Electrical Conductivity of Rubber Composites with Varying Crosslink Density under Cyclic Deformation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mixing, Calendaring, and Curing Process of Rubber Composites
2.3. Mechanical Properties and Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis (DMTA)
2.4. Electrical Conductivity
2.5. Online Measurements of Conductivity during Cyclic Mechanical Deformation
2.6. Solvent Uptake and Crosslink Density
3. Results and Discussion
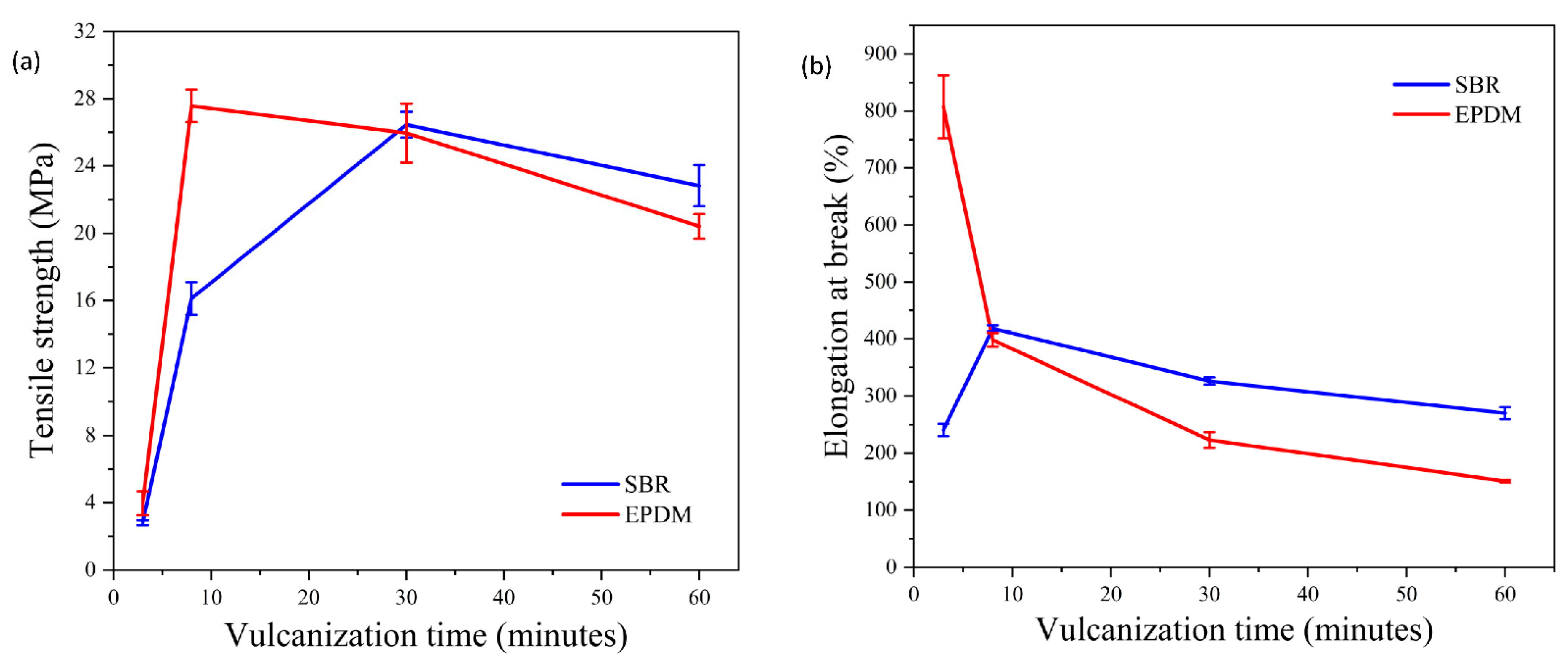
3.1. Mechanical Properties
3.2. Solvent Uptake and Crosslink Density
3.3. Dynamic Mechanical Thermal Analysis (DMTA)
3.4. Electrical Conductivity
3.5. Conductivity Changes during Cyclic Mechanical Deformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, P.-C.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.-Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, K.; Wong, Y.-K.; Tang, B.-Z.; Hong, S.-H.; Paik, K.-W. Enhanced electrical conductivity of nanocomposites containing hybrid fillers of carbon nanotubes and carbon black. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peidayesh, H.; Mosnáčková, K.; Špitalský, Z.; Heydari, A.; Šišková, A.O.; Chodák, I. Thermoplastic Starch–Based Composite Reinforced by Conductive Filler Networks: Physical Properties and Electrical Conductivity Changes during Cyclic Deformation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krajči, J.; Špitálský, Z.; Chodák, I. Relationship between conductivity and stress–strain curve of electroconductive composite with SBR or polycaprolactone matrices. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 55, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.-H.; Chen, D.-J. Percolation threshold and morphology of composites of conducting carbon black/polypropylene/EVA. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, C.-K.; Aoyagi, Y.; Chung, D. Carbon black pastes as coatings for improving thermal gap-filling materials. Carbon 2006, 44, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Thostenson, E.T.; Chou, T.-W. Sensors and actuators based on carbon nanotubes and their composites: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omastova, M.; Chodak, I.; Pionteck, J. Electrical and mechanical properties of conducting polymer composites. Synth. Met. 1999, 102, 1251–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneli, J.; Zaikov, G.; Khananashvili, L. Effects of mechanical deformations on the structurization and electric conductivity of electric conducting polymer composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 601–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flandin, L.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Interrelationships between electrical and mechanical properties of a carbon black-filled ethylene–octene elastomer. Polymer 2001, 42, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhradská, S.; Prokeš, J.; Omastová, M.; Chodák, I. Stability of electrical properties of carbon black-filled rubbers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 2918–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodák, I.; Podhradská, S.; Podhradská, J.J.; Jurčiová, J. Changes in electrical conductivity during mechanical deformation of carbon black filled elastomeric matrix. Open Macromol. J. 2010, 4, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- Flandin, L.; Chang, A.; Nazarenko, S.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Effect of strain on the properties of an ethylene–octene elastomer with conductive carbon fillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 76, 894–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surya, I.; Ismail, H. The effect of the addition of alkanolamide on properties of carbon black-filled natural rubber (SMR-L) compounds cured using various curing systems. Polym. Test. 2016, 50, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirityi, D.Z.; Pölöskei, K. Thermomechanical Devulcanisation of Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer (EPDM) Rubber and Its Subsequent Reintegration into Virgin Rubber. Polymers 2021, 13, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzocca, A. Evaluation of the polymer–solvent interaction parameter χ for the system cured styrene butadiene rubber and toluene. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2682–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Chodák, I.; Mošková, D.J.; Dosoudil, R.; Hudec, I. Cross-linking and properties of rubber magnetic composites cured with different curing systems. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruželák, J.; Sýkora, R.; Dosoudil, R.; Hudec, I. Relationship between the cross-link structure and properties of peroxide and sulfur-cured magnetic composites based on NR and NBR. J. Elastomers Plast. 2017, 49, 459–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, C.; Yee, V. The effects of crosslink density and crosslink type on the tensile and tear strengths of NR, SBR and EPDM gum vulcanizates. Eur. Polym. J. 1986, 22, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peidayesh, H.; Ahmadi, Z.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Abdouss, M.; Chodák, I. Baked hydrogel from corn starch and chitosan blends cross-linked by citric acid: Preparation and properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.; Ray, S. Separation of organic mixtures by pervaporation using crosslinked rubber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 270, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peidayesh, H.; Heydari, A.; Mosnáčková, K.; Chodák, I. In situ dual crosslinking strategy to improve the physico-chemical properties of thermoplastic starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peidayesh, H.; Ahmadi, Z.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Abdouss, M.; Chodák, I. Fabrication and properties of thermoplastic starch/montmorillonite composite using dialdehyde starch as a crosslinker. Polym. Int. 2020, 69, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, P.; Khastgir, D.; Saha, T. Conductive nitrile rubber composite containing carbon fillers: Studies on mechanical properties and electrical conductivity. Composites 1992, 23, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrau, S.; Demont, P.; Peigney, A.; Laurent, C.; Lacabanne, C. DC and AC conductivity of carbon nanotubes− polyepoxy composites. Macromolecules 2003, 36, 5187–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podhradska, S.; Omastova, M.; Chodak, I. Effect of uniaxial Deformation and Relaxation of Rubber/Carbon black Composites on their electrical Properties. KGK Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2015, 68, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chodák, I.; Krajči, J. Structure of reinforced filler network determined by electrical conductivity of the polymer/carbon black composite. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Composite Materials and Structures, Istanbul, Turkey, 13–15 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Voet, A.; Cook, F.R. Investigation of carbon chains in rubber vulcanizates by means of dynamic electrical conductivity. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1968, 41, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Property | Amount |
|---|---|
| Iodine adsorption | 120 mg/g |
| DBF adsorption | 125 mL/100 g |
| Specific surface area | 100–120 m2/g |
| pH | 5.5–8.5 |
| Particle diameter | 20–25 nm |
| Component | Concentration (phr) |
|---|---|
| Rubber (SBR or EPDM) a | 100 |
| CB | 70 |
| ZnO | 3 |
| Stearic acid | 1 |
| CBS | 1 |
| Sulfur | 1.75 |
| Sample Code | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | M 100 (MPa) | M 200 (MPa) | M 300 (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBR-3 | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 240 ± 29 | 7.3 ± 0.4 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | n/a |
| SBR-8 | 16.1 ± 2.6 | 418 ± 16 | 4.8 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 6.5 ± 0.6 | 11.0 ± 1.2 |
| SBR-30 | 26.5 ± 2.1 | 326 ± 17 | 10.7 ± 0.3 | 5.2 ± 0.1 | 13.3 ± 0.3 | 23.8 ± 0.6 |
| SBR-60 | 22.8 ± 3.3 | 270 ± 28 | 11.4 ± 0.2 | 5.9 ± 0.1 | 15.0 ± 0.2 | n/a |
| EPDM-3 | 4.0 ± 1.9 | 807 ± 146 | 14.8 ± 4.4 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 2.0 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.8 |
| EPDM-8 | 27.6 ± 2.6 | 398 ± 32 | 8.6 ± 0.4 | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 11.6 ± 0.8 | 20.0 ± 1.1 |
| EPDM-30 | 26.0 ± 4.7 | 223 ± 36 | 14.3 ± 0.5 | 9.7 ± 0.4 | 23.2 ± 0.8 | n/a |
| EPDM-60 | 20.4 ± 0.7 | 151 ± 2 | 16.3 ± 0.8 | 12.4 ± 0.9 | n/a | n/a |
| Sample Code | Solvent Uptake (%) | Crosslink Density ν (mol·m−3) |
|---|---|---|
| SBR-3 | 344 ± 20 | 236 ± 20 |
| SBR-8 | 267 ± 5 | 361 ± 12 |
| SBR-30 | 169 ± 2 | 779 ± 13 |
| SBR-60 | 160 ± 2 | 850 ± 18 |
| EPDM-3 | 371 ± 16 | 78 ± 9 |
| EPDM-8 | 105 ± 9 | 1113 ± 140 |
| EPDM-30 | 82 ± 1 | 1703 ± 16 |
| EPDM-60 | 79 ± 2 | 1812 ± 60 |
| Sample Code | Glass Transition Tg (°C) | Crosslink Density ν (mol·m−3) |
|---|---|---|
| SBR-3 | −33.1 | 236 ± 20 |
| SBR-8 | −30.3 | 361 ± 12 |
| SBR-30 | −28.6 | 779 ± 13 |
| SBR-60 | −25.1 | 850 ± 18 |
| EPDM-3 | −25.3 | 78 ± 9 |
| EPDM-8 | −26.9 | 1113 ± 140 |
| EPDM-30 | −24.9 | 1703 ± 16 |
| EPDM-60 | −21.1 | 1812 ± 60 |
| Sample Code | Current before Starting of Cyclic Deformation (μA) |
|---|---|
| SBR-3 | 0.66 ± 0.00 |
| SBR-8 | 0.70 ± 0.01 |
| SBR-30 | 0.72 ± 0.00 |
| SBR-60 | 0.70 ± 0.01 |
| EPDM-3 | 0.66 ± 0.02 |
| EPDM-8 | 0.69 ± 0.01 |
| EPDM-30 | 0.79 ± 0.04 |
| EPDM-60 | 0.73 ± 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peidayesh, H.; Špitalský, Z.; Chodák, I. Electrical Conductivity of Rubber Composites with Varying Crosslink Density under Cyclic Deformation. Polymers 2022, 14, 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173640
Peidayesh H, Špitalský Z, Chodák I. Electrical Conductivity of Rubber Composites with Varying Crosslink Density under Cyclic Deformation. Polymers. 2022; 14(17):3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173640
Chicago/Turabian StylePeidayesh, Hamed, Zdenko Špitalský, and Ivan Chodák. 2022. "Electrical Conductivity of Rubber Composites with Varying Crosslink Density under Cyclic Deformation" Polymers 14, no. 17: 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173640
APA StylePeidayesh, H., Špitalský, Z., & Chodák, I. (2022). Electrical Conductivity of Rubber Composites with Varying Crosslink Density under Cyclic Deformation. Polymers, 14(17), 3640. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14173640








