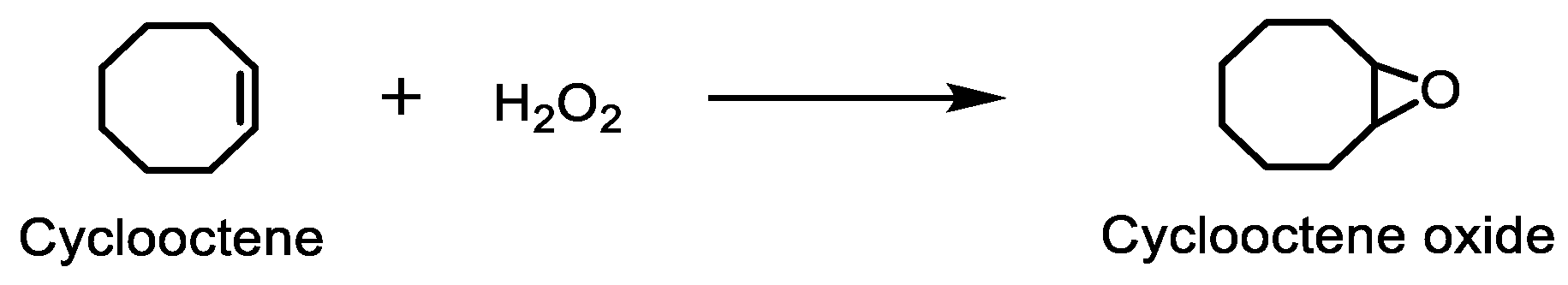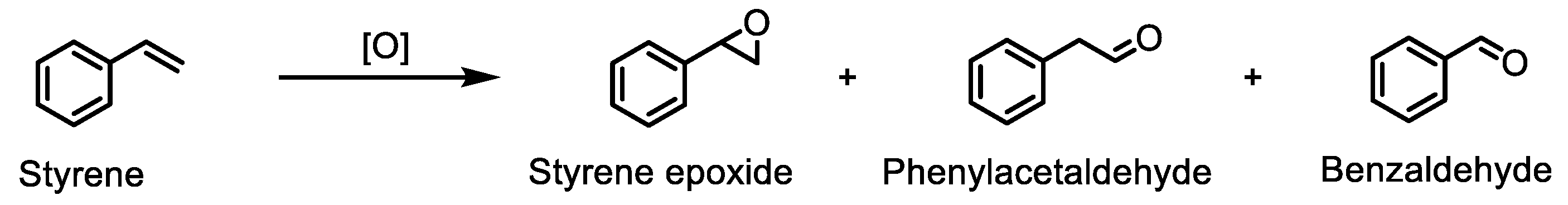Abstract
The synthesis, characterisation and homogeneous catalytic oxidation results of two manganese(III) porphyrins of the so-called second-generation of metalloporphyrin catalysts, containing one or four 3,5-dichloropyridyl substituents at the meso positions are reported for the first time. The catalytic efficiency of these novel manganese(III) porphyrins was evaluated in the oxidation of cyclooctene and styrene using aqueous hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant, under homogeneous conditions. High conversions were obtained in the presence of both catalysts, obtaining the corresponding epoxide as the major product. The asymmetric metalloporphyrin, chloro[5,10,15-tris(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-20-(3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-4, evidences a similar activity to that obtained with the well-known and highly efficient second-generation metalloporphyrin catalyst, chloro[5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2,6-dichlorophenyl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-2. CAT-4 was covalently attached onto Merrifield resin and 3-bromopropylsilica supports. The solid materials obtained were characterized by several techniques including diffuse reflectance, UV—VIS spectrophotometry, SEM and XPS. The catalytic results for the oxidation of cyclooctene and styrene using the immobilized catalysts are also presented. The Merrifield-supported catalyst showed to be very efficient, leading to five catalytic cycles in the oxidation of cyclooctene, using tert-butyl hydroperoxide as the oxidant.
Keywords:
manganese; porphyrins; homogeneous; heterogeneous; catalysis; oxidation; hydrogen peroxide 1. Introduction
Metalloporphyrins are effective and well-known biomimetic catalysts of the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes in the oxidation of several organic compounds [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11]. The first porphyrinic model system for alkenes’ epoxidation and alkanes’ hydroxylation was reported by Groves by using the iron(III) complex of 5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin (CAT-1) as the catalyst and iodosylbenzene (PhIO) as the oxygen atom donor [12]. Therefore, the so-called first-generation of metalloporphyrins as model systems of CYP450 was based on the metal complexes of the free-base 5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphyrin (Porph-1) (Figure 1). However, under the oxidative conditions of the reaction media, these metalloporphyrins can be rapidly destroyed or inactivated, namely by affording catalytically-inactive μ-oxo species.
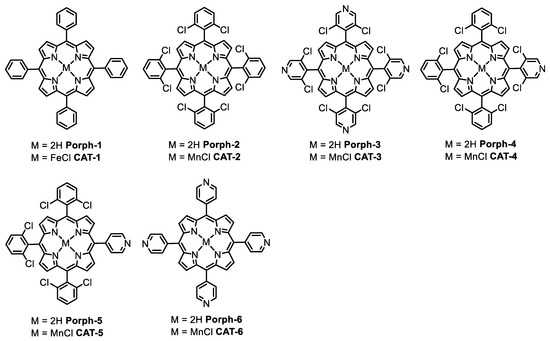
Figure 1.
The structures of Porph-1, Porph-2 and the metal complexes CAT-1, CAT-2 (first- and second-generation catalysts, respectively) and the structures of the porphyrin ligands and Mn(III) complexes used in the present work.
Since then, significant progress has been achieved by developing more robust and efficient biomimetic oxidation metalloporphyrin catalysts [4,13,14,15]. The introduction of electron-withdrawing or bulky substituents at the meso-phenyl rings of the macrocycle, as is the case of 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2,6-dichlorophenyl)porphyrin (Porph-2), led to the so-called second-generation of metalloporphyrins (Figure 1), known as more resistant towards oxidative degradation [13,14]. Subsequently, electron-withdrawing substituents were also introduced at the β-pyrrolic positions, thus resulting in the third-generation of metalloporphyrins which, due to an increase in the electrophilicity of their metal-oxo active species, showed to be more efficient, leading to high product yields and selectivities [15]. However, the third-generation of metalloporphyrins do not always give rise to more active and stable oxidation catalysts [16,17,18,19,20]. A possible reason for their lower efficiency may be related with steric effects due to an excess of electron-withdrawing substituents in the macrocycle [18]. Studies with third-generation manganese porphyrins also indicated that the presence of chlorine atoms at the β-pyrrolic positions stabilises Mn(II), thus being unfavourable to the formation of the active species, MnV = O [19,20]. Furthermore, the second-generation metalloporphyrins are, in general, more easily prepared and an increase in selectivity to the desired products can be obtained by varying other parameters, such as solvent, oxidant and axial ligands [18].
In recent years the use of heterogeneous catalysts based on metalloporphyrins has been explored, especially due to the possibility of recovery and reuse [3,10,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Most of those studies are based on 5,10,15,20-tetraarylporphyrins of the first- and second-generations, having suitable groups to covalently graft them to a support [27]. In some cases, the introduction of extra functionalities on the porphyrin core, such as sulfonic or amino groups, is required in order to allow its attachment to a support. Considering that 3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde is commercially available and the pyridine unit is complemented with electron-withdrawing and bulky substituents at adequate positions to protect the porphyrin ligand from oxidative degradation or inactivation, we envisaged that porphyrins built from that aldehyde would afford stable catalysts with excellent features for further immobilization through the pyridine unit(s). Thus, in the present work, two second-generation manganese(III) porphyrins containing 3,5-dichloropyridyl substituent(s) at the meso position(s) were prepared and characterized for the first time (Figure 1). The symmetric chloro[5,10,15,20-tetrakis(3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-3, and the asymmetric chloro[5,10,15-tris(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-20-(3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-4, were tested as homogeneous catalysts in the oxidation of cyclooctene and styrene using aqueous hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant. Their catalytic performance was compared with the already known counterparts chloro[5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2,6-dichlorophenyl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-2 [8,28], chloro[5,10,15-tris(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-20-(pyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-5 [29] and chloro[5,10,15,20-tetra(pyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-6 [30]. CAT-4 was immobilized onto solid supports of Merrifield resin and 3-bromopropylsilica and the resulting materials were tested as catalysts in the oxidation of cyclooctene and styrene under heterogeneous conditions. CAT-5 was also immobilized onto Merrifield resin and used as a catalyst in the oxidation of cyclooctene for comparison.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis of the Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Metalloporphyrin Catalysts
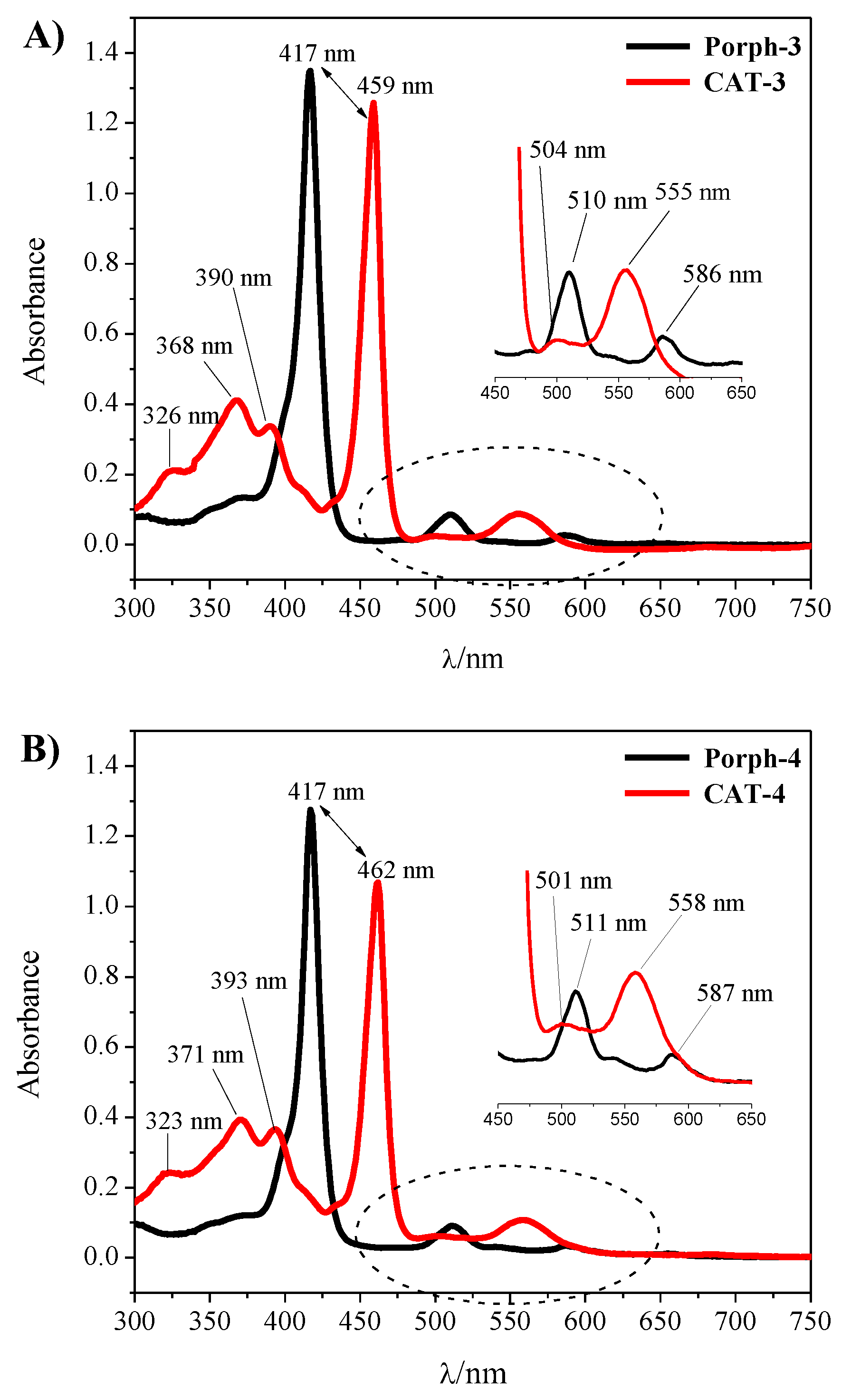
The synthetic approaches used to prepare the homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysts are summarized in Scheme 1. The novel free-base porphyrins and their manganese(III) complexes were synthesized according to the synthetic approach summarized in Scheme 1—Steps I and II, following well-established procedures [31,32]. The symmetric free-base porphyrin Porph-3 was prepared by the condensation of pyrrole with 3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde, while the asymmetric porphyrin Porph-4 required the use of 3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde and 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde in a stoichiometric ratio that favours the formation of the desired ligand (Scheme 1—Step I). The free-base porphyrins were metalated according to Adler’s conditions, using 10 equivalents (eq.) of MnCl2·4H2O, pyridine and DMF at 153 °C (Scheme 1—Step II) [32]. The metalation was monitored by TLC, which showed the disappearance of the starting porphyrin accompanied by the formation of a more polar compound, and by UV–VIS spectroscopy (Figure 2). In fact, the strong alterations observed in the Soret band (λ ≈ 417 nm) and Q bands (λ ≈ 500–650 nm) regions of the free-bases Porph-3 and Porph-4 spectra confirmed the success of manganese insertion and, consequently, the formation of CAT-3 and CAT-4. After metalation a bathochromic shift of the Soret band to ca. 460 nm was observed. Additionally, the presence of the manganese metal was also easily detected by the presence of the transition bands at λ ≈ 320–400 nm (Figure 2).
Scheme 1.
Synthetic strategy to prepare the novel homogeneous and supported Mn(III) porphyrin catalysts.
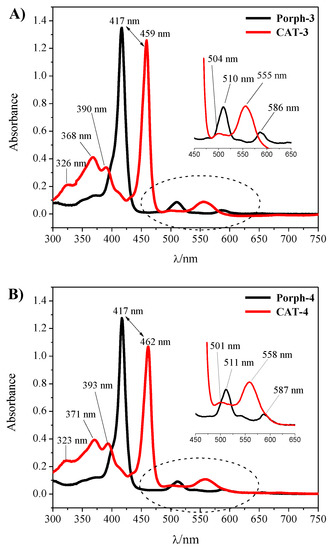
Figure 2.
UV–VIS spectra obtained before and after the complexation of (A) Porph-3; (B) Porph-4 with manganese. The spectra were acquired using chloroform as solvent for the free-base porphyrins and methanol for the Mn(III) complexes.
CAT-4 was selected (vide infra) to be covalently immobilized through its pyridine moiety to 3-bromopropyl-functionalized silica (Si) and Merrifield resin (MR) supports (commercially available) (Scheme 1—Step III). In both cases the immobilization was carried out using 1,2-dichlorobenzene as the solvent, at 190 °C in a sand bath [22]. The reactions were followed by UV–VIS spectroscopy and although some metalloporphyrin was still present in solution, the reaction was stopped after 96 h. The obtained solids were filtered, washed with 1,2-dichlorobenzene, CH3CN and dichloromethane (previously passed through an aluminum oxide column) and dried. The loading of the catalyst immobilized on the support was calculated by elemental analysis based on the amount of nitrogen present in the sample. Using these conditions, a loading of 7.2 µmol/g was obtained for the immobilization of CAT-4 on MR and of 17.8 µmol/g on the functionalized silica.
CAT-4 and CAT-5 were also immobilized onto MR using microwave (MW) assisted irradiation as heating source, in a multimode MW equipment, for 30 min. Under these conditions, metalloporphyrin loadings of 4.4 µmol/g and 7.3 µmol/g were achieved for CAT-4 and CAT-5, respectively.
2.2. Structural Characterization
The structures of the new derivatives were confirmed by adequate spectroscopic techniques (UV–VIS, NMR and mass spectrometry; please see Experimental Section and Figures S1–S6 of the Supplementary Material). In particular, the 1H NMR spectrum of the free-base porphyrin Porph-3 (Figure S1) presents the characteristic high field signal relative to the resonance of the inner NH protons of the porphyrin at δ = −2.66 ppm, while it is possible to identify two singlets in the aromatic region, one at δ = 8.68 ppm, corresponding to the eight protons of the β-pyrrolic positions and the other one at δ = 9.04 ppm due to the resonance of the eight protons of the meso-3,5-dichloropyridyl rings. In the 1H NMR spectrum of Porph-4 (Figure S2), the presence of the 3,5-dichloropyridyl moiety was easily identified by the singlet at δ = 9.00 ppm due to the resonance of its two protons. In this case, as a result of the macrocycle asymmetry, the signals due to the resonance of the β-pyrrolic protons appear as two doublets (J = 4.4 Hz) at δ = 8.61 and 8.70 ppm and as a singlet at δ = 8.68 ppm. The doublets were assigned to the four β-pyrrolic protons near the 3,5-dichloropyridyl ring while the singlet was identified as being due to the remaining four β-pyrrolic protons less affected by the asymmetry induced by the pyridine unit. The resonances of the protons of the 2,6-dichlorophenyl units appear as two multiplets at δ = 7.69–7.73 ppm for the three protons of the para positions and at δ = 7.79–7.81 ppm for the six protons of the meta positions. The resonance of the inner NH protons appears as a singlet at δ = −2.57 ppm. The structures of these porphyrins were consistent with their mass spectra, which showed the expected [M + H]+ ions at m/z = 894.9 Da for Porph-3 (Figure S3) and at m/z = 891.9 Da for Porph-4 (Figure S4). For the CAT-3 and CAT-4 complexes, the mass (Figures S5 and S6, respectively) and the UV–VIS spectra (Figure 2) were also consistent with the proposed structures.
The supported porphyrin materials CAT-4-Si, CAT-4-MR and CAT-5-MR were analysed by diffuse reflectance (Figure S7). The UV–VIS spectrum of the CAT-4 powder (Figure S7a) shows the Soret band at around 479 nm and the Q-bands at 583 nm and 623 nm. The UV–VIS spectrum of the CAT-5 powder (Figure S7b) shows the Soret band at 473 nm and the Q-bands at 578 nm and 620 nm. The presence of the broad bands in the Soret and the Q-bands regions in the UV–VIS spectra of the immobilized porphyrin materials (Figure S7c–e) confirms the presence of porphyrin.
The solids were also analysed by ATR infrared spectroscopy (Figure S8); however, in the spectra of CAT-4-Si (Figure S8c), CAT-4-MR (Figure S8e) and CAT-5-MR (Figure S8f) the bands due to the metalloporphyrin were not detected probably due to its low concentration and some overlap with the solid supports’ bands.
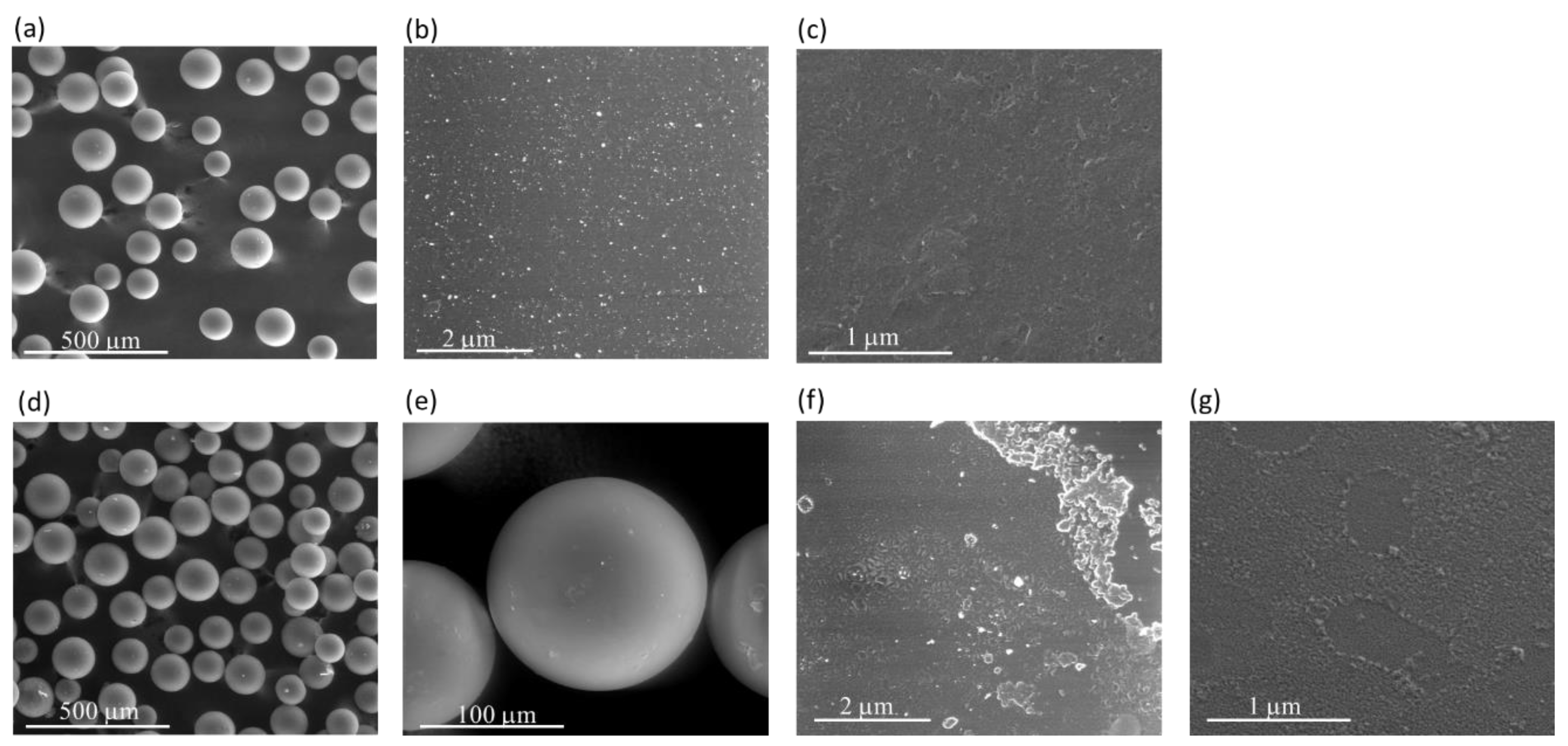
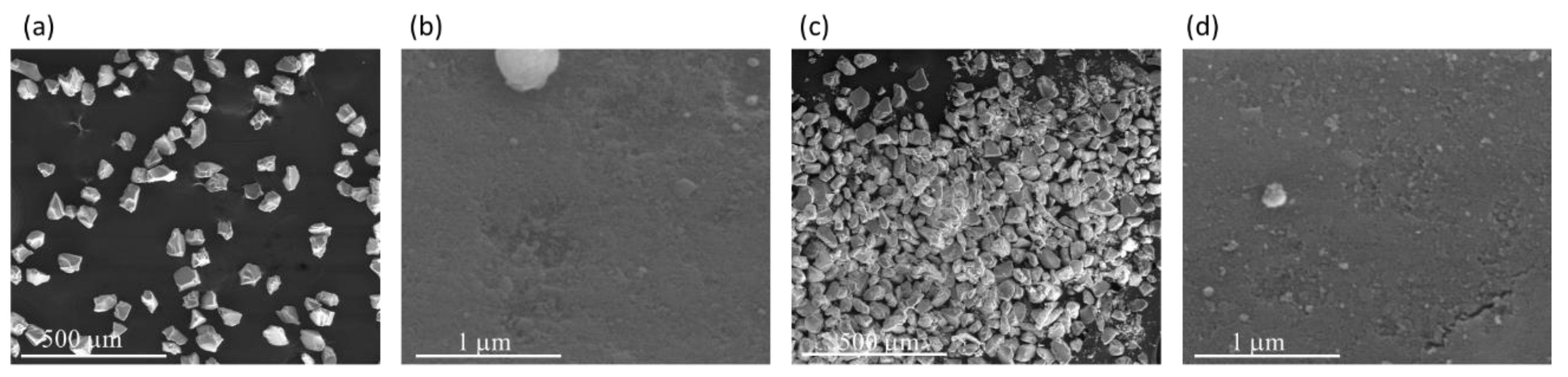
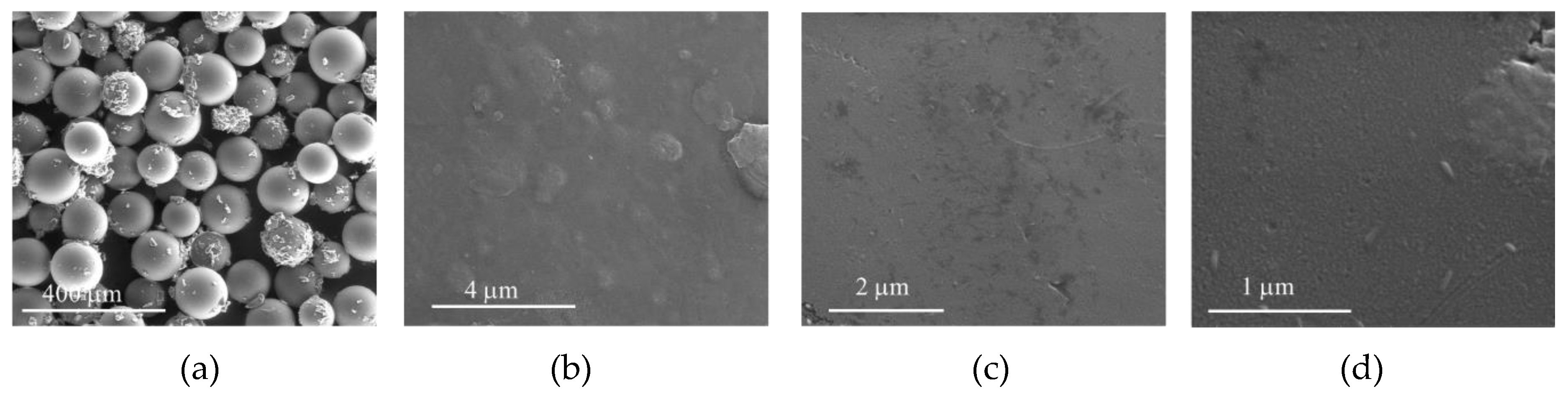
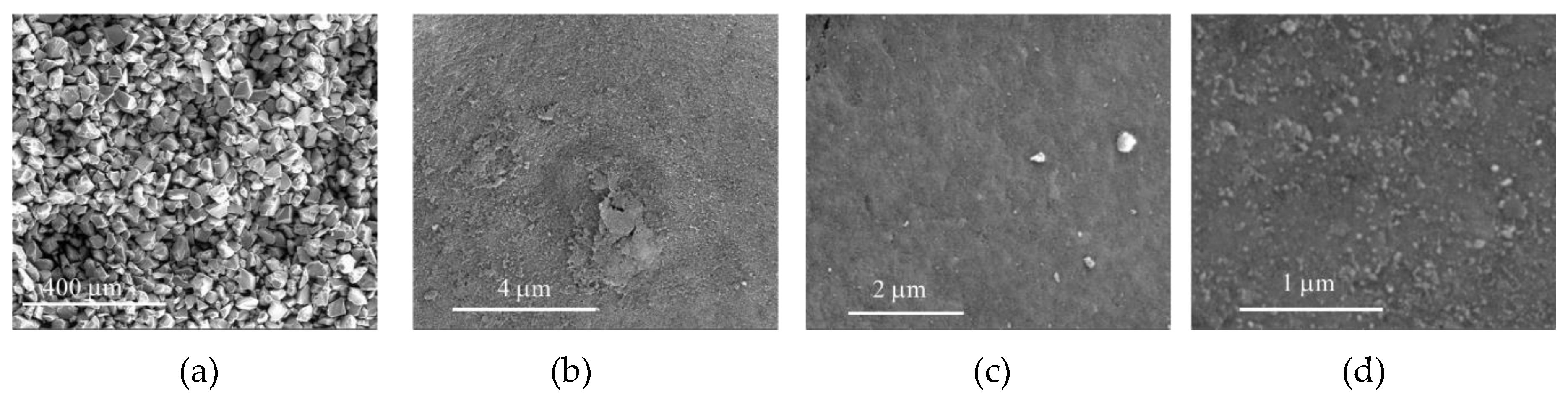
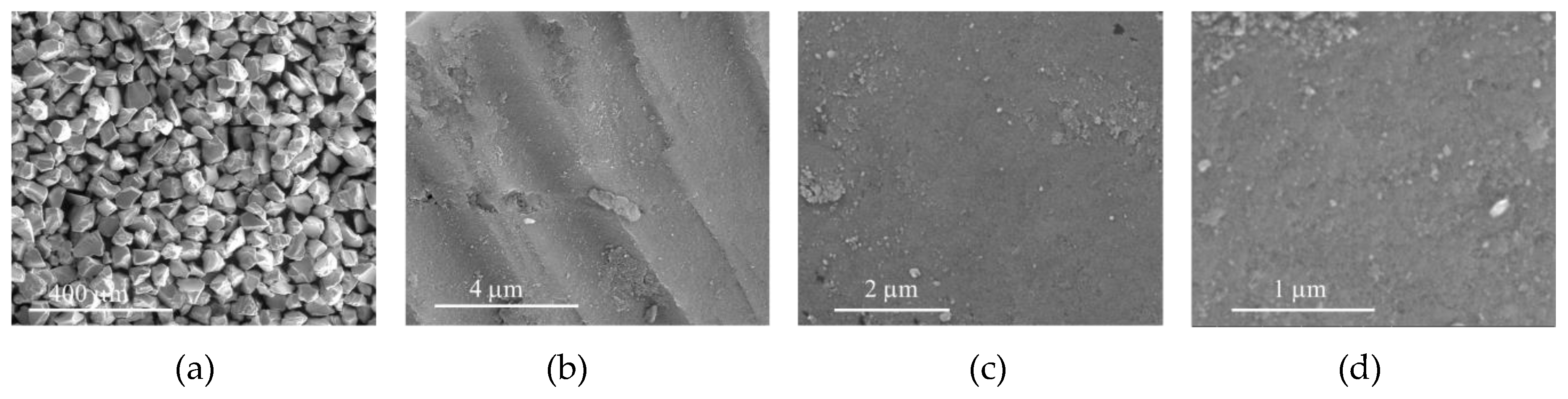
The morphology of CAT-4-MR and CAT-4-Si was analysed by the SEM technique and compared with the starting materials (Figure 3 and Figure 4). The images show that there are no major changes in the morphology of the immobilized porphyrin materials when compared with the original MR and silica supports, which means that the characteristics of the original materials are maintained after immobilization. In the case of CAT-4-MR (Figure 3d–g) a small change in the surface was observed, after immobilization, at various points presenting some roughness, which should result from the functionalization reaction. In the case of the material obtained by immobilization of CAT-4 on silica, this type of surface change is less evident (Figure 4).
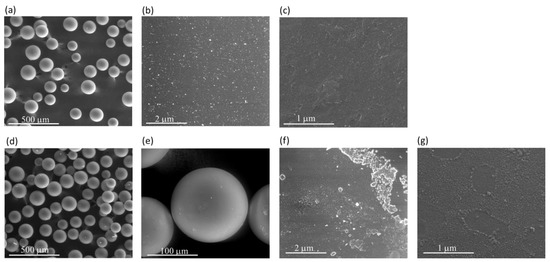
Figure 3.
SEM micrographs of (a) starting MR (200×), (b) starting MR (40,000×), (c) starting MR (100,000×), (d) CAT-4-MR (200×), (e) CAT-4-MR (1000×), (f) CAT-4-MR (40,000×) and (g) CAT-4-MR (100,000×).
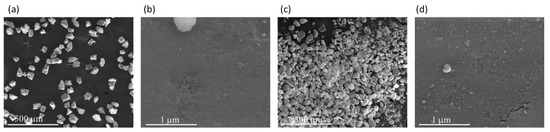
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs of (a) starting silica (200×), (b) starting silica (100,000×), (c) CAT-4-Si (200×) and (d) CAT-4-Si (100,000×).
The composition of the heterogeneous catalysts was determined by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and was compared with the starting materials. The elemental atomic percentages are summarized in Table 1. In the case of the solid material obtained by immobilization of CAT-4 on silica, the presence of nitrogen and chlorine and the increase in the atomic percentage of C 1s are in accordance with the anchorage of the manganese(III) porphyrin (Table 1, Entry 2). In addition, the decrease in the atomic percentage of bromine indicates the occurrence of the nucleophilic substitution. The decrease in bromine is, however, higher than expected for the immobilization of metalloporphyrin when compared to the increase in nitrogen and chlorine. The possible reason for the lower atomic percentage is because bromine can be lost during the immobilization due to the high temperature and/or by reaction with water present in the atmosphere. The manganese is not detected due to the low atomic percentage expected (at the detection limit level). In the case of the solid materials obtained by CAT-4 and CAT-5 immobilization on the MR (CAT-4-MR and CAT-5-MR, respectively), the increase in the atomic percentage of chlorine and the presence of nitrogen and manganese are the main evidences of metalloporphyrin anchorage (Table 1, Entries 4 and 5).

Table 1.
Surface atomic percentages for CAT-4-Si, CAT-4-MR and CAT-5-MR obtained by XPS 1.
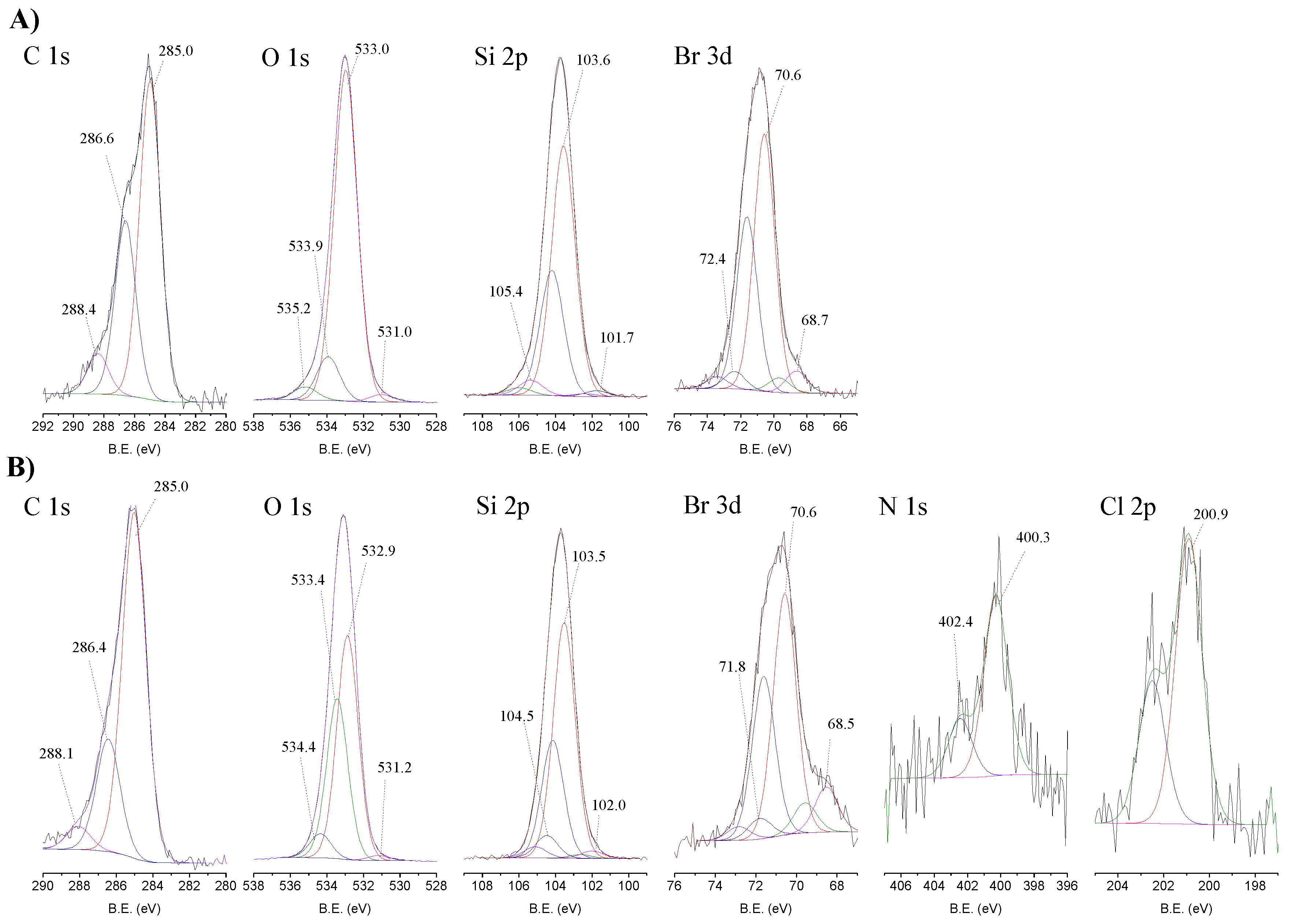
The high-resolution spectra of the elements present in the CAT-4-Si and in the starting 3-bromopropyl-functionalized silica are depicted in Figure 5. The XPS high-resolution spectra in the C 1s region of 3-bromopropylsilica (Figure 5A) and CAT-4-Si (Figure 5B) were deconvoluted into three components. The peak at 285.0 eV is attributed to the C-Si [33], and to the aliphatic C-C bonds that appear overlaid, the peak at 286.6 eV is ascribed to C-Br bonds and the peak at 288.4 eV is due to “adventitious carbon” contamination. “Adventitious” contamination is commonly present in samples exposed to air atmosphere. As in silica materials the amount of carbon is low, the carbon contamination due to “adventitious carbon”, which normally arises at approximately 284.8 eV, 286 eV and 288.5 eV becomes significant. For this reason, the bands present in the high-resolution C 1s spectra of silica and of CAT-4-Si have also a contribution of this contamination. In the spectrum of CAT-4-Si, the main peak at 285.0 eV corresponds to C-Si bonds, which overlaps with the aliphatic C-C bonds and the aromatic C=C bonds of the metalloporphyrin, the peak at 286.4 eV is ascribed to the C-Br bonds together with the C-N and C-Cl bonds of the metalloporphyrin and the peak at 288.1 eV is attributed to “adventitious carbon” contamination. The band at 286.4 eV is less intense in CAT-4-Si than in the starting silica due to the loss of bromine. The decrease in band intensity does not result only from the loss of bromine during the nucleophilic substitution, because the C-N and C-Cl bonds from the porphyrin, which appear at the same binding energy (B.E.), compensate for this decrease. Instead, bromine can be lost during the immobilization by reaction with the water.
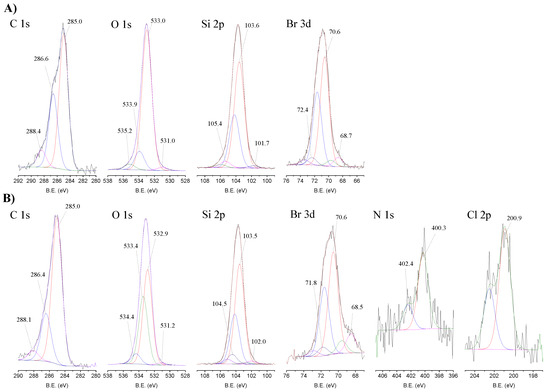
Figure 5.
High-resolution XPS spectra in the C 1s, O 1s, Si 2p, Br 3d, N 1s and Cl 2p regions with the corresponding fits for (A) Si and (B) CAT-4-Si.
The O 1s high-resolution spectrum of 3-bromopropylsilica (Figure 5A) was deconvoluted into four bands. The main peak observed at 533.0 eV is assigned to Si-O-Si bonds and the peak at 533.9 eV is ascribed to O-Si and O-C bonds. The peak at 531.0 eV can be attributed to “adventitious” material (B.E. ascribed to C=O bonds) and the peak at 535.2 eV is due to the presence of adsorbed water [34]. The O 1s high-resolution spectrum of CAT-4-Si (Figure 5B) shows an identical profile and can be deconvoluted into the same four bands with binding energies very close to those obtained for 3-bromopropylsilica. The peak at 533.4 eV attributed to O-Si and O-C bonds increases in the CAT-4-Si material probably due to the nucleophilic substitution of bromine by water.
The Si 2p high-resolution spectra of the starting 3-bromopropylsilica (Figure 5A) and of the CAT-4-Si (Figure 5B) were deconvoluted into three components (doublets for 2p orbitals) and the B.E. of the Si 2p components of CAT-4-Si do not differ significantly from the original silica. The bands at 103.5 eV (2p3/2) and 104.1 (2p1/2) eV are assigned to Si-O-Si bonds and the peaks at 102.0 eV (2p3/2) and 102.6 eV (2p1/2) are attributed to Si-C bonds. The bands at 104.5 eV (2p3/2) and 105.1 eV (2p1/2) may be attributed to Si-Br-O bonds, which might result from a possible nucleophilic substitution of the silica Si-O-Si groups by Br− and further oxidation.
The Br 3d high-resolution spectra of the starting 3-bromopropylsilica (Figure 5A) and of the CAT-4-Si (Figure 5B) were fitted with three main components (doublets for 3d orbitals). In the Br 3d high-resolution spectrum of CAT-4-Si the preeminent peaks at 70.6 eV (3d5/2) and 71.6 eV (3d3/2) are assigned to Br-C bonds and the peaks at 68.7 eV (3d5/2) and 69.7 eV (3d3/2) are attributed to Br− ions [35]. Regarding the peaks at 71.8 eV (3d5/2) and 72.8 eV (3d3/2), since there are no studies of XPS reported in the literature, the assignment to Br-Si-O is proposed, in coherence with the assignments made in the high-resolution spectrum Si 2p.
The N 1s high-resolution spectrum of CAT-4-Si (Figure 5B) was deconvoluted into two bands. The band at 400.3 eV is attributed to the central porphyrin nitrogen bonds, in accordance with reported works [36,37,38,39]. The peak at 402.4 eV is attributed to the nitrogen bonds of the pyridine moieties, in accordance with that described for protonated nitrogen atoms in pyridines [39,40,41]. This also indicates that the manganese(III) porphyrin is covalently bonded to the silica support through the nitrogen atom of the pyridine moiety.
The Cl 2p high-resolution spectrum of CAT-4-Si (Figure 5B) presents the doublet band at 200.9 eV and 202.5 eV attributed to the C-Cl bonds of the metalloporphyrin.
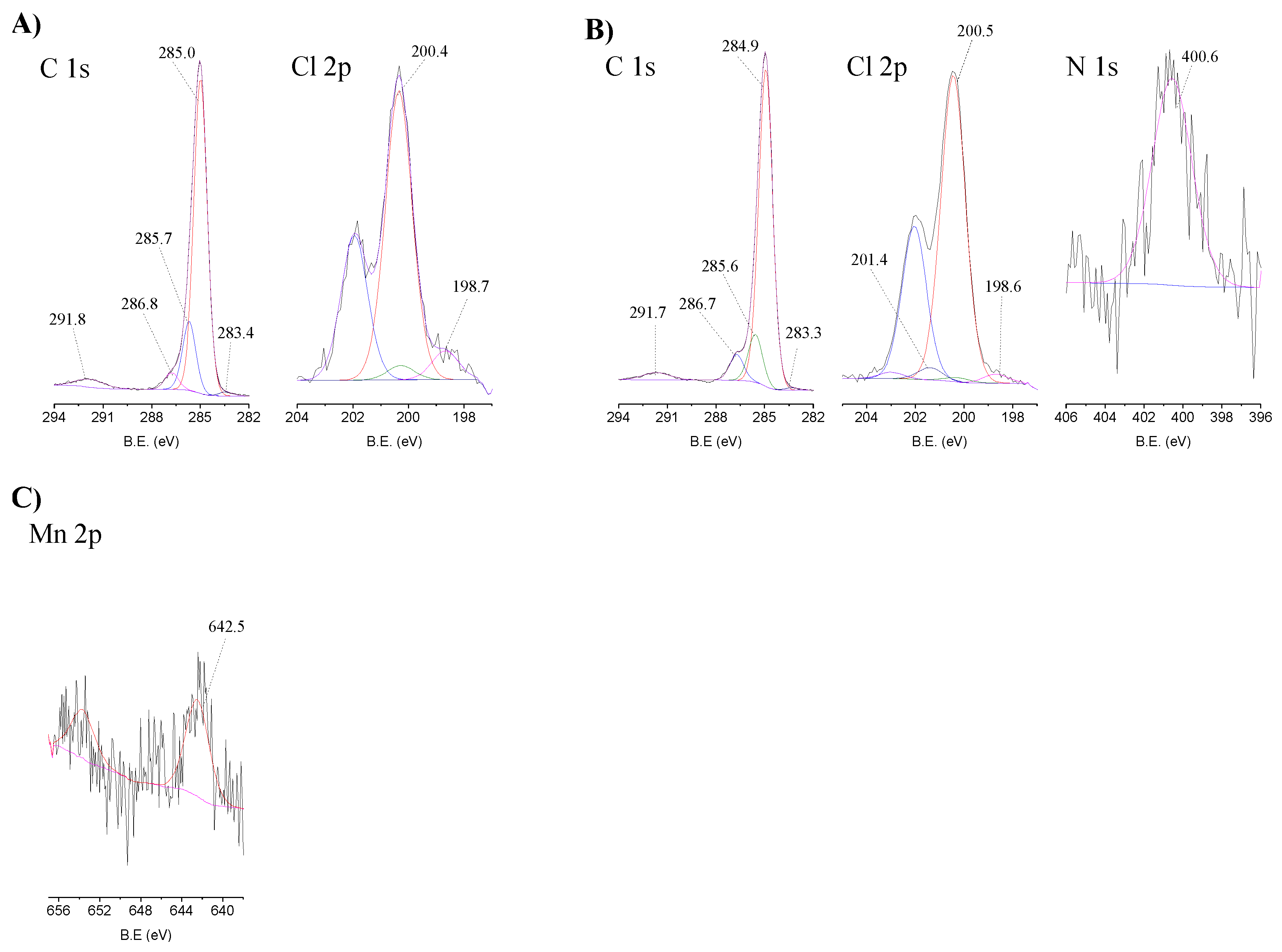
The high-resolution spectra in the relevant regions of MR, CAT-4-MR and CAT-5-MR are presented in Figure 6. The C 1s high-resolution spectra of the starting MR (Figure 6A) and of the Merrifield-supported materials (Figure 6B, illustrated for the case of CAT-4-MR) were fitted with five components. The peak centred at 284.9–285.0 eV corresponds to sp2 carbons (aromatic bonds of MR) and the π system of the metalloporphyrin, while the peak at 285.6–285.7 eV is due to sp3 carbons. The peak at 286.7–286.8 eV is attributed to C-Cl bonds of Merrifield overlaid with C-N and C-Cl bonds of the metalloporphyrin and the peak at 283.2–283.4 eV may be ascribed to a contamination already present in the starting material. The band at 291.5–291.8 eV (≈6.8 eV above the main C 1s peak) corresponds to a shake-up satellite of π–π* transitions of the aromatic rings [42].
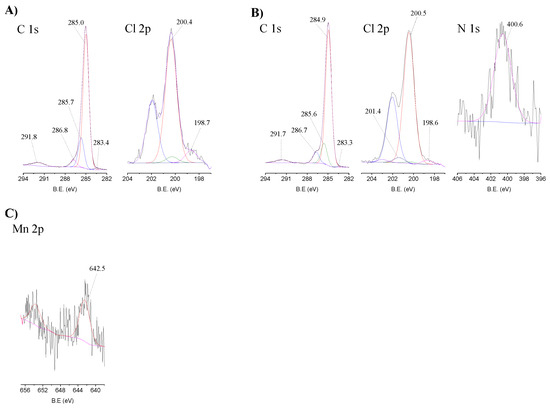
Figure 6.
High-resolution XPS spectra in the relevant regions with the corresponding fits for (A) MR, (B) CAT-4-MR and (C) CAT-5-MR.
The Cl 2p high-resolution spectrum of MR (Figure 6A) was deconvoluted into two components with the corresponding doublet bands. The main peaks at 200.4 eV (2p3/2) and 202.0 eV (2p1/2) are due to C-Cl bonds and the peaks at 198.7 eV (2p3/2) and 200.3 eV (2p1/2) correspond to Cl− ions. The high-resolution spectra of the Merrifield supported materials (Figure 6B) have an additional component attributed to C-Cl bonds of the metalloporphyrin at ≈ 201.4 eV (2p3/2) and ≈ 203.0 eV (2p1/2).
The N 1s high-resolution spectra of the Merrifield immobilized materials (Figure 6B for CAT-4-MR) exhibit a band at 400.2–400.6 eV attributed to the central porphyrin nitrogen bonds. In the case of CAT-4-MR and CAT-5-MR it was not possible to identify the band at about 402 eV that was present in the CAT-4-Si material corresponding to protonated nitrogen atoms. As the signal is very low due to the low loading of metalloporphyrin, the noise is very high and, therefore, we cannot state that this band is not present and that the immobilization did not occur by covalent bonding. However, in the Merrifield supported materials we cannot discard the possibility of the immobilization to occur through π–π stacking interaction between the aromatic rings.
The Mn 2p high-resolution spectra of the Merrifield supported materials also present a high noise due to the low loading of porphyrin. However, it was possible to identify a doublet with a band at about 642 eV (2p3/2), in agreement with a Mn(III) porphyrin (Figure 6C, displayed for CAT-5-MR) [43,44,45,46].
2.3. Oxidation of Cyclooctene Catalysed by CAT-3 and CAT-4 under Homogeneous Conditions
To evaluate the catalytic activity of the novel manganese(III) porphyrins, CAT-3 and CAT-4, in oxidation reactions, cyclooctene was selected as the model substrate and aqueous H2O2 as the oxygen donor (Scheme 2) and, for the required heterolytic cleavage of H2O2, ammonium acetate was selected as co-catalyst [28,47,48]. The reactions were carried out using acetonitrile as solvent at 30 °C and the oxidant was added gradually with additions of 0.5 eq. of H2O2 at every 15 min. The evolution of the reactions, along with the epoxide formation, were monitored by GC–FID.

Scheme 2.
Cyclooctene oxidation reaction in the presence of H2O2, catalysed by the Mn(III) porphyrins prepared.
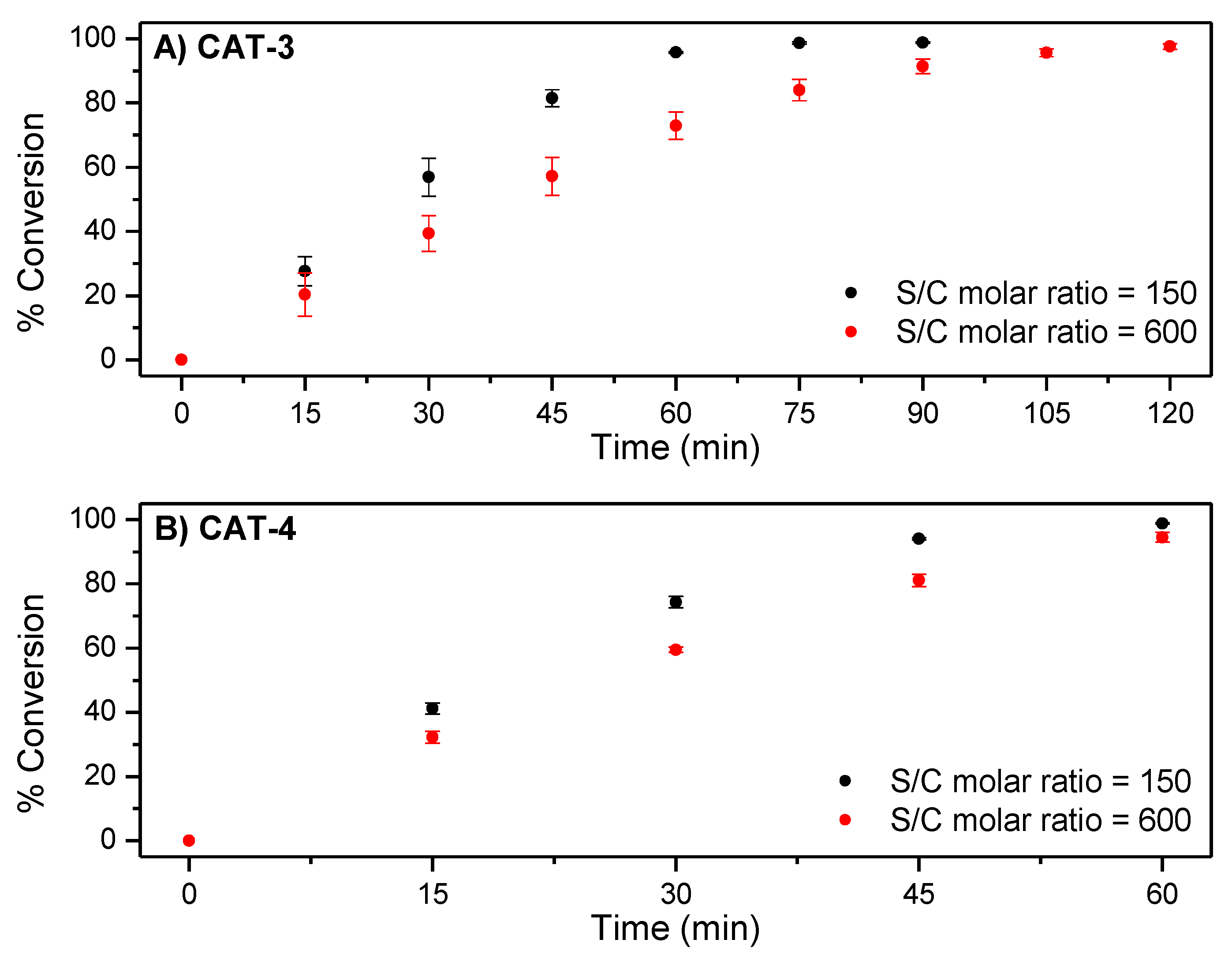
In the oxidations with CAT-3, for a substrate/catalyst (S/C) molar ratio of 150, an almost total conversion of cyclooctene (98.8%) to cyclooctene oxide (selectivity > 99%) was obtained after 90 min of reaction (Figure 7A and Table 2). A similar performance was observed in the presence of the asymmetric catalyst CAT-4, under the same S/C molar ratio of 150, but after 60 min of reaction (Figure 7B and Table 2).
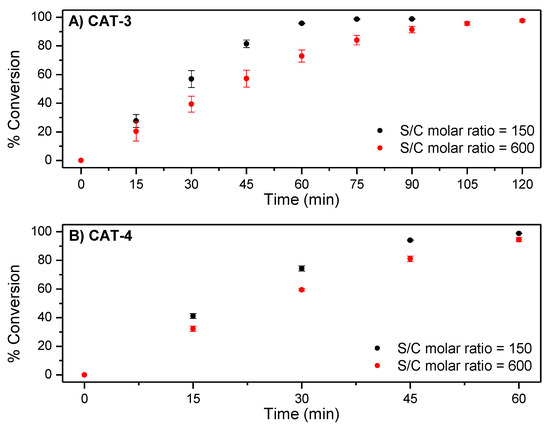
Figure 7.
Comparison of the catalytic efficiency for the oxidation of cyclooctene with H2O2 catalysed by (A) CAT-3 and (B) CAT-4. Data correspond to mean values of at least three non-simultaneous replicates and the vertical bars correspond to the standard deviations.

Table 2.
Results obtained for the oxidation of cyclooctene with H2O2 using CH3CN as solvent and ammonium acetate as co-catalyst in the presence of different Mn(III) porphyrins (a).
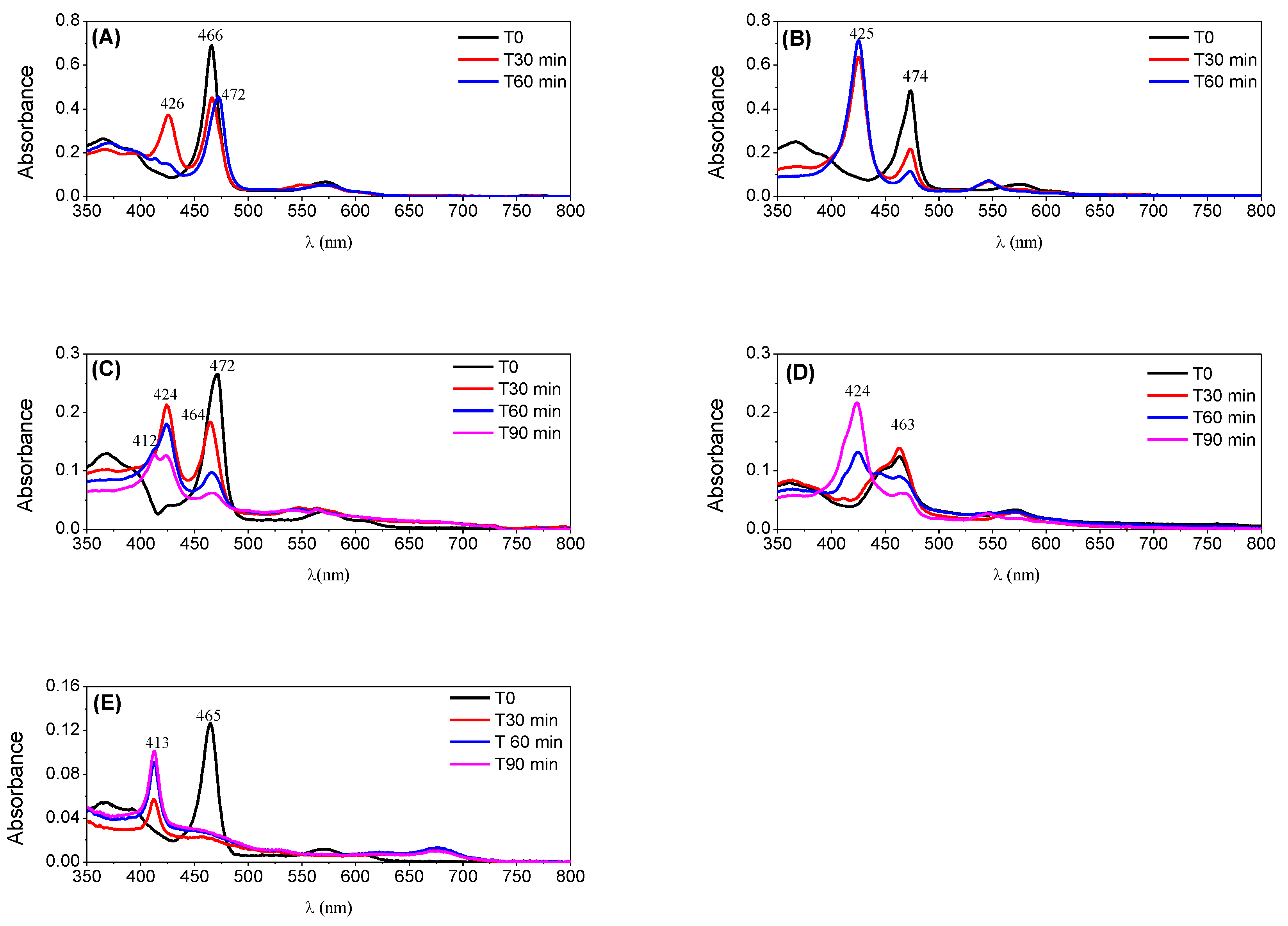
The excellent behaviour of both Mn(III) catalysts under the conditions tested with high conversion of cyclooctene and good stability of the catalysts confirmed by UV–VIS spectroscopy (Figure 8) led us to test a S/C molar ratio of 600 (see Table 2). Under these conditions, the oxidation of cyclooctene in the presence of CAT-3 was slightly slower (Figure 7A), but still a high conversion of the substrate was achieved after 120 min of reaction (97.6%). In the case of CAT-4, the efficiency of the catalyst was maintained with a substrate conversion of 98.2% after 75 min of reaction (Figure 7B).
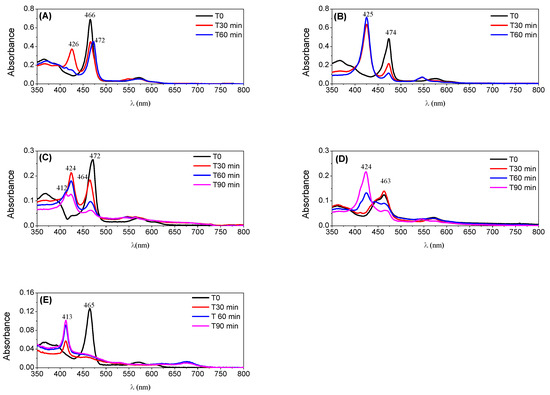
Figure 8.
UV–VIS monitoring of the catalysts along cyclooctene oxidation reactions for the S/C molar ratio of 150: (A) CAT-2; (B) CAT-4; (C) CAT-5; (D) CAT-3; and (E) CAT-6.
Taking into account the results obtained with the two novel metalloporphyrins, CAT-3 and CAT-4, it was important to compare their catalytic activity with the catalytic ability of already known porphyrins having related structural features (Figure 1), namely:
- (i)
- the chloro[5,10,15,20-tetrakis(2,6-dichlorophenyl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-2, a highly efficient catalyst having all the meso positions substituted by 2,6-dichlorophenyl units;
- (ii)
- the chloro[5,10,15-tri(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-20-(pyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-5, with one meso position substituted by a pyridine unit and the other three meso positions substituted by 2,6-dichlorophenyl groups; and
- (iii)
- the chloro[5,10,15,20-tetra(pyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III), CAT-6, with all the meso positions substituted by pyridine units.
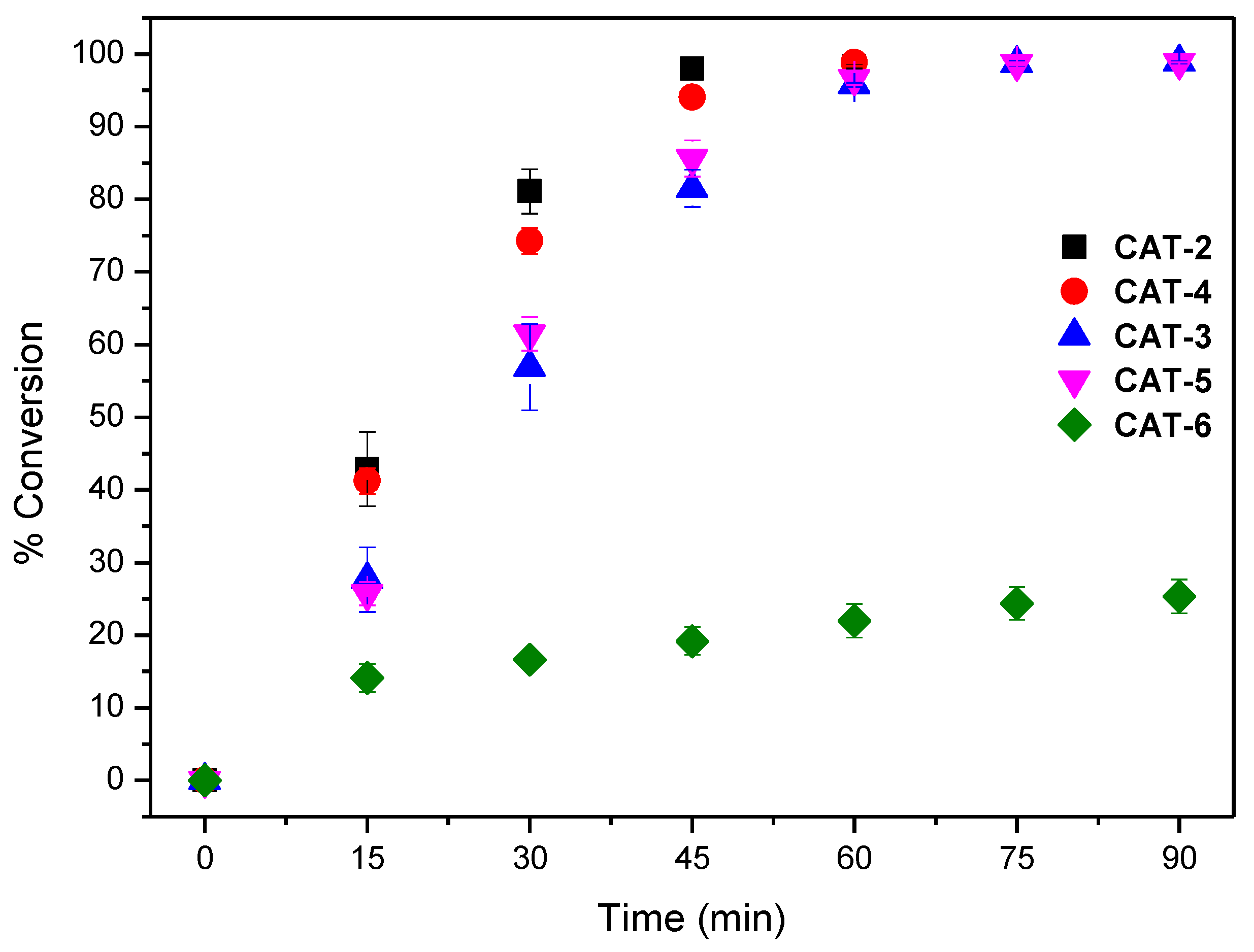
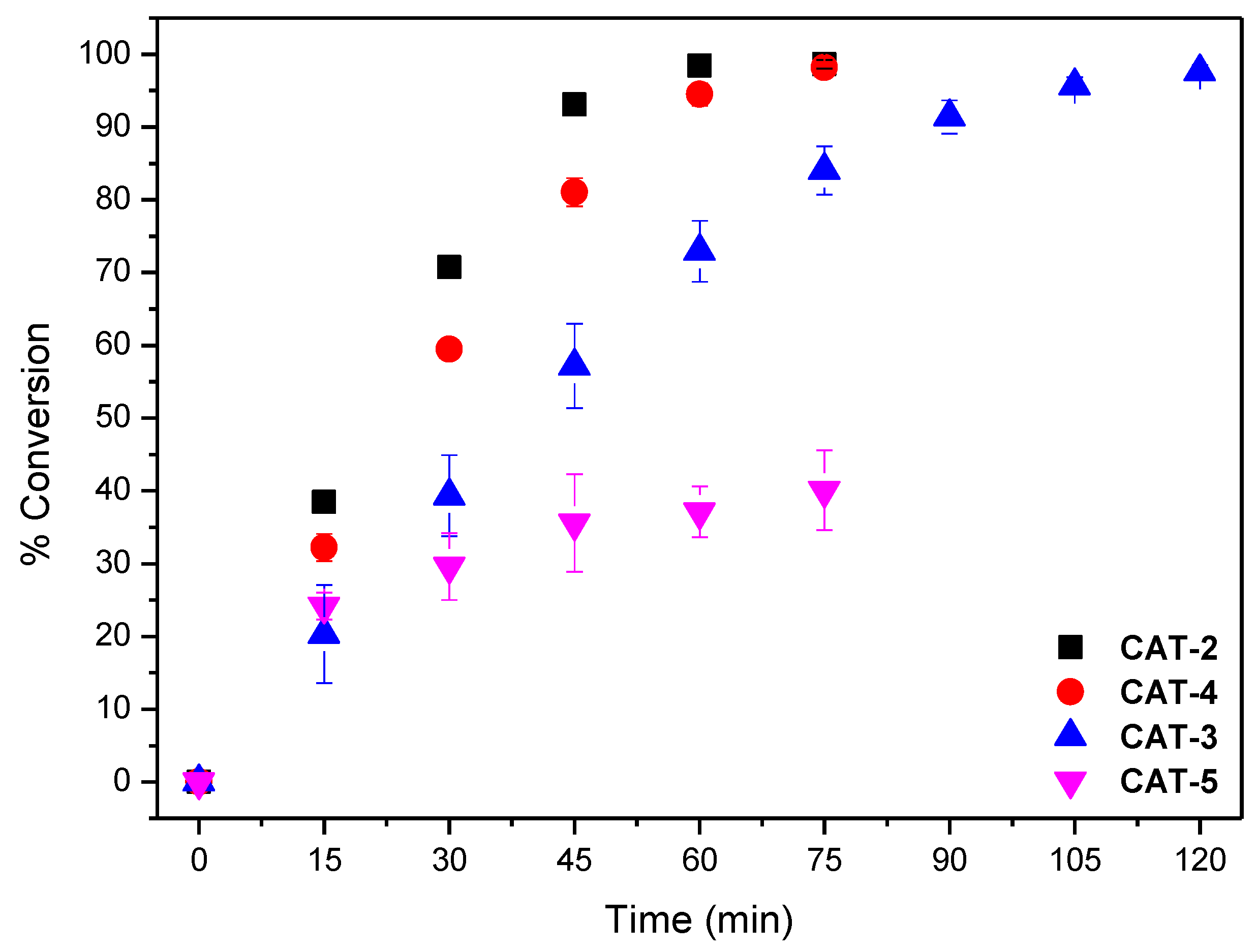
The results obtained using both S/C molar ratios of 150 and 600 are summarised in Table 2. To facilitate the discussion, the evolution of cyclooctene conversion at those S/C molar ratios during the reaction course for all the catalysts are depicted in Figure 9 and Figure 10. The assays performed show that the newly synthesized catalyst CAT-4 and the well-known and highly efficient catalyst CAT-2 exhibit similar activity, even when a S/C molar ratio of 600 is used. Moreover, CAT-4 was more efficient than its analogue CAT-5 that, despite achieving high cyclooctene conversion for the S/C molar ratio of 150 (98.8% after 90 min), when the S/C molar ratio was increased to 600 the conversion decreased to 40.1% only (Table 2).
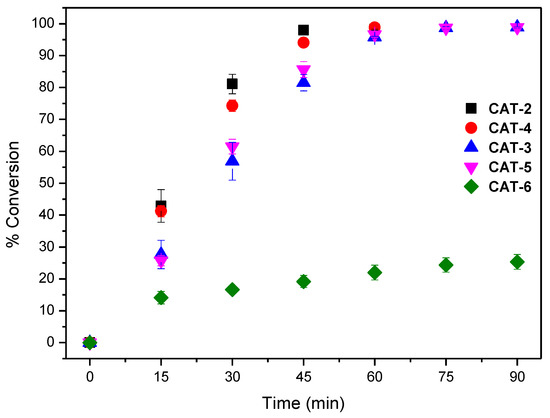
Figure 9.
Cyclooctene conversion in the oxidation reactions catalysed by different Mn(III) porphyrin catalysts vs. time for a S/C molar ratio of 150. Data correspond to mean values of at least three non-simultaneous replicates and the vertical bars correspond to the standard deviations.
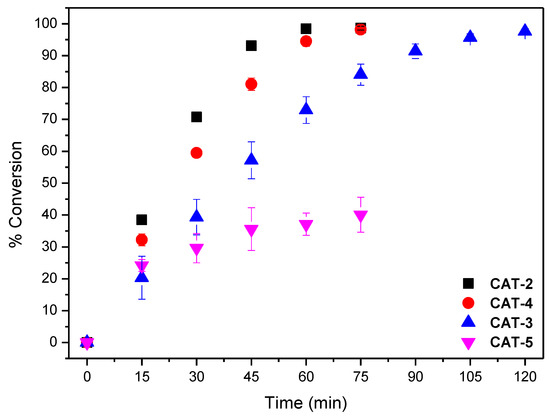
Figure 10.
Cyclooctene conversion in the oxidation reactions catalysed by different Mn(III) porphyrin catalysts vs. time for an S/C molar ratio of 600. Data correspond to the mean values of at least three non-simultaneous replicates and the vertical bars correspond to the standard deviations.
The new catalyst CAT-3 was also very efficient in the oxidation of cyclooctene, and its activity was much higher than its tetrapyridyl analogue CAT-6 that proved to be the least efficient of all, not exceeding 25.4% of conversion for a S/C molar ratio of 150 (Table 2 and Figure 9). In fact, after 30 min of reaction the UV–VIS spectrum of CAT-6 (Figure 8E) shows the absence of the Soret band of the Mn(III) species at λmax = 465 nm. Due to its low efficiency when using a S/C molar ratio of 150, CAT-6 was not tested for the S/C molar ratio of 600. A different situation was observed with the other catalysts (Figure 8A–D). After the addition of H2O2, besides the Soret band relative to the Mn(III) species, a band at λmax ≈ 425 ± 1 nm was observed. This band has been attributed to a Mn(IV)-OH species and results from the Mn(V) = O species which may be the main responsible for the oxidation process, but due to its instability is not easily detected [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57].
When an S/C molar ratio of 600 was used, the catalytic activity of CAT-3 was lower, however, a conversion of 97.6% was achieved after 120 min of reaction, its activity being higher than that achieved using CAT-5 (Figure 10 and Table 2). These results highlight the great importance of the presence of the chlorine atoms in the pyridyl substituents at the meso positions of the porphyrins on their stability and the consequent efficiency as catalysts. These atoms seem to minimize the destruction of the macrocycle core by the oxidizing radical HO resulting by the decomposition of H2O2 via a Fenton-type reaction [58,59].
2.4. Oxidation of Cyclooctene under Heterogeneous Catalysis
The good catalytic performance of CAT-4 in the oxidation of cyclooctene under homogeneous conditions led us to evaluate the catalytic activity of the solid materials obtained by its immobilization on MR and on functionalized silica, CAT-4-MR and CAT-4-Si, respectively. To evaluate the catalytic activity of the new heterogeneous materials, the oxidation of cyclooctene was performed using H2O2 or tert-butyl hydroperoxide (TBHP) as oxidants, ammonium acetate as co-catalyst and acetonitrile as solvent. The results obtained are summarized in Table 3.

Table 3.
Results obtained for the oxidation of cyclooctene catalysed by CAT-4-Si, CAT-4-MR or CAT-5-MR 1.
Both catalysts revealed to be effective in the epoxidation of cyclooctene, although their efficacy was dependent on the oxidant used and on the number of cycles.
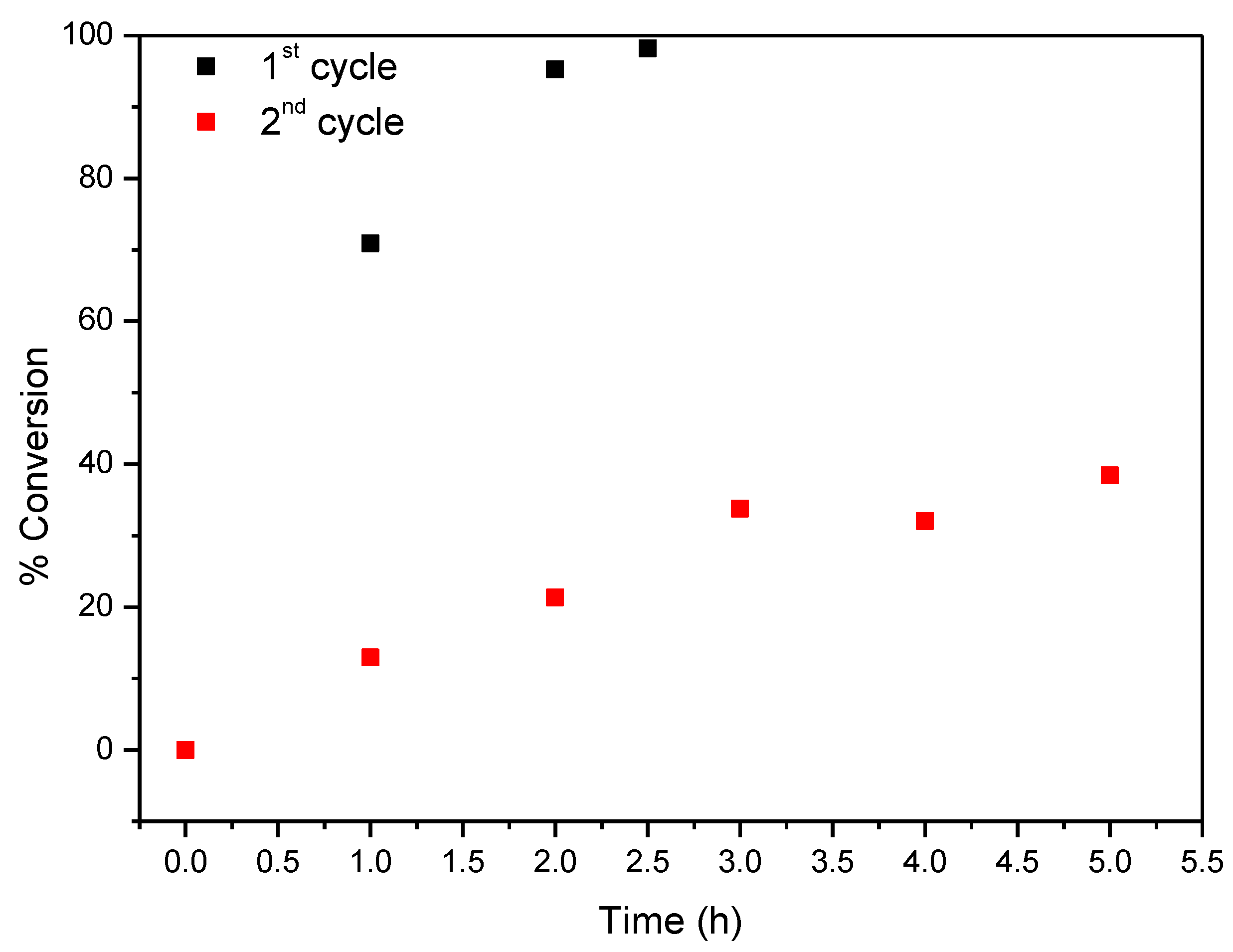
In the first cycle CAT-4-Si was highly efficient in the epoxidation of cyclooctene leading to excellent substrate conversion using both H2O2 and TBHP (Figure 11 and Figure 12, respectively). Using H2O2 as oxidant (0.5 eq. every 15 min), 98.2% of substrate conversion was obtained after only 2.5 h and using TBHP a conversion of 93.5% was achieved after 4 h. However, in the second cycle a drastic drop in substrate conversion was obtained in both cases (38.4% for H2O2 and 37.8% for TBHP).
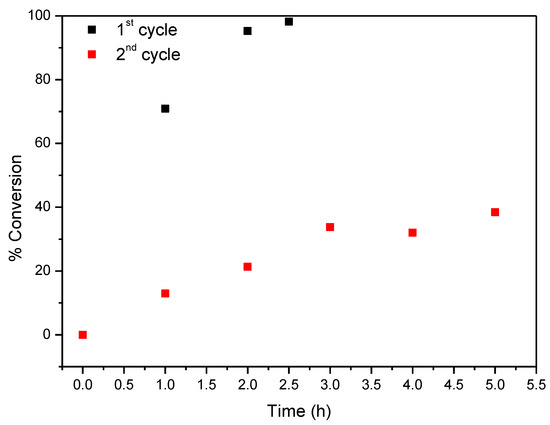
Figure 11.
Oxidation of cyclooctene using CAT-4-Si as catalyst and diluted (1:5) H2O2 as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min.
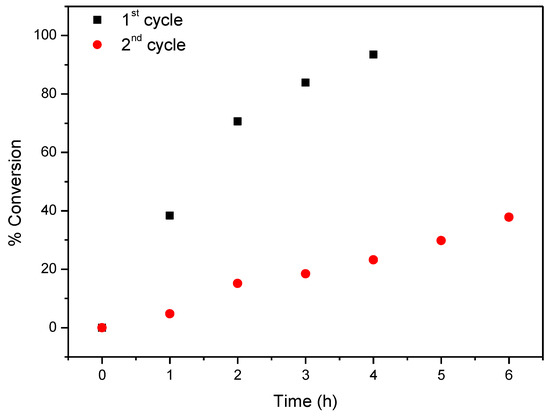
Figure 12.
Oxidation of cyclooctene using CAT-4-Si as catalyst and TBHP as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min.
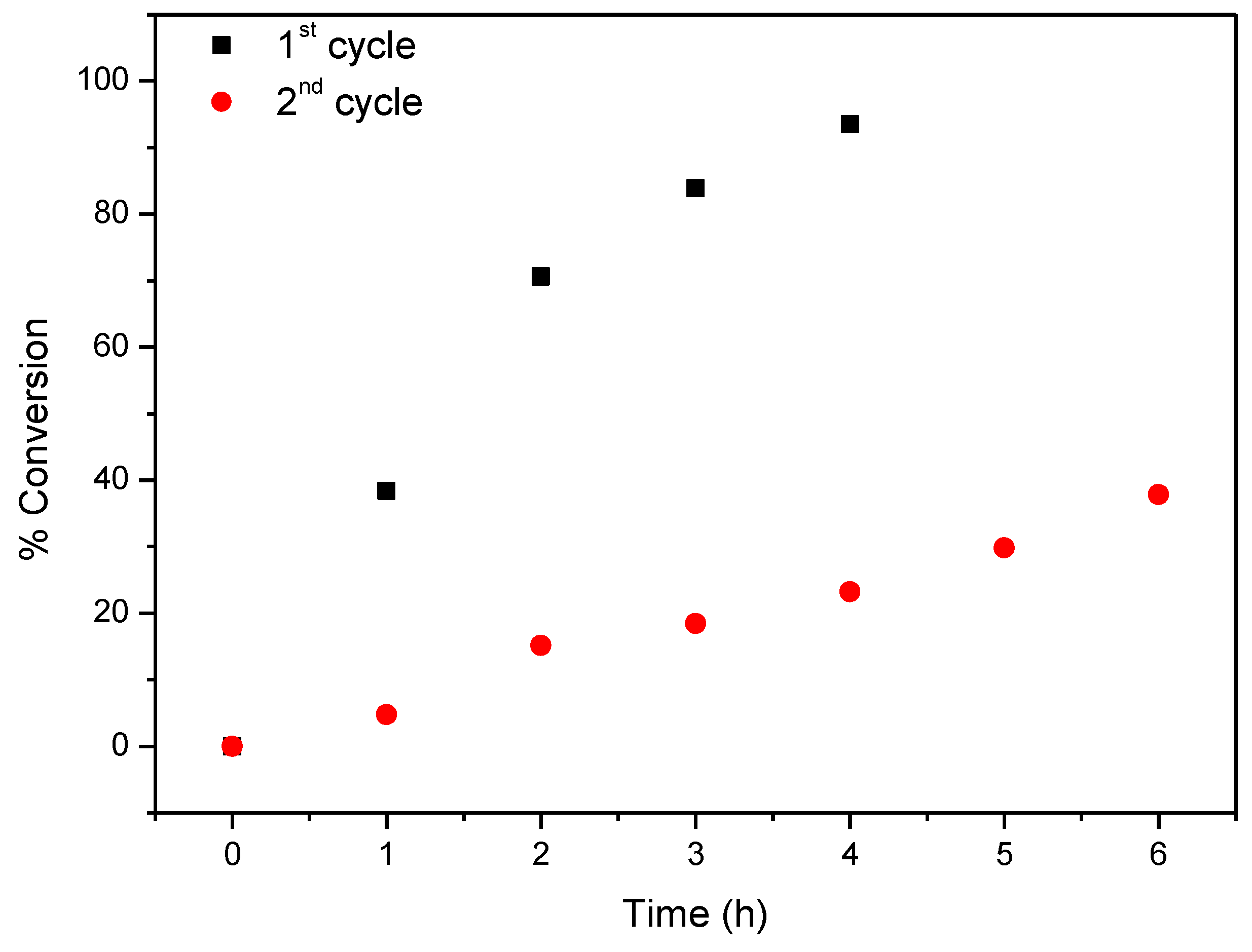
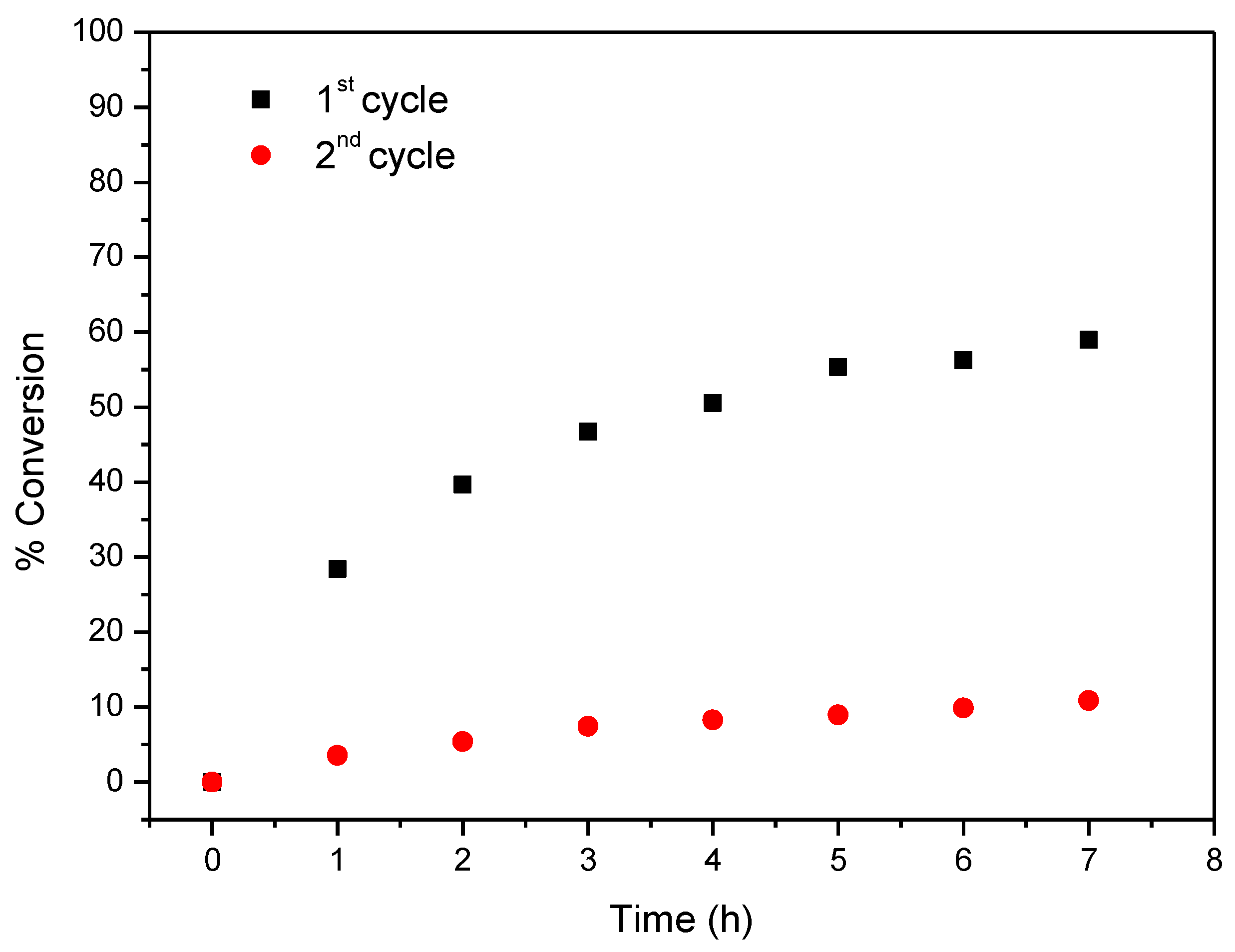
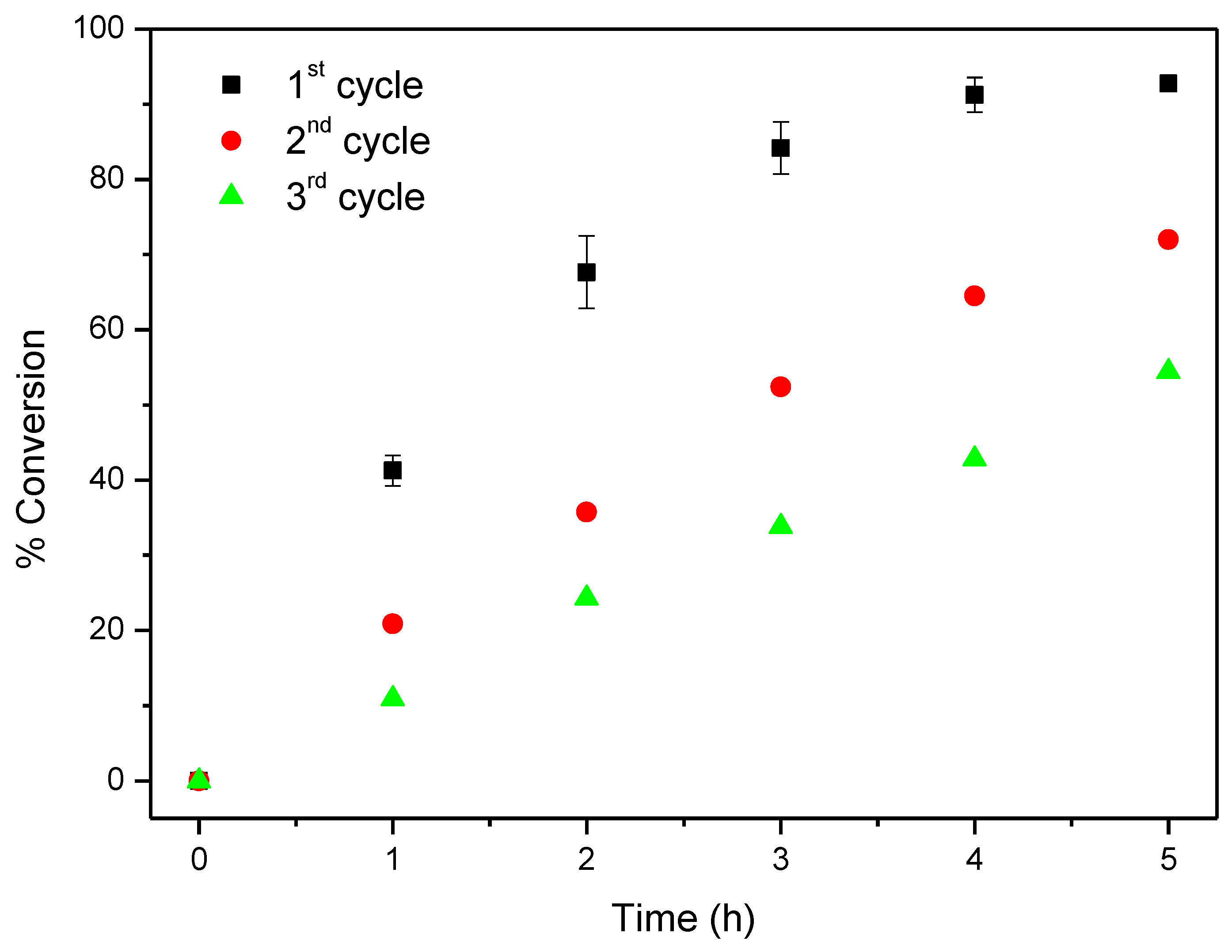
Considering now CAT-4-MR, the results show that this catalyst was less efficient when H2O2 was used as oxygen donor, notwithstanding how it was added. In the first cycle, after 24 h of reaction the conversion of cyclooctene was acceptable, being possible to reach 65.6% when the oxidant was diluted (1:5) in acetonitrile and the additions were 0.5 eq. every 15 min. On the other hand, 74.3% of conversion were registered when 30% (w/w) H2O2 was used directly with additions of 4 eq. every 2 h (Table 3). However, a drastic decrease in the conversion of cyclooctene was observed in the second cycle (Figure 13). Better results were obtained using TBHP as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min, reaching 88.6% of conversion after 6 h in the first catalytic cycle. Moreover, using this oxidant, the Merrifield-supported catalyst showed a high level of recyclability, with up to five cycles (Figure 14). In the fifth cycle, the reaction was slower, but was still possible to obtain a cyclooctene conversion of 41.5% after 6 h. The conversion of cyclooctene was negligible using CAT-4-MR without the addition of oxidant or in the presence of the starting MR using TBHP as oxidant, with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min, thus revealing that the incorporation of the metalloporphyrin on the support and the presence of TBHP are essential for the oxidation reaction to occur.
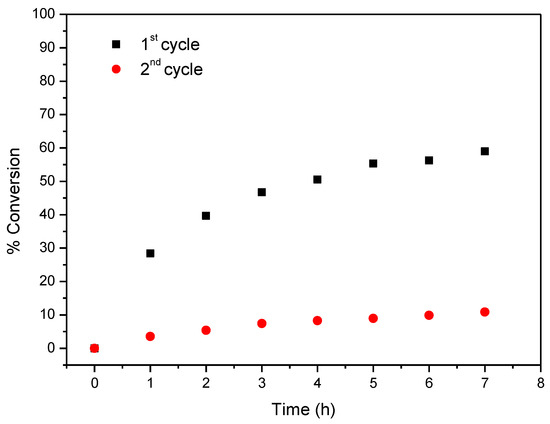
Figure 13.
Oxidation of cyclooctene using CAT-4-MR as catalyst and diluted (1:5) H2O2 as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min.
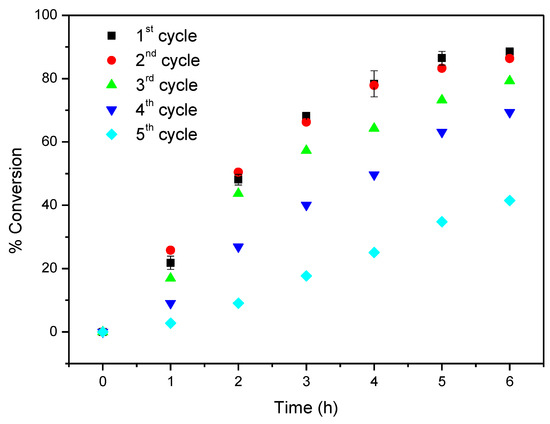
Figure 14.
Oxidation of cyclooctene using CAT-4-MR as catalyst and TBHP as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min.
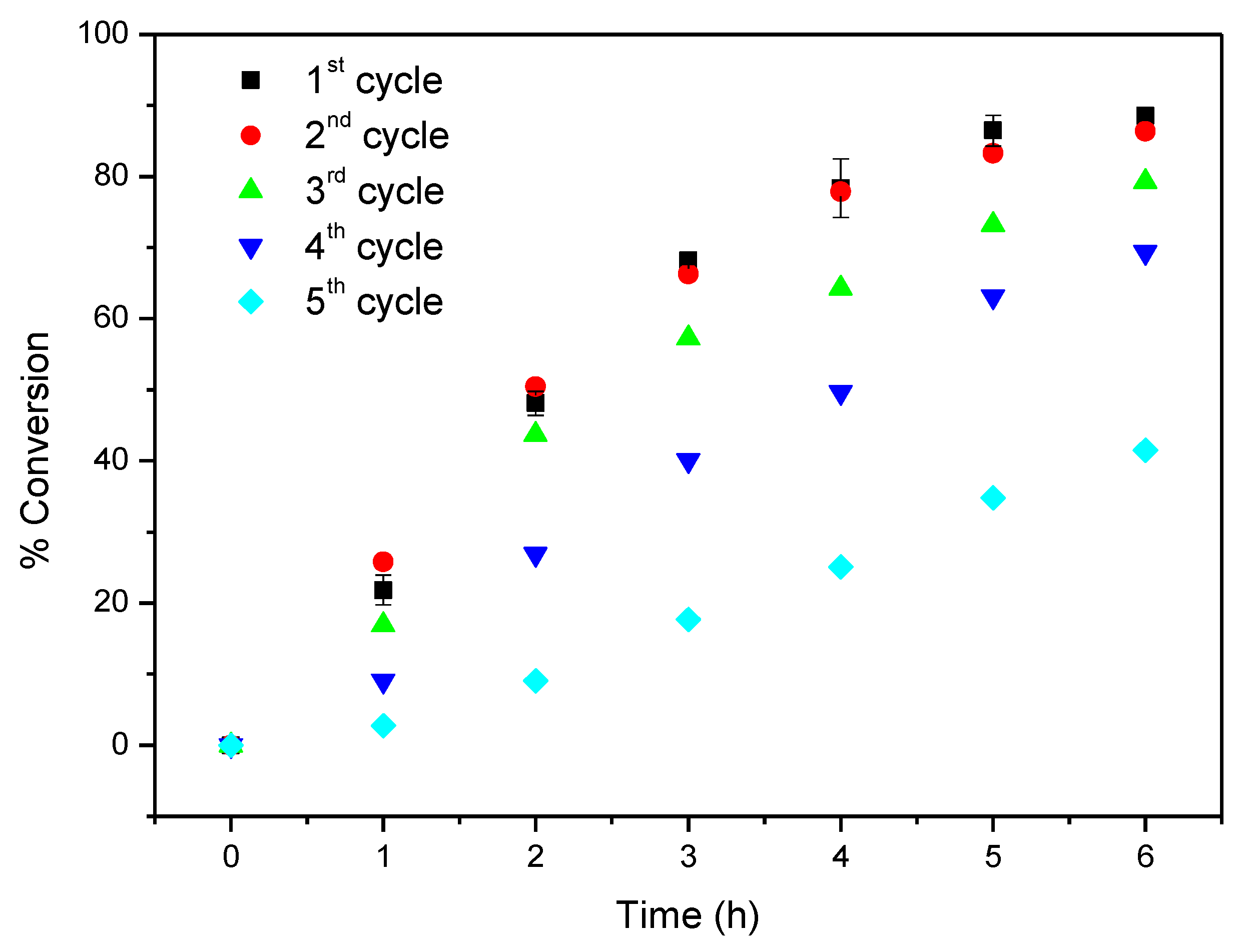
For comparative purposes CAT-5-MR was also evaluated in the oxidation of cyclooctene using TBHP as oxidant, under the same conditions previously used for CAT-4-MR (Table 3 and Figure 15). In the first cycle 92.8% of cyclooctene conversion was obtained after 5 h of reaction, with cyclooctene oxide being the only product formed. This result was surprisingly better than that obtained using CAT-4-MR as catalyst (88.6% of conversion after 6 h). However, in the second and third catalytic cycles a catalytic activity decrease was observed, with cyclooctene conversion of 72.0% and 54.4%, respectively, after 5 h of reaction (Table 3 and Figure 15). In the case of CAT-4-MR its catalytic efficiency is maintained in the second cycle and in the third and fourth cycles the conversion of cyclooctene is still higher than 60% (Table 3 and Figure 14). The absence of the chlorine atoms at the ortho positions of the pyridyl moiety in CAT-5-MR may facilitate the access of the co-catalyst, oxidant and substrate to the metal, which may justify the better result in the first catalytic cycle. On the other hand, the porphyrin nucleus is also more exposed to the oxidant, which may justify the decrease of the catalytic activity in the following catalytic cycles.
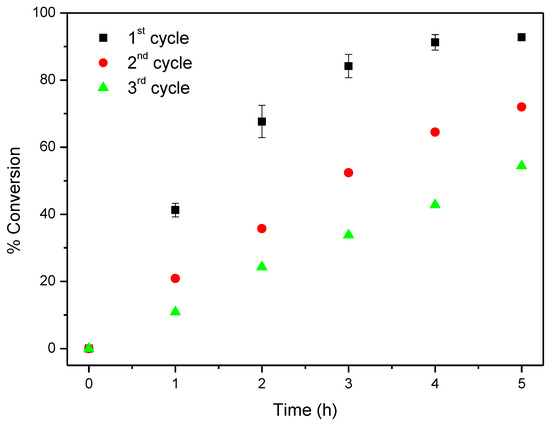
Figure 15.
Oxidation of cyclooctene using CAT-5-MR as catalyst and TBHP as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min.
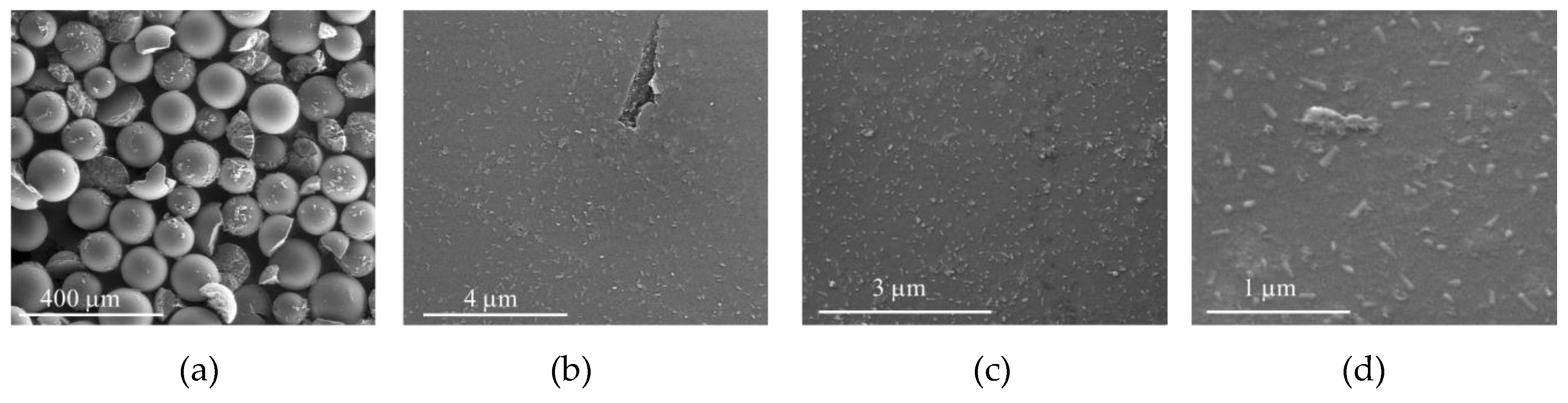
The morphology of the solid materials after oxidation reactions were examined by SEM (Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19) and the elemental composition of the solids was determined by XPS and is summarized in Table 4. In the case of CAT-4-MR, after oxidation using both H2O2 (CAT-4-MR-H2O2) and THBP (CAT-4-MR-TBHP), the SEM images reveal a greater fragmentation in relation to the CAT-4-MR material before oxidation and the formation of deposits in the surface of the material (Figure 3d, Figure 16a and Figure 17a). In the case of CAT-4-Si, after oxidation (CAT-4-Si-H2O2 and CAT-4-Si-TBHP) the fragmentation is less evident when compared to the material before oxidation (Figure 4c, Figure 18a and Figure 19a).
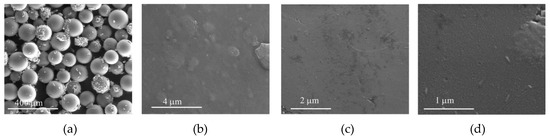
Figure 16.
SEM micrographs of CAT-4-MR-H2O2 after two cycles in oxidation reactions using H2O2 as the oxidant. (a) 250×, (b) 25,000×, (c) 40,000×, (d) 100,000×.
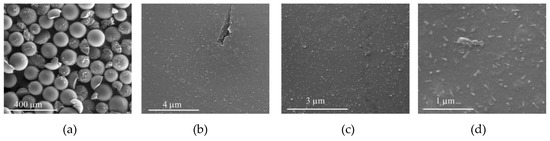
Figure 17.
SEM micrographs of CAT-4-MR-TBHP after five cycles in oxidation reactions using TBHP as the oxidant. (a) 250×, (b) 25,000×, (c) 40,000×, (d) 100,000×.
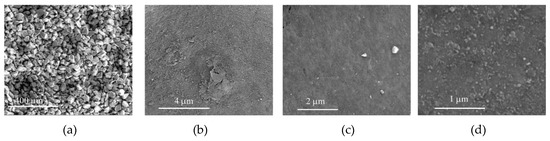
Figure 18.
SEM micrographs of CAT-4-Si-H2O2 after 2 cycles in oxidation reactions using H2O2 as the oxidant. (a) 250×, (b) 25,000×, (c) 40,000×, (d) 100,000×.
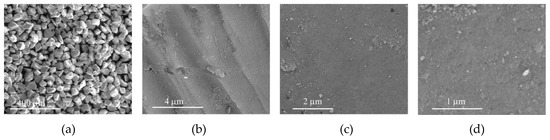
Figure 19.
SEM micrographs of CAT-4-Si-TBHP after 2 cycles in oxidation reactions using TBHP as the oxidant. (a) 250×, (b) 25,000×, (c) 40,000×, (d) 100,000×.

Table 4.
Comparison of the surface atomic percentages obtained by XPS for CAT-4-MR and CAT-4-Si with the obtained materials after catalysis: CAT-4-MR-H2O2, CAT-4-MR-TBHP, CAT-4-Si-H2O2 and CAT-4-Si-TBHP (a).
The higher magnification images reveal that the CAT-4-MR surface is more polished after oxidation (Figure 16b–d and Figure 17b–d) which may be due to a possible oxidation of surface structures. This surface change is much more evident in CAT-4-MR-H2O2; however, the detection of manganese and chlorine by XPS in CAT-4-MR-H2O2 in the same amount as in CAT-4-MR before oxidation reactions indicates that the elements arising from the metalloporphyrin are still present in the sample. Therefore, the inefficiency of CAT-4-MR in the second catalytic cycle may also be due to metalloporphyrin bleaching. In the case of CAT-4-MR-TBHP, it was not possible to detect manganese and there is a decrease in the atomic percentage of Cl 2p and C 1s. In contrast, in this sample a considerable increase of the N 1s is observed. This result is probably due to a deposition of ammonium acetate that is used as a co-catalyst in the oxidation reactions and may have not been efficiently removed. In fact, in the fifth catalytic cycle using TBHP as an oxidant, CAT-4-MR has a lower efficiency, probably as a result of the leaching of the catalyst from the support.
In the higher magnification SEM images of CAT-4-Si-H2O2 and CAT-4-Si-TBHP the changes in the surface of the solid materials are less pronounced (Figure 18b–d and Figure 19b–d). On the other hand, the XPS analysis of CAT-4-Si-H2O2 (Table 4) shows the presence of manganese and a decrease in the atomic percentage of C 1s, N 1s and Cl 2p, which indicates that the manganese porphyrin may be present in the support but in a catalytically inactive form due to bleaching. In the case of CAT-4-Si-TBHP the absence of manganese and the decrease in the atomic percentage of C 1s and Cl 2p suggest leaching of the catalyst, which justifies the loss of efficiency in the second catalytic cycle. In this case N 1s is also increased, possibly due to deposition of ammonium acetate.
2.5. Oxidation of Styrene under Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Conditions
Styrene is also a substrate commonly used to test the catalytic activity of metalloporphyrins in oxidation reactions [18,60,61,62]. Because styrene is a terminal olefin, different products can be found, depending on the reaction conditions and the catalyst used (Scheme 3).
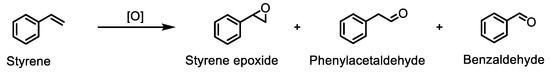
Scheme 3.
Styrene oxidation reaction in the presence of the synthesised Mn(III) porphyrins.
The mechanism of formation of phenylacetaldehyde and benzaldehyde is a subject of great discussion and is well documented in [18,48,52,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74].
2.5.1. Homogeneous Oxidation Using CAT-3 or CAT-4 Catalysts
In the assays under homogeneous conditions, the oxidation of styrene in the presence of CAT-3 and CAT-4 was carried out using a S/C molar ratio of 600, acetonitrile as solvent, ammonium acetate as co-catalyst and H2O2 as oxidant. For comparative purposes, the reactions were also carried out in the presence of the highly efficient second-generation catalyst CAT-2, using similar conditions. The results summarized in Table 5 confirm the high efficiency of the newly prepared catalysts in terms of conversion and selectivity for the epoxide.

Table 5.
Results obtained for the oxidation of styrene with H2O2 using CH3CN as the solvent and ammonium acetate as the co-catalyst (a).
In the presence of CAT-4 an excellent conversion of 99.0% after 105 min of reaction was obtained with 65.6% selectivity for the epoxide. With CAT-3 the high selectivity for epoxide was maintained (67.6%), accompanied by excellent styrene conversion (97.6%) after 150 min of reaction. In the presence of CAT-2 the total conversion of styrene after 75 min of reaction gave rise to a slight lower selectivity for the epoxide (62.7%). In all these reactions the formation of styrene epoxide was accompanied by a significant amount of phenylacetaldehyde (30.3%–36.7%) and traces of benzaldehyde (0.6%–2.1%) (Table 5).
2.5.2. Oxidation of Styrene Catalysed by CAT-4-MR Using TBHP as the Oxidant
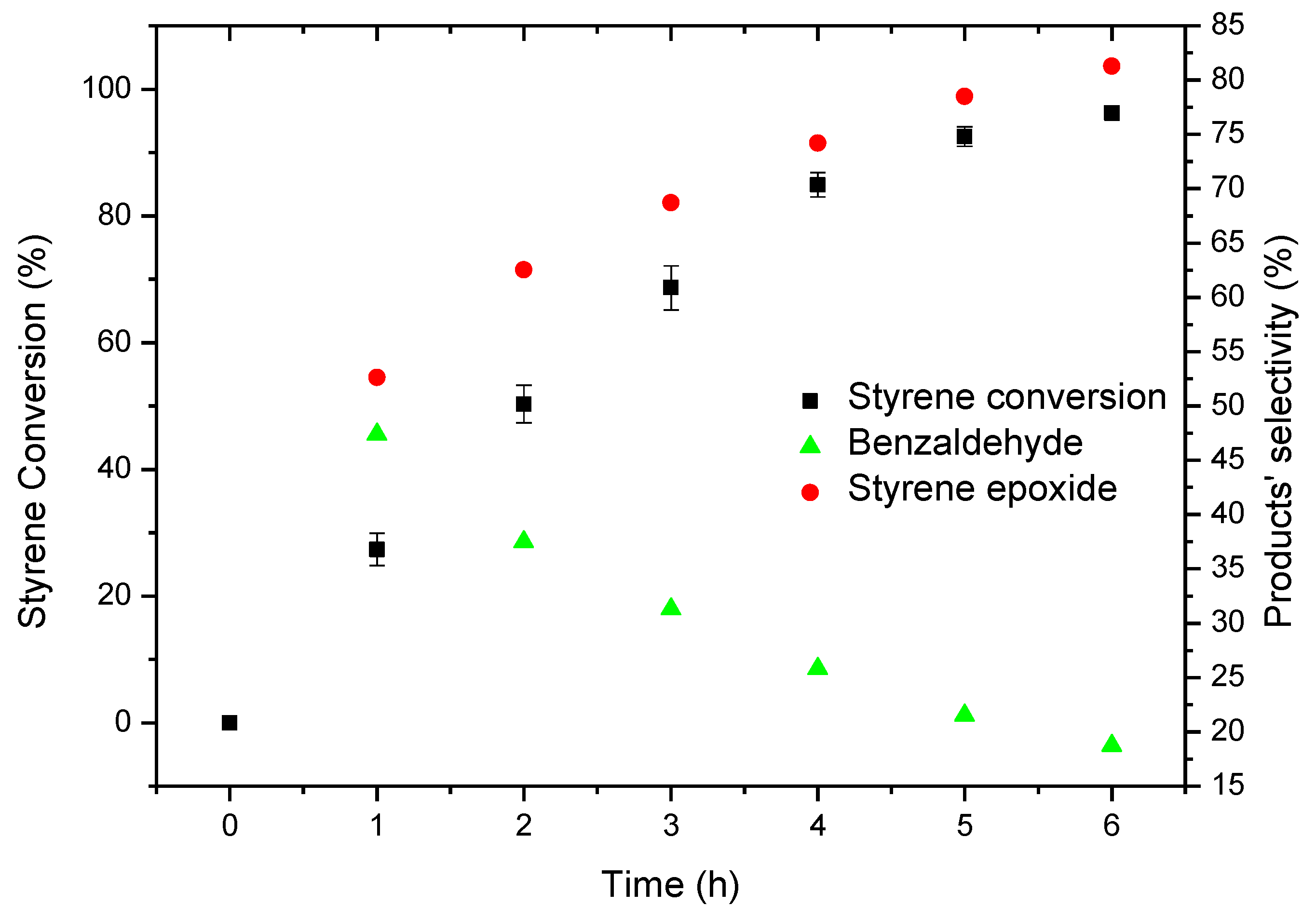
Since CAT-4 showed to be efficient in the oxidation of styrene in the presence of H2O2 under homogeneous conditions and given the good oxidation results for cyclooctene in the presence of CAT-4-MR as catalyst and TBHP as oxidant, this catalytic system was used in the oxidation of styrene. Therefore, the reactions were carried out using 5 × 10−7 mol of CAT-4-MR (S/C molar ratio of 150) with additions of 0.5 eq. of TBHP at regular intervals of 15 min, ammonium acetate as co-catalyst and acetonitrile as solvent. After 6 h of reaction, 96.2% of conversion was observed, styrene epoxide being the main product (81.3%) along with benzaldehyde formation (18.7%), whereas no phenylacetaldehyde was detected (Figure 20). The absence of phenylacetaldehyde may be related with the steric hindrance provided by the support, which disfavours the formation of the intermediate that leads to phenylacetaldehyde. There is also a considerable increase of benzaldehyde (18.7%) relatively to that observed using the homogeneous catalyst (CAT-4) and H2O2 (1.7% of benzaldehyde for 99% of conversion, after 105 min; please refer to Table 5). It should be noted that this product may be formed via radical mechanism and therefore a greater amount of benzaldehyde will be obtained for longer reaction times.
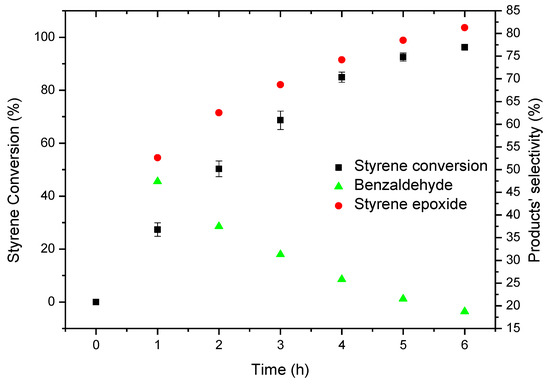
Figure 20.
Oxidation of styrene catalysed by CAT-4-MR using TBHP as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
Porph-2, Porph-5 and Porph-6 and their corresponding manganese(III) complexes were prepared in accordance with well-known procedures [31,32]. The free-base porphyrins and the manganese(III) complexes were synthesized using reagents and solvents of high purity. Pyrrole used in the synthesis of the free-base porphyrins was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and was previously distilled. Ammonium acetate, 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde, 3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinecarbo-xaldehyde, and 4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde were also acquired from Sigma-Aldrich. Manganese(II) chloride (MnCl2·4H2O) was purchased from Merck (Darmstadt, Germany) and nitrobenzene from Acros (Queluz, Portugal). Cyclooctene and styrene were obtained from Aldrich. Aqueous hydrogen peroxide (30% w/w) was purchased from Riedel-de-Haën (Seelze, Germany). Chlorobenzene was obtained from Carlo Erba (Barcelona, Spain) and used as internal standard for the GC analyses. The Merrifield resin (MR, 100–200 mesh, 3.5–4.5 mmol Cl/g, 1% cross-linked) and the 3-bromopropylsilica (200–400 mesh, extent of labelling: 1.5 mmol/g loading) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
3.2. Equipments
The 1H NMR spectrum of Porph-3 was obtained in a Bruker Avance 300 spectrometer (Wissembourg, France) operating at 300.13 MHz. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of Porph-4 were obtained on an Avance III HD 500 spectrometer (Wissembourg, France) at 500.13 and 125.76 MHz using CDCl3 as solvent and tetramethylsilane (TMS) as internal reference. The chemical shifts are reported in δ (ppm) and the coupling constants (J) in hertz (Hz). The mass spectra of Porph-3 and CAT-3 were obtained on a 4800 mass spectrometer (Foster City, California, EUA) MALDI TOF/TOF, Applied Biosystems 4700 Proteomics Analyser 66, without matrix. The mass spectra of Porph-4 and CAT-4 were obtained by electrospray mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) in positive ion mode and were acquired on a Q-TOF 2 instrument (Micromass, Manchester, UK). For the acquisition of the mass spectra the needle voltage was set at 3000 V with the ion source at 80 °C and cone voltage at 30 V. High-mass-resolving ESI-MS were conducted on a Q-Exactive® hybrid quadrupole Orbitrap® mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). The instrument was operated in positive mode, with a spray voltage at 3000 V and interfaced with a HESI II ion source. The analyses were performed through direct infusion of the prepared solutions at a flow rate of 10 μL/min into the ESI source, and the operating conditions were as follows: sheath gas (nitrogen) flow rate 5 (arbitrary units); auxiliary gas (nitrogen) 1 (arbitrary units); capillary temperature 320 °C, and S-lens RF level 50. Spectra were analysed using the acquisition software Xcalibur ver. 4.0 (Thermo Scientific, San Jose, CA, USA). The UV–VIS spectra were acquired on a dual beam spectrophotometer Shimadzu UV-2501-PC, in 1 × 1 cm glass cells. The GC–FID analyses were carried out on a Varian 3900 chromatograph using helium as the carrier gas (30 cm/s) equipped with a fused silica capillary DB-5 type column (30 m, 0.25 mm i.d., 0.25 µm film thickness).
The immobilizations using MW heating were carried out in a Milestone MW device, which operates at fixed frequency (2450 MHz) in multimode (run up to 12 flasks simultaneously).
Diffuse reflectance spectra were registered on a Jasco V-560 spectrophotometer (Tokyo, Japan), using MgO as reference. Attenuated total reflectance (ATR) FT–IR spectra were measured on a Bruker optics Tensor 27 (Easton, MD, EUA) equipped with a Specac Golden Gate Mk II ATR accessory having a diamond top plate and KRS-5 focusing lenses (resolution 4 cm−1, 256 scans). Routine powder X-ray diffraction (PXRD) data for all the prepared materials were collected at ambient temperature on a Empyrean PANalytical diffractometer (Cu Kα1,2 X-radiation, λ1 = 1.540598 Å; λ2 = 1.544426 Å, (Malvern, United Kingdom), equipped with an PIXcel 1D detector and a flat-plate sample holder in a Bragg-Brentano para-focusing optics configuration (45 kV, 40 mA). Intensity data were collected by the step-counting method (step 0.03°), in continuous mode, in the ca. 5° ≤ 2θ ≥ 60° range.
The SEM/EDS analyses were performed using a high-resolution (Schottky) environmental scanning electron microscope with X-ray microanalysis and electron backscattered diffraction analysis: Quanta 400 FEG ESEM/EDAX Genesis X4M (Thermo Scientific, Walthan, Massachusetts, USA) available at CEMUP (Centro de Materiais da Universidade do Porto, Portugal). Samples were coated with an Au/Pd thin film, by sputtering, using SPI Module Sputter Coater equipment.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed at CEMUP in a Kratos Axis Ultra - HSA spectrometer (Kratos Analytical, Manchester, UK) using non-monochromatised Al Kα radiation (1486.6 eV). The powdered samples were pressed into pellets prior to the XPS studies. Binding energies were calibrated relative to the base C 1s peak at 285.0 eV. The raw XPS spectra were deconvoluted by curve fitting peak components using the software CASAXPS (version 2.3.12, Casa Software Ltd, Teignmouth, UK) with no preliminary smoothing. Symmetric Gaussian–Lorentzian product functions were used to approximate the line shapes of the fitting components after a Shirley-type background subtraction. Atomic ratios were calculated from experimental intensity ratios and normalized by atomic sensitivity factors.
3.3. Synthesis of the Free-Base Porphyrins and Their Manganese(III) Complexes
3.3.1. Porph-3: 5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(3,5-Dichloropyridin-4-yl)Porphyrin
In a two-necked round bottom flask (1 L), equipped with a reflux condenser and a dropping funnel, 105 mL of glacial acetic acid and 75 mL of nitrobenzene were mixed and heated under stirring in an oil bath at 120 °C. Then, 5.00 g (0.0284 mol) of 3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde were added and, after total dissolution, 1.97 mL (0.0284 mol) of pyrrole were slowly added through the dropping funnel. The reaction was kept under magnetic stirring at 120 °C and protected from light for 45 min. After the end of the reaction, the acetic acid and the nitrobenzene were removed by distillation under reduced pressure. The black residue obtained was subjected to purification by a silica gel column chromatography eluted first with hexane to remove traces of nitrobenzene, then with dichloromethane and, finally, with a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol (3%) to elute the fraction containing the porphyrin. This fraction was further purified by silica preparative thin layer chromatography using a mixture of dichloromethane/methanol (3%) as eluent. Afterwards, the fraction containing the porphyrin was crystallized using a mixture of dichloromethane and hexane (1:5). The crystals were filtered under vacuum, in a Hirsch funnel with a membrane filter 0.2 μm NL16 (Schleicher and Schuell), washed with hexane and dried in the oven (55 °C). All the steps were performed with as little as possible exposure to light. The porphyrin was obtained pure in 0.2% yield (40 mg).
1H NMR (300.13 MHz, CDCl3) δ/ppm: −2.66 (2H, s-broad, NH); 8.68 (8H, s, H-β pyrrolic); 9.04 (8H, s, H-3,5-dichloropyridyl rings). UV–VIS (CHCl3) λmax nm (log ε): 417 (5.34), 510 (4.29), 586 (3.81). MALDI (TOF/TOF)-MS (m/z, %): 890 (15), 891 (32), 892 (53), 893 (87), 894 (80), 895 (100), 896 (72), 897 (69), 898 (51), 899 (34), 900 (27), 901 (11), 902 (5), 903 (3) assigned as isotope [M + H]+, consistent with the expected molecular formula [C40H18Cl8N8]. HRMS (ESI) analysis presented the most abundant peak at m/z = 894.9168 Da assigned as [M + H]+, also consistent with the expected molecular formula.
3.3.2. Porph-4: 5,10,15-Tris(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-20-(3,5-Dichloropyridin-4-yl)Porphyrin
The reaction occurred as described for Porph-3, although using 160 mL of glacial acetic acid, 120 mL of nitrobenzene, 2 mL (0.02883 mol) of pyrrole and a mixture of the required aldehydes: 3.78 g (3 eq.; 0.0216 mol) of 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde and 1.52 g (1.2 eq.; 0.00864 mol) of 3,5-dichloro-4-pyridinecarboxaldehyde. The reaction was also kept at 120 °C under magnetic stirring and protected from light for 45 min. The acetic acid and the nitrobenzene were removed by distillation under reduced pressure and the obtained residue was subjected to purification by a silica gel column chromatography. The first eluent was hexane, then a mixture of dichloromethane/hexane (5:1) was used to elute the fraction containing Porph-2. Finally, dichloromethane was used to remove the Porph-4 from the column. This porphyrin was crystallized and recrystallized with dichloromethane/hexane (1:5), always protected from light. The crystals were filtered under vacuum, in a Hirsch funnel with a membrane filter 0.2 μm NL16 (Schleicher and Schuell), washed with hexane and dried in the oven (55 °C) overnight. The porphyrin was obtained pure in 2.6% yield.
1H NMR (500.13 MHz, CDCl3) δ/ppm: −2.57 (2H, s-broad, NH); 7.69-7.73 (3H, m, H-para-2,6-dichlorophenyl rings); 7.79–7.81 (6H, m, H-meta-2,6-dichlorophenyl rings); 8.61 (2H, d, J = 4.4 Hz, H-β pyrrolic); 8.68 (4H, s, H-β pyrrolic); 8.70 (2H, d, J = 4.4 Hz, H-β pyrrolic); 9.00 (2H, s, H-3,5-dichloropyridyl ring). 13C NMR (125.76 MHz, CDCl3) δ/ppm: 110.6, 114.7, 114.9, 127.89 (C-meta-2,6-dichlorophenyl), 127.90 (C-meta-2,6-dichlorophenyl), 130.71 (C-para-2,6-dichlorophenyl), 130.73 (C-para-2,6-dichlorophenyl), 135.8 (C-3 and C-5 of 3,5-dichloropyridyl ring), 138.7, 139.21, 139.25, 147.45 (C-2 and C-6 of 3,5-dichloropyridyl ring). UV–VIS (CHCl3) λmax nm (log ε): 417 (5.33), 511 (4.24), 587 (3.88). ESI-MS (m/z, %): 888 (31), 889 (21), 890 (87), 891 (45), 892 (100), 893 (44), 894 (65), 895 (29), 896 (27), 897 (13), 898 (9), 899 (4) assigned as isotope [M + H]+, consistent with the expected molecular formula [C43H21Cl8N5]. HRMS (ESI) analysis provided the most abundant peak at m/z = 891.9311 Da assigned as [M + H]+, also consistent with the expected molecular formula.
3.3.3. Manganese(III) Porphyrins
In a 25 mL round bottom flask equipped with a reflux condenser and a magnetic bar, 50 mg of the free-base porphyrin were dissolved in 5.0 mL of DMF. The solution was refluxed in the dark, under a nitrogen atmosphere and then 0.5 mL of pyridine and 10 eq. of manganese(II) chloride (MnCl2·4H2O) were added. The progress of the reaction was monitored by UV–VIS (an aliquot of the reaction mixture was diluted in acetonitrile) and by TLC (using CH2Cl2 as eluent). The UV–VIS spectrum shows a Soret band shift to a higher wavelength thereby confirming the presence of the complex. The transition bands of manganese at λmax = 320–400 nm can also be observed. The reaction normally takes 2 h to be complete. The heating was switched off and the reaction mixture was kept under stirring overnight, in open air and protected from light. The solvent was removed by distillation in the rotary evaporator and the obtained residue was dissolved in dichloromethane and washed 2–3 times with water in a separating funnel, and finally with a saturated sodium chloride solution. The organic phase was passed through a glass funnel with cotton wool and anhydrous sodium sulphate to remove traces of water. The manganese complexes were crystallized in hexane, after dissolution in a minimal amount of dichloromethane. The crystals were filtered under vacuum, using a Hirsch funnel with a membrane filter 0.2 μm NL16 (Schleicher and Schuell), washed several times with hexane and placed in the oven (55 °C). The yield, based on the porphyrin, was higher than 90%.
CAT-3: Chloro[5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(3,5-Dichloropyridin-4-yl)Porphyrinate]Manganese(III)
UV–VIS (CH3OH) λmax nm (log ε): 326 (4.27), 368 (4.51), 390 (4.42), 459 (5.00), 504 (3.61), 555 (3.96). MALDI (TOF/TOF)-MS (m/z, %): 943 (29), 944 (19), 945 (90), 946 (43), 947 (100), 948 (54), 949 (72), 950 (34), 951 (32), 952 (14), 953 (9), 954 (6) assigned as isotope [M]+•, consistent with the expected molecular formula [C40H16Cl8MnN8]. HRMS (ESI) analysis provided the most abundant peak at m/z = 946.8317 Da assigned as [M]+•, also consistent with the expected molecular formula.
CAT-4: Chloro[5,10,15-Tris(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-20-(3,5-Dichloropyridin-4-yl)Porphyrinate]Manganese(III)
UV–VIS (CH3OH) λmax nm (log ε): 323 (4.40), 371 (4.61), 393 (4.58), 462 (5.04), 501 (3.83), 558 (4.07). ESI-MS (m/z, %): 940 (28), 941 (13), 942 (88), 943 (32), 944 (100), 945 (33), 946 (58), 947 (18), 948 (19), 949 (7), 950 (5), 951 (2) assigned as isotope [M]+•, consistent with the expected molecular formula [C43H19Cl8MnN5]. HRMS (ESI) analysis provided the most abundant peak at m/z = 943.8459 Da assigned as [M]+•, also consistent with the expected molecular formula.
3.4. Immobilization of CAT-4
3.4.1. Classic Heating
In a Schlenk flask 5 mg of CAT-4 were dissolved in 4 mL of 1,2-dichlorobenzene and, after total dissolution, 250 mg of MR or 3-bromopropylsilica were added. Using a sand bath and a magnetic stirrer, the mixture was stirred at 190 °C, being kept under nitrogen atmosphere and protect from light for 96 h.
3.4.2. Microwave Heating
In a MW reactor 5 mg of CAT-4 or CAT-5 were dissolved in 4 mL of 1,2-dichlorobenzene and, after total dissolution, 250 mg of MR were added. The reactions were carried out under magnetic stirring for 30 min at 800 W, without temperature control, but with the maximum temperature value set at 250 °C.
In both approaches, and after cooling, the material was filtered under vacuum, using a Hirsch funnel with a membrane filter 0.2 μm NL16 (Schleicher and Schuell), washed several times with 1,2-dichlorobenzene, CH3CN and dichloromethane (previously passed through an aluminum oxide column) and dried overnight in the oven (55 °C). The loading of immobilized catalyst was determined by elemental analysis based on the nitrogen amount present in the sample.
3.5. Oxidation Reactions
3.5.1. Homogeneous Catalysis
In a glass reactor with a stopper, the catalyst (variable amount according to the S/C molar ratio used: 5 × 10−7 mol in the case of the S/C molar ratio of 150 and 1.25 × 10−7 mol in the case of the S/C molar ratio of 600), acetonitrile (up to a reaction mixture volume of 2 mL), the substrate (7.5 × 10−5 mol), the internal standard (7.5 × 10−5 mol of chlorobenzene), and the co-catalyst (0.2 mmol; 15 mg of ammonium acetate) were added in this order. In the case of CAT-2, CAT-4 and CAT-5 a stock solution of the catalyst in acetonitrile was previously prepared and reserved in the fridge protected from light until use. Due to the low solubility of CAT-3 and CAT-6 in acetonitrile, the preparation of the stock solutions in this solvent was not possible. Therefore, in the case of these latter catalysts, it was necessary to weigh the amount required for each assay directly to the glass reactor. After addition of the co-catalyst, the solution was maintained under stirring for 3 min before the first addition of oxidant to ensure a complete solubilisation of the porphyrins.
The reaction mixtures were kept under stirring at 30 ± 1 °C and protected from light. The oxidant used was 30% (w/w) aqueous hydrogen peroxide diluted 1:5 in acetonitrile, with additions of 0.5 eq. at regular intervals of 15 min. Every 15 min, immediately before the addition of hydrogen peroxide, 10 µL of the reaction mixture were removed for analysis by GC–FID. The stability of the catalysts was checked by UV–VIS spectrophotometry.
3.5.2. Heterogeneous Catalysis
In a glass reactor with a stopper, 7.5 × 10−5 mol of substrate, the internal standard (7.5 × 10−5 mol of chlorobenzene), the catalyst (5.0 × 10−7 mol for a S/C molar ratio of 150), the co-catalyst (0.2 mmol; 15 mg of ammonium acetate) and acetonitrile were added until a reaction mixture final volume of 0.5 mL. The reaction mixtures were kept under stirring at 30 ± 1 °C and protected from light. The reactions were monitored by GC–FID. At the end of the reaction the catalyst was recovered by centrifugation and carefully washed using acetonitrile and dichloromethane (previously passed through an aluminium oxide column). The recovered catalyst was dried overnight at 55 °C to further reuse. Since some material is lost between reactions, the recovered catalyst was weighted, and the amount of substrate was recalculated after each cycle, in order to perform the reactions under identical conditions.
Leaching tests were carried out using cyclooctene as substrate and maintaining the same reaction conditions. After 1 h of reaction, the catalyst was filtered through a Hirsch funnel with a membrane filter 0.2 μm NL16 (Schleicher and Schuell). The filtrate was transferred to a glass reactor, protected from light, and left under stirring for further 5 h at 30 ± 1 °C, with additions of 0.5 eq. of TBHP every 15 min. The evolution of the reaction was monitored by GC–FID.
3.6. Monitoring the Oxidation Reactions
The reaction products were identified by GC–FID according to their retention times using chromatographic conditions previously established in our laboratory [71]. The GC–FID chromatographic conditions for cyclooctene oxidation monitoring were as follows: column initial temperature 80 °C for 1 min; column increasing temperature rate of 20 °C/min until 220 °C, which was maintained for 2 min; injector and detector temperatures were both set at 250 °C. The GC–FID chromatographic conditions for styrene oxidation monitoring were as follows: column initial temperature 80 °C for 2 min; column increasing temperature rate of 20 °C/min until 220 °C, which was maintained for 3 min; injector temperature was set at 250 °C and detector temperature was set at 270 °C.
Conversion (%) for each time (t) was determined by calculation of reacted substrate using the internal standard method, based on the chromatographic peak areas of substrate (Asubstrate) and of the internal standard (Achlorobenzene) for each chromatogram:
The products’ selectivity (%) was calculated as follows:
4. Conclusions
The symmetric chloro[5,10,15,20-tetrakis(3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III) (CAT-3) and the asymmetric chloro[5,10,15-tris(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-20-(3,5-dichloropyridin-4-yl)porphyrinate]manganese(III) (CAT-4) were synthesised and characterised for the first time. Both metalloporphyrins were tested as catalysts in the homogeneous oxidation of cyclooctene with aqueous hydrogen peroxide as the oxidant, using acetonitrile as the solvent and ammonium acetate as the co-catalyst. For a substrate/catalyst (S/C) molar ratio of 600, and in the presence of CAT-3, 97.6% of cyclooctene conversion was obtained after 120 min, whereas using the CAT-4 98.2% of conversion was attained after 75 min. The catalytic activity of CAT-4 is very similar to that obtained with the well-known second-generation catalyst CAT-2. On the other hand, CAT-4 showed to be more efficient than its analogue CAT-5. CAT-3 and CAT-4 also exhibited high stability. The presence of electron-withdrawing chlorine atoms in the substituents at the meso positions of the metalloporphyrins are responsible for preventing the macrocycle oxidation, thus resulting in higher catalyst stability.
CAT-4-Si and CAT-4-MR showed to be efficient catalysts in the epoxidation of cyclooctene. The best results were obtained with the Merrifield-supported catalyst, CAT-4-MR, using TBHP as oxidant with additions of 0.5 eq. every 15 min, allowing up to five catalytic cycles. CAT-4-Si exhibited high catalytic activity using both H2O2 and TBHP as oxidant in the first catalytic cycle, however in the second cycle its activity strongly decreased. The SEM and XPS analysis of the solid materials after oxidation show leaching and bleaching of the manganese porphyrin, which justifies the lower efficiency observed in the posterior catalytic cycles. CAT-5-MR was also highly efficient in the oxidation of cyclooctene, although presenting less robustness when compared to CAT-4-MR, allowing only three catalytic cycles. The higher recycling capacity of CAT-4-MR is probably due to the presence of the two extra chlorine atoms in the pyridyl substituent affording higher protection to the porphyrin nucleus relatively to the oxidizing reaction medium.
In the oxidation of styrene, for a S/C molar ratio of 600, high conversion was obtained using both CAT-3 (97.6% after 150 min) and CAT-4 (99.0% after 105 min) under homogeneous conditions with H2O2 as the oxidant. High selectivity to the corresponding epoxide was obtained (67.6% and 65.6%, respectively), similarly to the oxidation of styrene in the presence of CAT-2. Beyond the formation of styrene epoxide, phenylacetaldehyde (30.3%–36.7%) and traces of benzaldehyde (0.6%–2.1%) were also obtained. A different situation was observed using the solid CAT-4-MR as catalyst and TBHP as oxidant, since no phenylacetaldehyde was formed, thus resulting in higher selectivity to styrene epoxide (81.3%) along with the formation of benzaldehyde (18.7%). The absence of phenylacetaldehyde may be related with difficulties in the formation of the intermediate responsible for its production due to steric hindrance caused by the solid support.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4344/9/11/967/s1, Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum of Porph-3, using CDCl3 as solvent, Figure S2: 1H NMR spectrum of Porph-4, using CDCl3 as solvent, Figure S3: Mass spectrum (HRMS-ESI) of Porph-3, Figure S4: Mass spectrum (HRMS-ESI) of Porph-4, Figure S5: Mass spectrum (HRMS-ESI) of CAT-3, Figure S6: Mass spectrum (HRMS-ESI) of CAT-4, Figure S7: Diffuse reflectance UV-Vis spectra obtained for: a) CAT-4 powder, b) CAT-5 powder, c) CAT-4-Si, d) CAT-4-MR, e) CAT-5-MR, f) MR, g) Si, Figure S8: ATR spectra of a) CAT-4, b) CAT-5, c) CAT-4-Si, d) Si, e) CAT-4-MR, f) CAT-5-MR, g) MR.
Author Contributions
Catalysts preparation, catalytic assays and draft preparation: C.M.B.N.; catalyst characterisation: C.M.B.N. and S.L.H.R.; conceptualization of the work: M.A.F.F., M.M.Q.S. and M.G.P.M.S.N.; supervision: M.M.Q.S. and M.G.P.M.S.N.; manuscript final version preparation: C.M.B.N., M.A.F.F., M.M.Q.S. and M.G.P.M.S.N.
Funding
This research was funded by National Foundation for Science and Technology/Ministério da Educação e Ciência—FCT/MEC (POPH/FSE), grant numbers FCT UID/QUI/00062/2019 and UID/QUI/50006/2019.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are due to the University of Aveiro, to FCT/MEC for the financial support to Research Units QOPNA (FCT UID/QUI/00062/2019) and REQUIMTE/LAQV (FCT UID/QUI/50006/2019), through national funds and when applicable co-financed by the FEDER, within the PT2020 Partnership Agreement and “Compete” 2020, and also to the Portuguese NMR Network. The authors are also grateful to FCT (Portugal) and POPH/FSE for the Grant to C.M.B. Neves (PD/BD/52531/2014).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
References
- Gunter, M.J.; Turner, P. Metalloporphyrins as models for the cytochromes P-450. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1991, 108, 115–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meunier, B. Metalloporphyrins as versatile catalysts for oxidation reactions and oxidative DNA cleavage. Chem. Rev. 1992, 92, 1411–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, M.J.F.; Piñeiro, M.; Dias, L.D.; Pereira, M.M. Hydrogen Peroxide and Metalloporphyrins in Oxidation Catalysis: Old Dogs with Some New Tricks. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3615–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, D. A brief history of the contribution of metalloporphyrin models to cytochrome P450 chemistry and oxidation catalysis. C. R. Chim. 2007, 10, 392–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Huang, J. Metalloporphyrin-based oxidation systems: From biomimetic reactions to application in organic synthesis. Chem. Commun. 2009, 3996–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.M.Q.; De Paula, R.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Metalloporphyrins in the biomimetic oxidative valorization of natural and other organic substrates. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2009, 13, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagaki, S.; Ferreira, G.K.B.; Ucoski, G.M.; Castro, K.A.D.D.F. Chemical Reactions Catalyzed by Metalloporphyrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks. Molecules 2013, 18, 7279–7308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, C.M.B.; Pires, S.M.G.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Mimicking P 450 processes and the use of metalloporphyrins. Pure Appl. Chem. 2013, 85, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barona-Castaño, J.C.; Carmona-Vargas, C.C.; Brocksom, T.J.; De Oliveira, K.T. Porphyrins as Catalysts in Scalable Organic Reactions. Molecules 2016, 21, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, P.; Neves, C.M.B.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.D.G.P.M.S.; Cocco, G.; Sanjust, E. Immobilized lignin peroxidase-like metalloporphyrins as reusable catalysts in oxidative bleaching of industrial dyes. Molecules 2016, 21, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.M.Q.; Pires, S.M.G.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Oxidative Transformations of Organic Compounds Mediated by Metalloporphyrins as Catalysts. In Handbook of Porphyrin Science: With Applications to Chemistry, Physics, Materials Science, Engineering, Biology and Medicine; Kadish, K.M., Smith, K.M., Guilard, R., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2016; pp. 197–306. [Google Scholar]
- Groves, J.T.; Nemo, T.E.; Myers, R.S. Hydroxylation and Epoxidation Catalyzed by Iron-Porphine Complexes. Oxygen Transfer from lodosylbenzene. J. Am. Soc. 1979, 101, 1032–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traylor, P.S.; Dolphin, D.; Traylor, T.G. Sterically protected hemins with electronegative substituents: Efficient catalysts for hydroxylation and epoxidation. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappa, M.J.; Tolman, C.A. Steric and Electronic Control. Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 4711–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoli, J.F.; Brigaud, O.; Battioni, P.; Mansuy, D. Hydroxylation of Linear Alkanes Catalysed by Iron Porphyrins: Particular Efficacy and Regioselectivity of Perhalogenated Porphyrins. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1991, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, A.M.A.R.; Pereira, M.M.; Serra, A.C.; Johnstone, R.A.W.; Nunes, M.L.P.G. 5,10,15,20-Tetrakisaryl- and 2,3,7,8,12,13,17,18-Octahalogeno-5,10,15,20-tetrakisarylporphyrins and their Metal Complexes as Catalysts in Hypochlorite Epoxidations. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1994, 2053–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, Z.; Simkhovich, L. Hydroxylation of Simple Alkanes by Iodosylbenzene is Catalyzed more Efficiently by Second than by Third Generation Iron(IIl) Porphyrins. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 8171–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, A.A.; Santos, A.C.M.A.; Assis, M.D. Some factors influencing the selectivity of styrene oxidation by active oxygen donors catalyzed by three generations of ironporphyrins. Kinet. Catal. 2006, 47, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doro, F.G.; Smith, J.R.L.; Ferreira, A.G.; Assis, M.D. Oxidation of alkanes and alkenes by iodosylbenzene and hydrogen peroxide catalysed by halogenated manganese porphyrins in homogeneous solution and covalently bound to silica. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 164, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedermann, G.R.; Halma, M.; Castro, K.A.D.F.; Benedito, F.L.; Doro, F.G.; Drechsel, S.M.; Mangrich, A.S.; das Dores Assis, M.; Nakagaki, S. Intermediate species generated from halogenated manganese porphyrins electrochemically and in homogeneous catalysis of alkane oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 308, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, S.L.H.; Gonçalves, A.R.; Pereira, M.M.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Epoxidation reactions with hydrogen peroxide activated by a novel heterogeneous metalloporphyrin catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2006, 256, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, S.M.G.; De Paula, R.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Santos, I.C.M.S.; Tomé, A.C.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. A new silica-supported manganese chlorin as a biomimetic oxidation catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2009, 11, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, R.; Santos, I.C.M.S.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. An immobilized imidazolyl manganese porphyrin for the oxidation of olefins. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 404–405, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, M.J.F.; Silva, M.; Pereira, M.M.; Burrows, H.D. Inorganic helping organic: Recent advances in catalytic heterogeneous oxidations by immobilised tetrapyrrolic macrocycles in micro and mesoporous supports. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 22774–22789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagaki, S.; Mantovani, K.M.; Machado, G.S.; Castro, K.A.D.D.F.; Wypych, F. Recent Advances in Solid Catalysts Obtained by Metalloporphyrins Immobilization on Layered Anionic Exchangers: A Short Review and Some New Catalytic Results. Molecules 2016, 21, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, C.F.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Tomé, J.P.C.; Paz, F.A.A. Porphyrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks as Heterogeneous Catalysts in Oxidation Reactions. Molecules 2016, 21, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulé, E.; de Miguel, Y.R. Supported metalloporphyrin catalysts for alkene epoxidation. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2006, 4, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thellend, A.; Battioni, P.; Mansuy, D. Ammonium acetate as a very simple and efficient cocatalyst for manganese porphyrin-catalysed oxygenation of hydrocarbons by hydrogen peroxide. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 202, 1035–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.C.M.S.; Rebelo, S.L.H.; Balula, M.S.S.; Martins, R.R.L.; Pereira, M.M.M.S.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Cavaleiro, A.M.V. Association of Keggin-type anions with cationic meso-substituted porphyrins: Synthesis, characterization and oxidative catalytic studies. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2005, 231, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, H.; Hamid, H.; Endud, S.; Hamdan, H.; Ramli, Z. Iron-porphyrin encapsulated in poly ( methacrylic acid ) and mesoporous Al-MCM-41 as catalysts in the oxidation of benzene to phenol. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 96, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, A.M.A.R.; Varejão, J.M.T.B.; Pereira, M.M. Some New Aspects Related to the Synthesis of meso-Substituted Porphyrins. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 1991, 28, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.D.; Longo, F.R.; Kampas, F.; Kim, J. On the preparation of metalloporphyrins. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1970, 32, 2443–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Nahhal, I.M.; El-Shetary, B.A.; Mustafa, A.E.-K.B.; El-Ashgar, N.M.; Livage, J.; Chehimi, M.M.; Roberts, A. Structural characterization of immobilized-polysiloxane iminobis(N-diethylenediamineacetamide) ligand system. Solid State Sci. 2003, 5, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinska, M.E.; Rebelo, S.L.H.; Freire, C. Iron ( III ) porphyrin anchored onto organosilylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes as an active catalyst for epoxidation reactions under mild conditions. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 1494–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bataineh, S.A.; Britcher, L.G.; Griesser, H.J. XPS characterization of the surface immobilization of antibacterial furanones. Surf. Sci. 2006, 600, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallee, D.K.; Brace, J.; Winograd, N. X-ray Photoelectron Spectra of N-Methyltetraphenylporphyrins: Evidence for a Correlation of Binding Energies with Metal-Nitrogen Bond Distances. Inorg. Chem. 1979, 18, 1776–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.G.; Ghosh, A.; Almlöf, J. Electronic Effects of Peripheral Substituents in Porphyrins: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy and ab Initio Self-Consistent Field Calculations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 9990–10000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goll, J.G.; Moore, K.T.; Ghosh, A.; Therien, M.J. Synthesis, Structure, Electronic Spectroscopy, Photophysics, Electrochemistry, and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy of Highly-Electron-Deficient [5,10,15,20-Tetrakis(perfluoroalkyl)porphinato]zinc(II) Complexes and Their Free Base Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 8344–8354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarno, D.M.; Jiang, B.; Grosfeld, D.; Afriyie, J.O.; Matienzo, L.J.; Jones, W.E. Self-assembled Molecular Architectures on Surfaces: New Strategies Involving Metal-Organic Copolymers. Langmuir 2000, 16, 6191–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.J.J.; van Bekkum, H. XPS of Nitrogen-Containing Functional Groups on Activated Carbon. Carbon 1995, 33, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Dai, J.; Tan, K.L. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic studies of ionic interactions between sulfonated polystyrene and poly(styrene-co-4-vinylpyridine). Polymer 1996, 37, 5305–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heide, P. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy—An Introduction to Principles and Practices; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781118062531. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xia, C.-G.; Zhang, X.-M. Preparation and catalysis of DMY and MCM-41 encapsulated cationic Mn(III)–porphyrin complex. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 185, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Korin, E.; Bettelheim, A. Structures self-assembled from anionic graphene and cationic manganese porphyrin: Characterization and application in artificial photosynthesis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2288–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gao, S.; Xiong, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Kong, Y. Coordination of manganese porphyrins on amino-functionalized MCM-41 for heterogeneous catalysis of naphthalene hydroxylation. Chin. J. Catal. 2015, 36, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonangelo, A.R.; Grazia Bezzu, C.; McKeown, N.B.; Nakagaki, S. Highly active manganese porphyrin-based microporous network polymers for selective oxidation reactions. J. Catal. 2019, 369, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, S.L.H.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Oxidation of alkylaromatics with hydrogen peroxide catalysed by manganese(III) porphyrins in the presence of ammonium acetate. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2003, 201, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, S.L.H.; Pereira, M.M.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Mechanistic studies on metalloporphyrin epoxidation reactions with hydrogen peroxide: Evidence for two active oxidative species. J. Catal. 2005, 234, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, J.T.; Kruper, W.J.; Haushalter, R.C. Hydrocarbon Oxidations with Oxometalloporphinates. Isolation and Reactions of a (Porphinato)manganese(V) Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1980, 102, 6375–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, J.T.; Stern, M.K. Olefin Epoxidation by Manganese(IV) Porphyrins: Evidence for Two Reaction Pathways. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 3812–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, J.T.; Stern, M.K. Synthesis, Characterization, and Reactivity of Oxomanganese(IV) Porphyrin Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 8628–8638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, J.T.; Lee, J.; Marla, S.S. Detection and Characterization of an Oxomanganese(V) Porphyrin Complex by Rapid-Mixing Stopped-Flow Spectrophotometry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 6269–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Groves, J.T. Unusual Kinetic Stability of a Ground-State Singlet Oxomanganese(V) Porphyrin. Evidence for a Spin State Crossing Effect. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 2923–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camenzind, M.J.; Hollander, F.J.; Hill, C.L. Syntheses, Ground Electronic State, and Crystal and Molecular Structure of the Monomeric Manganese(IV) Porphyrin Complex Dimethoxy(5,10,15,20-tetraphenylporphinato)manganese(IV). Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 4301–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Horner, J.H.; Newcomb, M. Laser flash photolysis generation and kinetic studies of porphyrin-manganese-oxo intermediates. Rate constants for oxidations effected by porphyrin-MnV-oxo species and apparent disproportionation equilibrium constants for porphyrin-MnIV-oxo species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 6573–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Paglia Fragola, V.; Lupo, F.; Pappalardo, A.; Sfrazzetto, G.T.; Toscano, R.M.; Ballistreri, F.P.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Gulino, A. A surface-confined O=MnV(salen) oxene catalyst and high turnover values in asymmetric epoxidation of unfunctionalized olefins. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20561–20565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, F.; Reinhard, F.G.C.; Xia, C.; de Visser, S.P.; Wang, Y. Can Manganese(III)-Iodosylarene Act as an Oxidant Alongside High-Valent Manganese(V)-Oxo Complexes? Chem. Sel. 2018, 3, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballistreri, F.P.; Gangemi, C.M.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Tomaselli, G.A.; Toscano, R.M.; Sfrazzetto, G.T. (Salen)Mn(III) catalyzed asymmetric epoxidation reactions by hydrogen peroxide in water: A green protocol. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuiping, B.; Wensheng, X.; Dexin, F.; Mo, X.; Dong, G.; Zhongxue, G.; Yanshui, Z. Efficient decolorization of Malachite Green in the Fenton reaction catalyzed by [Fe(III)-salen]Cl complex. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215–216, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.-Y.; Li, X.-F.; Li, Y.-Z.; Chang, W.-B.; Huang, A.-J. Oxidation of styrene by various oxidants with different kinds of metalloporphyrins. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2002, 187, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.-H.; Yang, X.-L.; Wu, C.-D. A metalloporphyrin functionalized metal–organic framework for selective oxidization of styrene. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, R.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Homogeneous olefin epoxidation catalysed by an imidazolium-based manganese porphyrin. Catal. Commun. 2008, 10, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Visser, S.P.; Kumar, D.; Shaik, S. How do aldehyde side products occur during alkene epoxidation by cytochrome P450? Theory reveals a state-specific multi-state scenario where the high-spin component leads to all side products. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; De Visser, S.P.; Shaik, S. Multistate Reactivity in Styrene Epoxidation by Compound I of Cytochrome P450: Mechanisms of Products and Side Products Formation. Chem. Eur. J. 2005, 11, 2825–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liu, X. Mild oxidation of styrene and its derivatives catalyzed by ionic manganese porphyrin embedded in a similar structured ionic liquid. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontecave, M.; Mansuy, D. Alkene Epoxidation by lodosylbenzene Catalysed by Porphyrin and Non-porphyrin Iron Complexes: The Importance of the Porphyrin Ligand in Cytochrome P-450 and Heme Model Reactions. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmartin, C.; Smith, J.R.L. Alkene Epoxidation by lodosylbenzene Catalysed. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1995, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, J.T.; Myers, R.S. Catalytic Asymmetric Epoxidations with Chiral Iron Porphyrins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 5791–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuy, D.; Leclaire, J.; Fontecave, M.; Dansette, P. Regioselectivity of olefin oxidation by iodosobenzene catalyzed by metalloporphyrins: Control by the catalyst. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 2847–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collman, J.P.; Kodadek, T.; Brauman, J.I. Oxygenation of Styrene by Cytochrome P-450 Model Systems: A Mechanistic Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1986, 108, 2588–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, R.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Neves, M.G.P.M.S.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S. Oxidation of styrene and of some derivatives with H2O2 catalyzed by novel imidazolium-containing manganese porphyrins: A mechanistic and thermodynamic interpretation. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 345, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, A.M.A.R.; Serra, A.C. Observations on the origin of phenylacetaldehyde in styrene epoxidation and the mechanism of oxidations catalysed by manganese complexes of porphyrins. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 2002, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasasingham, R.D.; He, G.-X.; Bruice, T.C. Mechanism of Manganese Porphyrin-Catalyzed Oxidation of Alkenes. Role of Manganese( IV)-Oxo Species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7985–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, A.M.A.R.; Serra, A.C. On the mechanism of carboxylic acid co-catalyst assisted metalloporphyrin oxidations. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2001, 168, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).