Improved Copper–Epoxy Adhesion by Laser Micro- and Nano-Structuring of Copper Surface for Thermal Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Laser Irradiation and Surface Characterization
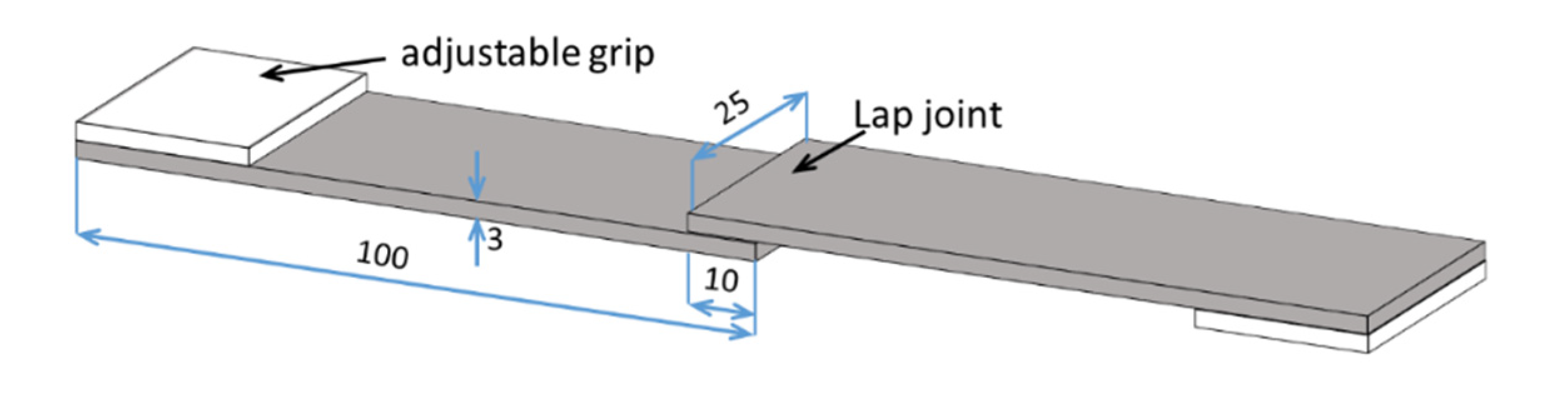
2.3. Joint Manufacturing Process and Mechanical Characterization
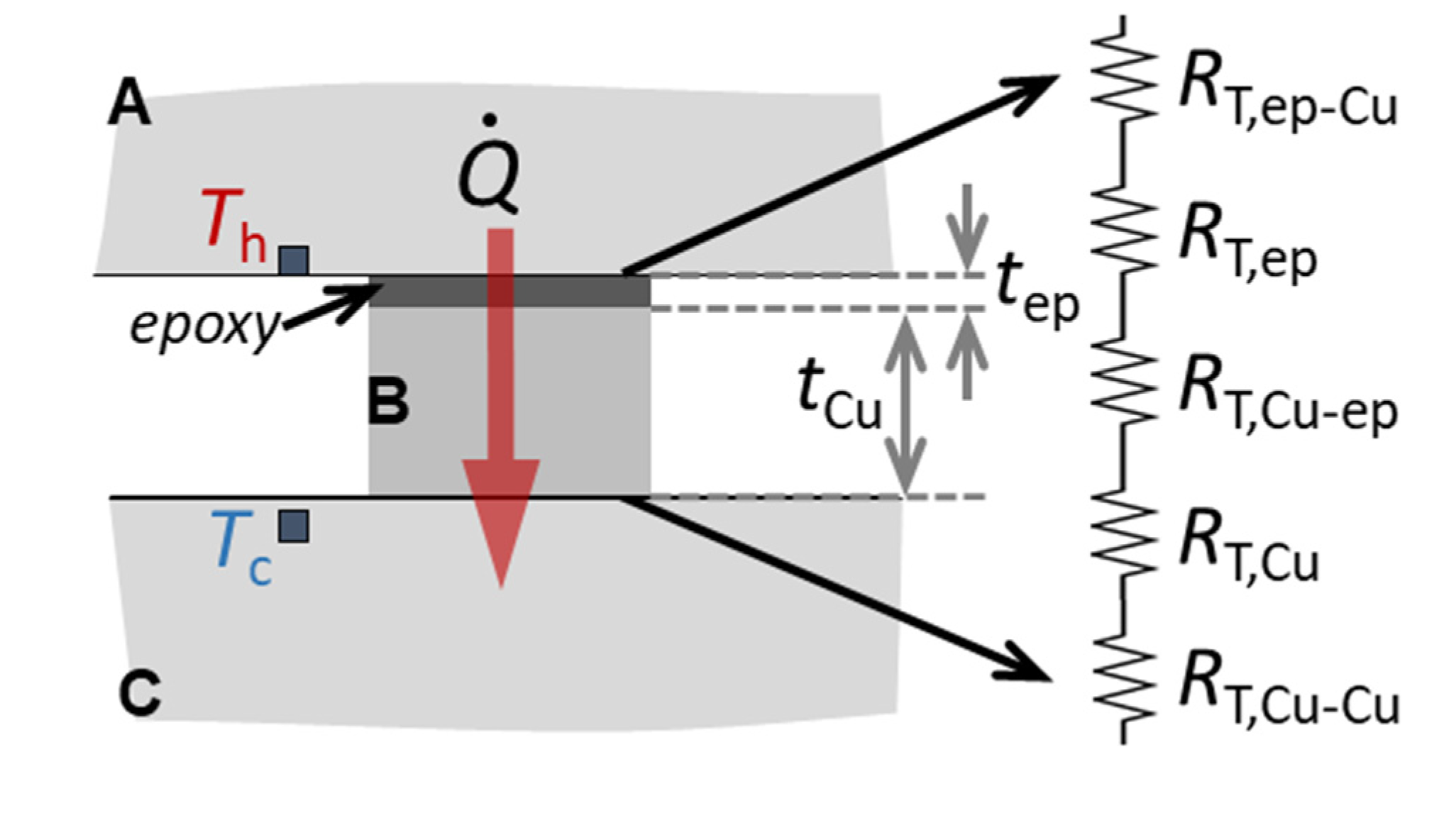
2.4. Thermal Characterization of the Joints at Cryogenic Temperatures
3. Results and Discussion
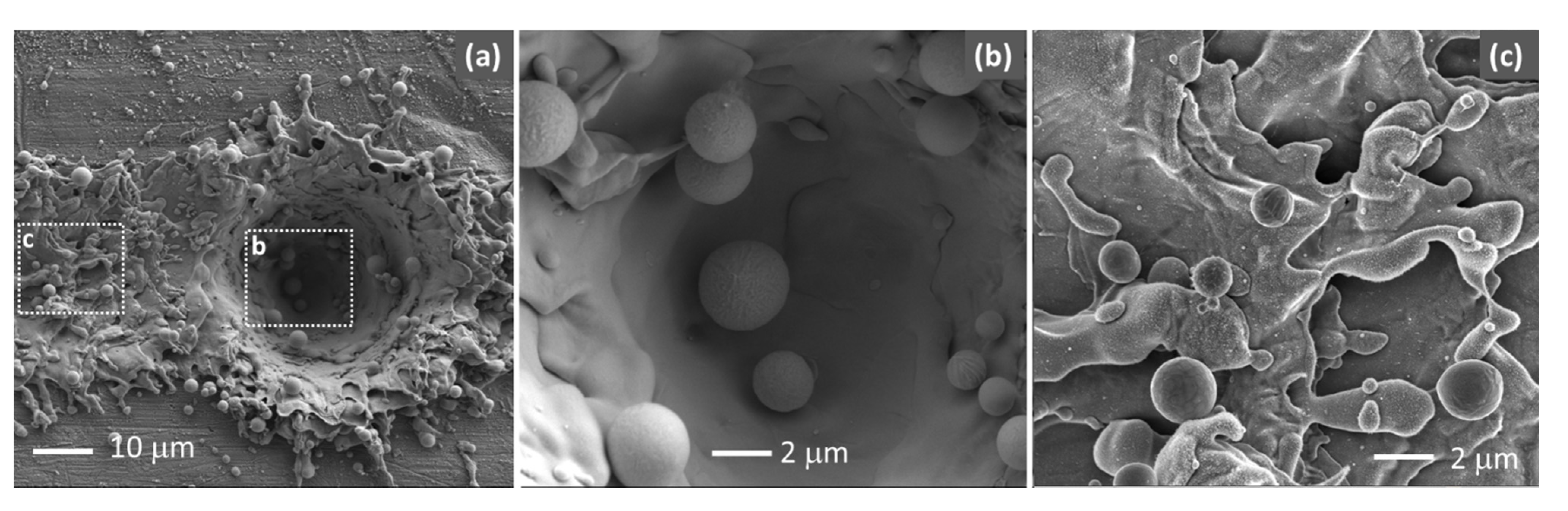
3.1. Laser-Induced Copper Surface Modifications
3.2. Time Evolution of Surface Characteristics after Laser Processing
3.3. Microstructural Characteristics of Cu/Epoxy/Cu Joints
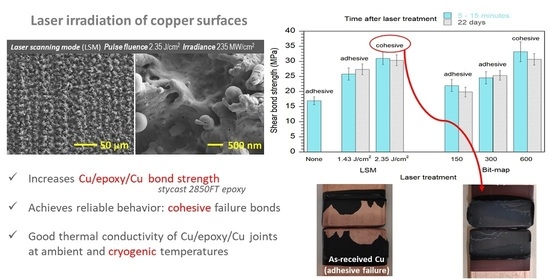
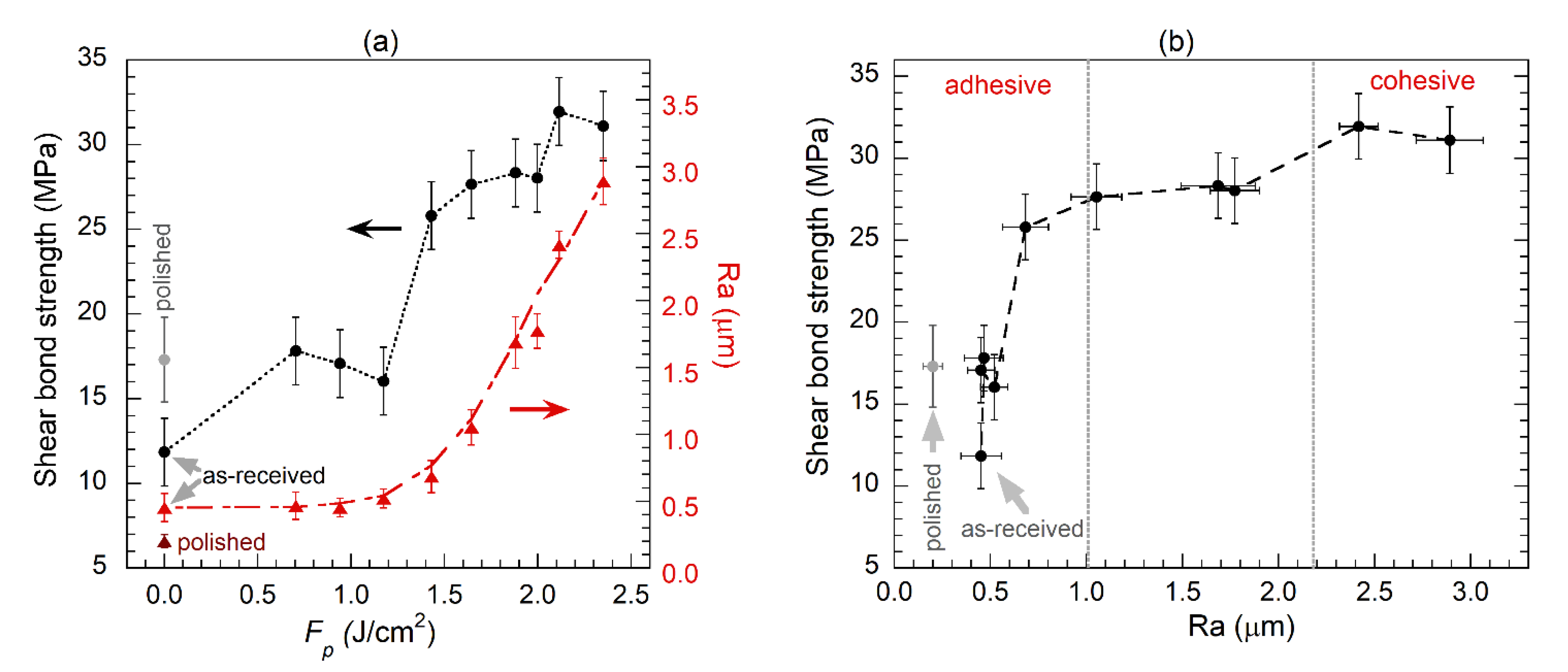
3.4. Mechanical Bonding Strength of Cu/Epoxy/Cu Joints
3.5. Thermal Properties of Cu/Epoxy/Cu Joints
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nothdurft, P.; Riess, G.; Kern, W. Copper/epoxy joints in printed circuit boards: Manufacturing and interfacial failure mechanisms. Materials 2019, 12, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.; Xia, J.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Hussain, G.; Li, Q.; Ostrikov, K. Adhesion and cohesion of epoxy-based industrial composite coatings. Compos. Part B 2020, 193, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtovic, A.; Brandl, E.; Mentens, T.; Maier, H.J. Laser induced surface nano-structuring of Ti–6Al–4V for adhesive bonding. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2013, 45, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.K.; Cho, K.; An, J.H.; Park, C.E. Adhesion improvement of copper/epoxy joints. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 5811–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Yu, J. Effects of oxidation treatments on the fracture toughness of lead frame/epoxy interfaces. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 277, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.-M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Englezos, P. Patterned superhydrophobic metallic surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4821–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidhya, Y.E.B.; Pattamatta, A.; Manivannan, A.; Vasa, N.J. Influence of fluence, beam overlap and aging on the wettability of pulsed Nd3+:YAG nanosecond laser-textured Cu and Al sheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 548, 149259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Liu, W.; Xue, W.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. Nanosecond laser ablated copper superhydrophobic surface with tunable ultrahigh adhesion and its renewability with low temperature annealing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, D.V.; Dunn, A.; Wasley, T.J.; Kay, R.W.; Stringer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Connaughton, C.; Shephard, J.D. Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.-J.; Mei, X.-S.; Tian, Y.-L.; Zhang, D.-W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.-P. Modification of wettability property of titanium by laser texturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, J.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, H.; Fan, P. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of picosecond laser microstructured aluminum in ambient air. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, C.-V.; Chun, D.M. Control of laser-ablated aluminum surface wettability to superhydrophobic or superhydrophilic through simple heat treatment or water boiling post-processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, C.-V.; Chun, D.M. Fast wettability transition from hydrophilic to superhydrophobic laser-textured stainless steel surfaces under low-temperature annealing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 409, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maressa, P.; Anodio, L.; Bernasconi, A.; Demir, A.G.; Previtali, B. Effect of surface texture on the adhesion performance of laser treated Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Adhes. 2014, 91, 518–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotella, G.; Alfano, M.; Schiefer, T.; Jansen, I. Enhancement of static strength and long term durability of steel/epoxy joints through a fiber laser surface pre-treatment. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 63, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, E.; Alfano, M.; Lubineau, G.; Buttner, U. Improving adhesion of copper/epoxy joints by pulsed laser ablation. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2015, 64, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romoli, L.; Moroni, F.; Khan, M.M.A. A study on the influence of surface laser texturing on the adhesive strength of bonded joints in aluminium alloys. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 66, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-M.; Cheng, S.-L.; Hong, S.-J.; Sheng, Y.-J.; Tsao, H.-K. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of CuO nanowire films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 114101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubero, A.; Nuñez-Chico, A.B.; Navarro, R.; Angurel, L.A.; Martínez, E. Electromagnetic behavior and thermal stability of a conduction-cooled, no-insulated 2G-HTS coil at intermediate temperatures. Cryogenics 2020, 108, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekin, J. Experimental Techniques for Low-Temperature Measurements, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press (OUP): Boulder, CO, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pekarčíková, M.; Mišík, J.; Drienovský, M.; Krajčovič, J.; Vojenčiak, M.; Búran, M.; Mošat’, M.; Húlan, T.; Skarba, M.; Cuninková, E.; et al. Composite Heat Sink Material for Superconducting Tape in Fault Current Limiter Applications. Materials 2020, 13, 1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelegrín, J.; Romano, G.; Martínez, E.; Angurel, L.A.; Navarro, R.; Ferdeghini, C.; Brisigotti, S.; Grasso, G.; Nardelli, D. Experimental and numerical analysis of quench propagation on MgB2 tapes and pancake coils. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 2013, 26, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seeber, B. (Ed.) Handbook of Applied Superconductivity; Institute of Physics Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 1998; Volume 1, pp. 1089–1090. [Google Scholar]
- Duthil, P. Materials Properties at Low Temperature; CERN Accelerator School: Erice, Italy, 2013; Available online: https://indico.cern.ch/event/194284/contributions/1472798/attachments/281498/393574/CAS_propmat_2013.pdf (accessed on 25 March 2021).
- Liu, J.M. Simple technique for measurements of pulsed Gaussian-beam spot sizes. Opt. Lett. 1982, 7, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennikov, V.; Özkurt, B.; Angurel, L.A.; Sotelo, A.; Özçelik, B.; de la Fuente, G.F. Microstructure and transport properties of Bi-2212 prepared by CO2 laser line scanning. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 2013, 26, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano-Pérez, J.J.; Lima-Santos, F.; Alonso-Velazquez, E.; Rodriguez-Lelis, J.M.; Tejero-Andrade, J.M. Tensiometro digital para medir ángulos de contacto líquido sólido. In Proceedings of the XV Congreso Internacional Anual De La Somim, Obregón, Sonora, Mexico, 23–25 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Arenas, J.M.; Narbón, J.J.; Alía, C. Optimum adhesive thickness in structural adhesives joints using statistical techniques based on Weibull distribution. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naito, K.; Onta, M.; Kogo, Y. The effect of adhesive thickness on tensile and shear strength of polyimide adhesive. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 36, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rośkowicz, M.; Godzimirski, J.; Komorek, A.; Jasztal, M. The effect of adhesive layer thickness on joint static strength. Materials 2021, 14, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

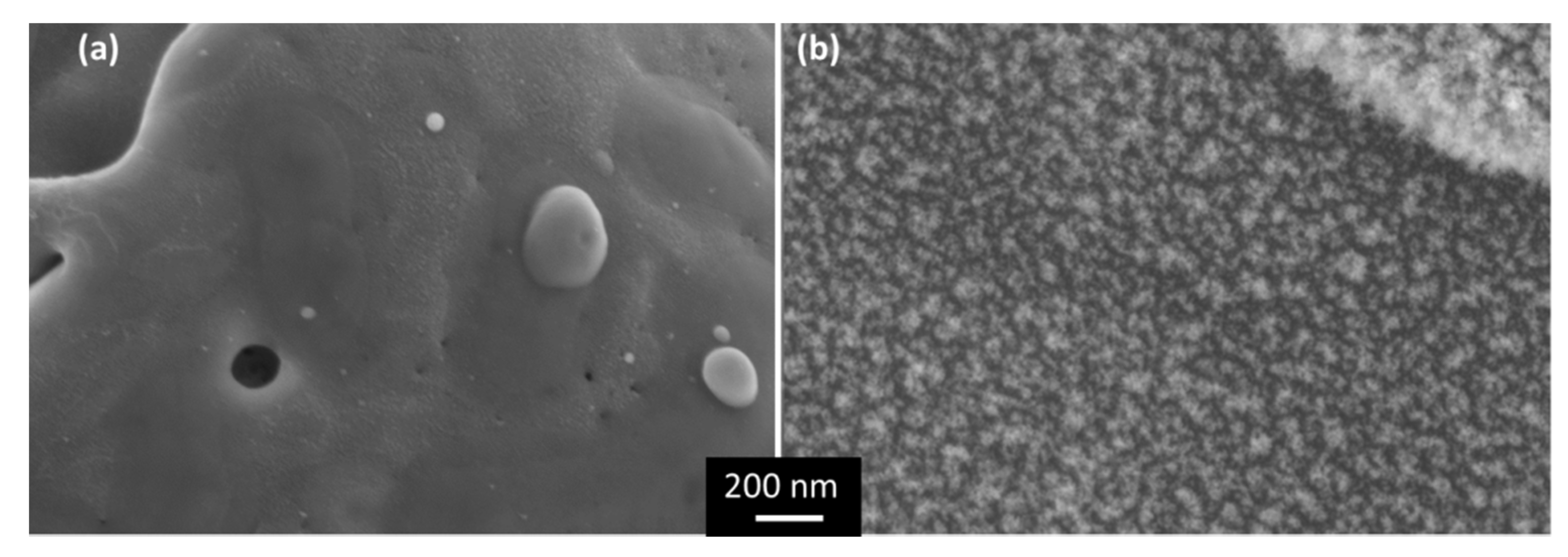



| Laser Processing | Oxygen Content, at % | Water Contact Angle (°) | Epoxy Contact Angle (°) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time < 1 h | 22 Days | <1 h | 1 Day | 22 Days | <1 h | 1 Day | 22 Days | ||
| None | 14.7 | 100 | 38 | ||||||
| LSM | Fp = 1.43 J/cm2 | 18.3 | 18.7 | 42 | 74 | 80 | 27 | 30 | 29 |
| Fp = 2.35 J/cm2 | 21.7 | 20.6 | <10 | 55 | 95 | 32 | 27 | 30 | |
| Bit-map | 150 dpi | 17.5 | 25.1 | ||||||
| 300 dpi | 20.6 | 27.4 | <10 | 29 | 79 | 27 | 31 | 27 | |
| 600 dpi | 27.4 | 33.3 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora, M.; Amaveda, H.; Porta-Velilla, L.; de la Fuente, G.F.; Martínez, E.; Angurel, L.A. Improved Copper–Epoxy Adhesion by Laser Micro- and Nano-Structuring of Copper Surface for Thermal Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111721
Mora M, Amaveda H, Porta-Velilla L, de la Fuente GF, Martínez E, Angurel LA. Improved Copper–Epoxy Adhesion by Laser Micro- and Nano-Structuring of Copper Surface for Thermal Applications. Polymers. 2021; 13(11):1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111721
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora, Mario, Hippolyte Amaveda, Luis Porta-Velilla, Germán F. de la Fuente, Elena Martínez, and Luis A. Angurel. 2021. "Improved Copper–Epoxy Adhesion by Laser Micro- and Nano-Structuring of Copper Surface for Thermal Applications" Polymers 13, no. 11: 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111721
APA StyleMora, M., Amaveda, H., Porta-Velilla, L., de la Fuente, G. F., Martínez, E., & Angurel, L. A. (2021). Improved Copper–Epoxy Adhesion by Laser Micro- and Nano-Structuring of Copper Surface for Thermal Applications. Polymers, 13(11), 1721. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13111721