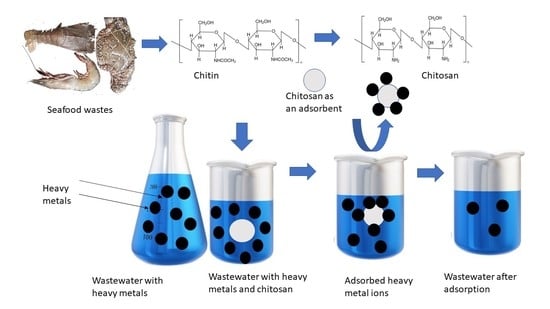
Recent Application Prospects of Chitosan Based Composites for the Metal Contaminated Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Chitin Sources and Composition
3. Production of Chitosan from Chitin
3.1. Production of Chitin
3.1.1. Preparation of Raw Materials
3.1.2. Deproteinization
3.1.3. Demineralization
3.1.4. Discoloration
3.2. Production of Chitosan from Chitin (Deacetylation)
4. Characteristics of Chitosan
4.1. Molecular Weight
4.2. Degree of Deacetylation
4.3. Solubility
5. Neutralization and Chemical and Physical Modification of Chitosan
6. Waste Treatment and Purification of Water
6.1. Chitosan Based Composites to Eliminate Heavy Metal Ions
6.2. Chitosan Based Nanocomposites to Eliminate Heavy Metal Ions
6.3. Mechanism
6.4. Isothermal and Kinetic Model
6.5. Reusability or Regeneration
| Adsorbent | Adsorbate | Kinetics | Isotherm | pH | Temperature (°C) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS/Fe3O4 NPs | Cr(VI) | PSO | L | 3.37 | 298 K | 162 | [55] |
| Zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 (ZIF-67)/modified bacterial cellulose/CS aerogel | Cu(II) | PSO | - | 6 | 25 | 200.6 | [61] |
| Cr(VI) | 152.1 | ||||||
| Magnetic graphene oxide/CS (Fe3O4/GO/CS) | Ni(II) | PFO | L | 6 | 25 | 80.48 | [75] |
| Magnetic thiolated/quaternized-CS | Pb(II) | PSO | S | 7 | 30 | 235.63 | [77] |
| As(III) | 67.69 | ||||||
| As(V) | 66.27 | ||||||
| Hg(II) | 28.00 | ||||||
| Cu(II) | 33.99 | ||||||
| Fe3O4/CS NPs | Pb(II) | - | L | 6 | - | 79.24 | [90] |
| Cd(II) | 36.42 | ||||||
| N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles (NOCC-MNPs)/chitosan-citrate gel beads (CCGBs) | Cu(II) | PSO | F | 294.11 | [91] | ||
| SiO2@CS | As(V) | PSO | F | 6–7 | 298 K | 198.6 | [93] |
| Hg(II) | L | 204.1 | |||||
| TiO2/CS | Cu(II) | PFO | L | 6 | 45 | 526.5–715.7 | [94] |
| Pb(II) | 475.5–579.1 | ||||||
| CS/vanillin CS/ortho-vanillin | Co(II) | PSO | L | 4 | 30 | 5.899–7.651 | [97] |
| Fe3O4/CS/polyethylenimine (PEI) | As(III) | PSO | L | 6.7 | 30 | 77.61 | [101] |
| As(V) | 86.50 | ||||||
| Polymer composite (CS-EDTA) | Pb(II) | PSO | L | 370.37 | [103] | ||
| Cd(II) | 243.90 | ||||||
| Cu(II) | 227.27 | ||||||
| Dimercaptosuccinic acid-functionalized magnetic CS (Fe3O4@CS@DMSA) | Cd(II) | PFO | L | 7.6 | 314.12 | [104] | |
| Crosslinked CS grafted with methyl methacrylate (M-CS) | Cu(II) | PSO | L | 4 | RT | 192.31 | [105] |
| Magnetically modified CS/3,3-diphenylpropylimine methyl benzaldehyde (PPIMB) | Pb(II) | PSO | L | 230.48 | [106] | ||
| Magnetic xanthate-modified CS/polyacrylic acid | Cu(II) | PSO | L | 5.5 | 30 | 206 | [107] |
| Cd(II) | - | 178 | |||||
| Pb(II) | - | 168 | |||||
| Co(II) | - | 140 | |||||
| Glucan/CS | Cu(II) | PSO | L | 7 | 25 | 342 | [108] |
| Co(II) | 232 | ||||||
| Ni(II) | 184 | ||||||
| Pb(II) | 395 | ||||||
| Cd(II) | 269 | ||||||
| CS/calcium alginate/bentonite | Pb(II) | PSO | R | 5 | 434.89 | [109] | |
| Cu(II) | 115.30 | ||||||
| Cd(II) | 102.38 | ||||||
| CS microspheres/sodium alginate hybrid beads | Pb(II) | PFO | L | 180 | [110] | ||
| Cr(VI) | PSO | L | 16 | ||||
| CS modified with carboxyl groups | Cu(II) | L | 3.5 | 25 | 220.5 | [111] | |
| Zn(II) | 124.3 | ||||||
| AgNPs/GO/CS nanocomposite | Mn(II) | PSO | F | 6 | 30 | 1605 | [112] |
| Microfluidically-generated CS microspheres | Cu(II) | PSO | L | 5.5 | 35 | 75.52 | [113] |
| CS grafted UiO-66-NH2 | Cu(II) | - | - | - | - | 364.96 | [114] |
| Pb(II) | 555.56 | ||||||
| CS-g-acrylamide-orange peel | Cr(VI) | PSO | F | 4 | 28 | 178.34 | [115] |
| Cu(II) | 5 | 28 | 181.88 |
7. Conclusions and Future Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, X.; Zhao, S.; Tian, Z.; Duan, G.; Pan, H.; Yue, Y.; Li, S.; Jian, S.; Yang, W.; Liu, K.; et al. MOFs meet wood: Reusable magnetic hydrophilic composites toward efficient water treatment with super-high dye adsorption capacity at high dye concentration. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 136851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arami, M.; Bahrami, H.; Khorramfar, S. Novel biosorbent (Canola hull): Surface characterization and dye removal ability at different cationic dye concentrations. Desalination 2010, 264, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arami, M. Modeling and sensitivity analysis of dyes adsorption onto natural adsorbent from colored textile wastewater. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 4043–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, L.; Noblet, J. Chapter 3.6—Water Contamination and Pollution. In Green Chemistry; Török, B., Dransfield, T., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 261–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Drinking water contamination and treatment techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 1043–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, M.; Duan, G.; Gong, X. One-step fabrication of eco-friendly superhydrophobic fabrics for high-efficiency oil/water separation and oil spill cleanup. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1296–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Li, Z.; Watanabe, M. Production of solid fuels by hydrothermal treatment of wastes of biomass, plastic, and biomass/plastic mixtures: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Parihar, R.D.; Sharma, A.; Bakshi, P.; Singh Sidhu, G.P.; Bali, A.S.; Karaouzas, I.; Bhardwaj, R.; Thukral, A.K.; Gyasi-Agyei, Y.; et al. Global evaluation of heavy metal content in surface water bodies: A meta-analysis using heavy metal pollution indices and multivariate statistical analyses. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, S.; Roy, A.; Sundaram, S.; Kumar Mallick, T. A Review on Heavy Metal Ions and Containing Dyes Removal Through Graphene Oxide-Based Adsorption Strategies for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 1570–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ngah, W.S.; Hanafiah, M.A.K.M. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater by chemically modified plant wastes as adsorbents: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3935–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, R.; Wen, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Yan, B.; Peng, S.; Ma, C.; Cao, X.; Ma, C.; et al. Antibiofouling Ultrathin Poly(amidoxime) Membrane for Enhanced U(VI) Recovery from Wastewater and Seawater. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21272–21285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, S.; Yuhana, N.Y.; Md Saleh, N.; Kamarudin, N.H.N.; Sulong, A.B. Review of chitosan composite as a heavy metal adsorbent: Material preparation and properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 259, 117613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malayoglu, U. Removal of heavy metals by biopolymer (chitosan)/nanoclay composites. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2741–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooja, G.; Kumar, P.S.; Indraganti, S. Recent advancements in the removal/recovery of toxic metals from aquatic system using flotation techniques. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yan, B.; Qian, Y.; Wen, J.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, N. Bio-inspired antibacterial cellulose paper–poly(amidoxime) composite hydrogel for highly efficient uranium(VI) capture from seawater. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 3935–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, O.; Goodarzi, V.; Saeb, M.R.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Borja, R. Competitive removal of heavy metal ions from squid oil under isothermal condition by CR11 chelate ion exchanger. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 334, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Duan, G.; Xu, W.; Jian, S. Magnetically separable and recyclable Fe3O4@PDA covalent grafted by l-cysteine core-shell nanoparticles toward efficient removal of Pb2+. Vacuum 2021, 189, 110229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar-Mohammadi, M.; Arami, M.; Bahrami, H.; Mazaheri, F.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Grafting of chitosan as a biopolymer onto wool fabric using anhydride bridge and its antibacterial property. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 76, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and Application of Granular Activated Carbon from Biomass Waste Materials for Water Treatment: A Review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanniri, E.; Yousefi, M.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Khorshidian, N.; Sohrabvandi, S.; Arab, M.; Koushki, M.R. Effective removal of lead (II) using chitosan and microbial adsorbents: Response surface methodology (RSM). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 178, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Abdi, J.; Hayati, B.; Shekarchi, A.A. Bio-based magnetic metal-organic framework nanocomposite: Ultrasound-assisted synthesis and pollutant (heavy metal and dye) removal from aqueous media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 480, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudha, P.N.; Gomathi, T.; Vinodhini, P.A.; Nasreen, K. Chapter Seven—Marine Carbohydrates of Wastewater Treatment. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 73, pp. 103–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, Z.; Hartland, A.; Mucalo, M.R. Use of low-cost biopolymers and biopolymeric composite systems for heavy metal removal from water. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 4389–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.; Safaei Ghomi, J.; Shahbazi-Alavi, H. Preparation of chitosan nanoparticles from shrimp shells and investigation of its catalytic effect in diastereoselective synthesis of dihydropyrroles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, S.P.; Kanatt, S.R.; Sharma, A.K. Chitosan. In Polysaccharides: Bioactivity and Biotechnology; Ramawat, K.G., Mérillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 219–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huang, W.-C.; Guo, N.; Zhang, S.; Xue, C.; Mao, X. Two-Step Separation of Chitin from Shrimp Shells Using Citric Acid and Deep Eutectic Solvents with the Assistance of Microwave. Polymers 2019, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaens, L.; Soetemans, L.; D’Hondt, E.; Elst, K. Sources of Chitin and Chitosan and their Isolation. In Chitin and Chitosan; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Aydemir, B.E.; Dumanli, A.G. Understanding the structural diversity of chitins as a versatile biomaterial. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2021, 379, 20200331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolaimate, A.; Desbrières, J.; Rhazi, M.; Alagui, A.; Vincendon, M.; Vottero, P. On the influence of deacetylation process on the physicochemical characteristics of chitosan from squid chitin. Polymer 2000, 41, 2463–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Goswami, P.; Paritosh, K.; Kumar, M.; Pareek, N.; Vivekanand, V. Seafood waste: A source for preparation of commercially employable chitin/chitosan materials. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birolli, W.G.; Delezuk, J.A.D.M.; Campana-Filho, S.P. Ultrasound-assisted conversion of alpha-chitin into chitosan. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 103, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Han, X.; Fan, Z.; Su, G.; Pan, D.; Li, Z. Research progress of adsorption and removal of heavy metals by chitosan and its derivatives: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 279, 130927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benettayeb, A.; Ghosh, S.; Usman, M.; Seihoub, F.Z.; Sohoo, I.; Chia, C.H.; Sillanpää, M. Some Well-Known Alginate and Chitosan Modifications Used in Adsorption: A Review. Water 2022, 14, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaweil, A.S.; Omer, A.M.; El-Aqapa, H.G.; Gaber, N.M.; Attia, N.F.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Mohy-Eldin, M.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M. Chitosan based adsorbents for the removal of phosphate and nitrate: A critical review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davarpanah, S.; Mahmoodi, N.M.; Arami, M.; Bahrami, H.; Mazaheri, F. Environmentally friendly surface modification of silk fiber: Chitosan grafting and dyeing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 4171–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Dey, R.; Eltaweil, A.S.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Ziora, Z.M. Insights into recent advances of chitosan-based adsorbents for sustainable removal of heavy metals and anions. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 103543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, R.; Gurunathan, B.; Sivakumar, K.; Varjani, S.; Ngo, H.H.; Gnansounou, E. Advancements in heavy metals removal from effluents employing nano-adsorbents: Way towards cleaner production. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißpflog, J.; Gündel, A.; Vehlow, D.; Steinbach, C.; Müller, M.; Boldt, R.; Schwarz, S.; Schwarz, D. Solubility and Selectivity Effects of the Anion on the Adsorption of Different Heavy Metal Ions onto Chitosan. Molecules 2020, 25, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung, T.S.; Tram, L.H.; Van Tan, N.; Van Hoa, N.; Minh, N.C.; Loc, P.T.; Stevens, W.F. Improved method for production of chitin and chitosan from shrimp shells. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 489, 107913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellis, A.; Guebitz, G.M.; Nyanhongo, G.S. Chitosan: Sources, Processing and Modification Techniques. Gels 2022, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokatlı, K.; Demirdöven, A. Optimization of chitin and chitosan production from shrimp wastes and characterization. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huq, T.; Khan, A.; Brown, D.; Dhayagude, N.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Sources, production and commercial applications of fungal chitosan: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Dhillon, G.; Kaur, S.; Jyoti Sarma, S.; Kaur Brar, S.; Verma, M.; Yadagiri Surampalli, R. Recent Development in Applications of Important Biopolymer Chitosan in Biomedicine, Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products. Curr. Tissue Eng. 2013, 2, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, N. Transformation of Seafood Wastes into Chemicals and Materials. In Green Chemistry and Chemical Engineering; Han, B., Wu, T., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Knidri, H.; Belaabed, R.; Addaou, A.; Laajeb, A.; Lahsini, A. Extraction, Chemical Modification and Characterization of Chitin and Chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Knidri, H.; Dahmani, J.; Addaou, A.; Laajeb, A.; Lahsini, A. Rapid and efficient extraction of chitin and chitosan for scale-up production: Effect of process parameters on deacetylation degree and molecular weight. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, A.M.; Phillips, G.O. Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- No, H.K.; Meyers, S.P. Preparation and characterization of chitin and chitosan—A review. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 1995, 4, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.H.; Williams, P.A.; Tverezovskaya, O. Extraction of chitin from prawn shells and conversion to low molecular mass chitosan. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F. Seafood processing by-products. In Seafoods: Chemistry, Processing Technology and Quality; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, I.; Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan preparation from marine sources. Structure, properties and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1133–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, B.K.; Haard, N.F. The use of proteolytic enzymes to extract carotenoproteins from shrimp wastes. J. Appl. Biochem. 1985, 7, 212–222. [Google Scholar]
- Özel, N.; Elibol, M. A review on the potential uses of deep eutectic solvents in chitin and chitosan related processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 262, 117942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeul, V.S.; Rayalu, S.S. Unprecedented Chitin and Chitosan: A Chemical Overview. J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Sahebi, H.; Zandavar, H.; Mirsadeghi, S. Fabrication of Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated by extracted shrimp peels chitosan as sustainable adsorbents for removal of chromium contaminates from wastewater: The design of experiment. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 175, 107130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Haque, M.A.; Ghosh, S.; Shinu, P.; Attimarad, M.; Kobayashi, G. Modified Shrimp-Based Chitosan as an Emerging Adsorbent Removing Heavy Metals (Chromium, Nickel, Arsenic, and Cobalt) from Polluted Water. Sustainability 2023, 15, 2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, B.T.; Torsabo, D.; Chik, C.E.N.C.E.; Wahab, F.; Sheikh Abdullah, S.R.; Abu Hassan, H.; Kasan, N.A. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) Approach to Optimization of Coagulation-Flocculation of Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment Using Chitosan from Carapace of Giant Freshwater Prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Polymers 2023, 15, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.I.H.; Ahmed, F. Cellulosic fibres modified by chitosan and synthesized ecofriendly carboxymethyl chitosan from prawn shell waste. J. Text. Inst. 2020, 111, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbon, N.M.; Sandanamsamy, S.; Kamaruzaman, S.F.S.; Ahmad, F. Chitosan extracted from mud crab (Scylla olivicea) shells: Physicochemical and antioxidant properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4266–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Saiz, P.; Lagaron, J.M. Chitosan for Film and Coating Applications. In Biopolymers—New Materials for Sustainable Films and Coatings; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Z.; Li, X.; Qiao, H.; Ke, H.; Luo, L.; Wei, Q. Multifunctional adsorbent based on metal-organic framework modified bacterial cellulose/chitosan composite aerogel for high efficient removal of heavy metal ion and organic pollutant. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 383, 123127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.S.; Liau, W.Y.; Tsai, G.J. Antibacterial effects of N-sulfonated and N-sulfobenzoyl chitosan and application to oyster preservation. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, T.; Tafi, E.; Paul, A.; Salvia, R.; Falabella, P.; Zibek, S. Current state of chitin purification and chitosan production from insects. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2020, 95, 2775–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, D.; Gzyra-Jagieła, K.; Draczyński, Z. The Kinetics of Chitosan Degradation in Organic Acid Solutions. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakizeh, M.; Moradi, A.; Ghassemi, T. Chemical extraction and modification of chitin and chitosan from shrimp shells. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 159, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterowd, J.G.; Sandford, P.A. Food Polysaccharides and Their Applications; Stephen, A.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Tharanathan, R.N.; Kittur, F.S. Chitin—The Undisputed Biomolecule of Great Potential. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2003, 43, 61–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.H. 7—High-performance superplasticizer based on chitosan. In Biopolymers and Biotech Admixtures for Eco-Efficient Construction Materials; Pacheco-Torgal, F., Ivanov, V., Karak, N., Jonkers, H., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2016; pp. 131–150. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, P.K.; Yang, J.-M.; Chang, Y.-H.; Su, W.-W. Modification of different molecular weights of chitosan by p-Coumaric acid: Preparation, characterization and effect of molecular weight on its water solubility and antioxidant property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Elango, J.; Wu, W. Recent Advancement of Molecular Structure and Biomaterial Function of Chitosan from Marine Organisms for Pharmaceutical and Nutraceutical Application. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-hefian, E.A.; Nasef, M.M.; Yahaya, A.H. Chitosan physical forms: A short review. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2011, 5, 670–677. [Google Scholar]
- Shaumbwa, V.R.; Liu, D.; Archer, B.; Li, J.; Su, F. Preparation and application of magnetic chitosan in environmental remediation and other fields: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, U.; Sreedhar, I.; Singh, S.A.; Patel, C.M.; Anitha, K.L. Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.T.N.; Le, V.T.; Dao, M.U.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Vu, T.T.; Nguyen, M.H.; Tran, D.L.; Le, H.S. Preparation of magnetic graphene oxide/chitosan composite beads for effective removal of heavy metals and dyes from aqueous solutions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 206, 1337–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, P. Magnetic thiolated/quaternized-chitosan composites design and application for various heavy metal ions removal, including cation and anion. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 136, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Anbarasu, A.; Pasupuleti, R.R.; Manigandan, S.; Praveenkumar, T.R.; Aravind Kumar, J. Treatment of heavy metals containing wastewater using biodegradable adsorbents: A review of mechanism and future trends. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoila, P.; Humelnicu, A.C.; Ignat, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Harabagiu, V. Chitin and Chitosan for Water Purification. In Chitin and Chitosan; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 429–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.-B.; Ni, W.-M.; Guan, B.-H. Application of chitosan as flocculant for coprecipitation of Mn(II) and suspended solids from dual-alkali FGD regenerating process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannamba, B.; Reddy, K.L.; AppaRao, B.V. Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhou, S.; Sun, W.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, H. Flocculation activity and evaluation of chitosan-based flocculant CMCTS-g-P(AM-CA) for heavy metal removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.-C.; Sharma, V.K. Water-stable metal-organic frameworks for aqueous removal of heavy metals and radionuclides: A review. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Zeng, G.M.; Huang, D.L.; Feng, C.L.; Hu, S.; Zhao, M.H.; Lai, C.; Wei, Z.; Huang, C.; Xie, G.X.; et al. Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, P.Z.; Shipley, H.J. Inorganic nano-adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals and arsenic: A review. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 29885–29907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, C.; Velmurugan, V.; Jacob, G.; Jeong, S.K.; Grace, A.N.; Bhatnagar, A. Role of nanomaterials in water treatment applications: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 306, 1116–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charpentier, T.V.J.; Neville, A.; Lanigan, J.L.; Barker, R.; Smith, M.J.; Richardson, T. Preparation of Magnetic Carboxymethylchitosan Nanoparticles for Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, N.; Li, P.-Y.; Liu, B.; Lai, H.-J.; Jin, T. One-Step Preparation of Chitosan-Based Magnetic Adsorbent and Its Application to the Adsorption of Inorganic Arsenic in Water. Molecules 2021, 26, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, F.; Ayati, A.; Tanhaei, B.; Sanati, A.L.; Afshar, S.; Kardan, A.; Dabirifar, Z.; Karaman, C. Removal of metal ions using a new magnetic chitosan nano-bio-adsorbent; A powerful approach in water treatment. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.L.; Zhou, S.F.; Jiao, W.Z.; Qi, G.S.; Liu, Y.Z. Removal of heavy metal ions by magnetic chitosan nanoparticles prepared continuously via high-gravity reactive precipitation method. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, F.L.; Wu, S.J.; Chen, Y.C. Combination of carboxymethyl chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles and chitosan-citrate complex gel beads as a novel magnetic adsorbent. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, R.; Chen, L.; Fan, M. A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic chitosan/nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel for highly efficient oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, T.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, W.; Long, J.; Fu, X. A biomimetic SiO2@chitosan composite as highly-efficient adsorbent for removing heavy metal ions in drinking water. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaz, A.; Ghorban, S.; Hosayni, L.; Irani, M.; Aliabadi, M. Chitosan nanofibers functionalized by TiO2 nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metal ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 58, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizat, M.A.; Aziz, F. 12—Chitosan Nanocomposite Application in Wastewater Treatments. In Nanotechnology in Water and Wastewater Treatment; Ahsan, A., Ismail, A.F., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, S.; Muralidhara, H.B.; Venkatesh, K.; Guna, V.K.; Gopalakrishna, K.; Kumar K., Y. Potential applications of cellulose and chitosan nanoparticles/composites in wastewater treatment: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 600–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shahrani, H.; Alakhras, F.; Al-Abbad, E.; Al-Mazaideh, G.; Hosseini-Bandegharaei, A.; Ouerfelli, N. Sorption of cobalt (II) ions from aqueous solutions using chemically modified chitosan. Glob. Nest J. 2018, 20, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobahi, T.R.A.; Abdelaal, M.Y.; Makki, M.S.I. Chemical modification of Chitosan for metal ion removal. Arab. J. Chem. 2014, 7, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, M.; Deng, S.; Cagnetta, G.; Wang, W.; Meng, P.; Liu, D.; Yu, G. Regeneration of chitosan-based adsorbents used in heavy metal adsorption: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 224, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, Y.; Dharaskar, S.; Khalid, M.; Sonawane, S. An environment friendly approach for heavy metal removal from industrial wastewater using chitosan based biosorbent: A review. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 43, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Katubi, K.M.; Amari, A.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. Polyethylenimine-Modified Magnetic Chitosan for the Uptake of Arsenic from Water. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, Z.M.; Şimşek, S. Insights into Effective Adsorption of Lead ions from Aqueous Solutions by Using Chitosan-Bentonite Composite Beads. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Ahmad, W.; Park, J.H.; Kumar, V.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Vaya, D.; Kim, H. One-step functionalization of chitosan using EDTA: Kinetics and isotherms modeling for multiple heavy metals adsorption and their mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algethami, J.S.; Alqadami, A.A.; Melhi, S.; Alhamami, M.A.M.; Fallatah, A.M.; Rizk, M.A. Sulfhydryl Functionalized Magnetic Chitosan as an Efficient Adsorbent for High-Performance Removal of Cd(II) from Water: Adsorption Isotherms, Kinetic, and Reusability Studies. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 2248249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutirman, Z.A.; Rahim, E.A.; Sanagi, M.M.; Abd Karim, K.J.; Wan Ibrahim, W.A. New efficient chitosan derivative for Cu(II) ions removal: Characterization and adsorption performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 153, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahraki, S.; Delarami, H.S.; Khosravi, F.; Nejat, R. Improving the adsorption potential of chitosan for heavy metal ions using aromatic ring-rich derivatives. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 576, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Shan, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Yao, B.; Gong, G.; Jin, X.; Wang, S. Characterization and Mechanistic Study of Heavy Metal Adsorption by Facile Synthesized Magnetic Xanthate-Modified Chitosan/Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, G.; Hao, C.; Li, X.; Li, T. Adsorption performance of a polysaccharide composite hydrogel based on crosslinked glucan/chitosan for heavy metal ions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 169, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, A. Preparation of Chitosan/Calcium Alginate/Bentonite Composite Hydrogel and Its Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption Properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablouh, E.; Hanani, Z.; Eladlani, N.; Rhazi, M.; Taourirte, M. Chitosan microspheres/sodium alginate hybrid beads: An efficient green adsorbent for heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2019, 29, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El-Soad, A.M.; Lazzara, G.; Abd El-Magied, M.O.; Cavallaro, G.; Al-Otaibi, J.S.; Sayyed, M.I.; Kovaleva, E.G. Chitosan Functionalized with Carboxyl Groups as a Recyclable Biomaterial for the Adsorption of Cu (II) and Zn (II) Ions in Aqueous Media. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shahawy, A.; Mubarak, M.F.; El Shafie, M.; Abdulla, H.M. Adsorption of Mn(ii) ions from wastewater using an AgNPs/GO/chitosan nanocomposite material. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 29385–29398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Bai, Z.; Jiang, H.; Prinsen, P.; Luque, R.; Zhao, S.; Xuan, J. Selective heavy metal removal and water purification by microfluidically-generated chitosan microspheres: Characteristics, modeling and application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.-Z.; Huang, T.; Zhang, N.; Lei, Y.-Z.; Wang, Y. Chitosan-assisted MOFs dispersion via covalent bonding interaction toward highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavithra, S.; Thandapani, G.; Sugashini, S.; Sudha, P.N.; Alkhamis, H.H.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Almutairi, M.H. Batch adsorption studies on surface tailored chitosan/orange peel hydrogel composite for the removal of Cr(VI) and Cu(II) ions from synthetic wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sources | Protein (%) | Ash (%) | Chitin (%) | Moisture (%) | Lipid (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shrimp shells | 32.77 | 32.46 | 36.43 | 45.65 | - |
| Shrimp shells (P. longirostris) | 29.23 | 25.06 | 26.98 | 3.25 | 15.48 |
| Shrimp shells (Penaeus durarum) | 34.02 | 42.26 | 23.72 | - | - |
| Insect cuticles (Cicada sloughs) | 39.8 | 11.7 | 36.6 | 8.7 | 2.7 |
| Crabs’ shells | 16.68 | 66.58 | 16.73 | - | - |
| Mussel shells | 9.99 | 23.25 | 23.25 | - | - |
| Squid gladius (L. vulgaris) | 36.52 | 2.57 | 31.2 | - | 0..32 |
| Source | Demineralization | Deproteinization | Decolorization | Deacetylation | Degree of Acetylation (DA) or Degree of Deacetylation (DD) (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shrimp shells | 2.5 M HCl (1:10 solid: solvent ratio w/v) for 4 min under MW at 650 W power | NaOH (20%) under MW irradiation at 500 W for 8 min. | - | 30% NaOH for 12 min at 500 W | 23.4% DA | [46] |
| Shrimp shells | HCl (7%) at ambient temperature for 24 h. | NaOH (10%) at ambient temperature for 24 h. | Ethanol for 6 h | NaOH (50% w/v) at a boiling temperature in the N2 atmosphere, Repeated twice | 78% DD | [55] |
| Shrimp shells | 1.5% HCl (1:30 w/v) for 20 h at room temperature | NaOH (5%) at 90 °C for 24 h (solvent: shell ratio 12:1, v/w). | Acetone (99.5%) at room temperature for 24 h. | 50% NaOH (15%, w/v) at 60 °C for 8 h. | - | [56] |
| Giant freshwater prawn carapace | 1 M HCl (1:10 solid: liquid ratio) at 60 °C, 250 rpm for 2 h. | 1 M NaOH (1:10 solid: liquid ratio) at 100 °C, 250 rpm for 2 h. | 95% ethanol (1:5 mass: volume ratio) for 30 min at ambient temperature | 60% NaOH (1:10 solid: liquid ratio), at 120 °C, 250 rpm for 2 h. | 85.2% | [57] |
| Prawn shells | 1 M HCl (1:16 solid: liquor ratio) at 100 °C for 4 h. | 1 M NaOH (1:16 solid: liquid ratio) at 100 °C for 4 h. | 50% NaOH (1:30 solid: liquid ratio), in presence of ethanol, at 80 °C for 4 h. | 89% DD | [58] | |
| Crab shell | 2.5% (w/v) HCl at 1:20 (w/v, shell: solution), 20 °C for 6 h. | 2% KOH at 1:20 (w/v, shell: solution), 90 °C for 2 h | Acetone for 10 min | 40% NaOH at 1:15 (w/v, chitin: solution) at 105 °C for 2 h. | 53.42% DD | [59] |
| Chitin/CS | Solvents | References |
|---|---|---|
| Chitin | Dimethylformamide + lithium chloride, Diethylformamide + lithium chloride, Hexafluoroisopropanol, Hexafluoroacetone + sequihydrate, 1,2-Chloroethanol + sulphuric acid, high concentrated organic acids (HCl, H2SO4, H3PO4) | [65,67,68] |
| CS | Aqueous citric acids, acetic acid, lactic acid, formic acid, glutamic acid, HCl acid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gamage, A.; Jayasinghe, N.; Thiviya, P.; Wasana, M.L.D.; Merah, O.; Madhujith, T.; Koduru, J.R. Recent Application Prospects of Chitosan Based Composites for the Metal Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Polymers 2023, 15, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061453
Gamage A, Jayasinghe N, Thiviya P, Wasana MLD, Merah O, Madhujith T, Koduru JR. Recent Application Prospects of Chitosan Based Composites for the Metal Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Polymers. 2023; 15(6):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061453
Chicago/Turabian StyleGamage, Ashoka, Nepali Jayasinghe, Punniamoorthy Thiviya, M. L. Dilini Wasana, Othmane Merah, Terrence Madhujith, and Janardhan Reddy Koduru. 2023. "Recent Application Prospects of Chitosan Based Composites for the Metal Contaminated Wastewater Treatment" Polymers 15, no. 6: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061453
APA StyleGamage, A., Jayasinghe, N., Thiviya, P., Wasana, M. L. D., Merah, O., Madhujith, T., & Koduru, J. R. (2023). Recent Application Prospects of Chitosan Based Composites for the Metal Contaminated Wastewater Treatment. Polymers, 15(6), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061453