Abstract
Ricinoleic acid (RA) is an important raw material for plasticizers, emulsifiers, and nanomaterials. In this work, a green and efficient method was developed for RA production. Results showed that Lipozyme TLIM can be used as a novel biocatalyst to catalyze the hydrolysis of castor oil (CO) for RA preparation. Response surface methodology (RSM) was used to evaluate and optimize the effects of reaction variables on the hydrolysis of CO. Reaction conditions were optimized as follows: 41.3 °C, enzyme load 8.9%, 39.2 h, and 40:1 molar ratio of water to oil. Under these optimized reaction variables, the maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO (96.2 ± 1.5%) was obtained. The effect of hydrolysis variables on the reaction was as follows: enzyme load > hydrolysis time > temperature. In conclusion, this is a green, simple, and efficient method for RA preparation and can provide a good alternative method for RA industrial production.
1. Introduction
Ricinoleic acid (RA), also known as cis-12-hydroxy-9-octadecenoic acid, is the only industrial fatty acid containing a hydroxy group in nature [1] and can be used as raw material for skin care products, plasticizers, emulsifiers, lubricants, and nanomaterials [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. Castor oil (CO) is one kind of nonedible oil derived from the plant seeds of Ricinus communis [1,9]. RA is the main fatty acid of CO, and the content of RA is ~90% in CO [10,11,12]. Therefore, the preparation of RA from CO has been considered an attractive method [13,14].
In previous reports, RA was produced by the hydrolysis of CO, and acids, bases, and enzymes were used as catalysts. When acid and base were used as catalysts, estolide byproducts easily formed by condensation between the hydroxyl and the carboxyl in RA [15]. RA products with bad odor and color were often obtained using high temperatures and chemical catalysts [14]. These factors made enzymes more suitable for RA preparation by the hydrolysis of CO.
Recently, some enzymes have been used to catalyze the hydrolysis of triacylglycerols for the preparation of fatty acids, especially for those fatty acids with unsaturated bonds and hydroxyl groups [16]. For example, the lipase from oat seeds was firstly used to catalyze the hydrolysis of CO [17]. After that, other lipases, Rhizopus oryzae lipase [18], Pseudomonas aeruginosa KKA-5 lipase [9], porcine pancreatic lipase (PPL), and castor bean lipase [19], were also used as catalysts for RA preparation by the hydrolysis of CO. Among them, the maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO was ~90% for 96 h using the purified lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa KKA-5 as catalyst and 10 mM CaCl2 to stabilize the lipase [9]. Khaskhelia et al. [18] also studied the hydrolysis of CO using Rhizopus oryzae lipase, achieving a similar hydrolysis ratio of CO (90%). However, these previous methods showed some disadvantages including their time-consuming nature, low hydrolysis ratio, and pH requirements. Therefore, a green and efficient method to prepare RA was more popular.
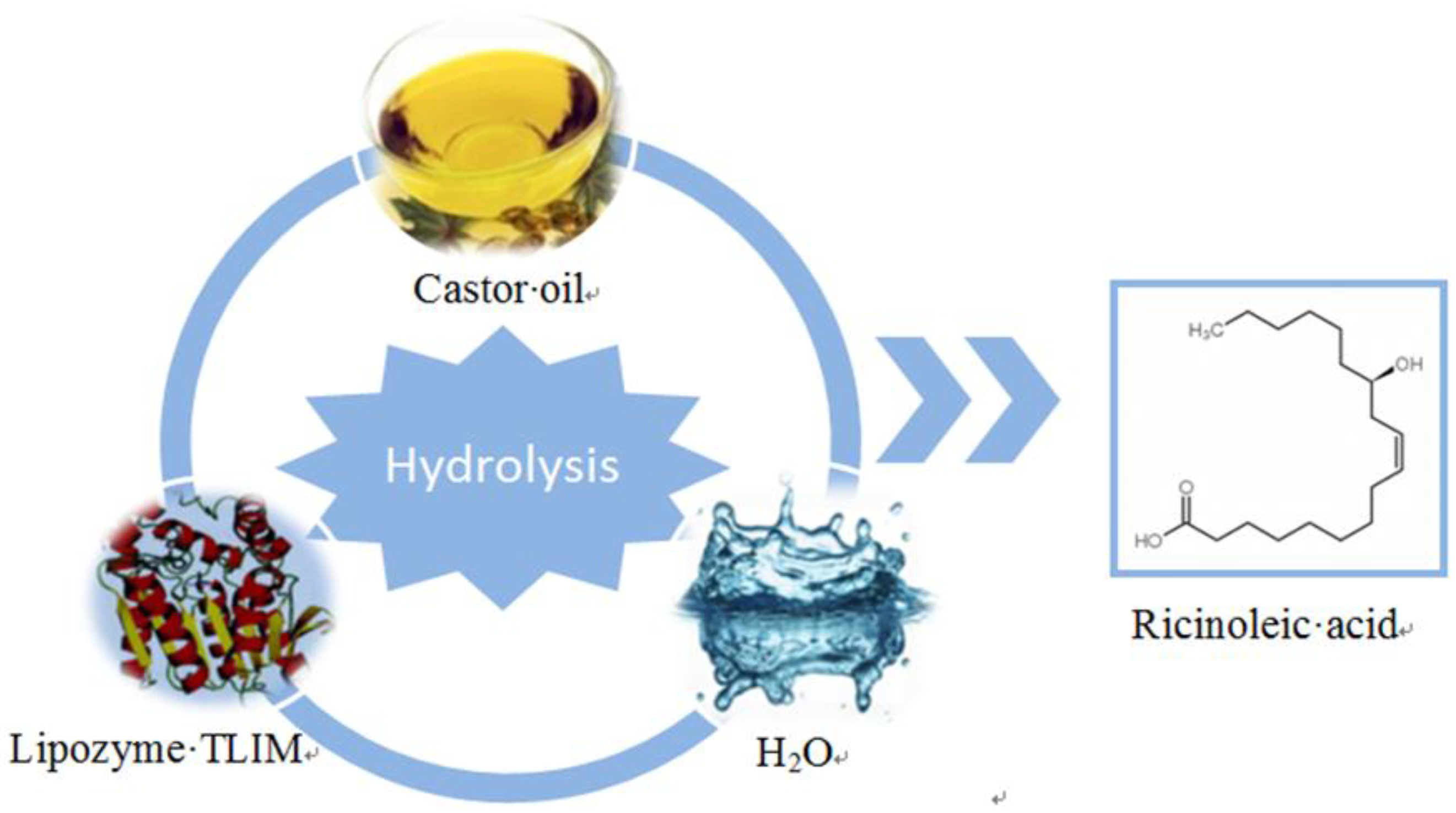
In this work, Lipozyme TLIM (lipase from Thermomyces lanuginose) was used as a novel biocatalyst for RA preparation by the hydrolysis of CO (Figure 1). Several immobilized lipases were screened and compared. The effect of reaction conditions (hydrolysis temperature, enzyme load, molar ratio of water to oil, and hydrolysis time) on the hydrolysis of CO was investigated and optimized by RSM.
Figure 1.
Enzymatic hydrolysis of castor oil (CO) to prepare ricinoleic acid (RA).
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Enzyme Screening
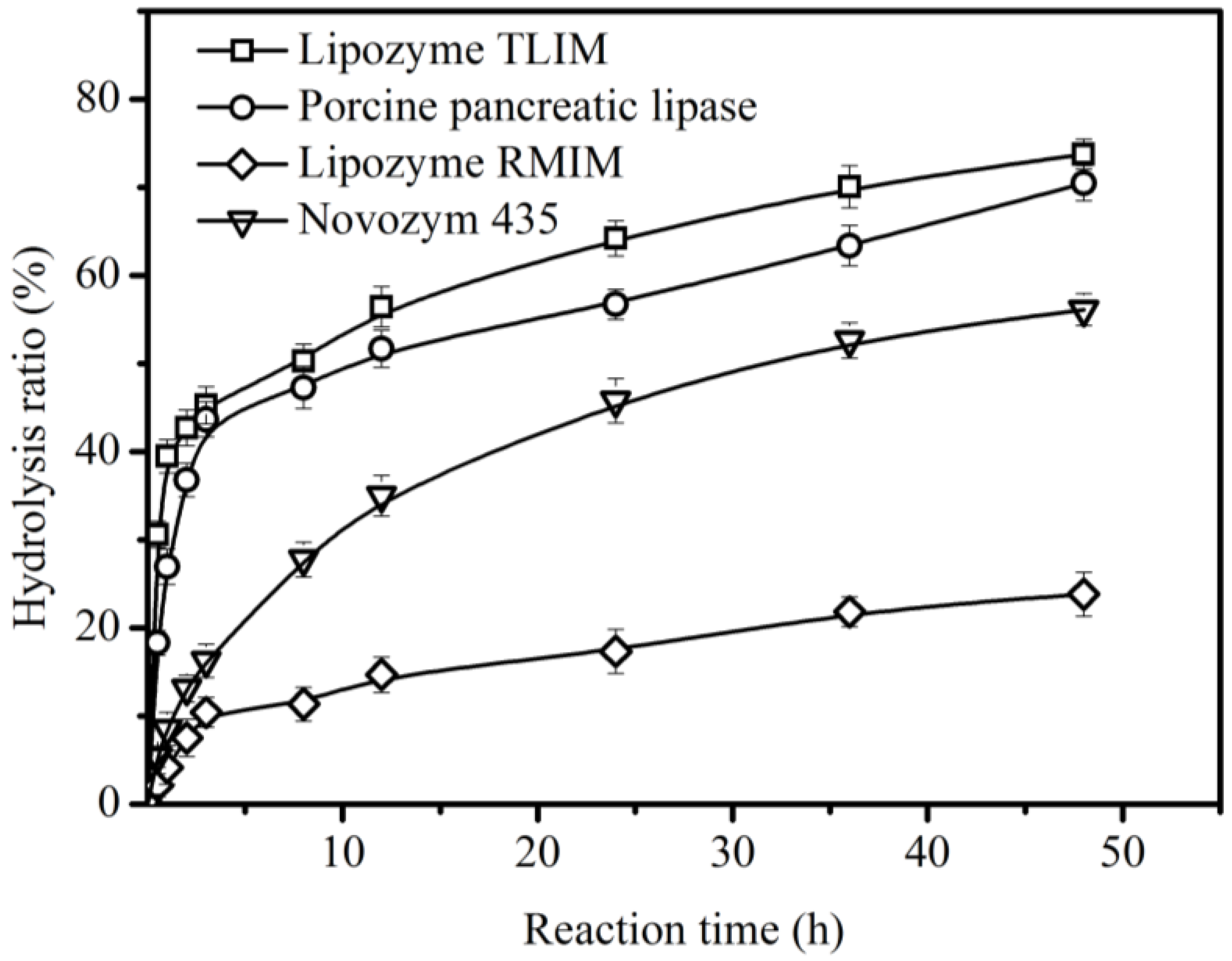
Four commercial lipases (Lipozyme TLIM, Lipozyme RMIM, Novozym 435, and Porcine pancreas lipase) were used as catalysts for the hydrolysis of CO. Among these lipases, higher hydrolysis ratios of CO (>70%) were obtained after 48 h using Lipozyme TLIM and Porcine pancreas lipase as biocatalysts (Figure 2). These results are attributed to the better hydrolysis activities for triacylglycerol of Lipozyme TLIM and Porcine pancreas lipase in aqueous solutions. Similar results showing that these two lipases have good catalyst performance can also be found in other oil hydrolysis studies [20,21,22,23]. However, the hydrolysis ratios of CO using Lipozyme RMIM and Novozym 435 were lower than 50%, which was ascribed to the amount of water present in the reaction system, resulting in the decrease of catalyst activity. In previous reports, Lipozyme RMIM and Novozym 435 were often used to catalyze esterification and transesterification in organic solvents [24,25,26,27,28,29,30]. Figure 2 also shows that the initial hydrolysis rate of CO of Lipozyme TLIM (0.066 mol/(L∙min)) was almost 2 times that of Porcine pancreas lipase (0.039 mol/(L∙min)); these were both greater than those of Novozym 435 (0.012 mol/(L∙min)) and Lipozyme RMIM (0.0046 mol/(L∙min)). Therefore, Lipozyme TLIM was the best catalyst for the hydrolysis.
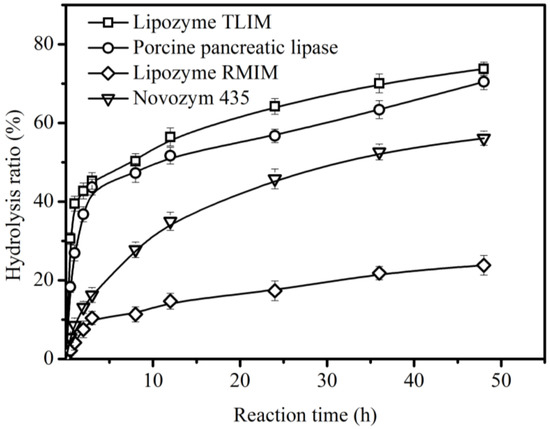
Figure 2.
Enzymatic hydrolysis of CO using different enzymes. Hydrolysis conditions: 1.78 g enzyme and 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 5.51 mL water, at 200 rpm, and at 40 °C.
2.2. Effect of Reaction Temperature
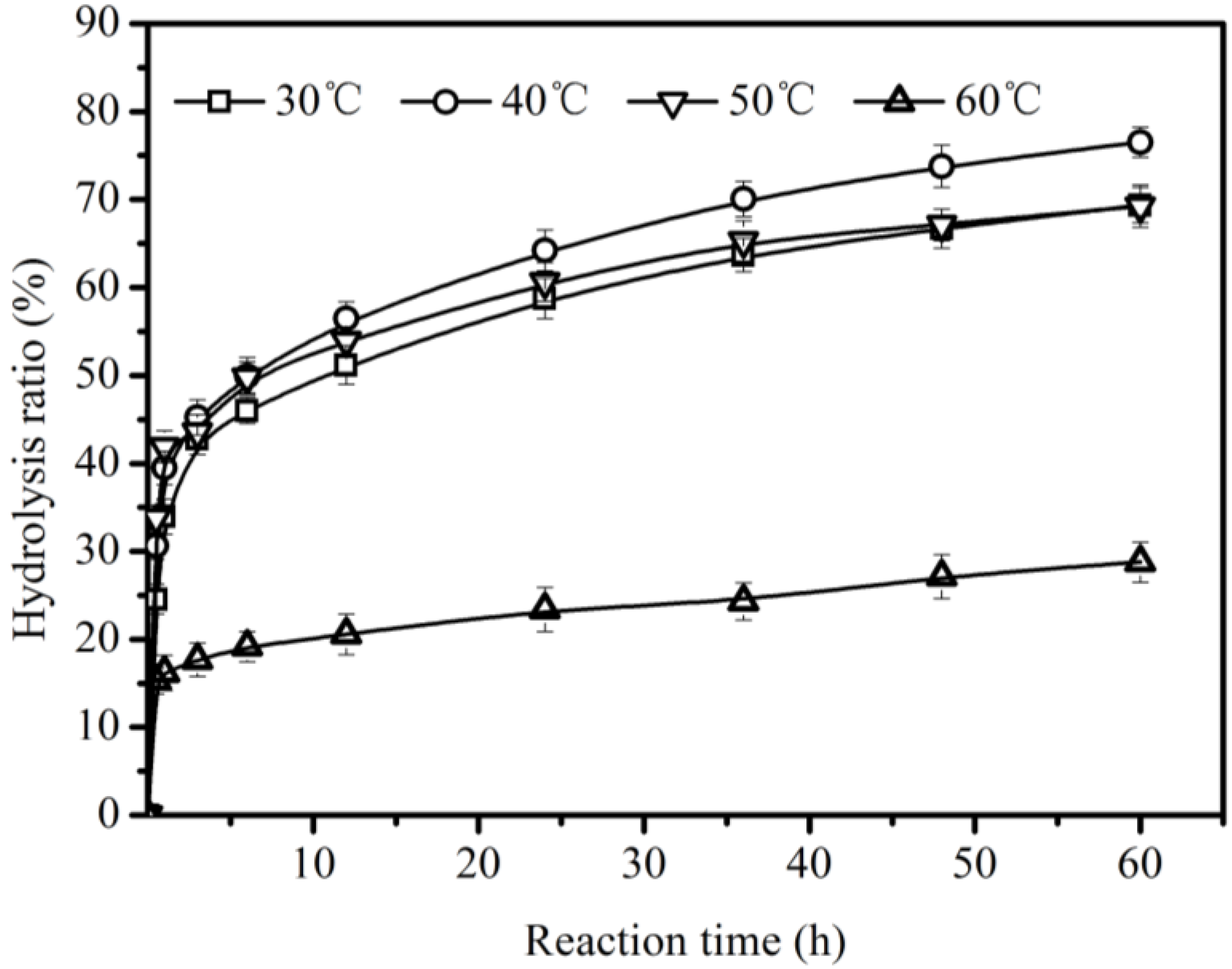
For evaluating the effect of hydrolysis temperatures on the hydrolysis of CO, experiments were performed at different temperatures from 30 °C to 60 °C (Figure 3). Figure 3 shows that the reaction temperature played an important role in the hydrolysis of CO, influencing the activity of Lipozyme TLIM and the viscosity of reaction system. When the reaction temperature increased from 30 °C to 40 °C, the hydrolysis ratio of CO increased from 69.4 ± 2.0% to 76.5 ± 1.7%; this was due to the decrease in the viscosity of the reaction system and the consequently decreased effect of mass transfer limitation on the hydrolysis [31]. However, when the temperature was higher than 40 °C, the hydrolysis ratio of CO decreased from 76.5 ± 1.7% at 40 °C to 28.8 ± 2.3% at 60 °C at 60 h, which was due to the deactivation of lipase TLIM at high temperature (>40 °C). In other reaction systems, similar deactivation of lipase TLIM can also be found [21,22].
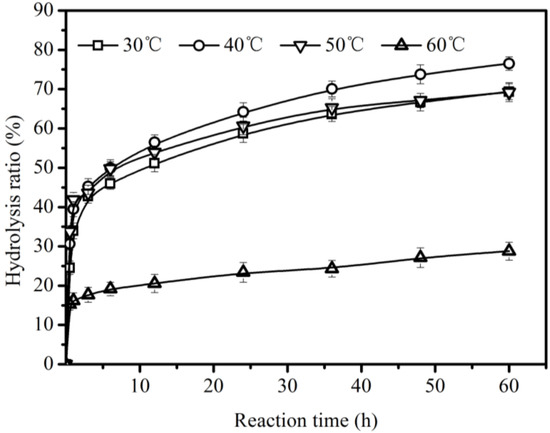
Figure 3.
Effect of reaction temperature on the hydrolysis of CO using Lipozyme TLIM. Reaction conditions: 1.78 g Lipozyme TLIM and 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 5.51 mL water at 200 rpm.
2.3. Effect of Enzyme Load
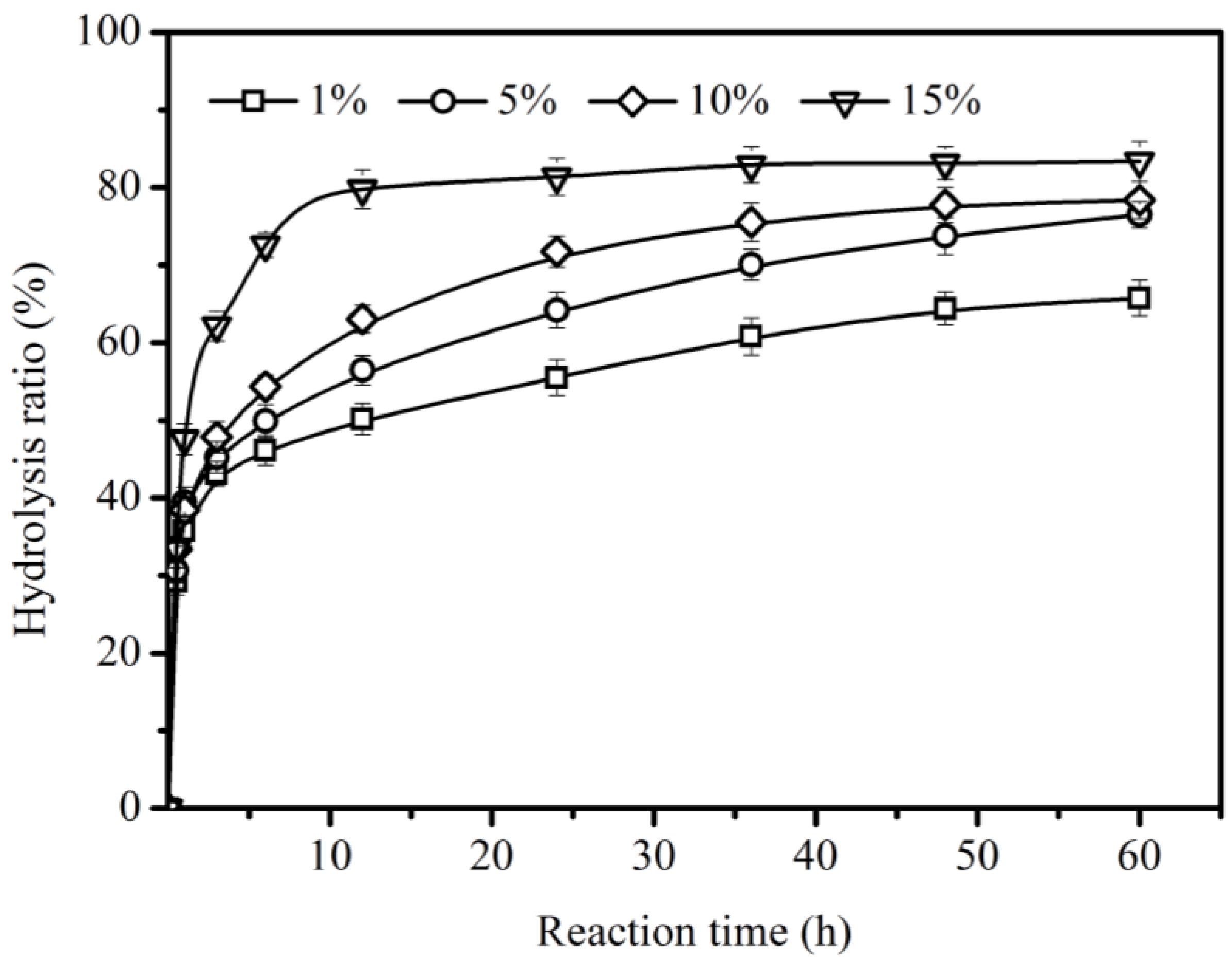
A sufficient amount of lipase is necessary for enzymatic hydrolysis because the enzymatic hydrolysis of oil takes place at the interface of water and oil and more active sites are provided at the interface by increasing the enzyme load [32]. In order to investigate the lipase TLIM load on the hydrolysis of CO, different lipase loads from 1% to 15% (relative to the weight of all substrates) were used. Figure 4 shows an appreciable effect of lipase load on the hydrolysis of CO, and the maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO increased from 65.8 ± 2.3% at 1% to 83.3 ± 2.6% at 15%. With lipase load ranging from 1% to 15%, the time to achieve equilibrium was shortened from 60 h to 12 h and the initial hydrolysis rate decreased in the order of 0.093 mol/(L∙min) (15%) > 0.072 mol/(L∙min) (10%) > 0.066 mol/(L∙min) (5%) > 0.063 mol/(L∙min) (1%). However, an excessive amount of enzyme can result in aggregation and great mass transfer limitation, especially with high enzyme load (>10%). Enzyme load also has a similar effect on other lipase-catalyzed reactions [18,20].
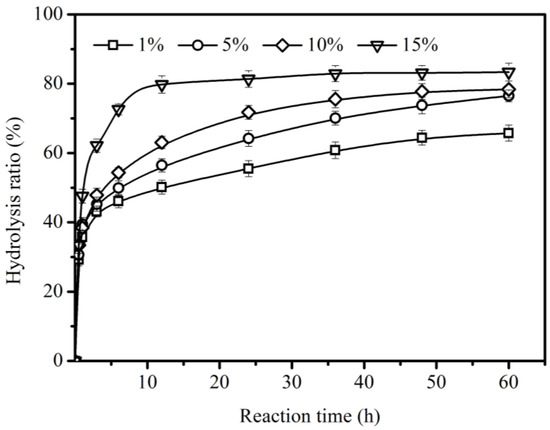
Figure 4.
Effect of enzyme load (relative to the weight of all substrates) on the hydrolysis of CO using Lipozyme TLIM. Reaction conditions: 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 5.51 mL water, at 40 °C, and at 200 rpm.
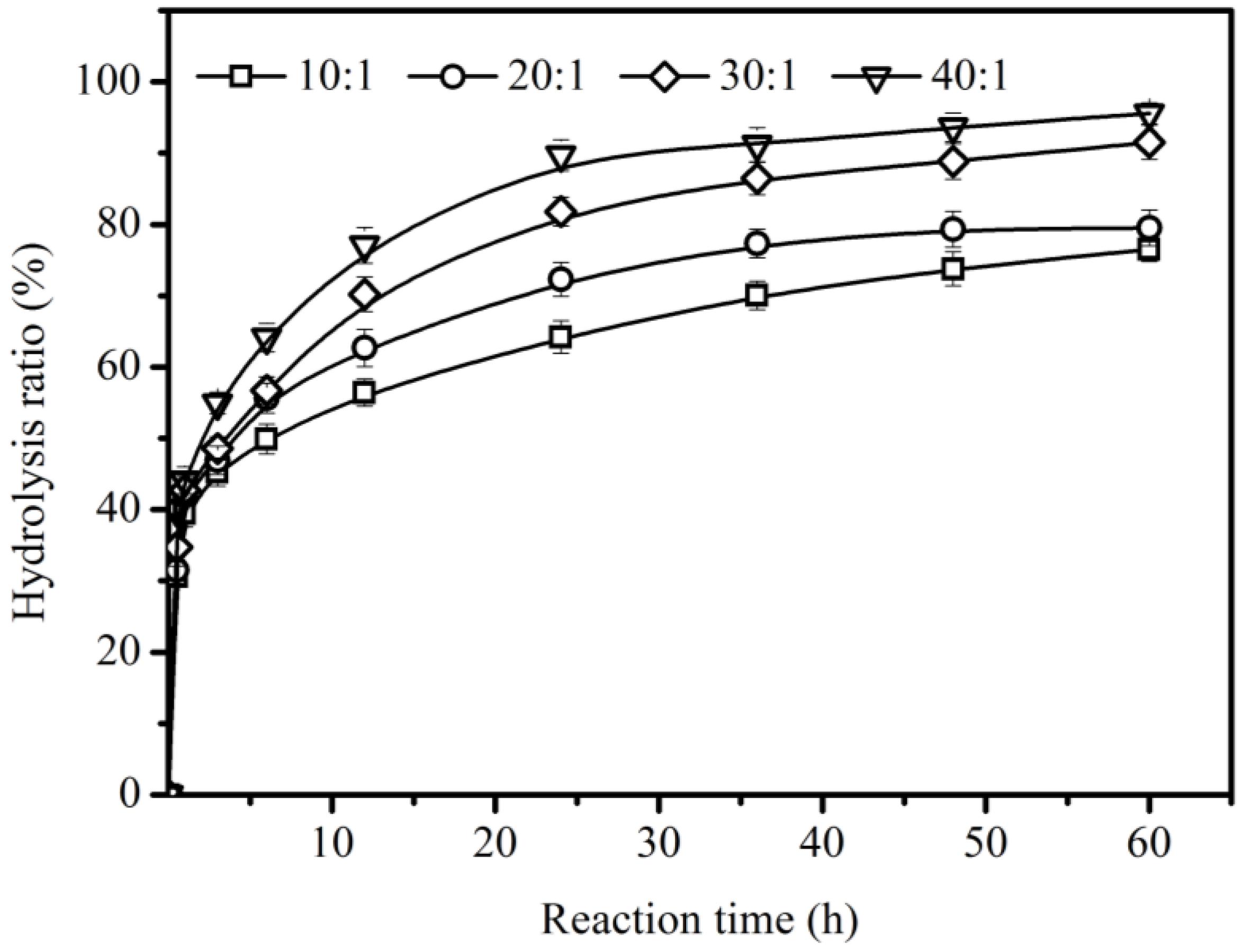
2.4. Effect of Substrate Ratio of Water to Oil
During lipase-catalyzed reactions, lipase can often be activated at the interface of water and oil, and great interfacial area plays a significant role in improving the hydrolysis. In order to achieve a good hydrolysis ratio of CO, the effect of the molar ratio of water to oil was evaluated (Figure 5). With the increase of the water-to-oil ratio from 10:1 to 40:1 (mol/mol), a greater interfacial area of water and oil was formed, which enhanced the hydrolysis ratio of CO. The maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO (95.6 ± 1.5%) can be achieved with a 40:1 (mol/mol) ratio at 48 h. These results indicated that sufficient water is essential for the reaction. In the previous reports, in order to obtain high hydrolysis ratios of CO, more water was used; for example, Puthli et al. [14] used a 150:1 molar ratio of water to CO and Rhizopus oryzae lipase to obtain 90% hydrolysis of CO, and Khaskheli et al. [18] used a 200:1 molar ratio of water to CO using Rhizopus oryzae lipase to achieve a 90% yield of fatty acids. Compared with these previous reports, a higher hydrolysis ratio of CO (95.6 ± 1.5%) was achieved using only a 40:1 molar ratio of water to CO, which can save on water use.
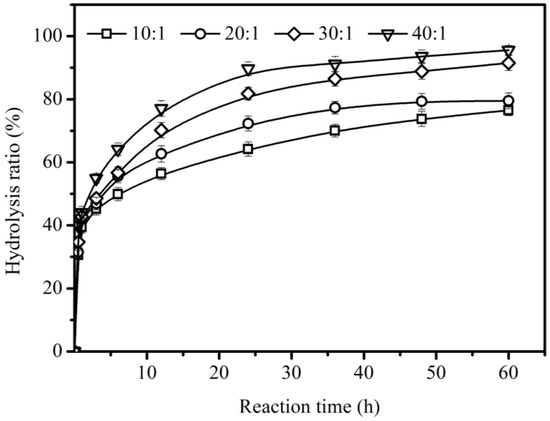
Figure 5.
Effect of molar ratio of water to oil on the hydrolysis of CO with 0.031 mol CO and 5% enzyme load (relative to the weight of all substrates), at 40 °C, and at 200 rpm.
2.5. Response Surface Analysis and Model Fitting
RSM—a combination of some mathematical and statistical procedures—is applied to investigate the relationship between independent variables and response and can be used to optimize experimental conditions [33]. Design-Expert 8.0 was used to analyze and predict the highest hydrolysis ratio of CO (Table 1 and Table 2). A quadratic polynomial equation was used to evaluate the relationship between hydrolysis ratio of CO and hydrolysis conditions.

Table 1.
Box–Behnken design and results of hydrolysis of CO as affected by hydrolysis time, hydrolysis temperature, and enzyme load with 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 22.04 mL water.

Table 2.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the quadratic model for the hydrolysis ratio of CO.
The Prob > F value and the coefficient R2 were <0.0001 and 0.9957, respectively, which showed that the model was adequate to illustrate the relationship between hydrolysis conditions and hydrolysis ratio. The relative effects of reaction conditions on the hydrolysis were as follows: enzyme load > hydrolysis time > hydrolysis temperature. The regression equation was as follows:
Y (%) = 95.26 + 3.72X1 + 10.99X2 + 6.48X3 − 3.87X1X2 − 1.58X1X3 − 4.24X2X3 − 3.24X12 − 8.75X22 − 5.35X32.
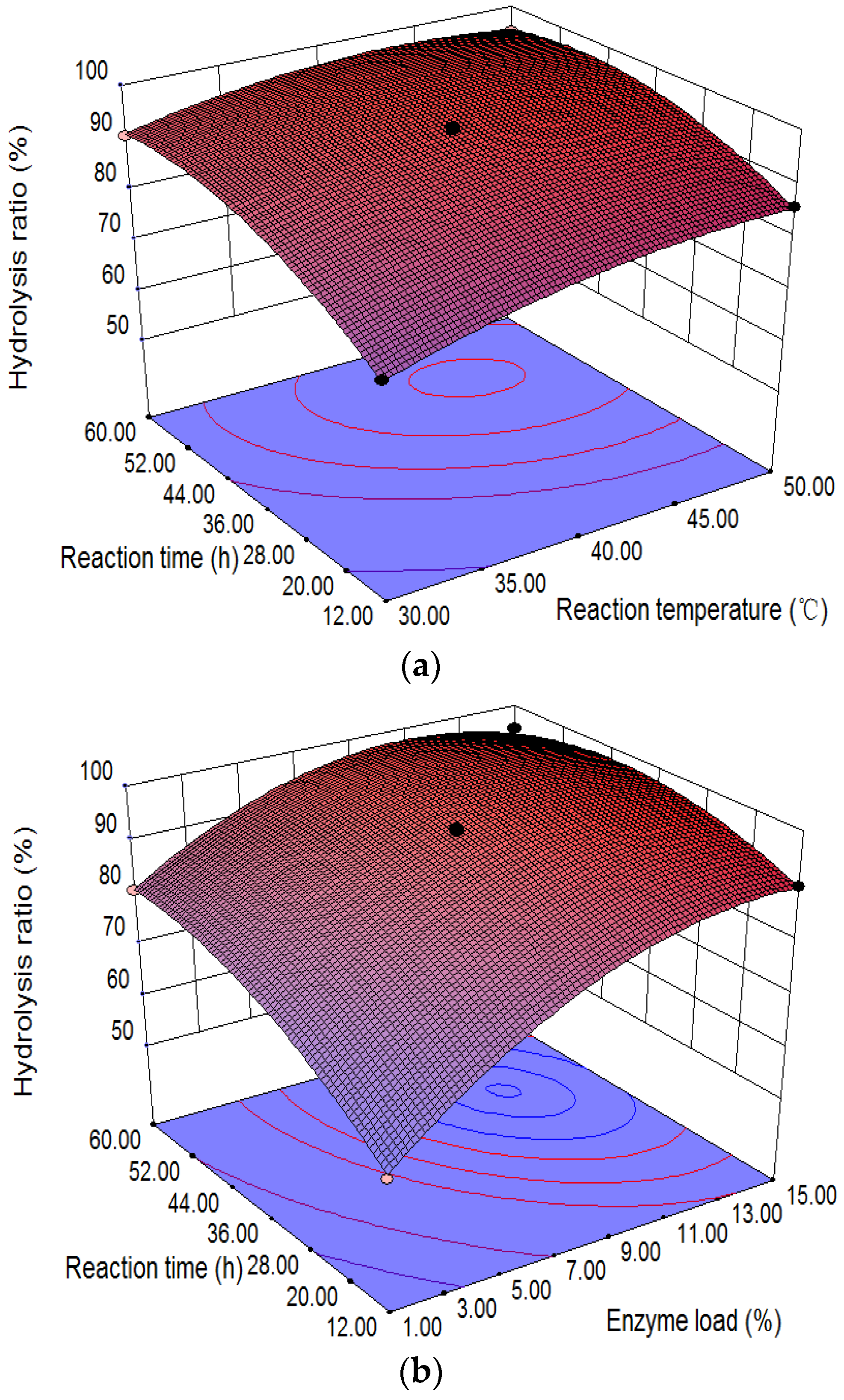
Figure 6a indicates the relationship of varying hydrolysis temperature and time with the hydrolysis of CO at 8% enzyme load and a 40:1 water–oil molar ratio. The maximum conversion of CO appears at 40–45 °C and 36–44 h, and the yield of RA decreased at higher hydrolysis temperatures (>45 °C).
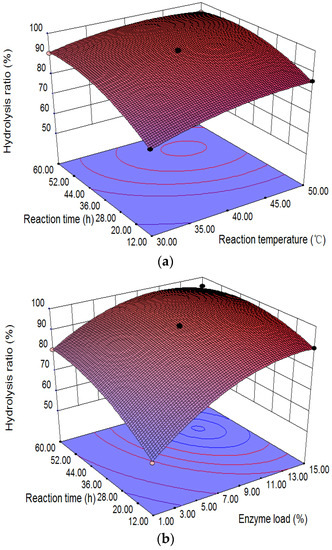
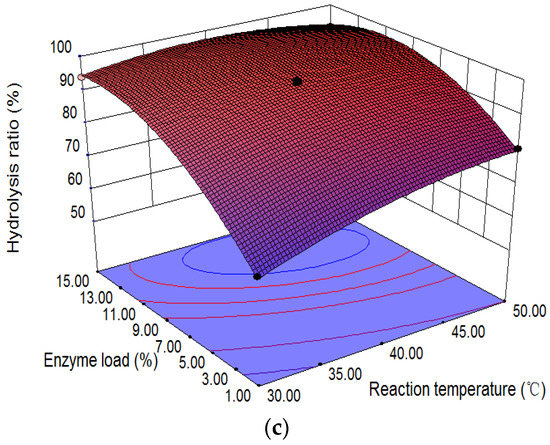
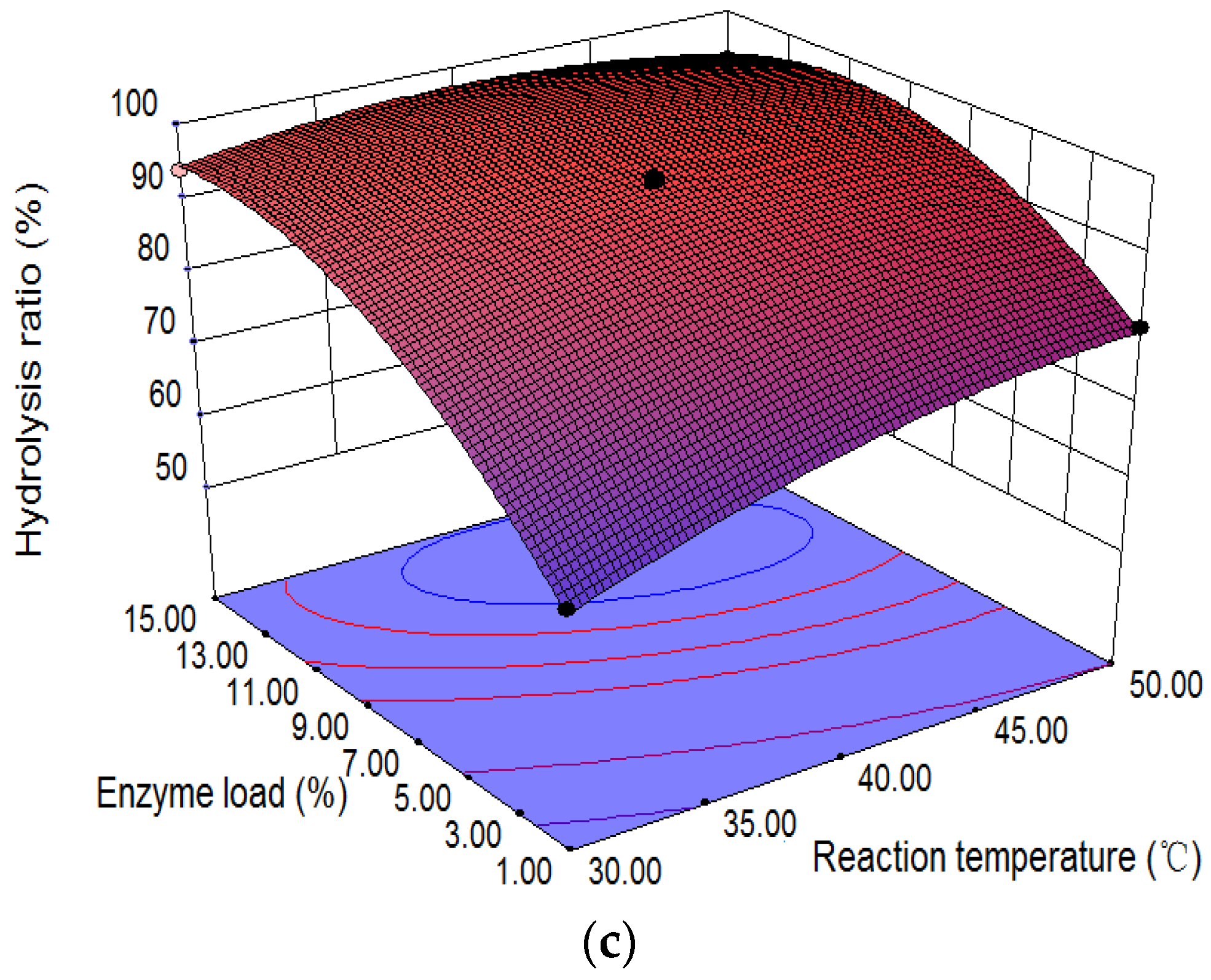
Figure 6.
3D surface plots between two variables for the hydrolysis of CO: (a) reaction temperature and time with 2.84 g enzyme and 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 22.04 mL water; (b) hydrolysis time and enzyme load with 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 22.04 mL water at 40 °C; (c) reaction temperature and enzyme load with 0.031 mol CO in the presence of 22.04 mL water for 36 h.
Figure 6b shows the effect of varying hydrolysis time and enzyme load on the yield of RA at a 40:1 molar ratio of water to oil and 40 °C. A proper amount of enzyme and a longer hydrolysis time were beneficial for the yield of RA, and enzyme loads (e.g., 8%) and longer hydrolysis time (e.g., 36 h) result in hydrolysis ratios of CO up to 95.7 ± 1.3%.
Figure 6c shows the relationship of enzyme load, hydrolysis temperature, and the hydrolysis reaction at a 40:1 molar ratio of water to oil for 36 h. The higher hydrolysis ratio of CO (>95.7%) appeared at higher temperature (40–45 °C) and lower enzyme load (7–11%).
2.6. Optimum Hydrolysis Conditions and Model Verification
The hydrolysis variables were optimized as follows: 41.3 °C, 39.2 h, and enzyme load 8.9%. Under these optimal variables, the maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO (96.2 ± 1.5%) was achieved, which was in accord with the predicted hydrolysis ratio of CO (97.6%). These results show that the quadratic regression model was valid. The maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO (96.2 ± 1.5%) achieved was greatly higher than those (<80%) of other enzymes in previous reports [33,34,35]. Further, this method is greener and more effective than those with ~90% hydrolysis ratio used by Sharon et al. [9] and Khaskhelia et al. [18].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
Novozym 435, Lipozyme RMIM, and Lipozyme TLIM were purchased from Novozymes A/S (Bagsvaerd, Denmark). Porcine pancreas lipase (PPL) was prepared in our laboratory. CO was purchased from Shanghai Reagent Factory (Shanghai, China).
3.2. Hydrolysis of CO
Hydrolysis of CO was conducted in a 250 mL three-necked flask. A quantity of 0.031 mol CO was mixed with 5.51 mL water at 200 rpm and 40 °C. The reaction was initialized by the addition of lipase (5%, w/w). The samples were taken out at specified time intervals and centrifuged to remove water and lipase.
3.3. Analysis Methods
According to the previous method [9], the hydrolysis ratio of CO (%) was calculated as follows:
The saponification value of CO used was 181 (a value provided by the supplier).
3.4. Experimental Design for RSM
For evaluating the relationship of reaction variables with the hydrolysis of CO, a Box–Behnken design with 3 levels and 3 factors was applied (Table 1). The factors and levels used in the experimental design were as follows: reaction temperature (30 °C, 40 °C, and 50 °C), hydrolysis time (12 h, 36 h, and 60 h), and enzyme load (1%, 8%, and 15%; w/w, relative to all substrates).
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Design-Expert 8.0 (Stat-Ease Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) was used to analyze the experimental data and a second-order polynomial model was generalized as follows:
where Y represents the hydrolysis ratio of CO; X1, X2, and X3 are the hydrolysis temperature, enzyme load, and hydrolysis time, respectively; and β0, βi, βii, and βij represent the intercept, linear, quadratic, and interaction terms, respectively.
4. Conclusions
In this work, Lipozyme TLIM was successfully used as a novel biocatalyst for RA preparation. The effect of hydrolysis conditions on the Lipozyme TLIM-catalyzed hydrolysis of CO was evaluated and optimized using RSM. The relative effects of hydrolysis conditions on the hydrolysis were as follows: enzyme load > hydrolysis time > hydrolysis temperature. Hydrolysis conditions were optimized by RSM as follows: 41.3 °C, 39.2 h, enzyme load 8.9%, and 40:1 molar ratio of water to oil. Under these optimal conditions, the maximum hydrolysis ratio of CO (96.2 ± 1.5%) was achieved. A quadratic regression model describing the reaction conditions and hydrolysis ratio of CO was also obtained from RSM.
Author Contributions
S.S. and J.G. designed the study, prepared all samples for analysis, collected and analyzed the data, interpreted the results, and wrote the manuscript. All authors gave final approval for publication.
Funding
Financial support came from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31771937) and the funding scheme for the Young Teachers Cultivating Program at Henan University of Technology.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Fangfang Pei for her help with the experiments on acid value measurement.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mutlu, H.; Meier, M.A.R. Castor oil as a renewable resource for the chemical industry. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Nie, X.; Jiang, J. Synthesis and properties of a novel environmental epoxidized glycidyl ester of ricinoleic acetic ester plasticizer for poly(vinyl chloride). Polymers 2017, 9, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Sen, R.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Maximization of bioconversion of castor oil into ricinoleic acid by response surface methodology. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4067–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.G.; Mannam, V.K.; Ye, R.; Zhao, H.; Ortega, S.; Montiel, M.C. Modification of oligo-ricinoleic acid and its derivatives with 10-undecenoic acid via lipase-catalyzed esterification. Polymers 2012, 4, 1037–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, F.C. Production, chemistry, and commercial applications of various chemicals from castor oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1974, 51, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Sierra, M.T.; Aguilera-Camacho, L.D.; Báez-García, J.E.; García-Miranda, J.S.; Moreno, K.J. Thermal stability and lubrication properties of biodegradable castor oil on AISI 4140 steel. Metals 2018, 8, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shombe, G.B.; Mubofu, E.B.; Mlowe, S.; Revaprasadu, N. Synthesis and characterization of castor oil and ricinoleic acid capped CdS nanoparticles using single source precursors. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2016, 43, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazariya, A.; Matsumura, S. Enzymatic synthesis and crosslinking of novel high molecular weight polyepoxyricinoleate. Polymers 2012, 4, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, C.; Furugoh, S.; Yamakido, T.; Ogawa, H.I.; Kato, Y. Purification and characterization of a lipase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa KKA-5 and its role in castor oil hydrolysis. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 20, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunniyi, D.S. Castor oil: A vital industrial raw material. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, S.; Madankar, C.S.; Mohanty, P.; Naik, S.N. Optimization of reactive extraction of castor seed to produce biodiesel using response surface methodology. Fuel 2012, 97, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Das, L.M.; Naik, S.N. Effect of castor oil, methyl and ethyl esters as lubricity enhancer for low lubricity diesel fuel (LLDF). Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 5307–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, V.K.; Pandit, A.B. Effect of various additives on enzymatic hydrolysis of castor oil. Biochem. Eng. J. 2009, 47, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthli, M.S.; Rathod, V.K.; Pandit, A.B. Enzymatic hydrolysis of castor oil: Process intensification studies. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 31, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana, G.; Subbarao, R.; Sastry, Y.S.R.; Kale, V.; Rao, T.C.; Gangadhar, A. High pressure splitting of castor oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1983, 61, 1204–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Lipase applications in oil hydrolysis with a case study on castor oil: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 33, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.J.; Farrell, H.M. Generation of ricinoleic acid from castor oil using the lipase from ground oat (Avena sativa L.) seeds as a catalyst. Biotechnol. Lett. 1991, 13, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaskheli, A.A.; Talpur, F.N.; Ashraf, M.A.; Cebeci, A.; Jawaid, S.; Afridi, H.I. Monitoring the Rhizopus oryzae lipase catalyzed hydrolysis of castor oil by ATR-FTIR spectroscopy. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2015, 113, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, H.M.; Sagiroglu, A. Production of ricinoleic acid from castor oil by immobilised lipases. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 39, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Sun, S. Enzymatic production of sterculic acid from the novel Phoenix tree seed oil: Optimization and kinetic study. Grasas Aceites 2017, 68, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Li, X. A novel and rapid method for fatty acid preparation by the lipase catalyzed hydrolysis of Phoenix tree seeds. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Sun, S.; Liang, S.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, M. Lipase-catalyzed hydrolysis of linseed oil: Optimization using response surface methodology. J. Oleo Sci. 2014, 63, 619–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, J.S.; Vieira, N.S.; Cunha, A.S.; Silva, A.M.; Záchia Ayub, M.A.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Combi-lipase for heterogeneous substrates: A new approach for hydrolysis of soybean oil using mixtures of biocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 6863–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, H.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Shieh, C.-J. High yield of wax ester synthesized from cetyl alcohol and octanoic acid by lipozyme RMIM and Novozym 435. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11694–11704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von der Haar, D.; Stäbler, A.; Wichmann, R.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. Enzymatic esterification of free fatty acids in vegetable oils utilizing different immobilized lipases. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 37, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Yang, R.; Hu, J. Lysophosphatidylcholine synthesis by lipase-catalyzed ethanolysis. J. Oleo Sci. 2015, 64, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köse, Ö. Immobilized Candida antarctica lipase-catalyzed alcoholysis of cotton seed oil in a solvent-free medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, S.; Bi, Y. Solvent-free enzymatic synthesis of feruloylated structured lipids by the transesterification of ethyl ferulate with castor oil. Food Chem. 2014, 158, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chávez-Flores, L.F.; Beltran, H.I.; Arrieta-Baez, D.; Reyes-Duarte, D. Regioselective Synthesis of Lactulose Esters by Candida antarctica and Thermomyces lanuginosus Lipases. Catalysts 2017, 7, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzich, N.I.; Bassi, A.S. Proposed kinetic mechanism of biodiesel production through lipase catalysed interesterification with a methyl acetate acyl acceptor and ionic liquid [BMIM][PF6] CO-solvent. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2011, 89, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamayurova, V.S.; Zinov’Eva, M.E.; Tran, H.T.T. Features of the enzymatic hydrolysis of castor oil. Catal. Ind. 2013, 5, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, V.K.; Pandit, A.B. Enzymatic hydrolysis of oil in a spray column. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Optimization of process variables in castor oil hydrolysis by candida rugosa lipase with buffer as dispersion medium. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2009, 14, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, C.; Nakazato, M.; Ogawa, H.I.; Kato, Y. Lipase-induced hydrolysis of castor oil: Effect of various metals. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 21, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Sen, R.; Basu, J.K.; De, S. Surfactant enhanced ricinoleic acid production using candida rugosa lipase. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).