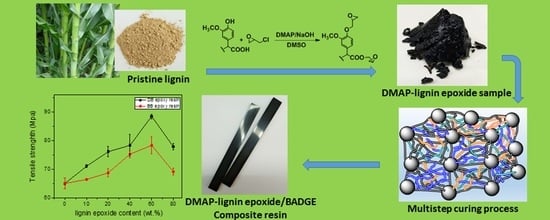
Preparation of a Dmap-Catalysis Lignin Epoxide and the Study of Its High Mechanical-Strength Epoxy Resins with High-Biomass Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Lignin Epoxides
2.3. Preparation of Epoxy Resins
2.3.1. Preparation of the DMAP-Lignin Epoxide Resin, BTEAC-Lignin Epoxide Resin, and BADGE Resin
2.3.2. Preparation of the Lignin Epoxide/BADGE Composite Epoxy Resin
2.4. Characterizations
2.5. Analysis of the Lignin Epoxidation
2.6. Molecular Weight Analysis
2.7. Test on the Mechanical, Thermomechanical, and Thermal Performance
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Lignin Epoxides
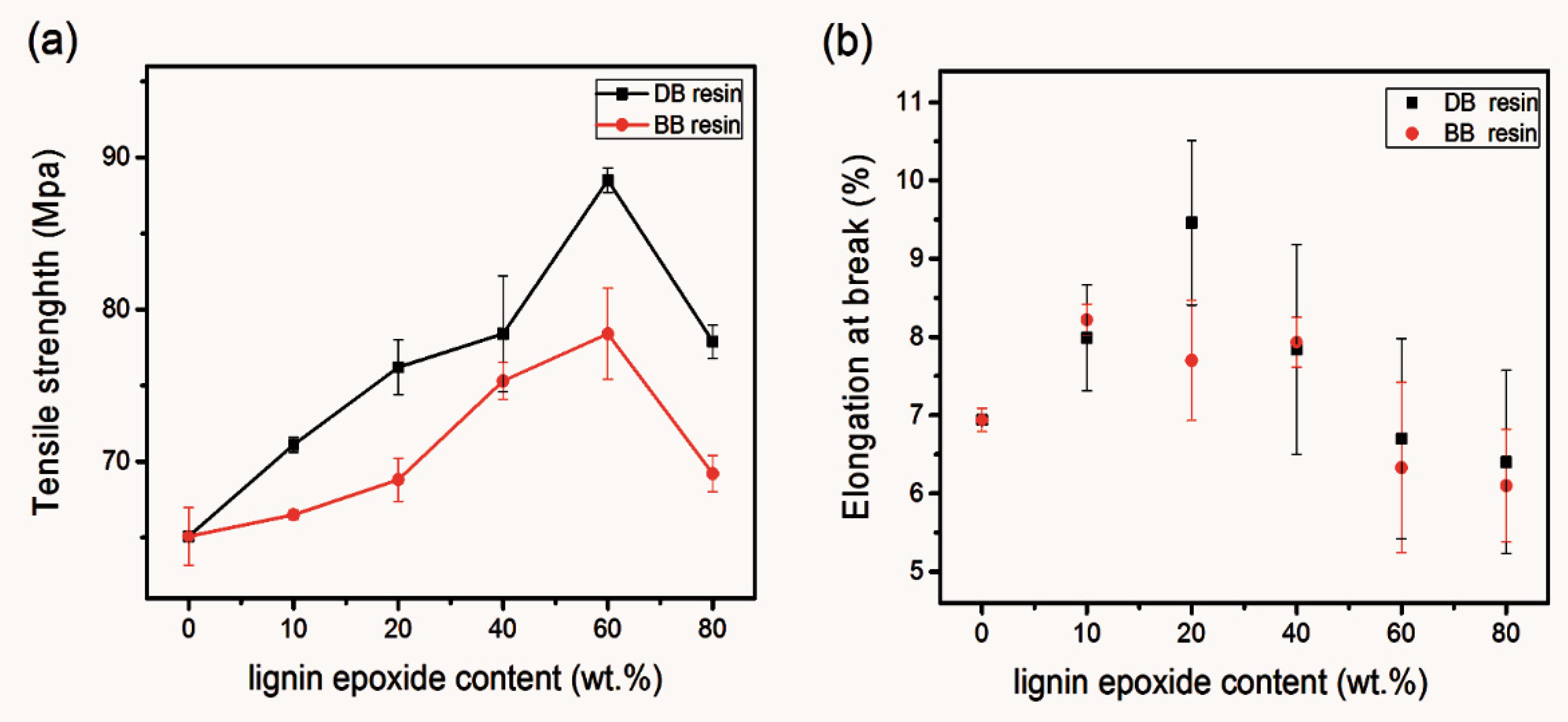
3.2. Evaluation of the Performance of the Prepared DMAP-Lignin Epoxide and Its Cured Resin
4. DMAP-Lignin Epoxide Perspectives and Challenges for Practical Application
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMAP | Dimethylaminopyridine |
| BTEAC | Benzyltriethylammonium chloride |
| BADGE | Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether |
| DB | DMAP-lignin epoxide/ BADGE |
| BB | BTEAC-lignin epoxide/BADGE |
| FRPs | Fiber-reinforced plastics |
| Mn | Number-average molecular weight |
| Mw | Weight-average molecular weight |
| Ɖ | Molecular weight distribution |
| ECH | Epichlorohydrin |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| TETA | Triethylene teramine |
| DMF | Dimethyl formamide |
| BDDGE | Butanediol diglycidyl ether |
| N2 | Nitrogen |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| 1H NMR | 1H nuclear magnetic resonance |
| p-NBD | p-Nitrobenzaldehyde |
| GPC | Gel permeation chromatography |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| DMA | Dynamic mechanical analysis |
| E’ | Storage modulus |
| E’’ | Loss modulus |
| Tg | Glass transition temperature |
| ρ | Crosslink density |
| Tα | 1st Phase transition temperature |
| Tβ | 2nd Phase transition temperatures |
| G | Guaiacyl |
| S | Syringyl |
| DB80 | DMAP-lignin epoxide/ BADGE (DB) with DMAP-lignin epoxide replacement of 80 wt% BADGE, while the other samples are named accordingly based on the weight percentage of lignin epoxide. |
| BB80 | BTEAC -lignin epoxide/ BADGE (BB) with BTEAC -lignin epoxide replacement of 80 wt% BADGE, while the other samples are named accordingly based on the weight percentage of lignin epoxide. |
References
- Liu, W.; Zhou, R.; Goh, H.L.S.; Huang, S.; Lu, X. From waste to functional additive: Toughening epoxy resin with lignin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5810–5817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ganewatta, M.S.; Tang, C. Sustainable polymers from biomass: Bridging chemistry with materials and processing. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 101, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, A.A.; Ojur Dennis, J.; Al-Hadeethi, Y.; Mkawi, E.M.; Abubakar Abdulkadir, B.; Usman, F.; Mudassir Hassan, Y.; Wadi, I.A.; Sani, M. State of the art and new directions on electrospun lignin/cellulose nanofibers for supercapacitor application: A systematic literature review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saratale, R.G.; Saratale, G.D.; Ghodake, G.; Cho, S.-K.; Kadam, A.; Kumar, G.; Jeon, B.-H.; Pant, D.; Bhatnagar, A.; Shin, H.S. Wheat straw extracted lignin in silver nanoparticles synthesis: Expanding its prophecy towards antineoplastic potency and hydrogen peroxide sensing ability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Maharjan, A.; Jun, H.-B.; Kim, B.S. Bioconversion of lignin and its derivatives into polyhydroxyalkanoates: Challenges and opportunities. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 66, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh Saratale, R.; Cho, S.-K.; Dattatraya Saratale, G.; Kadam, A.A.; Ghodake, G.S.; Kumar, M.; Naresh Bharagava, R.; Kumar, G.; Su Kim, D.; Mulla, S.I.; et al. A comprehensive overview and recent advances on polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) production using various organic waste streams. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.N.; Nechifor, M.; Tanasa, F.; Zanoaga, M.; McLoughlin, A.; Strozyk, M.A.; Culebras, M.; Teaca, C.-A. Valorization of lignin in polymer and composite systems for advanced engineering applications—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 828–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, V.K.; Thakur, M.K.; Raghavan, P.; Kessler, M.R. Progress in green polymer composites from lignin for multifunctional applications: A review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1072–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalami, S.; Chen, N.; Borazjani, H.; Nejad, M. Comparative analysis of different lignins as phenol replacement in phenolic adhesive formulations. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.; Yuan, Z.; Schmidt, J.; Xu, C. Preparation of bio-based rigid polyurethane foam using hydrolytically depolymerized Kraft lignin via direct replacement or oxypropylation. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Stubbs, L.P.; He, C. Carboxylated Lignin as an Effective Cohardener for Enhancing Strength and Toughness of Epoxy. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Wei, G.S.; Gao, J.M.; Song, Z.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Qiao, J.L. Effect of elastomeric nanoparticles on toughness and heat resistance of epoxy resins. Macromol. Rapid. Commun. 2002, 23, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Hwang, H.; Oh, S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, U.J.; Choi, J.W. Investigation of structural modification and thermal characteristics of lignin after heat treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 66, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.J.; Karaaslan, M.A.; Renneckar, S.; Ko, F. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of electrospun lignin-based nanofibers by heat treatment. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 9602–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.Q.; Li, H.; Yuan, T.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Sun, R.C. Heat treatment of industrial alkaline lignin and its potential application as an adhesive for green wood-lignin composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7269–7277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Pas, D.J.; Torr, K.M. Biobased epoxy resins from deconstructed native softwood lignin. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferdosian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Anderson, M.; Xu, C. Curing kinetics and mechanical properties of bio-based epoxy composites comprising lignin-bised epoxy resins. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 82, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, C.; Colonna, M.; Tagami, A.; Medina, L.; Sevastyanova, O.; Berglund, L.A.; Lawoko, M. Lignin-based epoxy resins: Unravelling the relationship between structure and material properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1920–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdosian, F.; Yuan, Z.S.; Anderson, M.; Xu, C. Synthesis of lignin-based epoxy resins: Optimization of reaction parameters using response surface methodology. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 31745–31753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.Y.; Barros, L.D.; Sain, M.; Tjong, J.S.Y.; Yan, N. Effects of reaction parameters on the glycidyl etherification of bark extractives during bioepoxy resin synthesis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1016–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asada, C.; Basnet, S.; Otsuka, M.; Sasaki, C.; Nakamura, Y. Epoxy resin synthesis using low molecular weight lignin separated from various lignocellulosic materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ding, D.C.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, H.Y.; Kenttamaa, H.I.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Renewable thermoset polymers based on lignin and carbohydrate derived monomers. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Das, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Wanninayake, N.; Pu, Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Ragauskas, A.J.; et al. Linking lignin source with structural and electrochemical properties of lignin-derived carbon materials. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 38721–38732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioia, C.; Lo Re, G.; Lawoko, M.; Berglund, L. Tunable thermosetting epoxies based on fractionated and well-characterized lignins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4054–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Synthesis of renewable thermoset polymers through successive lignin modification using lignin-derived phenols. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 5059–5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Abu-Omar, M.M. Renewable epoxy networks derived from lignin-based monomers: Effect of cross-linking density. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6082–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, P.J. Molecular theory of rubber elasticity. Polymer 1979, 20, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karumuri, S.; Hiziroglu, S.; Kalkan, A.K. Thermoset-cross-linked lignocellulose: A moldable plant biomass. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6596–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, C.; Wanaka, M.; Takagi, H.; Tamura, S.; Asada, C.; Nakamura, Y. Evaluation of epoxy resins synthesized from steam-exploded bamboo lignin. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 43, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, H.; Illers, K.H.; Mertes, J. A Generalized theory for the glass-transition temperature of cross-linked and uncrosslinked polymers. J. Polym. Sci. Pol. Phys. 1990, 28, 1483–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, K.H.; Kloxin, C.J.; Epps, T.H., III. Potential lignin-derived alternatives to bisphenol a in diamine-hardened epoxy resins. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 14812–14819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.N.; Rath, S.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Sudarshan, K.; Maheshwari, P.; Patri, M.; Praveen, S.; Khandelwal, P.; Pujari, P.K. Free volumes and structural relaxations in diglycidyl ether of bisphenol-A based epoxy-polyether amine networks. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 3589–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Kong, M.; Yang, Q.; Huang, Y.; Li, G. Toward simultaneous toughening and reinforcing of trifunctional epoxies by low loading flexible reactive triblock copolymers. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17380–17388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, B.; Zhang, L.; Wu, M.; Xing, A.; Miao, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, X. Environmentally friendly high performance homopolymerized epoxy using hyperbranched epoxy as a modifier. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 14211–14221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Resende, F.L.P.; Moutsoglou, A.; Raynie, D.E. Pyrolysis of lignin extracted from prairie cordgrass, aspen, and Kraft lignin by Py-GC/MS and TGA/FTIR. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 98, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H.-Q. Thermochemical conversion of lignin to functional materials: A review and future directions. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 4888–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandim-Giannetti, A.A.; Agnelli, J.A.M.; Lancas, B.Z.; Magnabosco, R.; Casarin, S.A.; Bettini, S.H.P. Lignin as additive in polypropylene/coir composites: Thermal, mechanical and morphological properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2563–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Type | Mn | Mw | Ɖ | ph–OH Content (mmol/g) | –COOH Content (mmol/g) | Ratio of G to S (G/S) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Softwood lignin | 2827 | 3153 | 1.12 | 3.05 | 1.71 | >50% |
| Sample | DMAP-Lignin Epoxide | BTEAC-Lignin Epoxide | BADGE | TETA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | (g) | (g) | (g) | |
| DMAP-lignin epoxide resin | 22.00 | - | - | 3.00 |
| BTEAC-lignin epoxide resin | - | 22.00 | - | 3.00 |
| BADGE resin | - | - | 22.00 | 3.00 |
| Sample | DMAP-Lignin Epoxide | BTEAC-Lignin Epoxide | BADGE | BDDGE | TETA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (g) | (g) | (g) | (g) | (g) | |
| DB0/BB0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 5.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| DB10 | 0.50 | - | 4.50 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| DB20 | 1.00 | - | 4.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| DB40 | 2.00 | - | 3.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| DB60 | 3.00 | - | 2.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| DB80 | 4.00 | - | 1.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| BB10 | - | 0.50 | 4.50 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| BB20 | - | 1.00 | 4.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| BB40 | - | 2.00 | 3.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| BB60 | - | 3.00 | 2.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| BB80 | - | 4.00 | 1.00 | 1.25 | 0.65 |
| FTIR Band Position (cm−1) | Assignment |
|---|---|
| 3450 cm−1 | stretching of –OH in hydroxyl group and carboxyl group |
| 3000, 2927, and 2846 cm−1 | stretching of alkyl C–H |
| 1700, and 1648 cm−1 | stretching of C=O in carboxyl group |
| 1600, 1506, and 1455 cm−1 | stretching of C=C–C bond in benzene ring |
| 1338 cm−1 | symmetric deformation of C–H bond |
| 1260 cm−1 | stretching of C–O in phenol group |
| 1222 cm−1 | stretching of C–O in phenoxy group |
| 1130 cm−1 | stretching of C–O in alkyl alcohol |
| 1030 cm−1 | stretching of C–O in ether group |
| 846, and 748 cm−1 | deformation of C–H of benzene ring |
| Samples | Epoxy Value (mmol/g) | Molecular Weight | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | MW | Ɖ | ||
| DMAP-lignin epoxide | 2.09 | 8244 | 17,085 | 2.07 |
| BTEAC-lignin epoxide | 2.16 | 9775 | 22,439 | 2.30 |
| Sample | Storage Modulus (MPa) | Tg (°C) | ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glassy Region at −50 °C | Glassy Region at 25 °C | Rubbery Region at Tg + 30 °C | |||
| BADGE resin | 11,300 | 8190 | 146.3 | 75 | 15.52 |
| DMAP-lignin epoxide resin | 6460 | 1200 | 28.4 | 46 | 3.26 |
| BTEAC-lignin epoxide resin | 5280 | 4286 | 43.8 | 90 | 4.47 |
| Sample | E′ at −50 °C | 1st Transition Tβ from E″ | E′ at 25 °C | 2nd Transition Tα from E″ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MPa) | (°C) | (MPa) | (°C) | |
| DB40 | 8168 | 4.8 | 5239 | 59.1 |
| DB80 | 9629 | −4.6 | 4426 | 37.6 |
| BB40 | 9200 | 16.4 | 6336 | 62.9 |
| BB80 | 8940 | 4.2 | 4350 | 52.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, L.; Meng, Y.; Lv, P.; Liu, W.; Pang, H. Preparation of a Dmap-Catalysis Lignin Epoxide and the Study of Its High Mechanical-Strength Epoxy Resins with High-Biomass Content. Polymers 2021, 13, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050750
Song L, Meng Y, Lv P, Liu W, Pang H. Preparation of a Dmap-Catalysis Lignin Epoxide and the Study of Its High Mechanical-Strength Epoxy Resins with High-Biomass Content. Polymers. 2021; 13(5):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050750
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Lingxia, Yeyun Meng, Peng Lv, Weiqu Liu, and Hao Pang. 2021. "Preparation of a Dmap-Catalysis Lignin Epoxide and the Study of Its High Mechanical-Strength Epoxy Resins with High-Biomass Content" Polymers 13, no. 5: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050750
APA StyleSong, L., Meng, Y., Lv, P., Liu, W., & Pang, H. (2021). Preparation of a Dmap-Catalysis Lignin Epoxide and the Study of Its High Mechanical-Strength Epoxy Resins with High-Biomass Content. Polymers, 13(5), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13050750