Colloidal Stability of CA, SDS and PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs): Effect of Molar Ratio and Salinity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Bare Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
2.3. Surface Modification of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with CA, SDS and PVA
2.4. Preparation of CA-IONPs, SDS-IONPs and PVA-IONPs in Saline Solution
2.5. Characterization of CA-IONPs, SDS-IONPs and PVA-IONPs
3. Results
3.1. Morphological and Crystallographic Analysis
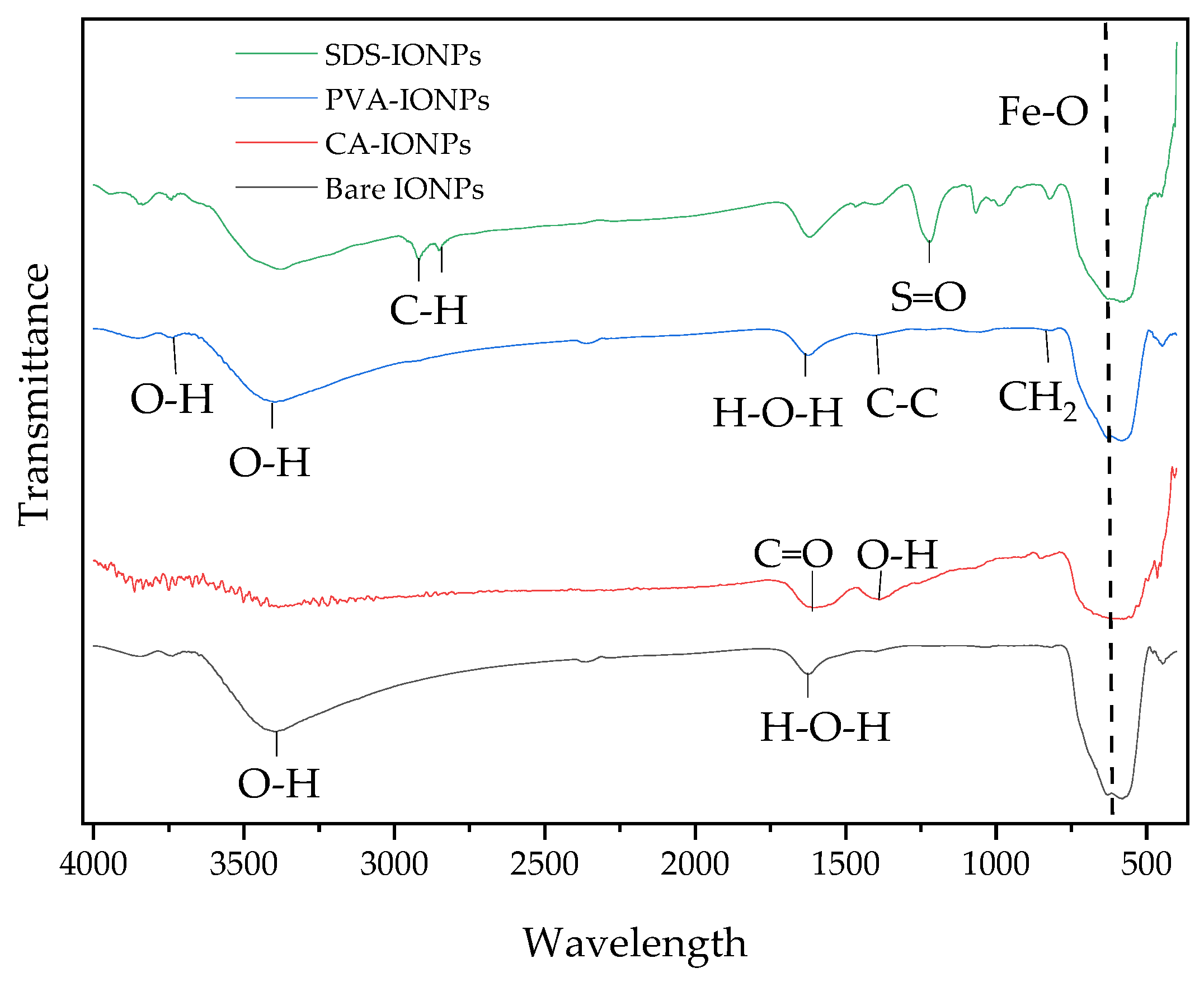
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. Colloidal Stability Analysis of Synthesized Nanoparticles
Zeta Potential Analysis
3.4. Effect on the Hydrodynamic Size
3.5. Effect on the Turbidity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Di Marco, M.; Guilbert, I.; Port, M.; Robic, C.; Couvreur, P.; Dubernet, C. Colloidal stability of ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide (USPIO) particles with different coatings. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 331, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matteo, C.; Candido, P.; Vera, R.; Francesca, V. Current and Future Nanotech Applications in the Oil Industry. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2012, 9, 784–793. Available online: http://www.magforce.de (accessed on 25 May 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kayal, S.; Ramanujan, R.V. Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; He, Q.; Jiang, C. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis and surface functionalization strategies. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2008, 3, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shalbafan, M.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Vakili-Nezhaad, G.R. Enhanced oil recovery by wettability alteration using iron oxide nanoparticles covered with PVP or SDS. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 607, 125509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalbafan, M.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Safaei, A. Experimental investigation of wettability alteration and oil recovery enhance in carbonate reservoirs using iron oxide nanoparticles coated with EDTA or SLS. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 180, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Cho, H. Improvement in the dispersion stability of iron oxide nanoparticles in highly concentrated brine solution using encapsulation with polymer-polymer crosslinked shells. Adv. Powder Technol. 2020, 31, 4743–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-W.; Lee, H.; Song, Y.; Sohn, D. Colloidal stability of iron oxide nanoparticles with multivalent polymer surfactants. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 443, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mak, K.Y.; Leung, C.W.; Chan, K.Y.; Chan, W.K.; Zhong, W.; Pong, P.W.T. Effect of synthesis conditions on the properties of citric-acid coated iron oxide nanoparticles. Microelectron. Eng. 2013, 110, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Zafar, H.; Zia, M.; ul Haq, I.; Phull, A.R.; Ali, J.S.; Hussain, A. Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2016, 9, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, A.; Esmaeilzadeh, F.; Sardarian, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Wang, X. Experimental investigation of wettability alteration of carbonate gas-condensate reservoirs from oil-wetting to gas-wetting using Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with Poly (vinyl alcohol), (PVA) or Hydroxyapatite (HAp). J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 184, 106530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Aulia, G.; Budianto, E.; Mohamed Jan, B.; Habib, S.H.; Amir, Z.; Abdul Patah, M.F. Surface-Functionalized Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles (SPNs) for Enhanced Oil Recovery: Effects of Surface Modifiers and Their Architectures. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 21477–21486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagaria, H.G.; Xue, Z.; Neilson, B.M.; Worthen, A.J.; Yoon, K.Y.; Nayak, S.; Cheng, V.; Lee, J.H.; Bielawski, C.W.; Johnston, K.P. Iron oxide nanoparticles grafted with sulfonated copolymers are stable in concentrated brine at elevated temperatures and weakly adsorb on silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3329–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kotsmar, C.; Yoon, K.Y.; Ingram, D.R.; Johnston, K.P.; Bryant, S.L.; Huh, C. Transport and retention of aqueous dispersions of paramagnetic nanoparticles in reservoir rocks. Proc.-SPE Symp. Improv. Oil Recover. 2010, 2, 1027–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.W.; Low, F.W.; Tai, M.F.; Hamid, S.B.A. Iron oxide nanoparticles decorated oleic acid for high colloidal stability. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Cai, C.; Sun, M.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, L.; Peng, Q.; Shavandi, A.; Yang, S. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized Via Green Tea Extract for Doxorubicin Delivery. Curr. Nanosci. 2020, 17, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.; Barick, K.C.; Bahadur, D. Development of citrate-stabilized Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Conjugation and release of doxorubicin for therapeutic applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Park, C.W.; Ahn, T.; Jung, B.; Seo, B.K.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.D. A direct surface modification of iron oxide nanoparticles with various poly(amino acid)s for use as magnetic resonance probes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 391, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghipour, E.; Javadpour, S.; Mehdizadeh, A.R. Citrate capped superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles used for hyperthermia therapy. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2012, 5, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-kharrag, R.; Amin, A.; Greish, Y.E. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous sodium dodecyl sulfate-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Ceram. Sci. Technol. 2011, 2, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, M.; Verma, S.R. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly Vinyl Alcohol Functionalized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Macromol. Symp. 2017, 376, 1700017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibshahi, R.; Omidkhah, M.; Jafari, A.; Fakhroueian, Z. Hybridization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles with MWCNTs and effect of surface modification on electromagnetic heating process efficiency A microfluidics enhanced oil reco. Fuel 2020, 282, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.; Ahmad, M.; Akhtar, M.S.; Shaari, A.; Riaz, S.; Naseem, S.; Masood, M.; Saeed, M.A. Magnetic properties of polyvinyl alcohol and doxorubicine loaded iron oxide nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery applications. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mote, V.; Purushotham, Y.; Dole, B. Williamson-Hall analysis in estimation of lattice strain in nanometer-sized ZnO particles. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2012, 6, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jun, Y.W.; Choi, J.S.; Cheon, J. Heterostructured magnetic nanoparticles: Their versatility and high performance capabilities. Chem. Commun. 2007, 391, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurchania, R.; Sawant, S.S.; Ball, R.J. Synthesis and characterization of magnetite/polyvinyl alcohol core-shell composite nanoparticles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 97, 3208–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Shah, Z.H.; Riaz, S.; Ahmad, N.; Islam, S.; Raza, M.A.; Naseem, S. Antimicrobial activity of citric acid functionalized iron oxide nanoparticles–Superparamagnetic effect. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 10942–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, L.; Sahoo, Y.; Kim, K.S.; Bergey, E.J.; Prasad, P.N. Nanochemistry: Synthesis and characterization of multifunctional nanoclinics for biological applications. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 3715–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebur, Q.M.; Hashim, A.; Habeeb, M.A. Fabrication, structural and optical properties for (polyvinyl alcohol-polyethylene oxide-iron oxide) nanocomposites. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuel, E.; Vaz, C.; Matias, W.G.; Dewez, D. Interaction Effect of EDTA, Salinity, and Oxide Nanoparticles on Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Chlamydomonas euryale. Plants 2021, 10, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, E.; Cheng, G.; Ma, X.; Pang, X.; Zhao, Q. Surface modification of zinc oxide nanoparticle by PMAA and its dispersion in aqueous system. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2006, 252, 5227–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, A.A.; Samuel, D.G.H.; Parthasarathy, V.; Kiruthiga, K. A facile one pot synthesis of highly stable PVA–CuO hybrid nanofluid for heat transfer application. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 207, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, F.; Luna, A.L.; Niederberger, M. From colloidal dispersions to aerogels: How to master nanoparticle gelation. Nano Today 2020, 30, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divandari, H.; Hemmati-Sarapardeh, A.; Schaffie, M.; Ranjbar, M. Integrating synthesized citric acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles with magnetic fields for enhanced oil recovery: Experimental study and mechanistic understanding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 174, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, F.; Güen, G.; Pişkin, E. Magnetically loaded poly(methyl methacrylate-co-acrylic acid) nano-particles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2006, 284, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, K.D. Handbook of Nanophysics: Nanoparticles and Quantum Dots, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, M.A.; Wani, M.Y.; Hashim, M.A. Microemulsion method: A novel route to synthesize organic and inorganic nanomaterials: 1st Nano Update. Arab. J. Chem. 2012, 5, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahn-Chique, K.; Puertas, A.M.; Romero-Cano, M.S.; Rojas, C.; Urbina-Villalba, G. Nanoemulsion stability: Experimental evaluation of the flocculation rate from turbidity measurements. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 178, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.G.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.D. Novel Evaluation Method for the Water-in-Oil (W/O) Emulsion Stability by Turbidity Ratio Measurements. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 19, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouar, S.L.; Baki, A.D.; Iddou, A. Studies of the mechanism of poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) adsorption on the calcite/water interface in the presence of sodium oleate (SOL). Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2007, 11, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Type of Surface Coating | Molar Ratio (M) | Crystallite Size from XRD (nm) | Size Measured from FE-SEM (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CA-IONPs | 0.07 | 9.726 | 34.9 |
| CA-IONPs | 0.5 | 12.399 | 33.9 |
| CA-IONPs | 1.0 | 10.643 | 42.7 |
| SDS-IONPs | 0.07 | 9.865 | 38.5 |
| SDS-IONPs | 0.5 | 8.595 | 33.9 |
| SDS-IONPs | 1.0 | 13.257 | 54 |
| PVA -IONPs | 0.07 | 9.635 | 34.3 |
| PVA -IONPs | 0.5 | 9.603 | 47.9 |
| PVA -IONPs | 1.0 | 9.969 | 52.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che Mohamed Hussein, S.N.; Amir, Z.; Jan, B.M.; Khalil, M.; Azizi, A. Colloidal Stability of CA, SDS and PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs): Effect of Molar Ratio and Salinity. Polymers 2022, 14, 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214787
Che Mohamed Hussein SN, Amir Z, Jan BM, Khalil M, Azizi A. Colloidal Stability of CA, SDS and PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs): Effect of Molar Ratio and Salinity. Polymers. 2022; 14(21):4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214787
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe Mohamed Hussein, Siti Nurliyana, Zulhelmi Amir, Badrul Mohamed Jan, Munawar Khalil, and Azlinda Azizi. 2022. "Colloidal Stability of CA, SDS and PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs): Effect of Molar Ratio and Salinity" Polymers 14, no. 21: 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214787
APA StyleChe Mohamed Hussein, S. N., Amir, Z., Jan, B. M., Khalil, M., & Azizi, A. (2022). Colloidal Stability of CA, SDS and PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IONPs): Effect of Molar Ratio and Salinity. Polymers, 14(21), 4787. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14214787







