Fabrication and Characterization of PLA/PBAT Blends, Blend-Based Nanocomposites, and Their Supercritical Carbon Dioxide-Induced Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation
2.2. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
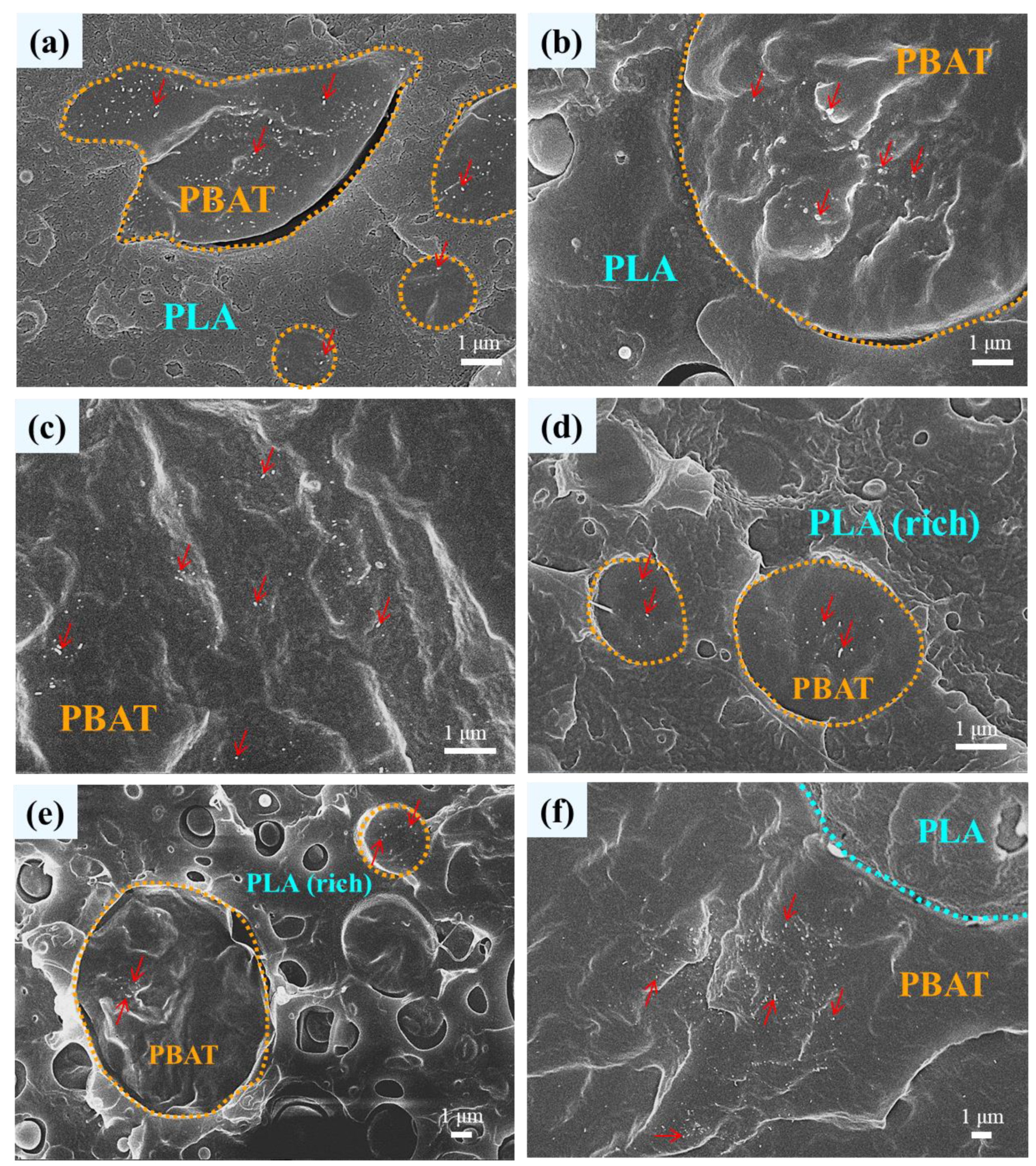
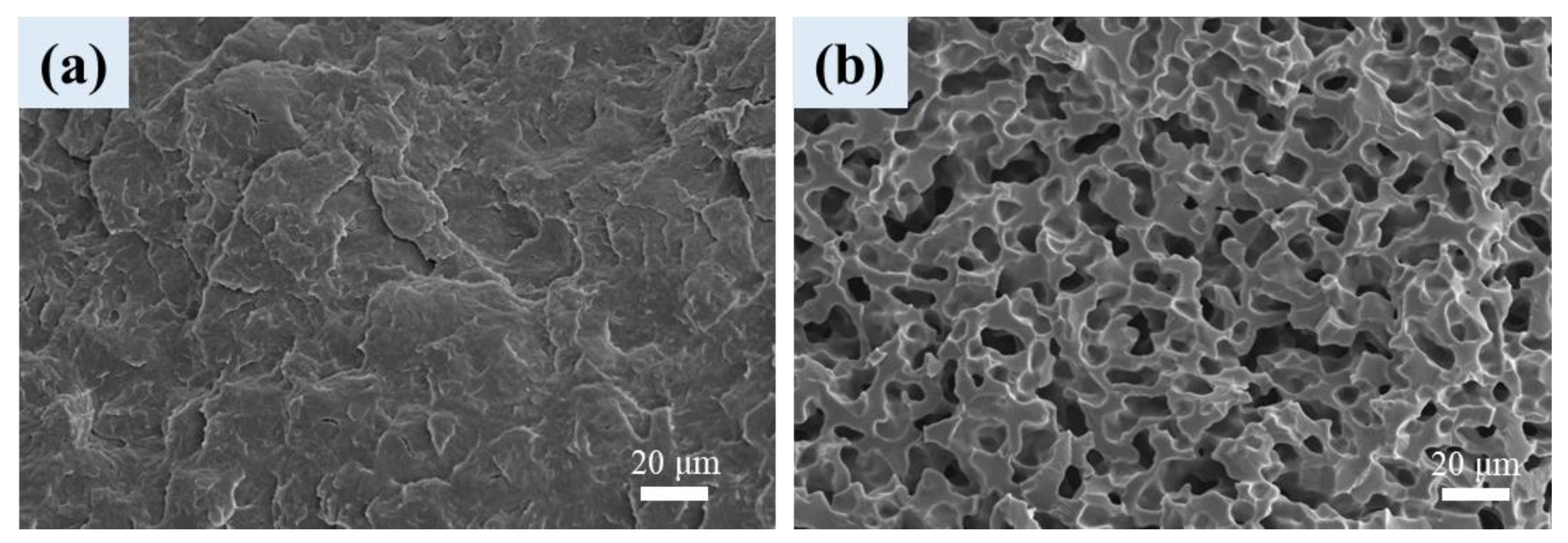
3.1. Phase Morphology of Unfoamed Samples
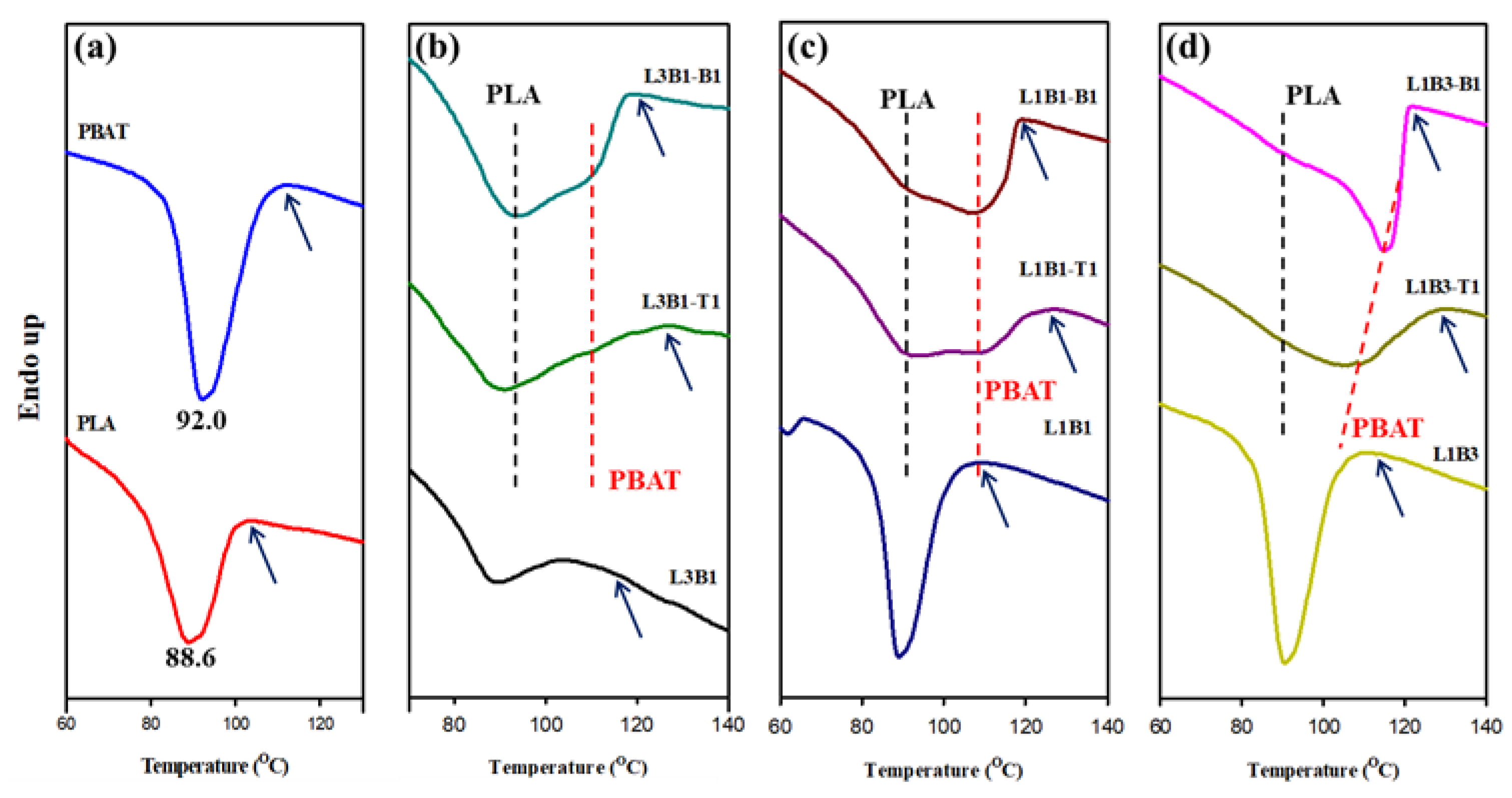
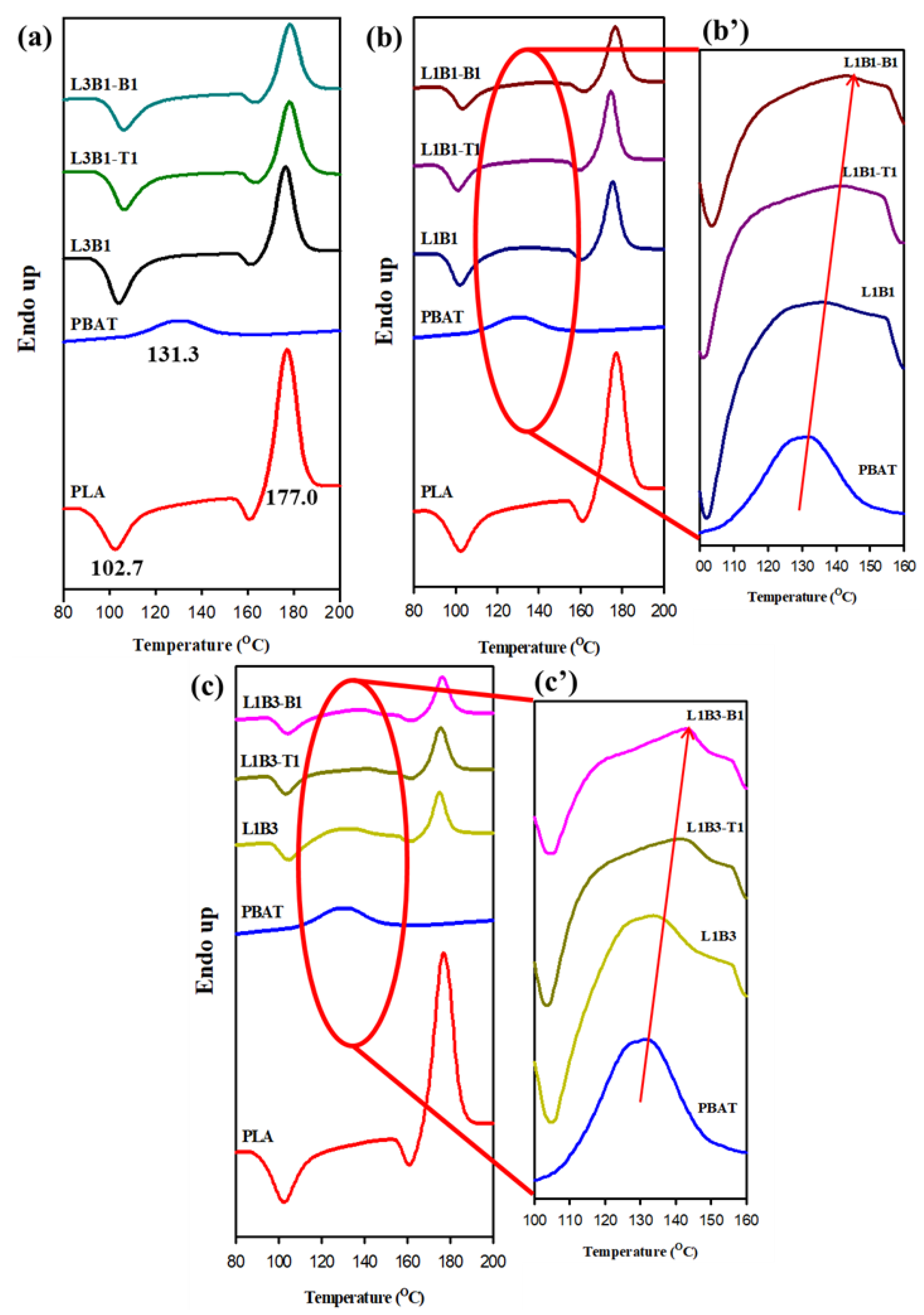
3.2. Crystallization and Melting Behavior of Unfoamed Samples
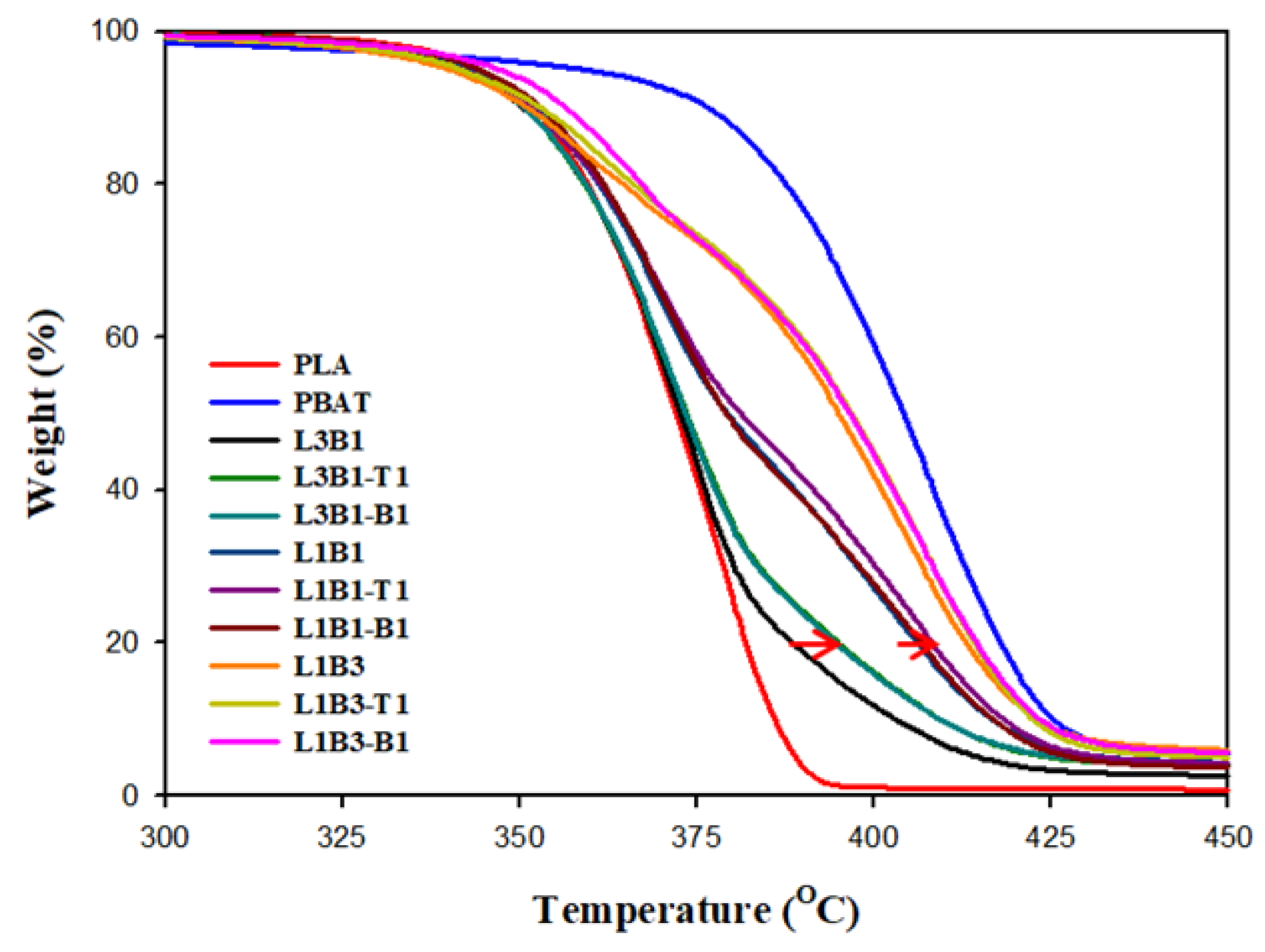
3.3. Thermal Stability of Unfoamed Samples
3.4. Mechanical Property of Unfoamed Samples
3.5. Electrical Conductivity of Unfoamed Samples
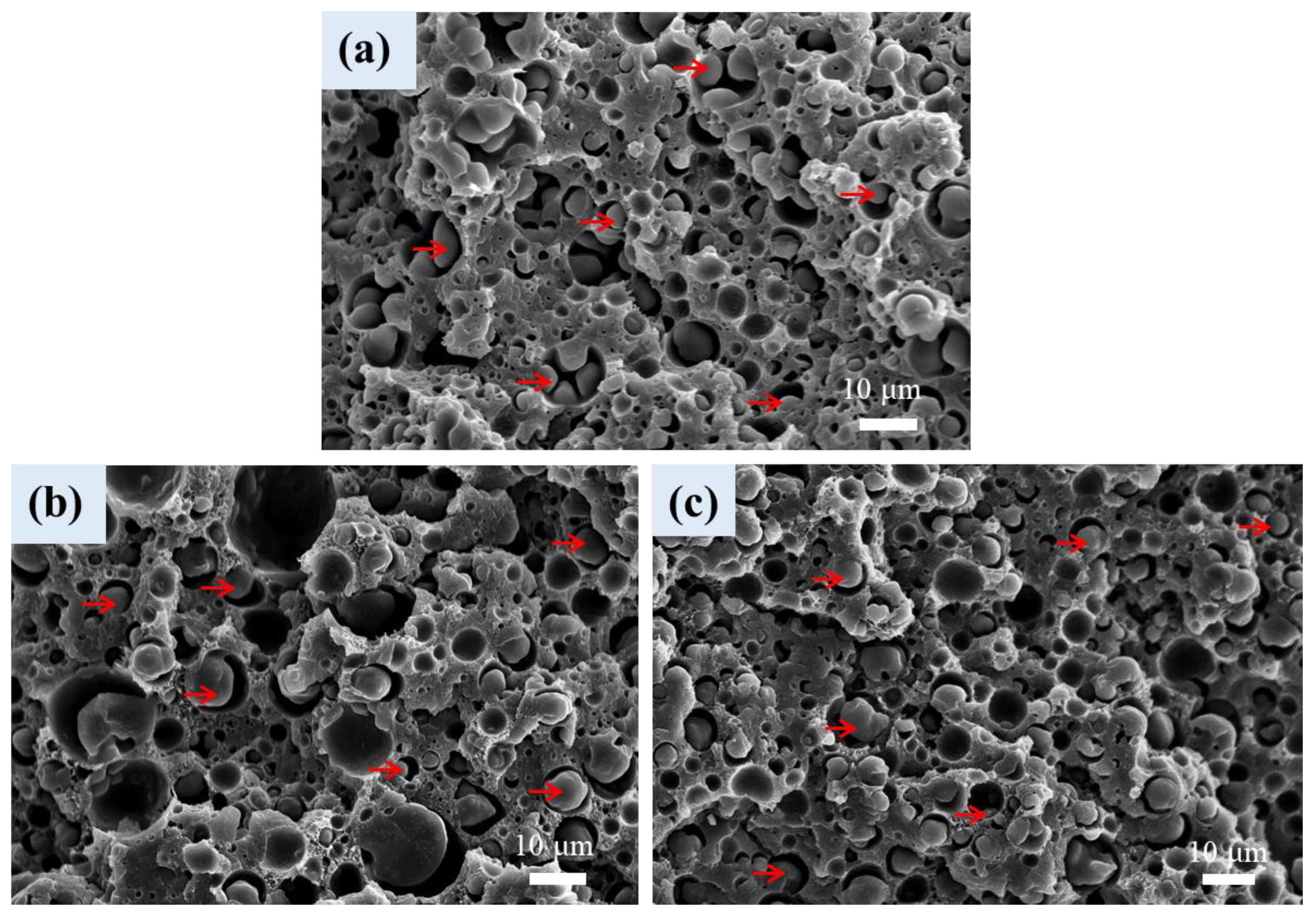
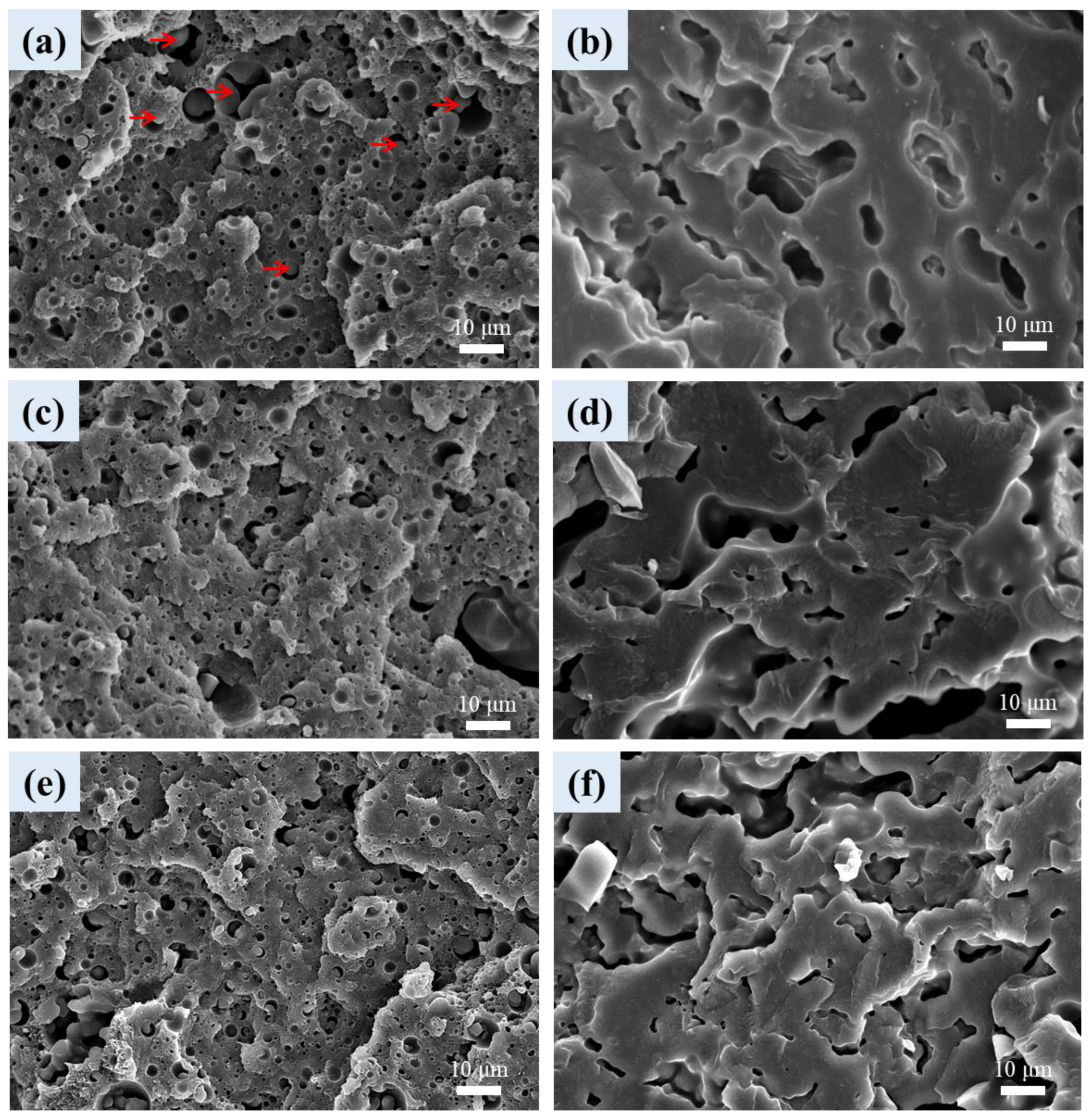
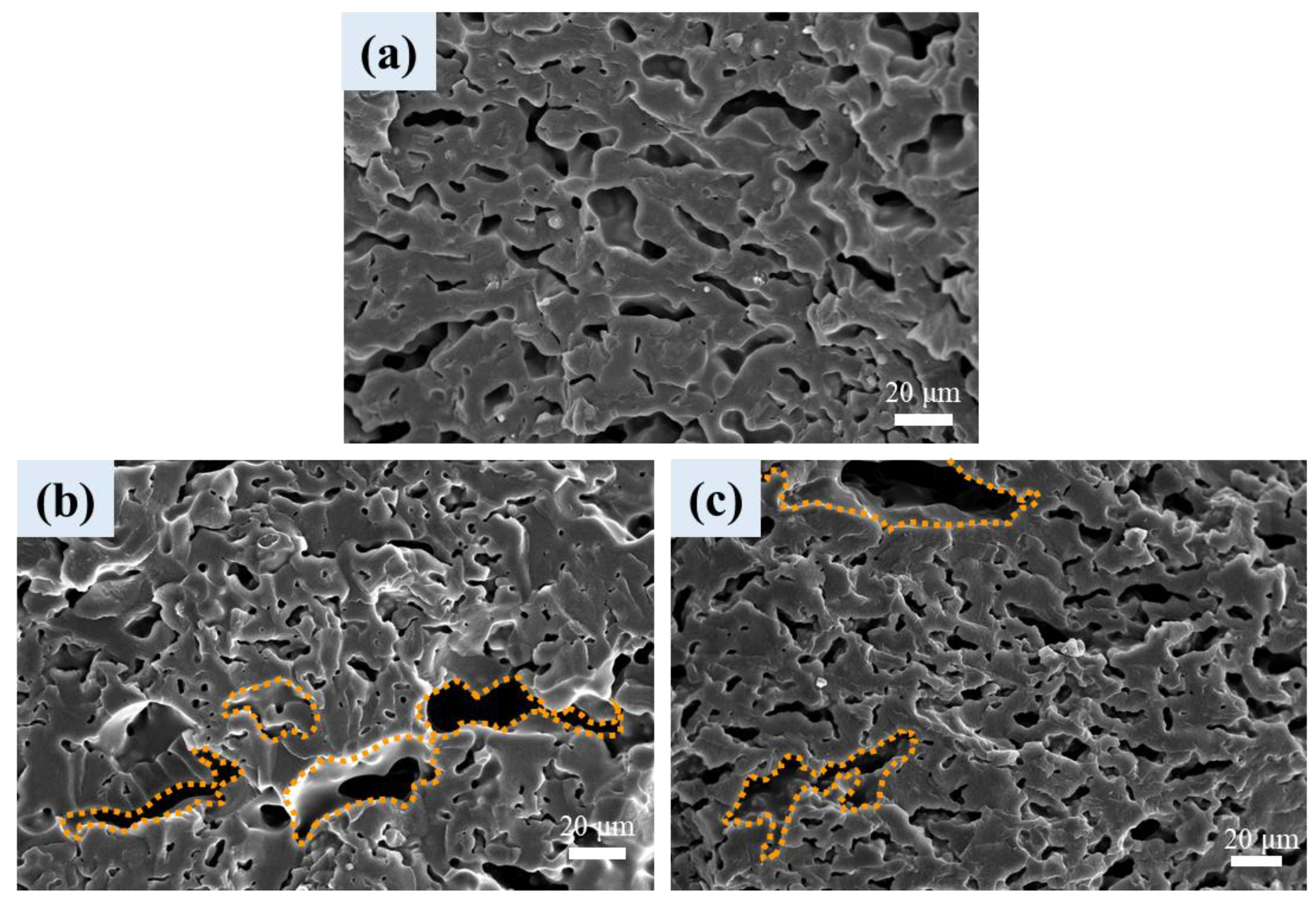
3.6. Cellular Structure of Foamed Samples
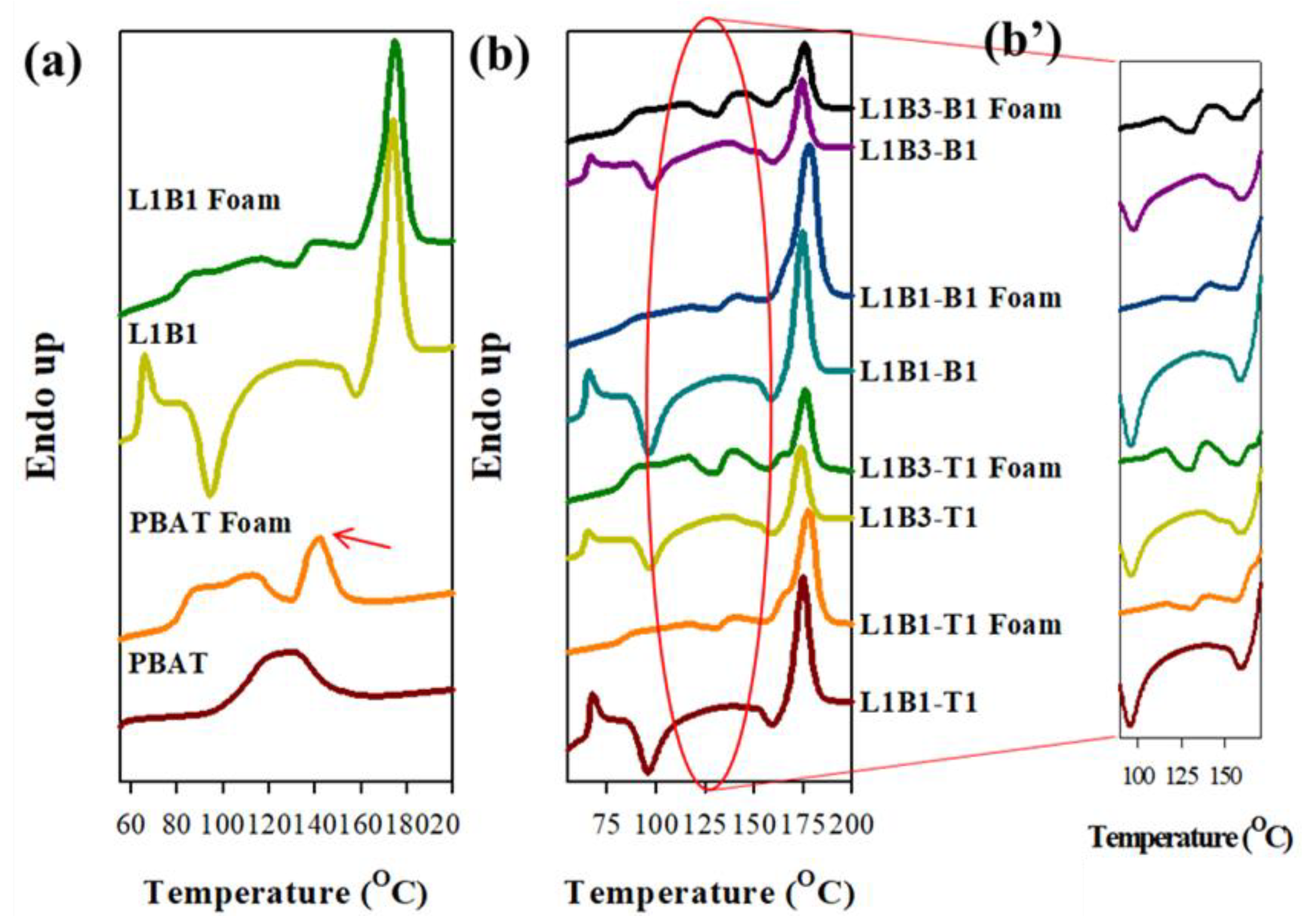
3.7. Melting Behavior of Foamed Samples
3.8. Hardness of Unfoamed/Foamed Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albano, C.; Reyes, J.; Ichazo, M.; Gonz´alez, J.; Brito, M.; Moronta, D. Analysis of the mechanical, thermal and morphological behaviour of polypropylene compounds with sisal fibre and wood flour, irradiated with gamma rays. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 76, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessanan, W.; Phinyocheep, P.; Amornsakchai, T. Sustainable materials with improved biodegradability and toughness from blends of poly(lactic acid), pineapple stem starch and modified natural rubber. Polymers 2024, 16, 232–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Abenojar, J.; Martínez, M.A.; Santiuste, C. Degradation of mechanical properties of flax/PLA composites in hygrothermal aging conditions. Polymers 2024, 16, 528–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, K.; Chang, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Chiu, F.C. PMMA-driven morphology modification and dramatic improvement in ductility for PVDF/PLA blends. Polymer 2022, 252, 124930–124941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benkraled, L.; Zennaki, A.; Zair, L.; Arabeche, K.; Berrayah, A.; Barrera, A.; Bouberka, Z.; Maschke, U. Effect of plasticization/annealing on thermal, dynamic mechanical, and rheological properties of poly(lactic acid). Polymers 2024, 16, 974–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ke, L.; Tang, M.; Shang, H.; Zhang, Z.L.; Xu, W.; Fu, Y.N.; Wang, Y.; Tang, D.; Huang, D.; et al. Pea pod-mimicking hydroxyapatite nanowhisker-reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites with bone-like strength. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboki, T. Mechanical properties and foaming behavior of injection molded cellulose fiber reinforced polypropylene composite foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2014, 50, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hikima, Y.; Ohshima, M.; Yusa, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Goto, H. Development of a simplified foam injection molding technique and its application to the production of high void fraction polypropylene foams. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 13734–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Hamidinejad, M.; Wang, S.; Bai, P.W.; Che, R.C.; Zhang, R.; Park, C.B. Advances in electromagnetic shielding properties of composite foams. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 14, 8896–8949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofar, M.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid) foaming. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1721–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, S.; Liu, B.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, D.; Cao, L.; He, L.; Gong, W. Rheological behavior, crystallization properties, and foaming performance of chain-extended poly(lactic acid) by functionalized epoxy. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 32799–32809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamad, K.; Kaseem, M.; Ayyoob, M.; Joo, J.; Deri, F. Polylactic acid blends: The future of green, light and tough. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 85, 83–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhou, J.; Odelius, K.; Guo, Z.; Guan, X.; Hakkarainen, M. Nanostructured phase morphology of a biobased copolymer for tough and UV-resistant polylactide. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, K.; Chang, Y.H.; Yadav, M.; Chiu, F.C. Enhanced thermal stability, toughness, and electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube-reinforced biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/poly(ethylene oxide) blend-based nanocomposites. Polymer 2020, 186, 122002–122014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y.; Yin, D.; Chen, S.; Tu, H.; Wei, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, H.; Jin, H. Highly enhanced mechanical, thermal, and crystallization performance of PLA/PBS composite by glass fiber coupling agent modification. Polymers 2023, 15, 3164–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boruvka, M.; Base, R.; Novak, J.; Brdlik, P.; Behalek, L.; Ngaowthong, C. Phase morphology and mechanical properties of super-tough PLLA/TPE/EMA-GMA ternary blends. Polymers 2024, 16, 192–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tamimi, A.; Pandžić, A.; Kadrić, E. Investigation and prediction of tensile, flexural, and compressive properties of tough PLA material using definitive screening design. Polymers 2023, 15, 4169–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Gu, T.; Qi, X.; Yang, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Y. Highly-toughened biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid) composites with heat resistance and mechanical-damage-healing ability by adding poly(butylene adipate-co-butylene terephthalate) and carbon nanofibers. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130558–130571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, S.; Chen, H.; Yu, X.; Zhao, X. Mechanical properties, rheological behaviors, and phase morphologies of high-toughness PLA/PBAT blends by in-situ reactive compatibilization. Compos. Part B 2019, 173, 107028–107038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Zhang, H. Mechanical properties and phase morphology of super-tough PLA/PBAT/EMA-GMA multicomponent blends. Mater. Lett. 2017, 192, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.D.; Wang, F.C.; Wu, Y.J. Effects of poly(butyleneadipate-co-terephthalate) as a macromolecular nucleating agent on the crystallization and foaming behavior of biodegradable poly(lactic acid). Cell. Polym. 2017, 36, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiuchok, O.; Iurzhenko, M.; Kolisnyk, R.; Mamunya, Y.; Godzierz, M.; Demchenko, V.; Yermolenko, D.; Shadrin, A. Polylactide/carbon black segregated composites for 3D printing of conductive products. Polymers 2022, 14, 4022–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alosime, E.M.; Basfar, A.A. A systematic investigation on the effect of carbon nanotubes and carbon black on the mechanical and flame retardancy properties of polyolefin blends. Polymers 2024, 16, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, K.; Veluri, S.; Chang, Y.H.; Yadav, M.; Chiu, F.C. Nanofillers-induced modifications in microstructure and properties of PBAT/PP blend: Enhanced rigidity, heat resistance, and electrical conductivity. Polymer 2020, 203, 122578–122590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, T.N.; Behera, K.; Chang, Y.H.; Chiu, F.C. Improving the ductility, toughness, and electrical conductivity of poly(lactic acid) by forming poly(lactic acid)/thermoplastic polyester elastomer blend and blend-based nanocomposites. Polym. Compos. 2022, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.K.; Thomas, B.; Thomas, S.B.; Tile, P.S.; Sakharwade, S.G. Carbon nanotubes as exceptional nanofillers in polymer and polymer/fiber nanocomposites: An extensive review. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 107358–107390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urquijoa, J.; Aranburua, N.; Dagréoub, S.; Guerrica-Echevarríaa, G.; Eguiazábala, J.I. CNT-induced morphology and its effect on properties in PLA/PBAT-based nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 93, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.; Heuzey, M.C.; Carreau, P.J.; Therriault, D.; Park, C.B. Mechanical and morphological properties of injection molded linear and branched-polylactide (PLA) nanocomposite foams. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livi, S.; Lins, L.C.; Sar, G.; Gerard, J.F.; Rumeau, J.D. Supercritical CO2−Ionic liquids: A successful wedding to prepare biopolymer foams. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E.; Azdast, T.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; Lee, P.C.; Park, C.B. Highly expanded finecell foam of polylactide/polyhydroxyalkanoate/nano-fibrillated polytetrafluoroethylene composites blown with mold-opening injection molding. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yin, D.; Liu, W.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Fabrication of biodegradable poly(lactic acid)/carbon nanotube nanocomposite foams: Significant improvement on rheological property and foamability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhao, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J.; Shi, Z. Biodegradable PLA/PBS open-cell foam fabricated by supercritical CO2 foaming for selective oil-adsorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 257, 117949–117959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, K.; Chang, Y.H.; Chiu, F.C. Manufacturing poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/high density polyethylene blend-based nanocomposites with enhanced burning anti-dripping and physical properties—Effects of carbon nanofillers addition. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 217, 108878–108889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample Code | Composition | Parts (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|
| PLA | PLA | 100 |
| PBAT | PBAT | 100 |
| L3B1 | PLA/PBAT | 75/25 |
| L1B1 | PLA/PBAT | 50/50 |
| L1B3 | PLA/PBAT | 25/75 |
| L3B1-T1 | PLA/PBAT/CNT | 75/25/1 * |
| L1B1-T1 | PLA/PBAT/CNT | 50/50/1 * |
| L1B3-T1 | PLA/PBAT/CNT | 25/75/1 * |
| L3B1-B1 | PLA/PBAT/CB | 75/25/1 * |
| L1B1-B1 | PLA/PBAT/CB | 50/50/1 * |
| L1B3-B1 | PLA/PBAT/CB | 25/75/1 * |
| Samples | Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti (°C) | TLc (°C) | TBc (°C) | TLm (°C) | TBm (°C) | |
| PLA | 105.0 | 88.6 | - | 177.0 | - |
| PBAT | 114.3 | - | 92.0 | - | 131.3 |
| L3B1 | 107.9 | 88.5 | - | 176.3 | |
| L3B1-T1 | 127.0 | 91.2 | - | 178.0 | |
| L3B1-B1 | 122.3 | 93.5 | 109.0 | 178.0 | |
| L1B1 | 112.0 | 88.8 | - | 175.2 | 136.2 |
| L1B1-T1 | 126.6 | 92.2 | 107.9 | 174.6 | 141.8 |
| L1B1-B1 | 119.5 | 89.5 | 107.2 | 176.6 | 143.3 |
| L1B3 | 115.0 | 90.0 | - | 175.0 | 133.7 |
| L1B3-T1 | 128.3 | - | 107.6 | 175.5 | 141.6 |
| L1B3-B1 | 122.2 | - | 115.0 | 176.5 | 143.0 |
| Samples | Properties | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T20% (°C) | T80% (°C) | TM (MPa) | TS (MPa) | EB (%) | Log ER (Ω-cm) | Cell Size (μm) | Porosity | |
| PLA | 360 | 382 | 2287 ± 49 | 61.5 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.1 | >14 | - | - |
| PBAT | 388 | 418 | 105 ± 2 | 5.6 ± 0.4 | 9.2 ± 1.3 | >14 | 7.76 ± 2.12 | 0.48 |
| L3B1 | 359 | 389 | 1812 ± 44 | 43.7 ± 1.1 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | >14 | 2.72 ± 1.27 | 0.19 |
| L3B1-T1 | 359 | 395 | 1687 ± 39 | 32.2 ± 1.3 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | >14 | 3.44 ± 1.37 | 0.26 |
| L3B1-B1 | 359 | 395 | 1662 ± 40 | 35.4 ± 1.2 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | >14 | 2.98 ± 1.26 | 0.24 |
| L1B1 | 361 | 406 | 1025 ± 55 | 13.1 ± 1.1 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | >14 | 0.84 ± 0.45 * | 0.22 |
| L1B1-T1 | 362 | 409 | 802 ± 21 | 9.3 ± 1.2 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 7.7 ± 0.5 | 0.53 ± 0.34 * | 0.19 |
| L1B1-B1 | 362 | 408 | 848 ± 38 | 8.9 ± 1.1 | 1.7 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 0.51 ± 0.35 * | 0.18 |
| L1B3 | 365 | 413 | 221 ± 5 | 7.5 ± 0.6 | 4.8 ± 0.5 | >14 | 5.25 ± 4.18 | 0.32 |
| L1B3-T1 | 366 | 414 | 229 ± 5 | 7.2 ± 0.7 | 5.0 ± 0.5 | 9.0 ± 0.7 | 3.32 ± 2.13 | 0.26 |
| L1B3-B1 | 367 | 415 | 244 ± 15 | 5.7 ± 0.4 | 4.0 ± 0.3 | 8.2 ± 0.2 | 4.30 ± 1.66 | 0.24 |
| Samples | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLA | PBAT | PBAT Foam | ||||
| Hardness | 82 | 51 | 40 | |||
| L3B1 | L3B1 foam | L3B1-T1 | L3B1-T1 foam | L3B1-B1 | L3B1-B1 foam | |
| Hardness | 71 | 60 | 73 | 61 | 72 | 63 |
| L1B1 | L1B1 foam | L1B1-T1 | L1B1-T1 foam | L1B1-B1 | L1B1-B1 foam | |
| Hardness | 61 | 53 | 62 | 55 | 63 | 58 |
| L1B3 | L1B3 foam | L1B3-T1 | L1B3-T1 foam | L1B3-B1 | L1B3-B1 foam | |
| Hardness | 53 | 41 | 55 | 43 | 54 | 43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behera, K.; Tsai, C.-H.; Liao, X.-B.; Chiu, F.-C. Fabrication and Characterization of PLA/PBAT Blends, Blend-Based Nanocomposites, and Their Supercritical Carbon Dioxide-Induced Foams. Polymers 2024, 16, 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141971
Behera K, Tsai C-H, Liao X-B, Chiu F-C. Fabrication and Characterization of PLA/PBAT Blends, Blend-Based Nanocomposites, and Their Supercritical Carbon Dioxide-Induced Foams. Polymers. 2024; 16(14):1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141971
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehera, Kartik, Chien-Hsing Tsai, Xiang-Bo Liao, and Fang-Chyou Chiu. 2024. "Fabrication and Characterization of PLA/PBAT Blends, Blend-Based Nanocomposites, and Their Supercritical Carbon Dioxide-Induced Foams" Polymers 16, no. 14: 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141971
APA StyleBehera, K., Tsai, C.-H., Liao, X.-B., & Chiu, F.-C. (2024). Fabrication and Characterization of PLA/PBAT Blends, Blend-Based Nanocomposites, and Their Supercritical Carbon Dioxide-Induced Foams. Polymers, 16(14), 1971. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16141971






