The First Catalytic Direct C–H Arylation on C2 and C3 of Thiophene Ring Applied to Thieno-Pyridines, -Pyrimidines and -Pyrazines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
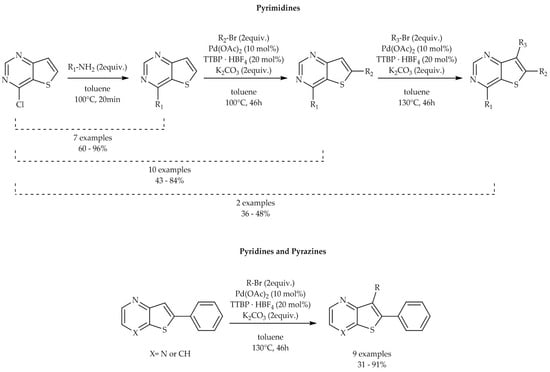
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crabtree, R.H.; Lei, A. Introduction: CH Activation. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8481–8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzouras, N.V.; Stamatopoulos, I.K.; Papastavrou, A.T.; Liori, A.A.; Vougioukalakis, G.C. Sustainable metal catalysis in C-H activation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 343, 25–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yuan, J.; Gao, M.; Tang, S.; Li, W.; Shi, R.; Lei, A. Oxidative Coupling between Two Hydrocarbons: An Update of Recent C–H Functionalizations. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 12138–12204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, N.; Schroder, N.; Glorius, F. Formal SN-Type Reactions in Rhodium (III)-Catalyzed C-H Bond Activation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1443–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, S.A.; Knauber, T.; Li, C.J. The Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling of Csp3-H Bonds: A Versatile Strategy for C-C Bond Formations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 74–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhl, N.; Hopkinson, M.N.; Wencel-Delord, J.; Glorius, F. Beyond Directing Groups: Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C-H Activation of Simple Arenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10236–10254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elrazaz, E.Z.; Serya, R.A.T.; Ismail, N.S.M.; Ella, D.A.A.E.; Abouzid, K.A.M. Thieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine based derivatives as kinase inhibitors and anticancer agents. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 1, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, L.E.; Liyanage, N.; Peddapuram, A.; Murphy, J.S.; Delcamp, J.H.; Hammer, N.I. Donor–Acceptor–Donor Thienopyrazines via Pd-Catalyzed C–H Activation as NIR Fluorescent Materials. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 81, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Wong, N.W.Y.; Forgione, P. One-Pot Tandem Palladium-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Cross-Coupling and C-H Activation Route to Thienoisoquinolines. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.W.Y.; Forgione, P. A one-pot double C-H activation palladium catalyzed route to a unique class of highly functionalized thienoisoquinolines. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 2738–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, J.F.; Queiroz, M.J.R.P.; Berteina-Raboin, S. Synthesis of New Thieno[3,2-b]pyridines and Thieno[2,3-b]pyrazines by Palladium Cross-Coupling. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 6945–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassoude, I.; Berteina-Raboin, S.; Massip, S.; Leger, J.M.; Jarry, C.; Essassi, E.; Guillaumet, G. Catalyst- and Base-Controlled Site-Selective sp2 and sp3 Direct Arylation of 5,7-Dimethyl-2-phenylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine Using Aryl Bromides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2572–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, K.L.; Sanford, M.S. Catalytic and Highly Regioselective Cross-Coupling of Aromatic C−H Substrates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11904–11905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Kan, J.; Wang, M.; Su, W.; Hong, M. Palladium-Catalyzed Direct Arylation of Electron-Deficient Polyfluoroarenes with Arylboronic Acids. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 3346–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.D.; Sun, C.L.; Fang, Z.; Li, B.J.; Li, Y.Z.; Shi, Z.J. Palladium-catalyzed direct arylation of (hetero)arenes with aryl boronic acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 1473–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campeau, L.-C.; Parisien, M.; Jean, A.; Fagnou, K. Catalytic Direct Arylation with Aryl Chlorides, Bromides, and Iodides: Intramolecular Studies Leading to New Intermolecular Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensaid, S.; Doucet, H. Influence of the solvent and of the reaction concentration for palladium-catalysed direct arylation of heteroaromatics with 4-bromoacetophenone. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2014, 17, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Su, M.; Li, T.; Gao, A.; Yang, W.; Sheng, L.; Zang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of thienopyrimidine hydroxamic acid based derivatives as structurally novel histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 128, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desroches, J.; Kieffer, C.; Primas, N.; Hutter, S.; Gellis, A.; El-Kashef, H.; Rathelot, P.; Verhaeghe, P.; Azas, N.; Vanelle, P. Discovery of new hit-molecules targeting Plasmodium falciparum through a global SAR study of the 4-substituted-2-trichloromethylquinazoline antiplasmodial scaffold. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 125, 68–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baugh, S.D.P.; Pabba, P.K.; Barbosa, J.; Coulter, E.; Desai, U.; Gay, J.P.; Gopinathan, S.; Han, Q.; Hari, R.; Kimball, S.D.; et al. Design, synthesis, and in vivo activity of novel inhibitors of delta-5 desaturase for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3836–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemnitzer, W.; Sirisoma, N.; May, C.; Tseng, B.; Drewe, J.; Cai, S.X. Discovery of 4-anilino-N-methylthieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines and 4-anilino-N-methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidines as potent apoptosis inducers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3536–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.H. A facile synthesis of new 4-(phenylamino) thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines using 3-aminothiophene-2-carboxamide. Heterocycl. Commun. 2007, 13, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.F.; Loubidi, M.; Scherrmann, M.C.; Berteina-Raboin, S. A Greener and Efficient Method for Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution of Nitrogen-Containing Fused Heterocycles. Molecules 2018, 23, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodring, J.L.; Patel, G.; Erath, J.; Behera, R.; Lee, P.J.; Leed, S.E.; Rodriguez, A.; Sciotti, R.J.; Mensa-Wilmot, K.; Pollastri, M.P. Evaluation of aromatic 6-substituted thienopyrimidines as scaffolds against parasites that cause trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, and malaria. Med. Chem. Commun. 2015, 6, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devine, W.; Woodring, J.L.; Swaminathan, U.; Amata, E.; Patel, G.; Erath, J.; Roncal, N.E.; Lee, P.J.; Leed, S.E.; Rodriguez, A.; et al. Protozoan Parasite Growth Inhibitors Discovered by Cross-Screening Yield Potent Scaffolds for Lead Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 5522–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Gopalsamy, A.; Cole, D.; Hu, Y.; Denny, R.; Ipek, M.; Liu, J.; Lee, J.; Hall, J.P.; Luong, M.; et al. Identification and SAR of a new series of thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidines as Tpl2 kinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 5952–5956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, D.G.; Douelle, F.; Manach, C.L.; Han, Z.; Paquet, T.; Taylor, D.; Njoroge, M.; Lawrence, N.; Wiesner, L.; Waterson, D.; et al. Structure–Activity Relationship Studies of Orally Active Antimalarial 2,4-Diamino-thienopyrimidines. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7572–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalsamy, A.; Shi, M.; Hu, Y.; Lee, F.; Feldberg, L.; Frommer, E.; Kim, S.; Collins, K.; Wojciechowicz, D.; Mallon, R. B-Raf kinase inhibitors: Hit enrichment through scaffold hopping. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2431–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snégaroff, K.; Lassagne, F.; Bentabed-Ababsa, G.; Nassar, E.; Ely, S.C.S.; Hesse, S.; Perspicace, E.; Derdour, A.; Mongin, F. Direct metallation of thienopyrimidines using a mixed lithium–cadmium base and antitumor activity of functionalized derivatives. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 4782–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]










| Entry | Pd(OAc)2 (mol %) | Ligand (mol %) | Cu (equiv.) | Base (equiv.) | Solvent | Br–X (1 equiv.) | Time (h) | T (°C) | Yield a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (10) | - | CuI (20) | K2CO3 (2) | Toluene | Bromo benzene | 24 | 120 | 0 |
| 2 | (10) | - | Cu(OAc)2 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | Toluene | Bromo benzene | 24 | 120 | 0 |
| 3 | (10) | - | CuI (20) | KOAc (2) | Toluene | Bromo benzene | 24 | 120 | 0 |
| 4 | (10) | - | Cu(OAc)2 (20) | KOAc (2) | Toluene | Bromo benzene | 24 | 120 | 0 |
| 5 | (5) | P(t-Bu)2 MeHBF4 (10) | - | K2CO3 (1) | DMA | Bromo benzene | 24 | 120 | 7 |
| 6 | (1) | P(t-Bu)2 MeHBF4 (3) | - | K2CO3 + AgOTf (0.2) + (0.1) | DMA | Bromo benzene | 24 | 145 | 0 |
| 7 | (5) | P(t-Bu)2 MeHBF4 (10) | - | K2CO3 (1) | DMA | 1-bromo- 4-methyl benzene | 96 | 120 | 26 |
| 8 | (5) | P(t-Bu)2 MeHBF4 (10) | - | K2CO3 (1) | DMA | 1-bromo- 4-(trifluoro methyl) benzene | 96 | 120 | 20 |
| 9 | (1) | - | - | KOAc (2) | DMA | Bromo aceto phenone | 24 | 150 | 0 |

| Entry | Amine Reagent | Product | Yield a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | 7, 86% |
| 2 |  |  | 8, 96% |
| 3 |  |  | 9, 82% |
| 4 |  |  | 10, 60% |
| 5 |  |  | 11, 86% |
| 6 |  |  | 12, 67% |
| 7 |  |  | 13, 68% |

| Entry | Pd Catalyst (equiv.) | Ligand (mol %) | Base (equiv.) | Solvent | Time (h) | T (°C) | Yield a (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 15 | |||||||
| 1 | Pd(OAc)2 (20%) | - | K2CO3 (4) | Toluene | 46 | 140 | 64 | 31 |
| 2 | Pd(OAc)2 (10%) | PCy3 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | Dioxane | 46 | 130 | 50 | 44 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 (10%) | TTBP · HBF4 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | Toluene | 46 | 130 | 81 | 9 |
| 4 | Pd(OAc)2 (10%) | Phenantroline (20) | K3PO4/K2CO3 (1)/(1) | DMA | 46 | 140 | 22 | 0 |
| 5 | Pd(OAc)2/ Bu4NBr (20%)/(2) | - | KOAc (6) | DMF | 24 | 80 | 26 | 0 |
| 6 | Pd(OAc)2/ Bu4NBr (20%)/(2) | - | KOAc (6) | Water | 24 | 80 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Pd(OAc)2 (10%) | TTBP · HBF4 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | Toluene | 46 | 100 | 72 | 0 |

| Entry | Amine Reagent | R2-Br | Product | Yield a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  |  | 14, 70% |
| 2 |  |  |  | 16, 58% |
| 3 |  |  |  | 17, 63% |
| 4 |  |  |  | 18, 61% |
| 5 |  |  |  | 19, 54% |
| 6 |  |  |  | 20, 43% |
| 7 |  |  |  | 21, 84% |
| 8 |  |  |  | 22, 55% |
| 9 |  |  |  | 23, 67% |

| Entry | Pd Catalyst (mol %) | Ligand (mol %) | Base (equiv.) | T (°C) | Yield a (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pd(OAc)2 (20) | - | K2CO3 (4) | 140 | 55 |
| 2 | Pd(OAc)2 (10) | TTBP·HBF4 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | 130 | 49 |
| 3 | Pd(OAc)2 (10) | PCy3 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | 130 | 34 |
| 4 | Pd(OAc)2 (10) | TTBP ·HBF4 (20) | K2CO3 (2) | 100 | 0 |

| Entry | Amine | R2-Br | R3-Br | Product | Yield a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  |  |  | 15, 48% |
| 2 |  |  |  |  | 24, 36% |

| Entry | R-Br | Product | Yield a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | 25, 91% |
| 2 |  |  | 26, 65% |
| 3 |  |  | 27, 89% |
| 4 |  |  | 28, 41% |
| 5 |  |  | 29, 84% |

| Entry | R-Br | Product | Yield a |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |  | 30, 47% |
| 2 |  |  | 31, 31% |
| 3 |  |  | 32, 38% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, J.F.; Queiroz, M.-J.R.P.; Berteina-Raboin, S. The First Catalytic Direct C–H Arylation on C2 and C3 of Thiophene Ring Applied to Thieno-Pyridines, -Pyrimidines and -Pyrazines. Catalysts 2018, 8, 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040137
Campos JF, Queiroz M-JRP, Berteina-Raboin S. The First Catalytic Direct C–H Arylation on C2 and C3 of Thiophene Ring Applied to Thieno-Pyridines, -Pyrimidines and -Pyrazines. Catalysts. 2018; 8(4):137. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040137
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Joana F., Maria-João R. P. Queiroz, and Sabine Berteina-Raboin. 2018. "The First Catalytic Direct C–H Arylation on C2 and C3 of Thiophene Ring Applied to Thieno-Pyridines, -Pyrimidines and -Pyrazines" Catalysts 8, no. 4: 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040137
APA StyleCampos, J. F., Queiroz, M.-J. R. P., & Berteina-Raboin, S. (2018). The First Catalytic Direct C–H Arylation on C2 and C3 of Thiophene Ring Applied to Thieno-Pyridines, -Pyrimidines and -Pyrazines. Catalysts, 8(4), 137. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8040137