Novel Polymer Material for Efficiently Removing Methylene Blue, Cu(II) and Emulsified Oil Droplets from Water Simultaneously
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SPCT
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiments
2.5. Separation of Oil-In-Water Emulsion
2.6. Regeneration and Reusability Experiments
2.7. Simultaneous Removal of Three Pollutants
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of SPCT
3.2. Adsorption of Dyes and Heavy Metal Ions
3.2.1. Effect of Pollutant Type on the Adsorption Capacity of SPCT
3.2.2. Effect of Dosage on the Removal Efficiency of SPCT
3.2.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.2.4. Adsorption Isotherm
3.2.5. Effect of Solution pH on the Adsorption Capacity of SPCT
3.3. Separation of Oil-In-Water Emulsion
3.4. Reusability of SPCT
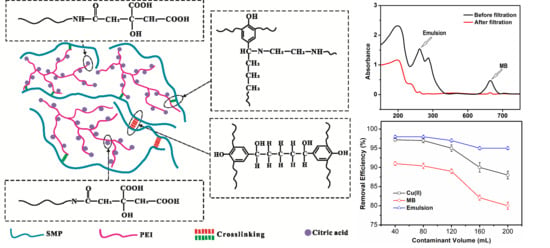
3.5. Simultaneous Removal of Three Pollutants
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnason, J.; Fletcher, B. A 40+ year record of Cd, Hg, Pb, and U deposition in sediments of Patroon Reservoir, Albany County, NY, USA. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.; Chan, G.; Lo, W.; Babel, S. Physico-chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 118, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Shah, J.; Ashfaq, T.; Gardazi, S.; Tahir, A.; Pervez, A.; Haroon, H.; Mahmood, Q. Waste biomass adsorbents for copper removal from industrial wastewater: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Wang, T.; Deng, W. Extraordinary capability for water treatment achieved by a perfluorous conjugated microporous polymer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, D.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. TiO2/sulfonated graphene oxide/Ag nanoparticle membrane: In situ separation and photodegradation of oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W. Immobilization of polyethylenimine nanoclusters onto a cation exchange resin through self-crosslinking for selective Cu(II) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Hiroishi, K.; Tokunoh, M.; Saegusa, T. Chelating properties of linear and branched poly(ethylenimines). Macromolecules 1987, 20, 1496–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayab, S.; Farrukh, A.; Oluz, Z.; Tuncel, E.; Tariq, S.; Rahman, H.; Kirchhoff, K.; Duran, H.; Yameen, B. Design and fabrication of branched polyamine functionalized mesoporous silica: An efficient absorbent for water remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 4408–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhiman, M.; Chalke, B.; Polshettiwar, V. Efficient synthesis of monodisperse metal (Rh, Ru, Pd) nanoparticles supported on fibrous nanosilica (KCC-1) for catalysis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3224–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Su, D.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Soy protein-based polyethylenimine hydrogel and its high selectivity for copper ion removal in wastewater treatment. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4163–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, D.; Ma, C.; Guan, E. Removal of organic pollutant in sulfonated drilling wastewater with novel solar-assisted catalytic oxidation process. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 726–731, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Chai, H.; Cao, Y.; Jia, D. Sulfonated graphene oxide as an adsorbent for removal of Pb2+ and methylene blue. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 524, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Dunderdale, G.; England, M.; Hozumi, A. Oil/water separation techniques: A review of recent progresses and future directions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16025–16058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Nguyen, Q.; Ping, Z. Hydrophilic modification of poly (vinylidene fluoride) microporous membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xu, Z.; Shen, H.; Yang, H. Preparation and characterization of PVDF-SiO2 composite hollow fiber UF membrane by sol-gel method. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 337, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, I.; Aroujalian, A.; Raisi, A.; Dabir, B.; Fathizadeh, M. Surface modification of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes by corona air plasma for separation of oil/water emulsions. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 430, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asatekin, A.; Kang, S.; Elimelech, M.; Mayes, A. Anti-fouling ultrafiltration membranes containing polyacrylonitrile-graft-poly(ethylene oxide) comb copolymer additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 298, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J. Salt-induced fabrication of superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic PAA-g-PVDF membranes for effective separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2014, 53, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pan, K.; Li, L.; Cao, B. Surface hydrophilicity and structure of hydrophilic modified PVDF membrane by nonsolvent induced phase separation and their effect on oil/water separation performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6401–6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, N.; Fu, C.; Li, K.; Tao, L.; Feng, L.; Wei, Y. Thermo and pH dual-responsive materials for controllable oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 2026–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Zang, G.; Shi, C.; Yu, H.; Sheng, G. A novel adsorbent TEMPO-mediated oxidized cellulose nanofibrils modified with PEI: Preparation, characterization, and application for Cu(II) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 316, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Tan, Y.; Che, Y.; Ma, Q. Fabrication and properties of superabsorbent complex gel beads composed of hydrolyzed polyacrylamide and chitosan. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 116, 3338–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larraza, I.; Lopez-Gonzalez, M.; Corrales, T.; Marcelo, G. Hybrid materials: Magnetite-polyethylenimine-montmorillonite, as magnetic adsorbents for Cr(VI) water treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 385, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Wang, C. Synthesis of beta-cyclodextrin-based electrospun nanofiber membranes for highly efficient adsorption and separation of methylene blue. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 26649–26657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Yin, J. Multi-responsive microgel of hyperbranched poly(ether amine) (hPEA-mGel) for the selective adsorption and separation of hydrophilic fluorescein dyes. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17976–17983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, Q.; Bai, N.; Dong, H.; Mao, D. One-step synthesis of cationic hydrogel for efficient dye adsorption and its second use for emulsified oil separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5598–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Ting, Y. Characterization of PEI-modified biomass and biosorption of Cu(II), Pb(II) and Ni(II). Water Res. 2005, 39, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubica, B.; Godunowa, H.; Tuteja-Krysa, M.; Stobinski, M.; Misiak, R. Sorption of lead(II) on transition metal hexacyanoferrates(II) and on nickel(II)-potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) resin composite in hydrochloric acid medium. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem 2004, 262, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Bai, R. Adsorptive removal of copper ions with highly porous chitosan/cellulose acetate blend hollow fiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, D.; Namasivayam, C. Experimental and kinetic studies on methylene blue adsorption by coir pith carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, Q.; Mao, D.; Bai, N.; Dong, H. A versatile bio-based material for efficiently removing toxic dyes, heavy metal ions and emulsified oil droplets from water simultaneously. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Peng, S.; Wu, X.; Ren, T.; Zeng, Z.; Xue, Q. A cellulose sponge with robust superhydrophilicity and under-water superoleophobicity for highly effective oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Xue, L.; Liu, F.; Jiang, L. An intelligent superwetting PVDF membrane showing switchable transport performance for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2943–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, I.; Srivastava, V.; Kumar, G.; Mishra, I. Characterization and utilization of mesoporous fertilizer plant waste carbon for adsorptive removal of dyes from aqueous solution. Colloid Surf. A 2006, 278, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Sun, B.; Shen, M.; Tan, X.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, C. Preparation of phosphorylated polyacrylonitrile-based nanofiber mat and its application for heavy metal ion removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 268, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Adsorbate | Pseudo-First-Order Kinetic Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Kinetic Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 (min−1) | qe (mg g−1) | R2 | K2 (g mg−1 min−1) | qe (mg g−1) | R2 | |
| MB | 0.0292 | 223 | 0.995 | 1.27 × 10−4 | 264 | 0.993 |
| Cu(II) | 0.0292 | 155 | 0.997 | 6.82 × 10−5 | 209 | 0.978 |
| Adsorbate | Langmuir | Freundlich | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KL (L mg−1) | qm (mg g−1) | R2 | KF (mg1−n Ln g−1) | n | R2 | |
| MB | 0.053 | 952 | 0.992 | 74.41 | 0.587 | 0.952 |
| Cu(II) | 0.209 | 167 | 0.991 | 37.71 | 0.446 | 0.798 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Lv, K. Novel Polymer Material for Efficiently Removing Methylene Blue, Cu(II) and Emulsified Oil Droplets from Water Simultaneously. Polymers 2018, 10, 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121393
Cao J, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Wang S, Wang X, Lv K. Novel Polymer Material for Efficiently Removing Methylene Blue, Cu(II) and Emulsified Oil Droplets from Water Simultaneously. Polymers. 2018; 10(12):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121393
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jie, Jianbei Zhang, Yuejun Zhu, Shanshan Wang, Xiujun Wang, and Kaihe Lv. 2018. "Novel Polymer Material for Efficiently Removing Methylene Blue, Cu(II) and Emulsified Oil Droplets from Water Simultaneously" Polymers 10, no. 12: 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121393
APA StyleCao, J., Zhang, J., Zhu, Y., Wang, S., Wang, X., & Lv, K. (2018). Novel Polymer Material for Efficiently Removing Methylene Blue, Cu(II) and Emulsified Oil Droplets from Water Simultaneously. Polymers, 10(12), 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10121393