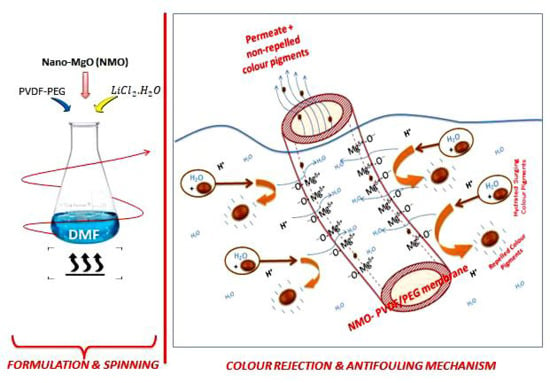
Permeability and Antifouling Augmentation of a Hybrid PVDF-PEG Membrane Using Nano-Magnesium Oxide as a Powerful Mediator for POME Decolorization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Nano-Hybrid PVDF/PEG-NMO
2.2.1. Dope formulation
2.2.2. Spinning of Nano-Hybrid PVDF/PEG-NMO Hollow Membrane
2.3. Characterization of Nano-Hybrid PVDF/PEG-NMO Fibre
2.3.1. Morphology Analysis
2.3.2. Hydrophilic and Porosity Analysis
2.3.3. Surface Charge Analysis
2.4. Membrane Performance
2.4.1. Permeability Analysis
2.4.2. POME Decolorization
2.4.3. Fouling Analysis
2.4.4. Characterization of used Membranes by FTIR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Nano-MgO on Membrane Characteristic
3.1.1. Morphological Studies
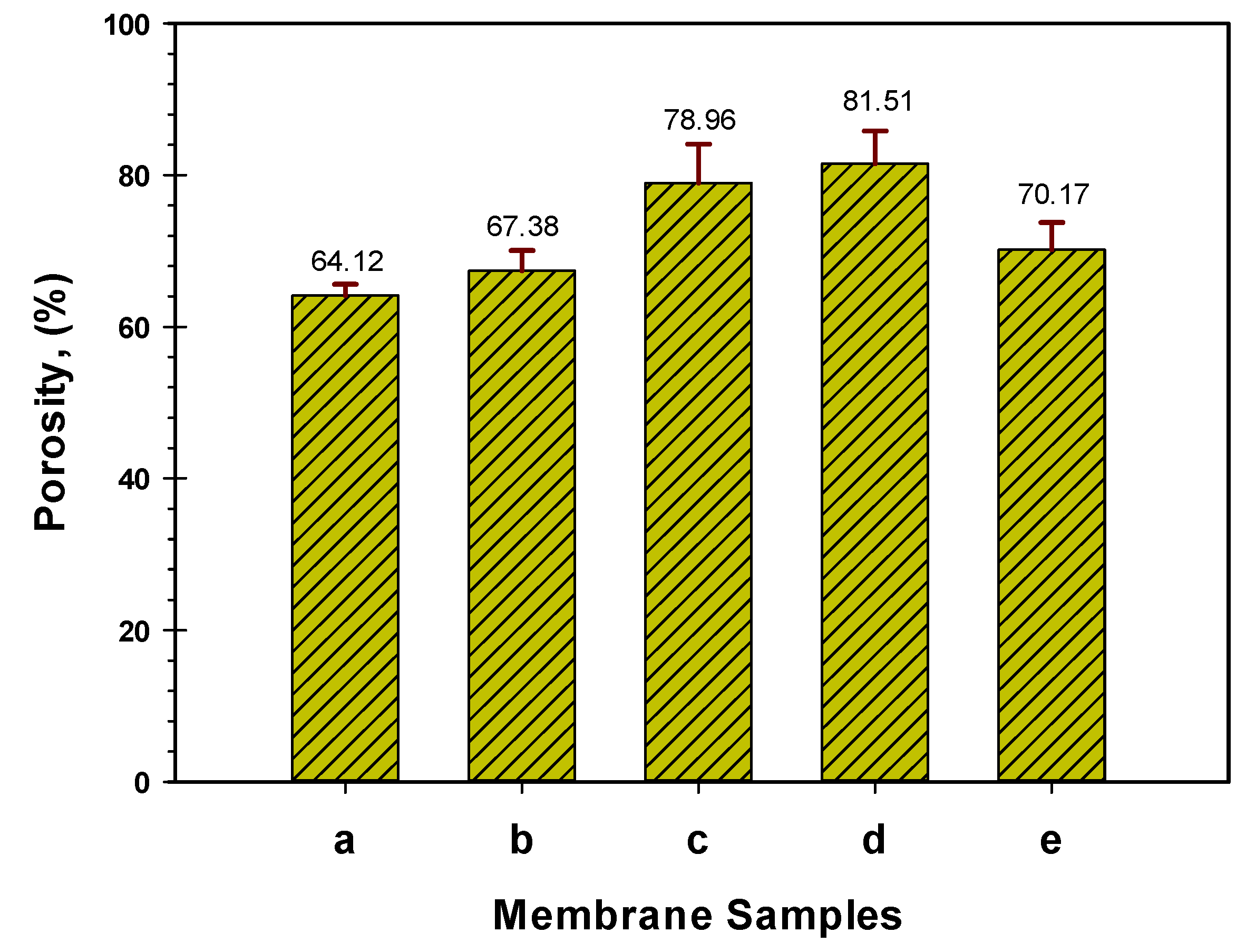
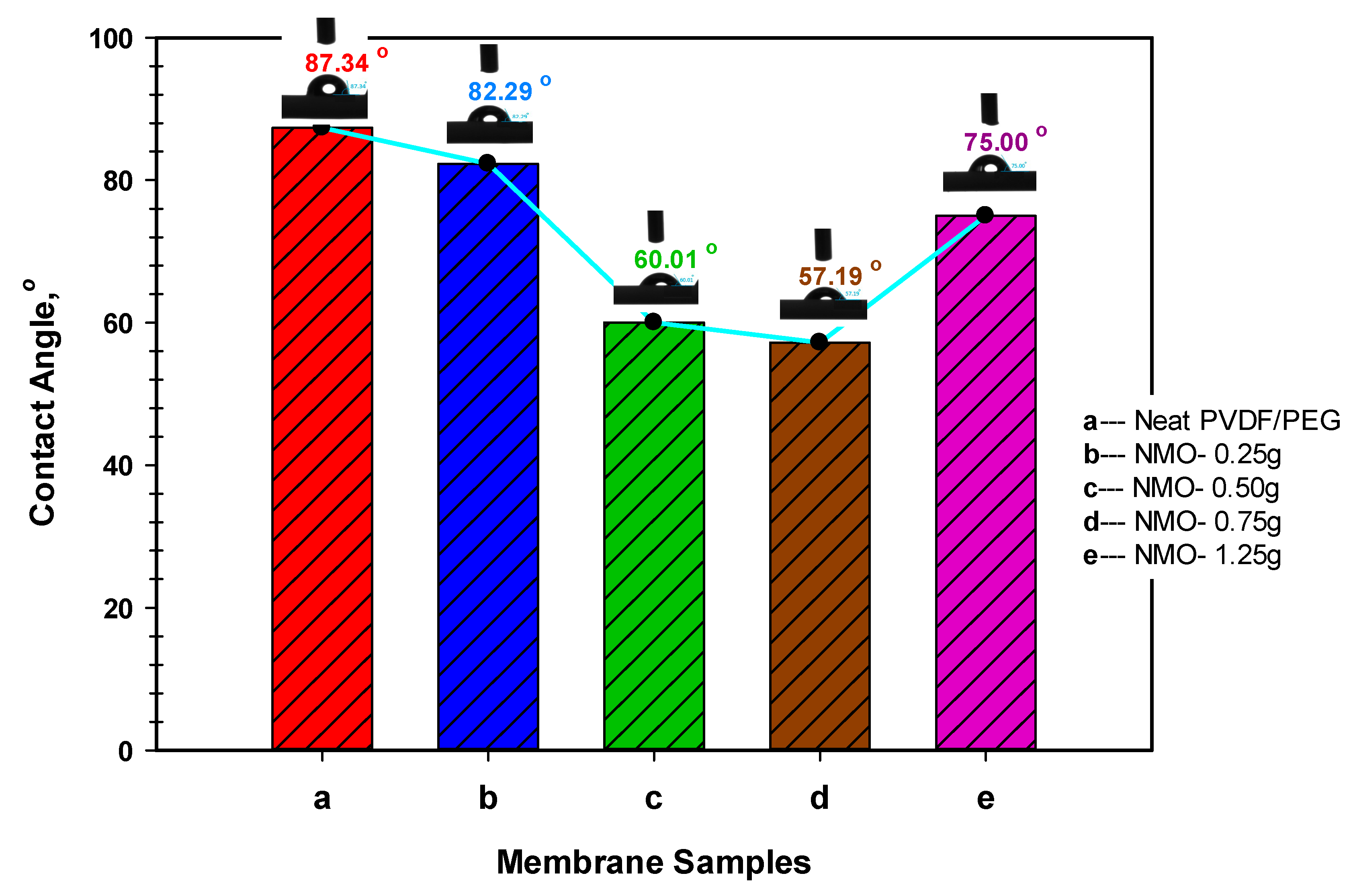
3.1.2. Membrane Hydrophilicity
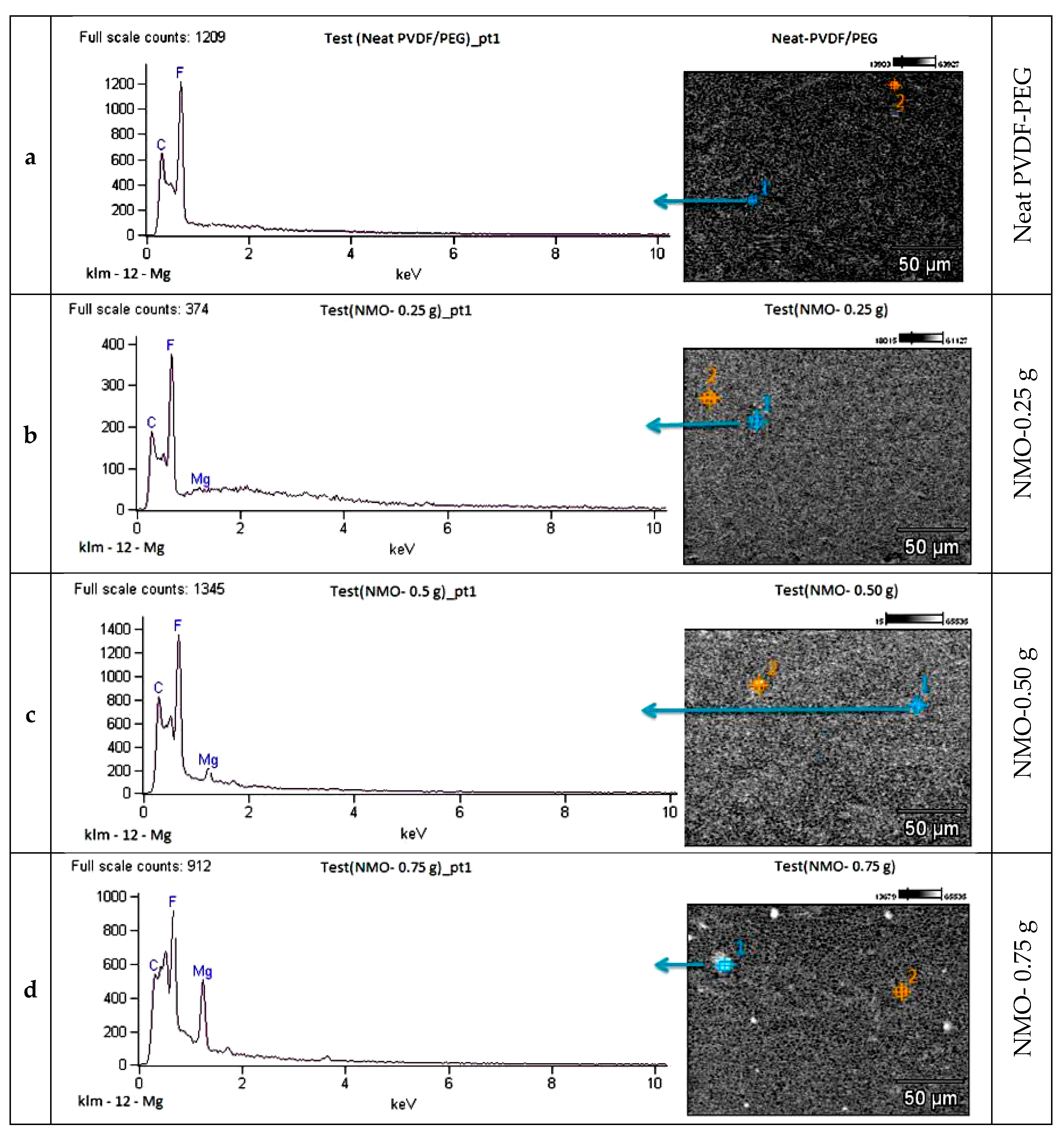
3.1.3. Elemental Analysis
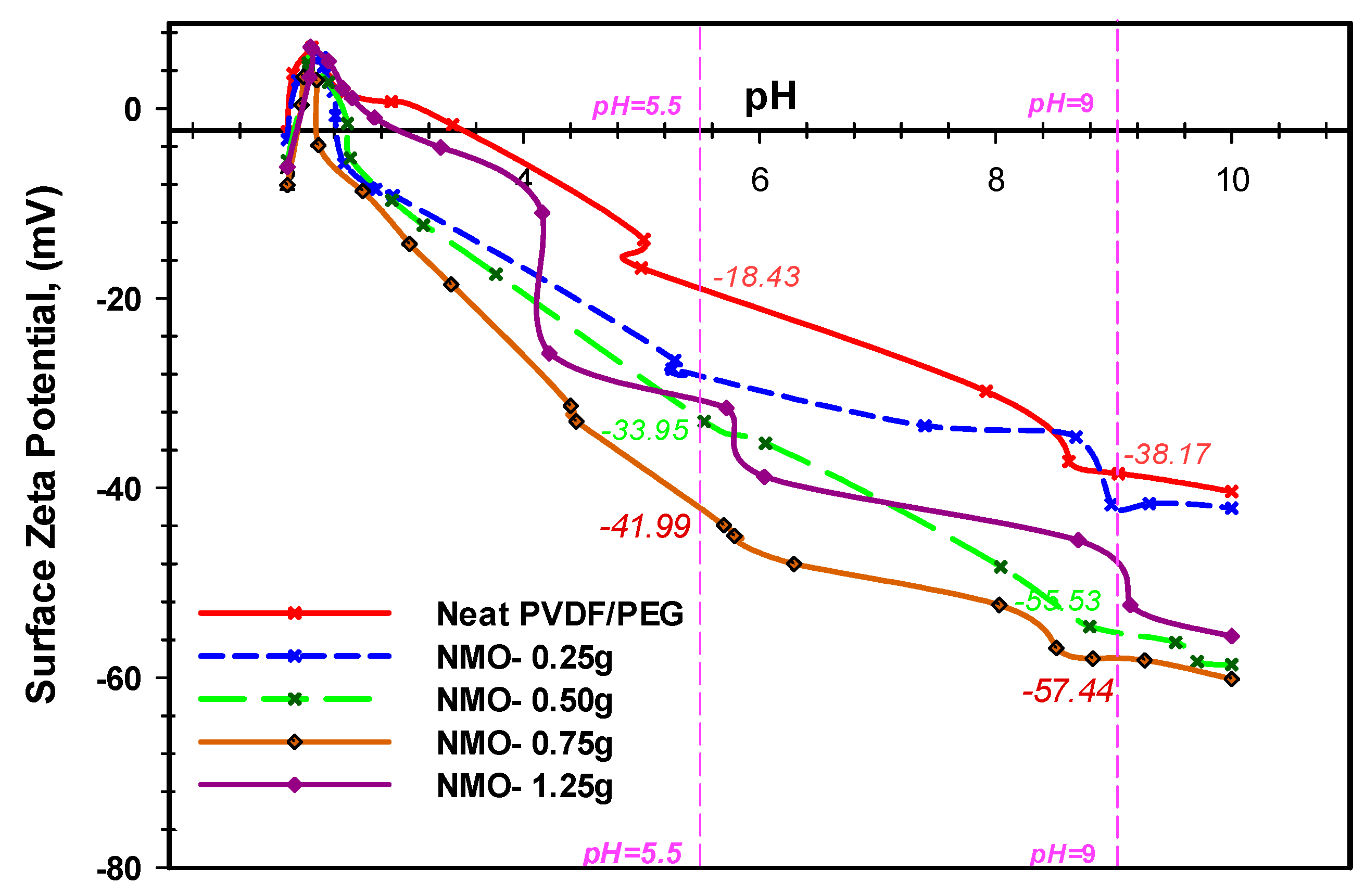
3.1.4. Surface Charge of Nano-MgO Membrane
3.2. Effect of Nano-MgO on Membrane Performance
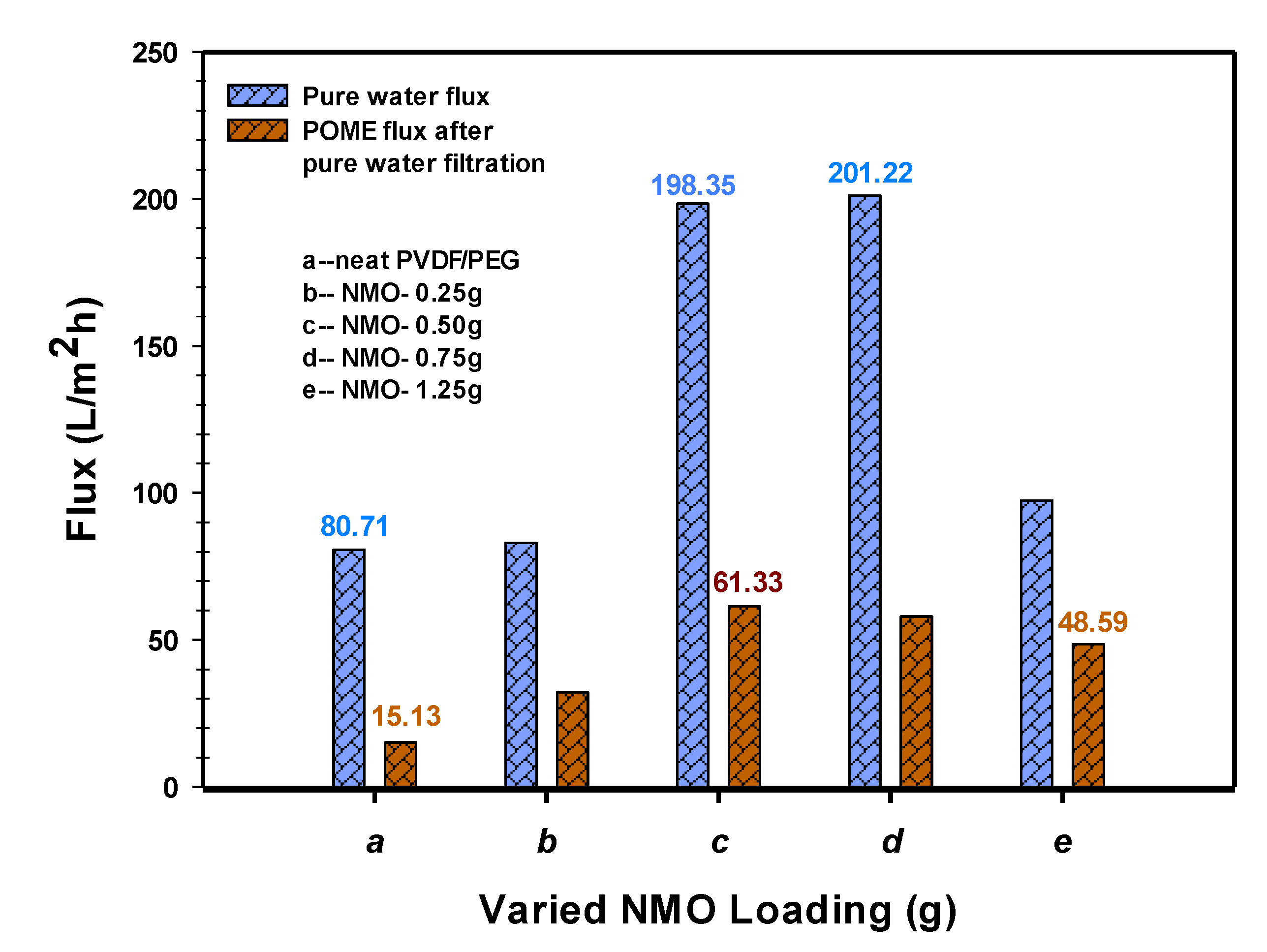
3.2.1. Permeability
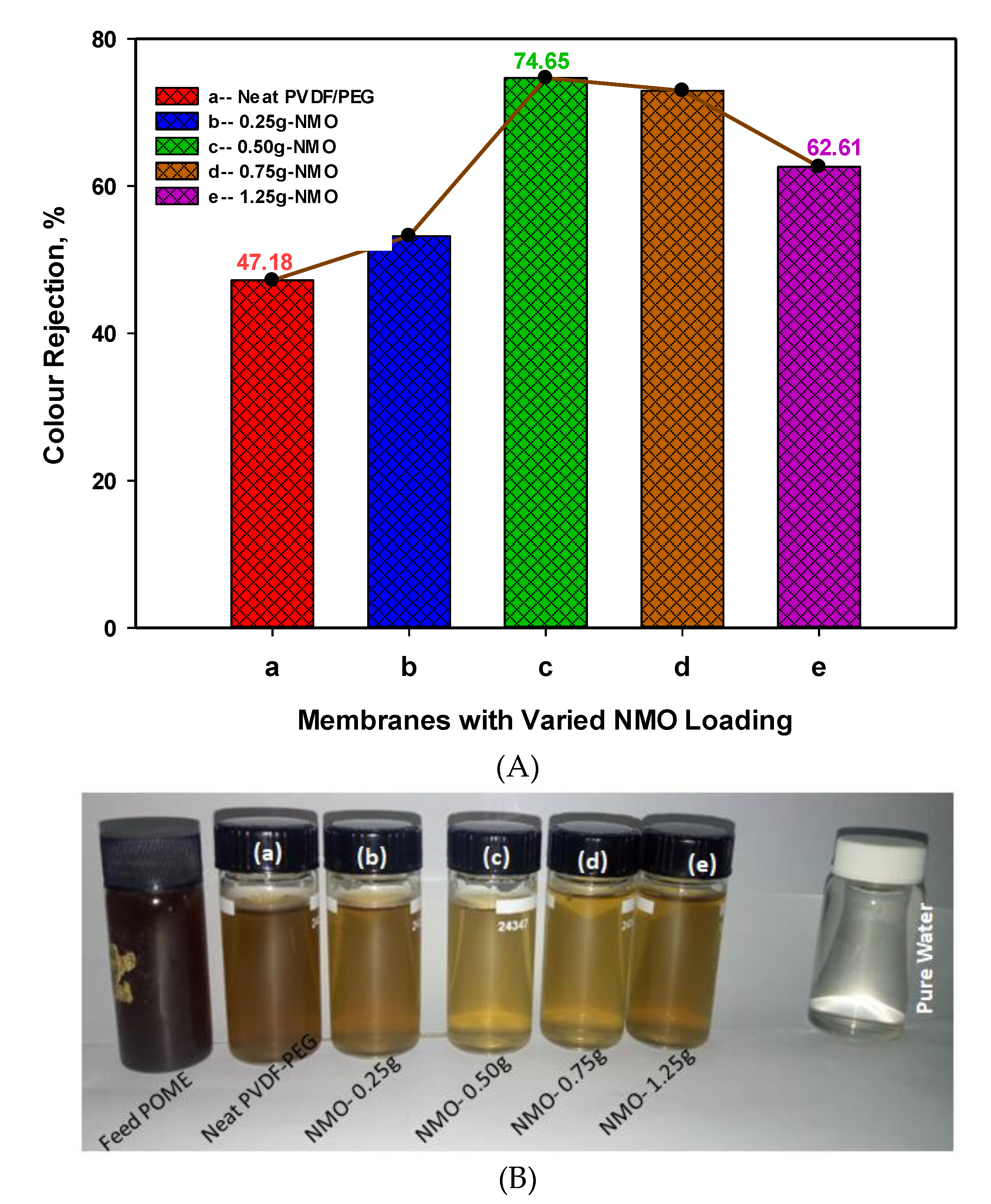
3.2.2. Rejection of Color Pigment from POME
3.2.3. Antifouling Performance and Membrane Reusability
3.2.4. FTIR Analysis of used Membranes
3.3. Performance Appraisal with Literatures
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nunes-Pereira, J.; Ribeiro, S.; Ribeiro, C.; Gombek, C.J.; Gama, F.M.; Gomes, A.C.; Patterson, D.A.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and copolymers as porous membranes for tissue engineering applications. Polym. Test. 2015, 44, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marquez, J.A.D.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Doma, B.T.; Huang, S.H.; Tsai, H.A.; Lee, K.R.; Lai, J.Y. Application of cosolvent-assisted interfacial polymerization technique to fabricate thin-film composite polyamide pervaporation membranes with PVDF hollow fiber as support. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 564, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Alberto, M.; Gorgojo, P.; Szekely, G.; Budd, P.M. High-flux PIM-1/PVDF thin film composite membranes for 1-butanol/water pervaporation. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 529, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramaniam, M.N.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Ng, B.C.; Ismail, A.F. AT-POME colour removal through photocatalytic submerged filtration using antifouling PVDF-TNT nanocomposite membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 191, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharupaneedi, S.P.; Nataraj, S.K.; Nadagouda, M.; Reddy, K.R.; Shukla, S.S.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Membrane-based separation of potential emerging pollutants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 850–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Ren, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lei, L.; Chen, F. Solvent effects on the morphology and performance of the anode substrates for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Vatanpour, V. Effect of solvent type on the physicochemical properties and performance of NLDH/PVDF nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Surya Murali, R.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.A.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil-water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, M.N.; Goh, P.S.; Lau, W.J.; Tan, Y.H.; Ng, B.C.; Ismail, A.F. Hydrophilic hollow fiber PVDF ultrafiltration membrane incorporated with titanate nanotubes for decolourization of aerobically-treated palm oil mill effluent. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Ye, Z.; He, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, J.; Shi, H.; Feng, Z. Application of dopamine-modified halloysite nanotubes/PVDF blend membranes for direct dyes removal from wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 323, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngang, H.P.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C.; Ooi, B.S. Preparation of thermoresponsive PVDF/SiO 2 -PNIPAM mixed matrix membrane for saline oil emulsion separation and its cleaning efficiency. Desalination 2017, 408, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Kong, Z.; Dong, Y.; Jin, G.; Tian, J.; Qin, Z. Fabrication of composite membrane with adsorption property and its application to the removal of endocrine disrupting compounds during filtration process. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Bokhary, A.; Maleki, E.; Liao, B. A review of membrane fouling and its control in algal-related membrane processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Farid, M.U.; Lee, E.J.; Yan, D.Y.S.; Jeong, S.; Kyoungjin An, A. Fouling behavior of negatively charged PVDF membrane in membrane distillation for removal of antibiotics from wastewater. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 551, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabuni, M.F.; Nik Sulaiman, N.M.; Aroua, M.K.; Yern Chee, C.; Awanis Hashim, N. Impact of in situ physical and chemical cleaning on PVDF membrane properties and performances. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 122, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zin, G.; Wu, J.; Rezzadori, K.; Petrus, J.C.C.; Di Luccio, M.; Li, Q. Modification of hydrophobic commercial PVDF microfiltration membranes into superhydrophilic membranes by the mussel-inspired method with dopamine and polyethyleneimine. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.H.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Ng, B.C.; Lai, G.S. Decolourization of aerobically treated palm oil mill effluent (AT-POME) using polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) ultrafiltration membrane incorporated with coupled zinc-iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Rostami, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Jalilian, E. Preparation of antibiofouling polyethersulfone mixed matrix NF membrane using photocatalytic activity of ZnO/MWCNTs nanocomposite. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 529, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Shao, X.S.; Zhou, Q.; Li, M.Z.; Zhang, Q.Q. The double effects of silver nanoparticles on the PVDF membrane: Surface hydrophilicity and antifouling performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 265, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauter, M.S.; Okemgbo, K.C.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P. Antifouling ultrafiltration membranes via post-fabrication grafting of biocidal nanomaterials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2861–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhaveri, J.H.; Murthy, Z.V.P. A comprehensive review on anti-fouling nanocomposite membranes for pressure driven membrane separation processes. Desalination 2016, 379, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Oh, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shin, H.S.; Chae, S.R. Fouling in membrane bioreactors: An updated review. Water Res. 2017, 114, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.R.; Lee, J.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, I.C.; Park, P.K. Graphene oxide-embedded thin-film composite reverse osmosis membrane with high flux, anti-biofouling, and chlorine resistance. J. Memb. Sci. 2015, 483, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Vatanpour, V.; Aber, S.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Preparation and characterization of a novel polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membrane modified with a CuO/ZnO nanocomposite to improve permeability and antifouling properties. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 192, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Bian, X.; Lu, X.; Shi, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Hou, Z.; Fan, K. Preparation and characterization of ZnO/polyethersulfone (PES) hybrid membranes. Desalination 2012, 293, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Pan, H.; Wang, X.; Chu, P.K.; Wu, S. Photo-Inspired Antibacterial Activity and Wound Healing Acceleration by Hydrogel Embedded with Ag/Ag@AgCl/ZnO Nanostructures. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 9010–9021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, M.; Deepa, M.; Subramanian, R.; Mohamed Musthafa, A. Synthesis, characterization of polyindole/Ag[sbnd]ZnO nanocomposites and its antibacterial activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 696, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Mao, L.; Jiang, C.; Ang, J.; Lu, X. Doping polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane with TiO2-PDA nanohybrid for simultaneous self-cleaning and self-protection. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 532, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodrow, K.; Brunet, L.; Mahendra, S.; Li, D.; Zhang, A.; Li, Q.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes impregnated with silver nanoparticles show improved biofouling resistance and virus removal. Water Res. 2009, 43, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maximous, N.; Nakhla, G.; Wong, K.; Wan, W. Optimization of Al2O3/PES membranes for wastewater filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemmireddy, V.K.; Hung, Y.C. Using Photocatalyst Metal Oxides as Antimicrobial Surface Coatings to Ensure Food Safety—Opportunities and Challenges. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 617–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, C.B.; Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. A review of ZnO nanoparticles as solar photocatalysts: Synthesis, mechanisms and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Perumal, E. Metal oxide nanoparticles as antimicrobial agents: a promise for the future. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Thuan, T.; Quynh, B.T.P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Ho, V.T.T.; Bach, L.G. Response surface methodology approach for optimization of Cu2+, Ni2+ and Pb2+ adsorption using KOH-activated carbon from banana peel. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, A.; Chaudhary, V.; Malik, R.; Tomer, V.K. Nanotechnology Based Solutions for Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128139028. [Google Scholar]
- Hikku, G.S.; Jeyasubramanian, K.; Vignesh Kumar, S. Nanoporous MgO as self-cleaning and anti-bacterial pigment for alkyd based coating. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 52, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakayode, S.O.; Baker, G.A.; Bwambok, D.K.; Bhawawet, N.; Elzey, B.; Siraj, N.; Macchi, S.; Pollard, D.A.; Perez, R.L.; Duncan, A.V.; et al. Molecular (Raman, NIR, and FTIR) spectroscopy and multivariate analysis in consumable products analysis 1. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2019, 1–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mao, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, H. Author’ s Accepted Manuscript inversion method. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 516, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizian, F.; Sadeghi, Z.; Hosseini, S.M. PVC Based Ion-Exchange Membrane Blended with Magnesium Oxide Nanoparticles for Desalination: Fabrication, Characterization and Performance. J. Appl. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2017, 21, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; He, G.; Li, H.; Zhao, R.; Han, Y.; Deng, Y. Antifouling enhancement of poly (vinylidene fluoride) microfiltration membrane by adding Mg(OH)2 nanoparticles. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 387–388, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, X.; Huo, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, L. Improving the hydrophilic and antifouling properties of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane by incorporation of novel nanohybrid GO@SiO2 particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Mohammed Sadiq, I.; Prathna, T.C.; Chandrasekaran, N. Antimicrobial activity of aluminium oxide nanoparticles for potential clinical applications. Sci. against Microb. Pathog. Commun. Curr. Res. Technol. Adv. 2011, 1, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, D.J.; Chang, C.L.; Huang, F.M.; Cheng, L.P. Effect of salt additive on the formation of microporous poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes by phase inversion from LiC1o 4 /water/DMF/PVDF system. Polymer (Guildf). 2002, 44, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, C.V.; Karuppasamy, K.; Sridevi, N.A.; Balakumar, S.; Shajan, X.S. Effect of electron beam irradiation on the mechanical and electrochemical properties of plasticized polymer electrolytes dispersed with nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 678, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, H.; Bai, H.; Shao, J.; Han, Q.; Ling, Y.; He, Y. Super-hydrophilic and fouling resistant PVDF ultrafiltration membranes based on a facile prefabricated surface. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 541, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadzadeh, D.; Ghanbari, M.; Lau, W.J.; Rahbari-Sisakht, M.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Kruczek, B.; Ismail, A.F. Surface modification of thin film composite membrane by nanoporous titanate nanoparticles for improving combined organic and inorganic antifouling properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lee, J.; Small, C.; Ma, J.; Elimelech, M. Comparison of organic fouling resistance of thin-film composite membranes modified by hydrophilic silica nanoparticles and zwitterionic polymer brushes. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 544, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Teow, Y.H.; Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W. Novel GO/OMWCNTs mixed-matrix membrane with enhanced antifouling property for palm oil mill effluent treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 177, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.-L.; Su, X.; He, J.; Wang, L.-L. Surface hydrophilicity modification of PVDF membranes with an external electric field in the phase inversion process. Membr. Water Treat. 2015, 6, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, X.Y.; Shih, K. In situ embedment and growth of anhydrous and hydrated aluminum oxide particles on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2011, 368, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.K.; Goh, K.; Bae, T.H.; Wang, R. Polymer-based membranes for solvent-resistant nanofiltration: A review. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 1653–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, M.M.R.; Kumbharkar, S.C.; Groth, A.M.; Li, K. Ultrafiltration PVDF hollow fibre membranes with interconnected bicontinuous structures produced via a single-step phase inversion technique. J. Memb. Sci. 2012, 407–408, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, G.; Wang, R. Novel membrane surface modification to enhance anti-oil fouling property for membrane distillation application. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 447, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.Y.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Qiblawey, H.; Zouari, N. Evaluating the effect of antiscalants on membrane biofouling using FTIR and multivariate analysis. Biofouling 2019, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Al-Sulaimi, S.; Farooque, A.M. Characterization of new and fouled SWRO membranes by ATR/FTIR spectroscopy. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yin, X.; Tian, L. Membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor (MBR) under sub-critical flux operation: Membrane foulant and gel layer characterization. J. Memb. Sci. 2008, 325, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Fu, Y.; Ren, N. Tracing biofouling to the structure of the microbial community and its metabolic products: A study of the three-stage MBR process. Water Res. 2013, 47, 6680–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugham, T.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Rana, D.; Doraiswamy, M. Separation of oil/water emulsions using nano MgO anchored hybrid ultrafiltration membranes for environmental abatement. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
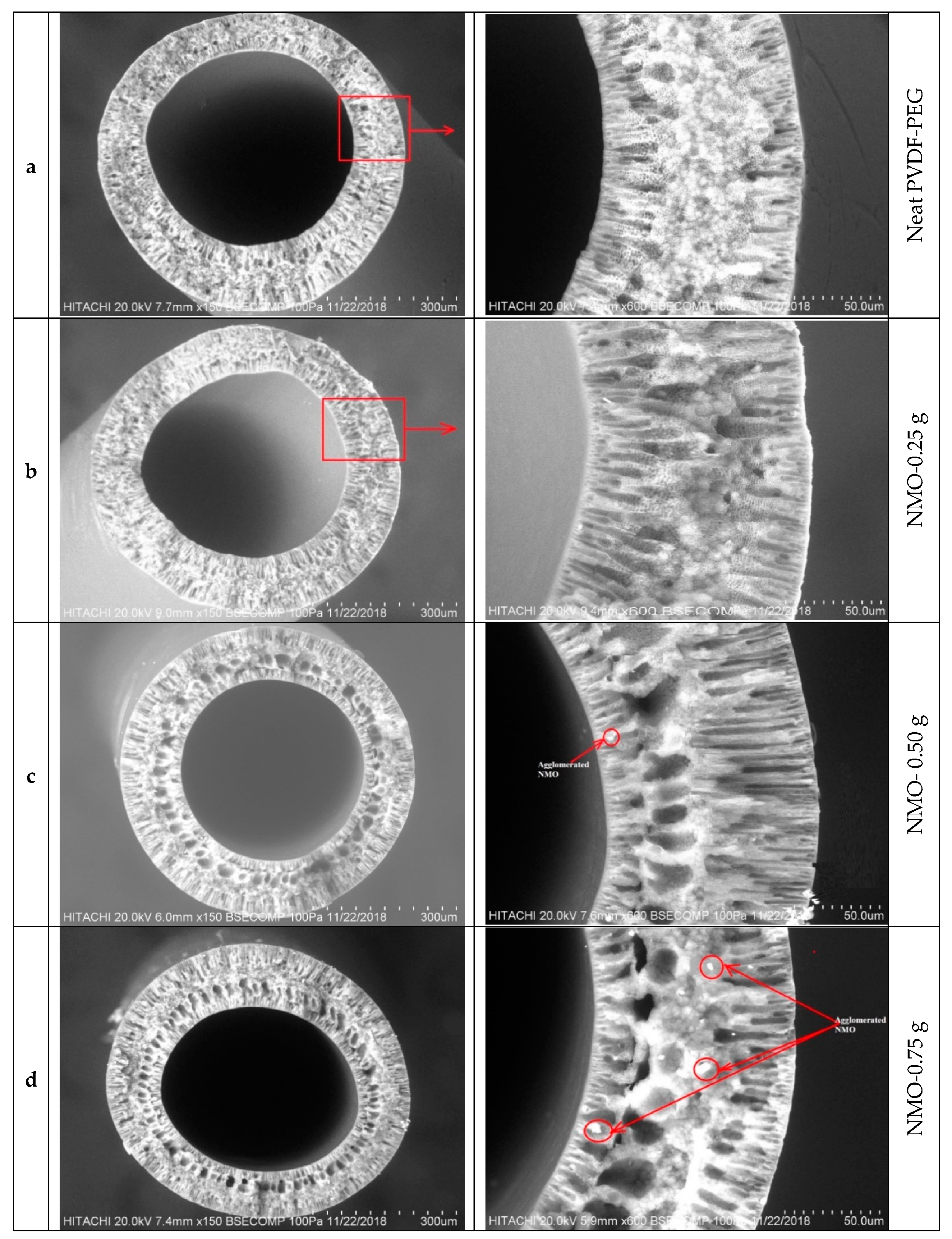
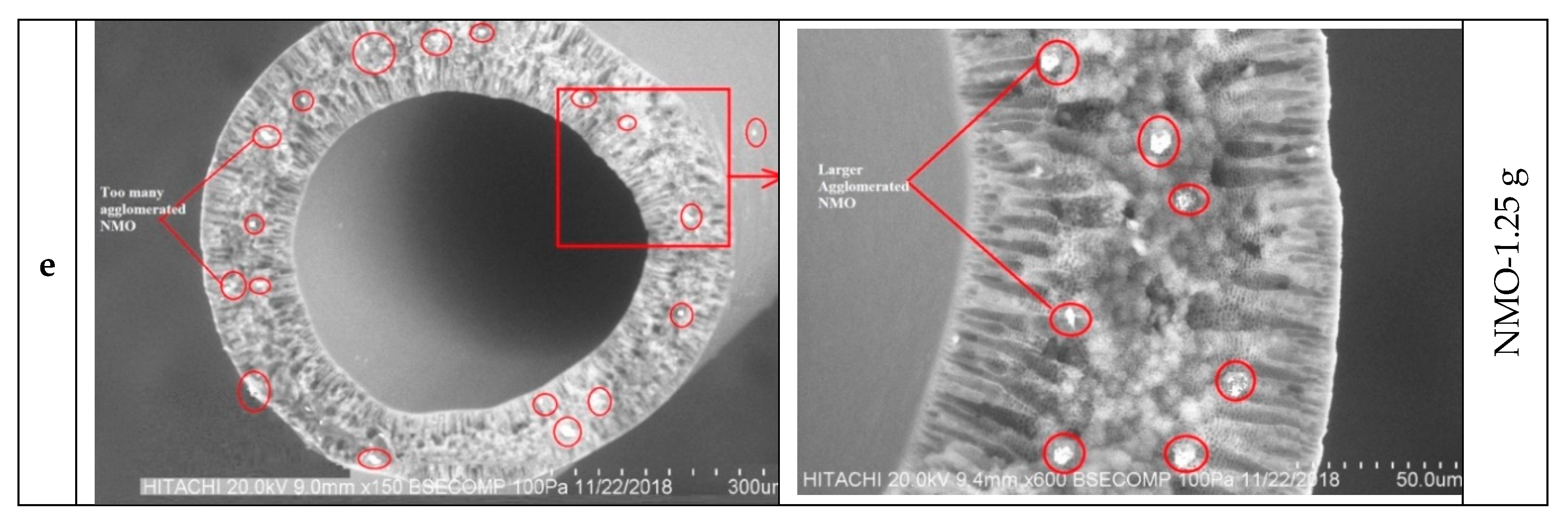




| Samples | PVDF/PEG (g) | DMF (g) | LiCl.H2O (g) | NMO (g) | Mass of Dope (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat PVDF/PEG | 30/10 | (3:1) | 158 | 2.0 | -- | 200.00 |
| NMO-0.25 g | 30/10 | (3:1) | 158 | 2.0 | 0.25 | 200.25 |
| NMO-0.50 g | 30/10 | (3:1) | 158 | 2.0 | 0.50 | 200.50 |
| NMO-0.75 g | 30/10 | (3:1) | 158 | 2.0 | 0.75 | 200.75 |
| NMO-1.25 g | 30/10 | (3:1) | 158 | 2.0 | 1.25 | 201.25 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdulsalam, M.; Che Man, H.; Goh, P.S.; Yunos, K.F.; Zainal Abidin, Z.; Isma M.I., A.; Ismail, A.F. Permeability and Antifouling Augmentation of a Hybrid PVDF-PEG Membrane Using Nano-Magnesium Oxide as a Powerful Mediator for POME Decolorization. Polymers 2020, 12, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030549
Abdulsalam M, Che Man H, Goh PS, Yunos KF, Zainal Abidin Z, Isma M.I. A, Ismail AF. Permeability and Antifouling Augmentation of a Hybrid PVDF-PEG Membrane Using Nano-Magnesium Oxide as a Powerful Mediator for POME Decolorization. Polymers. 2020; 12(3):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030549
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdulsalam, Mohammed, Hasfalina Che Man, Pei Sean Goh, Khairul Faezah Yunos, Zurina Zainal Abidin, Aida Isma M.I., and Ahmad Fauzi Ismail. 2020. "Permeability and Antifouling Augmentation of a Hybrid PVDF-PEG Membrane Using Nano-Magnesium Oxide as a Powerful Mediator for POME Decolorization" Polymers 12, no. 3: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030549
APA StyleAbdulsalam, M., Che Man, H., Goh, P. S., Yunos, K. F., Zainal Abidin, Z., Isma M.I., A., & Ismail, A. F. (2020). Permeability and Antifouling Augmentation of a Hybrid PVDF-PEG Membrane Using Nano-Magnesium Oxide as a Powerful Mediator for POME Decolorization. Polymers, 12(3), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12030549