Systematic Assessment of Phonon and Optical Characteristics for Gas-Source Molecular Beam Epitaxy-Grown InP1−xSbx/n-InAs Epifilms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. GS-MBE Growth of InP1−xSbx/n-InAs (001) Epifilms
2.2. Raman Scattering
2.3. Photoluminescence
3. Theoretical Background
3.1. Optical Constants
3.2. Dielectric Properties in the FIR → NIR Region
3.3. Dielectric Properties in the NIR → UV Region
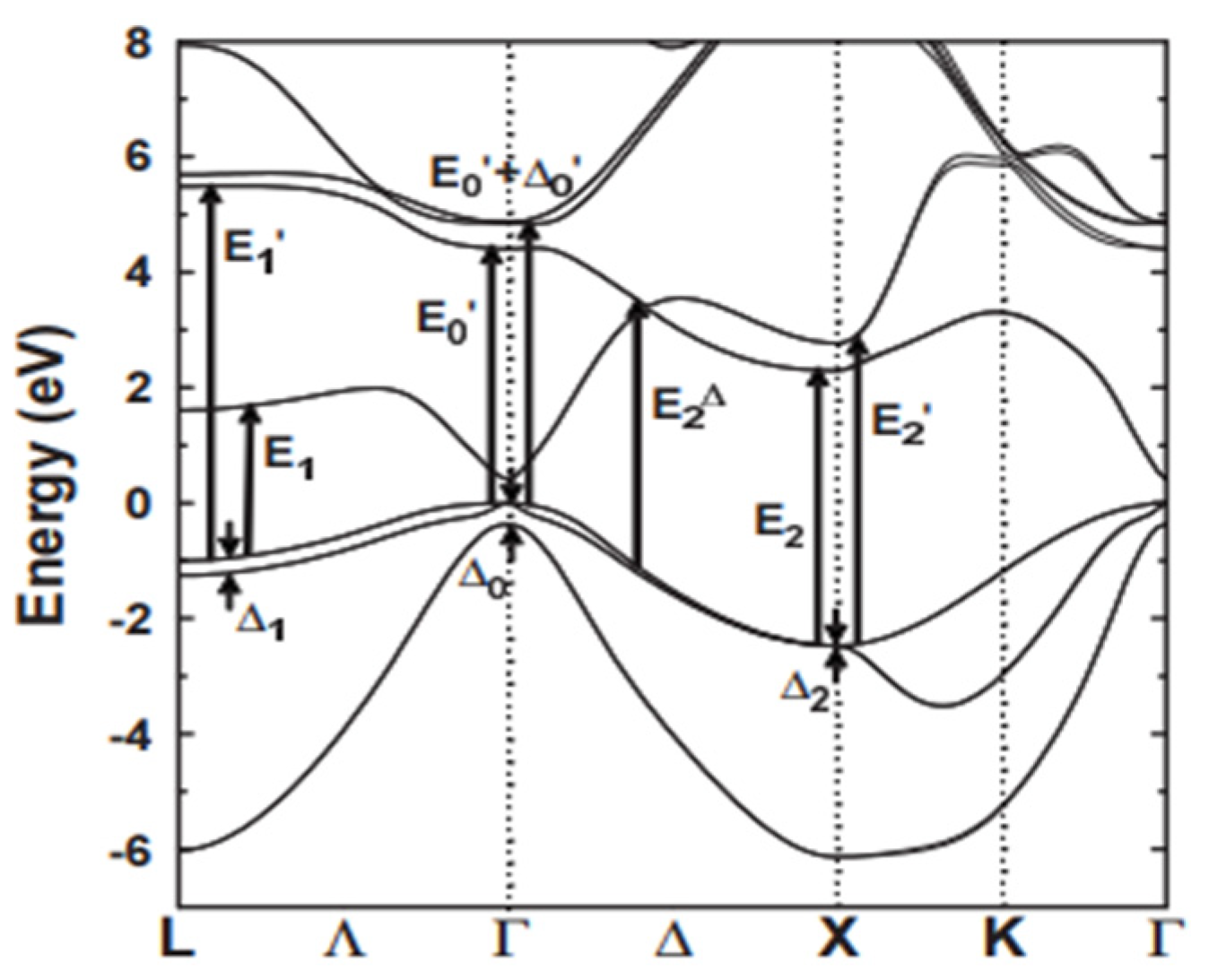
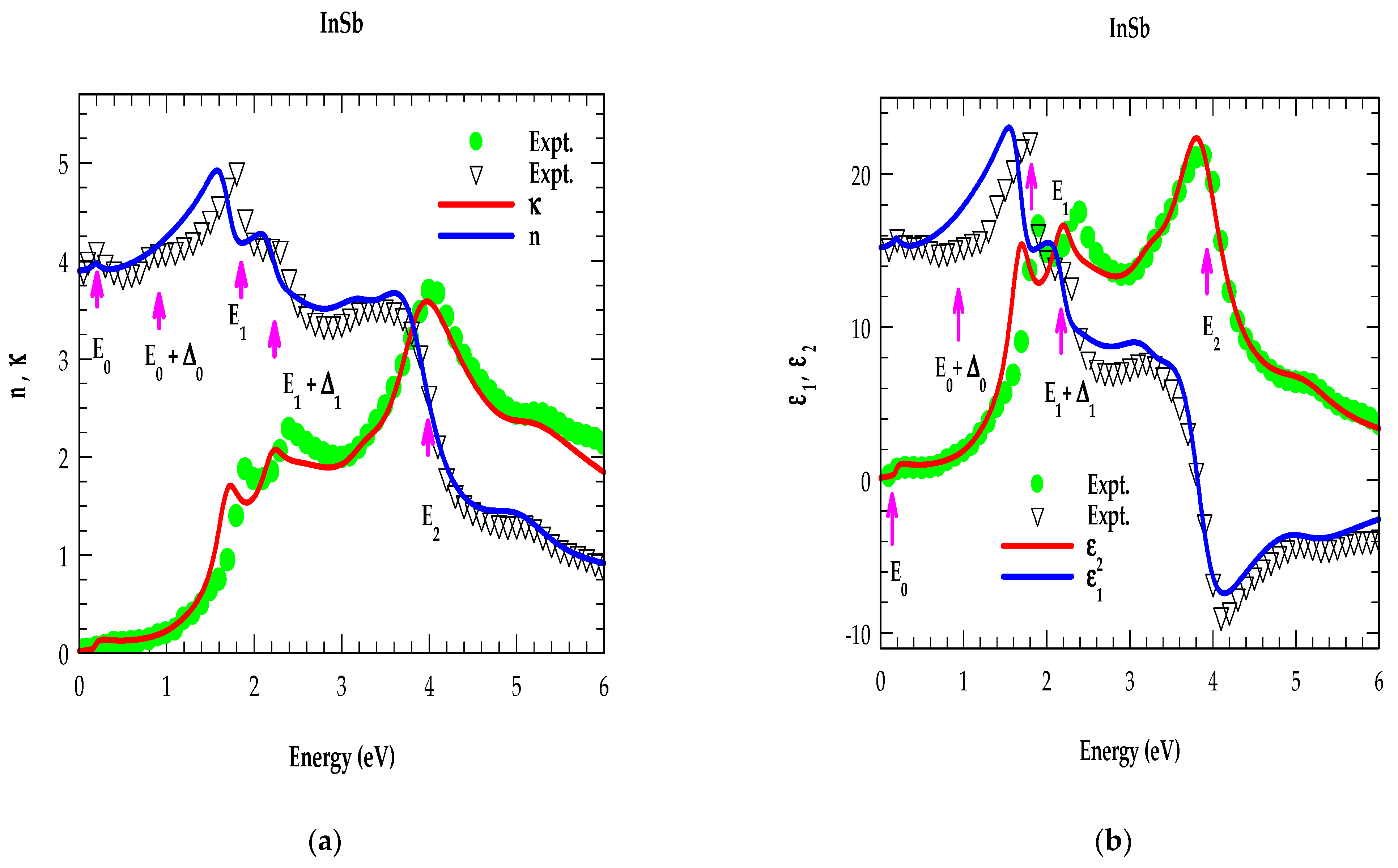
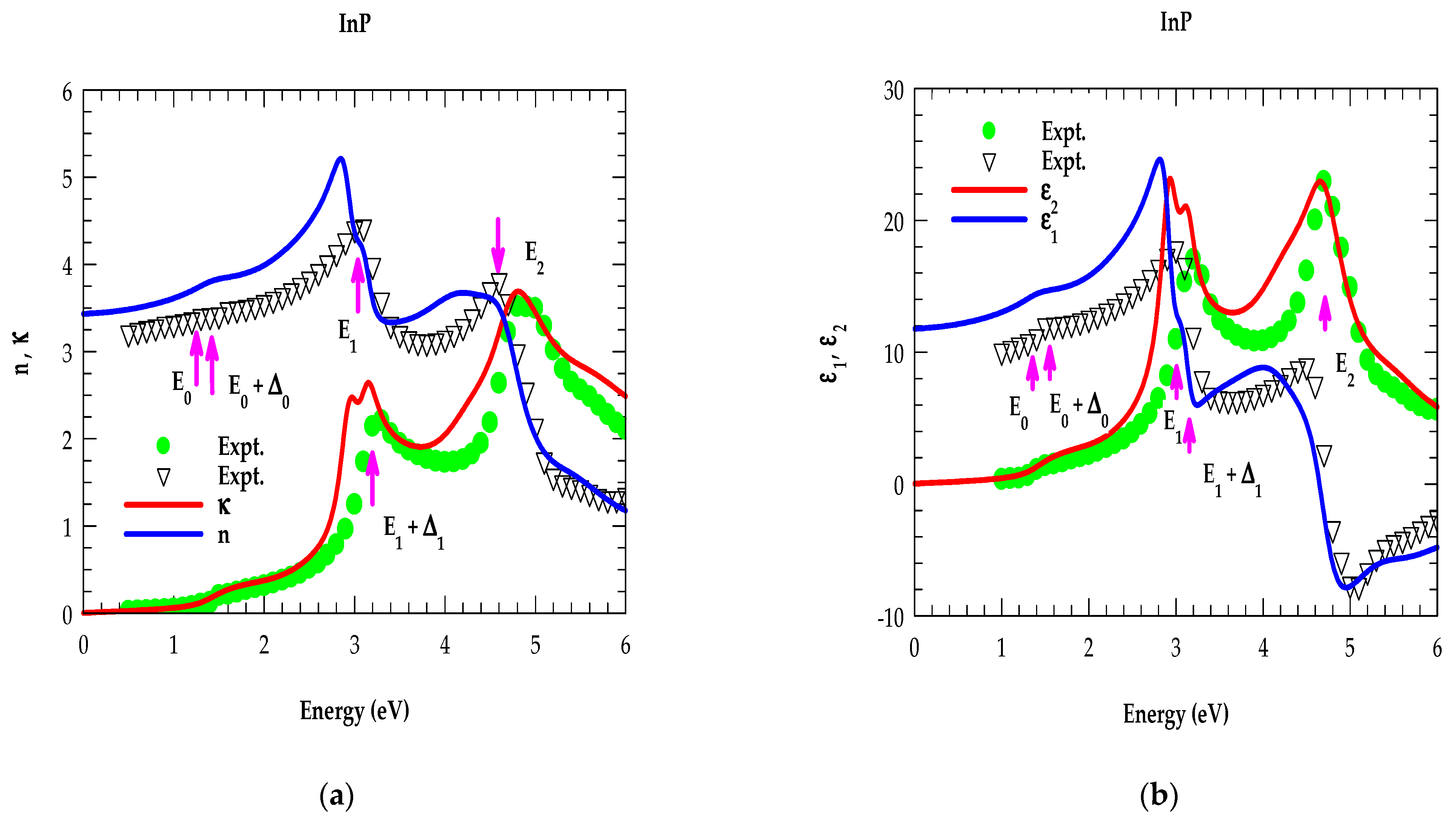
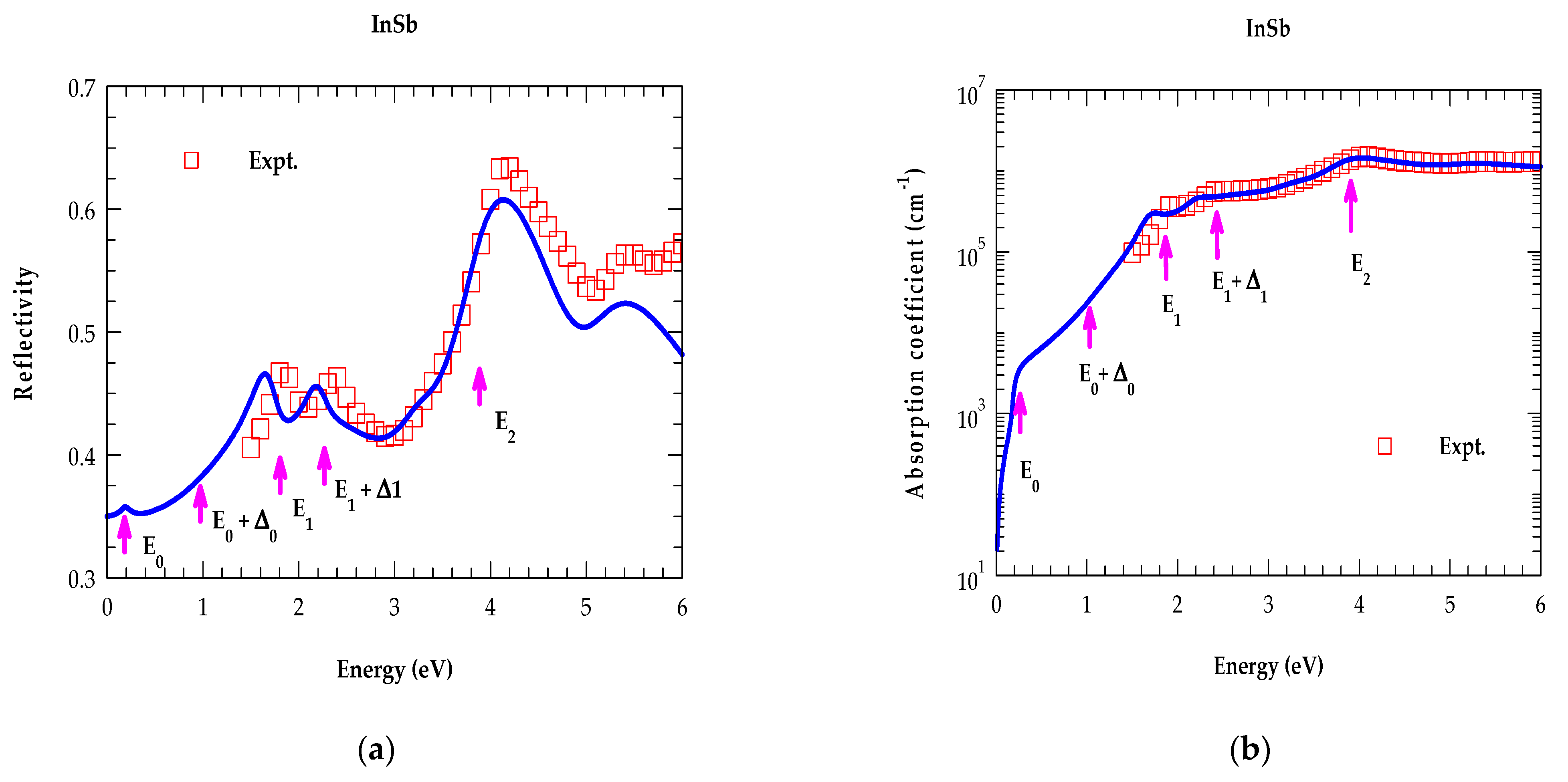
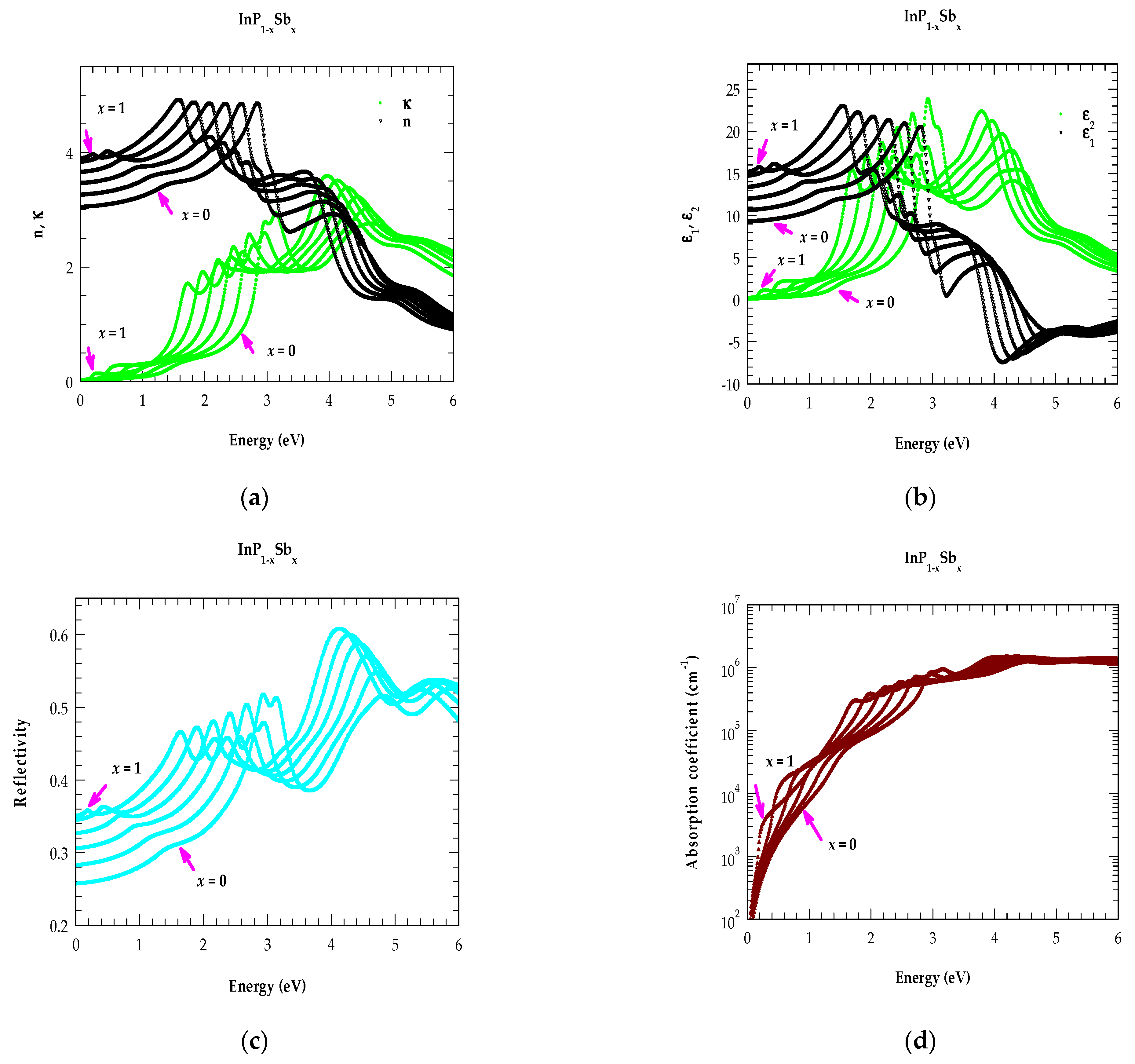
3.3.1. E0 and E0 + ∆0 Transition
3.3.2. E1 and E1 + ∆1 Transition
3.3.3. Transitions
4. Results and Discussion
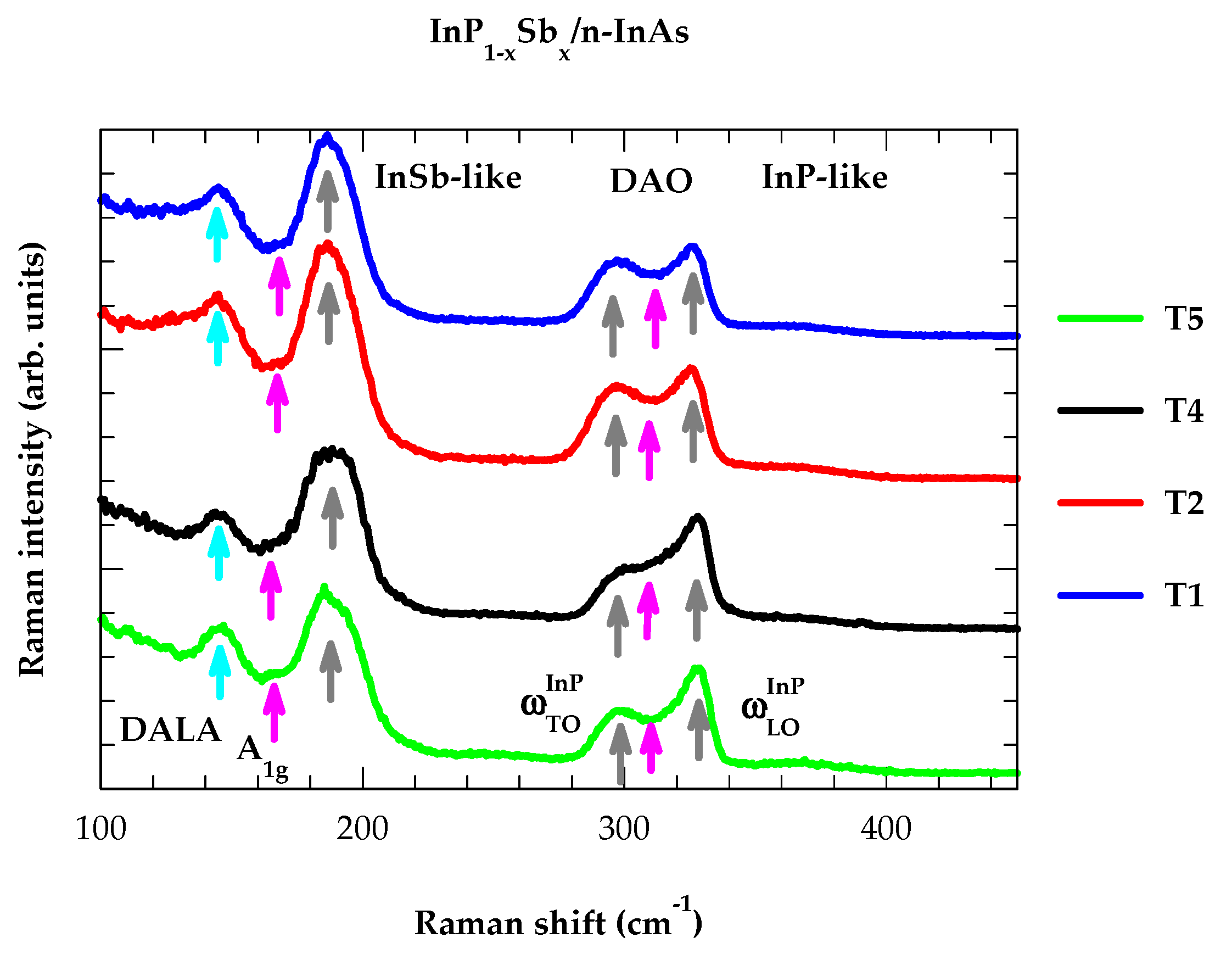
4.1. Raman Scattering
4.1.1. Polarization-Dependent Raman Spectra
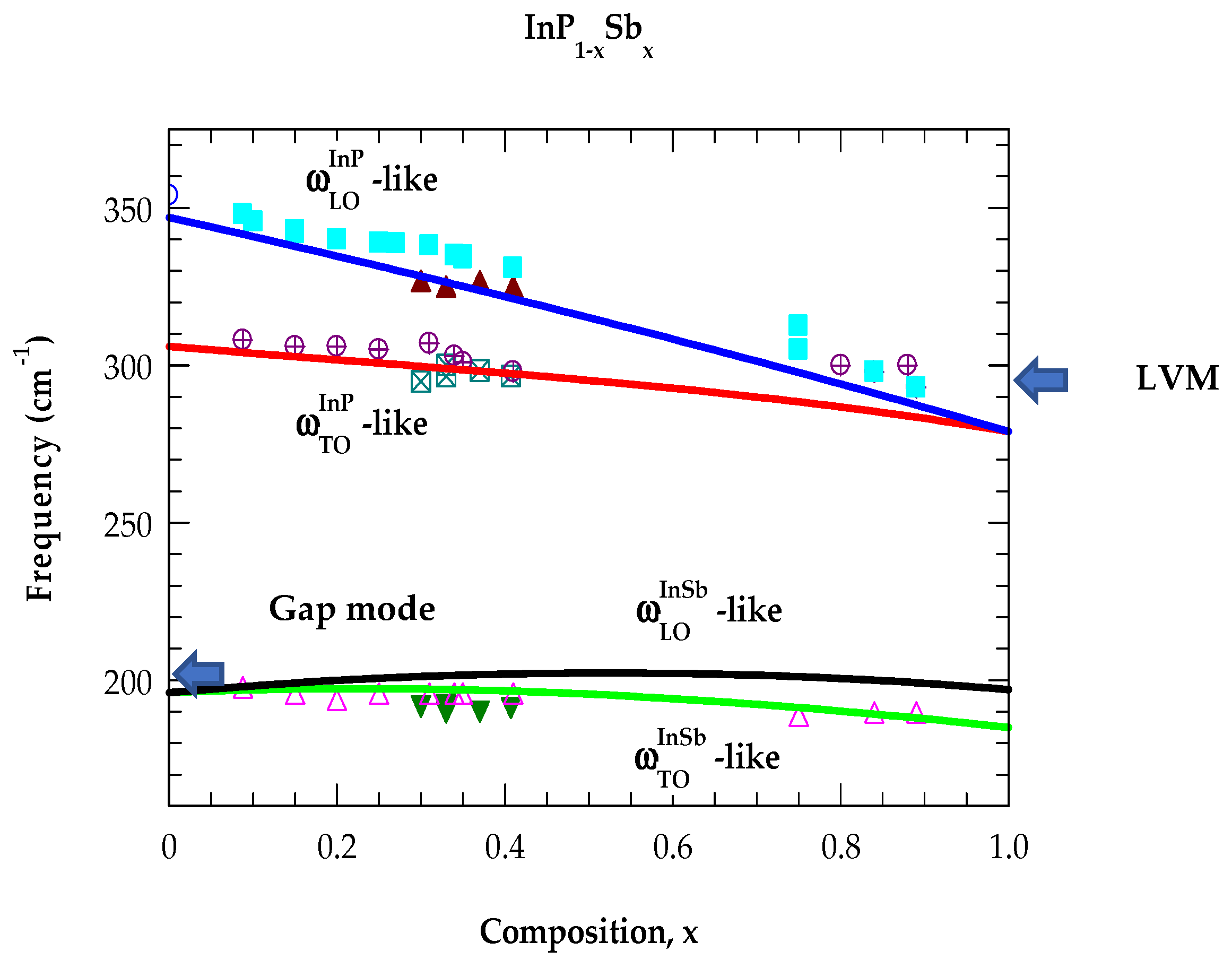
4.1.2. Analysis of Optical Constants in the FIR → NIR Region
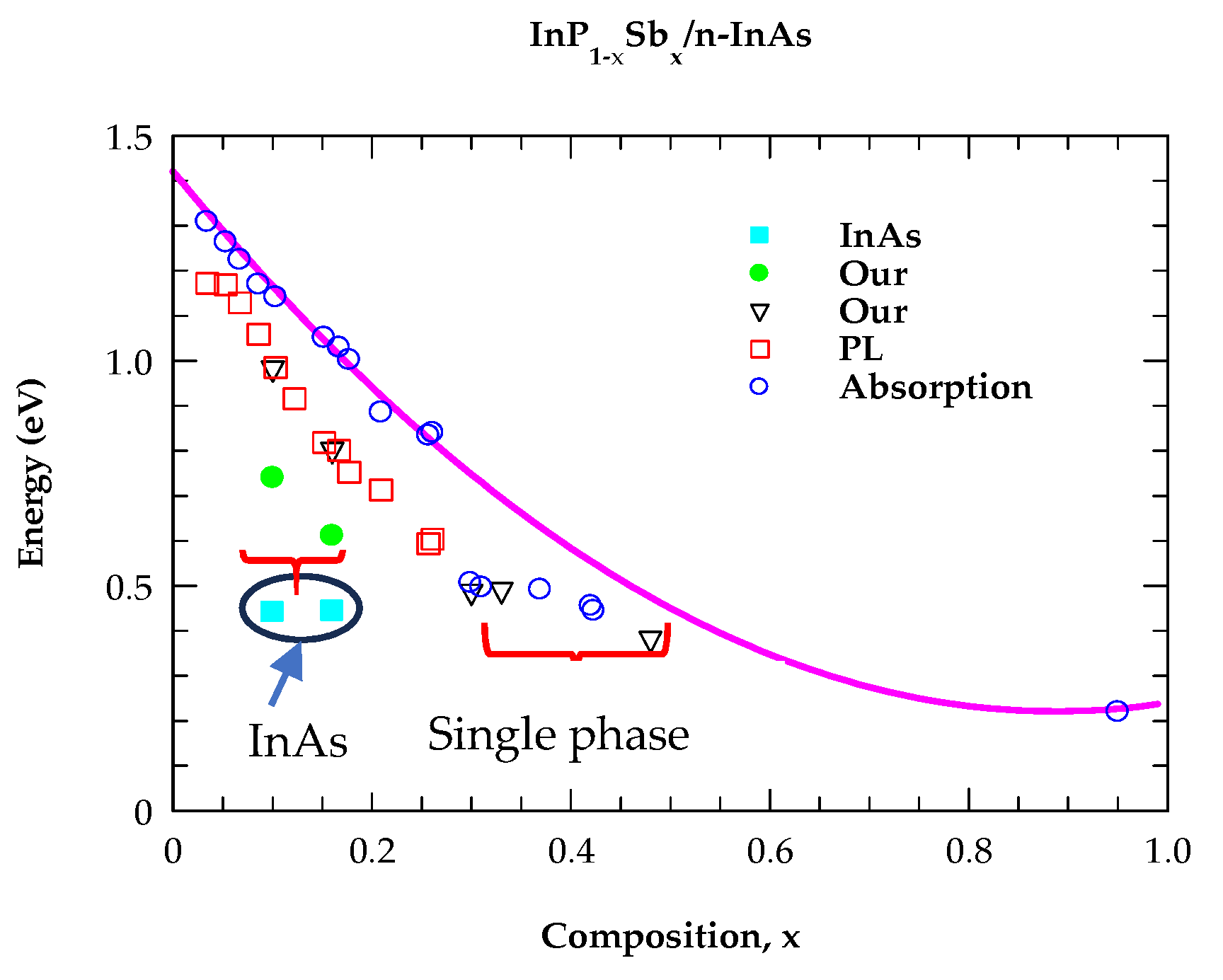
4.2. Analysis of Photoluminescence Spectra
4.2.1. Analysis of Optical Constants for Binary Materials in the NIR → UV Region
4.2.2. Analysis of Optical Constants for InP1−xSbx Alloys in the NIR → UV Region
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, H.; Lin, H.; Zhou, Z.; Wen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, S.; Da, N. Room-temperature InAsSb pBin detectors for mid-infrared application. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 128, 104475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, J.; Hao, X.; Teng, Y.; Huai, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y. Short wavelength infrared InPSb/InAs superlattice photodiode grown by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramkin, D.S.; Atuchin, V.V. Novel InGaSb/AlP Quantum Dots for Non-Volatile Memories. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi, M.; Leshchenko, E.D.; Johansson, J. Assembling your nanowire: An overview of composition tuning in ternary III–V nanowires. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 072001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.; Yang, W.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, Y. High operating temperature InAsSb-based midinfrared focal plane array with a band-aligned compound barrier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 031104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, Q.-X.; Sun, J.; Jiang, D.-W.; Wang, G.-W.; Xu, Y.-Q.; Niu, Z.-C. High performance MWIR detectors based on InAsSb nBn design. Chin. Phys. 2020, B29, 068501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalski, A.; Martyniuk, P.; Kopytko, M. InAs/GaSbtype-II superlattice infrared detectors: Future prospect. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2017, 4, 031304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Elias, D.; Uliel, Y.; Klin, O.; Snapi, N.; Weiss, E.; Shafir, I.; Westreich, O.; Katz, M. Short wavelength infrared InAs/InSb/AlSb type-II superlattice photodetector. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 84, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Elias, D.; Uliel, Y.; Klin, O.; Snapi, N.; Weiss, E.; Shafir, I.; Westreich, O.; Katz, M. Short wavelength infrared pBn GaSb/AlAsSb/InPSb photodetector. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2017, 85, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.M.; Dehzangi, A.; Adhikary, S.; Razeghi, M. High performance bias-selectable three-color short-wave/mid-wave/long wave infrared photodetectors based on type-II InAs/GaSb/AlSb superlattices. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfi, H.; Li, L.; Lei, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, R.Q.; Klem, J.F.; Johnson, M.B. Short-wave-length inter-band cascade infrared photodetectors operating above room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 023105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.P.; Jain, M.; Wicks, G.; Golding, T.; Hossain, K.; McEwan, K.; Howle, C.; Percy, B.; Marshall, A.R.J. Short-wave infrared barriode detectors using InGaAsSb absorption material lattice matched to GaSb. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 201103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Aphek, O. Extended wavelength SWIR detectors with reduced dark current. Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2015, 9451, 1945106. [Google Scholar]
- Rogalski, A.; Martyniuk, P. Mid-wavelength infrared nBn for HOT detectors. J. Electron. Mater. 2014, 43, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D. Mechanical, Electronic, and Optical Properties of Multi-Ternary Semiconductor Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, New Jersey Institute of Technology and Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, Newark, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, D.Z.-Y.; Soibel, A.; Höglund, L.; Nguyen, J.; Hill, C.J.; Khoshakhlagh, A.; Gunapala, S.D. Type-II Superlattice infrared detectors. Adv. Infrared Photodetect. 2011, 84, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Talazac, L.; Barbarin, F.; Varenne, C.; Cuminal, Y. Highly NO2 sensitive pseudo Schottky barrier diodes on p-type InP with improved electrical characteristics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 77, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vurgaftman, I.; Meyer, J.R.; Ram-Mohan, L.R. Band parameters for III–V compound semiconductors and their alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behet, M.; Stoll, B.; Heime, K. Lattice-matched growth of InPSb on InAs by low-pressure plasma MOVPE. J. Crys. Growth 1992, 124, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuken, M.; Eichel-Streiber, C.V.; Behres, A.; Schineller, B.; Heime, K.; Mendorf, C.; Brockt, G.; Lakner, H. MOVPE Growth of InPSb/InAs Heterostructures for Mid-Infrared Emitters. J. Electron. Mater. 1997, 26, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menna, R.J.; Capewell, D.R.; Martinelli, R.U.; York, P.K.; Enstrom, R.E. 3.06 mm InGaAsSb/InPSb diode lasers grown by organo-metallic vapor-phase epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 59, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspnes, D.E.; Studna, A.A. Dielectric functions and optical parameters of Si, Ge, GaP, GaAs, GaSb, InP, InAs, and InSb from 1.5 to 6.0 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seraphin, B.O.; Bennett, H.E. Semiconductors and Semimetals; Willardson, R.K., Beer, A.C., Eds.; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1967; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Stringfellow, G.B. Spinodal decomposition and clustering in III/V alloys. J. Electron. Mater. 1982, 11, 903–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jou, M.J.; Cherng, Y.T.; Jen, H.R.; Stringfellow, G.B. OMVPE growth of the new semiconductor alloys GaP1−xSbx and InP1−xSbx. J. Cryst. Growth 1988, 93, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reihlen, E.H.; Jou, M.J.; Fang, Z.M.; Stringfellow, G.B. Optical absorption and emission of InP1−xSbx alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 68, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biefeld, R.M.; Baucom, K.C.; Kurtz, S.R.; Follstaedt, D.M. The growth of InP1−xSbx by metalorganic chemical vapor deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 1993, 133, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Yoon, J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Jung, Y.W.; Ghong, T.H.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, H.; Chang, Y.-C. InAs critical-point energies at 22 K from spectroscopic ellipsometry. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 171912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drews, D.; Schneider, A.; Werninghaus, T.; Behres, A.; Heuken, M.; Heime, K.; Zahn, D.R.T. Characterization of MOVPE grown InPSb/InAs heterostructures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1998, 123–124, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringfellow, G.B. Miscibility gaps and spinodal decomposition in III/V quaternary alloys of the type AxByC1−x−yD. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 54, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kato, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ishida, T. LPE Growth of In1−xGaxAs1−yPy with Narrow Photoluminescence Spectrum on GaAs (111) B Substrates. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 21, L667–L669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onabe, K. Immiscibility in Type A1−xBxC1−yDy Strictly Regular Quaternary Solid Solutions. I. Unstable Regions. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1983, 22, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherng, M.J.; Cohen, R.M.; Stringfellow, G.B. GaAs1−xSbx growth by OMVPE. J. Electron. Mater. 1984, 13, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onda, T.; Ito, R. Behavior of Miscibility Gaps in the Phase Diagrams of III-V Semiconductor Solid Solutions: Quaternary Systems of the Type AxB1−xCyD1−y. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 30, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.M.; Ma, K.Y.; Jaw, D.H.; Cohen, R.M.; Stringfellow, G.B. Photoluminescence of InSb, InAs, and InAsSb grown by organometallic vapor phase epitaxy. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 7034–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanov, V.V.; Ermakov, B.S.; Kozhevnikov, V.A.; Stelmakh, K.F.; Vologzhanina, S.A. Lanthanide doping of AIIIBV crystals. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 826, 012010. [Google Scholar]
- Adachi, S. Band gaps and refractive indices of AlGaAsSb, GaInAsSb, and InPAsSb: Key properties for a variety of the 2–4-μm optoelectronic device applications. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 61, 4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S. Properties of Semiconductor Alloys: Group-IV, III-V and II-VI, Semiconductors; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, G.; Wang, D.L.; Wu, C.E.; Wu, C.J.; Lin, Y.T.; Lin, H.H. InAsPSb quaternary alloy grown by gas source molecular beam epitaxy. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 301–302, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cripps, S.A.; Hosea, T.J.C.; Krier, A.; Smirnov, V.; Batty, P.J.; Zhuang, Q.D.; Lin, H.H.; Liu, P.W.; Tsai, G. Mid-infrared photoreflectance study of InAs-rich InAsSb and GaInAsPSb, indicating negligible bowing for the spin-orbit splitting energy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 172106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackner, D.; Steger, M.; Thewalt, M.L.W.; Pitts, O.J.; Cherng, Y.T.; Watkins, S.P.; Plis, E.; Krishna, S. InAs/InAsSb strain balanced superlattices for optical detectors: Material properties and energy band simulations. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 111, 034507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, W.G. Advances in Solid State Physics; Madelung, O., Ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1971; Volume XI, p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, R.C. Infrared Studies of Crystal Defects; Barnes and Noble: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, R.C. Semiconductors and Semimetals; Weber, E., Ed.; Academic: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Chapter 4; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Harima, H. Properties of GaN and related compounds studied by means of Raman scattering. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, R967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, T. Phonon Raman Scattering in Semiconductors, Quantum Wells and Superlattices Basic Results and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Smołka, T.; Motyka, M.; Romanov, V.V.; Moiseev, K.D. Photoluminescence Spectroscopy of the InAsSb-Based p-i-n Heterostructure. Materials 2022, 15, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcherds, P.H.; Alfrey, G.F.; Woods, A.D.B.; Saunderson, D. H, Phonon dispersion curves in indium phosphide. J. Phys. C Solid State Phys. 1975, 8, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.L.; Rowe, J.M.; Nicklow, R.M. Lattice Dynamics of Grey Tin and Indium Antimonide. Phys. Rev. B 1971, 3, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova, N.S. X-Ray Thermal Diffuse Scattering Measurements of the [100] and [111] Phonon Dispersion Curves of Indium Arsenide. Phys. Stat. Solidi 1983, 119, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, D.N.; Lin, H.H. Structural and optical properties of InP1−xSbx/n-InAs epilayers grown by gas source molecular beam epitaxy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 638, 158008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenberg, K. A Method for the Solution of Certain Non-Linear Problems in Least Square: The Quarterly of Applied Mathematics. Q. Appl. Math. 1944, 2, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, I.F.; Mitra, S.S. Long wavelength optical phonons in mixed crystals. Adv. Phys. 1971, 20, 359–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval, S.J.; Rivera, A.L.; Irwin, J.C. Influence of reduced mass differences on the Raman spectra of ternary mixed compounds: Zn1−xFexS and Zn1−xMnxS. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 054303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Pozuelo, M.; Hicks, R.F.; Kodambaka, S. Self-catalyzed vapor–liquid–solid growth of InP1−xSbx nanostructures. J. Crystal Growth 2011, 319, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmer, G. Local crystal orientation in Ill-V semiconductors: Polarization selective Raman microprobe measurements. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 7768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menéndez, J. Characterization of Bulk Semiconductors Using Raman Spectroscopy, in Raman Scattering in Materials Science; Weber Willes, H., Roberto, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 42. [Google Scholar]
- Rettweiler, U.; Richter, W.; Resch, U.; Geurts, J.; Sporken, R.; Xhonneux, P.; Caudano, R. Epitaxial InSb(ll1) layers on Sb(ll1) substrates characterised by Raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1989, 1, SB93–SB97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, D.N. Dilute III-V Nitride Semiconductors and Material Systems—Physics and Technology; Erol, A., Ed.; Springer Series in Materials Science 105; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Chapter 9; p. 222. [Google Scholar]



| GS-MBE-Grown InP1−xSbx/n-InAs Samples | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | x (a) | 1 − x | |
| # T0 | 0.10 | 0.90 | |
| # T1 | 0.16 | 0.84 | |
| # T2 | 0.17 | 0.83 | |
| # T3 | 0.30 | 0.70 | |
| # T4 | 0.33 | 0.67 | |
| # T5 | 0.36 | 0.64 | |
| # T6 | 0.37 | 0.63 | |
| # T7 | 0.48 | 0.52 | |
| MDF Parameters | InSb | InP |
|---|---|---|
| (eV) | 0.18 | 1.35 |
| (eV) | 0.99 | 1.45 |
| (eV) | 0.015 | 0.23 |
| (eV)1.5 | 0.19 | 7.1 |
| (eV−1) | 0.007 | 0.009 |
| (eV) | 1.86 | 3.1 |
| (eV) | 2.37 | 3.31 |
| (eV) | 0.19 | 0.34 |
| 4.10 | 2.94 | |
| 2.70 | 0.96 | |
| (eV) | 1.87 | 1.64 |
| (eV) | 0.98 | 0.82 |
| (eV) | 3.85 | 4.70 |
| (eV) | 3.26 | 4.2 |
| (eV) | 3.63 | 4.40 |
| (eV) | 5.11 | 5.5 |
| 2.35 | 0.22 | |
| 0.50 | 0.50 | |
| 0.35 | 0.70 | |
| 0.34 | 0.36 | |
| (eV) | 0.17 | 0.12 |
| (eV) | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| (eV) | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| (eV) | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| 1.20 | 0.50 |
| Reihlen et al. (a) (10 K) | Our PL Data (b) (13 K) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (a) | Eg | EPL | x (b) | ||||
| 0.034 | 1.309 | 1.172 | 0.1 | 0.981 | 0.741 | 0.442 | |
| 0.053 | 1.264 | 1.169 | 0.16 | 0.80 | 0.612 | 0.444 | |
| 0.067 | 1.225 | 1.129 | 0.17 | ||||
| 0.086 | 1.17 | 1.059 | 0.30 | 0.485 | |||
| 0.103 | 1.142 | 0.985 | 0.33 | 0.489 | |||
| 0.122 | 0.916 | 0.36 | |||||
| 0.152 | 1.052 | 0.818 | 0.37 | ||||
| 0.167 | 1.03 | 0.801 | 0.48 | 0.380 | |||
| 0.177 | 1.002 | 0.752 | |||||
| 0.209 | 0.886 | 0.713 | |||||
| 0.257 | 0.834 | 0.594 | |||||
| 0.261 | 0.84 | 0.604 | |||||
| 0.299 | 0.507 | ||||||
| 0.31 | 0.497 | ||||||
| 0.369 | 0.492 | ||||||
| 0.42 | 0.456 | ||||||
| 0.423 | 0.445 | ||||||
| 0.95 | 0.22 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talwar, D.N.; Lin, H.-H. Systematic Assessment of Phonon and Optical Characteristics for Gas-Source Molecular Beam Epitaxy-Grown InP1−xSbx/n-InAs Epifilms. Crystals 2023, 13, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091367
Talwar DN, Lin H-H. Systematic Assessment of Phonon and Optical Characteristics for Gas-Source Molecular Beam Epitaxy-Grown InP1−xSbx/n-InAs Epifilms. Crystals. 2023; 13(9):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091367
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalwar, Devki N., and Hao-Hsiung Lin. 2023. "Systematic Assessment of Phonon and Optical Characteristics for Gas-Source Molecular Beam Epitaxy-Grown InP1−xSbx/n-InAs Epifilms" Crystals 13, no. 9: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091367
APA StyleTalwar, D. N., & Lin, H.-H. (2023). Systematic Assessment of Phonon and Optical Characteristics for Gas-Source Molecular Beam Epitaxy-Grown InP1−xSbx/n-InAs Epifilms. Crystals, 13(9), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst13091367








