Correlation between Solution Treatment Temperature, MicroStructure, and Yield Strength of Forged Ti-17 Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure
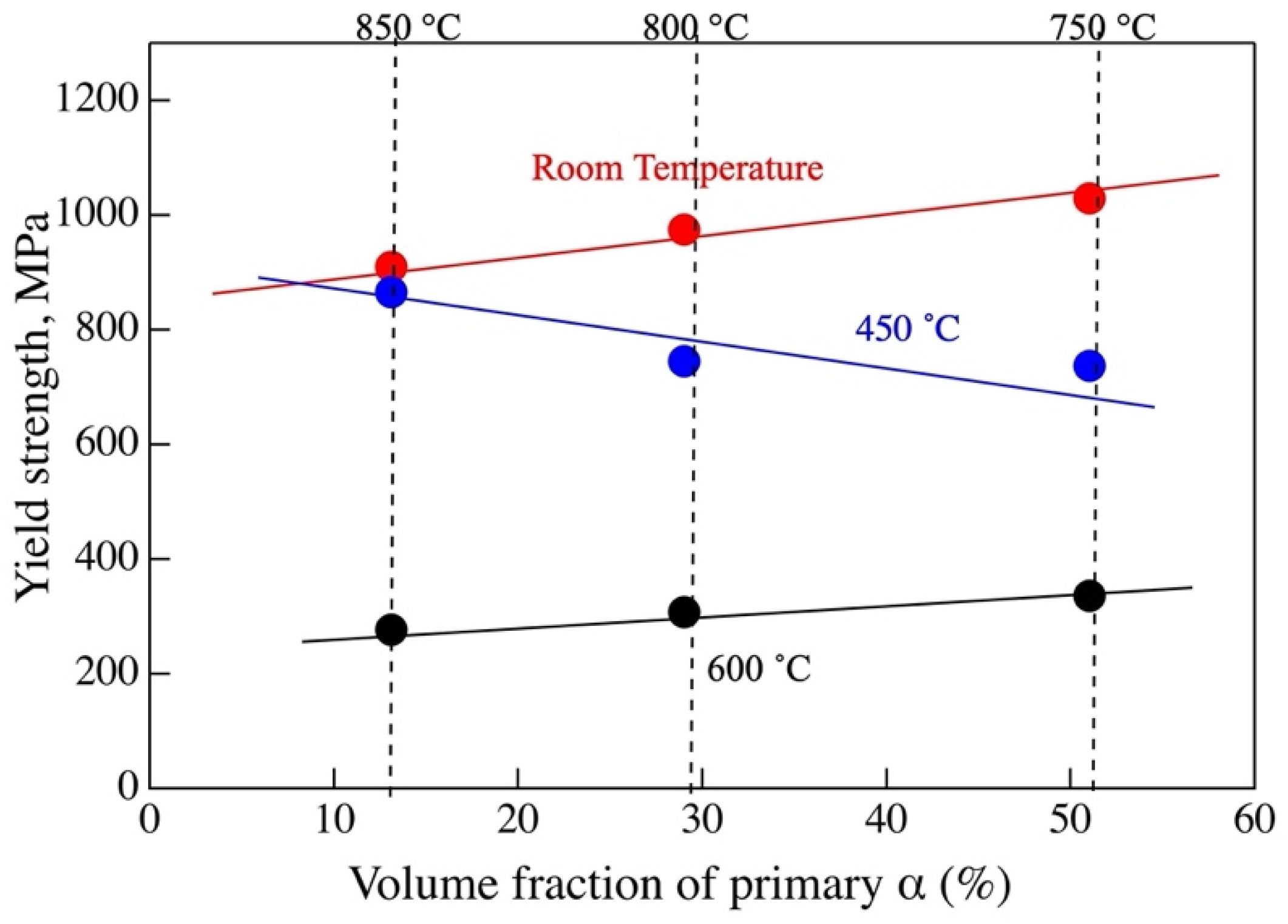
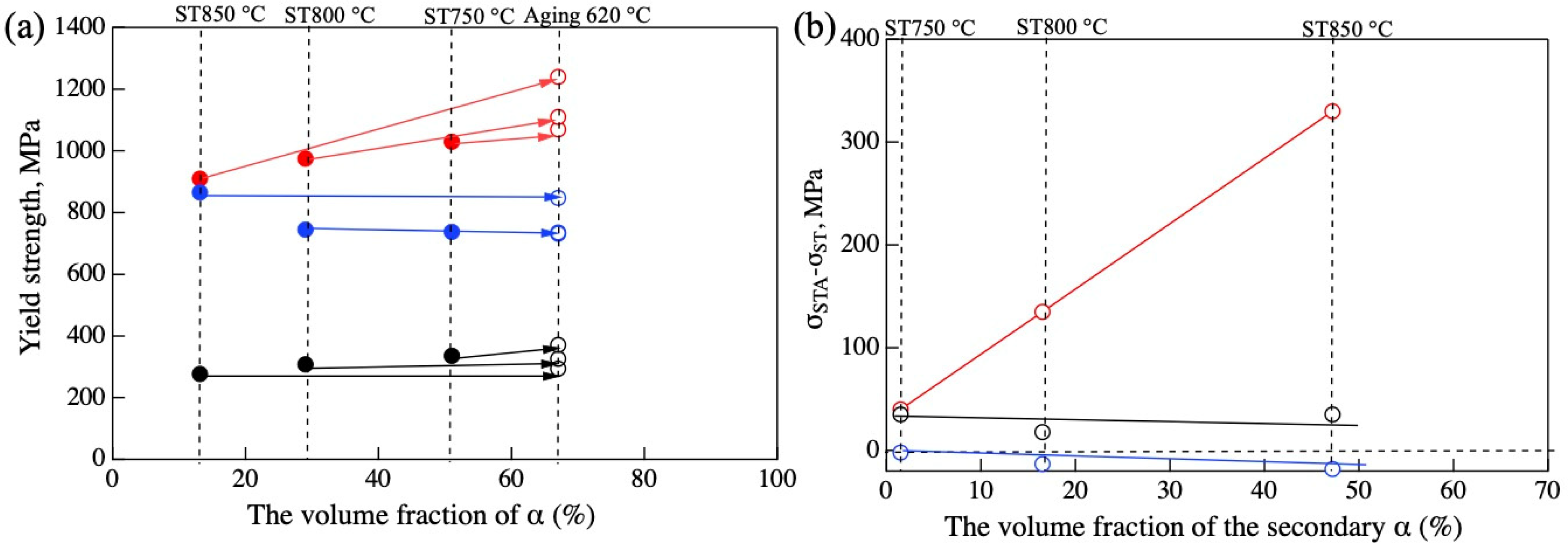
3.2. Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Mechanical Properties at Different Testing Temperatures
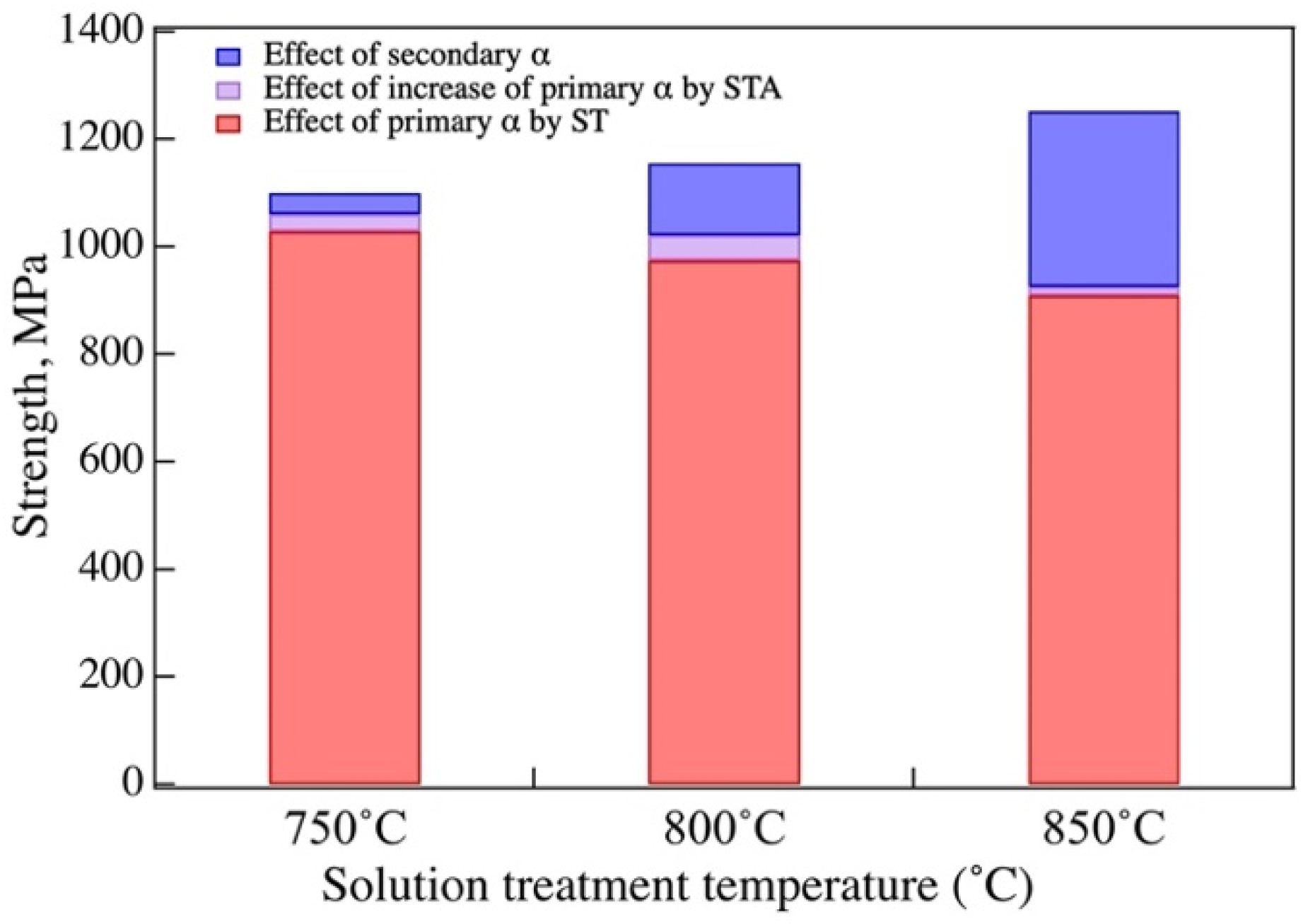
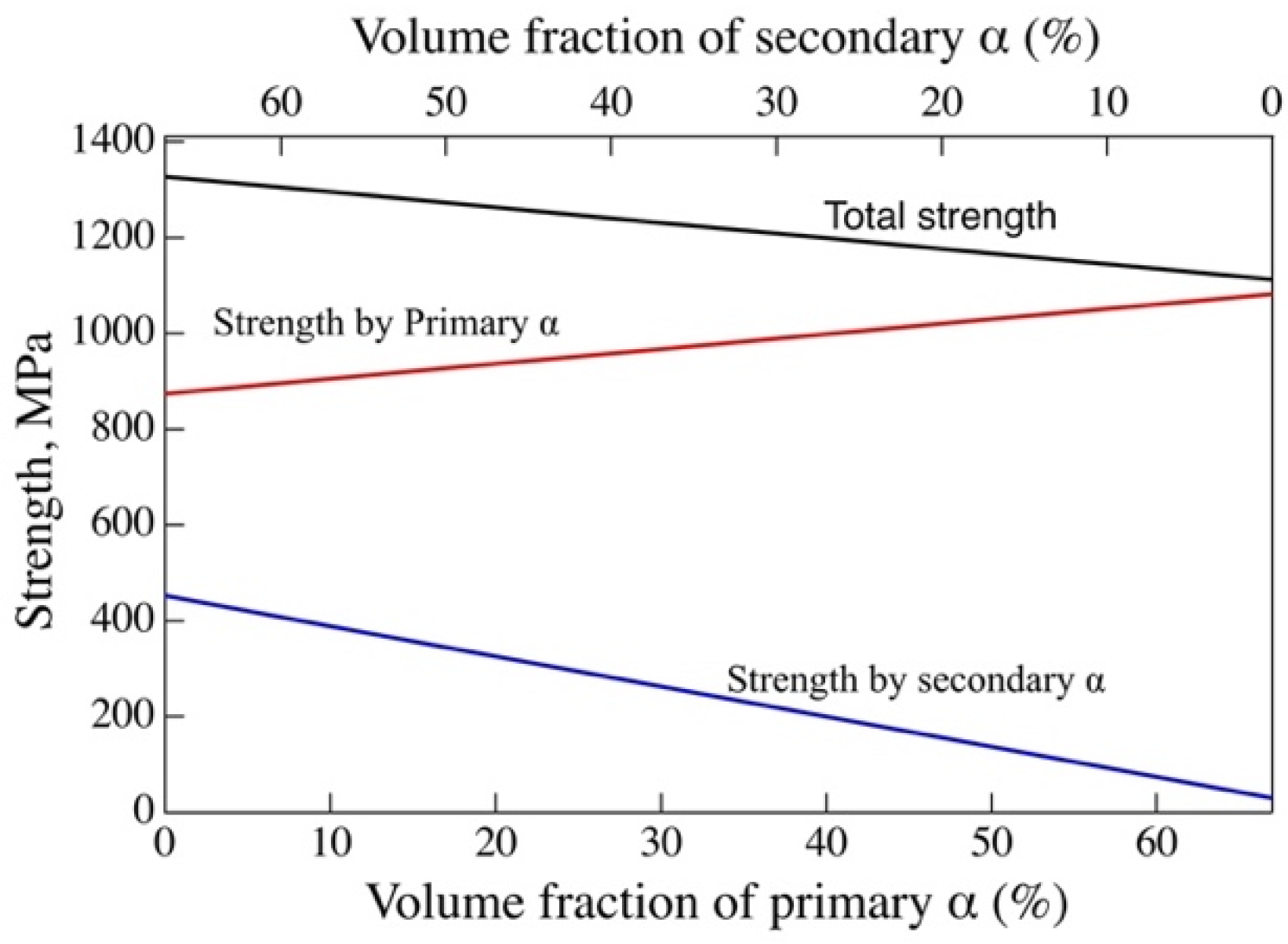
4.2. Effect of the Primary and Secondary α Phase on the Yield Strength
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farrahi, G.H.; Tirehdast, M.; Masoumi Khalil Abad, E.; Parsa, S.; Motakefpoor, M. Failure analysis of a gas turbine compressor. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2011, 18, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shlyannikov, V.N.; Ishtyryakov, I.S. Crack growth rate and lifetime prediction for aviation gas turbine engine compressor disk based on nonlinear fracture mechanics parameters. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2019, 103, 102313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lypchanskyi, O.; Sleboda, T.; Wojtaszek, M.; Muszka, K.; Lukaszek-Solek, A.; Stanik, R.; Gude, M. The analysis of flow behavior of Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo alloy based on the processing maps. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choda, T.; Oyama, H.; Murakami, S. Technologies for process design of titanium alloy forging for aircraft parts. KOBELCO Technol. Rev. 2015, 33, 44–49. [Google Scholar]
- Alluaibi, M.H.I.; Cojocaru, E.M.; Rusea, A.; Serban, N.; Coman, G.; Cojocaru, V.D. Microstructure and mechanical properties evolution during solution and ageing treatment for a hot deformed, above, β-transus, Ti-6246 alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H. Globularization and recrystallization of a Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo alloy under forging in the (α+β) region: Experiment, phenomenological modeling and machine learning. ISIJ Inter. 2021, 61, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, W.; Jia, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J. Microstructure coarsening behavior of Ti-17 alloy with equiaxed alpha during heat treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 618, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, W.; Jia, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J. Static globularization kinetics for Ti-17 alloy with initial lamellar microstructure. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 603, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, W.; Sun, X.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, J. Static coarsening behavior of the lamellar alpha in Ti-17 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 631, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zeng, W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. Development of the dynamic globularization prediction model for Ti-17 titanium alloy using finite element method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, W.; Sun, X.; Jia, Z. Microstructure evolution during isothermal forging and subsequent heat treatment of Ti-17 alloy with a lamellar colony structure. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 637, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Zhan, M. Review on globularization of titanium alloy with lamellar colony. Manuf. Rev. 2020, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Fu, M.W.; Hou, H.; Yao, Z.; Guo, H. Hot deformation behavior of Ti-5.0Al-2.40Sn-2.02Zr-3.86Mo-3.91Cr alloy with an initial lamellar microstructure in the α + β phase field. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1812–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zeng, W.; Wang, K.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, Y. The investigation on the unstable flow behavior of Ti17 alloy in α + β phase field using processing map. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 550, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, M.Q.; Han, T.; Liu, H.B. The deformation behavior of isothermally compressed Ti-17 titanium alloy in α + β field. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 546, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zeng, W.; Sun, Y.; Wang, K.; Lai, Y.; Zhou, Y. Modeling constitutive relationship of Ti17 titanium alloy with lamellar starting microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 538, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Naito, D.; Miyoshi, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Chiba, A.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Forging property, processing map, and mesoscale microstructural evolution modeling of a Ti-17 alloy with a lamellar (α+β) starting microstructure. STAM 2017, 18, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsumoto, H.; Yamanaka, K.; Chiba, A.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Itsumi, Y. Macro-mesoscale microstructural evolution modeling under hot forging of a Ti-17 alloy with a lamellar (α+β) starting microstructure. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 13005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Chiba, A. A Constitutive model and processing maps describing the high-temperature deformation behavior of Ti-17 alloy in the β -phase field. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2019, 21, 1800775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, Q. The effects of lamellar features on the fracture toughness of Ti-17 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Ji, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Effect of microstructure on fracture toughness and fatigue crack growth behavior of Ti17 alloy. Metals 2016, 6, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zeng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Z.; Sun, X. Effect of globularization behavior of the lamellar alpha on tensile properties of Ti-17 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 673, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinomi, M.; Akahori, T.; Nakai, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Nakano, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Motohashi, N.; et al. Quantitative and qualitative relationship between microstructural factors and fatigue lives under load- and strain-controlled conditions of Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Cr-4Mo (Ti-17) fabricated using a 1500-ton forging simulator. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niinomi, M.; Akahori, T.; Nakai, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A.; Nakano, T.; Kakeshita, T.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Motohashi, N.; et al. Quantitative relationship between microstructural factors and fatigue life of Ti-5Al-2Sn-2Zr-4Cr-4Mo (Ti-17) fabricated using a 1500-ton forging simulator. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 321, 11015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Motohashi, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Miyamoto, G.; Chandiran, E.; Yoshida, Y.; Itsumi, Y. Effect of forging temperature on microstructure evolution and tensile properties of Ti-17 alloys. Mater. Trans. 2019, 60, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Motohashi, N.; Matsumoto, H.; Miyamoto, G.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Niinomi, M.; Itsumi, Y. Effect of microstructure on tensile properties of Ti-17 alloys forged using a 1500-ton forging simulator. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 321, 04014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundiran, E.; Miyamoto, G.; Furuhara, T. Microstructure formation during thermomechanical processing in Ti-17 alloy. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 321, 12006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimagami, K.; Matsunaga, S.; Yumoto, A.; Ito, T.; Yamabe-Mitarai, Y. Solid solution hardening and precipitation hardening of α2-Ti3Al in Ti–Al–Nb alloys. Mater. Trans. 2017, 58, 1404–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
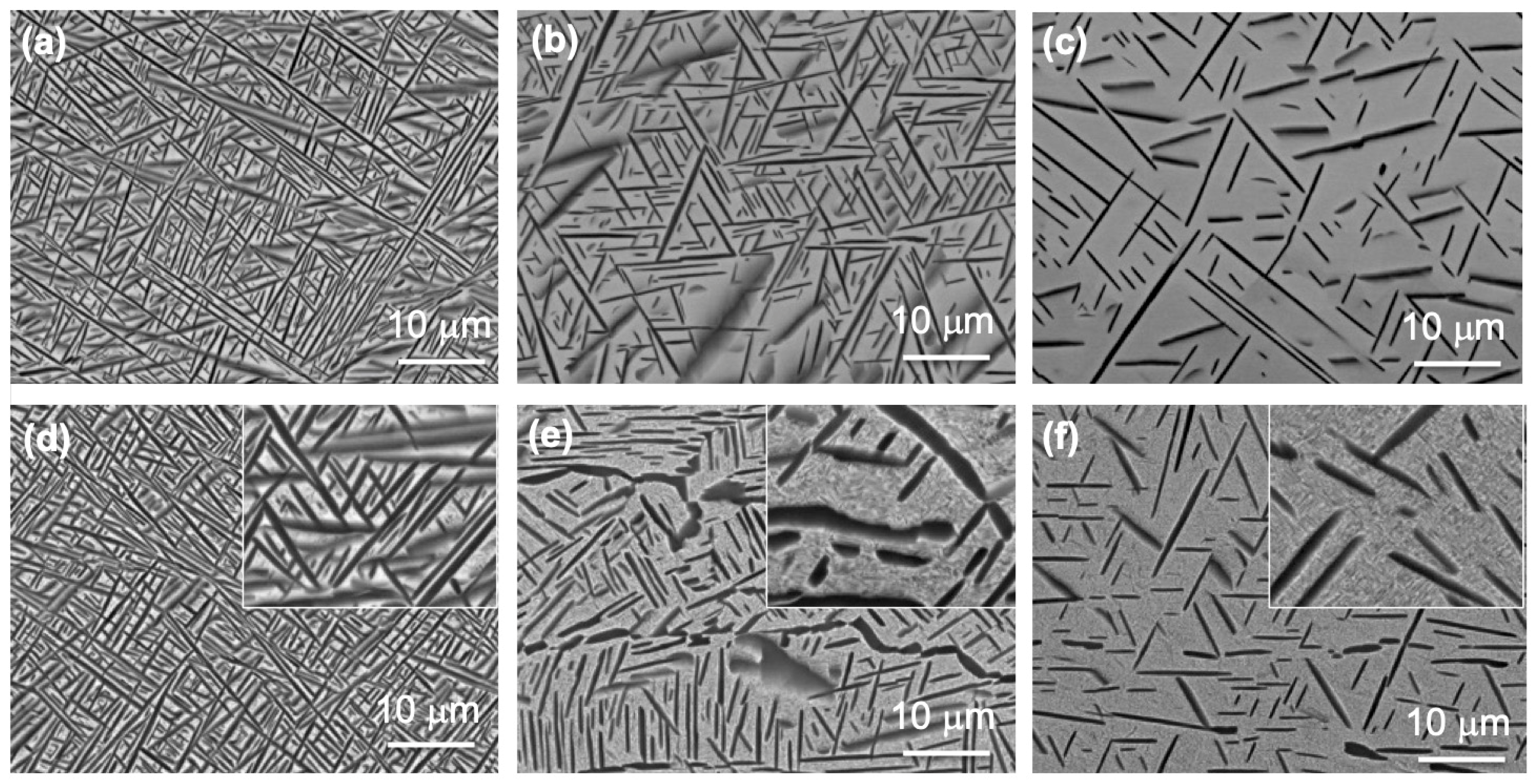
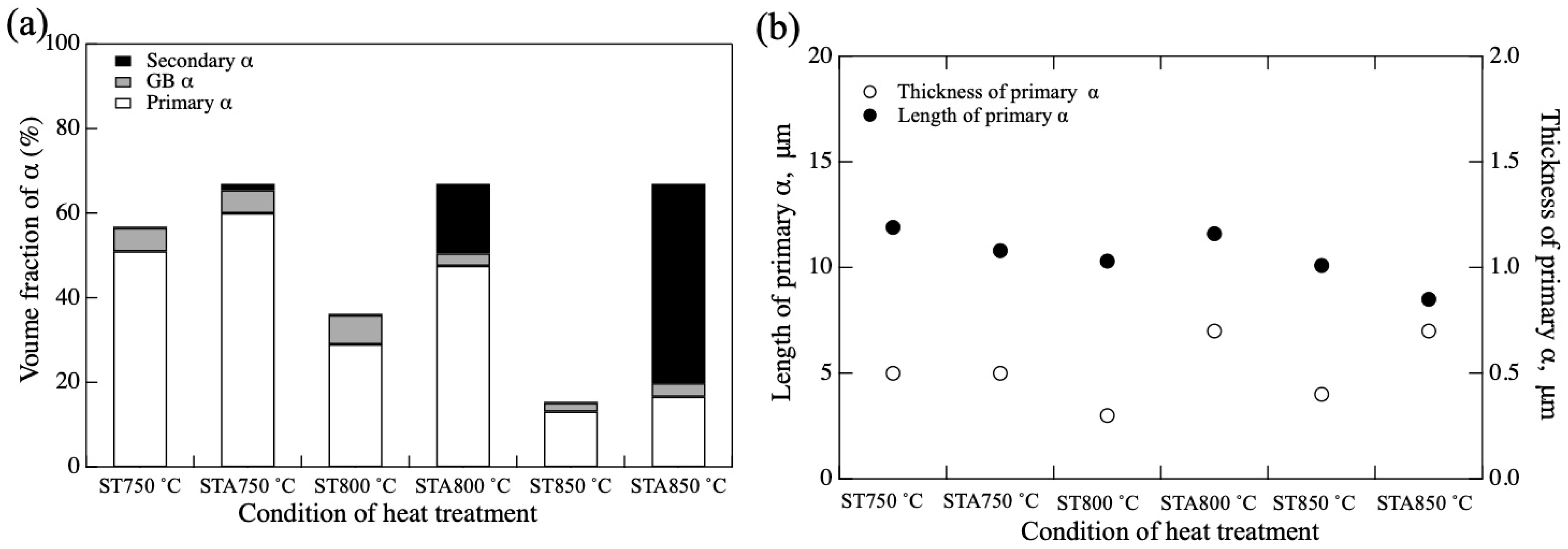
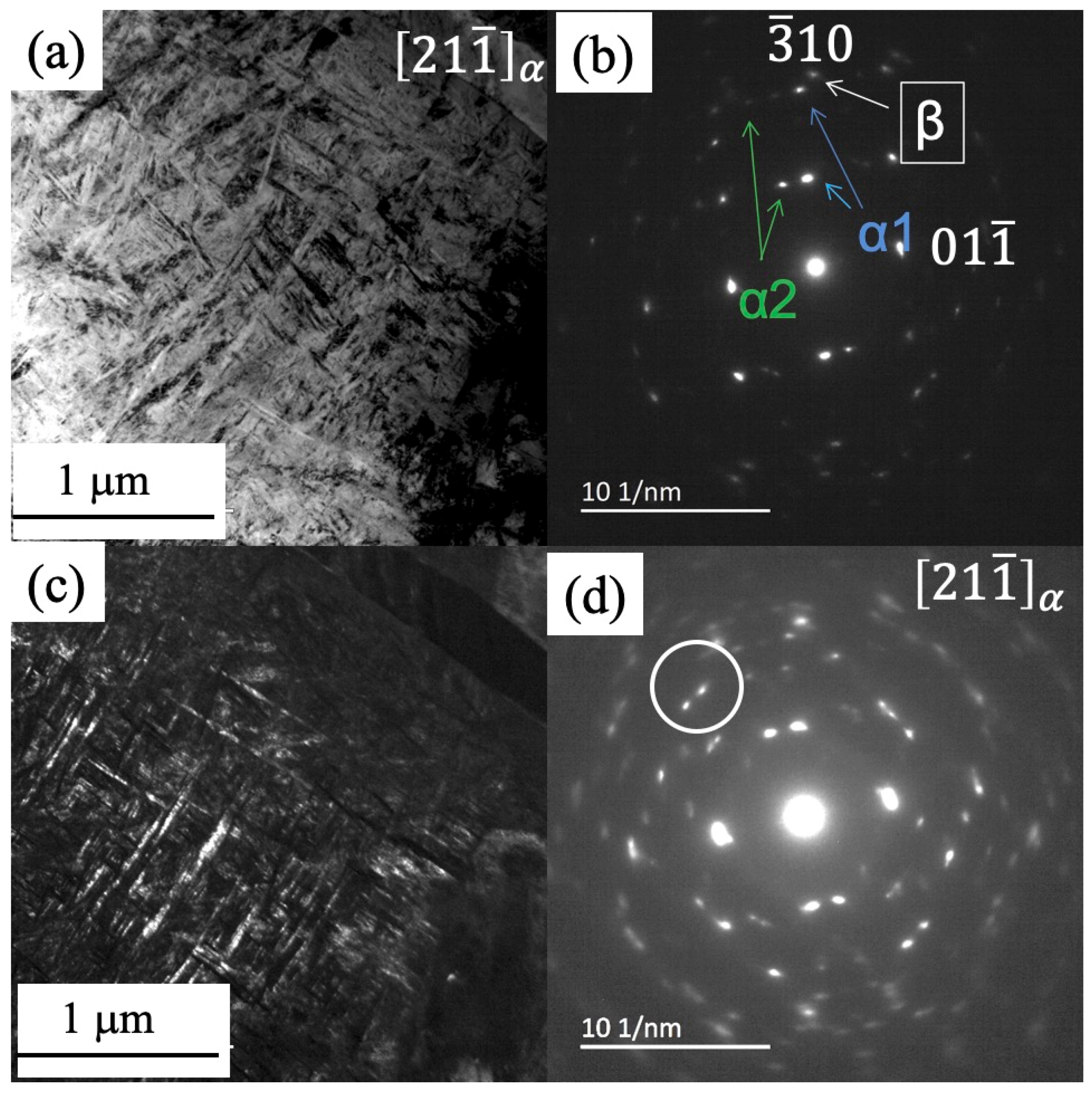

| Sample | Volume Fraction of Primary α (%) | Volume Fraction of Secondary α (%) | Volume Fraction of GB α (%) | Length of Primary α (μm) | Thickness of Primary α (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST at 750 °C | 51 | 0 | 5.5 | 11.9 | 0.5 |
| Aged after 750 °C ST | 60 | 1.5 | 5.5 | 10.8 | 0.5 |
| ST at 800 °C | 29 | 0 | 6.9 | 10.3 | 0.3 |
| Aged after 800 °C ST | 47.6 | 16.5 | 2.9 | 11.6 | 0.7 |
| ST at 850 °C | 13.1 | 0 | 2 | 10.1 | 0.4 |
| Aged after 850 °C ST | 16.6 | 47.2 | 3.2 | 8.5 | 0.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamabe-Mitarai, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Motohashi, N.; Hiroto, T.; Ishida, A.; Murakami, H.; Itsumi, Y. Correlation between Solution Treatment Temperature, MicroStructure, and Yield Strength of Forged Ti-17 Alloys. Crystals 2021, 11, 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060625
Yamabe-Mitarai Y, Kuroda S, Motohashi N, Hiroto T, Ishida A, Murakami H, Itsumi Y. Correlation between Solution Treatment Temperature, MicroStructure, and Yield Strength of Forged Ti-17 Alloys. Crystals. 2021; 11(6):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060625
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamabe-Mitarai, Yoko, Syuji Kuroda, Norie Motohashi, Takanobu Hiroto, Akira Ishida, Hideyuki Murakami, and Yoshio Itsumi. 2021. "Correlation between Solution Treatment Temperature, MicroStructure, and Yield Strength of Forged Ti-17 Alloys" Crystals 11, no. 6: 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060625
APA StyleYamabe-Mitarai, Y., Kuroda, S., Motohashi, N., Hiroto, T., Ishida, A., Murakami, H., & Itsumi, Y. (2021). Correlation between Solution Treatment Temperature, MicroStructure, and Yield Strength of Forged Ti-17 Alloys. Crystals, 11(6), 625. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11060625







