Effect of Recycling on the Mechanical, Thermal and Rheological Properties of Polypropylene/Carbon Nanotube Composites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
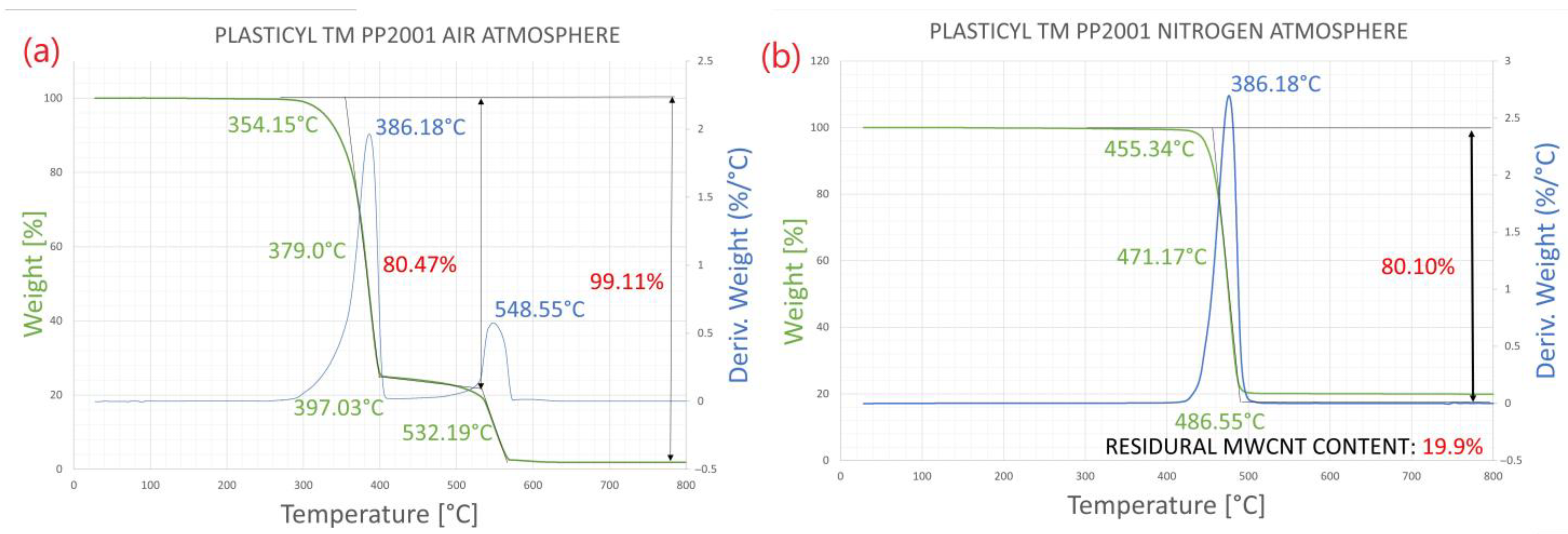
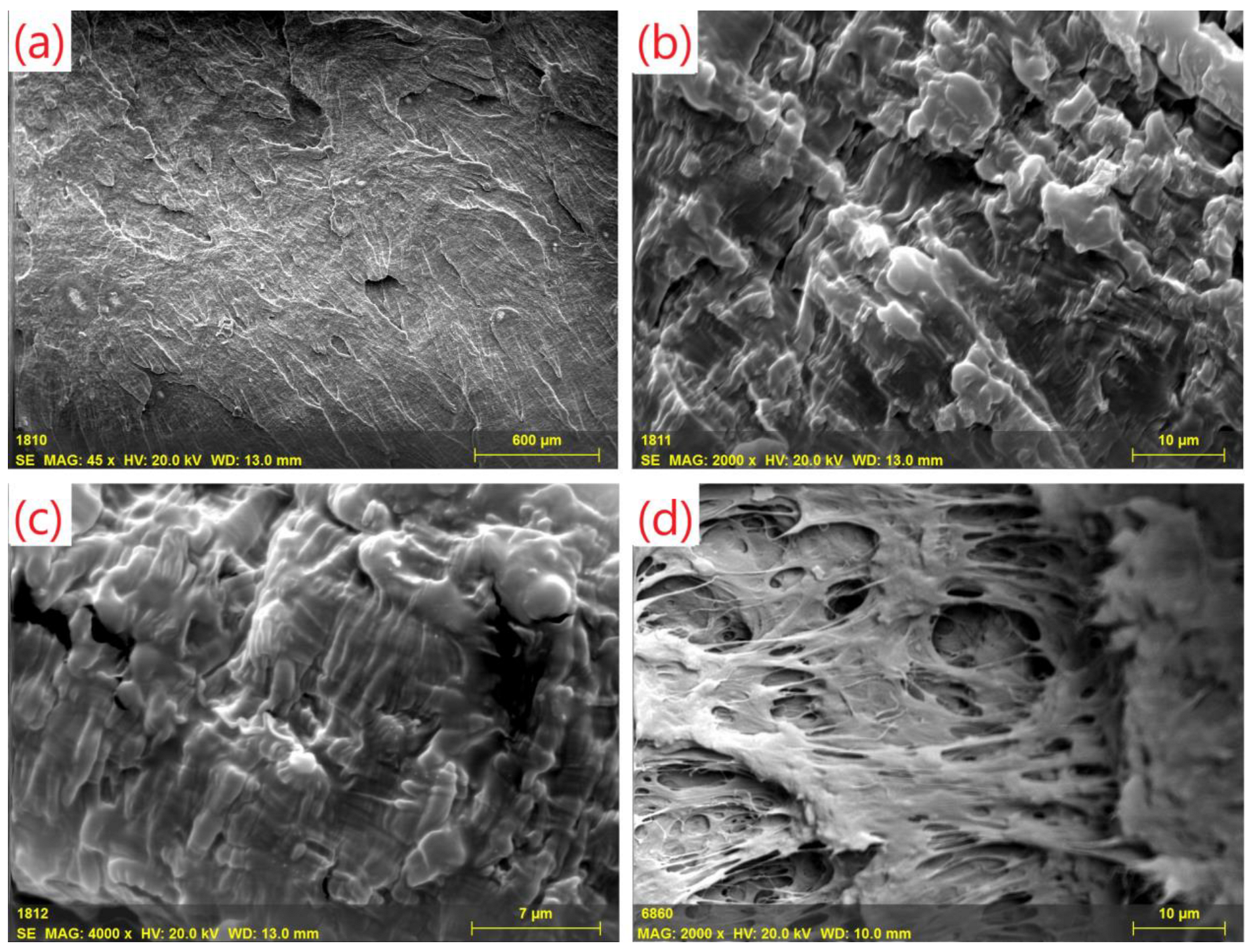
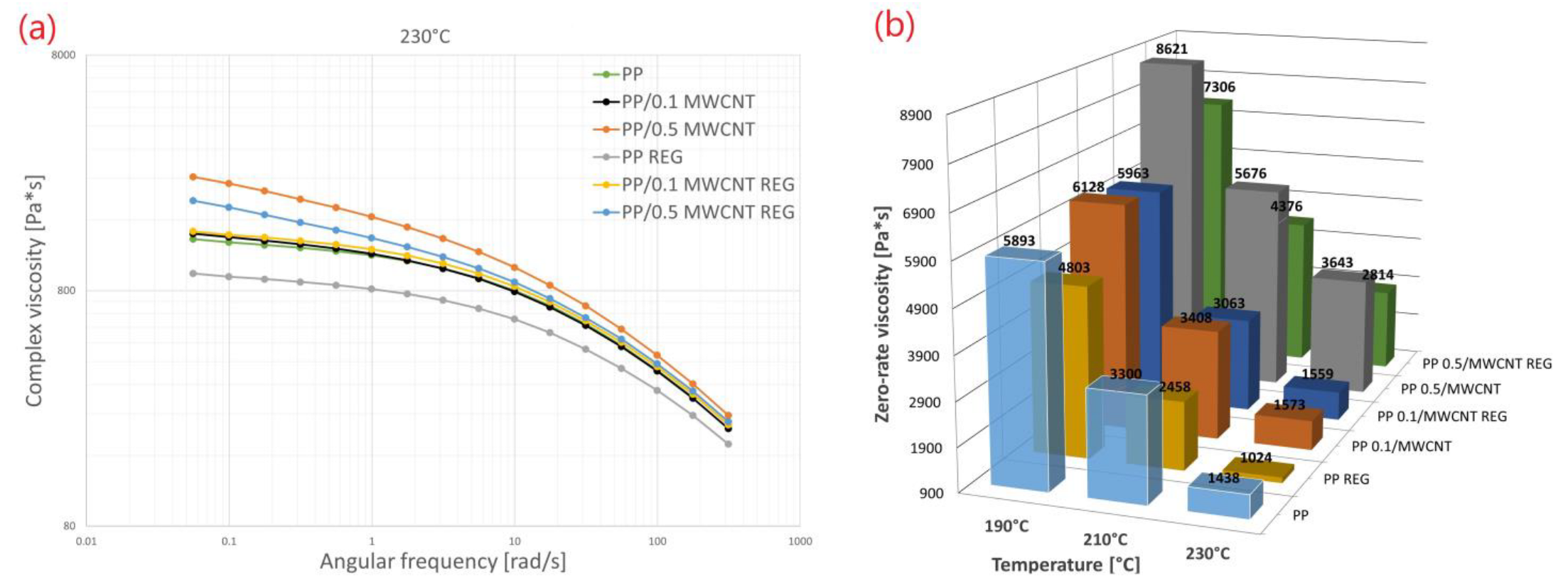
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Galli, P.; Haylock, J.C.; Simonazzi, T. Manufacturing and properties of polypropylene copolymers. In Polypropylene Structure, Blends and Composites; Karger-Kocsis, J., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kontopoulou, M.; Wang, W.; Gopakumar, T.G.; Cheung, C. Effect of composition and comonomer type on the rheology, morphology and properties of ethylene-a-olefin copolymer/polypropylene blends. Polymer 2003, 44, 7495–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, J.U.; Michler, G.H.; Grellmann, W.; Seidler, S.; Gahleitner, M.; Fiebig, J.; Nezbedova, E. Fracture toughness of polypropylene copolymers: Influence of interparticle distance and temperature. Polymer 1998, 39, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Xu, J.-T.; Wang, H.-T.; Feng, L.-X. Structure and properties of polypropylene/poly(ethylene-co-propylene) in-situ blends synthesized by spherical ZieglereNatta catalyst. Polymer 2001, 42, 5559–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Verma, M.; Gupta, A.; Chauhan, S.S.; Malik, R.S.; Choudhary, V. Multi walled carbon nanotubes induced viscoelastic response of polypropylene copolymer nanocomposites: Effect of filler loading on rheological percolation. Polim. Test. 2016, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetgin, S.H. Effect of multi walled carbon nanotube on mechanical, thermal and rheological propoerties of polypropylene. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4725–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theng, C.C.; Ma, C.C.M.; Huang, Y.W.; Yuen, S.M.; Weng, C.C.; Chen, C.H.; Su, S.F. Effect of MWCNT content on rheological and dynamic mechanical properties of multiwalled carbon nanotube/polypropylene composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubes of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguin, F.; Ehrburger, P. Special issue on carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2002, 40, 1619. [Google Scholar]
- Subramoney, S. Novel nanocarbons. Structure, properties, and potential applications. Adv. Mater. 1998, 10, 1157–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://mol.hu/images/mol_hu/pdf/vallalati_ugyfelek/polimer-termekek/termekek/pp-polipropilenek/tipplen/tipplen_k_499_hu_2018.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Available online: http://www.nanocyl.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/TDS-PLASTICYL-PP2001-V10.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Available online: https://www.labtechengineering.com/product/lte-26-and-ltem-26/ (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Yuen, S.M.; Ma, C.C.; Wu, H.H.; Kuan, H.C.; Chen, W.J.; Liao, S.H.; Hsu, C.-W.; Wu, H.-L. Preparation and thermal, electrical, and morphological properties of multiwalled carbon nanotube and epoxy composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.H.; Wang, Z.G. Influence of carbon nanotube aspect ratio on normal stress differences in isotactic polypropylene nanocomposite melts. Macromolecules 2008, 41, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Choudhary, V. Rheologic and mechanical properties of multiwalled carbon nanotubes-reinforced poly(trimethylene terephthalate) composites. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 3347–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.-K.; Park, S.-J. Electrical resistivity and rheological behaviors of carbon nanotubes-filled polypropylene composites. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 395, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumfleth, J.; Buschhorn, S.; Schulte, K. Comparison of rheological and electrical percolation phenomena in carbon black and carbon nanotube filled epoxy polimers. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiaming, B.; Ruth, D.G.; Richard, J.M.H.; Mo, S.; Masami, O. Influence of carbon nanotubes on the rheology and dynamic mechanical properties of polyamide-12 for laser sintering. Polym. Test. 2014, 36, 95–100. [Google Scholar]
- Prashantha, K.; Soulestin, J.; Lacrampe, M.F.; Claes, M.; Dupin, G.; Krawczak, P. Multi-walled carbon nanotube filled polypropylene nanocomposites based on masterbach route: Improvement of dispersion and mechanical properties through PP-g-MA addition. Express Polym. Lett. 2008, 2, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guptam, A.; Choudhary, V. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on mechanical and rheological properties of poly(trimethylene terephthalate. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyoti, J.; Singh, B.P.; Rajput, S.; Singh, V.N.; Dhakate, S. Detailed dynamic rheological studies of multiwall carbon nanotube-reinforced acrylonitrite butadiene styrene composite. J. Mater Sci. 2016, 51, 2643–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Choudhary, V. Polypropylene random copolymer/MWCNT nanocomposites; isothermal crystallization kinetics, structural, and morphological interpretations. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berczeli, M.; Hatoss, B.; Kókai, E. Surface treatment of polymer matrix nanocomposites for adhesion enhancement by cold plasma. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 1246, 012028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balázs, Á.; Balázs, P.; Dorottya, N. The effect of different printing parameters on mechanical and thermal properties of PLA specimens. Gradus 2020, 7, 166–173. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.wittmann-group.com/en/ecopower-55-550-t (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Dorottya, N.; Krisztian, B. Rheological study of high and linear low density polyethylene blends. Perner’s Contacts 2019, 2, 206. [Google Scholar]
- Ádám, B.; Weltsch, Z. Thermal and Mechanical Assessment of PLA-SEBS and PLA-SEBS-CNT Biopolymer Blends for 3D Printing. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.tainstruments.com/ares-g2/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwwNWKBhDAARIsAJ8HkheFMJaLRvmk9NkZS-59jTHH8uET3D2RlAuM77xAiHlvcx6JwmLFIJYaAsLsEALw_wcB (accessed on 29 June 2022).
- Ehrenstein, G.W.; Riedel, G.; Trawiel, P. Thermal Analysis of Plastics: Theory and Practice; Hanser Publishers: Munich, Germany, 2005; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- Pötschke, P.; Abdel-Goad, M.; Alig, I.; Dudkin, S.; Lellinger, D. Rheological and dielectrical characterization of melt mixed polycarbonate- multiwalled carbon nanotube composites. Polymer 2004, 45, 8863–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, O.; Sarno, M.; Rainone, N.G.; Nobile, M.R.; Ciambelli, P.; Neitzert, H.C.; Simon, G.P. Influence of the polymer structure and nanotube concentration ont he conductivity and rheological properties of polyethylene/CNT composites. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2008, 40, 2440–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menard, K.P. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis: A Practical Introduction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dubnikova, I.; Kuvardina, E.; Krasheninnikov, V.; Lomakin, S.; Tchmutin, I.; Kuznetsov, S. The effect of multiwalled carbon nanotube dimensions ont he morphology, mechanical, and electrical properties of melt mixed polypropylene-based composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Mark, J.; Ngai, K.; Graessley, W.; Mandelkern, L.; Samulski, E.; Wignall, G.; Koenig, J. Physical Properties of Polymers; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.S. Rheological characterization of carbon nanotubes/poly(ethylene oxide) composites. Rheol. Acta 2006, 46, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.Q.; Zhang, L.C.; Zarudi, I. Mechanical and rheological properties of carbon nanotube-reinforced polyethylene composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, J.F.; Martı’nez-Salazar, J.; Trujillo, M.; Arnal, M.L.; Müller, A.J.; Bredeau, S.; Dubois, P. Rheology, Processing, Tensile Properties, and Crystallization of Polyethylene/Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 4719–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreau, P.J.; de Kee, D.C.R.; Chhabra, R.P. Rheology of Polymeric Systems; Hanser Publisher: Munich, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gahleitner, M. Melt rheology of polyolefins. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2001, 26, 895–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrea, A.M.; Jaroslav, B.; David, B. Low dose cosmic radiation effects on polycarbonate. Perner’s Contacts 2019, 2, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrios, B. Microstructure and properties of Polypropylene/Carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Materials 2010, 3, 2884–2946. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrios, G.P.; Lazaros, T.; George, Z.P.; Dimitrios, N.B.; Konstantinos, C. β-nucleated propylene-ethylene random copolymer filled with multi-walled carbon nanotubes:mechanical, thermal and rheological properties. Polymer 2014, 55, 3758–3769. [Google Scholar]
- Bing-Xing, Y.; Jia-Hua, S.; Pramoda, K.P.; Suat Hong, G. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of polypropylene using polypropylene-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, A.J.; Senthilvelan, S. Mechanical and tribological properties of carbon nanotube reinforced polypropylene composites. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part L J. Mater. Des. Appl. 2016, 232, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beate, K.; Regine, B.; Liane, H.; Petra, P. Ultralow percolation threshold in polyamide 6.6/MWCNT composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 114, 119–125. [Google Scholar]


| Sample | Young Modulus (MPa) | Tensile Stress at Yield (Mpa) | Tensile Strain at Yield (%) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Young Modulus (MPa) | Std. dev (MPa) | Relative std. dev (%) | Difference from the Unreinforced Original PP (%) | Tensile Stress at Yield (Mpa) | Std. dev (MPa) | Relative std. dev (%) | Difference from the Unreinforced Original PP (%) | Tensile Strain at Yield (%) | Std. dev (%) | Relative std. dev (%) | Difference from the Unreinforced Original PP (%) | |
| PP | 999 | 3.9 | 0.39 | - | 22.12 | 0.23 | 1.03 | - | 5.33 | 0.09 | 1.75 | - |
| PP REG | 958 | 9.1 | 0.95 | −4.1 | 21.44 | 0.15 | 0.71 | −3.1 | 5.47 | 0.09 | 1.70 | 2.6 |
| PP 0.1/MWCNT | 1174 | 16.1 | 1.37 | 17.5 | 22.56 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 1.9 | 4.52 | 0.03 | 0.69 | −15.2 |
| PP 0.1/MWCNT REG | 1041 | 61.6 | 5.92 | 4.2 | 22.50 | 0.19 | 0.83 | 1.7 | 5.20 | 0.36 | 6.92 | −2.5 |
| PP 0.5/MWCNT | 1226 | 12.3 | 1.00 | 22.7 | 22.92 | 0.08 | 0.37 | 3.6 | 4.50 | 0.06 | 1.39 | −15.5 |
| PP 0.5/MWCNT REG | 1156 | 67.1 | 5.81 | 15.7 | 22.44 | 0.23 | 1.03 | 1.4 | 4.75 | 0.37 | 7.73 | −10.9 |
| Sample | Second Heating | Cooling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆Hm (J/g) | Tpm (°C) | Xc (%) | ∆Hc (J/g) | Tpc (°C) | Teic (°C) | |
| PP | 99.40 | 162.2 | 47.3 | 90.0 | 120.1 | 115.7 |
| PP REG | 100.80 | 162.4 | 48.2 | 89.2 | 121.6 | 118.7 |
| PP 0.1/MWCNT | 110.70 | 163.7 | 52.9 | 102.4 | 126.6 | 123.6 |
| PP 0.1/MWCNT REG | 99.50 | 163.2 | 47.6 | 91.4 | 125.6 | 122.7 |
| PP 0.5/MWCNT | 107.70 | 163.8 | 51.5 | 98.2 | 127.9 | 125.2 |
| PP 0.5/MWCNT REG | 101.40 | 164.0 | 48.5 | 92.7 | 128.0 | 125.3 |
| Sample | 190 °C | 210 °C | 230 °C | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zero-Shear-Rate Viscosity (Pa*s) | Std. dev (Pa*s) | Relative std. dev (%) | Difference from the Original Zero-Shear-Rate Viscosity (%) | Zero-Shear-Rate Viscosity (Pa*s) | Std. dev (Pa*s) | Relative std. dev (%) | Difference from the Original Zero-Shear-Rate Viscosity (%) | Zero-Shear-Rate Viscosity (Pa*s) | Std. dev (Pa*s) | Relative std. dev (%) | Difference from the Original Zero-Shear-Rate Viscosity (%) | |
| PP | 5893 | 234.2 | 3.97 | - | 3300 | 83.8 | 2.54 | - | 1438 | 35.4 | 2.46 | - |
| PP 0.1/MWCNT | 6128 | 172.9 | 2.82 | +3.98 | 3408 | 35.8 | 1.05 | +3.27 | 1573 | 45.6 | 2.90 | +9.38 |
| PP 0.5/MWCNT | 8621 | 109.5 | 1.27 | +46.29 | 5676 | 193.9 | 3.42 | +72 | 3643 | 48.3 | 1.32 | +153.33 |
| PP REG | 4803 | 4,6 | 0.10 | −18.5 | 2458 | 91.1 | 3.71 | −25.52 | 1024 | 59.5 | 5.81 | −28.79 |
| PP 0.1/MWCNT REG | 5963 | 100.4 | 1.68 | +1.18 | 3063 | 84.5 | 2.76 | −7.19 | 1559 | 27.9 | 1.79 | +8.41 |
| PP 0.5/MWCNT REG | 7306 | 15.0 | 0.21 | +23.97 | 4376 | 3408.0 | 0.62 | +32.6 | 2814 | 104.6 | 3.72 | +95.68 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bata, A.; Nagy, D.; Weltsch, Z. Effect of Recycling on the Mechanical, Thermal and Rheological Properties of Polypropylene/Carbon Nanotube Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 5257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235257
Bata A, Nagy D, Weltsch Z. Effect of Recycling on the Mechanical, Thermal and Rheological Properties of Polypropylene/Carbon Nanotube Composites. Polymers. 2022; 14(23):5257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235257
Chicago/Turabian StyleBata, Attila, Dorottya Nagy, and Zoltán Weltsch. 2022. "Effect of Recycling on the Mechanical, Thermal and Rheological Properties of Polypropylene/Carbon Nanotube Composites" Polymers 14, no. 23: 5257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235257
APA StyleBata, A., Nagy, D., & Weltsch, Z. (2022). Effect of Recycling on the Mechanical, Thermal and Rheological Properties of Polypropylene/Carbon Nanotube Composites. Polymers, 14(23), 5257. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14235257







