a limited amount of Ni particles, further supporting the challenges in its reduction. This observation aligns with its low H2 uptake. The Ni particle sizes determined by HRTEM closely match those obtained from XRD and exhibit the same variation trend (Table 1).
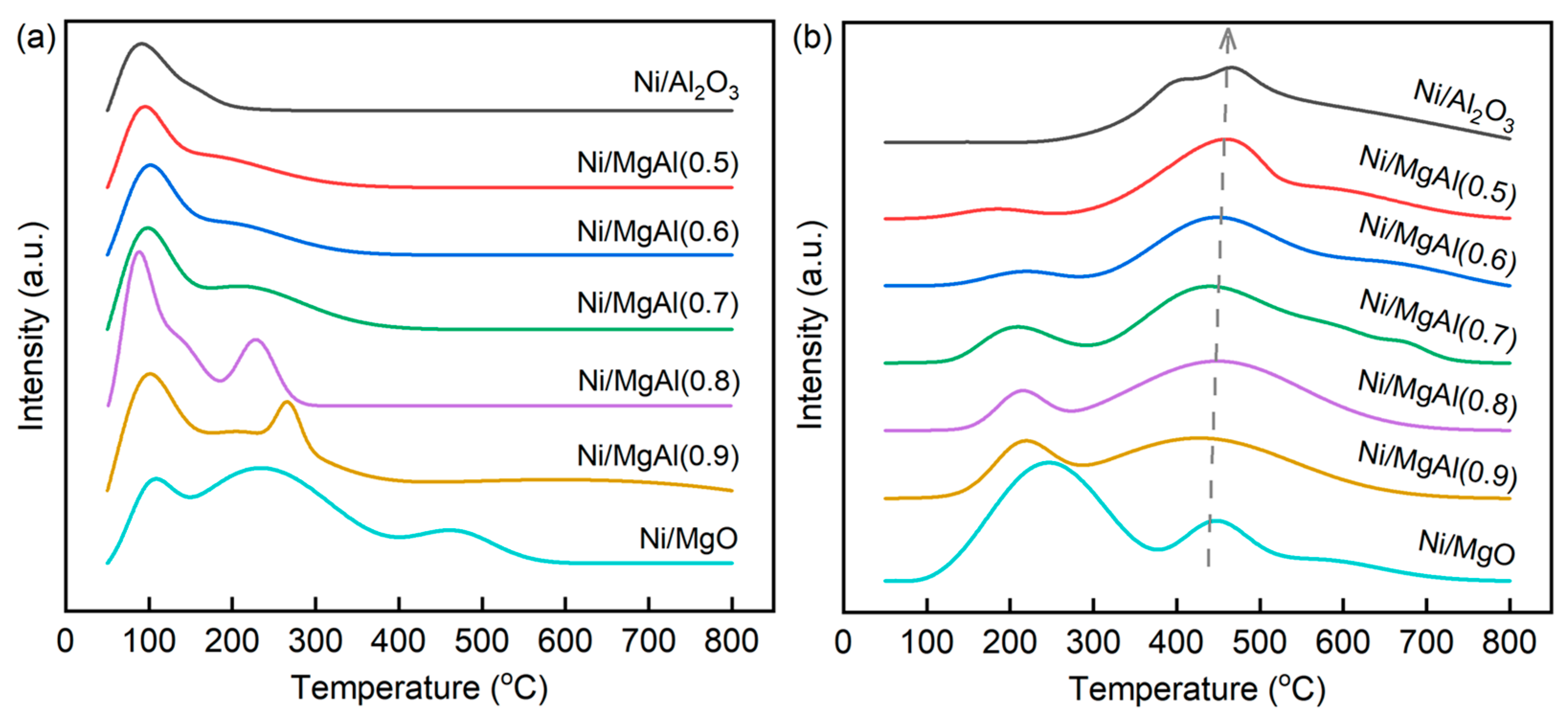
The interactions of CO2 with the catalysts can be analyzed using CO2-TPD. Figure S4 and Figure 5a show the CO2-TPD profiles of the supports and catalysts, respectively. The desorption peaks below 200 °C, between 200 and 400 °C, and above 400 °C are generally assigned to the release of carbon oxides from weak, medium, and strong basic sites, respectively [41,42,43]. The total basicity of each sample, which reflects the overall number of basic sites, can be estimated by integrating the areas of all desorption peaks. Compared to the supports, the catalysts exhibit a reduced total basicity due to the coverage of basic sites by Ni particles. Among the catalysts, Ni/Al2O3 shows the lowest total basicity, consisting exclusively of weak basic sites. In contrast, Ni/MgO exhibits the highest total basicity, encompassing weak, medium, and strong basic sites. Ni/MgAl(x) contains both weak and medium basic sites, and as x increases, both the total basicity and the proportion of medium basic sites increase. Accordingly, the strength of CO2–catalyst interactions follow the order of Ni/Al2O3 < Ni/MgAl(0.5) < Ni/MgAl(0.6) < Ni/MgAl(0.7) < Ni/MgAl(0.8) < Ni/MgAl(0.9) < Ni/MgO.
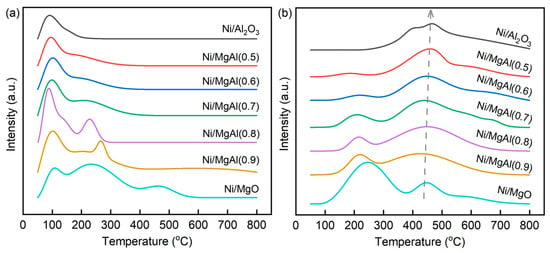
Figure 5.
(a) CO2-TPD and (b) CH4-TPD curves of various catalysts.
CH4-TPD measurements are used to investigate the ability of metal sites to adsorb and activate CH4. Figure 5b presents the CH4-TPD profiles of the catalysts. The desorption peaks below 300 °C and above 400 °C correspond to weak (σ sites) and strong (τ site) adsorption sites for CH4, respectively [44]. From Ni/MgO to Ni/MgAl(x) with the decreasing x, and further to Ni/Al2O3, the proportion of σ sites decreases, while that of τ sites increases. Additionally, the τ-site peak shifts toward higher temperatures, indicating stronger interactions between CH4 and Ni. Consequently, the strength of CH4–Ni interactions follows the order of Ni/MgO < Ni/MgAl(0.9) < Ni/MgAl(0.8) < Ni/MgAl(0.7) < Ni/MgAl(0.6) < Ni/MgAl(0.5) < Ni/Al2O3. This trend is opposite to that observed for CO2–catalyst interactions.
The number of metal active sites (indicated by H2 uptake), CH4–Ni interactions, and CO2–catalyst interactions are key factors influencing the DRM and CSCRM performance of the catalysts. Ni/MgAl(0.6), Ni/MgAl(0.7), and Ni/MgAl(0.8) possess the highest number of active sites while exhibiting moderate CH4–Ni interactions and CO2–catalyst interactions. This balance likely promotes a suitable match between the CH4 activation and CO2 activation, leading to the high initial activity in both the DRM and CSCRM, as shown in Figure 1. In contrast, Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3 exhibit the lowest number of active sites; moreover Ni/MgO shows the strongest CO2–catalyst interactions but the weakest CH4–Ni interactions, whereas Ni/Al2O3 demonstrates the weakest CO2–catalyst interactions but the strongest CH4–Ni interactions. This imbalance leads to a mismatch between the CH4 activation and CO2 activation, ultimately resulting in the low activity in both the DRM and CSCRM.
Regarding Ni/MgAl(0.6), Ni/MgAl(0.7), and Ni/MgAl(0.8), the initial activity in the DRM follows the sequence of Ni/MgAl(0.7) > Ni/MgAl(0.6) > Ni/MgAl(0.8), whereas in the CSCRM, the order is Ni/MgAl(0.8) > Ni/MgAl(0.7) > Ni/MgAl(0.6). It has been established that the competitive dissociative adsorption of CO2 and H2O occurs on the basic sites of the catalyst [29,45,46]. Thus, a higher number of stronger basic sites are preferred in the CSCRM to enhance the CO2 adsorption and activation, explaining the highest CSCRM activity of Ni/MgAl(0.8). In the DRM, where no steam is introduced, the strong CO2 adsorption could hinder the transfer of activated CO2, making relatively weaker basic sites more favorable [47,48]. Consequently, Ni/MgAl(0.7) exhibits the highest DRM activity. This indicates that the CSCRM requires more and stronger basic sites for effective CO2 adsorption and activation compared to DRM.
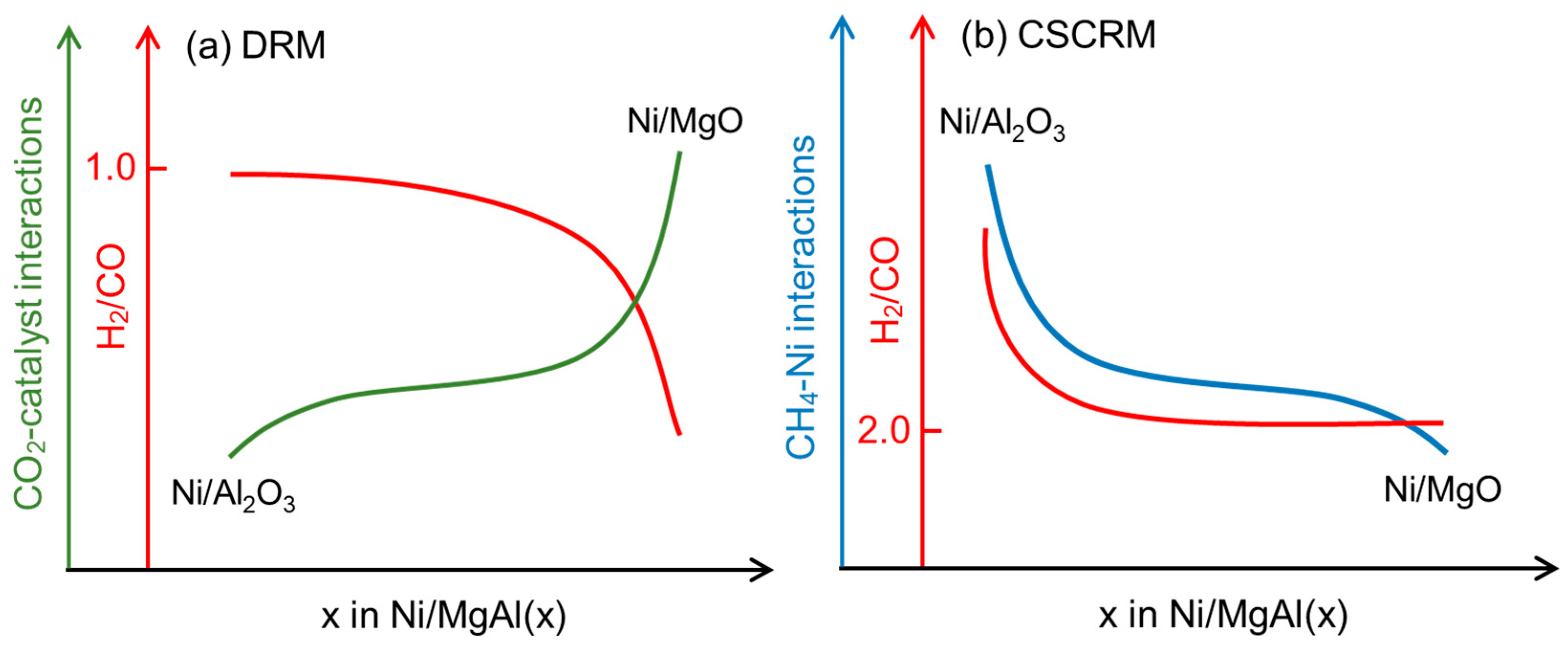
The H2/CO molar ratio in the DRM is influenced by the CO2–catalyst interactions or the basicity of the catalysts (Figure 6a). Previous studies have shown that an increased catalyst basicity enhances CO2 adsorption and activation, as well as the CO selectivity in the RWGS [49,50]. Considering that Ni/MgO has the highest total basicity and the strongest CO2–catalyst interactions, more RWGSs are expected to occur on this catalyst, resulting in the lowest H2/CO ratio (Figure 1c). Likewise, Ni/MgAl(0.9), with the second-highest basic strength, exhibits the second-lowest H2/CO ratio. In contrast, the H2/CO ratio in the CSCRM is likely affected by the CH4–Ni interactions (Figure 6b). Ni/Al2O3 displays the strongest CH4–Ni interactions and CH4 adsorption, which are likely to promote the CH4 decomposition [51]. Additionally, the acid sites of γ-Al2O3 can further facilitate the CH4 decomposition [23,36,52]. As a result, Ni/Al2O3 yields a notably higher H2/CO in the CSCRM compared to the other catalysts (Figure 1f).
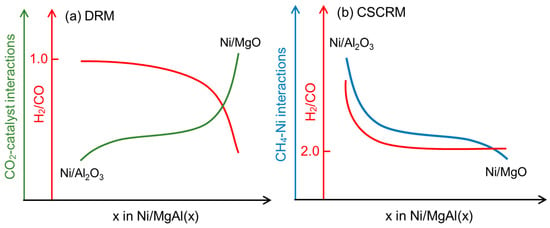
Figure 6.
A schematic diagram of the correlation between the reactant–site interactions, H2/CO ratio, and Mg/Al ratio in the (a) DRM and (b) CSCRM.
2.2.2. Spent Catalysts
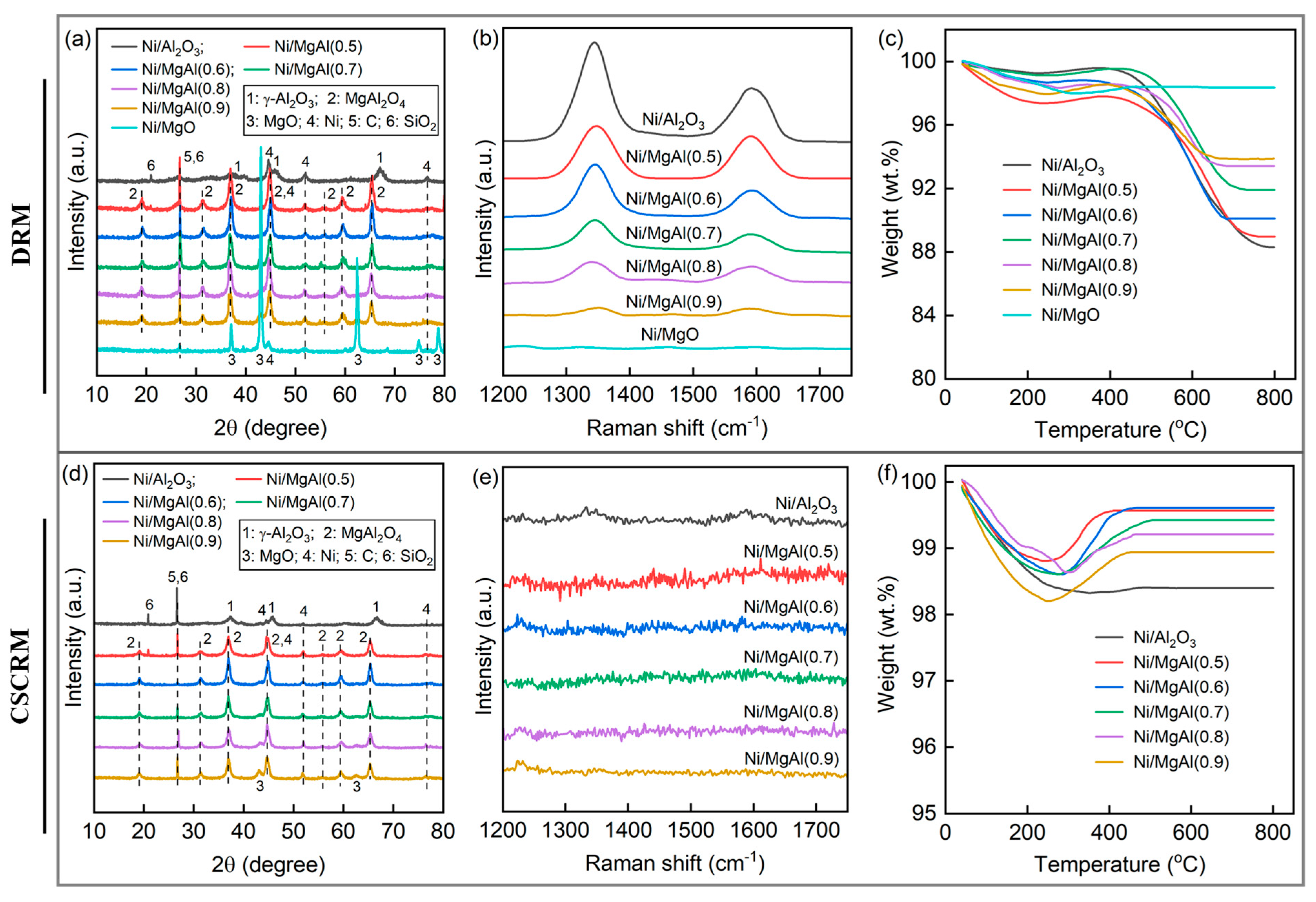
After 30 h of TOS testing in either the DRM or CSCRM, most catalysts experience partial deactivation, as evidenced by the decline in CH4 and CO2 conversions shown in Figure 1. It is widely recognized that the deactivation mechanisms in methane reforming reactions are primarily associated with the coke formation and metal particle sintering. The presence and quantity of coke can be analyzed by the XRD, Raman, and TGA. As presented in Figure 7a, all spent catalysts in the DRM exhibit distinct Ni diffraction peaks, suggesting the growth of the Ni crystallite size. Indeed, the Ni crystallite size of each spent catalyst (Table 3) is larger than that of its fresh counterpart (Table 1). In addition to Ni, γ-Al2O3, MgAl2O4, and MgO, crystalline silica is detected, which is attributed to the quartz sand used to dilute the catalyst. Although efforts were made to separate the spent catalyst from quartz sand particles using a magnet, some quartz sand remained in the catalyst. Since the (006) plane of coke at 2θ = 26.6° (JCPDS #26-1076) overlaps completely with the (101) plane of the quartz sand (JCPDS #46-1045), it is impossible to determine the presence of the coke formation from the XRD patterns alone.
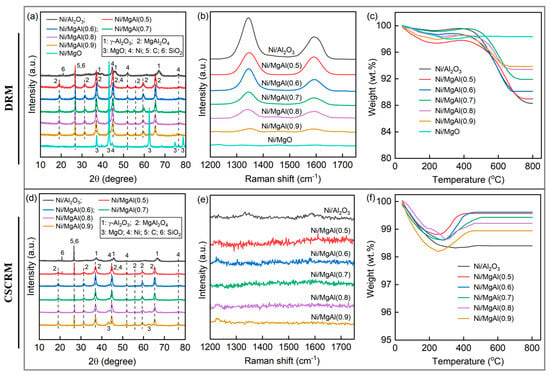
Figure 7.
(a,d) XRD patterns, (b,e) Raman spectra, and (c,f) TGA profiles of spent catalysts ((a–c) DRM; (d–f) CSCRM).

Table 3.
Ni particle sizes and coke deposition of spent catalysts in DRM and CSCRM.
Figure 7b shows the Raman spectra of spent catalysts in DRM. Except for Ni/MgO, all catalysts display two peaks at around 1340 and 1590 cm−1, corresponding to the structural defects of graphite (D bond) and in-plane carbon–carbon stretching vibrations of graphite layers (G bond), respectively [53,54]. This confirms the coke formation. From Ni/Al2O3 to Ni/MgAl(0.5), Ni/MgAl(0.6), …, and Ni/MgAl(0.9), the peak intensities of both the D bond and G bond gradually decrease, implying a reduction in the coke deposition. No peaks are observed for Ni/MgO, indicating the absence of the coke formation. This trend aligns with the basic intensity and total basicity of the catalysts, as more and stronger basic sites enhance the CO2 adsorption, thereby supplying more surface oxygen to inhibit the coke deposition [55,56].
Figure 7c further presents the TGA profiles of the spent catalysts. These curves can be divided into three regions: (1) the desorption of H2O and CO2 below 200 °C, (2) the removal of the amorphous carbon and oxidation of metallic Ni between 200 and 400 °C, and (3) the gasification of graphitic carbon above 400 °C [55,57]. The amorphous carbon is readily oxidized, whereas the graphitic carbon is less reactive, leading to a catalyst deactivation [14,58,59]. Based on the TGA curves, the amount of graphitic carbon in each catalyst is determined, as listed in Table 3. Consistent with the Raman analysis, catalysts with a stronger basicity exhibit a lower graphitic carbon deposition. Notably, no detectable carbon formation was observed on Ni/MgO, whereas Ni/γ-Al2O3 shows the highest coke content (11.3 wt.%) and coking rate (0.38 wt.%/h).
Like the spent catalysts in the DRM, those in the CSCRM exhibit an increase in the Ni crystallite size (Figure 7d and Table 3). However, both the D bond and G bond are indiscernible in the spent catalysts of the CSCRM, except for very weak signals observed for Ni/Al2O3 (Figure 7e). Although the CH4 decomposition occurs in the CSCRM, as evidenced by the H2/CO ratio exceeding two, the formed coke can react with steam at high temperatures, releasing carbon oxides and hydrogen. Consequently, no coke is detected in the spent catalysts. This is further supported by the TGA analysis (Figure 7f), where no weight loss is observed above 400 °C, confirming the absence of the graphitic carbon. Since Ni/MgO is only tested for 10 h in the CSCRM due to its low activity, its spent sample is not analyzed.
Figures S5 and S6 present the HRTEM and EDS mapping images as well as the Ni particle size distributions of the spent catalysts in the DRM and CSCRM, respectively. Similarly to the XRD results, the HRTEM analysis confirms an increase in the Ni particle size after 30 h of operation (Table 3). However, Ni particles maintain a uniform distribution on the supports. Both XRD and HRTEM analyses indicate that the Ni particle growth is more pronounced in the CSCRM than in the DRM. This difference can be explained by the role of steam in accelerating Ni particle sintering. As demonstrated by Sehested et al. [60], steam enhances sintering kinetics through the generation of Ni2–OH complexes on the nickel surface. These complexes have a significantly lower energy barrier for formation compared to nickel adatoms, while their diffusion energy barrier is much higher. This dual effect—easy formation but hindered mobility—promotes a localized structural reorganization, ultimately driving the particle coalescence and growth under steam-containing environments.
The lattice parameters of MgAl2O4 in the spent Ni/MgAl(x) catalysts are determined from the XRD patterns and summarized in Table 2. In both the DRM and CSCRM, the lattice parameters of the spent catalysts are consistently larger than those of their fresh counterparts, indicating the reduction of Ni from the Ni-MgAl2O4 matrix during the reforming process. Interestingly, Ni/MgAl(0.7) undergoes the least change in the lattice parameter of MgAl2O4 before and after the DRM reaction, while Ni/MgAl(0.8) exhibits the smallest variation in the CSCRM. The structural stability of MgAl2O4 throughout the reaction process is beneficial, contributing to the superior stability of Ni/MgAl(0.7) in the DRM and Ni/MgAl(0.8) in the CSCRM. In addition, the relatively small Ni particle size and low coke deposition (in DRM) further enhance the catalytic performance of Ni/MgAl(0.7) in the DRM and Ni/MgAl(0.8) in the CSCRM. Based on these findings, these two catalysts are selected for a 100 h TOS evaluation in the following section.
2.3. Long-Term Test of Screened Catalysts
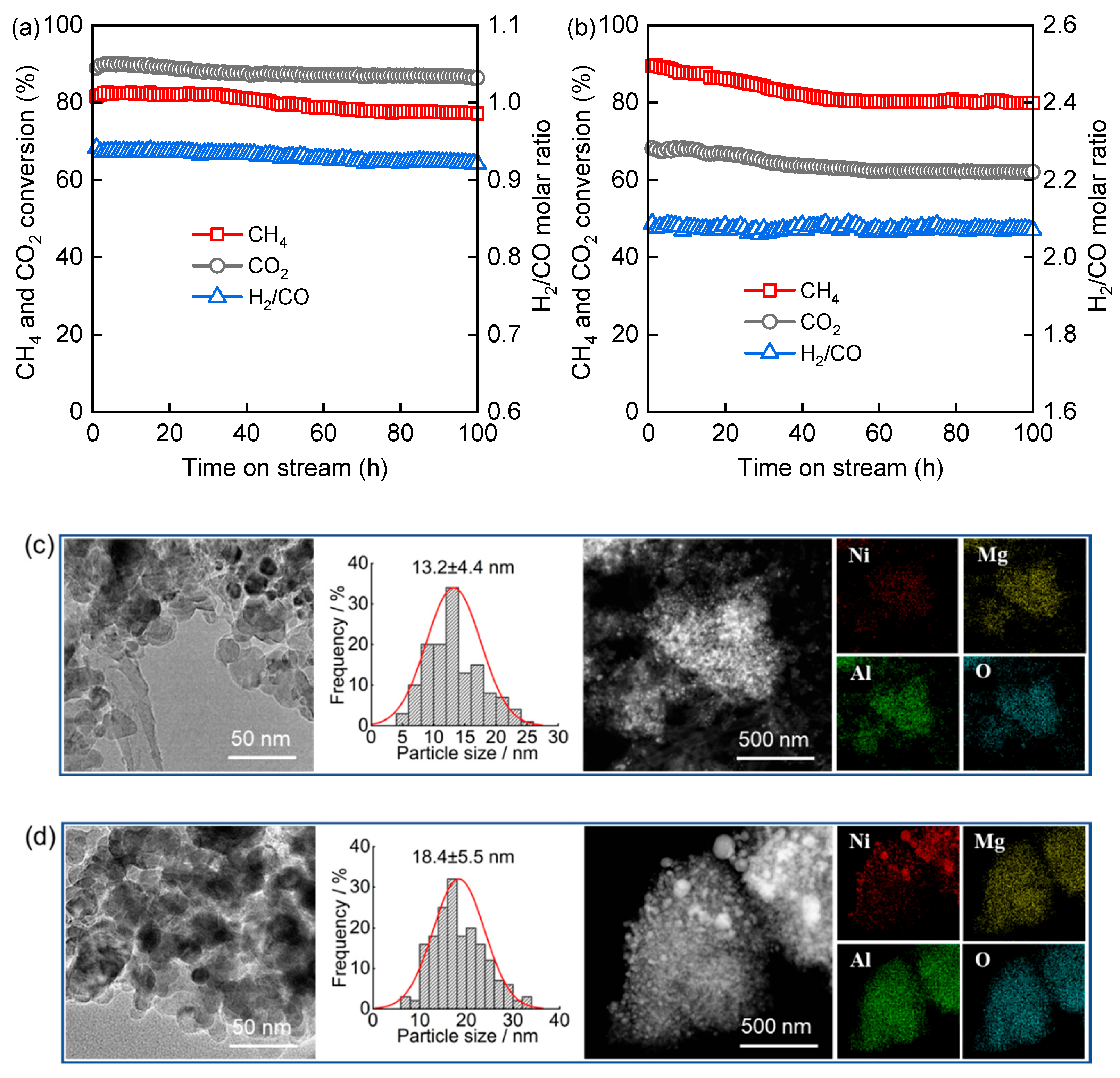
Over 100 h of the DRM reaction, Ni/MgAl(0.7) exhibits excellent stability (Figure 8a), with CH4 and CO2 conversions of 77.2% and 86.4% at 100 h, declining by only 5.4% and 2.9%, respectively, compared to their values at 1 h. The H2/CO ratio remains stable between 0.92 and 0.94. In comparison, Ni/MgAl(0.8) shows a relatively lower stability in the CSCRM (Figure 8b), with CH4 and CO2 conversions of 80.0% and 62.1% at 100 h, decreasing by 10.5% and 8.9%, respectively, from their initial values. Nevertheless, most of the activity loss occurs within the first 50 h of the CSCRM, after which the catalyst remains stable. Additionally, the H2/CO ratio stays steady at 2.06–2.09 throughout the process. For Ni/MgAl(0.8) in the CSCRM, the average Ni particle size increases from 7.1 nm in the fresh state to 11.8 nm after 30 h of the TOS and further to 18.4 nm after 100 h of the TOS (Figure 8d). This substantial growth indicates a pronounced sintering of Ni particles, which accounts for the observed decline in catalytic activity. In comparison, Ni/MgAl(0.7) in the DRM shows a more moderate increase in the Ni particle size, from 7.6 nm to 11.5 nm and then to 13.2 nm (Figure 8c) over the same period. It is noteworthy that Ni particles remain well-dispersed on both Ni/MgAl(0.7) and Ni/MgAl(0.8) despite varying degrees of particle size growth.
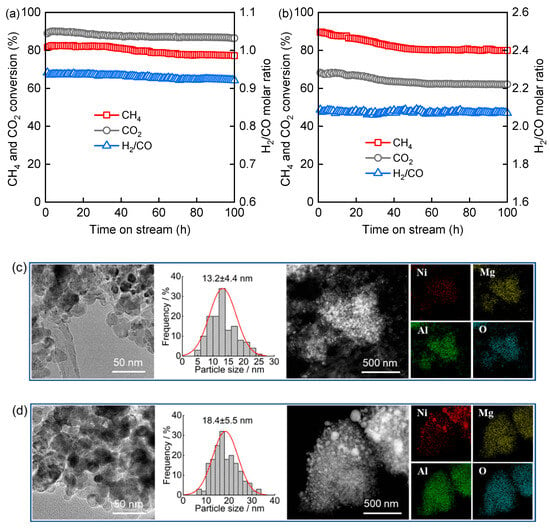
Figure 8.
Catalytic performance of (a) Ni/MgAl(0.7) in DRM and (b) Ni/MgAl(0.8) in CSCRM, as well as HRTEM, Ni particle size distribution, and EDS mapping of (c) spent Ni/MgAl(0.7) and (d) spent Ni/MgAl(0.8).
Regarding the coke deposition, no graphitic carbon is detected on Ni/MgAl(0.8) during the initial 30 h of the CSCRM (Figure 7e,f), and only a minimal amount (0.5 wt.%) forms after 100 h of evaluation (Figures S7 and S8). In contrast, Ni/MgAl(0.7) in the DRM exhibits a higher coke deposition, reaching 7.7 wt.% after 30 h and 9.5 wt.% after 100 h. As shown in Figure 8c,d, carbon nanotubes are observed on the spent Ni/MgAl(0.7) but are absent on the spent Ni/MgAl(0.8). Despite the relatively high initial coking rate of Ni/MgAl(0.7) (0.26 wt.%/h during the first 30 h), the markedly lower rate observed thereafter (0.026 wt.%/h from 30 to 100 h, only one-tenth of the initial rate) highlights good anti-coking properties. In addition, the lattice parameters of MgAl2O4 in Ni/MgAl(0.7) and Ni/MgAl(0.8) after 100 h of operation are determined to be 8.0673 and 8.0904 Å, respectively, based on their XRD patterns (Figure S9). Compared to the values after 30 h (8.0652 Å for Ni/MgAl(0.7) and 8.0817 Å for Ni/MgAl(0.8)), Ni/MgAl(0.7) demonstrates a greater structural stability of MgAl2O4. Therefore, Ni/MgAl(0.7) is a promising candidate for the DRM process. As for Ni/MgAl(0.8), although it experiences an initial activity decay, its performance remains stable thereafter, making it a good catalyst for the CSCRM. Nevertheless, extended stability testing beyond 100 h would be required to fully assess both catalysts’ durability.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
Mg(NO3)2·6H2O (≥99.0%), Al(NO3)3·9H2O (≥99.0%), and Ni(NO3)2·6H2O (≥98.0%) were purchased from Shanghai Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). NH3·H2O (25–28%) and absolute ethanol (≥99.7%) were obtained from Shanghai Titan Scientific Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Urea (≥ 99.0%) and MgO (≥99.9%) were obtained from Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). γ-Al2O3 (≥99.0%) was purchased from Alfa Aesar China (Tian Jin) Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China). All chemicals were used without further purification.
3.2. Support Preparation
The MgO-Al2O3 mixed oxide supports were synthesized using the co-precipitation method. First, predetermined amounts of Mg(NO3)2·6H2O and Al(NO3)3·9H2O were dissolved in 150 mL deionized water. NH3·H2O was then added at a rate of 30 mL/h using a metering pump under vigorous stirring until the solution reached a pH of 10.5. The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 h, after which the resulting precipitate was filtered, repeatedly washed with absolute ethanol, and dried at 120 °C for 12 h. Finally, the precipitate was calcined in a muffle furnace by heating from room temperature to 830 °C at 5 °C/min and holding at 830 °C for 2 h. The Mg/Al molar ratio in MgO-Al2O3 was adjusted by varying the amounts of Mg and Al nitrates. In this study, five MgO-Al2O3 supports were prepared with Mg/Al ratios of 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, and 0.9. For simplicity, these supports are denoted as MgAl(x), where x (= 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, and 0.9) represents the Mg/Al molar ratio.
3.3. Catalyst Preparation
A series of Ni/MgAl(x) catalysts with a Ni loading of 10 wt.% were synthesized by urea hydrolysis using pre-synthesized MgAl(x) supports. First, 0.55 g of Ni(NO3)2·6H2O and 1 g of urea were dissolved in 60 mL of deionized water in a round-bottomed flask under stirring, followed by the addition of 1 g of MgAl(x) and continued stirring for 2 h. The mixture was then gradually heated to 90 °C in a water bath under vigorously stirring. When the pH value of the solution reached 8.0, the mixture was cooled to room temperature and allowed to age statically for 6 h. The resulting solid was filtered, repeatedly washed with deionized water, dried at 120 °C for 12 h, and calcined at 830 °C for 2 h. Finally, the obtained catalyst powder (Ni/MgAl(x)) was pressed, crushed, and sieved to obtain particles in the 80–100 mesh range for subsequent catalytic performance evaluation. For comparison, Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3 catalysts were prepared using the same method with commercial MgO and Al2O3 supports, maintaining a Ni loading of 10 wt.%.
3.4. Catalyst Characterization
The specific surface area, pore volume, and average pore diameter of the samples were acquired by a N2 physical adsorption instrument (Micromeritics ASAP 2460). The Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) method was employed to calculate the specific surface area, while the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda (BJH) equation was used to determine the pore volume and average pore diameter. H2 temperature-programmed reduction (H2-TPR), CO2 temperature-programmed desorption (CO2-TPD), and CH4 temperature-programmed desorption (CH4-TPD) were conducted on a Micromeritics AutoChem 2920 instrument. For H2-TPR, about 100 mg of catalysts was loaded into a quartz tube, purged with N2 until the baseline stabilized, and then heated from room temperature to 800 °C at 10 °C/min in a flow of 10% H2/N2 (v/v, 30 mL/min). A thermal conductivity detector (TCD) was used to record the variation in the outlet signal with temperature. For CO2-TPD, the reduced catalyst was loaded into a quartz tube, purged with He at 150 °C for 30 min, and then cooled to 50 °C. CO2 was introduced for pulse adsorption until saturation, followed by He purging for 2 h to remove weakly adsorbed CO2. The temperature was then increased from 50 to 800 °C at 10 °C/min under He flow, with the desorbed species monitored using a TCD to quantify CO2 uptake. The procedure for CH4-TPD was similar to that of CO2-TPD. H2 chemisorption experiments were performed on a Micromeritics AutoChem 2930 instrument. The crystal structure of the samples was characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) using a Bruker D8 Advance equipped with a Cu Kαradiation source (λ = 1.5406 Å) over a 2θ range of 10–80°. The actual Ni loading of the catalyst was measured by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES, Agilent 725ES). The micromorphology of the samples was observed by a field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM, Nova NanoSEM 450). High-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM, JEOL JEM-2100) with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping was employed to analyze the dispersion and particle size of metallic Ni. The amount of carbon deposition on the spent catalysts was quantified using a thermogravimetric analyzer (TGA, PerkinElmer TGA-4000). Raman spectroscopy was performed on a laser micro-Raman spectrometer (LabRAM HR Evolution) with a laser wavelength of 532 nm. The measurement range was set from 1000 to 1800 cm−1 to identify the types of carbon deposits on the catalyst surface.
3.5. Catalytic Performance Test
The catalytic performance in DRM and CSCRM reactions was evaluated using a fixed-bed reactor (a 10 mm diameter U-shaped quartz tube). Then, 0.05 g of 80–100 mesh catalyst was uniformly mixed with 0.45 g of quartz sand of the same size and loaded into the isothermal section of the reactor, which was supported by high-temperature quartz wool. Prior to the reaction, the catalyst was reduced in 30% H2/N2 (v/v, 100 mL/min) by heating from room temperature to 800 °C at 10 °C/min, followed by maintaining at 800 °C for 2 h. After reduction, the hydrogen flow was stopped, and the system was purged with N2 for 30 min to remove residual H2. The temperature was then adjusted to 750 °C for the DRM or CSCRM reaction. For DRM, the reaction conditions were as follows: T = 750 °C, P = 0.1 MPa, CH4:CO2 = 1:1 (v/v), total gas flow rate = 100 mL/min, and GHSV = 120 L/(gcat·h). For CSCRM, the conditions were as follows: T = 750 °C, P = 0.1 MPa, CH4:H2O:CO2 = 2.5:2:1 (v/v/v), total gas flow rate = 110 mL/min, and GHSV = 132 L/(gcat·h).
The product gas was first passed through an ice trap to remove steam and then mixed with 10 mL/min of N2 as an internal standard. The resulting gas mixture was analyzed online by a dual-channel microgas chromatograph (Inficon 3000). The conversions of CH4 () and CO2 (), as well as the H2/CO molar ratio (), were calculated using Equations (3)–(5), respectively.
where Fi,in and Fi,out are the molar flow rates of species i at the reactor inlet and outlet, respectively.
4. Conclusions
Five Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts (Ni/MgAl(x), x = 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, and 0.9) were successfully synthesized via co-precipitation and urea hydrolysis, with Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3 prepared for comparison. The characterization reveals that all catalysts possess mesoporous structures. The reducibility of Ni/MgAl(x) surpasses that of Ni/MgO and Ni/Al2O3, which is attributed to the formation of less reducible phases in the latter systems: a NiO-MgO solid solution in Ni/MgO and a NiAl2O4 spinel in Ni/Al2O3. In contrast, Ni/MgAl(x) forms a MgAl2O4 spinel structure with a partial Ni incorporation into the lattice, resulting in more metal active sites. Ni/MgO shows the strongest CO2–catalyst interactions (facilitating CO2 adsorption and activation) but the weakest CH4–Ni interactions (for CH4 adsorption and activation), whereas Ni/Al2O3 displays the opposite behavior. This activation imbalance results in their poor performance in both the DRM and CSCRM. In comparison, Ni/MgAl(x) (x = 0.6–0.8) exhibits a high catalytic performance, which is mainly attributed to their abundant active sites and balanced activation capability. Notably, Ni/MgAl(0.7) achieves the highest DRM activity, while Ni/MgAl(0.8) excels in the CSCRM, highlighting the importance of fine-tuning the catalyst composition for specific reforming conditions. Both catalysts also exhibit a good stability during 100 h of operation, demonstrating their potential for long-term applications.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/catal15070659/s1, Figure S1: (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution curves of supports. Figure S2: (a) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (b) pore size distribution curves of catalysts. Figure S3: Lattice fringes of reduced (a) Ni/MgAl(0.7) and (b) Ni/MgAl(0.8) catalysts. Figure S4: CO2-TPD curves for supports and catalysts (solid lines: supports; dashed lines: catalysts). Figure S5: HRTEM, Ni particle size distributions, and EDS mapping images of the spent catalysts in DRM. Figure S6: HRTEM, Ni particle size distributions, and EDS mapping images of the spent catalysts in CSCRM. Figure S7: Raman spectra of spent Ni/MgAl(0.7) in DRM and spent Ni/MgAl(0.8) in CSCRM after 100 h. Figure S8: TGA profiles of spent Ni/MgAl(0.7) in DRM and spent Ni/MgAl(0.8) in CSCRM after 100 h. Figure S9: XRD patterns of spent Ni/MgAl(0.7) in DRM and spent Ni/MgAl(0.8) in CSCRM after 100 h.
Author Contributions
T.Z.: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing—original draft. Y.Z.: Data curation, Investigation, Writing—original draft. H.C.: Resources, Writing—review and editing. Z.Z.: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22278143).
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and the Supplementary Information.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M.P.; Zhang, L.; Hurynovich, V.; He, Y. Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO2, CH4, and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 935, 173359. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radlik, M.; Adamowska-Teyssier, M.; Krzton, A.; Koziel, K.; Krajewski, W.; Turek, W.; Da Costa, P. Dry reforming of methane over Ni/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 catalysts: Effect of Ni loading on the catalytic activity and on H2/CO production. C. R. Chim. 2015, 18, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Fatesh, A.S.; Kumar, R.; Kasim, S.O.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Fakeeha, A.H.; Abasaeed, A.E.; Alrasheedu, R.; Bagabas, A.; Chaudhary, M.L.; Frusteri, F.; et al. The effect of modifier identity on the performance of Ni-based catalyst supported on γ-Al2O3 in dry reforming of methane. Catal. Today 2020, 348, 236–242. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, M.; Mihet, M.; Lazar, M.D. Hydrogen and/or syngas production by combined steam and dry reforming of methane on nickel catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 26254–26264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Qi, L.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Z. Syngas production via combined steam and carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Ni-CexM1-xO2 (M = Ti or Zr) catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 12978–12988. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Chen, M.; Lv, C.; Wen, X.; Cui, Y.; Wu, C.; Yang, B.; Miao, Z.; Hu, X. Recent progresses in the design and fabrication of highly efficient Ni-based catalysts with advanced catalytic activity and enhanced anti-coke performance toward CO2 reforming of methane. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 581923. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, U.S.; Ali, M.; Azhar, M.R.; Al-Yaseri, A.; Keshavarz, A.; Iglauer, S. Current advances in syngas (CO + H2) production through bi-reforming of methane using various catalysts: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 32809–32845. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Tian, X.; Deng, Z.; Shi, W.; Fan, W.; Wang, F. Review and outlook of confined Ni catalysts for the dry reforming of methane reaction. Energy Fuels 2024, 38, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Ganesh, I. A review on magnesium aluminate (MgAl2O4) spinel: Synthesis, processing and applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 63–112. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Lou, H.; Zhao, H.; Chai, D.; Zheng, X. Dry reforming of methane over nickel catalysts supported on magnesium aluminate spinels. Appl. Catal. A 2004, 273, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hadian, N.; Rezaei, M.; Mosayebi, Z.; Meshkani, F. CO2 reforming of methane over nickel catalysts supported on nanocrystalline MgAl2O4 with high surface area. J. Nat. Gas Chem. 2012, 21, 200–206. [Google Scholar]
- Hadian, N.; Rezaei, M. Combination of dry reforming and partial oxidation of methane over Ni catalysts supported on nanocrystalline MgAl2O4. Fuel 2013, 113, 571–579. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Eissa, A.A.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Kim, W.; Seo, D.; Lee, K.; Yoon, W. One-pot synthesis of a highly mesoporous Ni/MgAl2O4 spinel catalyst for efficient steam methane reforming: Influence of inert annealing. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 4447–4458. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Hu, Y.; Cui, H.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Z. Ni-based catalysts supported on MgAl2O4 with different properties for combined steam and CO2 reforming of methane. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 232, 116379. [Google Scholar]
- Cosimo, J.I.D.; Díez, V.K.; Xu, M.; Iglesia, E.; Apesteguía, C. Structure and surface and catalytic properties of Mg-Al basic oxides. J. Catal. 1998, 178, 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Luan, C.; Vinokurov, V.A.; Huang, W. Highly stable and anti-coking Ni/MoCeZr/MgAl2O4-MgO complex support catalysts for CO2 reforming of CH4: Effect of the calcination temperature. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 179, 166–177. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, V.R.; de Camargo, A.C.; de Souza, T.L.; Cardozo, L.; Alves, H.J. Dry reforming of methane over Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts: Thermodynamic equilibrium analysis and experimental application. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 5252–5263. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Li, S.; Liang, X. Enhanced activity and stability of MgO-promoted Ni/Al2O3 catalyst for dry reforming of methane: Role of MgO. Fuel 2021, 284, 119082. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Huang, Q.; Xu, X.; Peng, H.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Methane dry reforming over Ni/Mg-Al-O: On the significant promotional effects of rare earth Ce and Nd metal oxides. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 242–253. [Google Scholar]
- Park, H.; Kim, B.; Lee, Y.; Ahn, S.; Kim, K.; Hong, G.; Yun, S.; Jeon, B.; Bae, J.; Roh, H. CO2 reforming of CH4 using coke oven gas over Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts: Effect of the MgO:Al2O3 ratio. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1468. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, X.; Yu, F.; Yu, P.; Yu, H.; Zhao, T.; Li, M.; Wang, H. Local coordination configuration of Ni and Co in MgAl2O4 spinel structure and the performance of NiCo/MgO-Al2O3 catalyst for dry reforming of methane. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160708. [Google Scholar]
- Schiaroli, N.; Lucarelli, C.; de Luna, G.S.; Fornasari, G.; Vaccari, A. Ni-based catalysts to produce synthesis gas by combined reforming of clean biogas. Appl. Catal. A 2019, 582, 117087. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, K.; Roh, H.; Seo, Y.; Seo, D.; Yoon, W.; Park, S. Coke study on MgO-promoted Ni/Al2O3 catalyst in combined H2O and CO2 reforming of methane for gas to liquid (GTL) process. Appl. Catal. A 2008, 340, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, K.; Roh, H.; Jung, U.; Seo, D.; Seo, Y.; Yoon, W. Combined H2O and CO2 reforming of CH4 over nano-sized Ni/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts for synthesis gas production for gas to liquid (GTL): Effect of Mg/Al mixed ratio on coke formation. Catal. Today 2009, 146, 166–171. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Cui, H.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, Z. Bimetallic Ni-Co/SBA-15 catalysts prepared by urea co-precipitation for dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. A 2018, 554, 95–104. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Feng, X. Ordered mesoporous Ni–Mg–Al2O3 as an effective catalyst for CO2 reforming of CH4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 7192–7201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, D.; Ming, S.; Fu, G.; Wang, C.; Lv, Z. Hydrophobic driving fabrication of highly dispersed PtNi in Zr-doped 3D hollow flower-like MgAl2O4 spheres with abundant O vacancies for enhanced dry reforming of methane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 685, 244–254. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, K.; Lee, S.; Jung, U.; Roh, H.; Yoon, W. Syngas production via combined steam and carbon dioxide reforming of methane over Ni-Ce/MgAl2O4 catalysts with enhanced coke resistance. Fuel Process. Technol. 2014, 119, 151–157. [Google Scholar]
- Dan, M.; Mihet, M.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Lazar, M. Biogas upgrading to syngas by combined reforming using Ni/CeO2-Al2O3 with bimodal pore structure. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2022, 341, 112015. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Jung, U.; Kim, Y.; Im, H.; Lee, T.; Lee, K.; Koo, K. Influence of supports on the catalytic activity and coke resistance of Ni catalyst in dry reforming of methane. Catalysts 2022, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y. Solid-solution catalysts for CO2 reforming of methane. Catal. Today 2009, 148, 206–211. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Lotina, A.; Martin, A.J.; Folgado, M.A.; Daza, L. Dry reforming of methane to syngas over La-promoted hydrotalcite clay-derived catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 12342–12350. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Phu, H.; Kim, T.; Kim, Y.; Kang, K.; Cho, H.; Kim, J.; Ro, I. Role of phase in NiMgAl mixed oxide catalysts for CO2 dry methane reforming (DRM). Catal. Today 2023, 411, 113894. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Li, L.; Wei, N.; Li, J.; Basset, J. Effect of NiAl2O4 formation on Ni/Al2O3 stability during dry reforming of methane. ChemCatChem 2015, 7, 2508–2516. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Ran, J.; Huang, X.; Ou, Z.; Niu, J. Unrevealing the influence that preparation and reaction parameters have on Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for dry reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 34066–34074. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.; Tai, C.; Huang, C.; Chien, Y. Low-loss microwave dielectrics in the spinel-structured (Mg1-xNix)Al2O4 solid solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 93, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Han, R.; Xing, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; Song, C.; Liu, Q. Two birds with one stone: MgO promoted Ni-CaO as stable and coke-resistant bifunctional materials for integrated CO2 capture and conversion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 307, 122808. [Google Scholar]
- Boukha, Z.; Jiménez-González, C.; de Rivas, B.; González-Velasco, J.R.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I.; López-Fonseca, R. Synthesis, characterisation and performance evaluation of spinel-derived Ni/Al2O3 catalysts for various methane reforming reactions. Appl. Catal. B 2014, 158, 190–201. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, Y.; Hong, J. Enhancement of surface morphology and catalytic kinetics of NiAl2O4 spinel-derived Ni catalyst to promote dry reforming of methane at low temperature for the direct application to a solid oxide fuel cell. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136978. [Google Scholar]
- Charisiou, N.D.; Papageridis, K.N.; Tzounis, L.; Sebastian, V.; Hinder, S.J.; Baker, M.A.; AlKetbi, M.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Goula, M.A. Ni supported on CaO-MgO-Al2O3 as a highly selective and stable catalyst for H2 production via the glycerol steam reforming reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 256–273. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, J.; Feng, Q.; Ji, S.; Wang, Z. A La-promoted Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst with superior methanation performance for the production of synthetic natural gas. Catal. Today 2020, 339, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fakeeha, A.; Kurdi, A.; Al, B.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Abasaeed, A.E.; Al-Fatesh, A.S. Performance study of methane dry reforming on Ni/ZrO2 catalyst. Energies 2022, 15, 3841. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Cao, K.; Ye, R.; Tang, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Shan, B. Deciphering the stability mechanism of Pt-Ni/Al2O3 catalysts in syngas production via DRM. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 491, 151966. [Google Scholar]
- Guilhaume, N.; Bianchi, D.; Wandawa, R.A.; Yin, W.; Schuurman, Y. Study of CO2 and H2O adsorption competition in the combined dry/steam reforming of biogas. Catal. Today 2021, 375, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ponugoti, P.V.; Pathmanathan, P.; Rapolu, J.; Gomathi, A.; Janardhanan, V.M. On the stability of Ni/γ-Al2O3 catalyst and the effect of H2O and O2 during biogas reforming. Appl. Catal. A 2023, 651, 119033. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, X.; Dong, L.; Su, T.; Li, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, X.; Ji, H. CO2 methanation on Co/TiO2 catalyst: Effects of Y on the support. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 210, 115245. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Tian, C.; Liu, X.; Sun, N.; Song, C.; Zheng, H.; Gao, K.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xuan, Y.; et al. Ni-phyllosilicate nanotubes coated by CeO2 for ultra-efficiency of 36.9% and near-limit CO2 conversion in solar-driven conversion of CO2-to-fuel. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140063. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Lotina, A.; Daza, L. Influence of the operating parameters over dry reforming of methane to syngas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar]
- Wysocka, I.; Mielewczyk-Gryn, A.; Lapinski, M.; Cieslik, B.; Rogala, A. Effect of small quantities of potassium promoter and steam on the catalytic properties of nickel catalysts in dry/combined methane reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 3847–3864. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, D.; Kim, Y.; Ko, E.; Han, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.; Kang, D. Methane pyrolysis and carbon formation mechanisms in molten manganese chloride mixtures. Appl. Energy 2023, 336, 120810. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, A.; Park, M.; Jo, J.; Lee, D.; Bae, J. Combined steam and CO2 reforming of CH4 using coke oven gas on nickel-based catalyst: Effects of organic acids to nickel dispersion and activity. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 771–781. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jie, X.; Qiu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Al-Megren, H.A.; Alshihri, S.; Edwards, P.P.; Xiao, T. The importance of inner cavity space within Ni@SiO2 nanocapsule catalysts for excellent coking resistance in the high-space-velocity dry reforming of methane. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 259, 118019. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.; Gong, B.; Xie, X.; Luo, X.; Qin, Z.; Ji, H. Effect of cobalt on the activity of nickel-based/magnesium-substituted hydroxyapatite catalysts for dry reforming of methane. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 76, 281–291. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, K.; Lee, J.; Jung, U.; Kim, S.; Yoon, W. Combined H2O and CO2 reforming of coke oven gas over Ca-promoted Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst for direct reduced iron production. Fuel 2015, 153, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.A.; Fakeeha, A.H.; Abasaeed, A.E.; Al-Fatesh, A.S. Dry reforming of methane using Ni catalyst supported on ZrO2: The effect of different sources of zirconia. Catalysts 2021, 11, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Han, J.; Bao, Z.; Cao, B.; Li, Y.; Street, J.; Yu, F. Biogas reforming of carbon dioxide to syngas production over Ni-Mg-Al catalysts. Mol. Catal. 2017, 436, 248–258. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Lou, H.; Zheng, X. The deposition of coke from methane on a Ni/MgAl2O4 catalyst. Carbon 2007, 45, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Zhan, Y.; Street, J.; To, F.; Yu, F. Natural gas reforming of carbon dioxide for syngas over Ni-Ce-Al catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 18364–18374. [Google Scholar]
- Sehested, J.; Gelten, J.; Remediakis, I.; Bengaard, H.; Norskov, J. Sintering of nickel steam-reforming catalysts: Effects of temperature and steam and hydrogen pressures. J. Catal. 2004, 223, 432–443. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).