Base Promoted Intumescence of Phenols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparations of Sodium Phenolates
2.3. Thermal Treatment
2.4. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
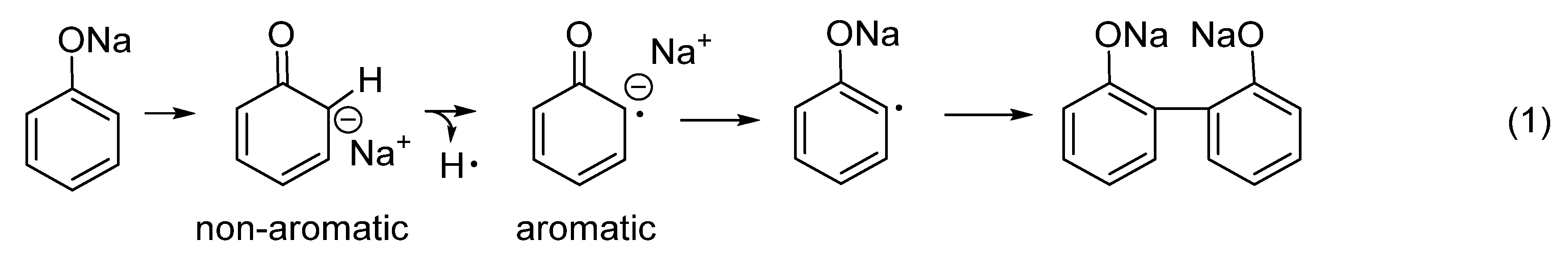
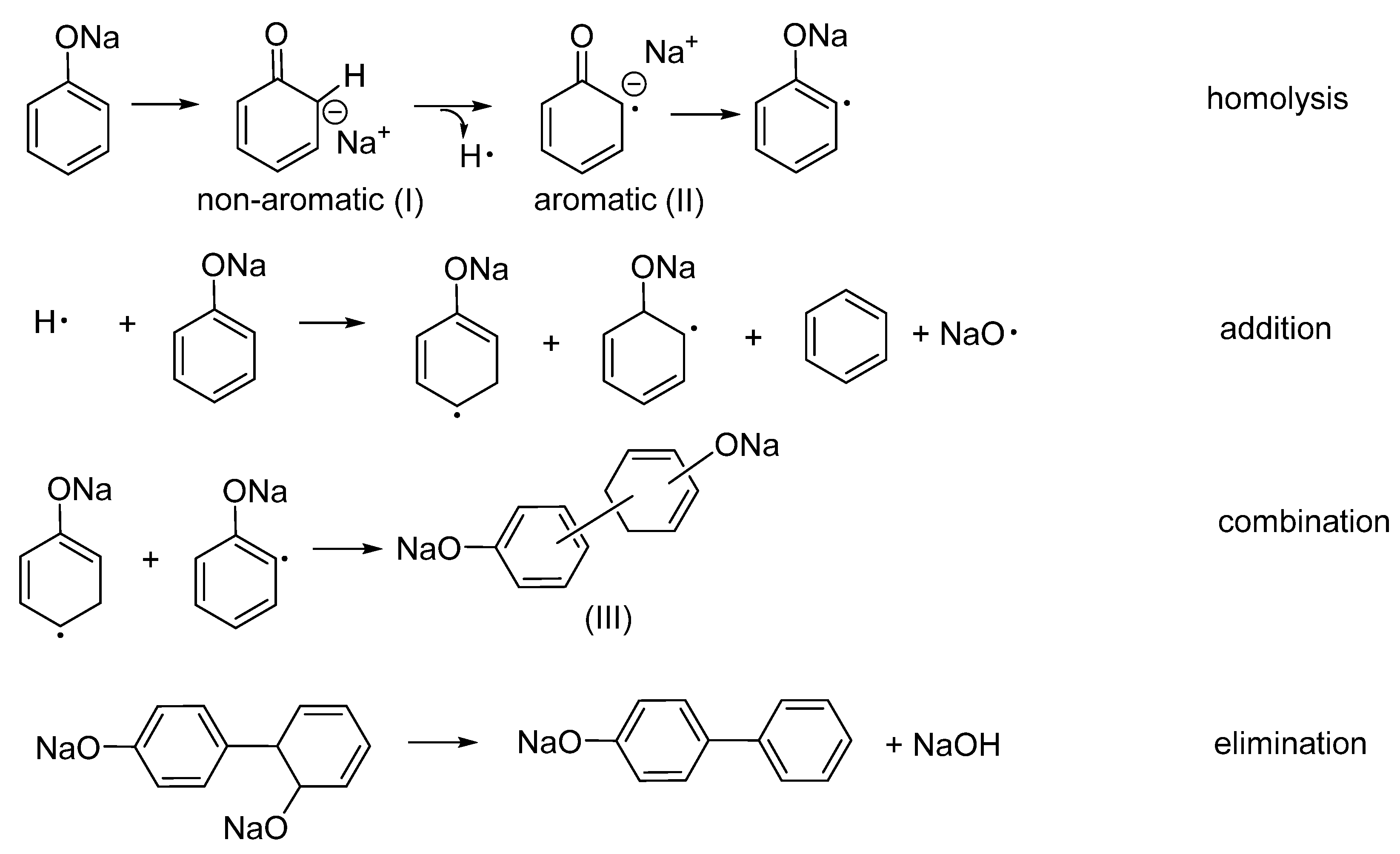
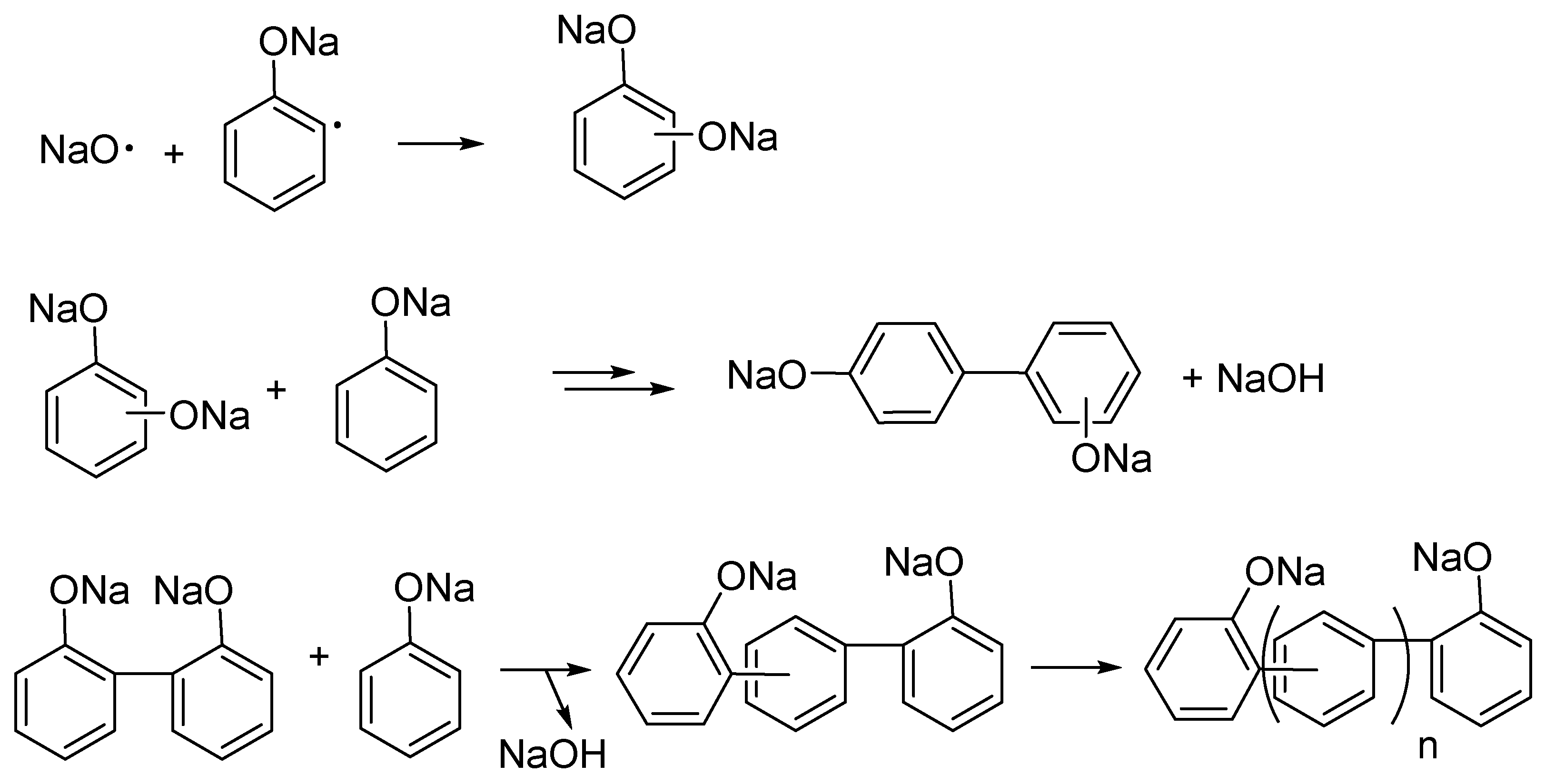
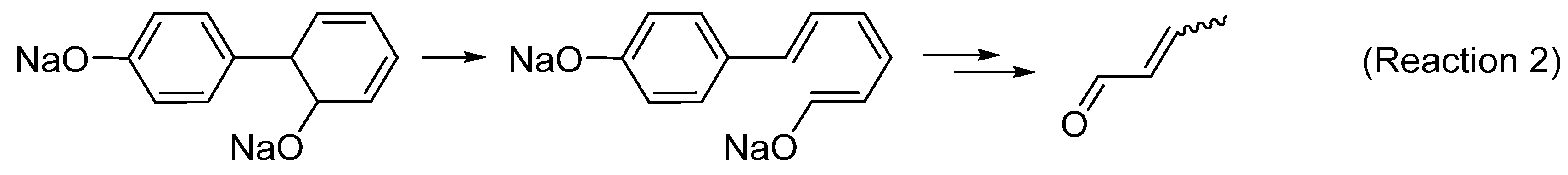
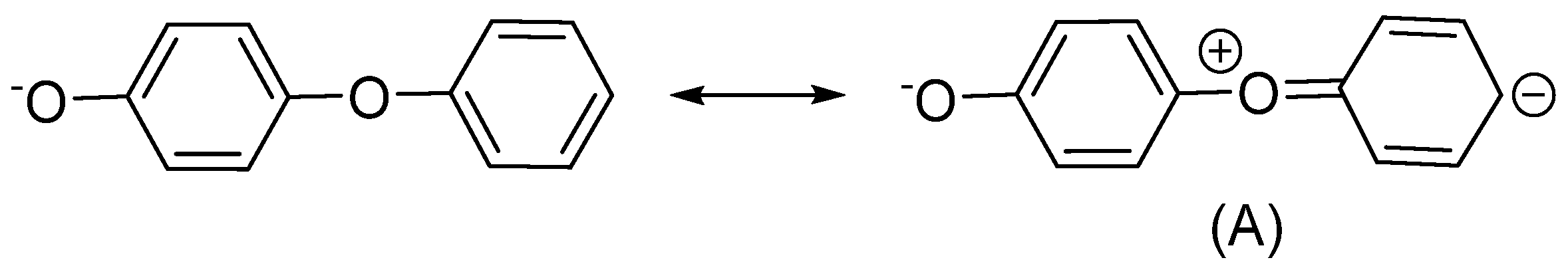
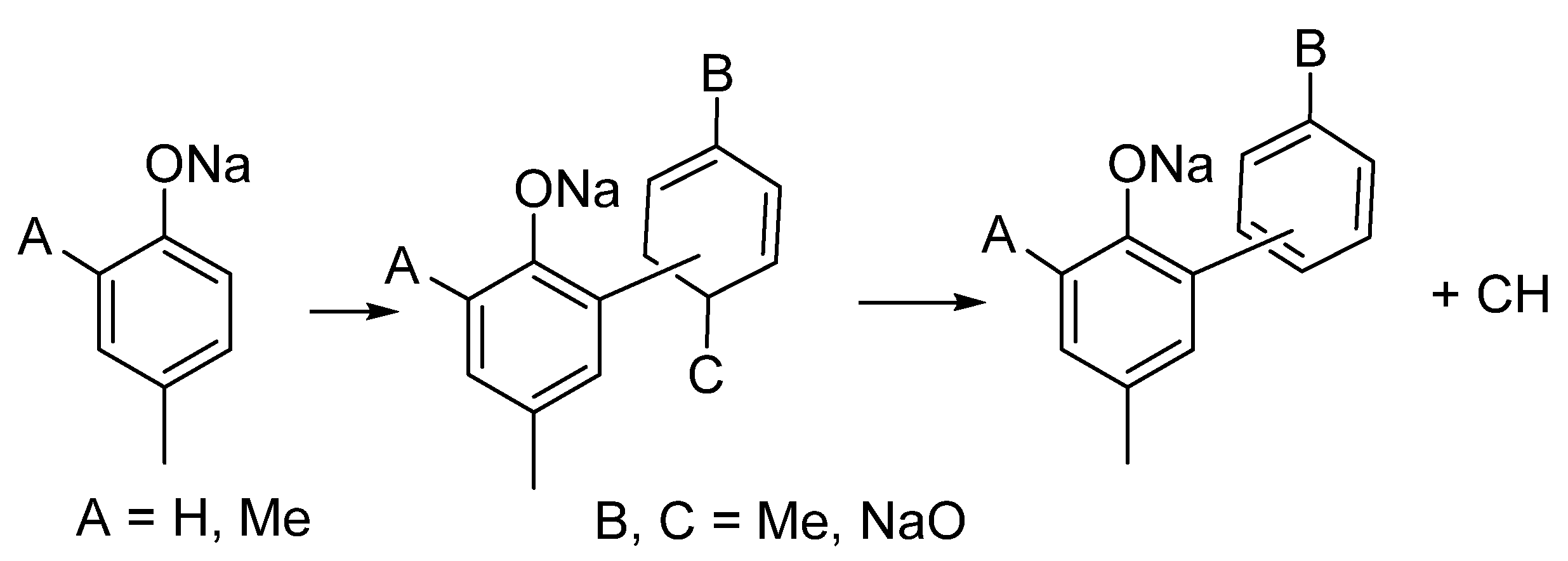
3.1. Intumescent Process of Sodium Phenolate
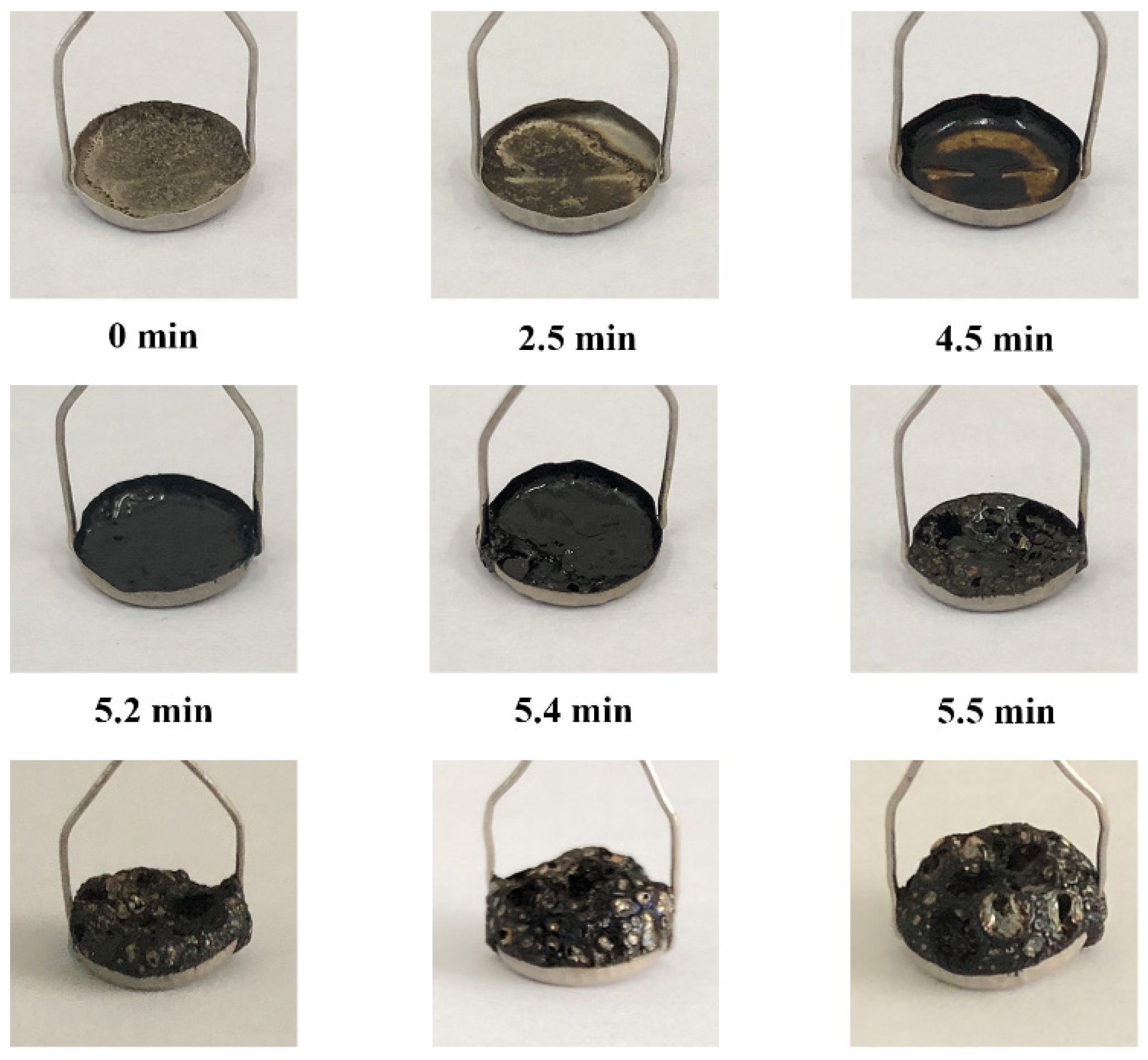
3.1.1. Appearance
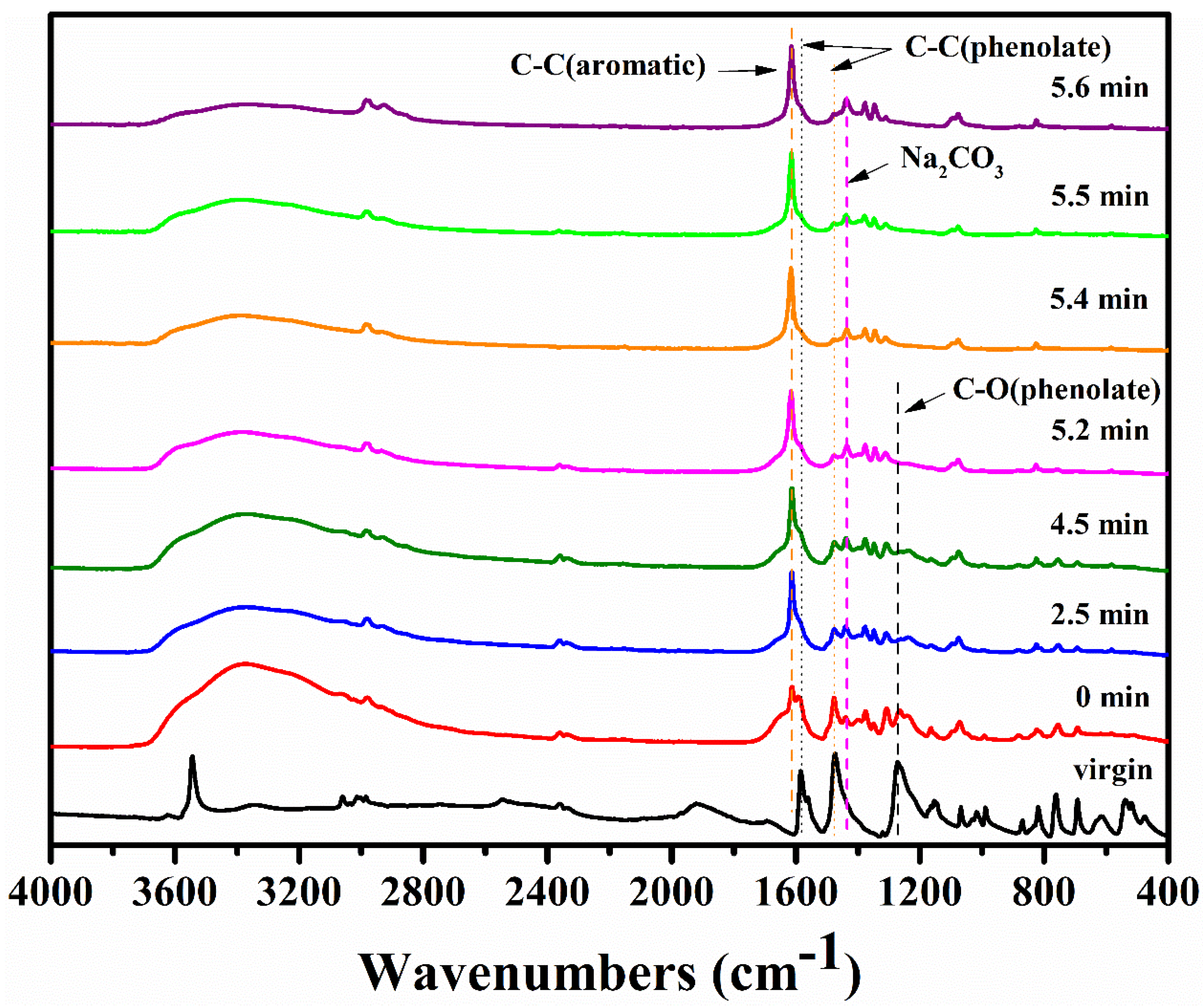
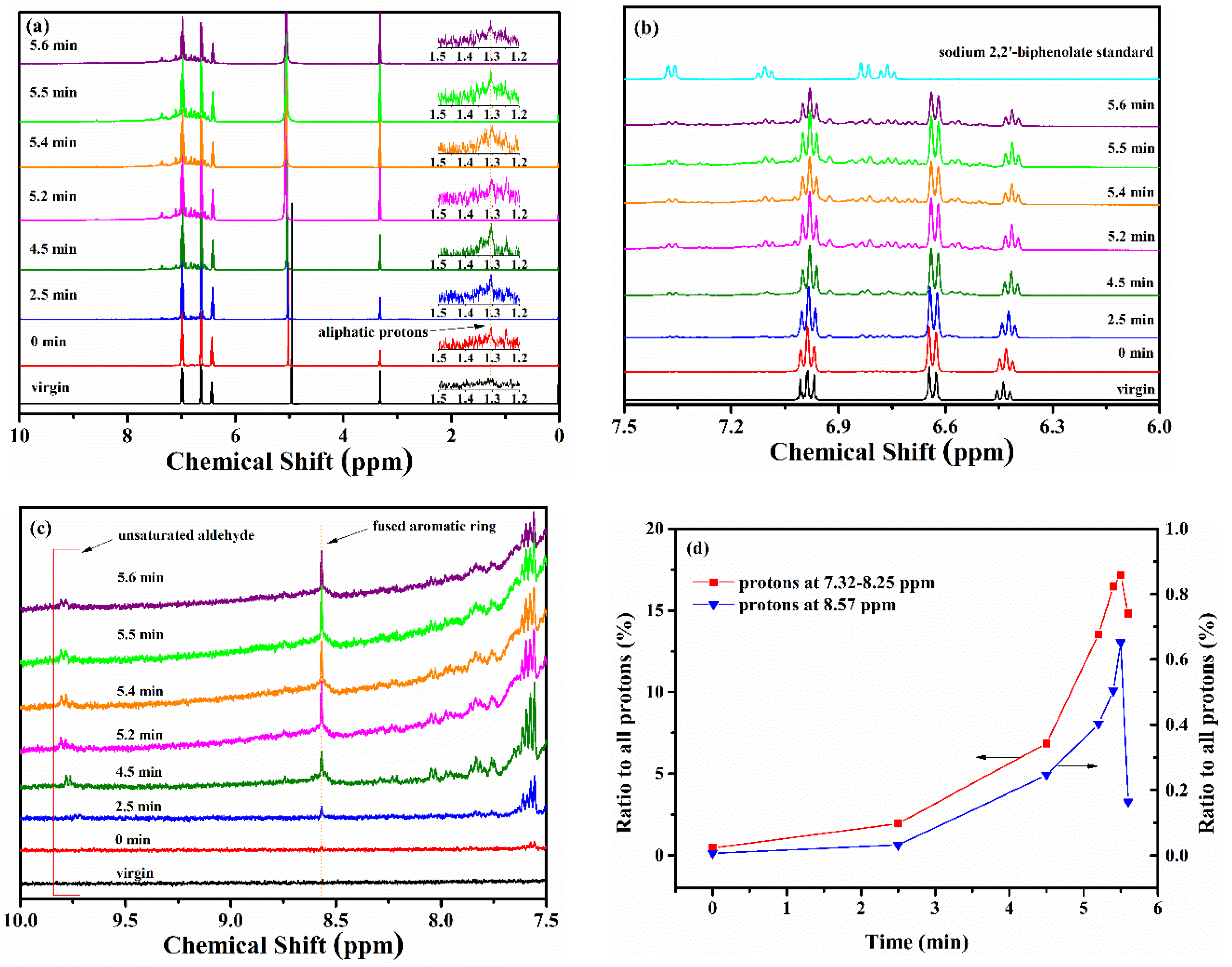
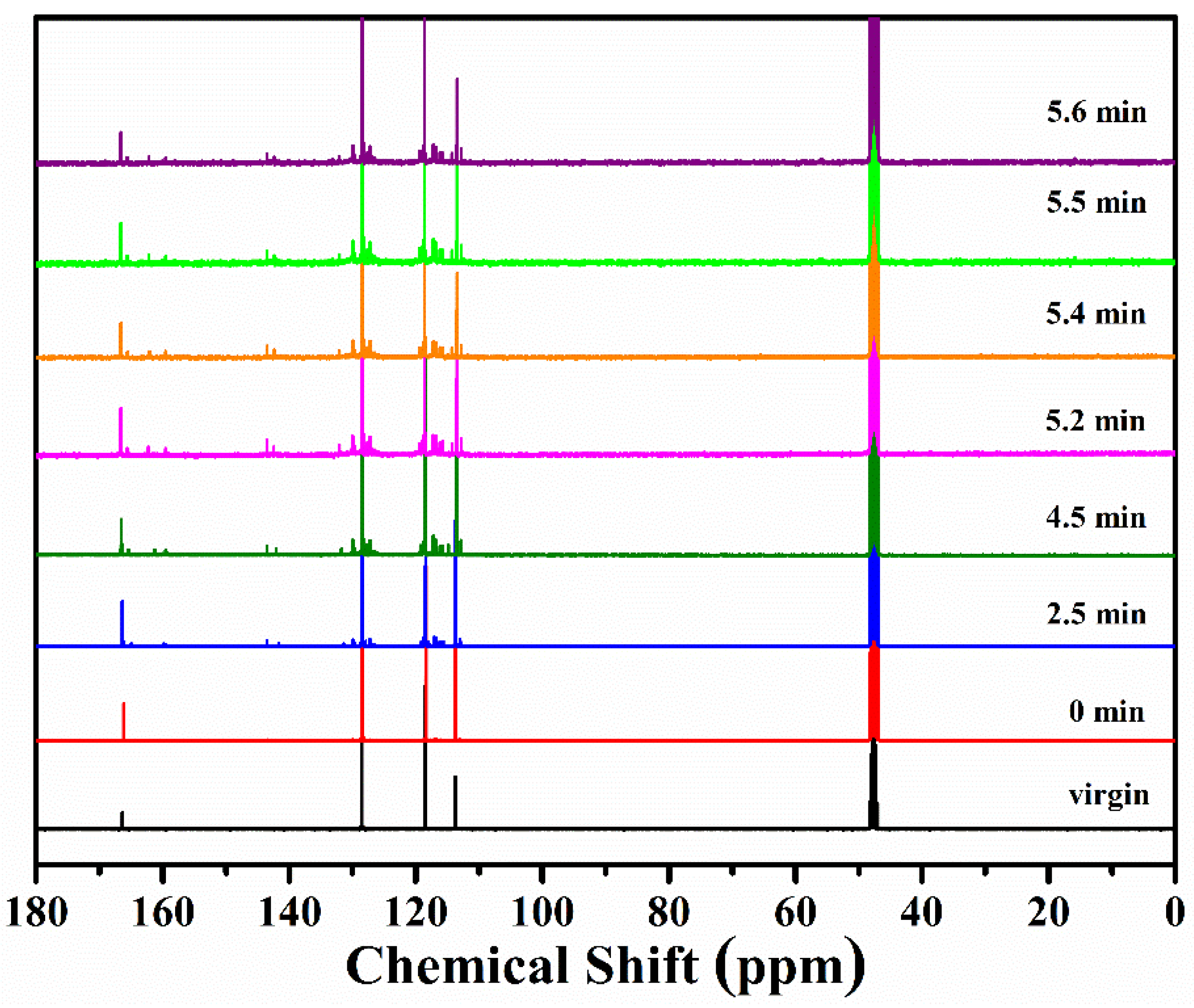
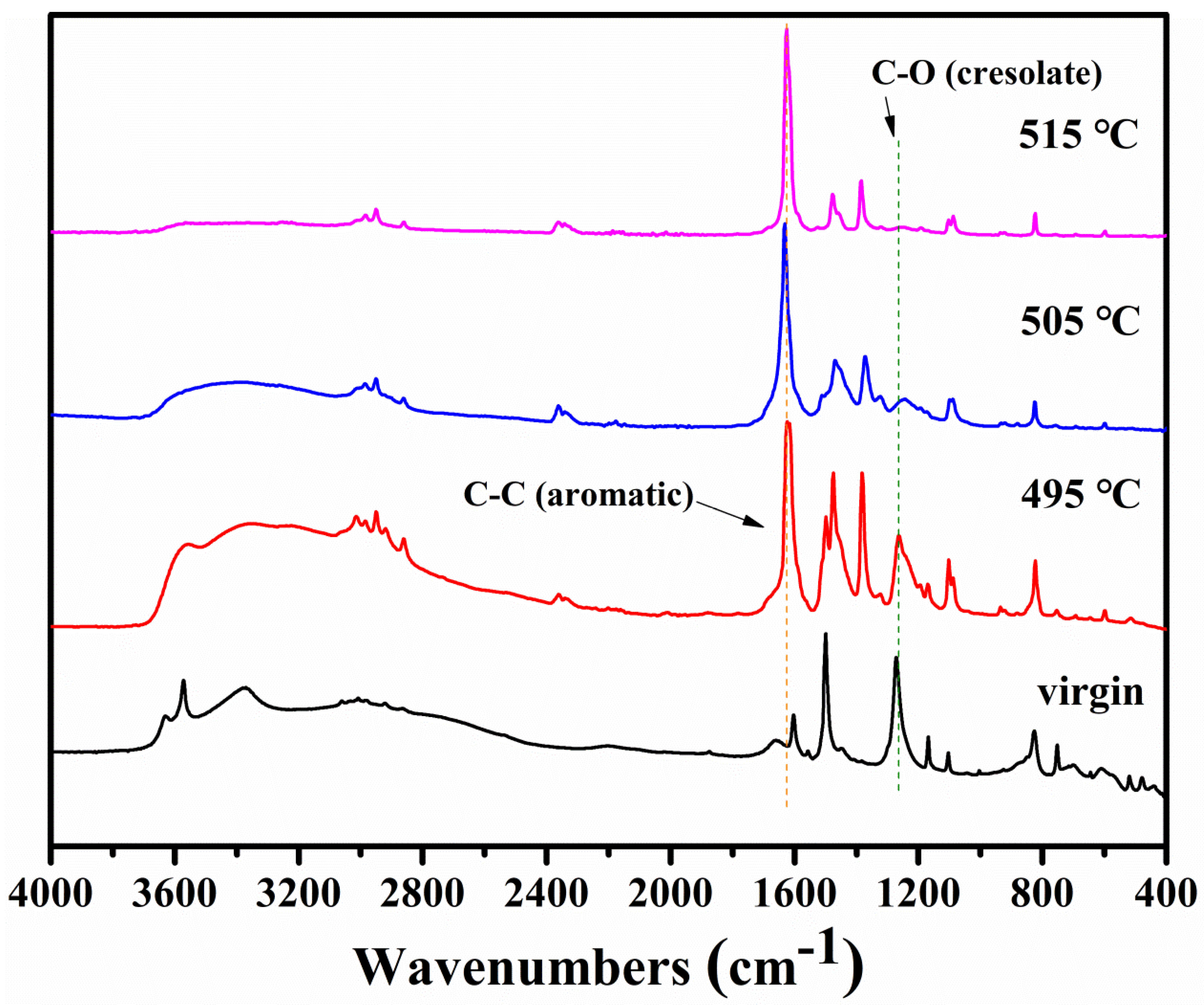
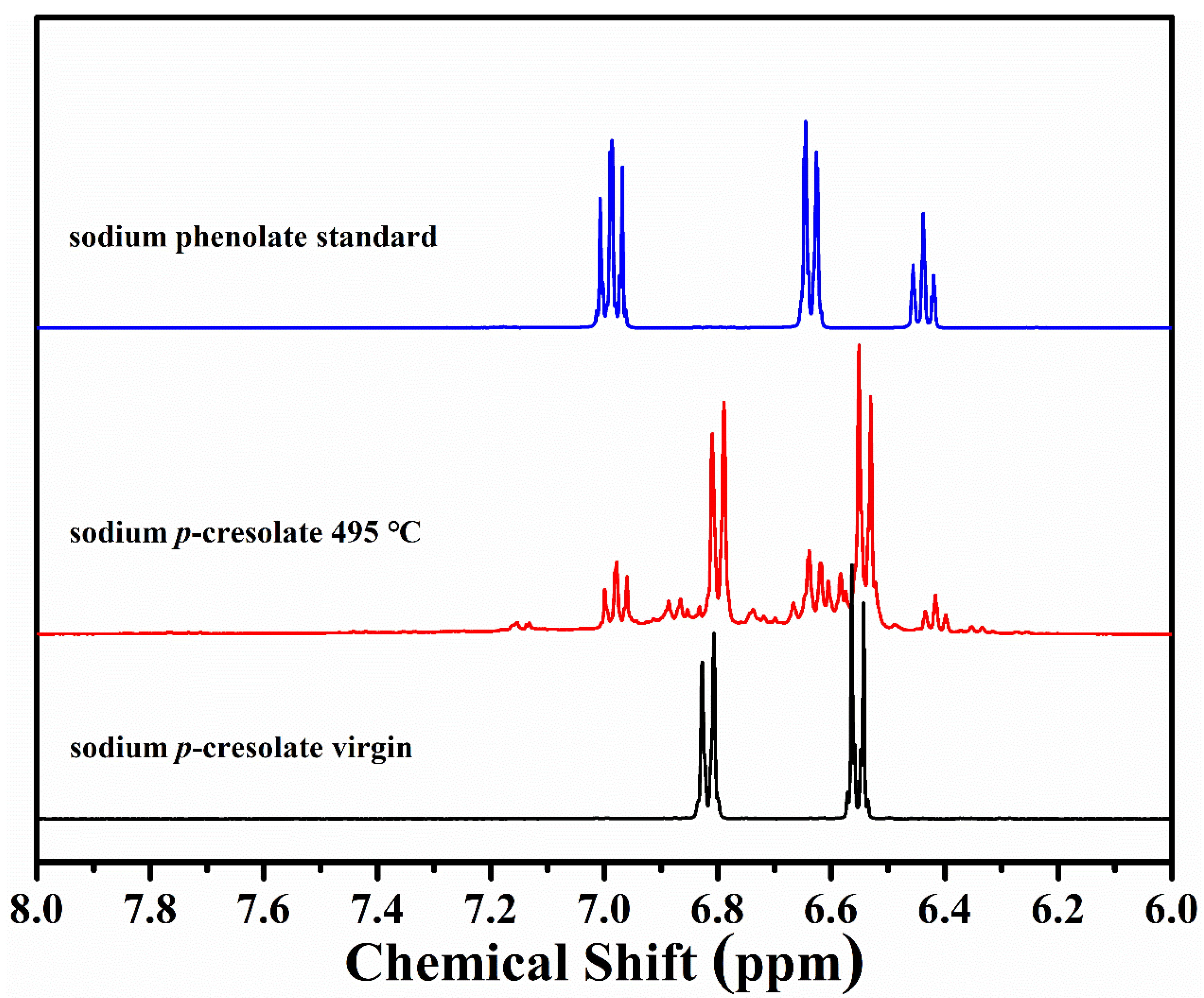
3.1.2. FTIR and NMR Studies of Residues
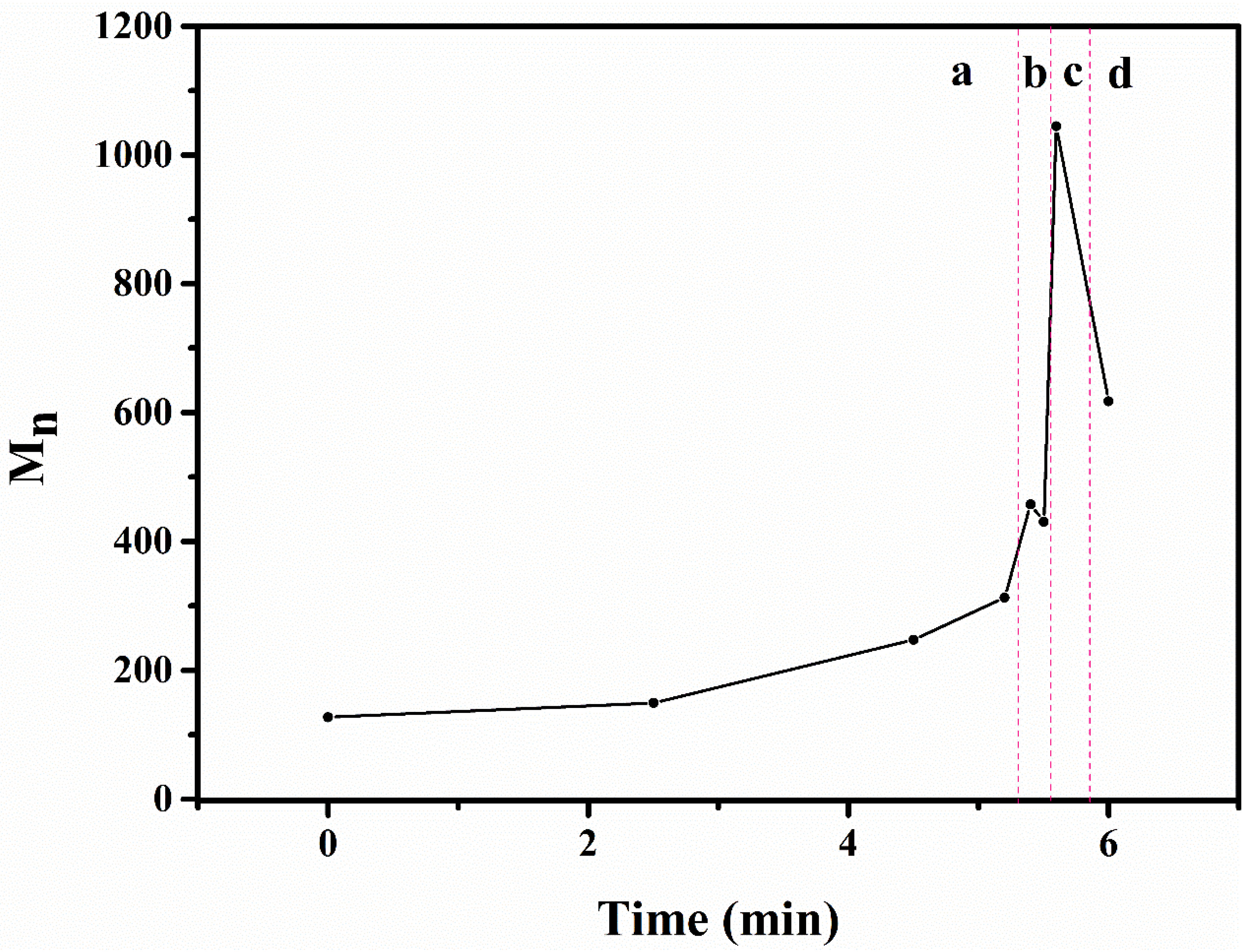
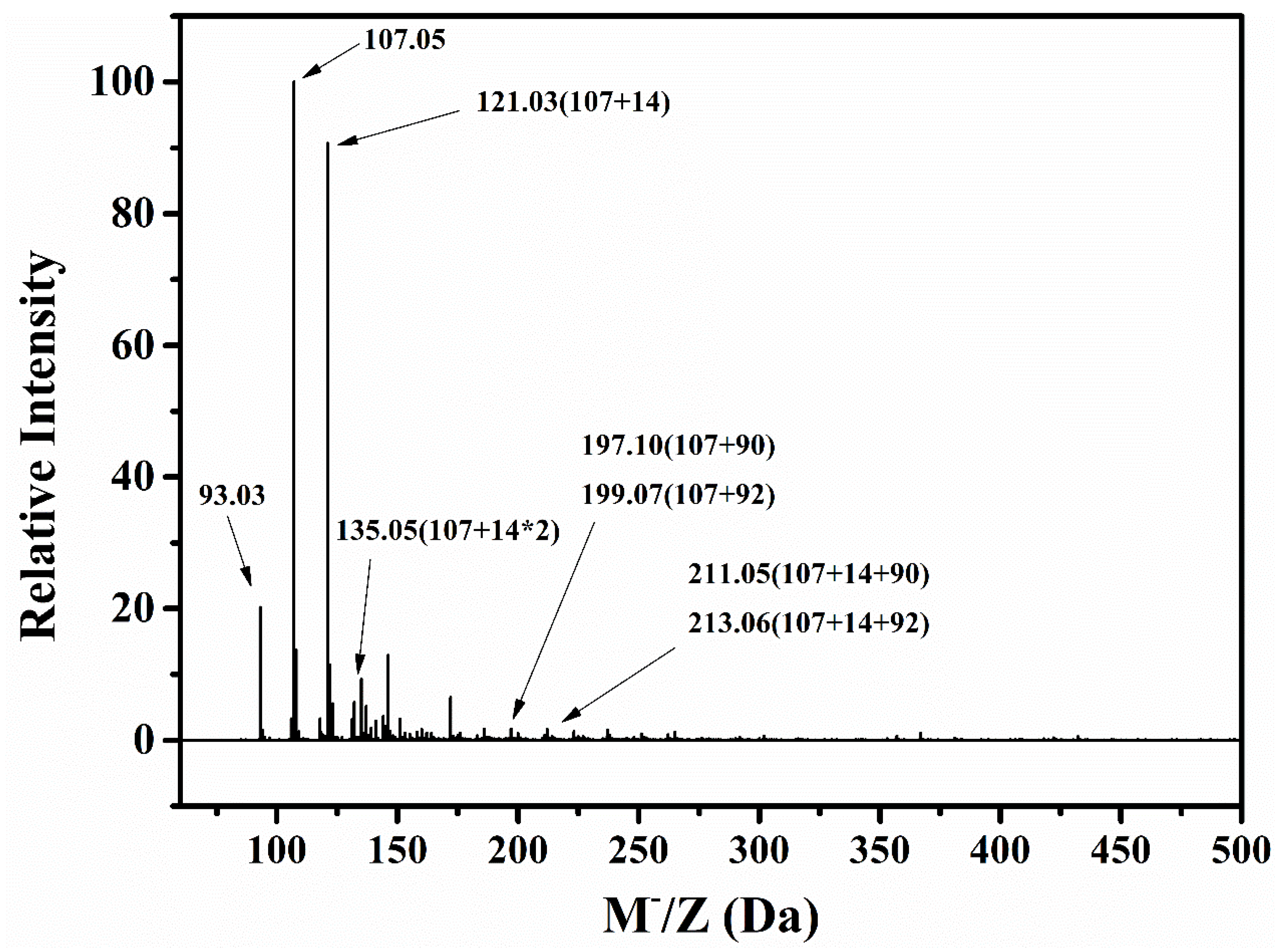
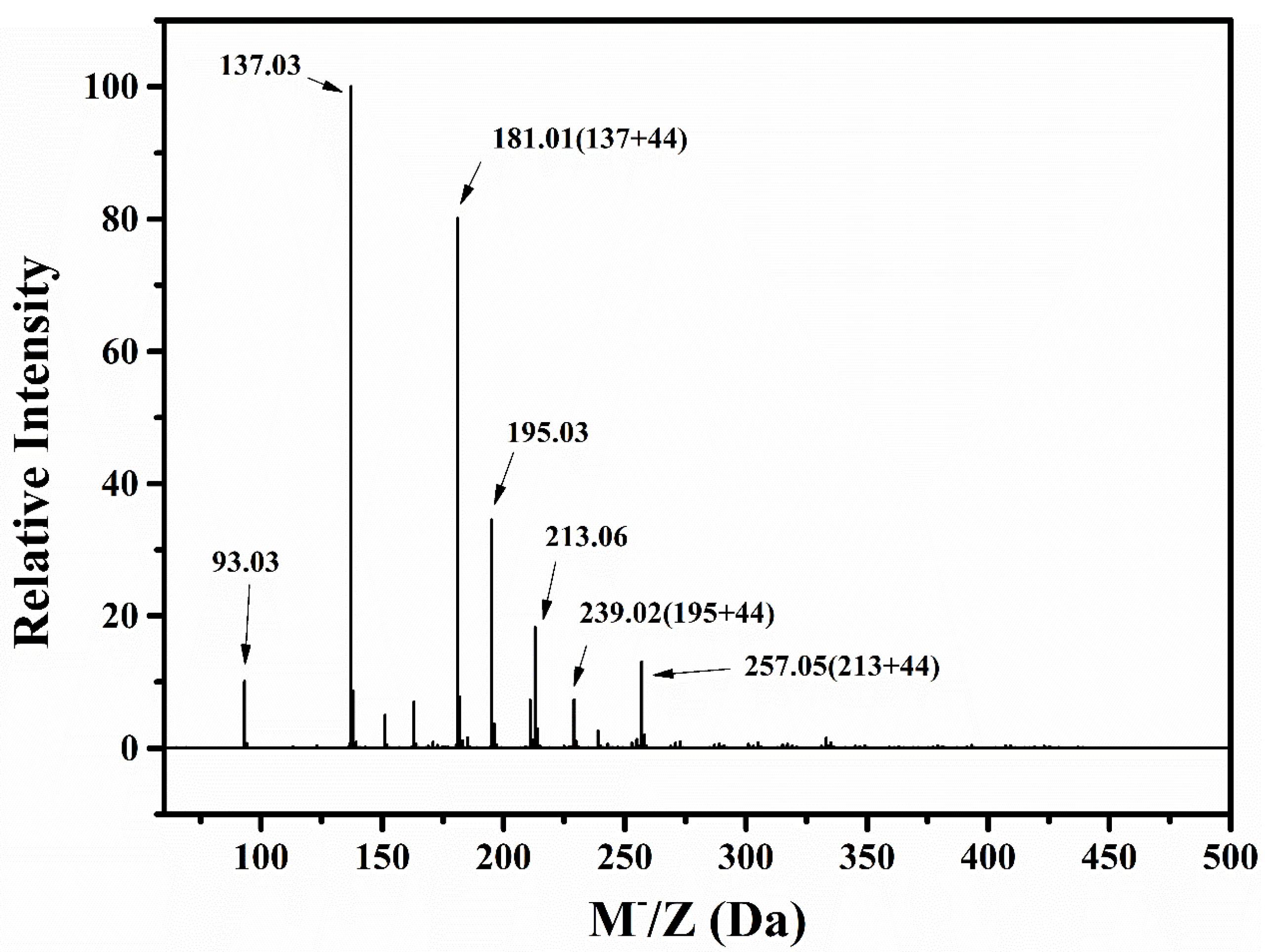
3.1.3. Molecular Weights of Degraded Materials
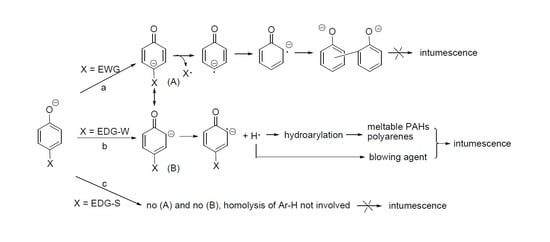
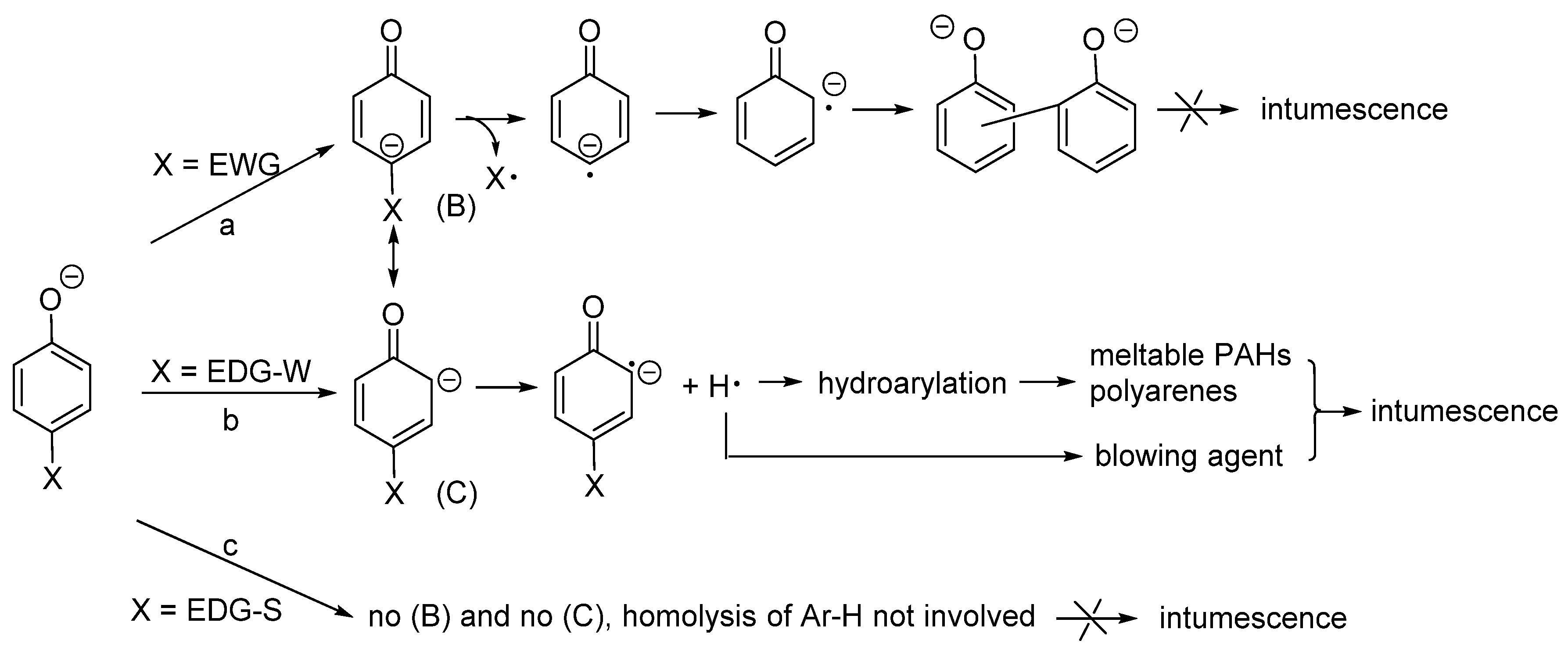
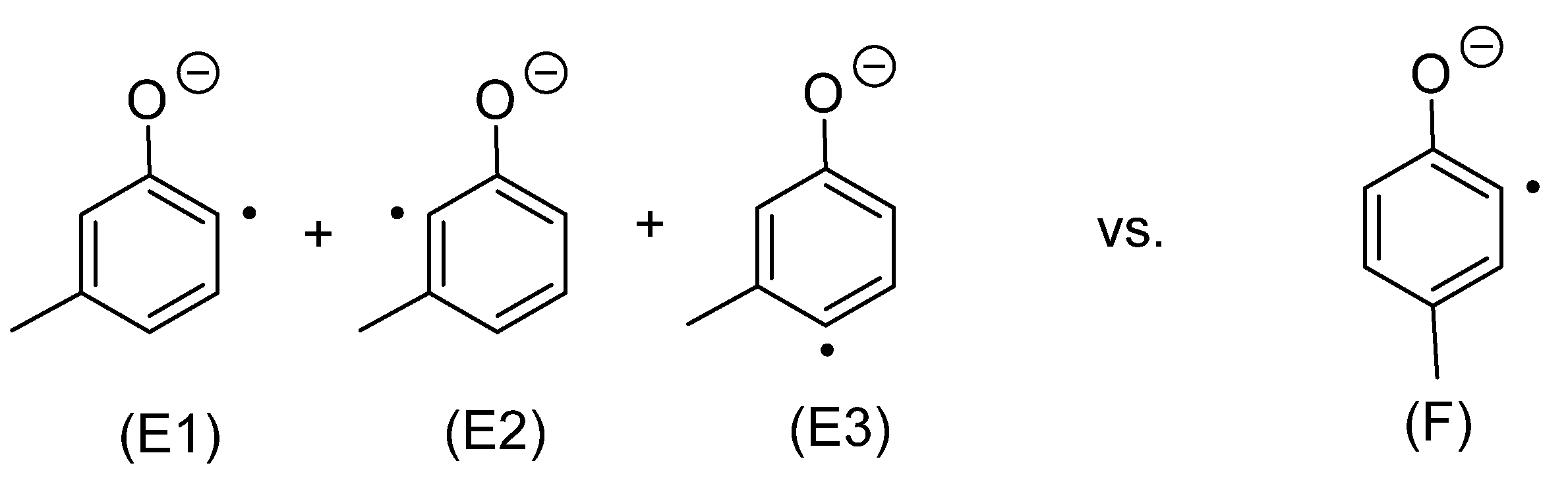
3.2. Substituents’ Effect on the Intumescence
3.2.1. Sodium Alkylphenolates
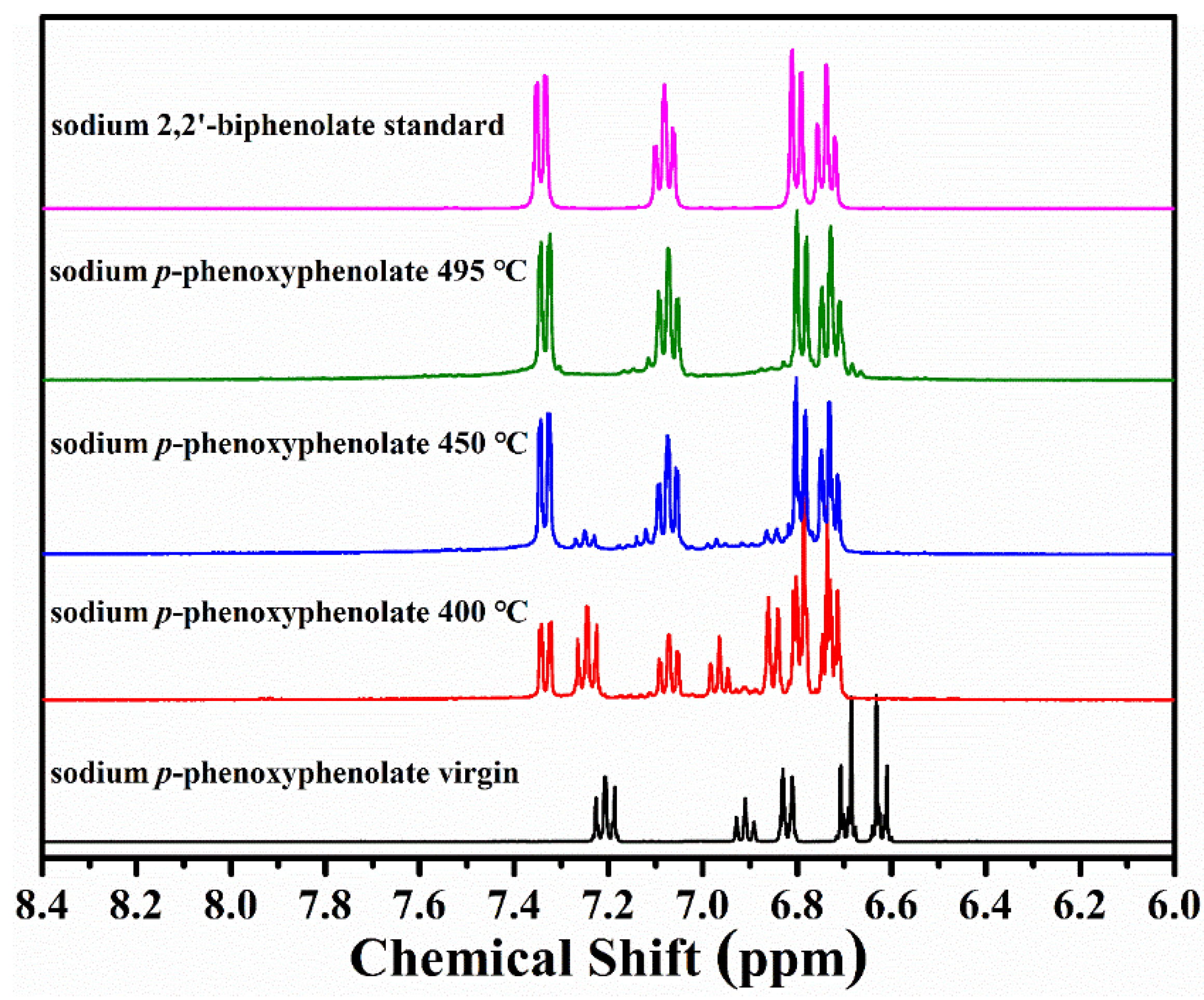
3.2.2. Sodium p-Phenoxyphenolate
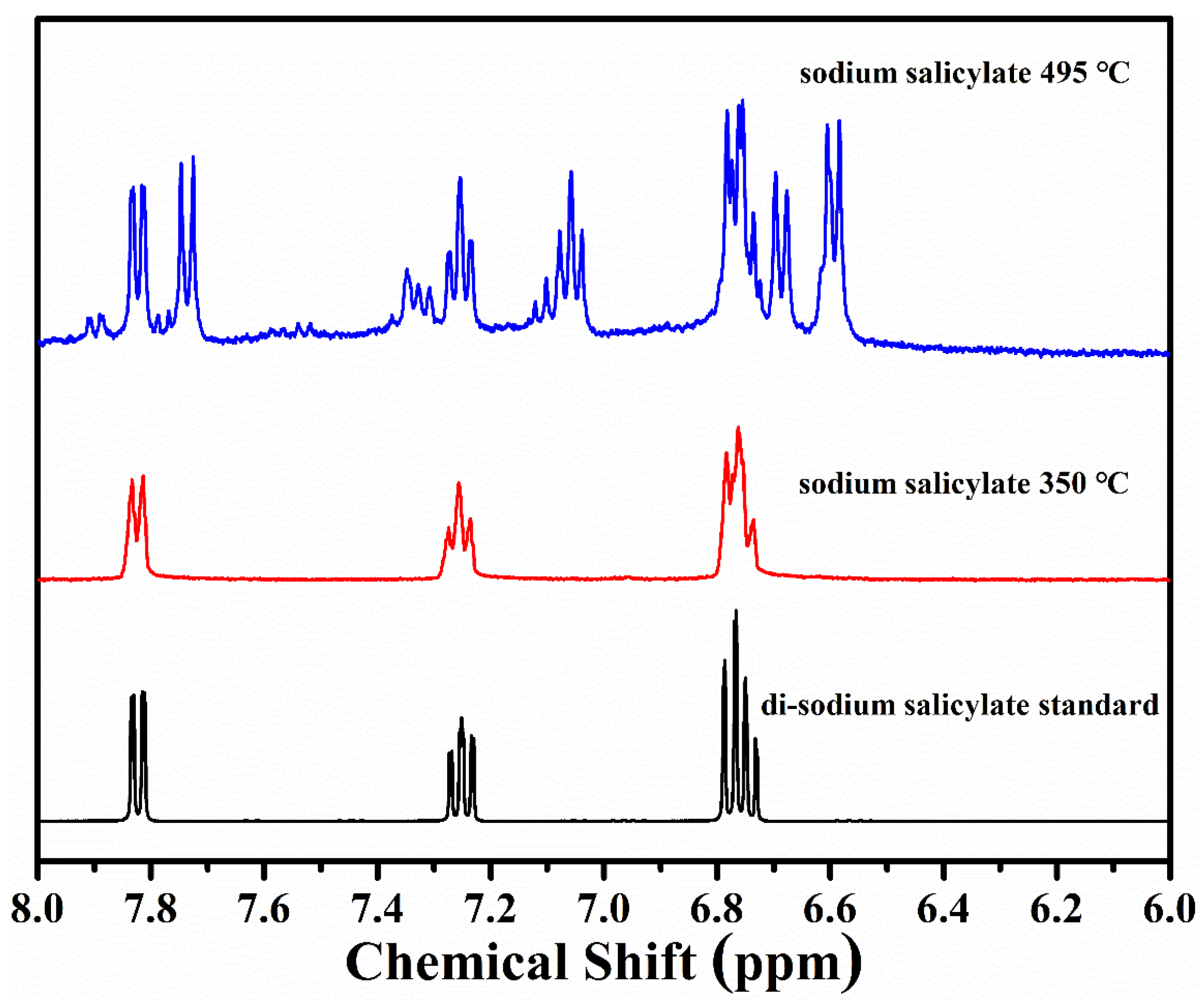
3.2.3. Biphenolates and Sodium Salicylates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tramm, H.; Clar, C.; Kuhnel, P.; Schuff, W. Fireproofing of Wood. US2106938, 1938. [Google Scholar]
- Olson, J.W.; Bechle, C.W. Bituminous Flame Resistant Compositions and Articles Coated Therewith. US2442706, 1941. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.; Juda, W.; Soll, S. Fire-Retardant Composition and Process. US2452054, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Ballistreri, A.; Montaudo, G.; Scamporrino, E.; Puglisi, C.; Vitalini, D.; Cucinella, S. Intumescent flame retardants for polymers. IV. The polycarbonate–aromatic sulfonates system. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-1 Polym. Chem. 1988, 26, 2113–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Martinasso, G. Intumescent fire-retardant systems. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1989, 23, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.W.; Chow, W.K. A brief review of intumescent fire retardant coatings. Arch. Sci. Rev. 2003, 46, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Martinasso, G.; Costa, L.; Gobetto, R. Thermal-degradation of pentaerythritol diphosphate, model-compound for fire retardant intumescent systems. II. intumescence step. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1990, 28, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, K.M.; Baum, H.R.; Kashiwagi, T. Three-dimensional modeling of intumescent behavior in fires. Fire Safety Sci. 1997, 5, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bourbigot, S.; Duquesne, S.; Leroy, J.M. Modeling of heat transfer of a polypropylene-based intumescent system during combustion. J. Fire Sci. 1999, 17, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weil, E.D. Fire-protective and flame-retardant coatings—A state-of-the-art review. J. Fire Sci. 2011, 29, 259–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandersall, H.L. Intumescent coating systems, their development and chemistry. J. Fire Flammability 1971, 2, 97–140. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, R.G.; Khanna, A.S. Intumescent coatings: A review on recent progress. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 2017, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, M.; Weil, E.D. Fire Retardant Materials, Vol. 2, Mechanisms and Modes of Action in Flame Retardancy of Polymers; Horrocks, A.R., Price, D., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2001; pp. 31–68. [Google Scholar]
- Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Trossarelli, L.; Costanzi, F.; Landoni, G. Study of the mechanism of intumescence in fire retardant polymers. IV. evidence of ester formation in ammonium polyphosphate pentaerythritol mixtures. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1984, 8, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Trossarelli, L. Study of the mechanism of intumescence in fire retardant polymers. V. mechanism of formation of gaseous products in the thermal-degradation of ammonium polyphosphate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1985, 12, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camino, G.; Costa, L.; Trossarelli, L.; Costanzi, F.; Pagliari, A. Study of the mechanism of intumescence in fire retardant polymers. VI. mechanism of ester formation in ammonium polyphosphate pentaerythritol mixtures. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1985, 12, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delobel, R.; Ouassou, N.; Lebras, M.; Leroy, J.M. Fire retardance of polypropylene—Action of diammonium pyrophosphate pentaerythritol intumescent mixture. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1989, 23, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delobel, R.; Lebras, M.; Ouassou, N.; Alistiqsa, F. Thermal behaviors of ammonium polyphosphate-pentaerythritol and ammonium pyrophosphate-pentaerythritol intumescent additives in polypropylene formulations. J. Fire Sci. 1990, 8, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Lebras, M.; Delobel, R. Carbonization mechanisms resulting from intumescence association with the ammonium polyphosphate-pentaerythritol fire-retardant system. Carbon 1993, 31, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Lebras, M.; Delobel, R.; Breant, P.; Tremillon, J.M. Carbonization mechanisms resulting from intumescence. II. association with an ethylene terpolymer and the ammonium polyphosphate pentaerythritol fire-retardant system. Carbon 1995, 33, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbigot, S.; Le Bras, M.; Duquesne, S.; Rochery, M. Recent advances for intumescent polymers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2004, 289, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yao, Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Cao, W.H. On the origin of alkali-catalyzed aromatization of phenols. Polymers 2019, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, H.; Walker, P.L., Jr. The effects of impregnation of coal by alkali salts upon carbonization properties. Fuel Process. Technol. 1979, 2, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakowski, D.J.; Jones, J.M. Uncatalysed and potassium-catalysed pyrolysis of the cell-wall constituents of biomass and their model compounds. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 83, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulijn, J.A.; Cerfontain, M.; Kapteijn, F. Mechanism of the potassium catalysed gasification of carbon in CO2. Fuel 1984, 63, 1043–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, P. Pyrolysis of cellulose, xylan and lignin with the K2CO3 and ZnCl2 addition for bio-oil production. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.X.; Chen, M.G.; Zhu, X.F.; Min, F.F.; Tan, Z.C. Catalytic effects of eight inorganic additives on pyrolysis of pine wood sawdust by microwave heating. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2008, 82, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nzihou, A.; Stanmore, B.; Lyczko, N.; Minh, D.P. The catalytic effect of inherent and adsorbed metals on the fast/flash pyrolysis of biomass: A review. Energy 2019, 170, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apaydin-Varol, E.; Puttun, A.E. Preparation and characterization of pyrolytic chars from different biomass samples. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 98, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthomieu, C.; Boussac, A. FTIR and EPR study of radicals of aromatic-amino-acids 4-methylimidazole and phenol generated by uv irradiation. Biospectroscopy 1995, 1, 187–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonella, M.; Suter, H.U. Formation of phenolate anion-counterion complexes can explain the vibrational properties of the phenolate anion in solution. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 7867–7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, W.W. (Ed.) Sadtler Handbook of Proton NMR Spectra; Sadtler Research Laboratories Inc: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Thonhauser, T.; Ceresoli, D.; Marzari, N. NMR shifts for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from first-principles. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2009, 109, 3336–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bax, A.; Ferretti, J.A.; Nashed, N.; Jerina, D.M. Complete proton and carbon-13 NMR assignment of complex polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Org. Chem. 1985, 50, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffee, A.L.; Fookes, C.J.R. Polycyclic aromatic-hydrocarbons in Australian coals. III. structural elucidation by proton nuclear magnetic-resonance spectroscopy. Org. Geochem. 1988, 12, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Morales, Y.; Miranda-Olvera, A.D.; Portales-Martínez, B.N.; Dominguez, J. Determination of 13C NMR chemical shift structural ranges for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and PAHs in asphaltenes: An experimental and theoretical density functional theory study. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7950–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, E.; Christensen, K.; Grant, D.M.; Walling, C. Substituent effects on carbon-13 chemical shifts in 4-substituted biphenyls and benzenes. Substituent effect transmitted through eight covalent bonds. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 2686–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todeschini, R.; Gramatica, P.; Provenzani, R.; Marengo, E. Weighted holistic invariant molecular descriptors. II. theory development and applications on modeling physicochemical properties of polyaromatic hydrocarbons. Chemometrics Intell. Lab. Syst. 1995, 27, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.N.; Wilkie, C.A. A TGA/FTIR and mass spectral study on the thermal degradation of bisphenol A polycarbonate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 86, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faix, O.; Meier, D.; Fortmann, I. Thermal-degradation products of wood - gas-chromatographic separation and mass-spectrometric characterization of monomeric lignin derived products. Holz Als Roh-und Werkst. 1990, 48, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Y.; Yao, Q.; Cao, W.; Zhao, Y. Base Promoted Intumescence of Phenols. Polymers 2020, 12, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020261
Ji Y, Yao Q, Cao W, Zhao Y. Base Promoted Intumescence of Phenols. Polymers. 2020; 12(2):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020261
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Yu, Qiang Yao, Weihong Cao, and Yueying Zhao. 2020. "Base Promoted Intumescence of Phenols" Polymers 12, no. 2: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020261
APA StyleJi, Y., Yao, Q., Cao, W., & Zhao, Y. (2020). Base Promoted Intumescence of Phenols. Polymers, 12(2), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12020261