Cefotaxime Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.3. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles
2.4. Characterization of Synthesized C-Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
2.4.1. Ultraviolet (UV)–Visible Spectroscopy
2.4.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.4.3. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
2.4.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.5. Determination of Loading Efficiency of Cefotaxime (CTX) onto C-AuNPs
2.6. Assessment of Antibacterial Activity
2.6.1. Agar Well Diffusion Method
2.6.2. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Cefotaxime-Loaded Gold Nanoparticles (C-AuNPs)
3.2. Characterization of Cefotaxime-Loaded Gold Nanoparticles (C-AuNPs)
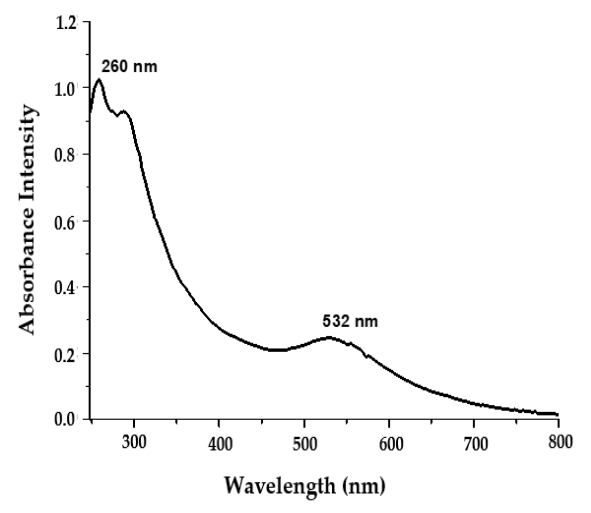
3.2.1. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
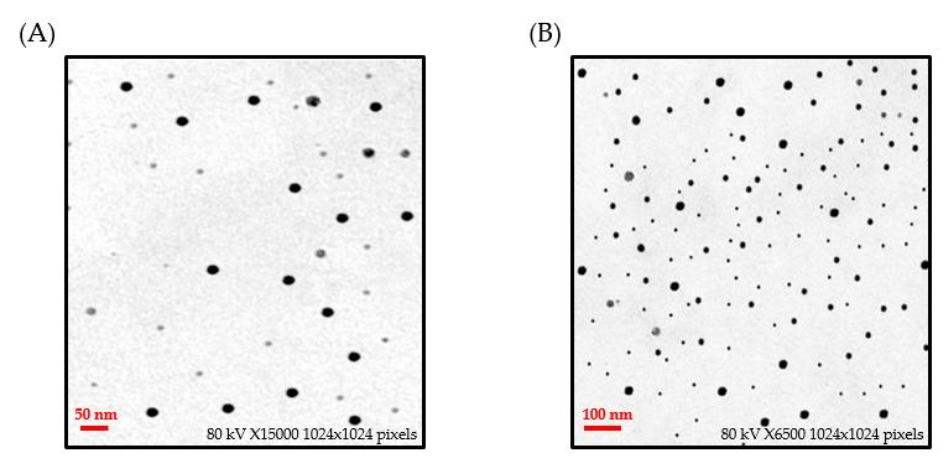
3.2.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy
3.2.3. Size Determination via Dynamic Light Scattering
3.2.4. Zeta-Potential Study
3.2.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
3.2.6. Percent Loading of CTX over C-AuNPs
3.3. Antibacterial Activity Analysis of C-AuNPs
3.4. Determination of Minimal Inhibitory Concentration of CTX and C-AuNPs
3.5. Hypothesis on Mechanistic Aspects of the Antibacterial Potential of C-AuNPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castle, S.S. Cefotaxime. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- LeFrock, J.L.; Prince, R.A.; Leff, R.D. Mechanism of action, antimicrobial activity, pharmacology, adverse effects, and clinical efficacy of cefotaxime. Pharmacotherapy 1982, 2, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jindal, A.K.; Pandya, K.; Khan, I.D. Antimicrobial resistance: A public health challenge. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2015, 71, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bujdáková, H.; Lausová, A.; Jankovicová, S.; Prodinger, W.M.; Kallová, J.; Milosovic, P.; Kettner, M. Study of beta-lactam resistance in ceftazidime-resistant clinical isolates of Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1998, 10, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Babic, M.; Hujer, A.M.; Bonomo, R.A. What’s new in antibiotic resistance? Focus on beta-lactamases. Drug Resist. Updates 2006, 9, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souli, M.; Wennersten, C.B.; Eliopoulos, G.M. In vitro activity of BAY 12-8039, a new fluoroquinolone, against species representative of respiratory tract pathogens. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1998, 10, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, H.F. Solving staphylococcal resistance to beta-lactams. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonzé, E.; Vanhove, M.; Dive, G.; Sauvage, E.; Frère, J.M.; Charlier, P. Crystal structures of the Bacillus licheniformis BS3 class A beta-lactamase and of the acyl-enzyme adduct formed with cefoxitin. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, A.; Prabhune, A.; Perry, C.C. Antibiotic mediated synthesis of gold nanoparticles with potent antimicrobial activity and their application in antimicrobial coatings. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6789–6798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baptista, P.V.; McCusker, M.P.; Carvalho, A.; Ferreira, D.A.; Mohan, N.M.; Martins, M.; Fernandes, A.R. Nano-Strategies to Fight Multidrug Resistant Bacteria—“A Battle of the Titans”. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mba, I.E.; Nweze, E.I. Nanoparticles as therapeutic options for treating multidrug-resistant bacteria: Research progress, challenges, and prospects. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewabe, A.; Marew, T.; Birhanu, G. The contribution of nano-based strategies in overcoming ceftriaxone resistance: A literature review. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2021, 9, e00849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, J.K.; Das, G.; Fraceto, L.F.; Campos, E.V.R.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.D.P.; Acosta-Torres, L.S.; Diaz-Torres, L.A.; Grillo, R.; Swamy, M.K.; Sharma, S.; et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnology 2018, 16, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishwa, B.; Moin, A.; Gowda, D.V.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Hegazy, W.A.H.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Khafagy, E.S.; Allam, A.N. Pulmonary Targeting of Inhalable Moxifloxacin Microspheres for Effective Management of Tuberculosis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, A.; Wani, S.U.D.; Osmani, R.A.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Arab, H.H.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Allam, A.N. Formulation, characterization, and cellular toxicity assessment of tamoxifen-loaded silk fibroin nanoparticles in breast cancer. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saqr, A.; Wani, S.U.D.; Gangadharappa, H.V.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Khafagy, E.S.; Lila, A.S.A. Enhanced Cytotoxic Activity of Docetaxel-Loaded Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles against Breast Cancer Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Lila, A.S.; Ishida, T. Liposomal Delivery Systems: Design Optimization and Current Applications. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alhariri, M.; Azghani, A.; Omri, A. Liposomal antibiotics for the treatment of infectious diseases. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1515–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.J.; Wong, E.H.H.; Boyer, C.; Qiao, G.G. Antimicrobial polymeric nanoparticles. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 76, 40–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okkeh, M.; Bloise, N.; Restivo, E.; De Vita, L.; Pallavicini, P.; Visai, L. Gold Nanoparticles: Can They Be the Next Magic Bullet for Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria? Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Saqr, A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Alalaiwe, A.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alshahrani, S.M.; Anwer, M.K.; Khan, S.; Lila, A.S.A.; Arab, H.H.; Hegazy, W.A.H. Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles by Using Green Machinery: Characterization and In Vitro Toxicity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, S.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Shakil, S.; Hussain, T.; Alshammari, T.M.; Ahmad, W.; Tabrez, S.; Al-Qahtani, M.H.; Abuzenadah, A.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Cefotaxime Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles and Their Use to Target Drug-Resistant CTX-M-Producing Bacterial Pathogens. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2802–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamaila, S.; Zafar, N.; Riaz, S.; Sharif, R.; Nazir, J.; Naseem, S. Gold Nanoparticles: An Efficient Antimicrobial Agent against Enteric Bacterial Human Pathogen. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Robinson, S.M.; Gupta, A.; Saha, K.; Jiang, Z.; Moyano, D.F.; Sahar, A.; Riley, M.A.; Rotello, V.M. Functional gold nanoparticles as potent antimicrobial agents against multi-drug-resistant bacteria. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10682–10686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshammari, F.; Alshammari, B.; Moin, A.; Alamri, A.; Al Hagbani, T.; Alobaida, A.; Baker, A.; Khan, S.; Rizvi, S.M. Ceftriaxone Mediated Synthesized Gold Nanoparticles: A Nano-Therapeutic Tool to Target Bacterial Resistance. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Huang, K.; Li, H.-H.; Lu, Y.-G.; Zheng, D.-L. Antibacterial Properties of Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Their Application in Oral Biology. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 5616379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.N.; Smith, K.; Samuels, T.A.; Lu, J.; Obare, S.O.; Scott, M.E. Nanoparticles functionalized with ampicillin destroy multiple-antibiotic-resistant isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter aerogenes and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2768–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.-C.; Tsai, P.-J.; Chen, Y.-C. Functional gold nanoparticles as photothermal agents for selective-killing of pathogenic bacteria. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Dai, T.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation and photodynamic therapy for infections. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 635, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norman, R.S.; Stone, J.W.; Gole, A.; Murphy, C.J.; Sabo-Attwood, T.L. Targeted Photothermal Lysis of the Pathogenic Bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, with Gold Nanorods. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, B.; Habib, H.; Abbasi, S.A.; Ihsan, A.; Nasir, H.; Imran, M. Development of Cefotaxime Impregnated Chitosan as Nano-antibiotics: De Novo Strategy to Combat Biofilm Forming Multi-drug Resistant Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akinyemi, K.O.; Oladapo, O.; Okwara, C.E.; Ibe, C.C.; Fasure, K.A. Screening of crude extracts of six medicinal plants used in South-West Nigerian unorthodox medicine for anti-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2005, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticles: Preparation, properties, and applications in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, T.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles: A Novel Nanomaterial for Various Medical Applications and Biological Activities. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, Y.; Ullah, I.; Ul-Islam, M.; Alghamdi, K.M.; Khalil, A.; Kamal, T. Adopting a green method for the synthesis of gold nanoparticles on cotton cloth for antimicrobial and environmental applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengani, M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Rajeswari, V.D. Recent trends and methodologies in gold nanoparticle synthesis—A prospective review on drug delivery aspect. OpenNano 2017, 2, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles: Optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mollick, M.M.R.; Rana, D.; Dash, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bhowmick, B.; Maity, D.; Mondal, D.; Pattanayak, S.; Roy, S.; Chakraborty, M.; et al. Studies on green synthesized silver nanoparticles using Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) pulp extract having anticancer (in vitro) and antimicrobial applications. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 2572–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, R. Progress in nanoparticles characterization: Sizing and zeta potential measurement. Particuology 2008, 6, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, A.S.; Singh, P.; Mijakovic, I. Interactions of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles with Bacterial Biofilms: Molecular Interactions behind Inhibition and Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.G.; El-Kased, R.F.; Elmazar, M.M. Thermoresponsive gels containing gold nanoparticles as smart antibacterial and wound healing agents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Nazam, N.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Ahmad, K.; Baig, M.H.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, I. Mechanistic Insights into the Antimicrobial Actions of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Implications for Multidrug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarkar, P.; Yarlagadda, V.; Ghosh, C.; Haldar, J. A review on cell wall synthesis inhibitors with an emphasis on glycopeptide antibiotics. Medchemcomm 2017, 8, 516–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, P.A. Cellular impermeability and uptake of biocides and antibiotics in Gram-positive bacteria and mycobacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 92, 46S–54S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadeer, N.S.; Fülöp, G.; Chen, S.; Käll, M.; Murphy, C.J. Interactions of Bacterial Lipopolysaccharides with Gold Nanorod Surfaces Investigated by Refractometric Sensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24915–24925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Zone of Inhibition (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | Escherichia coli | Klebsiella oxytoca | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Staphylococcus aureus |
| CTX (20 µg/well) | 28 ± 0.5 mm | 17 ± 1.2 mm | 21 ± 1.5 mm | 15 ± 0.8 mm |
| C-AuNPs (4.19 µg/well) | 26 ± 0.7 mm | 15 ± 0.9 mm | 20 ± 0.8 mm | 13 ± 1.0 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Hagbani, T.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Hussain, T.; Mehmood, K.; Rafi, Z.; Moin, A.; Abu Lila, A.S.; Alshammari, F.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Rahamathulla, M.; et al. Cefotaxime Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. Polymers 2022, 14, 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040771
Al Hagbani T, Rizvi SMD, Hussain T, Mehmood K, Rafi Z, Moin A, Abu Lila AS, Alshammari F, Khafagy E-S, Rahamathulla M, et al. Cefotaxime Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. Polymers. 2022; 14(4):771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040771
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Hagbani, Turki, Syed Mohd Danish Rizvi, Talib Hussain, Khalid Mehmood, Zeeshan Rafi, Afrasim Moin, Amr Selim Abu Lila, Farhan Alshammari, El-Sayed Khafagy, Mohamed Rahamathulla, and et al. 2022. "Cefotaxime Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity" Polymers 14, no. 4: 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040771
APA StyleAl Hagbani, T., Rizvi, S. M. D., Hussain, T., Mehmood, K., Rafi, Z., Moin, A., Abu Lila, A. S., Alshammari, F., Khafagy, E.-S., Rahamathulla, M., & Abdallah, M. H. (2022). Cefotaxime Mediated Synthesis of Gold Nanoparticles: Characterization and Antibacterial Activity. Polymers, 14(4), 771. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14040771









