Biodegradable Polymer Coated Granular Urea Slows Down N Release Kinetics and Improves Spinach Productivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Preparation of Polymeric Solution
2.1.2. Coating of Urea Fertilizer Using Fluidized Bed Coater
2.1.3. Characterization of Formulated Urea Granules
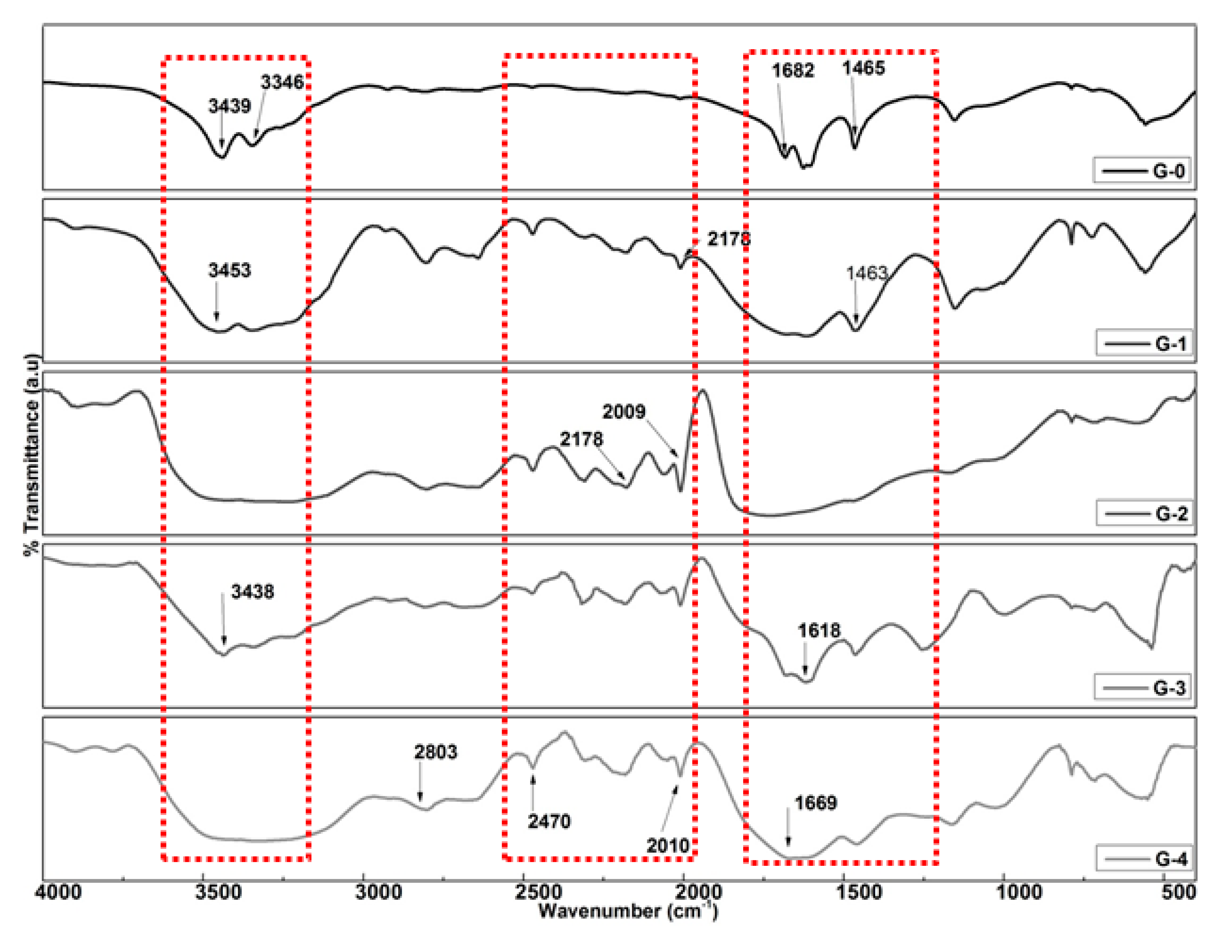
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
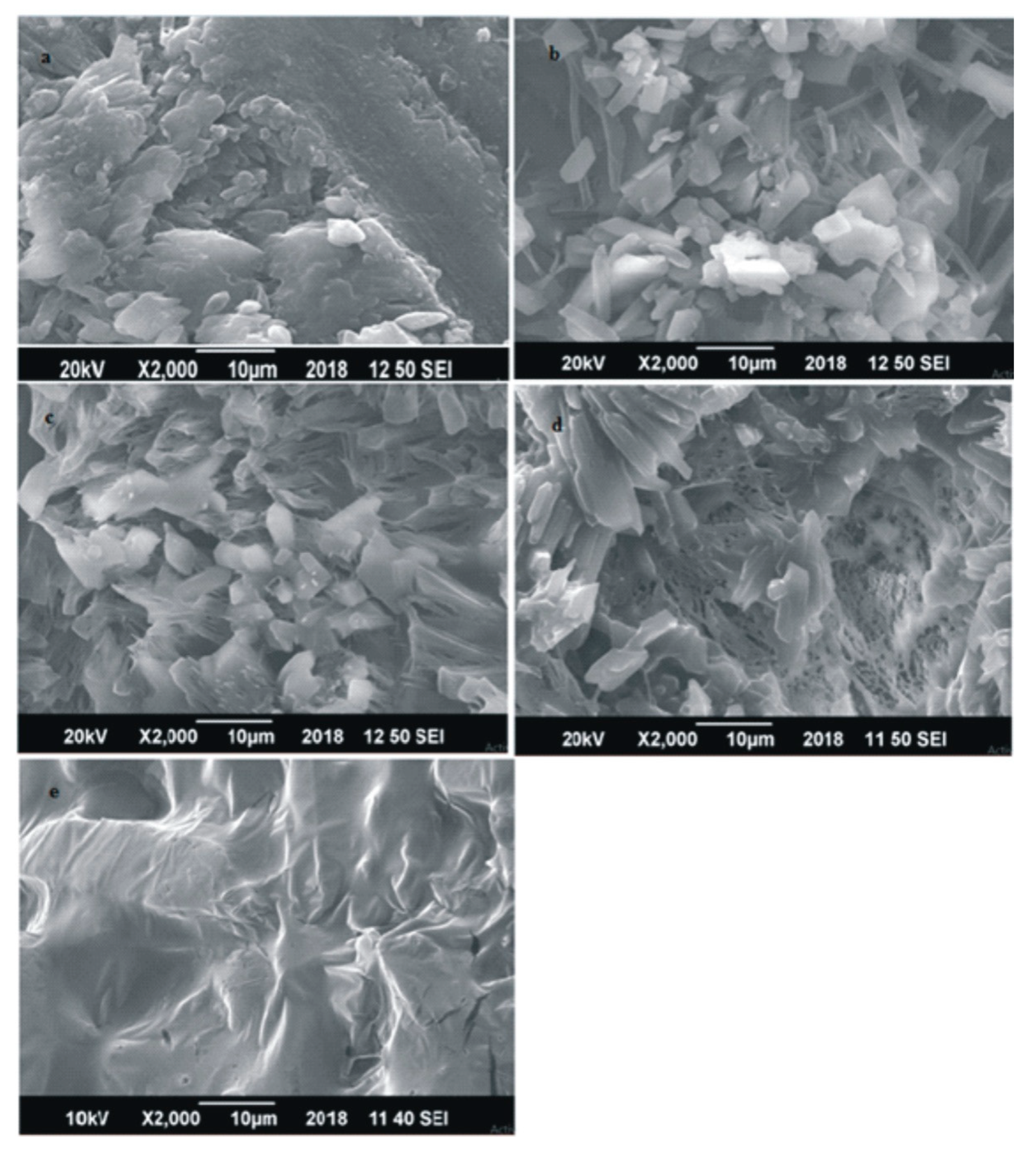
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
X-ray Diffract
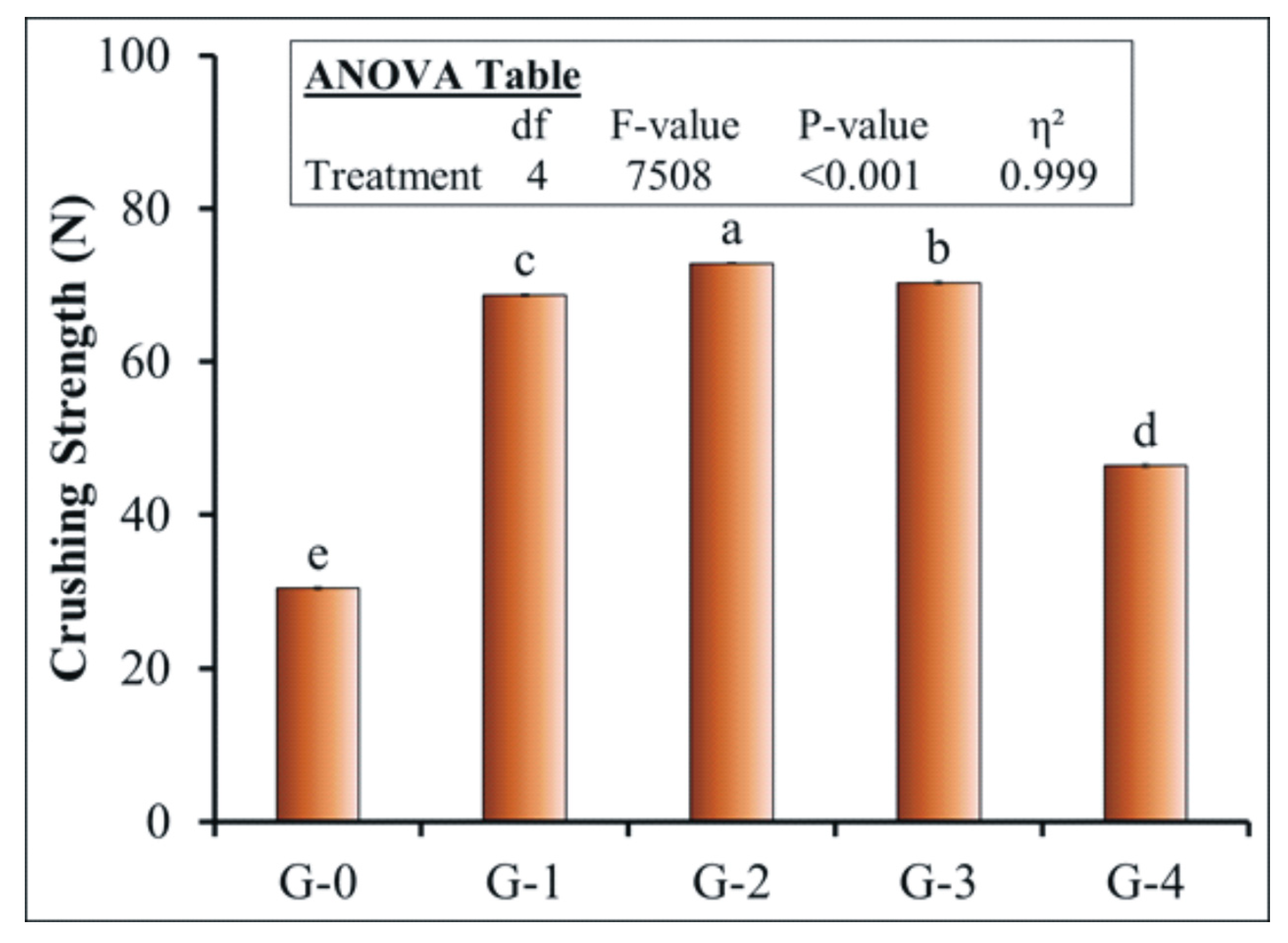
Crushing Strength
UV-Visible Spectrophotometer
2.1.4. Procedure for Release Rate
Release Kinetics
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.2.1. Soil Sampling and Analysis
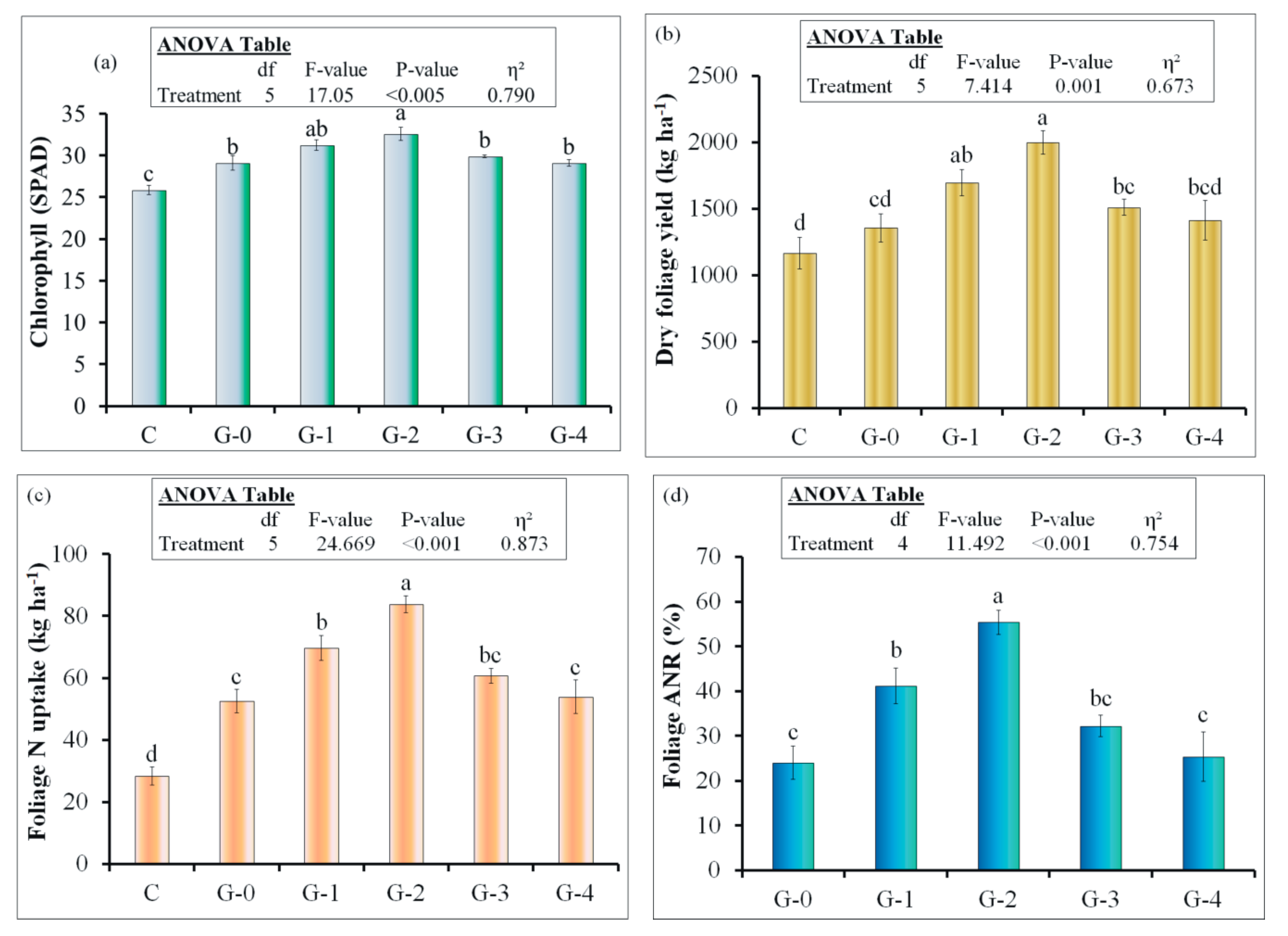
2.2.2. Plant Analysis
2.2.3. Apparent N Recovery
2.2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. Effect of Coating on Surface Morphology
3.2. FTIR
3.3. XRD
3.4. Effect of Coating on the Crushing Strength
3.5. Effect of Coating on the Rate of Urea Release
3.6. Release Kinetics
3.7. Pot Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Symbols | |
| ANR | Apparent nitrogen recovery |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| UV–VIS | Ultraviolet visible (UV) spectroscopy |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| FBC | Fluidized bed coater |
| G-0 | Uncoated urea |
| G-1 | 10% starch + 5% polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) + 5% molasses |
| G-2 | 10% starch + 5% PVA + 5% paraffin wax |
| G-3 | 5% gelatin + 10% gum arabic + 5% PW |
| G-4 | 5% molasses + 5% gelatin + 10% gum arabic |
| C | Control (untreated soil) |
| EC | Electrical conductivity (EC) |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
References
- Elferink, M.; Schierhorn, F. Global demand for food is rising. Can we meet it? Harv. Bus. Rev. 2016, 7, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Horrigan, L.; Lawrence, R.S.; Walker, P. How sustainable agriculture can address the environmental and human health harms of industrial agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reganold, J.P.; Elliott, L.F.; Unger, Y.L. Long-term effects of organic and conventional farming on soil erosion. Nature 1987, 330, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matson, P.A.; Naylor, R.; Ortiz-Monasterio, I. Integration of environmental, agronomic, and economic aspects of fertilizer management. Science 1998, 280, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, A.; Maynard, D.; Mills, H. Variations in nitrate accumulation among spinach cultivars. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1974, 99, 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Leghari, S.J.; Wahocho, N.A.; Laghari, G.M.; HafeezLaghari, A.; MustafaBhabhan, G.; HussainTalpur, K.; Bhutto, T.A.; Wahocho, S.A.; Lashari, A.A. Role of nitrogen for plant growth and development: A review. Adv. Environ. Biol. 2016, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Bevis, L. Soil Fertility and Poverty in Developing Countries. Choices 2019, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Naz, M.Y.; Sulaiman, S.A. Slow release coating remedy for nitrogen loss from conventional urea: A review. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Lam, S.K.; Mosier, A.; Luo, Y.; Chen, D. Ammonia volatilization from synthetic fertilizers and its mitigation strategies: A global synthesis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 232, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, N.; Raza, A. Nutrient use efficiency (NUE) for sustainable wheat production: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beig, B.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Jahan, Z.; Hussain, A.; Zia, M.H.; Mehran, M.T. Coating materials for slow release of nitrogen from urea fertilizer: A review. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1510–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Naderi, S.; Supuk, E.; Abbas, R.; Hassanpour, A. Urea finishing process: Prilling versus granulation. Procedia Eng. 2015, 102, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow-and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Efficiency in Agriculture; IFA, International Fertilizer Industry Association: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Paradelo, R.; Basanta, R.; Barral, M. Water-holding capacity and plant growth in compost-based substrates modified with polyacrylamide, guar gum or bentonite. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 243, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lligadas, G.; Ronda, J.; Galià, M.; Cádiz, V. Development of novel phosphorus-containing epoxy resins from renewable resources. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2006, 44, 6717–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shavit, U.; Shaviv, A.; Shalit, G.; Zaslavsky, D. Release characteristics of a new controlled release fertilizer. J. Control. Release 1997, 43, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, O.A. Polyethylene-coated urea. 1. Improved storage and handling properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.-H.; Geng, Y.-Q. Improving the quality of polymer-coated urea with recycled plastic, proper additives, and large tablets. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, J.; Rajasekharan Pillai, V. Membrane-encapsulated controlled-release urea fertilizers based on acrylamide copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1996, 60, 2347–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, M.; Jarosiewicz, A. Use of polysulfone in controlled-release NPK fertilizer formulations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4634–4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.; Man, Z.B.; Basit, A.; Thanh, T.H. Review on materials & methods to produce controlled release coated urea fertilizer. J. Control. Release 2014, 181, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sempeho, S.I.; Kim, H.T.; Mubofu, E.; Hilonga, A. Meticulous overview on the controlled release fertilizers. Adv. Chem. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.C.; Liu, Z. Superhydrophobic controlled-release fertilizers coated with bio-based polymers with organosilicon and nano-silica modifications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 19943–19953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andelkovic, I.B.; Kabiri, S.; Tavakkoli, E.; Kirby, J.K.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Losic, D. Graphene oxide-Fe (III) composite containing phosphate–A novel slow release fertilizer for improved agriculture management. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, A.; Khan Niazi, M.B.; Hussain, A.; Beig, B.; Jahan, Z.; Zafar, N.; Zia, M. Slow-release urea fertilizer from sulfur, gypsum, and starch-coated formulations. J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 1218–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lü, S.; Gao, C.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Liu, M.; Wu, L. Highly efficient adsorption of ammonium onto palygorskite nanocomposite and evaluation of its recovery as a multifunctional slow-release fertilizer. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 252, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolybaba, M.; Tabil, L.; Panigrahi, S.; Crerar, W.; Powell, T.; Wang, B. Biodegradable polymers: Past, present, and future. In Proceedings of the ASABE/CSBE North Central Intersectional Meeting, New Bern, NC, USA, 8–12 April 2006; American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.C.; Xie, J. Bio-based elastic polyurethane for controlled-release urea fertilizer: Fabrication, properties, swelling and nitrogen release characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.-M.; Li, H.-F.; Wang, C.-S.; Yang, J.; Huang, G.; Meng, X.; Zhou, Q. Degradable polyester/urea inclusion complex applied as a facile and environment-friendly strategy for slow-release fertilizer: Performance and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Ye, M.; Park, K. Biodegradable polymers for microencapsulation of drugs. Molecules 2005, 10, 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, M.K.; Naiji, M.; Kianmehr, M.H. Nitrogen release dynamics of a slow release urea pellet and its effect on growth, yield, and nutrient uptake of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2019, 42, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Yao, J. An eco-friendly slow-release urea fertilizer based on waste mulberry branches for potential agriculture and horticulture applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroto, A.S.; Guimarães, G.G.; Colnago, L.A.; Klamczynski, A.; Glenn, G.; Ribeiro, C. Controlled release of nitrogen using urea-melamine-starch composites. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, H.; Chu, H.; Li, J. Preparation and characterization of slow-release and water-retention fertilizer based on starch and halloysite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 1210–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beig, B.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Jahan, Z.; Pervaiz, E.; Abbas Shah, G.; Ul Haq, M.; Zafar, M.I.; Zia, M. Slow-Release Urea Prills Developed Using Organic and Inorganic Blends in Fluidized Bed Coater and Their Effect on Spinach Productivity. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeem, B.; KuShaari, K.; Naqvi, M.; Kok Keong, L.; Almesfer, M.K.; Al-Qodah, Z.; Naqvi, S.R.; Elboughdiri, N. Production and Characterization of Controlled Release Urea Using Biopolymer and Geopolymer as Coating Materials. Polymers 2020, 12, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, T.F.; Murawski, A.; Quirino, R.L. Bio-based polymers with potential for biodegradability. Polymers 2016, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zahrani, S. Controlled-release of fertilizers: Modelling and simulation. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1999, 37, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, Z.; He, X.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Zou, C.; Chen, X. The effects of controlled release urea on maize productivity and reactive nitrogen losses: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 246, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Khan Niazi, M.B.; Hussain, A.; Farooq, W.; Zia, M.H. Synthesis and characterization of zinc-coated urea fertilizer. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejcuś, K.; Śpitalniak, M.; Dąbrowska, J. Swelling behaviour of superabsorbent polymers for soil amendment under different loads. Polymers 2018, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Perez-Puyana, V.; Cordobés, F.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Development of superabsorbent soy protein-based bioplastic matrices with incorporated zinc for horticulture. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4825–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhi, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chi, C.P.; Chu, S.; Hayat, K.; Zhou, P. Rice straw as renewable components of horticultural growing media for purple cabbage. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 141274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Samarrai, M.N.; Hamzah, R.; Sam, S.; Noriman, N.; Dahham, O.S.; Idrus, S.; Adam, T. Slow release material from epoxidized natural rubber and rice husk composites for agriculture applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1019, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, G.; Nardi, S.; Cardarelli, M.; Ertani, A.; Lucini, L.; Canaguier, R.; Rouphael, Y. Protein hydrolysates as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canellas, L.P.; Olivares, F.L.; Aguiar, N.O.; Jones, D.L.; Nebbioso, A.; Mazzei, P.; Piccolo, A. Humic and fulvic acids as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battacharyya, D.; Babgohari, M.Z.; Rathor, P.; Prithiviraj, B. Seaweed extracts as biostimulants in horticulture. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 196, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ţolescu, C.; Iovu, H. Polymer conditioned fertilizers. UPB Sci. Bull Ser. B 2010, 72, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, M.M.; Cabral-Albuquerque, E.C.; Alves, T.L.; Pinto, J.C.; Fialho, R.L. Use of polyhydroxybutyrate and ethyl cellulose for coating of urea granules. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9984–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, M.; Zhan, F.; Wu, L. Preparation and properties of a slow-release membrane-encapsulated urea fertilizer with superabsorbent and moisture preservation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 4206–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Lyu, X.; Zheng, W. Synchronized relationships between nitrogen release of controlled release nitrogen fertilizers and nitrogen requirements of cotton. Field Crop. Res. 2015, 184, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.F.; Fogler, H.S. Fluidized Bed Reactors, Diffusion and Reaction in Porous Catalysts; Professional Reference Shelf, University of Michigan: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goniva, C.; Kloss, C.; Deen, N.G.; Kuipers, J.A.; Pirker, S. Influence of rolling friction on single spout fluidized bed simulation. Particuology 2012, 10, 582–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I.; Kalayci, M.; Kaya, Y.; Torun, A.; Aydin, N.; Wang, Y.; Arisoy, Z.; Erdem, H.; Yazici, A.; Gokmen, O. Biofortification and localization of zinc in wheat grain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 9092–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babadi, F.E.; Yunus, R.; Rashid, S.A.; Salleh, M.A.M.; Ali, S. New coating formulation for the slow release of urea using a mixture of gypsum and dolomitic limestone. Particuology 2015, 23, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, S. Utilization of polyethylene and paraffin waxes as controlled delivery systems for different fertilizers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2000, 39, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubkowski, K. Coating fertilizer granules with biodegradable materials for controlled fertilizer release. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. (EEMJ) 2014, 13, 2573–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houba, V.J.G.; Van Der Lee, J.J.; Novozamsky, I.; Walinga, I. Soil and Plant Analysis: A Series of Syllabi, Part 5; Wageningen Agricultural University, Department of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Sadaf, J.; Shah, G.A.; Shahzad, K.; Ali, N.; Shahid, M.; Ali, S.; Hussain, R.A.; Ahmed, Z.I.; Traore, B.; Ismail, I.M. Improvements in wheat productivity and soil quality can accomplish by co-application of biochars and chemical fertilizers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naz, M.; Sulaiman, S.; Ariwahjoedi, B.; Shaari, K.Z.K. Characterization of modified tapioca starch solutions and their sprays for high temperature coating applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, M.; Cea, M.; Medina, J.; González, A.; Diez, M.; Cartes, P.; Monreal, C.; Navia, R. Evaluation of biodegradable polymers as encapsulating agents for the development of a urea controlled-release fertilizer using biochar as support material. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yan, J.; Rajulu, A.V.; Xiang, A.; Luo, X. Fabrication and properties of polyvinyl alcohol/starch blend films: Effect of composition and humidity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 96, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.Y.; Sulaiman, S.A. Testing of starch-based carbohydrate polymer coatings for enhanced urea performance. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2014, 11, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrova, E.; Aleksandrov, B.; Khadisova, Z.T.; Krasavtsev, B. Structural and Mechanical Properties of Paraffin Wax Composites. Chem. Technol. Fuels Oils 2018, 54, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempeho, S.I.; Kim, H.T.; Mubofu, E.; Pogrebnoi, A.; Shao, G.; Hilonga, A. Encapsulated urea-Kaolinite Nanocomposite for controlled release fertilizer formulations. J. Chem. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodpran, T.; Benjakul, S.; Vittayanont, M.; Nalinanon, S. Physico-chemical properties of gelatin films incorporated with different hydrocolloids. Int. Proc. Chem. Biol. Environ. Eng. 2013, 53, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Félix, D.; Pérez-Martínez, C.; Castillo-Ortega, M.; Pérez-Tello, M.; Romero-García, J.; Ledezma-Pérez, A.; Del Castillo-Castro, T.; Rodríguez-Félix, F. pH-and temperature-sensitive semi-interpenetrating network hydrogels composed of poly (acrylamide) and poly (γ-glutamic acid) as amoxicillin controlled-release system. Polym. Bull. 2012, 68, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitanggang, E.P.O.; Purnomo, C.W. The Effects Of Binder On The Release Of Nutrient From Matrix-Based Slow Release Fertilizer. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Stafa-Zurich, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Enríquez, D.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Ramírez-Wong, B.; Torres-Chávez, P.; Castillo-Ortega, M.; Rodríguez-Félix, D.; Armenta-Villegas, L.; Ledesma-Osuna, A. Preparation, characterization and release of urea from wheat gluten electrospun membranes. Materials 2012, 5, 2903–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaño, N.M.; García-Oliva, F.; Jaramillo, V.J. Dissolved organic carbon affects soil microbial activity and nitrogen dynamics in a Mexican tropical deciduous forest. Plant Soil 2007, 295, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Yin, X.; Savoy, H.J.; McClure, A.; Essington, M.E. Ammonia Volatilization Loss and Corn Nitrogen Nutrition and Productivity with Efficiency Enhanced UAN and Urea under No-tillage. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor Affendi, N.M.; Yusop, M.K.; Othman, R. Efficiency of Coated Urea on Nutrient Uptake and Maize Production. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 1394–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, M.R.; Gitelson, A.A.; Rundquist, D.C. A comparison of two techniques for nondestructive measurement of chlorophyll content in grapevine leaves. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadchina, T.M.; Dmitrieva, V.V. Leaf chlorophyll content as a possible diagnostic mean for the evaluation of plant nitrogen uptake from the soil. J. Plant Nutr. 1995, 18, 1427–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Starch | PVA * | Molasses | Gelatin | Gum Arabic | Paraffin Wax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g/100 g of Urea) | ||||||
| G-1 | 10 | 5 | 5 | - | - | - |
| G-2 | 10 | 5 | - | - | - | 5 |
| G-3 | - | - | - | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| G-4 | - | - | 5 | 5 | 10 | - |
| Name of Model | Treatment | Adjusted R2 | Value of “a” | Value of “b” | χ2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modified hyperbola | G-0 | 0.7185 | 0.0924 | 0.0731 | 0.0614 |
| G-1 | 0.8136 | 0.0798 | 0.0627 | 0.0366 | |
| G-2 | 0.9200 | 0.0327 | 0.0242 | 0.0109 | |
| G-3 | 0.7853 | 0.0712 | 0.0546 | 0.0444 | |
| G-4 | 0.9116 | 0.0287 | 0.0198 | 0.0129 | |
| Schwartz and Sinclair formula | G-0 | 0.5954 | - | 0.1583 | 0.08832 |
| G-1 | 0.8282 | - | 0.0851 | 0.02908 | |
| G-2 | 0.8082 | - | 0.0509 | 0.02633 | |
| G-3 | 0.6891 | - | 0.1132 | 0.06629 | |
| G-4 | 0.8609 | - | 0.0344 | 0.02817 | |
| Modified Schwartz and Sinclair formula | G-0 | 0.53761 | 1 | 0.1583 | 0.10094 |
| G-1 | 0.80368 | 1 | 0.0851 | 0.03324 | |
| G-2 | 0.81366 | 0.97 | 0.0509 | 0.02559 | |
| G-3 | 0.64477 | 1 | 0.1132 | 0.07118 | |
| G-4 | 0.8465 | 1 | 0.0344 | 0.03110 |
| Sampling Occasion | Treatment | pH − | EC (dS m−1) | TOC (Mg ha−1) | DOC | Nmin | PAP | PAK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kg ha−1) | ||||||||
| Initial | Control | 8.1 ± 0.06 a* | 0.19 ± 0.03 NS** | 3.9 ± 0.3 c | 11.1 ± 0.3 c | 9.2 ± 0.5 d | 7.6 ± 0.3 c | 295 ± 12 b |
| Final | C | 8.0 ± 0.29 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 4.7 ± 0.4 bc | 12.3 ± 0.4 bc | 10.7 ± 0.5 d | 8.8 ± 0.6 bc | 316 ± 8 ab |
| G-0 | 7.9 ± 0.01 a | 0.21 ± 0.01 | 5.0 ± 0.2 b | 13.6 ± 0.2 b | 19.4 ± 1.1 c | 9.1 ± 0.6 ab | 332 ± 17 ab | |
| G-1 | 7.4 ± 0.05 b | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 6.1 ± 0.5 a | 16.2 ± 0.5 a | 23.2 ± 0.6 a | 9.8 ± 0.5 ab | 334 ± 25 ab | |
| G-2 | 7.2 ± 0.03 b | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 6.1 ± 0.4 a | 16.5 ± 1.0 a | 24.2 ± 0.6 a | 10.5 ± 0.4 a | 357 ± 15 a | |
| G-3 | 7.4 ± 0.06 b | 0.21 ± 0.02 | 5.6 ± 0.4 ab | 15.5 ± 0.4 a | 22.6 ± 0.4 ab | 9.6 ± 0.6 ab | 349 ± 9 a | |
| G-4 | 7.4 ± 0.06 b | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 5.6 ± 0.3 ab | 15.1 ± 0.6 a | 20.7 ± 0.8 bc | 9.1 ± 0.5 ab | 336 ± 23 ab | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beig, B.; Niazi, M.B.K.; Jahan, Z.; Kakar, S.J.; Shah, G.A.; Shahid, M.; Zia, M.; Haq, M.U.; Rashid, M.I. Biodegradable Polymer Coated Granular Urea Slows Down N Release Kinetics and Improves Spinach Productivity. Polymers 2020, 12, 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112623
Beig B, Niazi MBK, Jahan Z, Kakar SJ, Shah GA, Shahid M, Zia M, Haq MU, Rashid MI. Biodegradable Polymer Coated Granular Urea Slows Down N Release Kinetics and Improves Spinach Productivity. Polymers. 2020; 12(11):2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112623
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeig, Bilal, Muhammad Bilal Khan Niazi, Zaib Jahan, Salik Javed Kakar, Ghulam Abbas Shah, Muhammad Shahid, Munir Zia, Midrar Ul Haq, and Muhammad Imtiaz Rashid. 2020. "Biodegradable Polymer Coated Granular Urea Slows Down N Release Kinetics and Improves Spinach Productivity" Polymers 12, no. 11: 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112623
APA StyleBeig, B., Niazi, M. B. K., Jahan, Z., Kakar, S. J., Shah, G. A., Shahid, M., Zia, M., Haq, M. U., & Rashid, M. I. (2020). Biodegradable Polymer Coated Granular Urea Slows Down N Release Kinetics and Improves Spinach Productivity. Polymers, 12(11), 2623. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12112623








