Modulation of the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) Utilizing Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Monomers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Thermosensitive PNVCL Hydrogel
2.3. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
2.5. Phase Transition Determination
2.5.1. Cloud Point Analysis
2.5.2. UV-Vis Spectrometry Analysis
2.6. Swelling Analysis
2.7. Gelation Determination
3. Results and Discussion
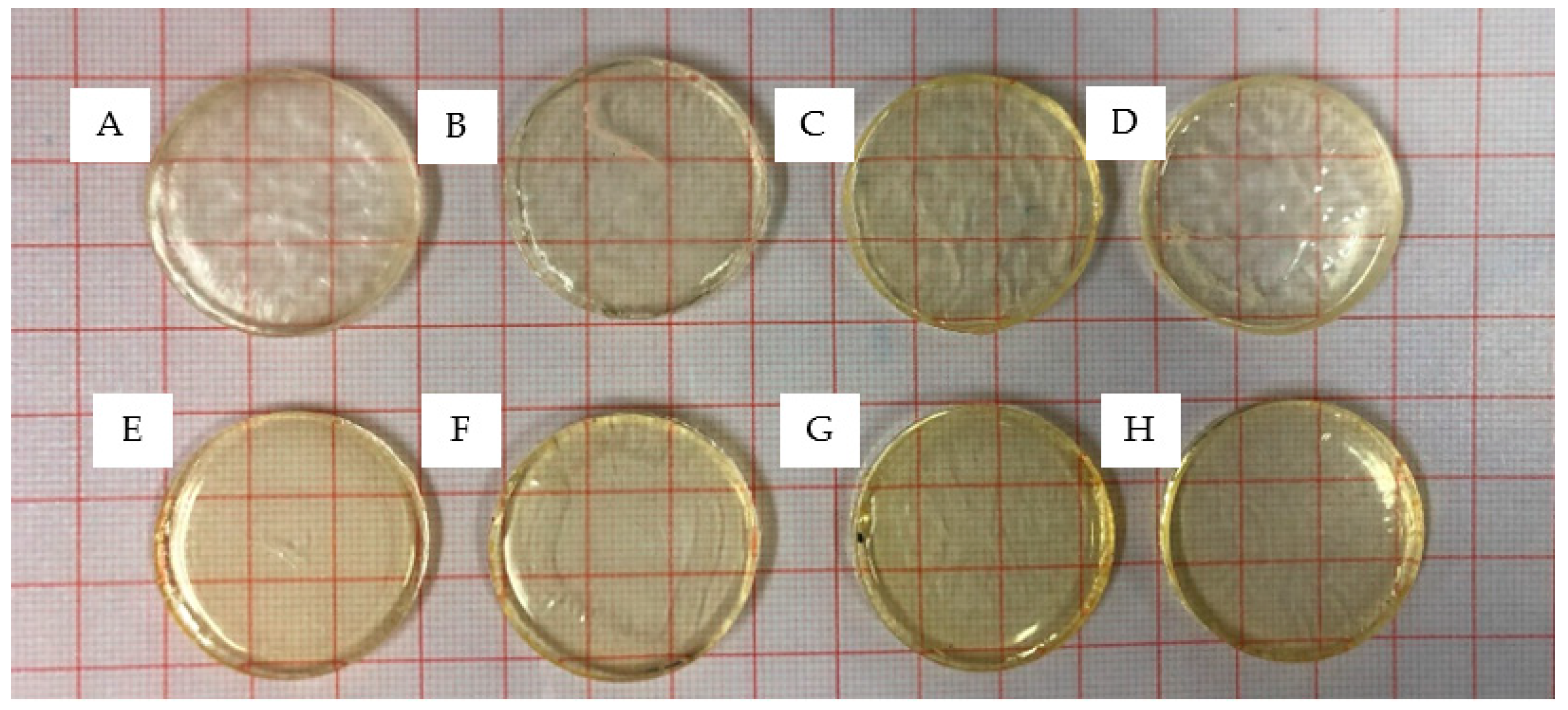
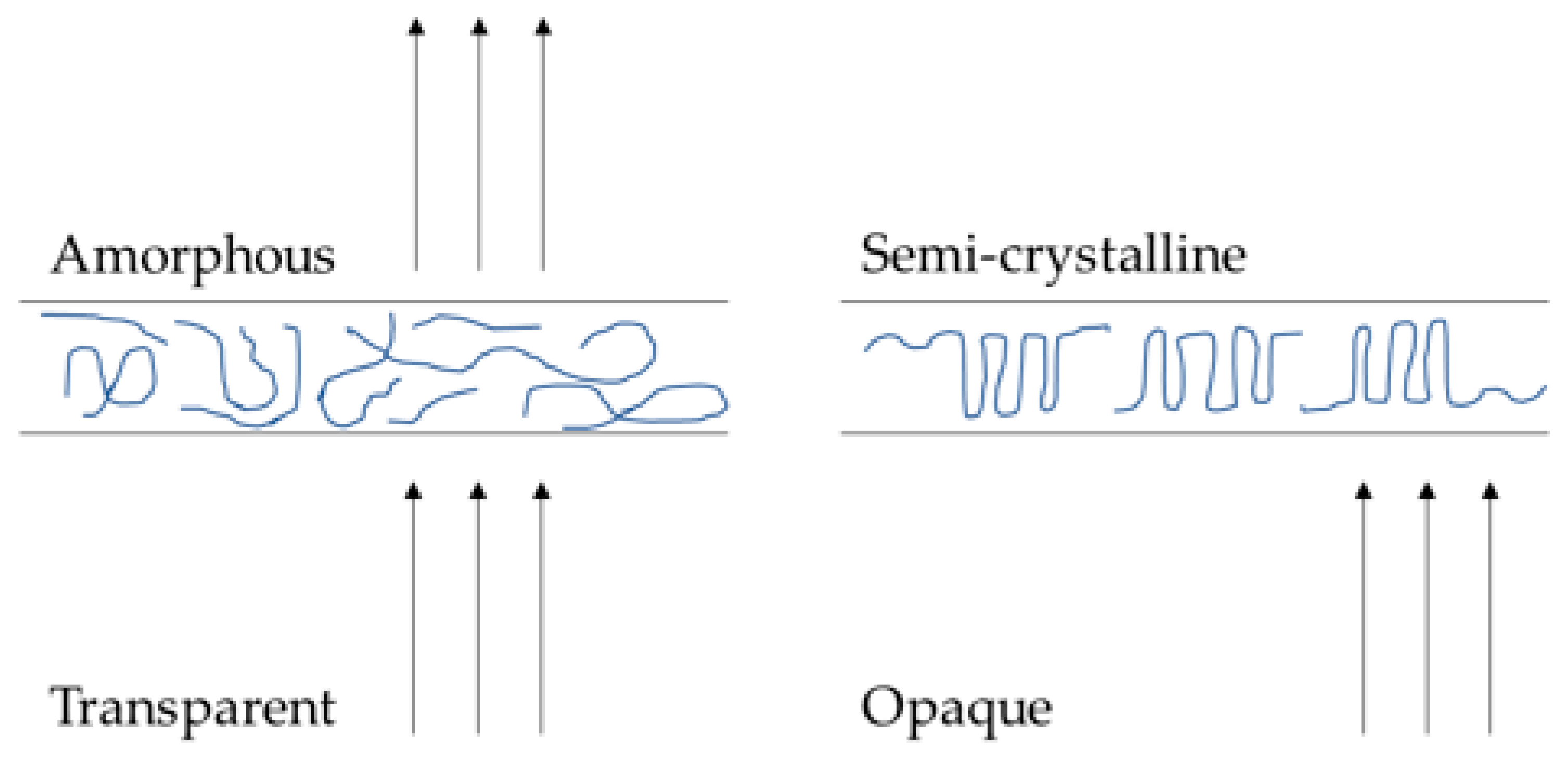
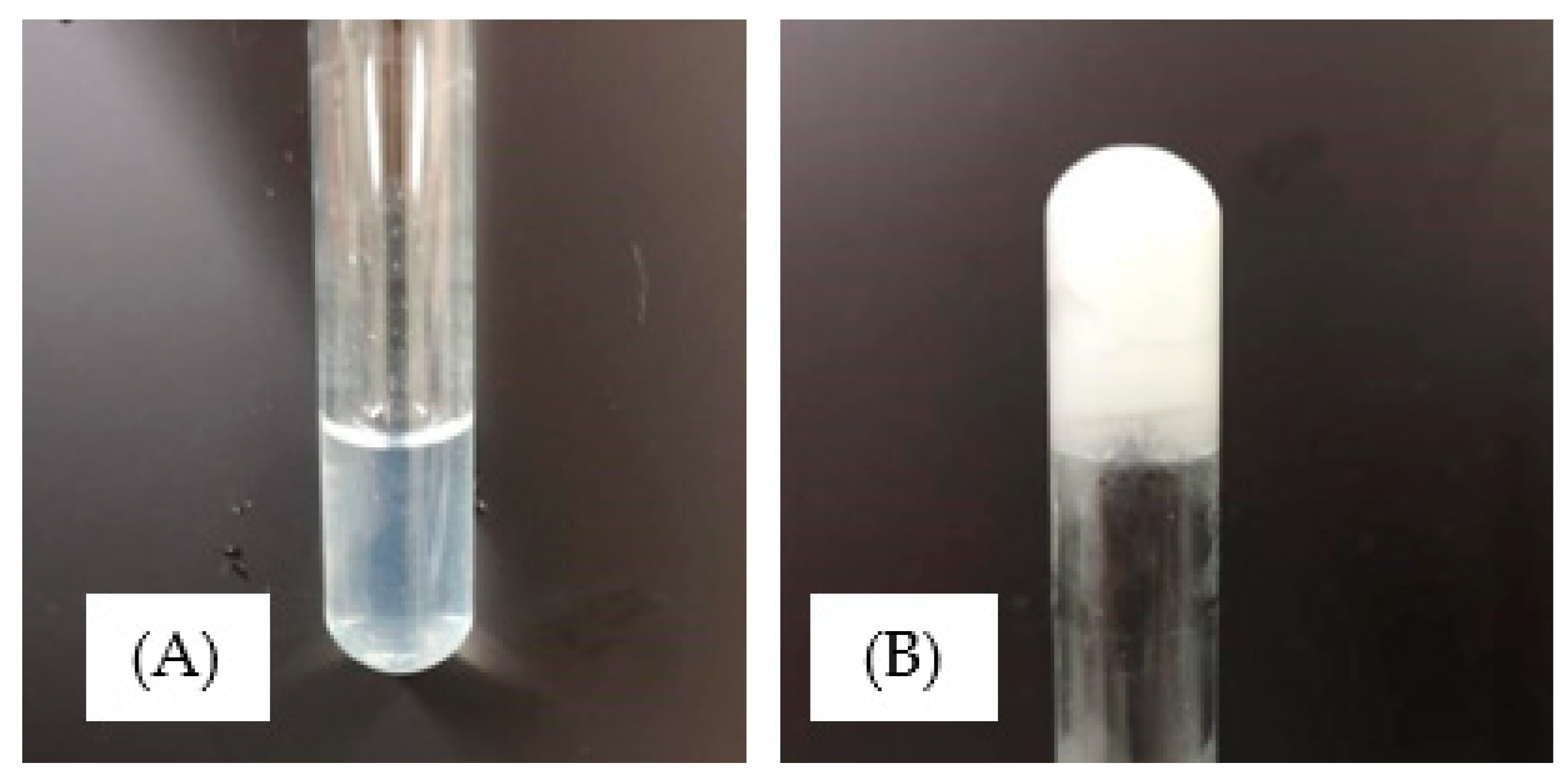
3.1. Photopolymerisation of Xerogels

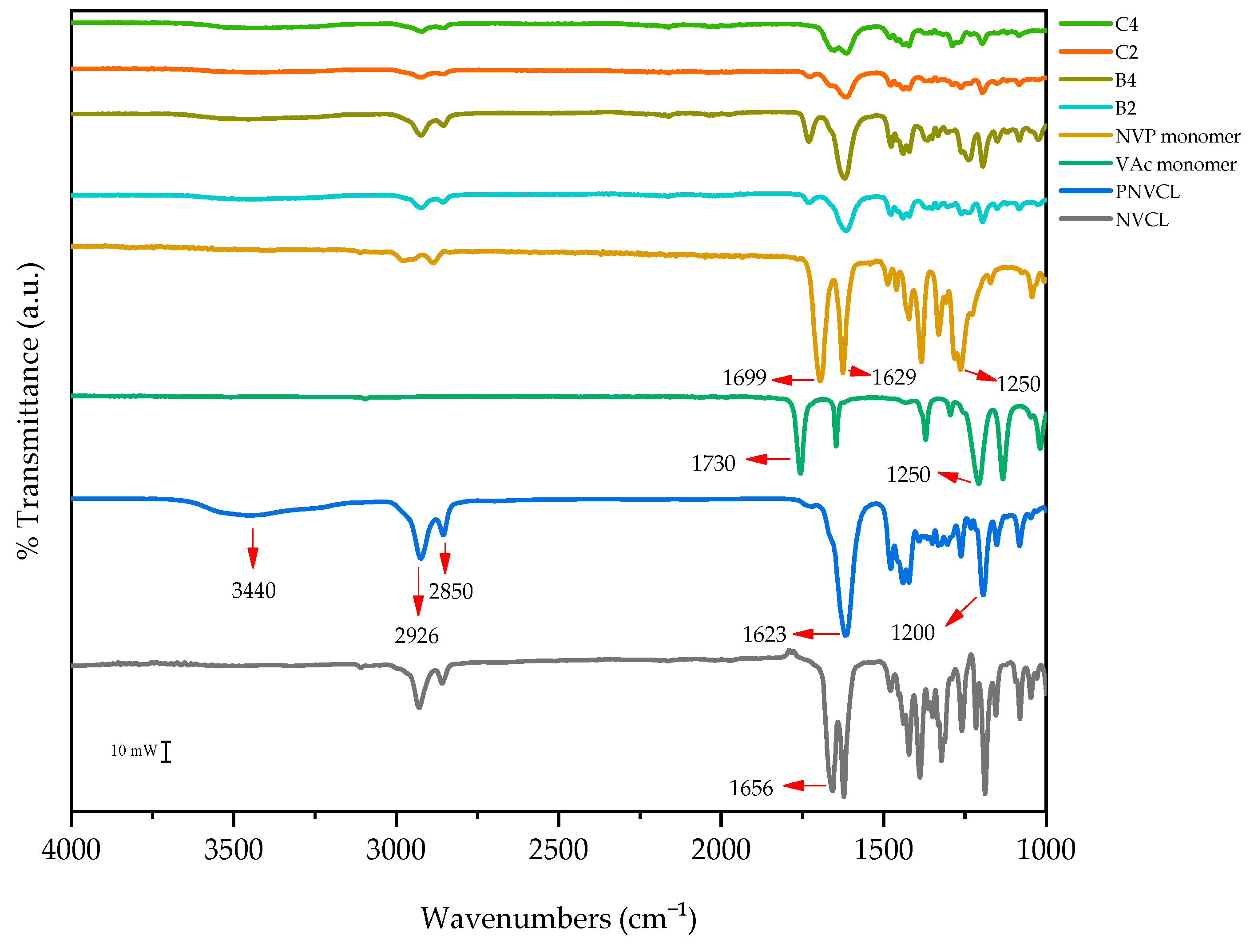
3.2. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
3.4. Phase Transition Determination
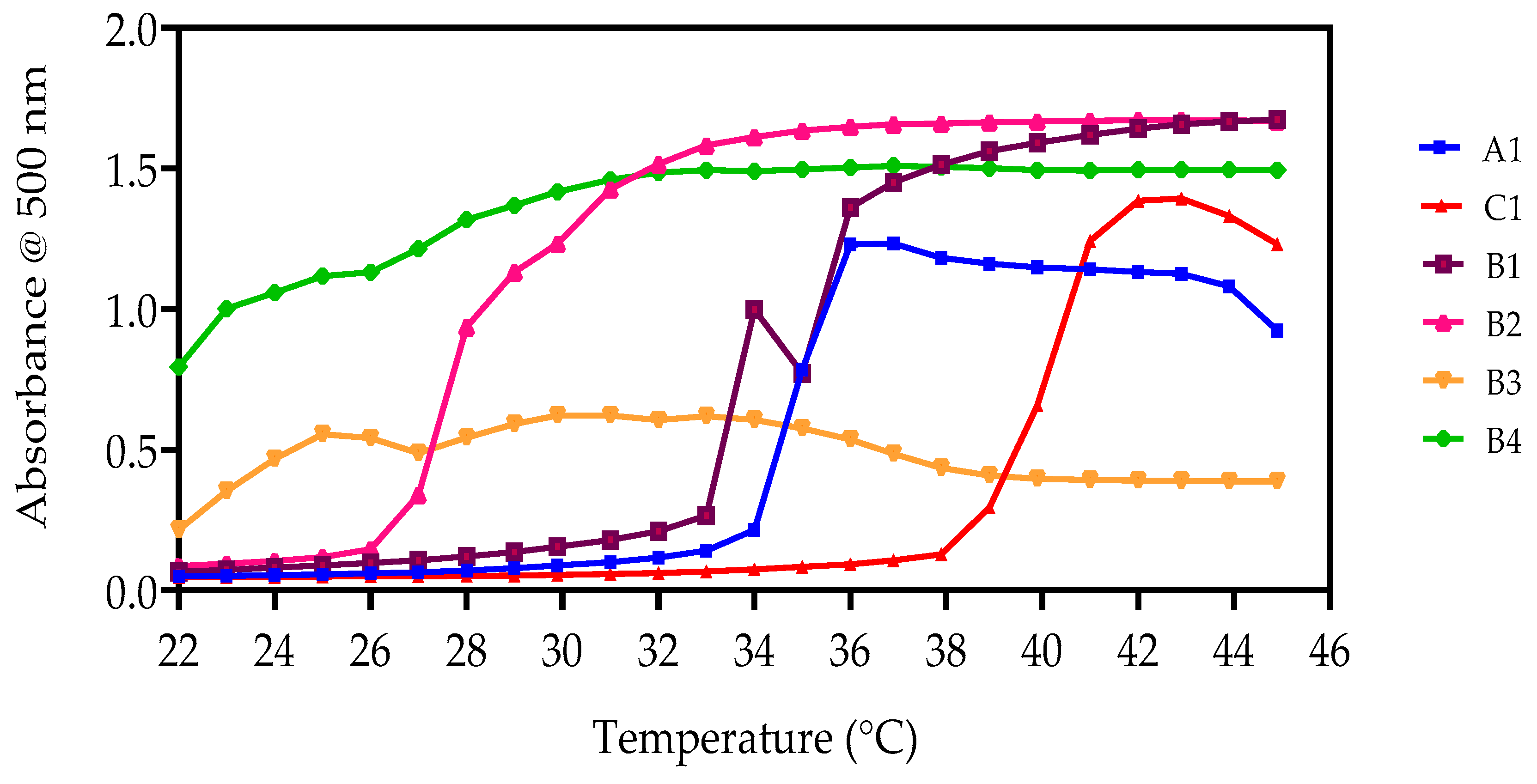
3.4.1. Cloud Point Analysis
3.4.2. UV-Spectroscopy Analysis
3.4.3. Gelation Determination
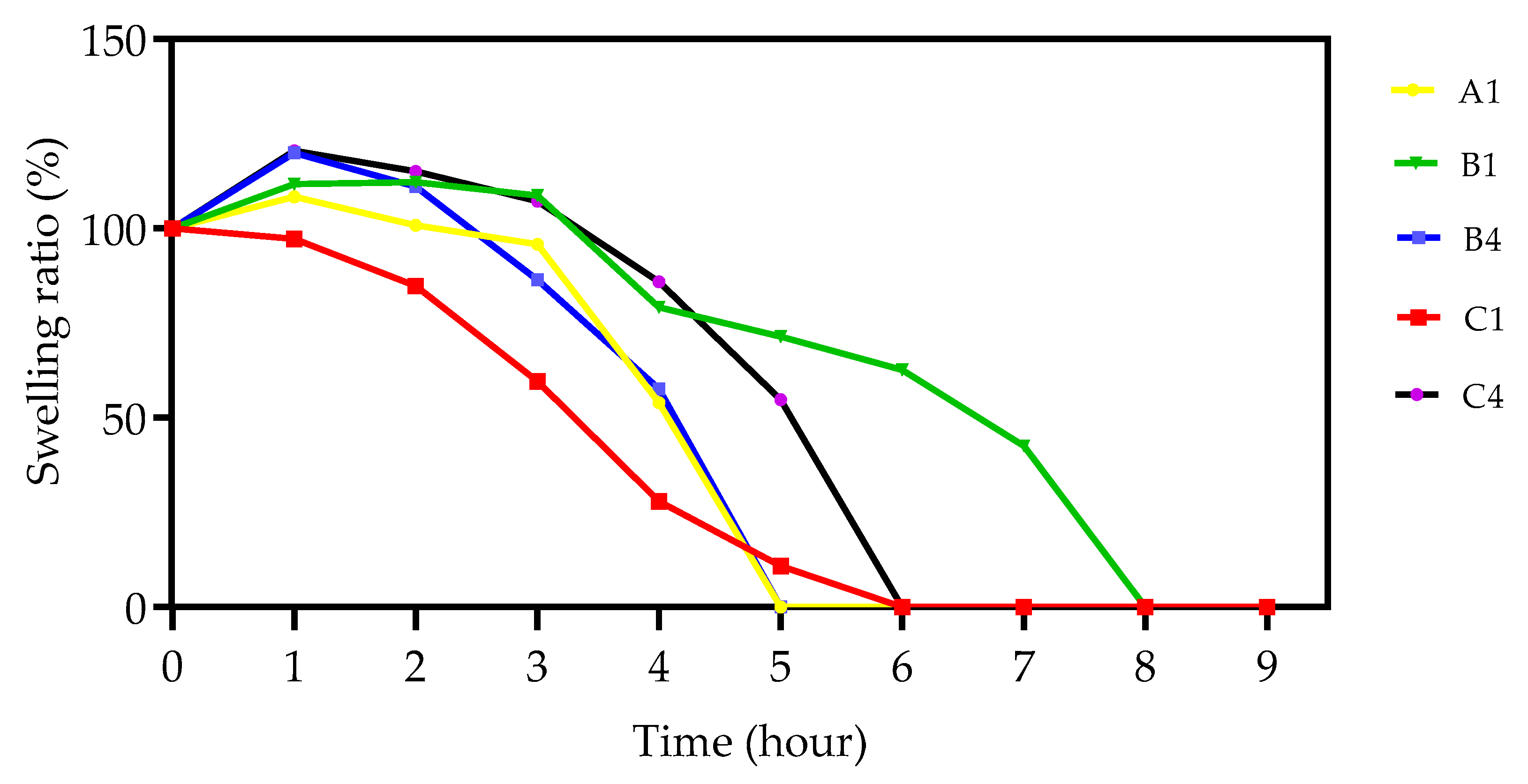
3.5. Swelling Analysis
4. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Y.; Bae, J.; Fang, Z.; Li, P.; Zhao, F.; Yu, G. Hydrogels and Hydrogel-Derived Materials for Energy and Water Sustainability. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 7642–7707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaith, B.S.; Jindal, R.; Mittal, H.; Kumar, K. Temperature, pH and electric stimulus responsive hydrogels from Gum ghatti and polyacrylamide-synthesis, characterization and swelling studies. Der Chem. Sin. 2010, 1, 44–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Hydrogels as Drug Delivery Systems; Pros and Cons. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 5, 7–24. [Google Scholar]
- Drozdova, M.G.; Demina, T.S.; Dregval, O.A.; Gaidar, A.I.; Andreeva, E.R.; Zelenetskii, A.N.; Akopova, T.A.; Markvicheva, E. Macroporous Hyaluronic Acid/Chitosan Polyelectrolyte Complex-Based Hydrogels Loaded with Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles: Preparation, Characterization and In Vitro Evaluation. Polysaccharides 2022, 3, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddu, V.M.; Liu, S.X. Rheological Properties of Hydrogels Produced By Cellulose Derivatives Crosslinked With Citric Acid, Succinic Acid and Sebacic Acid. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2021, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Luo, L.L.; Shao, Z.B.; Sun, S.L. Tough, antibacterial and self-healing ionic liquid/multiwalled carbon nanotube hydrogels as elements to produce flexible strain sensors for monitoring human motion. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 160, 110779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Shah, J.; Sreeharsha, N.; Gupta, S.; Shinu, P. Emerging role of hydrogels in drug delivery systems, tissue engineering and wound management. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Othman, M.B.H.; Javed, F.; Ahmad, Z.; Akil, H.M. Classification, processing and application of hydrogels: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 57, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulrez SK, H.; Al-Assaf, S.; Phillips, G.O. Hydrogels: Methods of Preparation, Characterisation and Applications. Prog. Mol. Environ. Bioeng. From Anal. Model. Technol. Appl. 2011, 51, 117–140. [Google Scholar]
- Yahia, L.H. History and Applications of Hydrogels. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.-X.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, H.-J.; Li, P.-Y.; Chen, S.-Q.; He, W.-D. Hybrid cryogels composed of P(NIPAM-co-AMPS) and metal nanoparticles for rapid reduction of p-nitrophenol. Polymer 2020, 193, 122352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Chen, S.Q.; Ullah, M.; Siddiq, M.; He, W.D. Highly porous cryogels loaded with bimetallic nanoparticles as an efficient antimicrobial agent and catalyst for rapid reduction of water-soluble organic contaminants. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.C.; Li, G.; Kim, J.; Youk, J.H. One-pot synthesis of poly(N-vinylcaprolactam)-based biocompatible block copolymers using a dual initiator for ROP and RAFT polymerization. Polymer 2013, 54, 6119–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, S.F.; Lopes, M.V.; Rossi-bergmann, B.; Santos, A.M. Synthesis and characterization of poly(N-vinylcaprolactam)-based spray dried microparticles exhibiting temperature and pH-sensitive properties for controlled release of ketoprofen. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.N.; Yusoh, K.B.; Haslinda, J.; Haji, B. Polymer in novel drug delivery systems: A review. Mater. Express 2018, 8, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozano, S.; Özdemir, T.; Usanmaz, A. Polymerization of N-vinylcaprolactam and characterization of poly(N-vinylcaprolactam). J. Macromol. Sci. Part A Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 48, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingji, D.; Ruihe, W.; Jiafang, X.; Jiayue, M.; Xiaohui, W.; Jiawen, X. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects Synthesis and application of a temperature sensitive poly rheology control of water-based drilling fluid. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 644, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Jiang, J.; Hou, J.; Li, G.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y. Supporting information Water-Soluble Copolymers and Their Hydrogels with pH-Tunable Diverse Thermoresponsive Behaviors Enabled by Hydrogen Bonding. Polym. Chem. 2022, 13, 5700–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez-Lemus, N.A.; Licea-Claverie, A. Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam), a comprehensive review on a thermoresponsive polymer becoming popular. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 53, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, M.J.; Lyons, S.G.; Geever, L.M. Synthesis and characterisation of novel poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) hydrogels, cross-linked with N-hydroxyethyl acrylamide (HEA). Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 10, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, M.B.; Halligan, S.; Killion, J.A.; Wang, W.; Dong, Y.; Nugent, M.; Geever, L.M. The Effect Acetic Acid has on Poly(N-Vinylcaprolactam) LCST for Biomedical Applications. Polym. Technol. Eng. 2017, 57, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, S.; Reddy, S.K.; Usha, C.; Naulakha, N.K.; Adithyakumar, C.R.; Reddy, M.L.K. Advancements in the Research of 4D Printing-A Review. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 376, 012123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Gao, G.; Jiang, Z. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects Double-layer temperature-sensitive hydrogel fabricated by 4D printing with fast shape deformation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Arya, S.; Gupta, V.; Furukawa, H.; Khosla, A. 4D printing: Fundamentals, materials, applications and challenges. Polymer 2021, 228, 123926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Qi, H.J.; Dunn, M.L. Active materials by four-dimension printing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 131901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.; Haleem, A. 4D printing applications in medical field: A brief review. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2018, 7, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.S.; Balu, R.; Mettu, S.; Choudhury, N.R.; Dutta, N.K. 4D Printing of Hydrogels: Innovation in Material Design and Emerging Smart Systems for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uboldi, M.; Pasini, C.; Pandini, S.; Baldi, F.; Briatico-Vangosa, F.; Inverardi, N.; Maroni, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Melocchi, A.; Gazzaniga, A.; et al. Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-D.; Lai, J.-H.; Wang, M. 4D Printing of Self-Folding Hydrogel Tubes for Potential Tissue Engineering Applications. Nano Life 2021, 11, 2141001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champeau, M.; Heinze, D.A.; Viana, T.N.; de Souza, E.R.; Chinellato, A.C.; Titotto, S. 4D Printing of Hydrogels: A Review. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halligan, S.C.; Dalton, M.B.; Murray, K.A.; Dong, Y.; Wang, W.; Lyons, J.G.; Geever, L.M. Synthesis, characterisation and phase transition behaviour of temperature-responsive physically crosslinked Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) based polymers for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, D.; Reis, R.L.; Kundu, S.C. Trends in Biomaterials for Three-Dimensional Cancer Modeling; INC: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, W.; Gao, L.; Venkatesan, J.K.; Wang, G.; Madry, H.; Cucchiarini, M. Translational applications of photopolymerizable hydrogels for cartilage repair. J. Exp. Orthop. 2019, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, S.; Geever, L.M.; Halligan, E.; Tie, B.S.H.; Breheny, C. A Development of New Material for 4D Printing and the Material Properties Comparison between the Conventional and Stereolithography Polymerised NVCL Hydrogels. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Bilotti, E.; Bastiaansen, C.W.M.; Peijs, T. Transparent semi-crystalline polymeric materials and their nanocomposites: A review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 2351–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, S.; Halligan, E.; Tie, B.S.H.; Breheny, C.; Geever, L.M. Lower Critical Solution Temperature Tuning and Swelling Printing Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathan, A.J.; Scobell, A. Polymerization and Characterization of N-Vinylcaprolactam. Master’s Thesis, The Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences of Middle East Technical University, Ankara, Turkey, 2008; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- Halligan, S.; Murray, K.; Hopkins, M.; Rogers, I.; Lyons, J.; Vrain, O.; Geever, L. Enhancing and controlling the critical attributes of Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) through electron beam irradiation for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 137, 48639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.M.; Mallikarjuna, B.; Rao, K.S.V.K.; Siraj, S.; Rao, K.C.; Subha, M.C.S. Novel thermo/pH sensitive nanogels composed from poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) for controlled release of an anticancer drug. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 891–897. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Jiao, A.; Yu, S.; You, J.B.; Kim, D.H.; Im, S.G. Initiated chemical vapor deposition of thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) thin films for cell sheet engineering. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7691–7698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Detrembleur, C.; De Pauw-Gillet, M.C.; Mornet, S.; Duguet, E.; Jérôme, C. Gold nanorods coated with a thermo-responsive poly(ethylene glycol)-b-poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) corona as drug delivery systems for remotely near infrared-triggered release. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 799–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallon, M.; Halligan, S.; Pezzoli, R.; Geever, L.; Higginbotham, C. Synthesis and characterisation of novel temperature and pH sensitive physically cross-linked poly (N-vinylcaprolactam-co-itaconic acid) hydrogels for drug delivery. Gels 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, V.T.; Török, G.; Cser, L.; Káli, G.; Sibilev, A.I. Molecular dynamics of Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) hydrate. Appl. Phys. A 2002, 74, s478–s480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirsh, Y.E.; Yanul, N.A.; Kalninsh, K.K. Structural transformations and water associate interactions in poly-N-vinylcaprolactam-water system. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboo, S.; Kestur, U.S.; Flaherty, D.P.; Taylor, L.S. Congruent Release of Drug and Polymer from Amorphous Solid Dispersions: Insights into the Role of Drug-Polymer Hydrogen Bonding, Surface Crystallization, and Glass Transition. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 1261–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsili, L.; Bo, M.D.; Eisele, G.; Donati, I.; Berti, F.; Toffoli, G. Characterization of Thermoresponsive Poly-N-Vinylcaprolactam Polymers for Biological Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Indulekha, S.; Gottipalli, R.; Reddy, B.P.K.; Chikate, T.R.; Gupta, R.; Jahagirdar, D.N.; Prasad, R.; De, A.; Srivastava, R. NIR light-triggered shrinkable thermoresponsive PNVCL nanoshells for cancer theranostics. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 44026–44034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozinsky, V.I.; Simenel, I.A.; Kurskaya, E.A.; Kulakova, V.K.; Galaev, I.Y.; Mattiasson, B.; Grinberg, V.Y.; Grinberg, N.V.; Khokhlov, A.R. Synthesis of N-vinylcaprolactam polymers in water-containing media. Polymer 2000, 41, 6507–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wei, W.; Wang, L.; Su, Z.; Ma, G. A thermosensitive hydrogel based on quaternized chitosan and poly (ethylene glycol) for nasal drug delivery system. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Fu, X.; Song, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, G. Synthesis and self-assembly of a new amphiphilic thermosensitive poly(N-vinylcaprolactam)/poly(ε-caprolactone) block copolymer. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Zhang, L.M. Phase-transition and aggregation characteristics of a thermoresponsive dextran derivative in aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 2414–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermagoret, A.; Mathieu, K.; Thomassin, J.-M.; Fustin, C.-A.; Duchêne, R.; Jérôme, C.; Detrembleur, C.; Debuigne, A. Double thermoresponsive di- and triblock copolymers based on N-vinylcaprolactam and N-vinylpyrrolidone: Synthesis and comparative study of solution behaviour. Polym. Chem. 2014, 5, 6534–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Peñas, A.; Biswas, C.S.; Liang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, P.; Stadler, F.J. Effect of Hydrophobic Interactions on Lower Critical Solution Temperature for Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-dopamine Methacrylamide) Copolymers. Polymers 2019, 11, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrintaj, P.; Ramsey, J.D.; Samadi, A.; Atoufi, Z.; Yazdi, M.K.; Ganjali, M.R.; Amirabad, L.M.; Zangene, E.; Farokhi, M.; Formela, K.; et al. Poloxamer: A versatile tri-block copolymer for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2020, 110, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhuo, R.; Cui, J.; Zhang, J. A novel thermo-responsive drug delivery system with positive controlled release. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 235, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalupov, Z.; Zdenka, Š. Stimuli-sensitive hydrogels in controlled and sustained drug delivery. Medicina 2003, 39, 19–24. [Google Scholar]



| Material | Chemical Structures |
|---|---|
| N-vinylcaprolactam (NVCL) |  |
| Vinylacetate (VAc) |  |
| N-vinylpyrrolidone (NVP) |  |
| 4-(2hydroxyethoxy) phenyl-(2-hydroxy-2-propyl) ketone (Irgacure® 2959) | 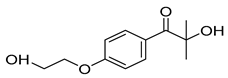 |
| ID Code | Formulation | Photoinitiator | Monomer | Comonomers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irgacure® 2959 (wt%) | NVCL (wt%) | NVP (wt%) | VAc (wt%) | ||
| A1 | P(NVCL100) | 0.1 | 100 | -- | -- |
| B1 | P(NVCL90-VAc10) | 0.1 | 90 | -- | 10 |
| B2 | P(NVCL80-VAc20) | 0.1 | 80 | -- | 20 |
| B3 | P(NVCL70-VAc30) | 0.1 | 70 | -- | 30 |
| B4 | P(NVCL60-VAc40) | 0.1 | 60 | -- | 40 |
| C1 | P(NVCL90-NVP10) | 0.1 | 90 | 10 | -- |
| C2 | P(NVCL80-NVP20) | 0.1 | 80 | 20 | -- |
| C3 | P(NVCL70-NVP30) | 0.1 | 70 | 30 | -- |
| C4 | P(NVCL60-NVP40) | 0.1 | 60 | 40 | -- |
| Sample | Wavelength (cm−1) | Functional Group |
|---|---|---|
| Monomers | ||
| NVP | 1250 | C=O |
| 1640 | C-H | |
| VAc | 1730 | C=O |
| NVCL | 1656 | C=C |
| Polymerised Samples | ||
| PNVCL | 1623 | C=O |
| 2926 | C-H | |
| 3440 | O-H | |
| PNVCL/VAc | 1735 | C=O |
| PNVCL/NVP | 1386 | C-N-C |
| 1425 | C-N | |
| 1699 | C=O | |
| ID Code | Tcp (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| 5 wt% | 10 wt% | |
| A1 | 32 | 33 |
| B1 | 26 | 27 |
| B2 | 25 | 26 |
| B3 | 23 | 24 |
| B4 | 21 | 22 |
| C1 | 39 | 39 |
| C2 | 41 | 42 |
| C3 | 47 | 48 |
| C4 | 53 | 54 |
| ID Code | UV-Spectrometry LCST (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| 5 wt% | 10 wt% | |
| A1 | 35 | 36 |
| B1 | 34 | 34 |
| B2 | 29 | 30 |
| C1 | 36 | 37 |
| ID Code | Gelation Temperature (°C) | |
|---|---|---|
| 5 wt% Concentration | 10 wt% Concentration | |
| A1 | 39 | 39 |
| B1 | 34 | 35 |
| B2 | 32 | 33 |
| B3 | 30 | 31 |
| B4 | 26 | 27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halligan, E.; Zhuo, S.; Colbert, D.M.; Alsaadi, M.; Tie, B.S.H.; Bezerra, G.S.N.; Keane, G.; Geever, L.M. Modulation of the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) Utilizing Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Monomers. Polymers 2023, 15, 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071595
Halligan E, Zhuo S, Colbert DM, Alsaadi M, Tie BSH, Bezerra GSN, Keane G, Geever LM. Modulation of the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) Utilizing Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Monomers. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071595
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalligan, Elaine, Shuo Zhuo, Declan Mary Colbert, Mohamad Alsaadi, Billy Shu Hieng Tie, Gilberto S. N. Bezerra, Gavin Keane, and Luke M. Geever. 2023. "Modulation of the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) Utilizing Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Monomers" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071595
APA StyleHalligan, E., Zhuo, S., Colbert, D. M., Alsaadi, M., Tie, B. S. H., Bezerra, G. S. N., Keane, G., & Geever, L. M. (2023). Modulation of the Lower Critical Solution Temperature of Thermoresponsive Poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) Utilizing Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Monomers. Polymers, 15(7), 1595. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071595









