On the Analysis of Cryogels and Xerogels Using Cellulose Nanofibers and Graphene Oxide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
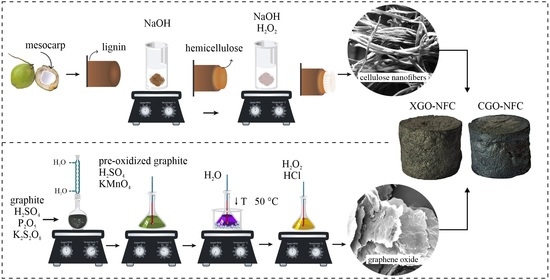
2.1. Synthesis of GO
2.2. Synthesis of NFC
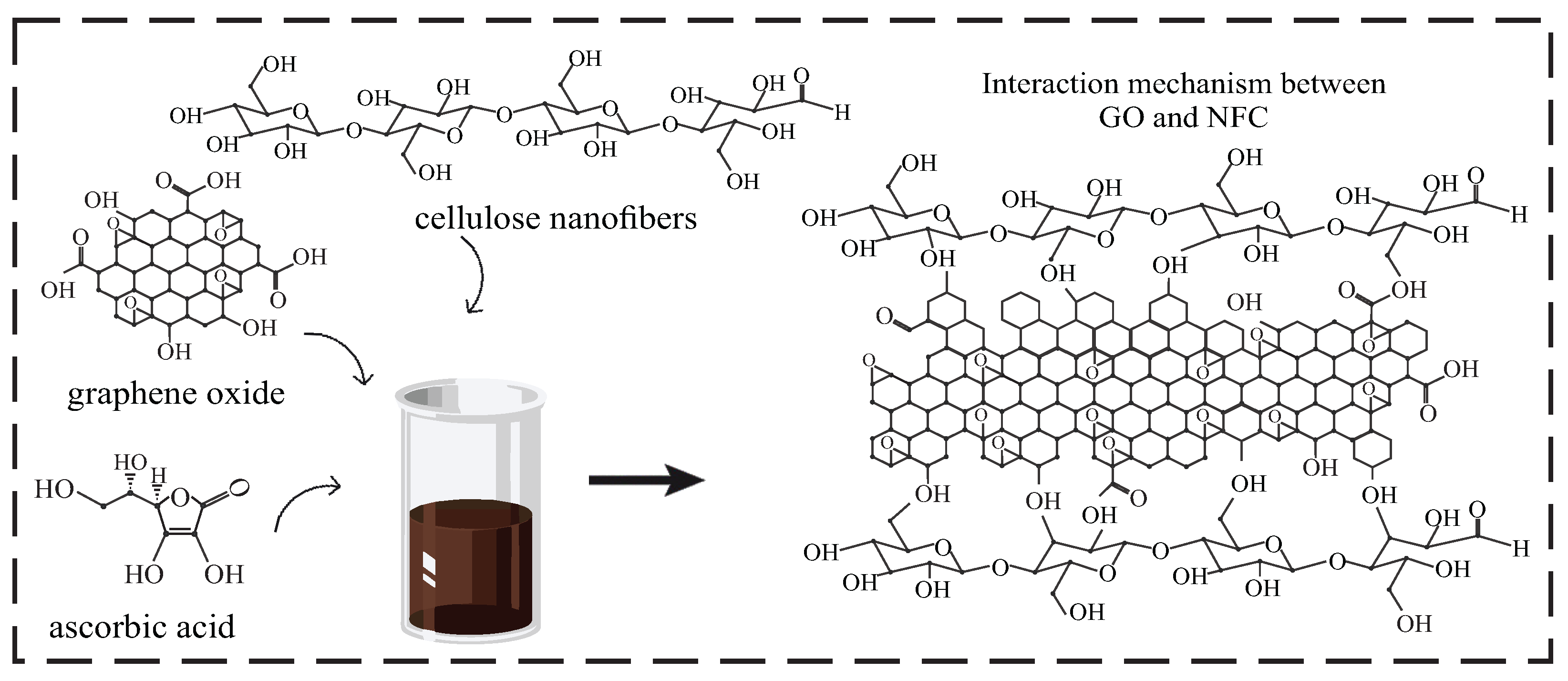
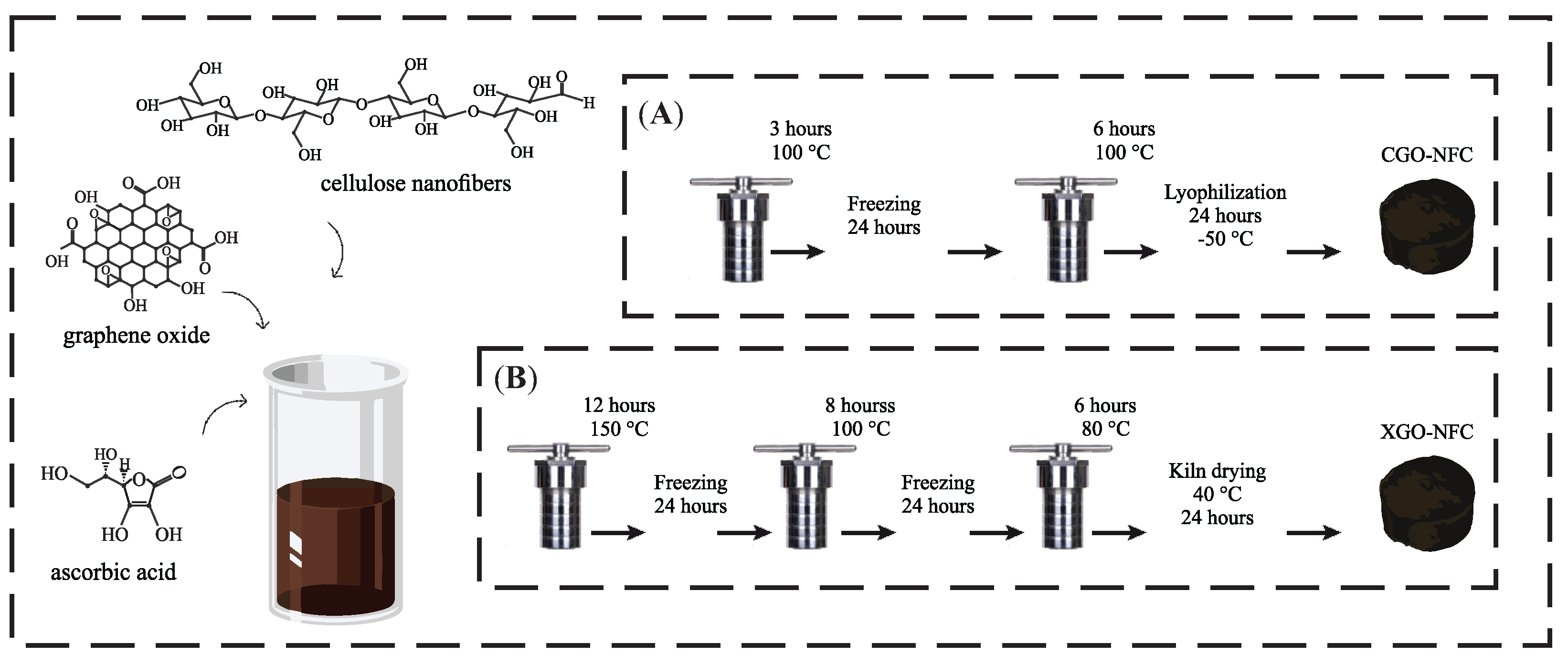
2.3. Synthesis of CGO-NFC and XGO-NFC
2.4. Influence Factors on the Developed Nanomaterials
2.5. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
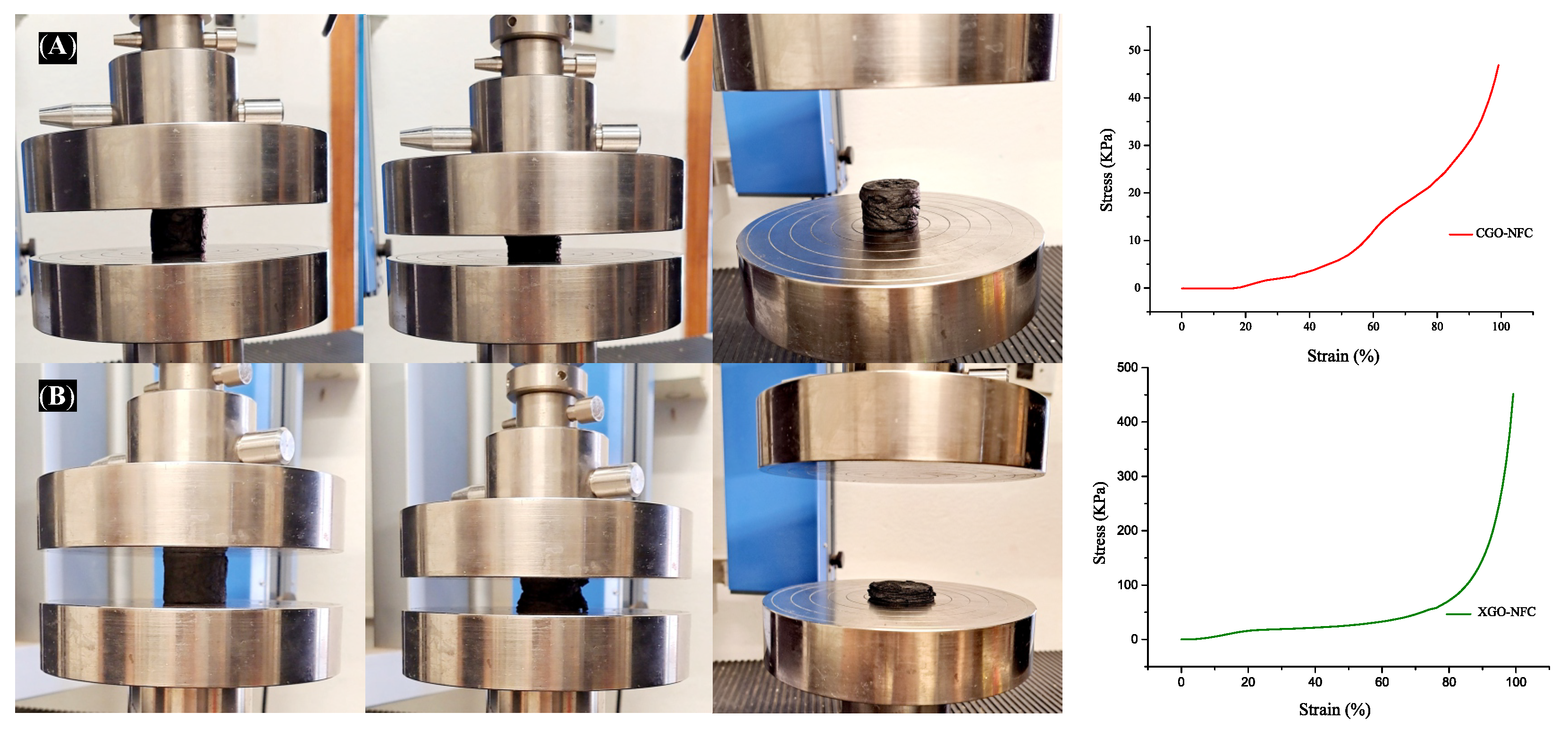
3.1. Factors Defined for the Nanomaterials
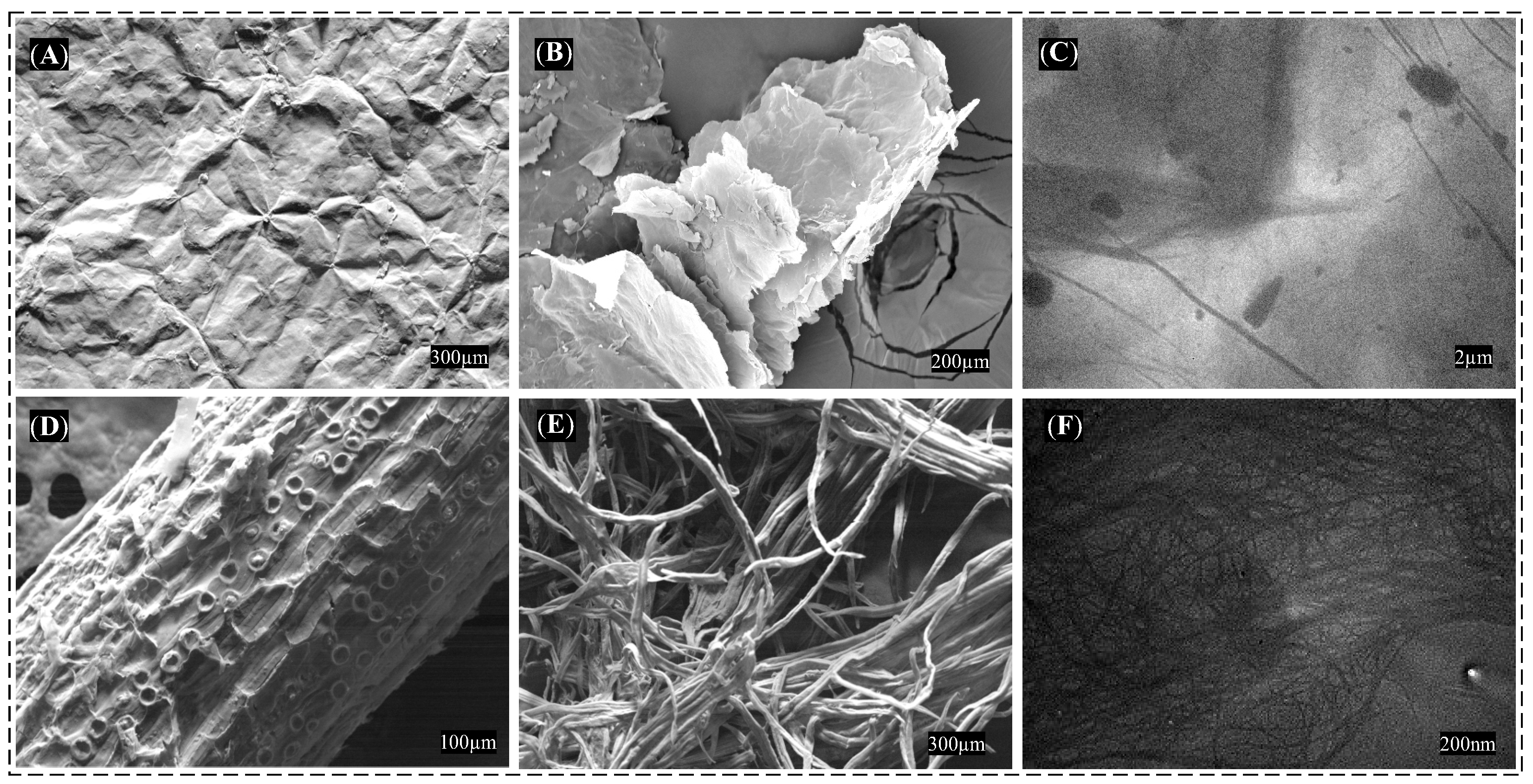
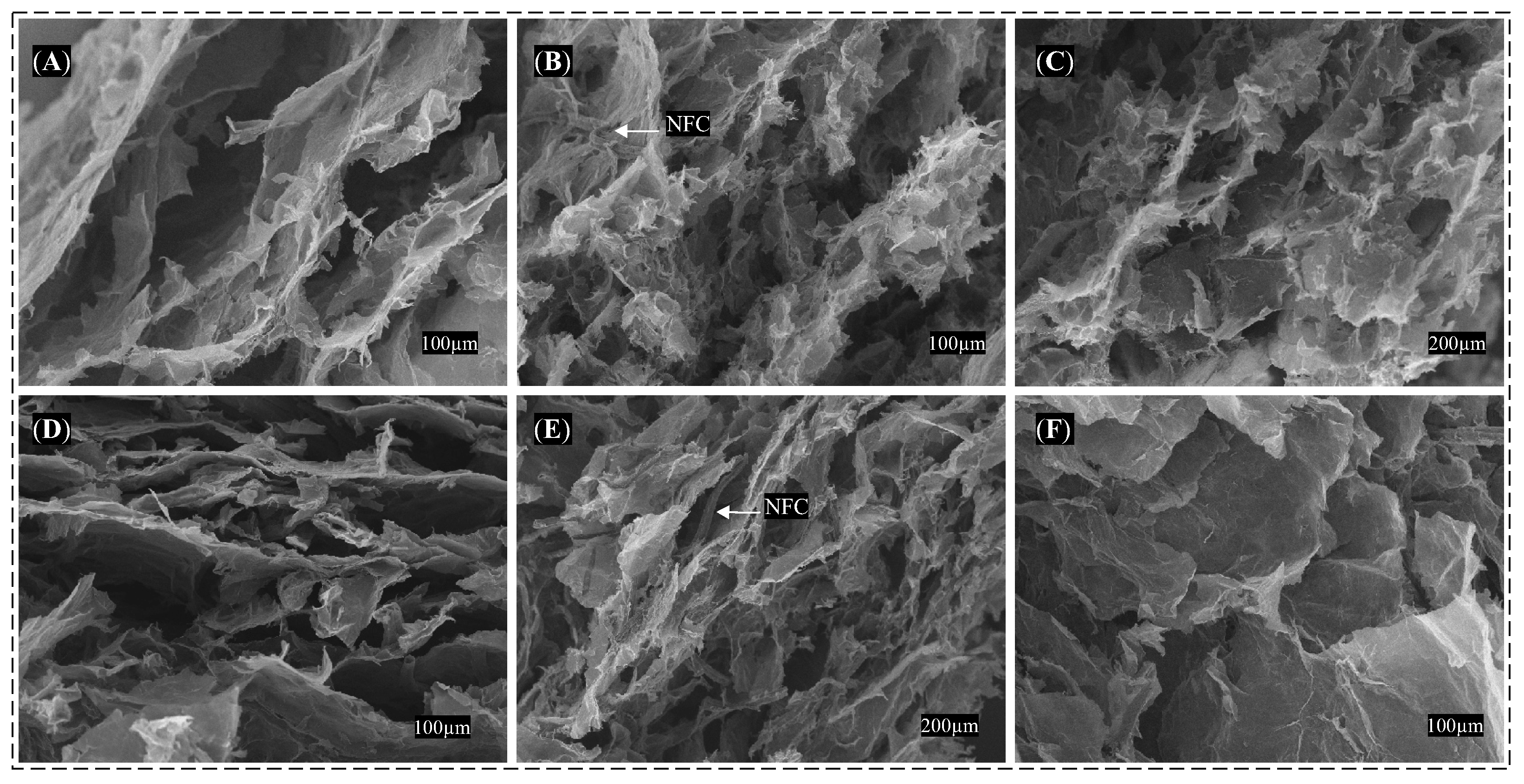
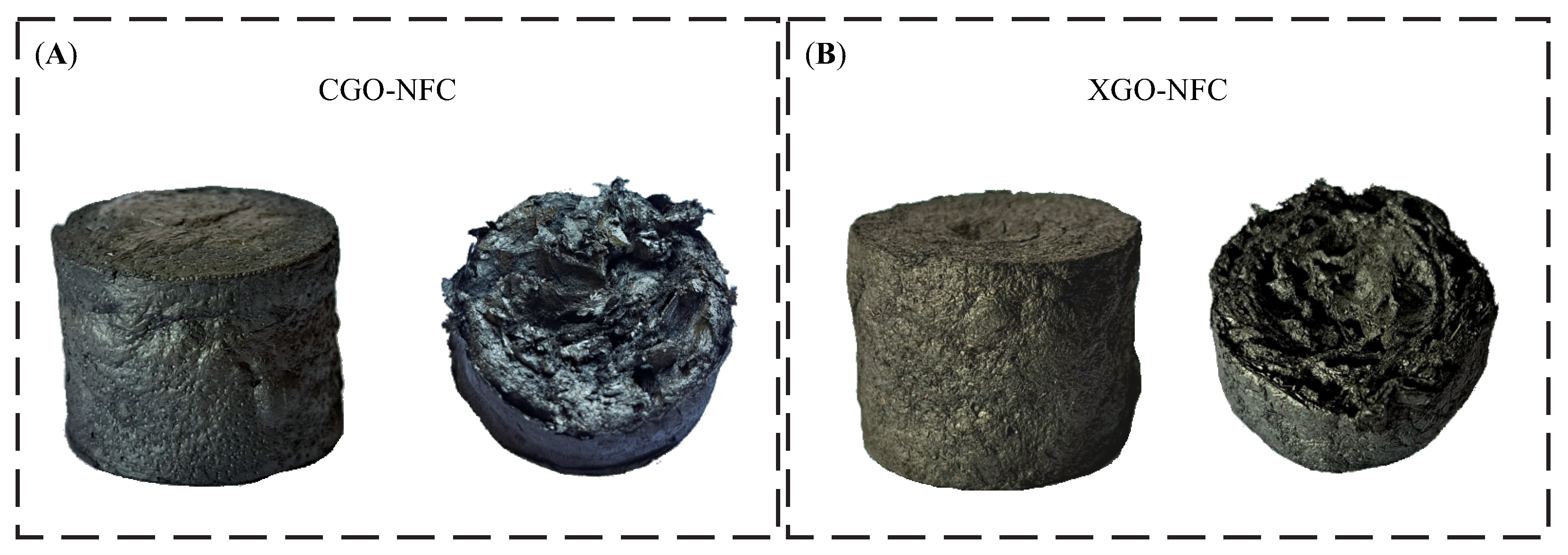
3.2. Morphological Characterization
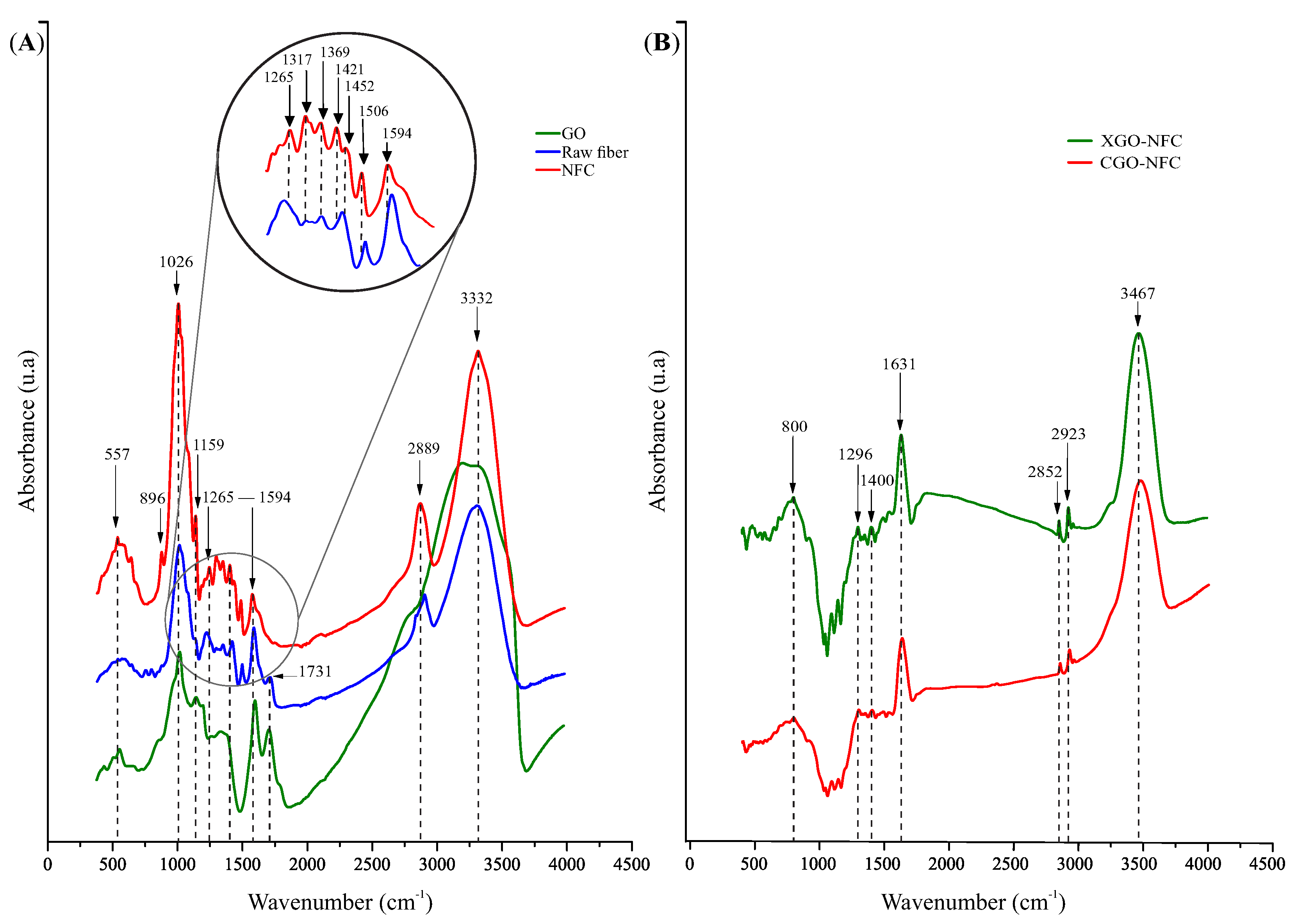
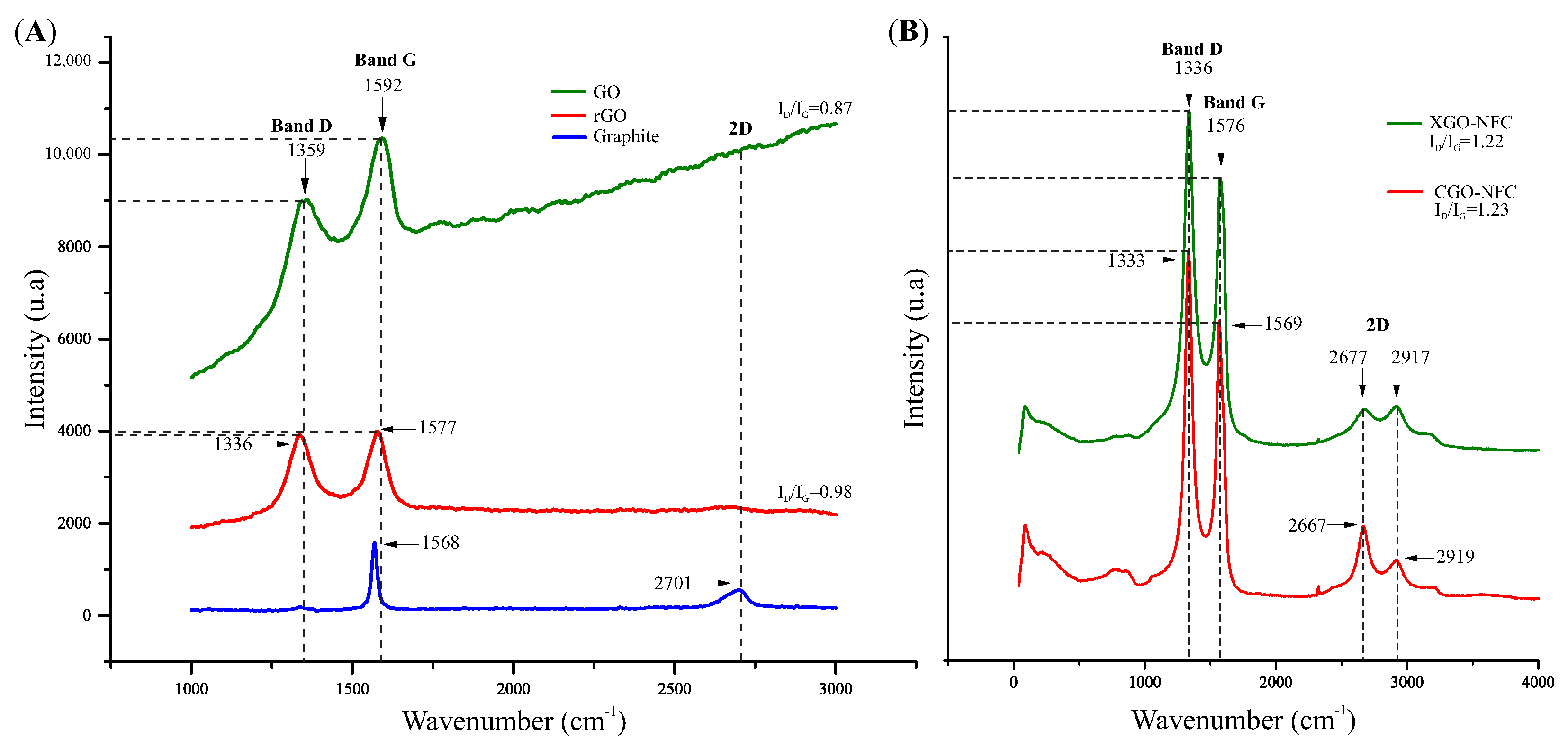
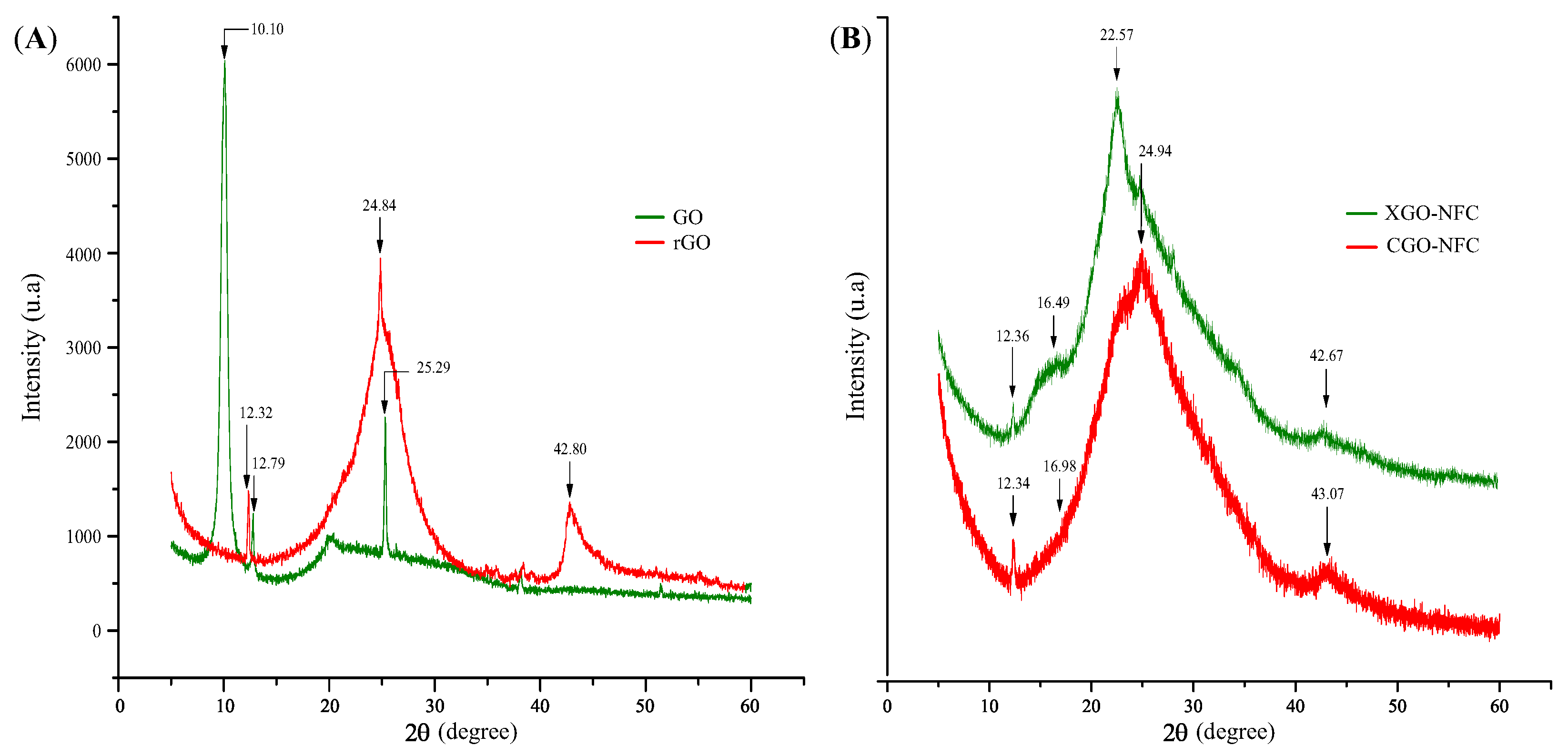
3.3. Structural Characterization
3.4. Thermal Characterization
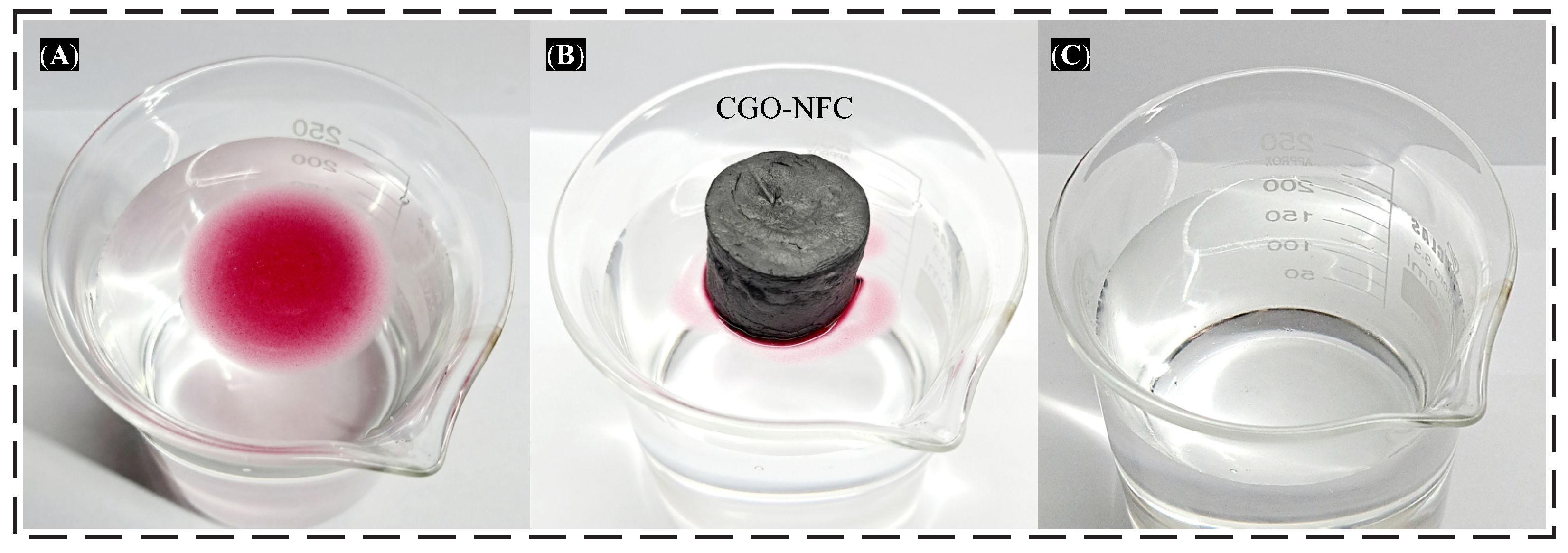
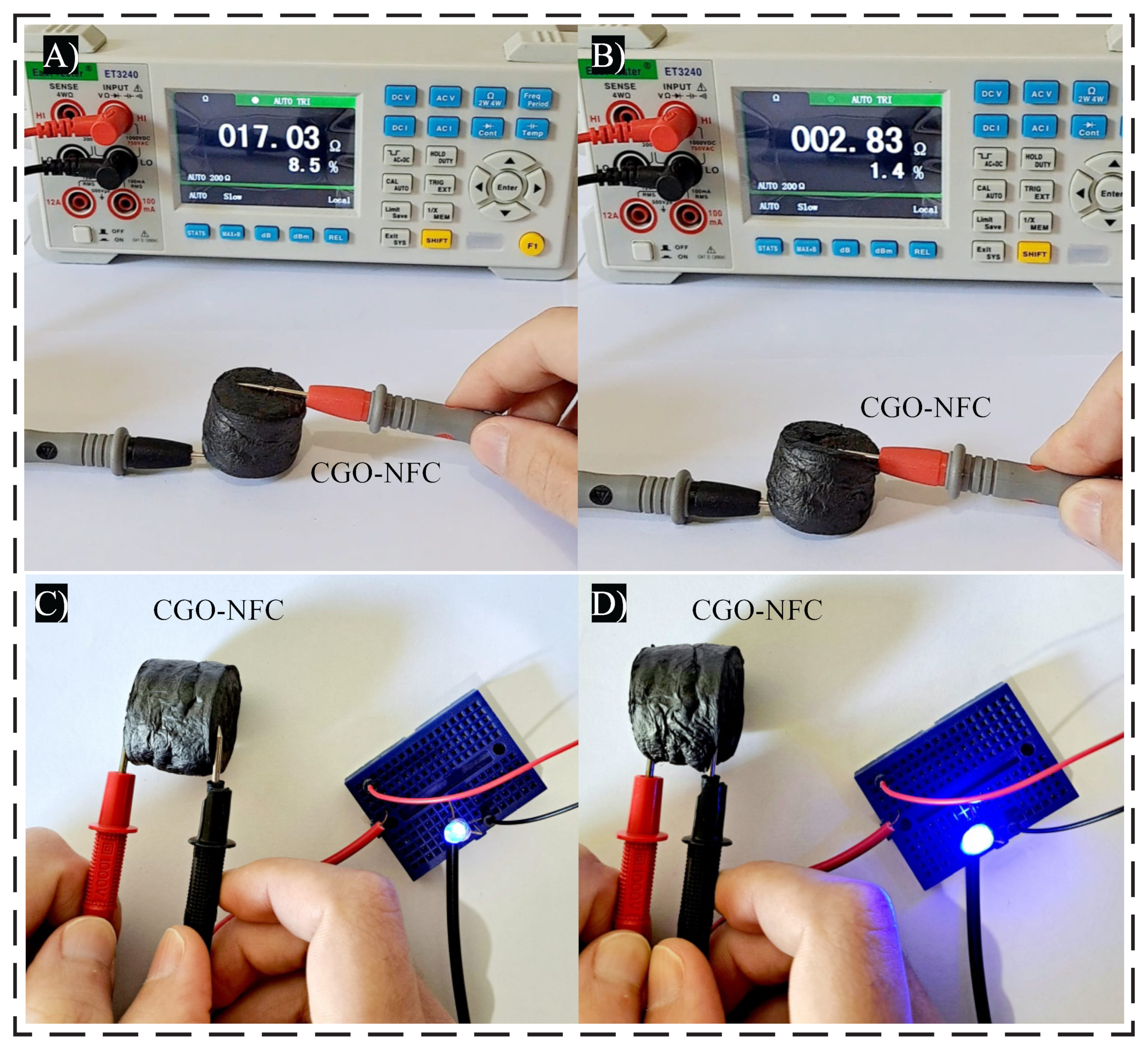
3.5. Challenges and Important Issues
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Fu, J.; He, J.; Wang, B.; He, Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Y. Synthesis of a superhydrophilic coral-like reduced graphene oxide aerogel and its application to pollutant capture in wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 260, 117860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, S.S. Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies. Nature 1931, 127, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamy-Mendes, A.; Silva, R.F.; Durães, L. Advances in carbon nanostructure–silica aerogel composites: A review. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 1340–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel-Castro, T.A.; Ibarra-Alonso, M.; Oliva, J.; Martínez-Luévanos, A. Porous aerogel and core/shell nanoparticles for controlled drug delivery: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 915–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios, E.; Fox, D.; Li Sip, Y.Y.; Catarata, R.; Calderon, J.E.; Azim, N.; Afrin, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhai, L. Nanomaterials in advanced, high-performance aerogel composites: A review. Polymers 2019, 11, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.M.; Al-Enzi, F.; Gabriel, V.A.; Tezel, F.H. Effect of pore size and heterogeneous surface on the adsorption of CO2, N2, O2, and Ar on carbon aerogel, RF aerogel, and activated carbons. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 322, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Sajid, M.; Khan, S.; Bilal, M. Aerogel-based adsorbents as emerging materials for the removal of heavy metals from water: Progress, challenges, and prospects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 291, 120923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Shi, T.; Liu, H.; Wu, D.; Wang, X. Polyimide/phosphorene hybrid aerogel-based composite phase change materials for high-efficient solar energy capture and photothermal conversion. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 207, 118173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Yang, S.; Tao, E.; Liu, L.; Ma, D.; Li, Y. Graphene oxide/montmorillonite composite aerogel with slit-shaped pores: Selective removal of Cu2+ from wastewater. J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 923, 166335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Singh, A.K.; Patel, J.; Sreevidya, S.; Carabineiro, S.A. Facile preparation of methionine-functionalized graphene oxide/chitosan polymer nanocomposite aerogel for the efficient removal of dyes and metal ions from aqueous solutions. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummers, W.S., Jr.; Offeman, R.E. Preparation of graphitic oxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Liang, H.; Tian, W.; Li, C.; Gao, Q.; Wang, N.; Guo, R.; Mo, Z. An antibacterial and antifouling amidoxime-functionalized graphene oxide aerogel for selective uranium adsorption in Salt Lake water. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 649, 129367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Li, D.; Tan, S.; Huang, L. Preparation and oil–water separation of 3D kapok fiber-reduced graphene oxide aerogel. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Yue, Q.; Xu, X.; Kong, W.; Gao, B.; Cai, Z.; Chen, Y. A tunable amphiphilic Enteromorpha-modified graphene aerogel for oil/water separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 142958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diyana, Z.; Jumaidin, R.; Selamat, M.Z.; Ghazali, I.; Julmohammad, N.; Huda, N.; Ilyas, R. Physical properties of thermoplastic starch derived from natural resources and its blends: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Du, H.; Zheng, T.; Liu, K.; Ji, X.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Si, C. Cellulose based composite foams and aerogels for advanced energy storage devices. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 130817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Yu, H. Cellulose-based flexible functional materials for emerging intelligent electronics. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2000619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervin, N.T.; Andersson, L.; Ng, J.B.S.; Olin, P.; Bergström, L.; Wågberg, L. Lightweight and strong cellulose materials made from aqueous foams stabilized by nanofibrillated cellulose. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüneberger, F.; Künniger, T.; Huch, A.; Zimmermann, T.; Arnold, M. Nanofibrillated cellulose in wood coatings: Dispersion and stabilization of ZnO as UV absorber. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 87, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; Si, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, B. Cellulose nanocrystals and cellulose nanofibrils based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 209, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xu, Z. Ultralight, highly compressible, hydrophobic and anisotropic lamellar carbon aerogels from graphene/polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanofiber aerogel as oil removing absorbents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 121804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Adak, B.; Faruk, M.O.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Nanocellulose coupled 2D graphene nanostructures: Emerging paradigm for sustainable functional applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 10882–10916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimic-Misic, K.; Phiri, J.; Nieminen, K.; Maloney, T.; Gane, P. Characterising exfoliated few-layer graphene interactions in co-processed nanofibrillated cellulose suspension via water retention and dispersion rheology. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 242, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.Q.; Xin, X.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Z.R.; Xu, Y.J. Photoredox catalysis over graphene aerogel-supported composites. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4590–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Lu, C.H.; Yang, H.H. Magnetic nanomaterials for magnetic bioanalysis. In Novel Nanomaterials for Biomedical, Environmental and Energy Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 89–109. [Google Scholar]
- Haleem, A.; Pan, J.M.; Shah, A.; Hussain, H.; He, W.D. A systematic review on new advancement and assessment of emerging polymeric cryogels for environmental sustainability and energy production. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 316, 123678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Su, G.; Li, Q.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhuo, B.; Li, X.; Ti, P.; Yuan, Q. Performance of the highly sensitive humidity sensor constructed with nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene oxide/polydimethylsiloxane aerogel via freeze drying. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, P.M.; Prakash, J.; Alexander, R.; Kaushal, A.; Patwardhan, A.W.; Joshi, J.B.; Dasgupta, K. Ultra-fast detection and monitoring of cancerous volatile organic compounds in environment using graphene oxide modified CNT aerogel hybrid gas sensor. Talanta Open 2022, 6, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Wang, Y.; Xie, P.; Zhang, C.; Li, M.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Wei, C.; Yu, C.; Chen, Y. A resilient and lightweight cellulose/graphene oxide/polymer-derived multifunctional carbon aerogel generated from Pickering emulsion toward a wearable pressure sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Xu, T.; Liang, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, D.; Si, C. Compressible cellulose nanofibrils/reduced graphene oxide composite carbon aerogel for solid-state supercapacitor. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Jia, S.; Wei, J.; Shao, Z. Construction of hierarchical porous derived from the cellulose nanofiber/graphene/Zn/Co ZIF 3D conductive carbon aerogels for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Alloy Compd. 2022, 920, 165868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.Y.; Lee, B.M.; Jeong, Y.G. Microstructures and electrochemical characterization of graphene oxide/carboxymethylated cellulose nanofibril-derived hybrid carbon aerogels for freestanding supercapacitor electrodes. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2023, 18, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, T.; Guo, L.; Han, W. Covalent Crosslinking Cellulose/Graphene Aerogels with High Elasticity and Adsorbability for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption. Polymers 2023, 15, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoviatdoost, A.; Naderi, M.; Ghazitabar, A.; Gholami, F. Fabrication of high-performance ultralight and reusable graphene aerogel/cellulose fibers nanocomposite to remove organic pollutants. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, H.; Xu, S.; Dong, P.; Long, A.; Xiao, L.; Feng, S.; Chen, C.P. Cellulose nanocrystal regulated ultra-loose, lightweight, and hierarchical porous reduced graphene oxide hybrid aerogel for capturing and determining organic pollutants from water. Carbon 2023, 204, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, B.; Yuan, B. Flame-retardant cellulose nanofiber aerogel modified with graphene oxide and sodium montmorillonite and its fire-alarm application. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 1877–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Ren, P.; Dai, Z.; Zong, Z.; Zhang, F.; Jin, Y.; Ren, F. Construction of interconnected and oriented graphene nanosheets networks in cellulose aerogel film for high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding. Cellulose 2021, 28, 3135–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfanian, E.; Moaref, R.; Ajdary, R.; Tam, K.C.; Rojas, O.J.; Kamkar, M.; Sundararaj, U. Electrochemically synthesized graphene/TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils hydrogels: Highly conductive green inks for 3D printing of robust structured EMI shielding aerogels. Carbon 2023, 210, 118037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zeng, L.; Chang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Yan, K.; Xie, L.; Xue, B.; Zheng, Q. Composite phase change materials embedded into cellulose/polyacrylamide/graphene nanosheets/silver nanowire hybrid aerogels simultaneously with effective thermal management and anisotropic electromagnetic interference shielding. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhou, M.; Deng, S.; Du, Z.; Cheng, X.; Wang, H. Poly (ethylene glycol)-grafted nanofibrillated cellulose/graphene hybrid aerogels supported phase change composites with superior energy storage capacity and solar-thermal conversion efficiency. Cellulose 2020, 27, 4679–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhao, S.; Deng, W.; Min, P.; Lu, X.H.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.Z. Highly thermally conductive phase change composites with anisotropic graphene/cellulose nanofiber hybrid aerogels for efficient temperature regulation and solar-thermal-electric energy conversion applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2023, 248, 110367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, M.A.; Rafiee, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, H.; Yu, Z.Z.; Koratkar, N. Enhanced mechanical properties of nanocomposites at low graphene content. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3884–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Rentsch, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, J. Biomimetic, Highly reusable and hydrophobic graphene/polyvinyl alcohol/cellulose nanofiber aerogels as oil-removing absorbents. Polymers 2022, 14, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragg, W.H.; Bragg, W.L. The reflection of X-rays by crystals. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1913, 88, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A., Jr.; Conrad, C. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1959, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aegerter, M.A.; Leventis, N.; Koebel, M.M. Advances in sol-gel derived materials and technologies. In Aerogels Handbook; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, M.; Medeiros, E.; Malmonge, J.; Gregorski, K.; Wood, D.; Mattoso, L.; Glenn, G.; Orts, W.; Imam, S. Cellulose nanowhiskers from coconut husk fibers: Effect of preparation conditions on their thermal and morphological behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 81, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahma, F.; Iwamoto, S.; Hori, N.; Iwata, T.; Takemura, A. Effect of pre-acid-hydrolysis treatment on morphology and properties of cellulose nanowhiskers from coconut husk. Cellulose 2011, 18, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; Xing, C.; Shi, X.; Matuana, L.M.; Zhou, H.; Ma, X. Fabrication and characteristics of cellulose nanofibril films from coconut palm petiole prepared by different mechanical processing. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 65, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, D.M.; Almeida, J.S.; Vale, M.d.S.; Leitão, R.C.; Muniz, C.R.; de Figueirêdo, M.C.B.; Morais, J.P.S.; Rosa, M.d.F. A comprehensive approach for obtaining cellulose nanocrystal from coconut fiber. Part I: Proposition of technological pathways. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 93, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, X.; Xiang, X.; Chen, S. Preparation of carboxymethyl cellulose/graphene composite aerogel beads and their adsorption for methylene blue. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 202, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanpour, M. Microcrystalline cellulose/graphene oxide aerogel for adsorption of cationic dye from aqueous solution. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuinstra, F.; Koenig, J.L. Raman spectrum of graphite. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 53, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahriary, L.; Athawale, A.A. Graphene oxide synthesized by using modified hummers approach. Int. J. Renew. Energy Environ. Eng. 2014, 2, 58–63. [Google Scholar]
- Stobinski, L.; Lesiak, B.; Malolepszy, A.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Mierzwa, B.; Zemek, J.; Jiricek, P.; Bieloshapka, I. Graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide studied by the XRD, TEM and electron spectroscopy methods. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2014, 195, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, P.; He, L.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Y.; Liu, Z. Ultralight, mechanically enhanced, and thermally improved graphene-cellulose-polyethyleneimine aerogels for the adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Determination of Ideal Compounds | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nanomaterial | GO (mg/mL) | GO:AA | GO:NFC | pH | Reduction Steps | Temperature | Time | Drying |
| CGO-NFC | 5 | 1:3 | 1:0.25 | acid | 2 steps | 1° step: 100 °C 2° step: 100 °C | 1° step: 3 h 2° step: 6 h | lyophilization |
| XGO-NFC | 5 | 1:3 | 1:0.25 | acid | 3 steps | 1° step: 150 °C 2° step: 100 °C 3° step: 80 °C | 1° step: 12 h 2° step: 8 h 3° step: 6 h | evaporation |
| Nanomaterial | Density g/cm | Shrinkage (%) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGO-NFC | 0.0154 | 2.86 | 98.62 |
| XGO-NFC | 0.0249 | 6.54 | 98.19 |
| Wavenumber (cm−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO | NFC | Raw Fiber | CGO-NFC | XGO-NFC | Functional Group | Assignment |
| 578 | - | - | - | - | C-H | Methyl group bending vibration. |
| - | - | - | 796 | 800 | C-H | Deformation of the C-H bonds present in aromatic rings. |
| 875 | 896 | - | - | - | C-H | Aromatic deformation in GO and glycosidic ring vibration in amorphous domains of NFC. |
| 1039 | 1026 | 1035 | - | - | C-O | Primary alcohol stretching vibrations in GO and stretching vibrations of cellulose, lignin, and hemicellulose. |
| 1164 | 1159 | 1155 | - | - | C-O | Stretching vibrations of C-OH in GO and asymmetric stretching of ether in NFC and raw fiber. |
| 1218 | 1265 | 1243 | 1298 | 1296 | C-O | Stretching vibrations of carboxylic acid in GO and nanomaterials, and stretching of ester, ether, and phenol groups in NFC and raw fiber. |
| - | 1317 | 1315 | - | - | O-H | Hydroxyl group in planar bending in NFC and raw fiber. |
| - | 1369 | 1369 | - | - | C-H | Deformation vibration in NFC and raw fiber. |
| - | - | - | 1402 | 1400 | C-H3 | Asymmetric deformation vibration. |
| - | 1421–1452 | 1438 | - | - | C-H | Methyl group deformation in NFC and raw fiber. |
| - | 1506 | 1517 | - | - | C=C | Stretching of the skeletal vibration of the aromatic ring in NFC and raw fiber. |
| 1620 | 1594 | 1608 | 1631 | 1631 | C=C | Stretching vibrations of the sp² carbon skeletal network in GO and stretching of the skeletal vibration of the aromatic ring in NFC, raw fiber, and nanomaterials. |
| 1726 | - | 1731 | - | - | C=O | Stretching vibrations of the C=O group in the carboxyl group in GO and raw fiber. |
| - | 2889 | 2921 | 2852–2921 | 2852–2923 | C-H | Stretching vibrations of the methyl group in NFC, raw fiber, and nanomaterials. |
| 3213–3319 | 3332 | 3322 | 3467 | 3467 | O-H | Stretching vibrations of the hydroxyl group in GO, NFC, raw fiber, and nanomaterials. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moggio, B.C.; Bergamasco, R.; Andrade, C.M.G.; Aylon, L.B.R. On the Analysis of Cryogels and Xerogels Using Cellulose Nanofibers and Graphene Oxide. Polymers 2023, 15, 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183833
Moggio BC, Bergamasco R, Andrade CMG, Aylon LBR. On the Analysis of Cryogels and Xerogels Using Cellulose Nanofibers and Graphene Oxide. Polymers. 2023; 15(18):3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183833
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoggio, Bianca Cristina, Rosangela Bergamasco, Cid Marcos Gonçalves Andrade, and Linnyer Beatrys Ruiz Aylon. 2023. "On the Analysis of Cryogels and Xerogels Using Cellulose Nanofibers and Graphene Oxide" Polymers 15, no. 18: 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183833
APA StyleMoggio, B. C., Bergamasco, R., Andrade, C. M. G., & Aylon, L. B. R. (2023). On the Analysis of Cryogels and Xerogels Using Cellulose Nanofibers and Graphene Oxide. Polymers, 15(18), 3833. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15183833