Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and N-Methylol Dimethyl Phosphonopropion Amide (MDPA) System for Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Surface Functionalization of Cellulose
2.3. In-Situ Sonochemical Synthesis of ZnO NPs on Cotton Fabric
2.4. MDPA Application
2.5. Characterization and Testing of Functional Properties
3. Results
3.1. Content Analysis
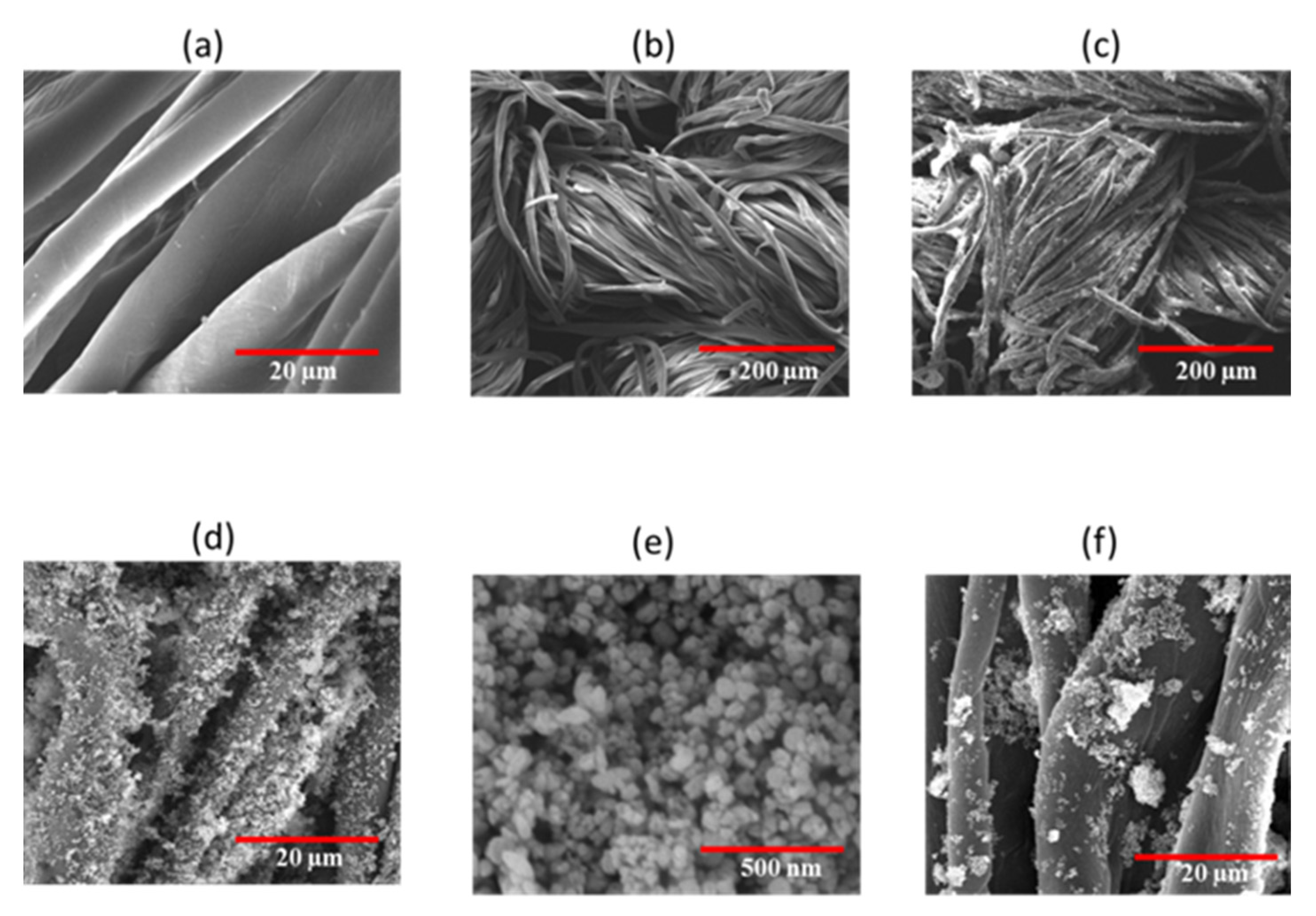
3.2. SEM Analysis
3.3. Particle Size
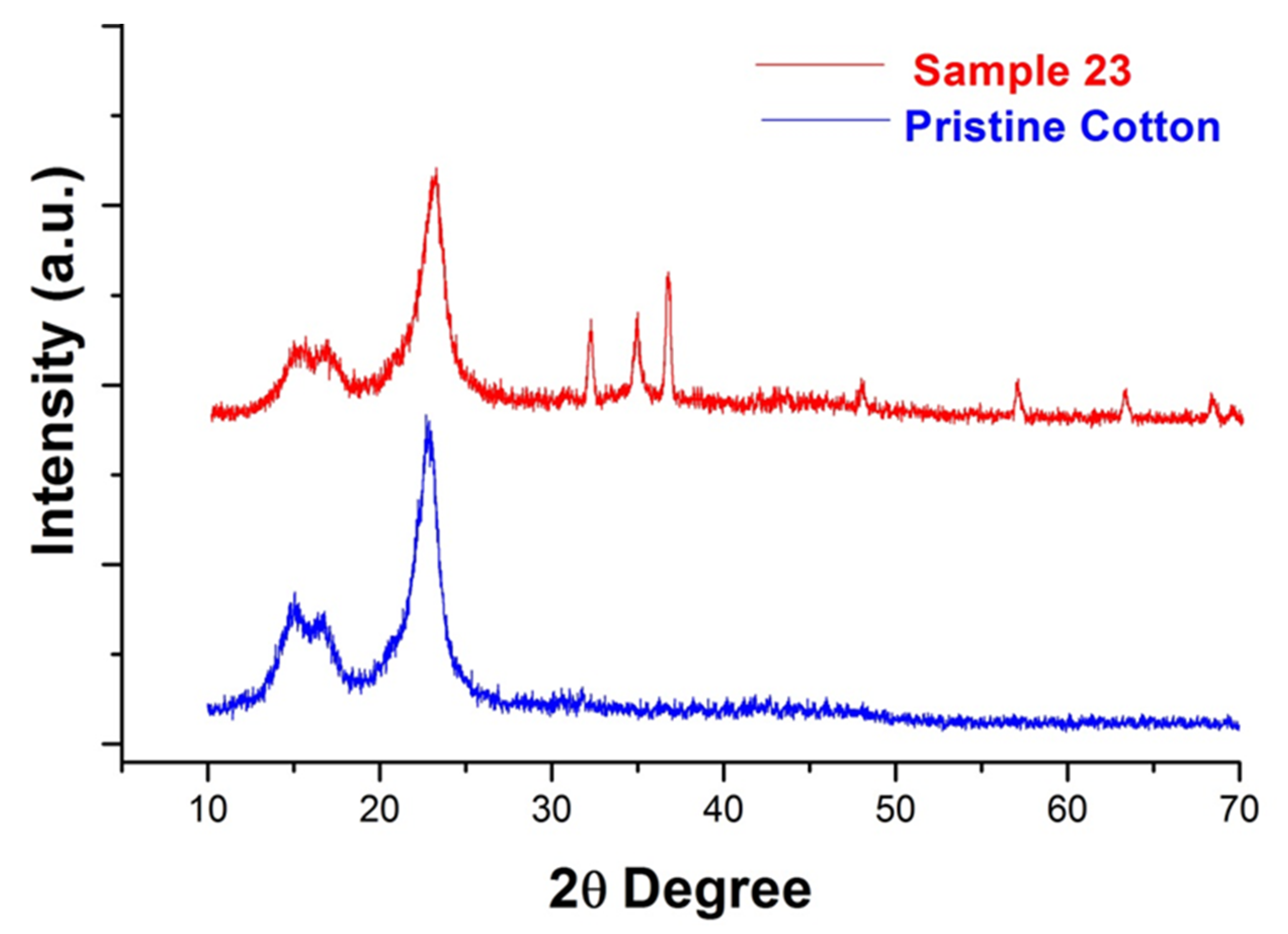
3.4. XRD Analysis
3.5. FTIR Analysis
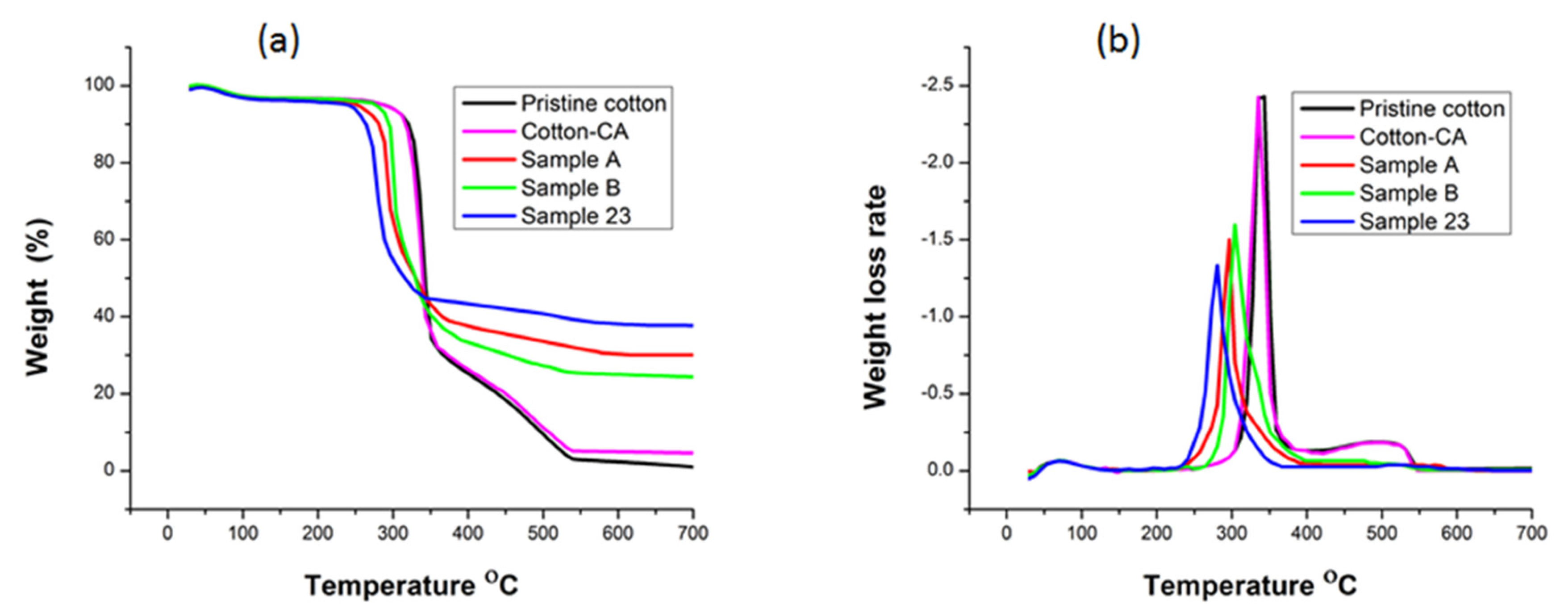
3.6. Thermal Stability
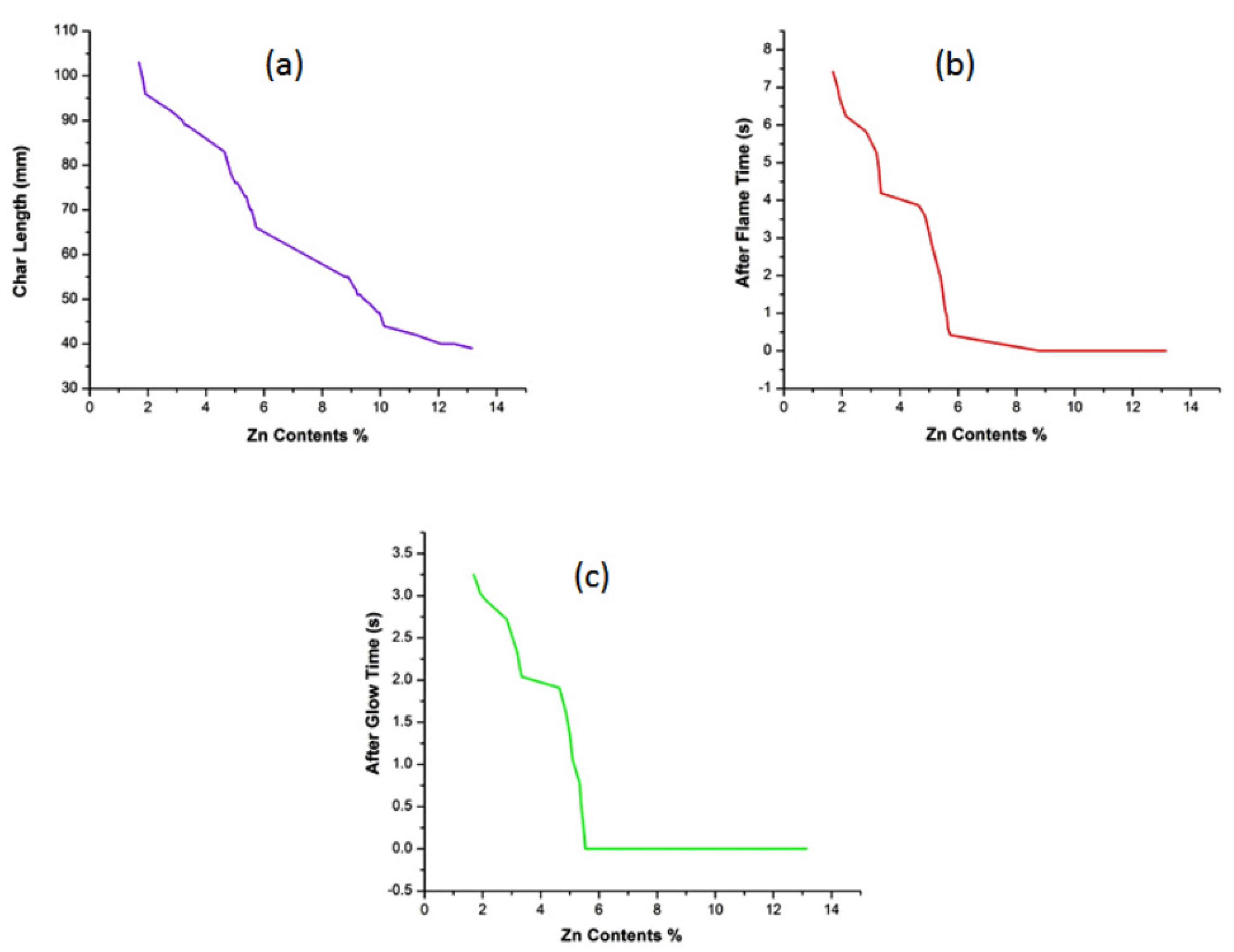
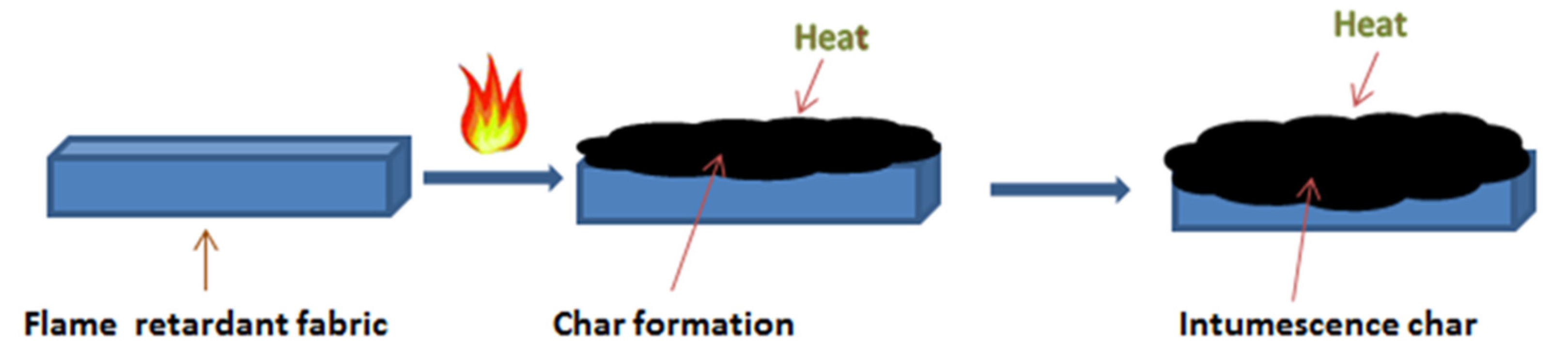
3.7. Vertical Flame Test
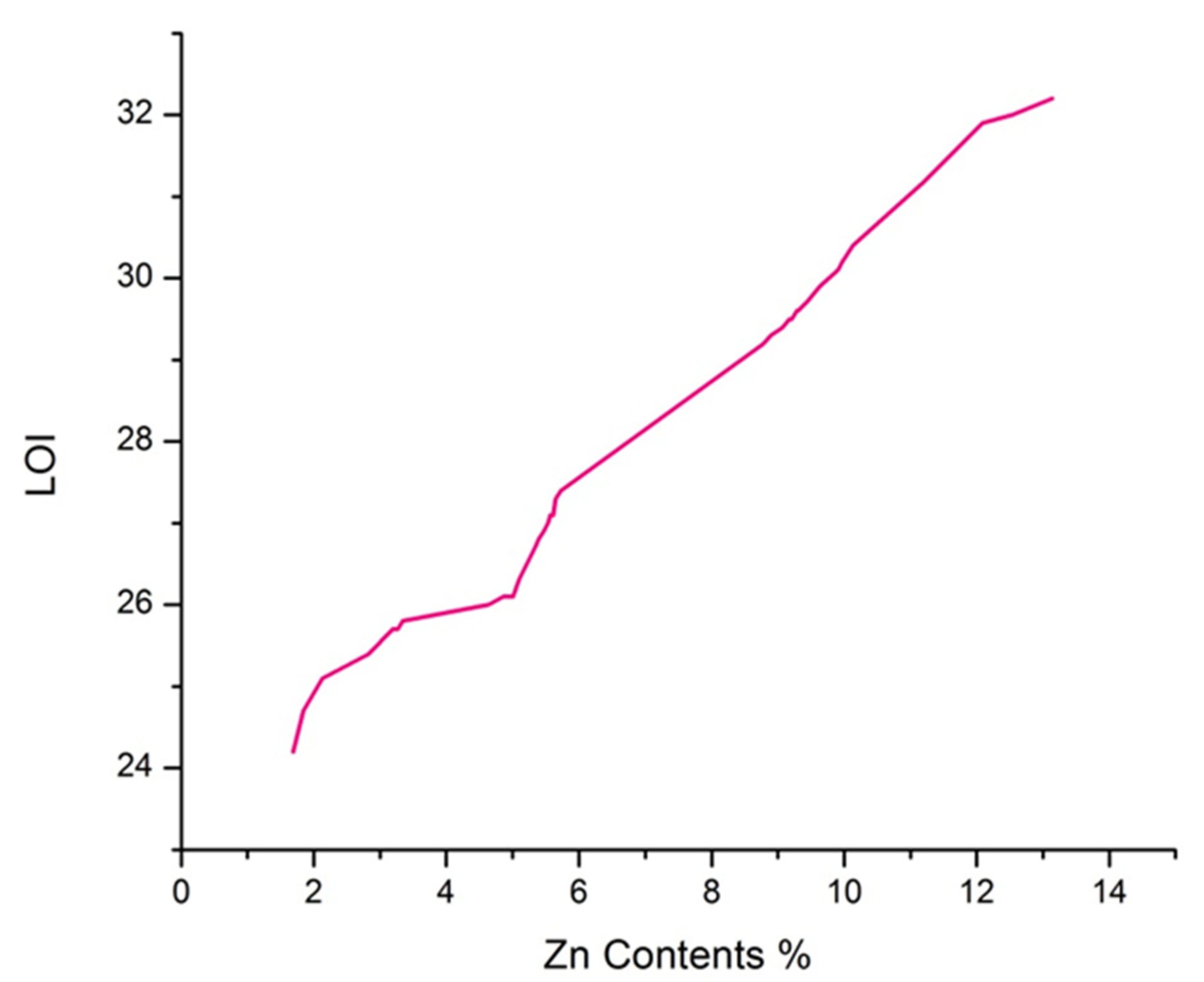
3.8. Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI)
3.9. Antibacterial Activity
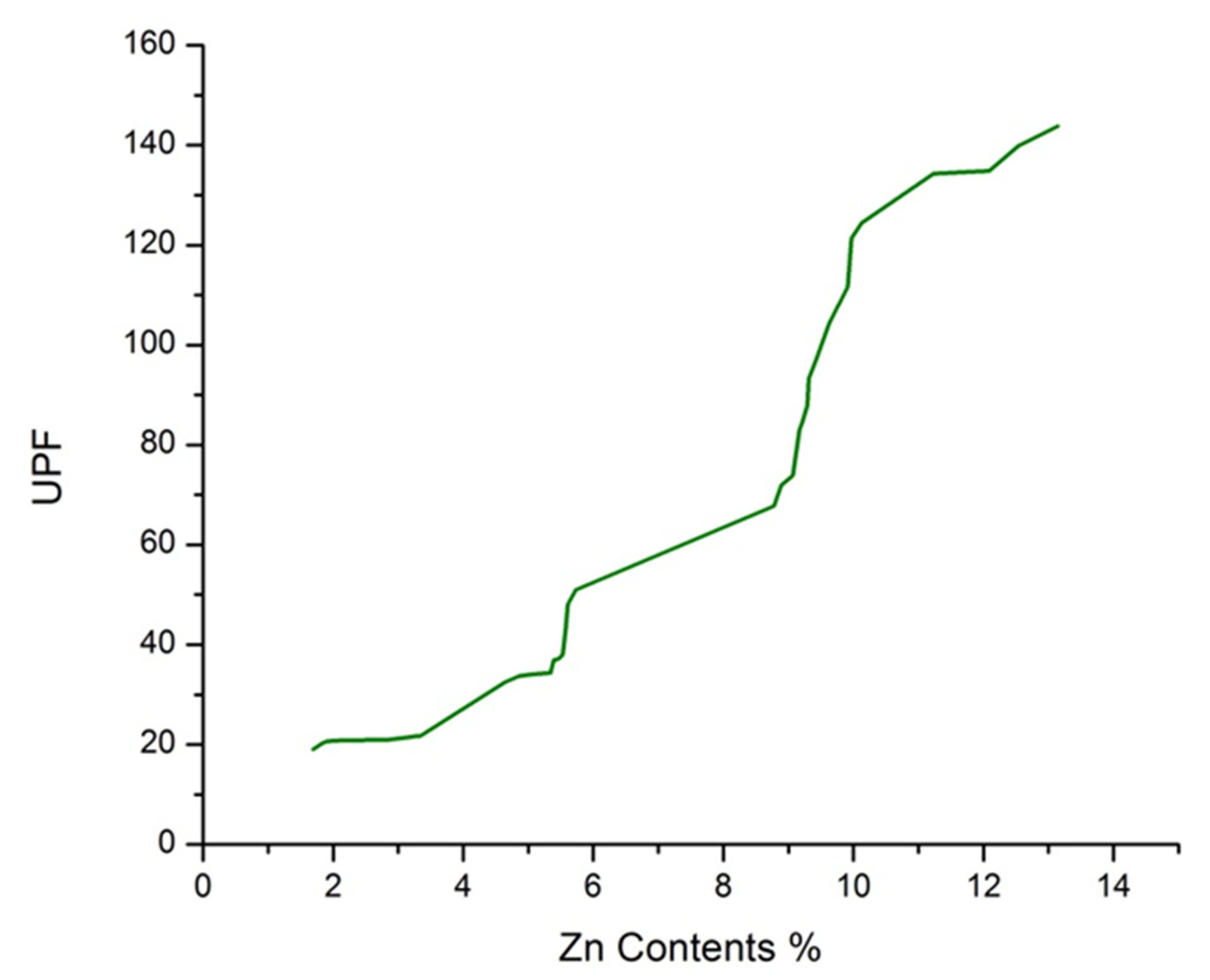
3.10. Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF)
3.11. Wash Durability
4. Conclusions and Future Prospectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mahbubul, B.M.; Khan, M.A. An Overview on Surface Modification of Cotton Fiber for Apparel Use. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravandi, S.A.H.; Valizadeh, M. Properties of fibers and fabrics that contribute to human comfort. In Improving Comfort in Clothing; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 61–78. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, J.; Chan, W.-Y. Textile fibers and fabrics. In Latest Material and Technological Developments for Activewear; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Cheema, H.A.; El-Shafei, A.; Hauser, P.J. Conferring Flame Retardancy on Cotton Using Novel Halogen-Free Flame Retardant Bifunctional Monomers: Synthesis, Characterizations and Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, G.T.; Plohl, D.; Derksen, L.; Lauer, D.; Neldner, P.; Ali, W.; Fuchs, S.; Gutmann, J.S.; Opwis, K. A Green Water-soluble Cyclophosphazene as a Flame Retardant Finish for Textiles. Molecules 2019, 24, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.M.L.; Islam, M.T.; Repon, M.R.; Hossain, M.M.; Sarker, P. Comparative Dyeing Behavior and UV Protective Characteristics of Cotton Fabric Treated with Polyphenols Enriched Banana and Watermelon Biowaste. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 21, 100417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Di, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. A Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma for Preparing Cotton-Fabric-Supported Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.K.; Zong, L.; Tan, Y.; Ji, Q.; Yun, W.; Shi, R.; Xia, Y. Improve the Flame Retardancy of Cellulose Fibers by Grafting Zinc Ion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleemi, S.; Naveed, T.; Riaz, T.; Memon, H.; Awan, J.A.; Siyal, M.I.; Xu, F.; Bae, J. Surface Functionalization of Cotton and Pc Fabrics Using SiO2 and ZnO Nanoparticles for Durable Flame Retardant Properties. Coatings 2020, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Huo, S.; Wang, M.; Cheng, L. Synthesis of a Phosphorus/Nitrogen-Containing Additive with Multifunctional Groups and Its Flame-Retardant Effect in Epoxy Resin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7777–7786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of a Phosphorus–Nitrogen-Containing Flame Retardant and Its Application in Epoxy Resin. High Perform. Polym. 2019, 31, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, T.N.; Naidu, T.M.; Kim, M.S.; Parvatamma, B.; Prashanthi, Y.; Koo, B.H. Influence of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Char Forming Agent Polymer on Flame Retardancy of Intumescent Flame Retardant Coatings. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.; Chang, S.; Condon, B.; Slopek, R.; Graves, E.; Yoshioka-Tarver, M. Structural Effect of Phosphoramidate Derivatives on the Thermal and Flame Retardant Behaviors of Treated Cotton Cellulose. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 4715–4724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huong, N.T.; Khanh, V.T.H.; Linh, N.P.D. Optimizing Content of Pyrovatex CP New and Knittex FFRC in Flame Retardant Treatment for Cotton Fabric. Ind. Textila 2021, 72, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.C.; Condon, B.; Smith, J.; Nam, S. Flame Resistant Cotton Fabric Containing Casein and Inorganic Materials Using an Environmentally-Friendly Microwave Assisted Technique. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 2246–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, D.V.I.; De, B.J. Phosphorus Flame Retardants: Properties, Production, Environmental Occurrence, Toxicity and Analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Parveen, T.; Umar, K.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Role of Nanomaterials in the Treatment of Waste Water. Water 2020, 12, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, A.A.; Ahmad, H.; Parveen, T.; Ahmad, A.; Oves, M.; Ismail, I.M.I.; Qari, H.A.; Umar, K.; Ibrahim, M.N.M. Recent Advances in Metal Decorated Nanomaterials and Their Various Biological Applications: A Review. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaly, A.R.; Dawood, N. Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment Coupled with a Photocatalyst for Antimicrobial Performance of Ihram Cotton Fabric. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Wiener, J.; Tamulevičienė, A.; Tamulevičius, T.; Lazauskas, A.; Saskova, J.; Račkauskas, S. One Step In-Situ Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Multifunctional Cotton Fabrics. Materials 2021, 14, 3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramova, A.V.; Abramov, V.O.; Fedulov, I.S.; Baranchikov, A.E.; Kozlov, D.A.; Veselova, V.O.; Kameneva, S.V.; Ivanov, V.K.; Cravotto, G. Strong Antibacterial Properties of Cotton Fabrics Coated with Ceria Nanoparticles under High-Power Ultrasound. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, M.; Padrão, J.; Ribeiro, A.I.; Fernandes, R.D.V.; Melro, L.; Nicolau, T.; Mehravani, B.; Alves, C.; Rodrigues, R.; Zille, A. Polysaccharides and Metal Nanoparticles for Functional Textiles: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tănase, M.A.; Soare, A.C.; Oancea, P.; Răducan, A.; Mihăescu, C.I.; Alexandrescu, E.; Petcu, C.; Diţu, L.M.; Ferbinţeanu, M.; Cojocaru, B.; et al. Facile in Situ Synthesis of Zno Flower-like Hierarchical Nanostructures by the Microwave Irradiation Method for Multifunctional Textile Coatings. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.P.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Hoang, C.N.; Le, T.K.; Lund, T.; Nguyen, H.K.H.; Huynh, T.K.X. Characterization and Photocatalytic Activity of New Photocatalysts Based on Ag, F-Modified ZnO Nanoparticles Prepared by Thermal Shock Method. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espitia, P.J.P.; Soares, N.d.F.F.; Coimbra, J.S.D.R.; de Andrade, N.J.; Cruz, R.S.; Medeiros, E.A.A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Antimicrobial Activity and Food Packaging Applications. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1447–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moezzi, A.; McDonagh, A.M.; Cortie, M.B. Zinc Oxide Particles: Synthesis, Properties and Applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 185–186, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, R.D.; Soni, M.; Potdar, T. A Flame Retardant, Antimicrobial and UV Protective Polyester Fabric by Solvent Crazing Route. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hady, M.M.A.; Farouk, A.; Sharaf, S. Flame Retardancy and UV Protection of Cotton Based Fabrics Using Nano ZnO and Polycarboxylic Acids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Jose, S.; Basu, G.; Chowdhury, R. Fire Retardant Finish of Jute Fabric with Nano Zinc Oxide. Cellulose 2017, 24, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbič, A.; Gorjanc, M.; Simončič, B. Zinc Oxide for Functional Textile Coatings: Recent Advances. Coatings 2019, 9, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.; Militky, J.; Petru, M.; Tomkov, B.; Ali, A.; Javed, A.; Azeem, M.; Křemenáková, D. Ultra-Fast Growth of ZnO Nanorods on Cotton Fabrics and Their Self-Cleaning and Physiological Comfort Properties. Coatings 2021, 11, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magovac, E.; Vončina, B.; Jordanov, I.; Grunlan, J.C.; Bischof, S. Layer-by-Layer Deposition: A Promising Environmentally Benign Flame-Retardant Treatment for Cotton, Polyester, Polyamide and Blended Textiles. Materials 2022, 15, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, S.F.; Montazer, M. In Situ Sonosynthesis of Nano TiO2 on Cotton Fabric. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, A.; Azeem, M.; Wiener, J.; Thukkaram, M.; Saskova, J.; Mansoor, T. Ultrasonically Assisted In Situ Deposition of ZnO Nano Particles on Cotton Fabrics for Multifunctional Textiles. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; He, M.; Li, W.; Cheng, D.; Wang, X. Growing ZnO Nanoparticles on Polydopamine-Templated Cotton Fabrics for Durable Antimicrobial Activity and UV Protection. Polymers 2018, 10, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnarowicz, J.; Chudoba, T.; Lojkowski, W. A Review of Microwave Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanomaterials: Reactants, process Parameters and Morphologies. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajerani, A.; Burnett, L.; Smith, J.V.; Kurmus, H.; Milas, J.; Arulrajah, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Abdul Kadir, A. Nanoparticles in Construction Materials and Other Applications, and Implications of Nanoparticle Use. Materials 2019, 12, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Ma, J.; Dai, H. Preparation and Characterization of Self-Reinforced Antibacterial and Oil-Resistant Paper Using a NaOH/Urea/ZnO Solution. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.Z.; Bremner, D.H.; Wan, N.; Wang, X. Development of Antibacterial ZnO-Loaded Cotton Fabric Based on in Situ Fabrication. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2016, 122, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, V.H.T.; Lee, B.-K. Development of Multifunctional Self-Cleaning and UV Blocking Cotton Fabric with Modification of Photoactive ZnO Coating via Microwave Method. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 338, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, D.; Gao, Y.; Cao, K.; Wei, Q. Rapid Surface Functionalization of Cotton Fabrics by Modified Hydrothermal Synthesis of ZnO. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zou, Y.; An, D.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L. Investigation of Antibacterial Properties of Nano-ZnO Assembled Cotton Fibers. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 990–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, P.M.; Balaji, S.; Prabhawathi, V.; Neelakandan, R.; Manoharan, P.T.; Doble, M. Effective Antibacterial Adhesive Coating on Cotton Fabric Using ZnO Nanorods and Chalcone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Lee, M.; Choe, E.K. Characterization of Cotton Fabric Scouring by FT-IR ATR Spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Liang, Q.; Lu, Y. Microstructure and Properties of Copper Plating on Citric Acid Modified Cotton Fabric. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, P.; Dai, F. Durable and High-Efficiency Casein-Derived Phosphorus-Nitrogen-Rich Flame Retardants for Cotton Fabrics. Cellulose 2022, 29, 2681–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazant, P.; Kuritka, I.; Munster, L.; Kalina, L. Microwave Solvothermal Decoration of the Cellulose Surface by Nanostructured Hybrid Ag/ZnO Particles: A Joint XPS, XRD and SEM Study. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1275–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, Ö.; Van, L.L.; Rahier, H.; De Clerck, K. The Effect of Water Immersion on the Thermal Degradation of Cotton Fibers. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, H. Surface Activation of Cotton Fiber by Seeding Silver Nanoparticles and in Situ Synthesizing ZnO Nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4365–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaan, S.; Sun, G. Effect of Phosphorus and Nitrogen on Flame Retardant Cellulose: A Study of Phosphorus Compounds. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2007, 78, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, M.H.; Fallah, S.A.; Zanjanchi, M.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Nano-Sized Zinc Oxide Coating on Cellulosic Fibers: Photoactivity and Flame-Retardancy Study. Chin. J. Chem. 2011, 29, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhen, X.; Yang, C.Q. Correlation between Limiting Oxygen Index and Phosphorus Content of the Cotton Fabric Treated with a Hydroxy-Functional Organophosphorus Flame Retarding Finish and Melamine-Formaldehyde. J. Fire Sci. 2004, 22, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, R.K.K.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Hong, N.; Jiang, S. Combustion and Thermal Degradation Mechanism of a Novel Intumescent Flame Retardant for Epoxy Acrylate Containing Phosphorus and Nitrogen. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriviriyanun, A.; O’Rear, E.A.; Yanumet, N. Self-Extinguishing Cotton Fabric with Minimal Phosphorus Deposition. Cellulose 2008, 15, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.L.; Kan, C.W.; Yuen, C.W.M. Effect of Zinc Oxide on Flame Retardant Finishing of Plasma Pre-Treated Cotton Fabric. Cellulose 2011, 18, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, H.N.; Hong, K.V.T.; Ha, T.N.; Phan, D.N. Application of Plasma Activation in Flame-Retardant Treatment for Cotton Fabric. Polymers 2020, 12, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ding, F.; Li, S.; Li, R.; Li, Z.; Huang, D.; Ren, X. Flame-Retardant Cotton Fabrics Modified with Phosphoramidate Derivative via Electron Beam Irradiation Process. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 51, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.K.; Sakai, W.; Nguyen, C. Preparation of a Novel Flame Retardant Formulation for Cotton Fabric. Materials 2020, 13, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhlouf, G.; Abdelkhalik, A.; Ameen, H. Synthesis of a Novel Highly Efficient Flame-Retardant Coating for Cotton Fabrics with Low Combustion Toxicity and Antibacterial Properties. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8785–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomak, E.D.; Cavdar, A.D. Limited Oxygen Index Levels of Impregnated Scots Pine Wood. Thermochim. Acta 2013, 573, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Gao, A.; Zhang, Y. Flame Retardant Finishing of Cotton Fabric Based on Synergistic Compounds Containing Boron and Nitrogen. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The Antimicrobial Activity of Nanoparticles: Present Situation and Prospects for the Future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirelkhatim, A.; Mahmud, S.; Seeni, A.; Kaus, N.H.M.; Ann, L.C.; Bakhori, S.K.M.; Hasan, H.; Mohamad, D. Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Antibacterial Activity and Toxicity Mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.; Nazam, N.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Ahmad, K.; Baig, M.H.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, I. Mechanistic Insights into the Antimicrobial Actions of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Implications for Multidrug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anita, S.; Ramachandran, T.; Rajendran, R.; Koushik, C.V.; Mahalakshmi, M. Preparation and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and a Study of the Anti-Microbial Property of Cotton Fabric Treated with the Particles. J. Text. Apparel Technol. Manag. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, D.A.R.; Gusatti, M.; Ternus, R.Z.; Fiori, M.A.; Riella, H.G. In Situ Growth of ZnO Nanostructures on Cotton Fabric by Solochemical Process for Antibacterial Purposes. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Ananthaswamy, H.N. Toxic Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation on the Skin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2004, 195, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.R. Acute Effects of UVR on Human Eyes and Skin. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2006, 92, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, A.; Azeem, M.; Saskova, J. P024_0663_ UV Protective Fabrics by Application of Ball Milled Neem Tree Leaves. In Proceedings of the 19th World Textile Conference-Autex 2019, Ghent, Belgium, 11–15 June 2019; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gies, P.; Slevin, T.; Harrison, S.; Plowman, P.; Dain, S.; Moller, L.; Mawley, F.; Swift, N. Australian/New Zealand Standard, AS/NZS 4399: 2017: Sun Protective Clothing–Evaluation and Classification; Standards Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2017; ISBN 1760358843. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Yu, M. Study of the Preparation and Properties of UV-blocking Fabrics of a PET/TiO2 Nanocomposite Prepared by in Situ Polycondensation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 1588–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S. Nanomaterials for UV Protective Textiles. J. Ind. Text. 2021, 16, 1528083721988949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebeid, O.K.; Zhao, T. Review on: Developing UV Protection for Cotton Fabric. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghamsari, M.S.; Alamdari, S.; Han, W.; Park, H.H. Impact of Nanostructured Thin ZnO Film in Ultraviolet Protection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | Zinc Acetate (M) | NaOH (M) | Sonication Time (Minutes) | MDPA (g/L) | Zn Contents | P Contents | Add-On | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | Std. Dev. | (%) | Std. Dev. | (%) | Std. Dev. | |||||
| 1 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 30 | 300 | 1.69 | 0.071 | 3.88 | 0.083 | 16.92 | 0.157 |
| 2 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 60 | 300 | 1.84 | 0.041 | 3.86 | 0.079 | 17.11 | 0.128 |
| 3 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 90 | 300 | 2.13 | 0.093 | 3.83 | 0.062 | 17.45 | 0.152 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 120 | 300 | 1.91 | 0.080 | 3.84 | 0.074 | 17.22 | 0.161 |
| 5 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 30 | 300 | 2.83 | 0.107 | 3.81 | 0.086 | 18.31 | 0.186 |
| 6 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 60 | 300 | 3.19 | 0.099 | 3.79 | 0.053 | 18.61 | 0.148 |
| 7 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 90 | 300 | 3.34 | 0.138 | 3.78 | 0.094 | 18.91 | 0.226 |
| 8 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 120 | 300 | 3.27 | 0.071 | 3.79 | 0.062 | 18.78 | 0.142 |
| 9 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 30 | 300 | 4.64 | 0.108 | 3.75 | 0.057 | 20.38 | 0.171 |
| 10 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 60 | 300 | 4.86 | 0.067 | 3.73 | 0.082 | 20.70 | 0.132 |
| 11 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 90 | 300 | 5.09 | 0.103 | 3.72 | 0.065 | 20.96 | 0.155 |
| 12 | 0.05 | 0.3 | 120 | 300 | 5.01 | 0.055 | 3.72 | 0.068 | 20.84 | 0.133 |
| 13 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 30 | 300 | 5.34 | 0.073 | 3.71 | 0.054 | 21.23 | 0.123 |
| 14 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 60 | 300 | 5.47 | 0.085 | 3.70 | 0.073 | 21.43 | 0.163 |
| 15 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 90 | 300 | 5.65 | 0.051 | 3.70 | 0.064 | 21.60 | 0.127 |
| 16 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 120 | 300 | 5.53 | 0.054 | 3.70 | 0.062 | 21.51 | 0.112 |
| 17 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 30 | 300 | 8.78 | 0.077 | 3.63 | 0.076 | 25.32 | 0.168 |
| 18 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 60 | 300 | 9.07 | 0.067 | 3.61 | 0.058 | 25.65 | 0.143 |
| 19 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 90 | 300 | 9.31 | 0.043 | 3.58 | 0.050 | 25.48 | 0.194 |
| 20 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 120 | 300 | 9.17 | 0.071 | 3.60 | 0.074 | 25.77 | 0.203 |
| 21 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 30 | 300 | 11.23 | 0.064 | 3.50 | 0.049 | 28.24 | 0.162 |
| 22 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 60 | 300 | 12.09 | 0.076 | 3.47 | 0.038 | 29.21 | 0.181 |
| 23 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 90 | 300 | 13.14 | 0.068 | 3.44 | 0.067 | 30.47 | 0.129 |
| 24 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 120 | 300 | 12.54 | 0.059 | 3.46 | 0.052 | 29.79 | 0.117 |
| 25 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 30 | 300 | 5.39 | 0.059 | 3.72 | 0.068 | 21.31 | 0.134 |
| 26 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 60 | 300 | 5.61 | 0.068 | 3.69 | 0.048 | 21.54 | 0.108 |
| 27 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 90 | 300 | 5.73 | 0.042 | 3.69 | 0.056 | 21.72 | 0.112 |
| 28 | 0.15 | 0.1 | 120 | 300 | 5.57 | 0.054 | 3.70 | 0.072 | 21.52 | 0.138 |
| 29 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 30 | 300 | 8.89 | 0.050 | 3.62 | 0.058 | 25.42 | 0.116 |
| 30 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 60 | 300 | 9.21 | 0.024 | 3.59 | 0.037 | 25.82 | 0.089 |
| 31 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 90 | 300 | 9.43 | 0.041 | 3.55 | 0.048 | 26.11 | 0.102 |
| 32 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 120 | 300 | 9.29 | 0.032 | 3.58 | 0.064 | 25.91 | 0.113 |
| 33 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 30 | 300 | 9.63 | 0.064 | 3.54 | 0.028 | 26.31 | 0.094 |
| 34 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 60 | 300 | 9.91 | 0.034 | 3.53 | 0.038 | 26.65 | 0.097 |
| 35 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 90 | 300 | 10.13 | 0.051 | 3.52 | 0.058 | 26.91 | 0.124 |
| 36 | 0.15 | 0.3 | 120 | 300 | 9.97 | 0.079 | 3.53 | 0.046 | 26.57 | 0.146 |
| A | 0.1 | 0.3 | 90 (magnetic stirring) | 300 | 7.83 | 0.102 | 3.67 | 0.061 | 24.09 | 0.188 |
| B | - | - | - | 300 | - | - | 3.92 | 0.077 | 14.93 | 0.93 |
| Sample | Flammability Test | LOI | Bacterial Reduction % | UV Protection | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| After Flame Time | After Glow Time | Char Length | S. aureus | E. coli | ||||||||||
| (s) | Std. Dev. | (s) | Std. Dev. | (mm) | Std. Dev. | (%) | Std. Dev. | R (%) | Std. Dev. | R (%) | Std. Dev. | UPF | Std. Dev. | |
| Untreated | 19.34 | 3.216 | 9.62 | 1.867 | Completely burned | - | 17.6 | 0.262 | - | - | - | - | 4.78 | 0.117 |
| 1 | 7.42 | 0.117 | 3.25 | 0.130 | 103 | 1.923 | 24.2 | 0.291 | 41.78 | 3.448 | 30.34 | 3.379 | 19.12 | 0.500 |
| 2 | 7.02 | 0.133 | 3.11 | 0.080 | 99 | 2.121 | 24.7 | 0.254 | 43.29 | 3.526 | 34.67 | 4.539 | 20.31 | 0.365 |
| 3 | 6.,24 | 0.176 | 2.94 | 0.107 | 95 | 1.224 | 25.1 | 0.071 | 47.86 | 3.720 | 40.45 | 3.423 | 20.87 | 0.254 |
| 4 | 6.74 | 0.119 | 3.03 | 0.084 | 96 | 0.707 | 24.8 | 0.187 | 45.76 | 4.211 | 37.47 | 4.502 | 20.64 | 0.145 |
| 5 | 5.83 | 0.212 | 2.72 | 0.175 | 92 | 2.000 | 25.4 | 0.141 | 49.97 | 5.535 | 41.23 | 5.051 | 20.94 | 0.333 |
| 6 | 5.26 | 0.168 | 2.33 | 0.167 | 90 | 2.345 | 25.7 | 0.100 | 51.79 | 4.442 | 45.57 | 3.760 | 21.53 | 0.390 |
| 7 | 4.19 | 0.222 | 2.04 | 0.074 | 89 | 0.704 | 25.8 | 0.158 | 59.93 | 3.761 | 50.78 | 4.039 | 21.72 | 0.289 |
| 8 | 4.84 | 0.253 | 2.17 | 0.137 | 89 | 1.000 | 25.7 | 0.072 | 52.79 | 5.963 | 45.91 | 2.483 | 21.67 | 0.354 |
| 9 | 3.87 | 0.224 | 1.91 | 0.113 | 83 | 1.870 | 26.0 | 0.122 | 69.86 | 4.751 | 59.92 | 3.621 | 32.52 | 0.418 |
| 10 | 3.58 | 0.178 | 1.62 | 0.077 | 78 | 3.114 | 26.1 | 0.212 | 73.32 | 3.729 | 65.76 | 3.305 | 33.71 | 0.294 |
| 11 | 2.82 | 0.204 | 1.06 | 0.059 | 76 | 1.581 | 26.3 | 0.108 | 78.84 | 4.300 | 74.65 | 2.734 | 34.13 | 0.206 |
| 12 | 3.12 | 0.147 | 1.34 | 0.123 | 76 | 1.214 | 26.1 | 0.123 | 75.54 | 4.326 | 71.78 | 2.152 | 33.98 | 0.214 |
| 13 | 2.09 | 0.213 | 0.78 | 0.092 | 73 | 1.225 | 26.7 | 0.119 | 81.45 | 3.413 | 77.87 | 2.160 | 34.39 | 0.231 |
| 14 | 1.56 | 0.167 | 0.27 | 0.054 | 71 | 1.870 | 26.9 | 0.164 | 85.42 | 4.032 | 82.98 | 3.313 | 37.17 | 0.376 |
| 15 | 0.59 | 0.108 | 0 | 0 | 68 | 2.645 | 27.3 | 0.137 | 94.43 | 1.606 | 91.46 | 4.328 | 49.09 | 1.586 |
| 16 | 1.17 | 0.125 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 2.549 | 27.0 | 0.094 | 89.95 | 2.142 | 84.56 | 2.688 | 37.98 | 0.906 |
| 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 2.738 | 29.2 | 0.146 | 100 | 0 | 98.64 | 0.869 | 67.74 | 1.103 |
| 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 53 | 2.121 | 29.4 | 0.086 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 73.89 | 1.623 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51 | 2.236 | 29.6 | 0.092 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 93.34 | 2.465 |
| 20 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 52 | 2.915 | 29.5 | 0.128 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 82.98 | 2.613 |
| 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 2.167 | 31.2 | 0.114 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 134.32 | 3.181 |
| 22 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 1.788 | 31.9 | 0.099 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 134.87 | 2.776 |
| 23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 0.707 | 32.2 | 0.102 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 143.76 | 3.439 |
| 24 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 | 1.581 | 32.0 | 0.110 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 139.93 | 2.645 |
| 25 | 1.97 | 0.145 | 0.53 | 0.036 | 73 | 1.140 | 26.8 | 0.146 | 84.49 | 2.597 | 80.54 | 2.172 | 36.89 | 0.581 |
| 26 | 0.92 | 0.115 | 0 | 0 | 69 | 2.726 | 27.0 | 0.173 | 93.23 | 2.100 | 87.76 | 2.338 | 48.04 | 1.034 |
| 27 | 0.42 | 0.078 | 0 | 0 | 65 | 1.643 | 27.4 | 0.085 | 95.67 | 1.378 | 92.51 | 2.311 | 50.96 | 1.452 |
| 28 | 1.02 | 0.106 | 0 | 0 | 70 | 2.126 | 27.1 | 0.167 | 90.42 | 2.404 | 85.78 | 1.636 | 42.74 | 1.215 |
| 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 55 | 2.166 | 29.3 | 0.118 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 71.87 | 1.092 |
| 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51 | 1.789 | 29.5 | 0.090 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 84.45 | 1.467 |
| 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 50 | 1.562 | 29.7 | 0.114 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 97.12 | 3.991 |
| 32 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 51 | 3.741 | 29.6 | 0.158 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 87.92 | 2.032 |
| 33 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 1.303 | 29.9 | 0.172 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 104.45 | 2.279 |
| 34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 | 0.836 | 30.1 | 0.126 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 111.56 | 3.003 |
| 35 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 44 | 1.870 | 30.4 | 0.132 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 124.47 | 5.080 |
| 36 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 47 | 1.224 | 30.2 | 0.121 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 121.34 | 2.711 |
| A | 2.13 | 0.754 | 0 | 0 | 76 | 3.824 | 27.7 | 0.192 | 96.27 | 7.358 | 93.52 | 5.674 | 52.05 | 6.092 |
| B | 8.04 | 0.246 | 5.21 | 0.232 | 127 | 4.949 | 23.8 | 0.097 | - | - | - | - | 13.23 | 0.268 |
| Sample | Tonset 10% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Residue at Tmax (%) | Residue at 600 °C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine cotton | 319.23 | 343.15 | 47.04 | 2.29 |
| Cotton-CA | 317.12 | 335.52 | 62.93 | 4.19 |
| Sample A | 280.34 | 296.13 | 68.47 | 30.91 |
| Sample B | 295.18 | 304.32 | 67.11 | 24.25 |
| Sample 23 | 266.07 | 280.19 | 70.21 | 38.17 |
| Fabric Treatment | After Flame Time (s) | After Glow Time (s) | Char Length (mm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MDPA + ZnO NPs | 0 | 0 | 39 | This study |
| MDPA | 0 | 0 | 59 | [14] |
| MDPA + Dihydroxy ethylene urea | 0.64 | 0 | 103 | [56] |
| Diethyl methacryloylphosphoramidate | 0 | 0 | 125 | [57] |
| Bis(hydroxymethyl)phosphinic-methacrylate | 0 | 0 | 90 | [58] |
| Melamine salt of tannic phosphate | 0 | 0 | 65 | [59] |
| Fabric Treatment | LOI | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| MDPA + ZnO NPs | 32.2 | This study |
| MDPA | 26.3 | [14] |
| Diethyl methacryloylphosphoramidate | 30.2 | [57] |
| Hydroxyl-functional organophosphorus | 31.6 | [52] |
| N,N-dimethylformamide + Zinc ion | 30 | [8] |
| MDPA + Dihydroxy ethylene urea | 28.1 | [56] |
| ZnO NPs Synthesis Method | Bacterial Reduction % | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | E. coli | ||
| Sonochemical method | 100 | 100 | This study |
| Wet chemical method | >99.99 | 80 | [65] |
| Microwave Irradiation Method | 100 | 100 | [23] |
| Solochemical process | 100 | - | [66] |
| UPF Value | Protection Level |
|---|---|
| Below 15 | Not good |
| 15–24 | Good |
| 24–39 | Very good |
| 40 and above | Excellent |
| ZnO NPs Synthesis Method | UPF | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Sonochemical Method | 143.76 | This study |
| One-step hydrothermal method | 80.2 | [31] |
| Two-step hydrothermal method | 157.8 | [35] |
| Microwave Irradiation Method | 96.56 | [23] |
| Sample | Zn Contents (%) | P Contents (%) | Flammability Test | LOI | Bacterial Reduction (%) | UPF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| After Flame Time (s) | After Glow Time (s) | Char Length (mm) | S. aureus | E. coli | |||||
| After 5 wash cycles | |||||||||
| Sample A | 5.76 | 3.30 | 5.94 | 3.15 | 89 | 26.7 | 72.43 | 70.28 | 41.37 |
| Sample B | - | 3.48 | 10.32 | 5.19 | 134 | 22.1 | - | - | 11.81 |
| Sample 23 | 11.38 | 3.11 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 30.3 | 100 | 100 | 132.92 |
| After 10 wash cycles | |||||||||
| Sample A | 4.74 | 3.13 | 7.03 | 3.52 | 93 | 24.9 | 63.23 | 60.96 | 34.87 |
| Sample B | - | 3.32 | 10.72 | 5.89 | 145 | 21.6 | - | - | 11.09 |
| Sample 23 | 10.61 | 2.99 | 0 | 0 | 49 | 29.8 | 100 | 100 | 125.53 |
| After 20 wash cycles | |||||||||
| Sample A | 3.97 | 3.04 | 7.82 | 4.23 | 96 | 23.5 | 54.47 | 50.52 | 30.76 |
| Sample B | - | 3.24 | 11.29 | 6.08 | 149 | 20.4 | - | - | 10.61 |
| Sample 23 | 10.17 | 2.93 | 0 | 0 | 52 | 29.6 | 100 | 100 | 123.16 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javed, A.; Wiener, J.; Saskova, J.; Müllerová, J. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and N-Methylol Dimethyl Phosphonopropion Amide (MDPA) System for Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics. Polymers 2022, 14, 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163414
Javed A, Wiener J, Saskova J, Müllerová J. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and N-Methylol Dimethyl Phosphonopropion Amide (MDPA) System for Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics. Polymers. 2022; 14(16):3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163414
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaved, Asif, Jakub Wiener, Jana Saskova, and Jana Müllerová. 2022. "Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and N-Methylol Dimethyl Phosphonopropion Amide (MDPA) System for Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics" Polymers 14, no. 16: 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163414
APA StyleJaved, A., Wiener, J., Saskova, J., & Müllerová, J. (2022). Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and N-Methylol Dimethyl Phosphonopropion Amide (MDPA) System for Flame Retardant Cotton Fabrics. Polymers, 14(16), 3414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14163414







