Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy 15 (HLD15)-Associated Mutation of EPRS1 Leads to Its Polymeric Aggregation in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures, Inhibiting Oligodendroglial Cell Morphological Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Primary and Secondary Antibodies
2.2. Plasmid Constructions
2.3. Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.4. Transfection
2.5. Confocal Microscopic Mages
2.6. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Immunoblotting
2.7. Affinity-Precipitation Assay for Rab7 Regulatory Molecules
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Ethics Statement
3. Results
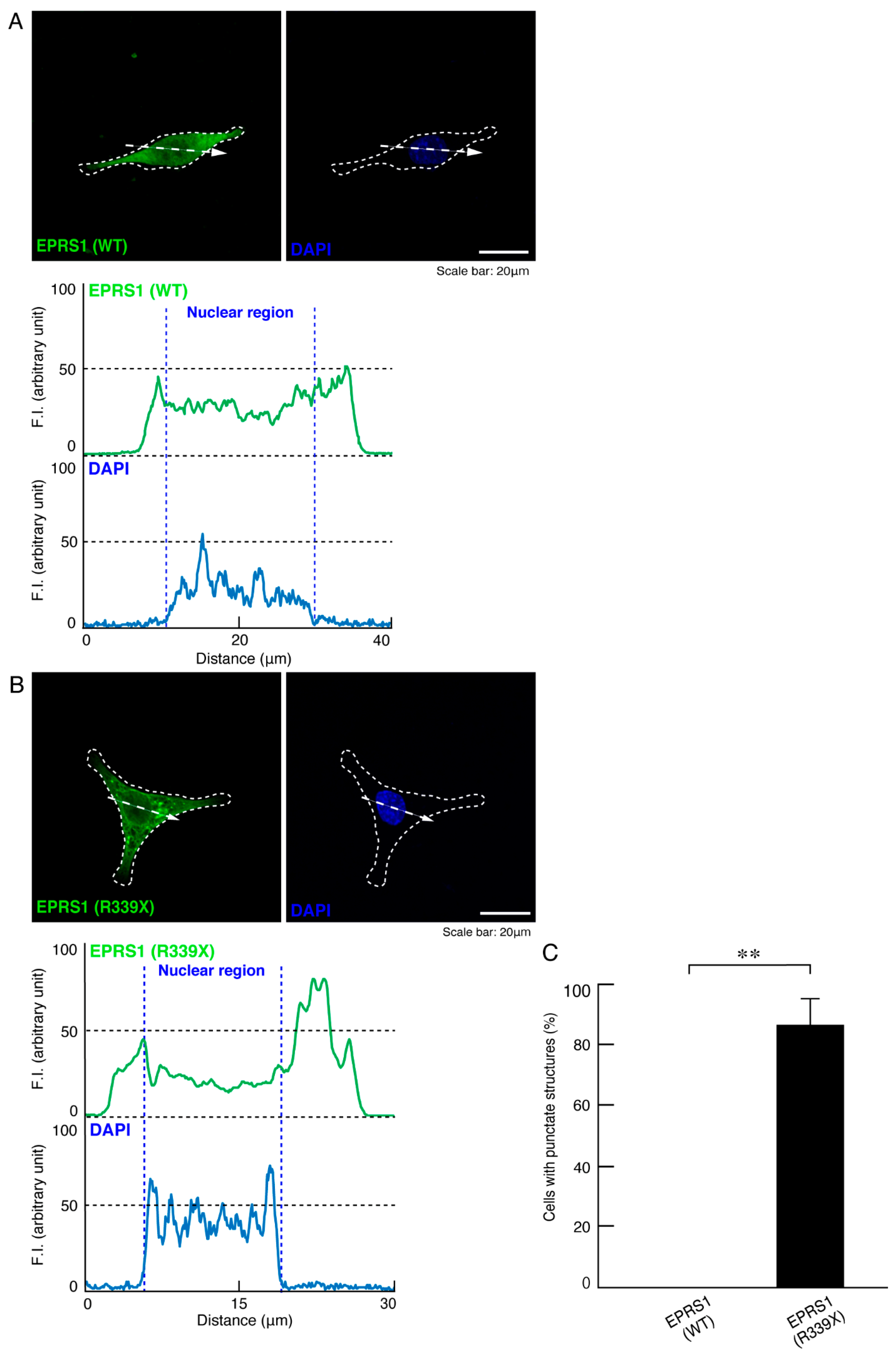
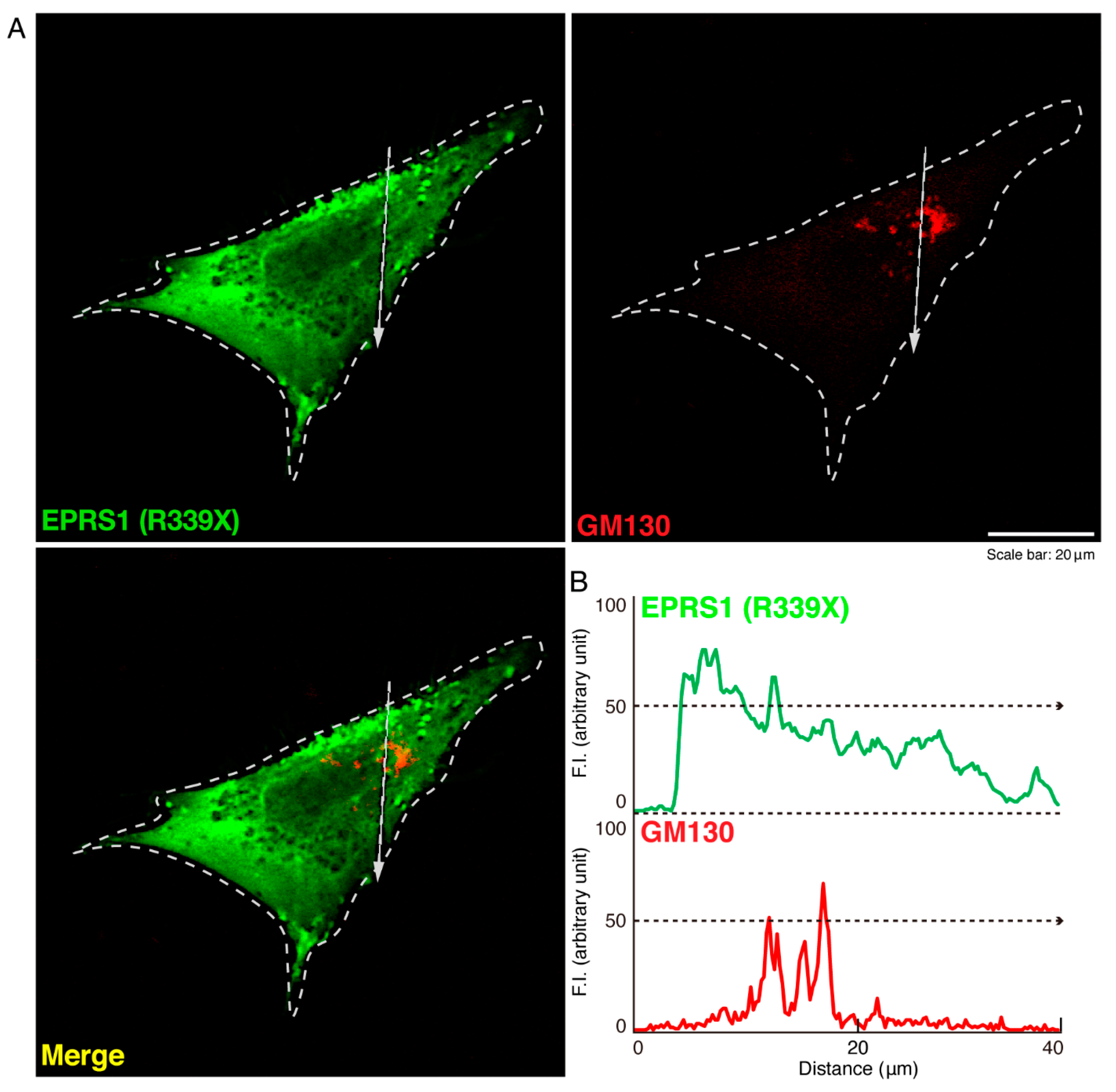
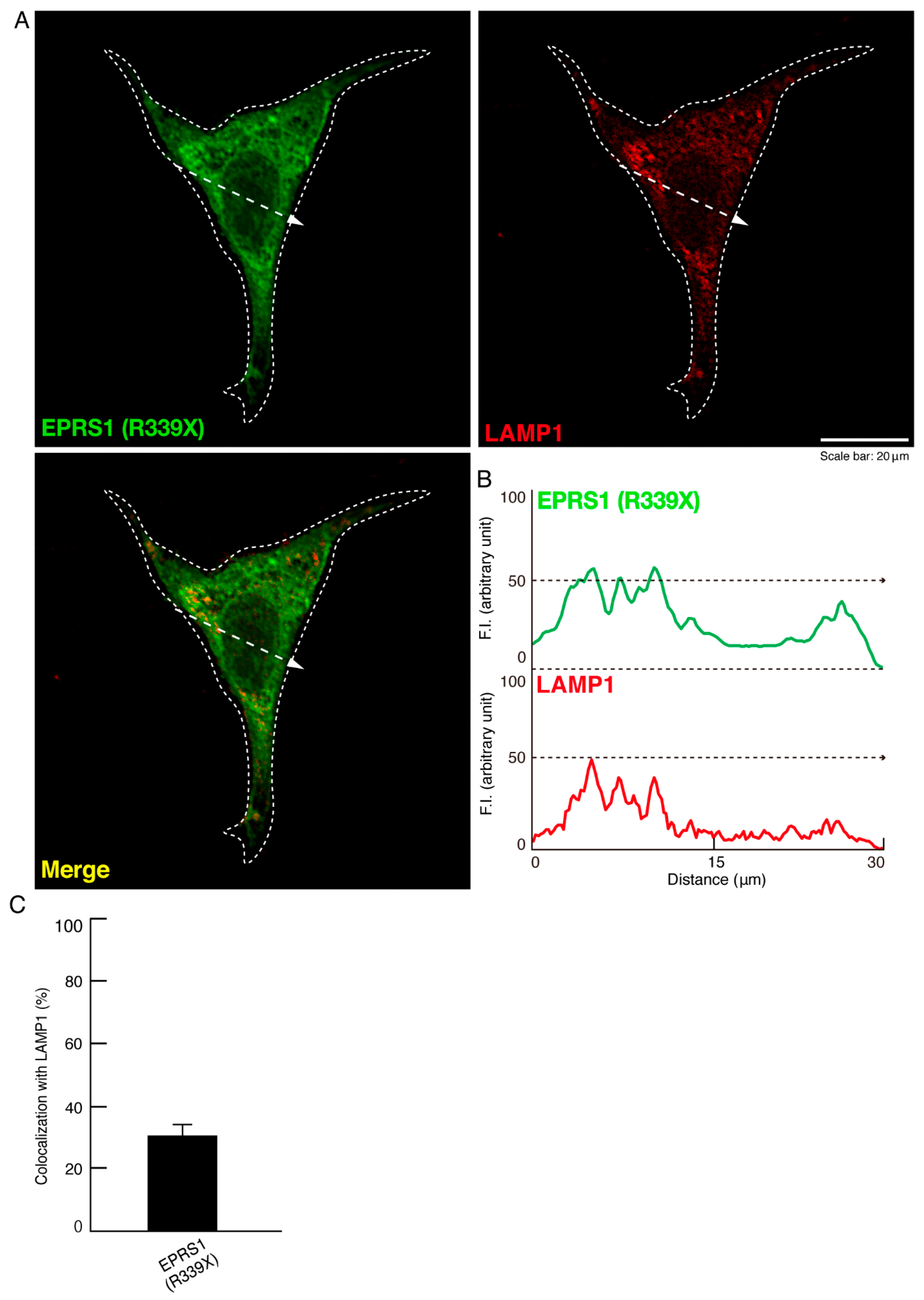
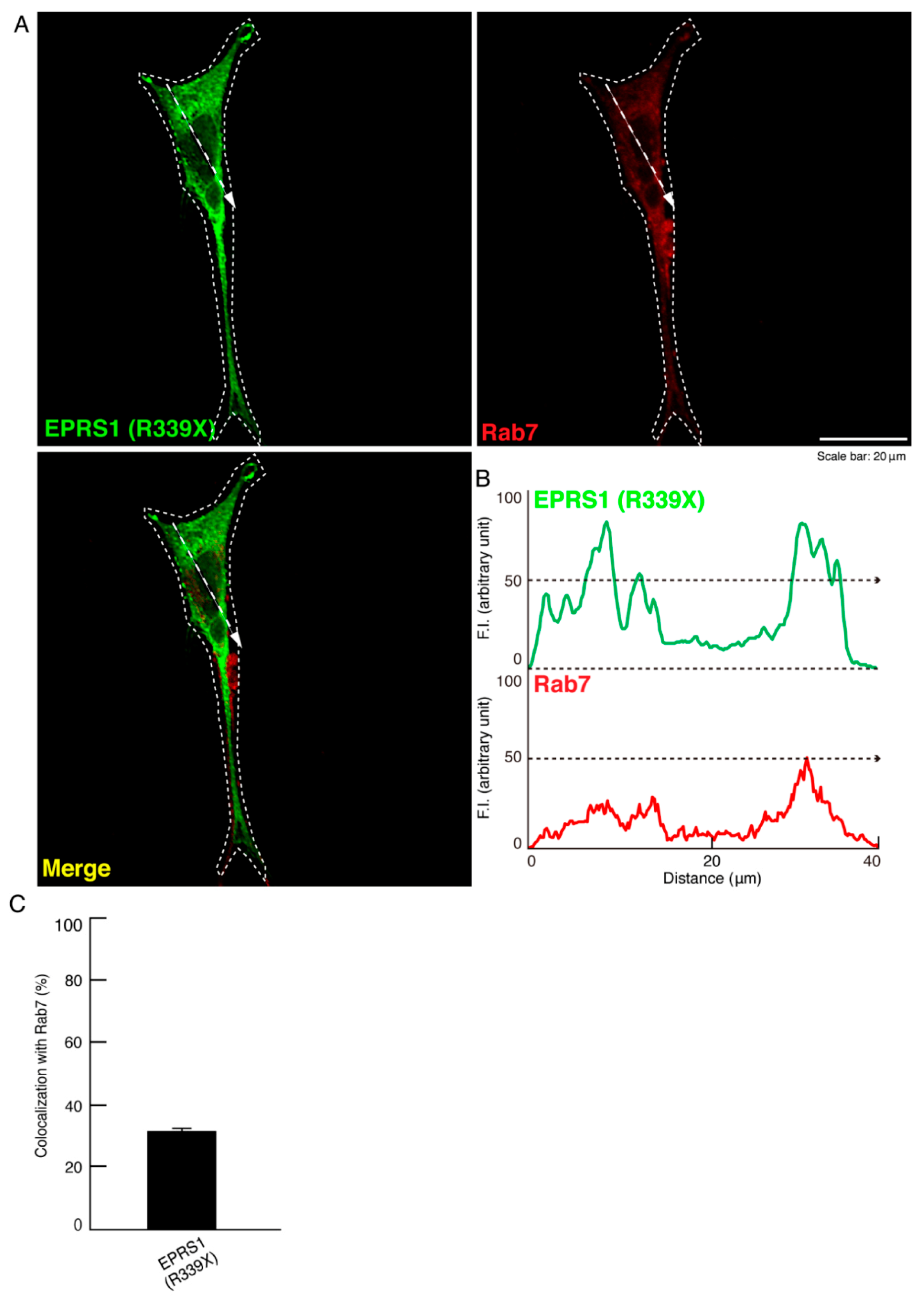
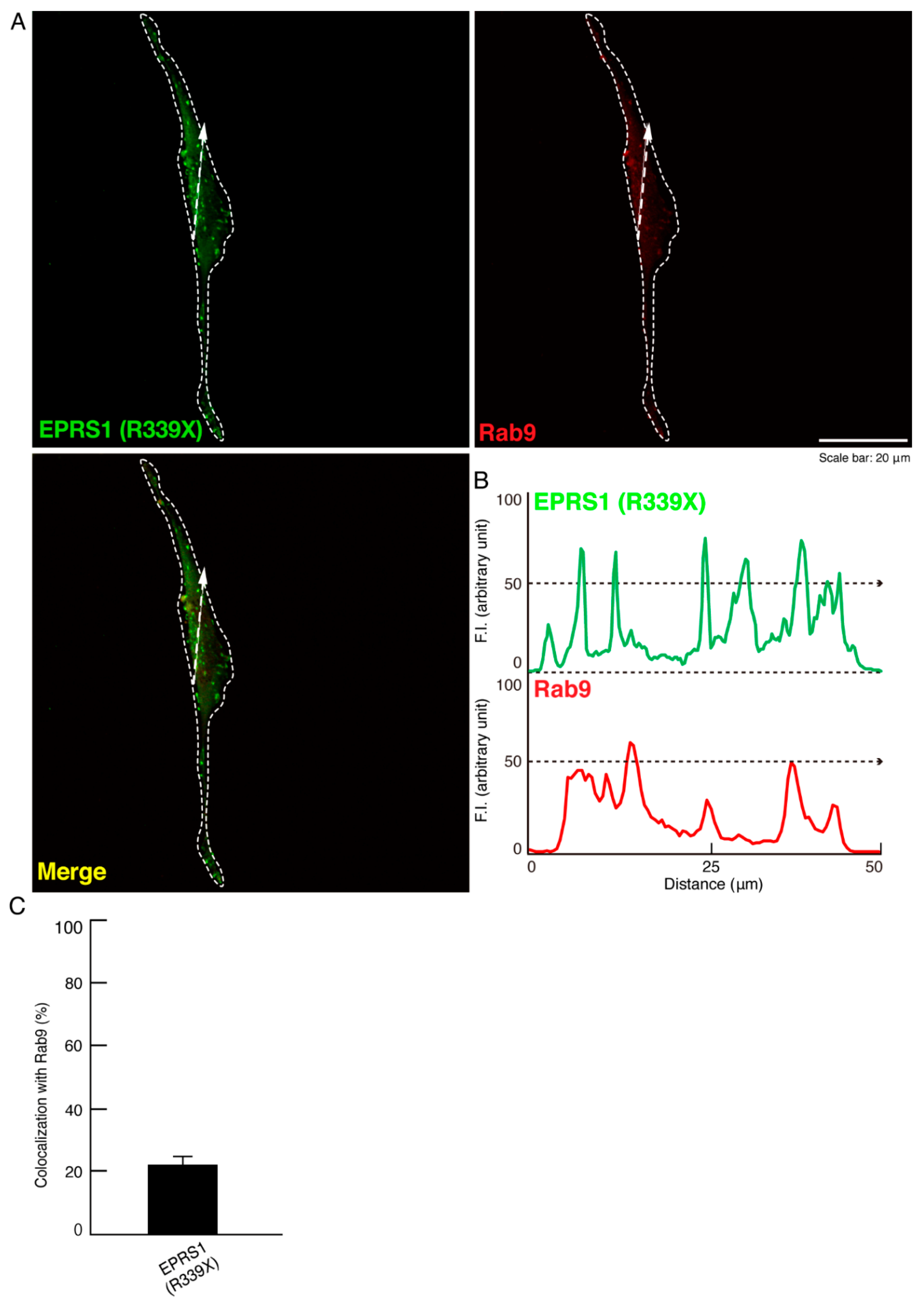
3.1. The R339X Mutant Proteins of EPRS1 Are Localized in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures
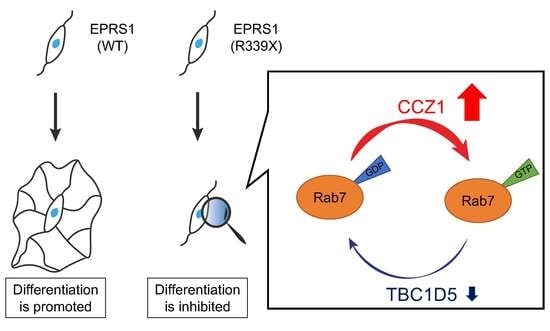
3.2. The R339X Mutant Proteins of EPRS1 Form Protein Aggregates and Modulate Signals Regulating Rab7
3.3. Expression of the R339X Mutant Proteins of EPRS1 in Cells Inhibits Morphological Differentiation
4. Discussion
| Disease | Treatment | Effect | Reference (See References) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HLD1 | Lonaprisan | Improve the poor motor phenotype and increase in the number of myelinated axons | [31] |
| HLD1 | Curcumin | Improve the poor motor phenotype and increase in the number of myelinated axons | [32] |
| HLD1 | Ketogenic diet | Restore oligodendrocyte integrity and increase CNS myelination | [33] |
| HLD1 | Transplantation with neural stem cells | Induce neural regeneration in the CNS | [34] |
| HLD1 | Deferiprone | Induce reduced oligodendrocyte apoptosis and enabled myelin formation | [35] |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simons, M.; Lyons, D.A. Axonal selection and myelin sheath generation in the central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2013, 25, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, P.D.; Ishibashi, N.; Jonas, R.A.; Gallo, V. Congenital cardiac anomalies and white matter injury. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saab, A.S.; Nave, K.-A. Myelin dynamics: Protecting and shaping neuronal functions. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2017, 47, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Rub, M.; Miller, R.H. Emerging cellular and molecular strategies for enhancing Central Nervous System (CNS) remyelination. Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaunchak, A.S.; Colman, D.R.; Nave, K.-A. Misalignment of PLP/DM20 Transmembrane domains determines protein misfolding in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 14961–14971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Fenstermaker, A.G.; Way, S.W.; Clayton, B.; Jamison, S.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D.; Popko, B. Oligodendrocyte-specific activation of PERK signaling protects mice against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5980–5991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbern, J.; Cambi, F.; Shy, M.; Kamholz, J. The molecular pathogenesis of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K. Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease: Molecular and cellular pathologies and associated phenotypes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1190, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, N.I.; Ffrench-Constant, C.; Van Der Knaap, M.S. Hypomyelinating leukodystrophies—Unravelling myelin biology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Lacrampe, A.; Hu, F. Physiological and pathological functions of TMEM106B: A gene associated with brain aging and multiple brain disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 141, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.I.; Gutierrez Salazar, M.; Guerrero, K.; Thiffault, I.; Salomons, G.S.; Gauquelin, L.; Tran, L.T.; Forget, D.; Gauthier, M.S.; Waisfisz, Q.; et al. Bi-allelic mutations in EPRS, encoding the glutamyl-prolyl-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, cause a hypomyelinating leukodystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Torii, T.; Tago, K.; Tanoue, A.; Takashima, S.; Yamauchi, J. BIG1/Arfgef1 and Arf1 regulate the initiation of myelination by Schwann cells in mice. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Hattori, K.; Ito, A.; Harada, H.; Oizumi, H.; Ohbuchi, K.; Mizoguchi, K.; Yamauchi, J. PP1C and PP2A are p70S6K phosphatases whose inhibition ameliorates HLD12-associated inhibition of oligodendroglial cell morphological differentiation. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Okura, N.; Fukui, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y.; Torii, T.; Ooizumi, H.; Ohbuchi, K.; Mizoguchi, K.; et al. Rare neurologic disease-associated mutations of AIMP1 Are Related with inhibitory neuronal differentiation which is reversed by ibuprofen. Medicines 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattori, K.; Tago, K.; Memezawa, S.; Ochiai, A.; Sawaguchi, S.; Kato, Y.; Sato, T.; Tomizuka, K.; Ooizumi, H.; Ohbuchi, K.; et al. The infantile leukoencephalopathy-associated mutation of C11ORF73/HIKESHI proteins generates de novo interactive activity with filamin A, inhibiting oligodendroglial cell morphological differentiation. Medicines 2021, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Hall, A. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors for Rho GTPases: Turning on the switch. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1587–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J.; Sondek, J. GEF means go: Turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, W.T.; Ellerbroek, S.M.; Der, C.J.; Burridge, K.; Wennerberg, K. XPLN, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RhoA and RhoB, but not RhoC. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 42964–42972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, J.; Miyamoto, Y.; Torii, T.; Takashima, S.; Kondo, K.; Kawahara, K.; Nemoto, N.; Chan, J.R.; Tsujimoto, G.; Tanoue, A. Phosphorylation of cytohesin-1 by Fyn is required for initiation of myelination and the extent of myelination during development. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, J.; Torii, T.; Kusakawa, S.; Sanbe, A.; Nakamura, K.; Takashima, S.; Hamasaki, H.; Kawaguchi, S.; Miyamoto, Y.; Tanoue, A. The mood stabilizer valproic acid improves defective neurite formation caused by charcot-marie-tooth disease-associated mutant Rab7 through the JNK signaling pathway. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 3189–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.-T.; Xie, Y.-X.; Zhou, B.; Huang, N.; Farfel-Becker, T.; Sheng, Z.-H. Characterization of LAMP1-labeled nondegradative lysosomal and endocytic compartments in neurons. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 3127–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, F.; Bucci, C. Multiple roles of the small GTPase Rab7. Cells 2016, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langemeyer, L.; Fröhlich, F.; Ungermann, C. Rab GTPase function in endosome and lysosome biogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 957–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, A.; Jia, J.; Mukhopadhyay, R.; Willard, B.; Kinter, M.; Fox, P.L. Two-site phosphorylation of EPRS coordinates multimodal regulation of noncanonical translational control activity. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 164–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halawani, D.; Gogonea, V.; DiDonato, J.A.; Pipich, V.; Yao, P.; China, A.; Topbas, C.; Vasu, K.; Arif, A.; Hazen, S.L.; et al. Structural control of caspase-generated glutamyl-tRNA synthetase by appended noncatalytic WHEP domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 8843–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenweg, M.E.; Ghezzi, D.; Haack, T.; Abbink, T.E.; Martinelli, D.; Van Berkel, C.G.; Bley, A.; Diogo, L.; Grillo, E.; Naudé, J.T.W.; et al. Leukoencephalopathy with thalamus and brainstem involvement and high lactate ‘LTBL’ caused by EARS2 mutations. Brain 2012, 135, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciara, E.; Rokicki, D.; Lazniewski, M.; Mierzewska, H.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Bekiesińska-Figatowska, M.; Piekutowska-Abramczuk, D.; Iwanicka-Pronicka, K.; Szymańska, E.; Stawiński, P.; et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of newly reported mitochondrial disease entity caused by biallelic PARS2 mutations. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Tang, B.; Mao, X.; Peng, J.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, N. The genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of PARS2-related infantile-onset encephalopathy. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvainickas, A.; Nägele, H.; Qi, W.; Dokládal, L.; Jimenez-Orgaz, A.; Stehl, L.; Gangurde, D.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, Z.; Dengjel, J.; et al. Retromer and TBC1D5 maintain late endosomal RAB7 domains to enable amino acid–induced mTORC1 signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 3019–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Torii, T.; Tanoue, A.; Yamauchi, J. VCAM1 acts in parallel with CD69 and is required for the initiation of oligodendrocyte myelination. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prukop, T.; Epplen, D.B.; Nientiedt, T.; Wichert, S.P.; Fledrich, R.; Stassart, R.M.; Rossner, M.J.; Edgar, J.M.; Werner, H.B.; Nave, K.A.; et al. Progesterone antagonist therapy in a Pelizaeus-Merzbacher mouse model. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 94, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epplen, D.B.; Prukop, T.; Nientiedt, T.; Albrecht, P.; Arlt, F.A.; Stassart, R.M.; Kassmann, C.M.; Methner, A.; Nave, K.A.; Werner, H.B.; et al. Curcumin therapy in a Plp1 transgenic mouse model of Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, S.K.; Berghoff, S.A.; Trevisiol, A.; Spieth, L.; Düking, T.; Schneider, L.V.; Schlaphoff, L.; Dreha-Kulaczewski, S.; Bley, A.; Burfeind, D.; et al. Ketogenic diet ameliorates axonal defects and promotes myelination in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Henry, R.G.; Kang, S.M.; Strober, J.; Lim, D.A.; Ryan, T.; Perry, R.; Farrell, J.; Ulman, M.; Rajalingam, R.; et al. Long-term safety, immunologic response, and imaging outcomes following neural stem cell transplantation for Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 13, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobuta, H.; Yang, N.; Ng, Y.H.; Marro, S.G.; Sabeur, K.; Chavali, M.; Stockley, J.H.; Killilea, D.W.; Walter, P.B.; Zhao, C.; et al. Oligodendrocyte death in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease Is rescued by iron chelation. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Type | Responsible Gene | Mutation from | Number in OMIM |
|---|---|---|---|
| HLD1 (PMD) | plp1 | Amplification, deletion, mutation, splice site mutation | 312080 |
| HLD2 | gjc2 | mutation, deletion | 608804 |
| HLD3 | aimp1 | mutation, deletion | 260600 |
| HLD4 | hspd1 | mutation | 612233 |
| HLD5 | fam126a | mutation, splice site mutation | 610532 |
| HLD6 | tubb4a | mutation | 612438 |
| HLD7 | polr3a | mutation | 607694 |
| HLD8 | polr3b | mutation | 614381 |
| HLD9 | rars1 | mutation | 616140 |
| HLD10 | pycr2 | mutation, splice site mutation | 616420 |
| HLD11 | polr1c | mutation | 616494 |
| HLD12 | vps11 | mutation | 616683 |
| HLD13 | hikeshi | mutation | 616881 |
| HLD14 | ufm1 | mutation, deletion | 617899 |
| HLD15 | eprs | mutation | 617951 |
| HLD16 | tmem106b | mutation, recurrent mutation | 617964 |
| HLD17 | aimp2 | mutation | 618006 |
| HLD18 | degs1 | mutation | 618404 |
| HLD19 | tmem63a | mutation | 618688 |
| HLD20 | cnp | mutation | 619071 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sawaguchi, S.; Goto, M.; Kato, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Tago, K.; Oizumi, H.; Ohbuchi, K.; Mizoguchi, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Yamauchi, J. Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy 15 (HLD15)-Associated Mutation of EPRS1 Leads to Its Polymeric Aggregation in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures, Inhibiting Oligodendroglial Cell Morphological Differentiation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071074
Sawaguchi S, Goto M, Kato Y, Tanaka M, Tago K, Oizumi H, Ohbuchi K, Mizoguchi K, Miyamoto Y, Yamauchi J. Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy 15 (HLD15)-Associated Mutation of EPRS1 Leads to Its Polymeric Aggregation in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures, Inhibiting Oligodendroglial Cell Morphological Differentiation. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071074
Chicago/Turabian StyleSawaguchi, Sui, Mizuki Goto, Yukino Kato, Marina Tanaka, Kenji Tago, Hiroaki Oizumi, Katsuya Ohbuchi, Kazushige Mizoguchi, Yuki Miyamoto, and Junji Yamauchi. 2021. "Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy 15 (HLD15)-Associated Mutation of EPRS1 Leads to Its Polymeric Aggregation in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures, Inhibiting Oligodendroglial Cell Morphological Differentiation" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071074
APA StyleSawaguchi, S., Goto, M., Kato, Y., Tanaka, M., Tago, K., Oizumi, H., Ohbuchi, K., Mizoguchi, K., Miyamoto, Y., & Yamauchi, J. (2021). Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy 15 (HLD15)-Associated Mutation of EPRS1 Leads to Its Polymeric Aggregation in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures, Inhibiting Oligodendroglial Cell Morphological Differentiation. Polymers, 13(7), 1074. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071074