Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
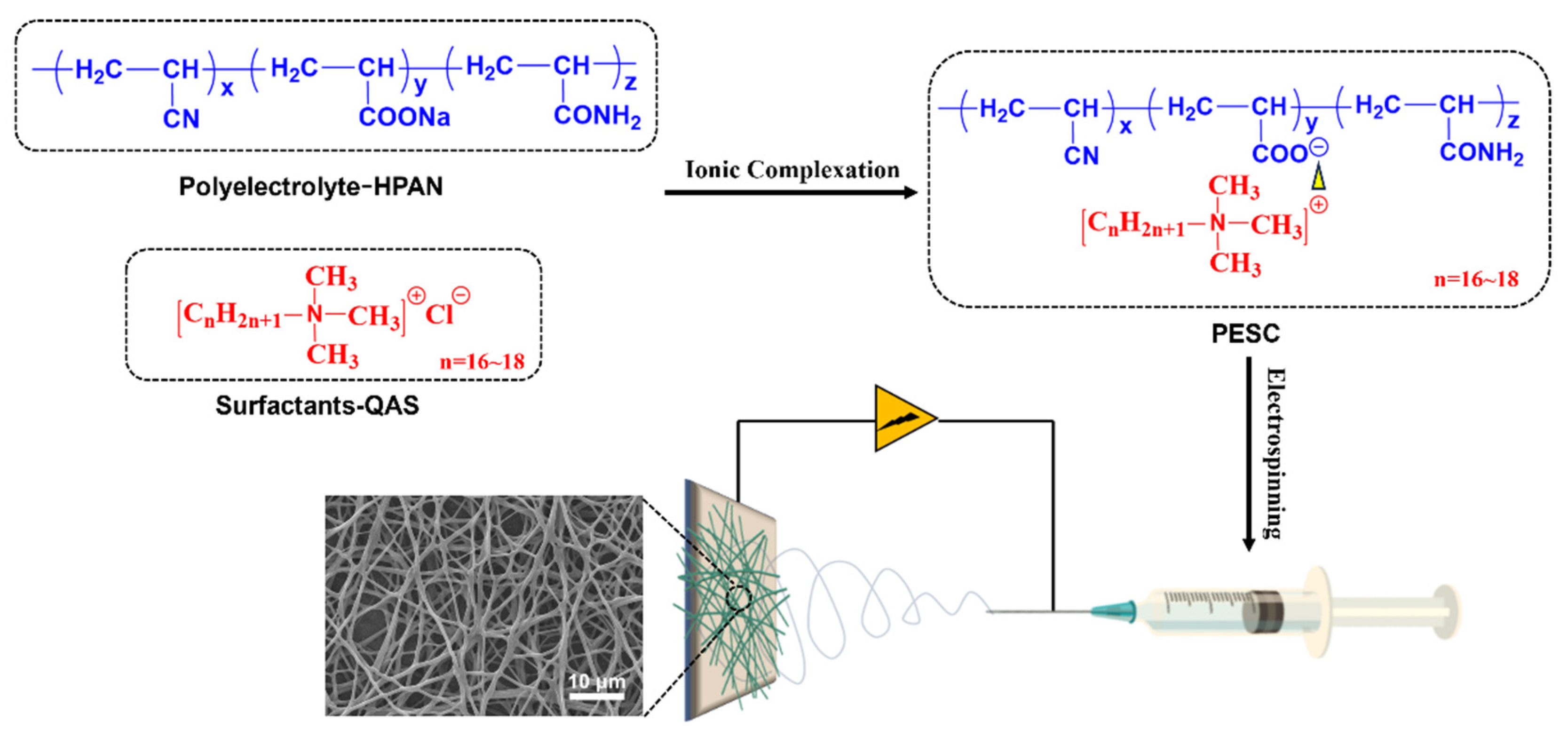
2.2. Preparation of PESC Polymers
2.3. Preparation of PESCs and PESCs/PCL Electrospun Fibers
2.4. Analysis of the Formation Process of PESCs
2.5. Characterization
2.6. Antibacterial Activity Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
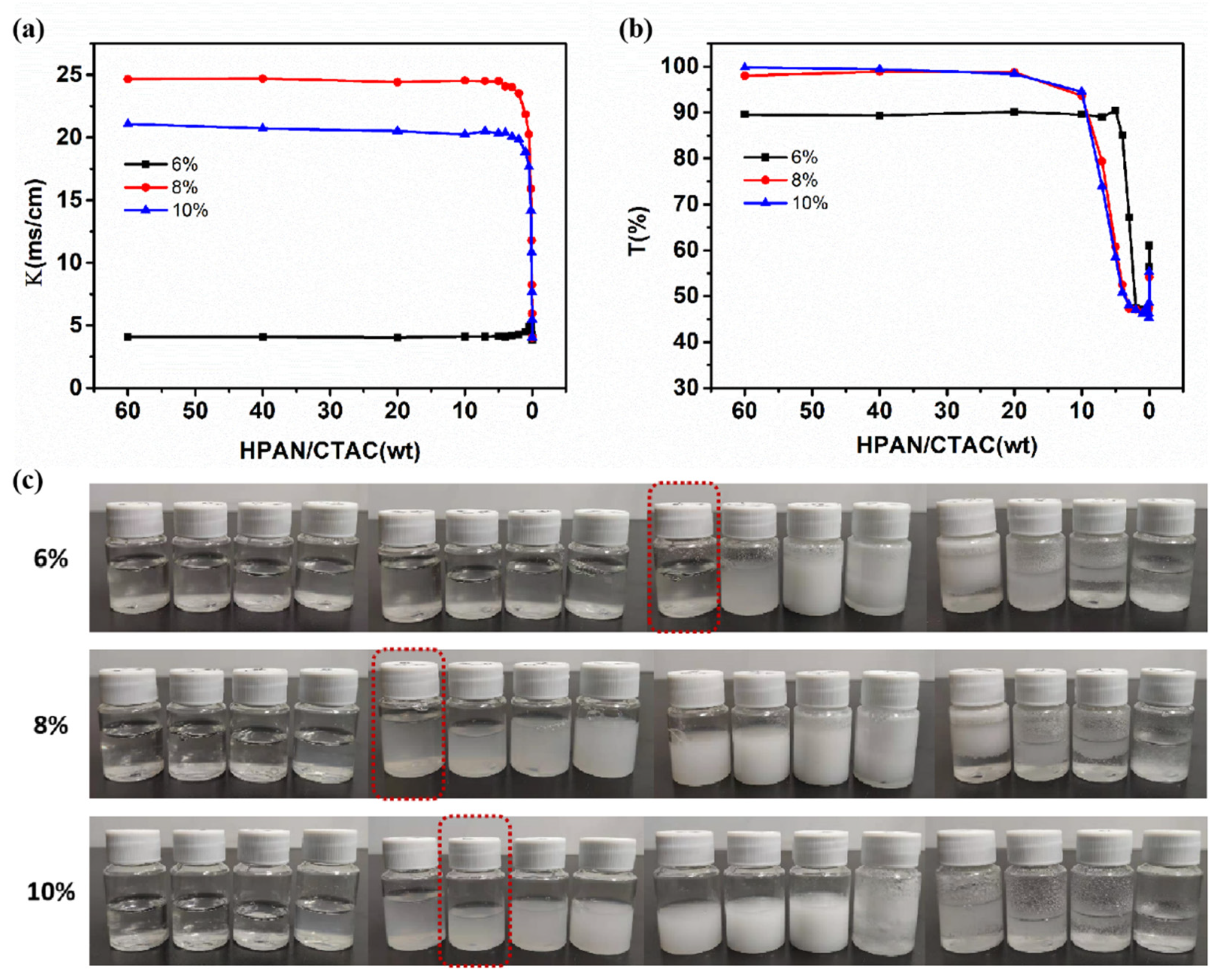
3.1. Effects of NaOH Solution Concentration and PAN-to-NaOH Mass Ratio on PESC System
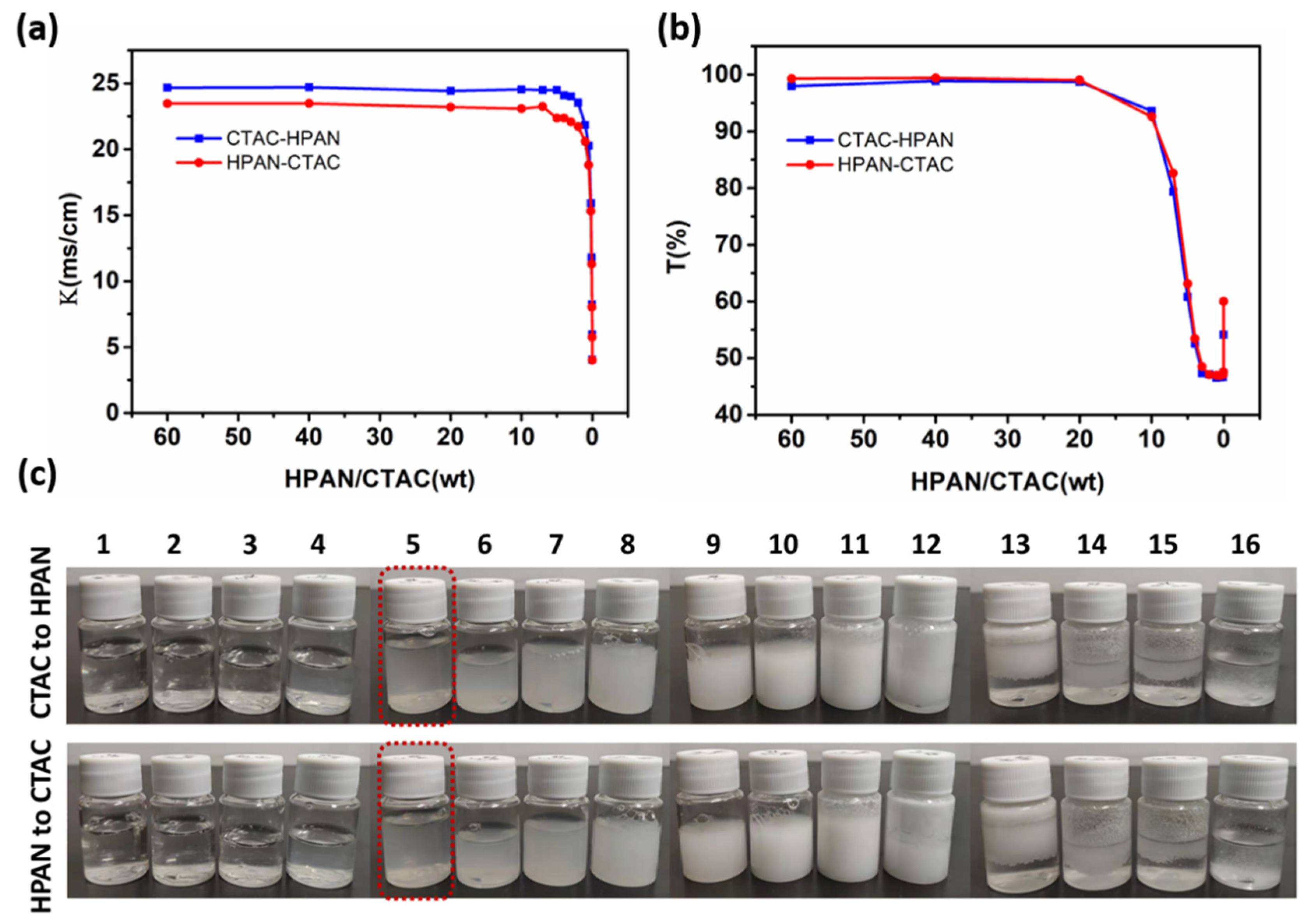
3.2. Effects of Raw Material Adding Sequence on the PESC System
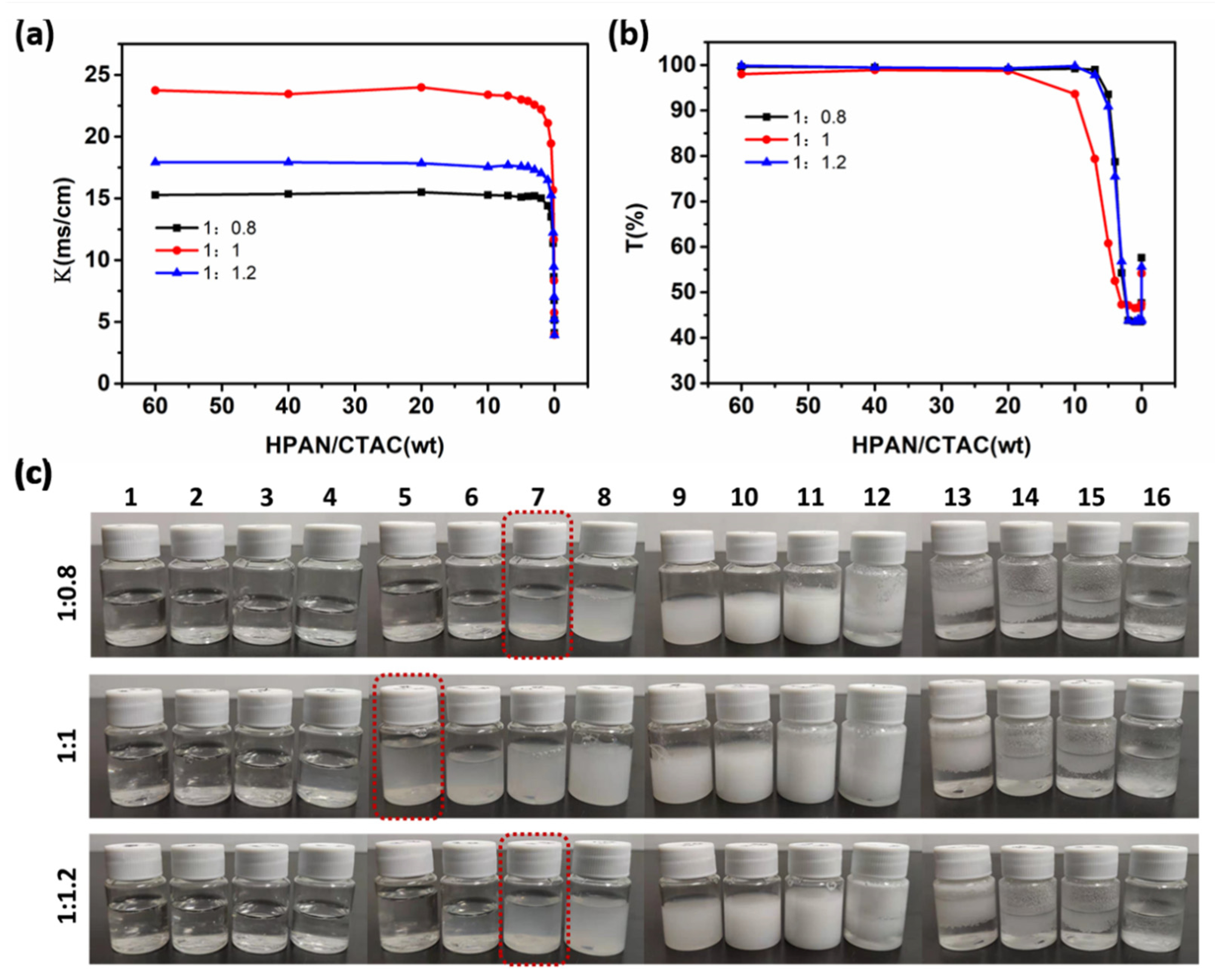
3.3. Effects of Alkyl Chain Length on PESC System
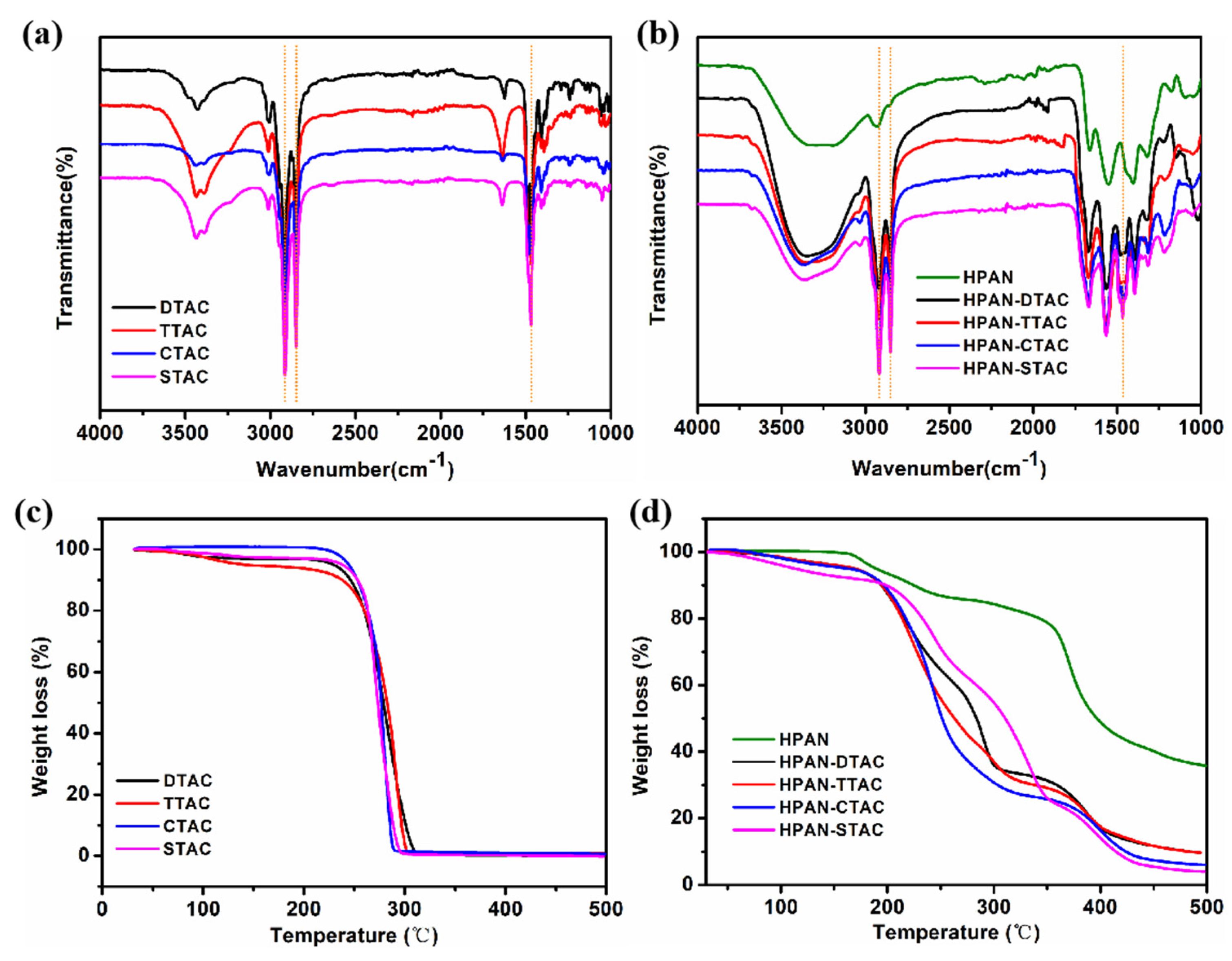
3.4. Characterization of Solid PESCs
3.5. Characterization of PESCs and PESC/PCL NFs
3.6. Mechanical Analysis
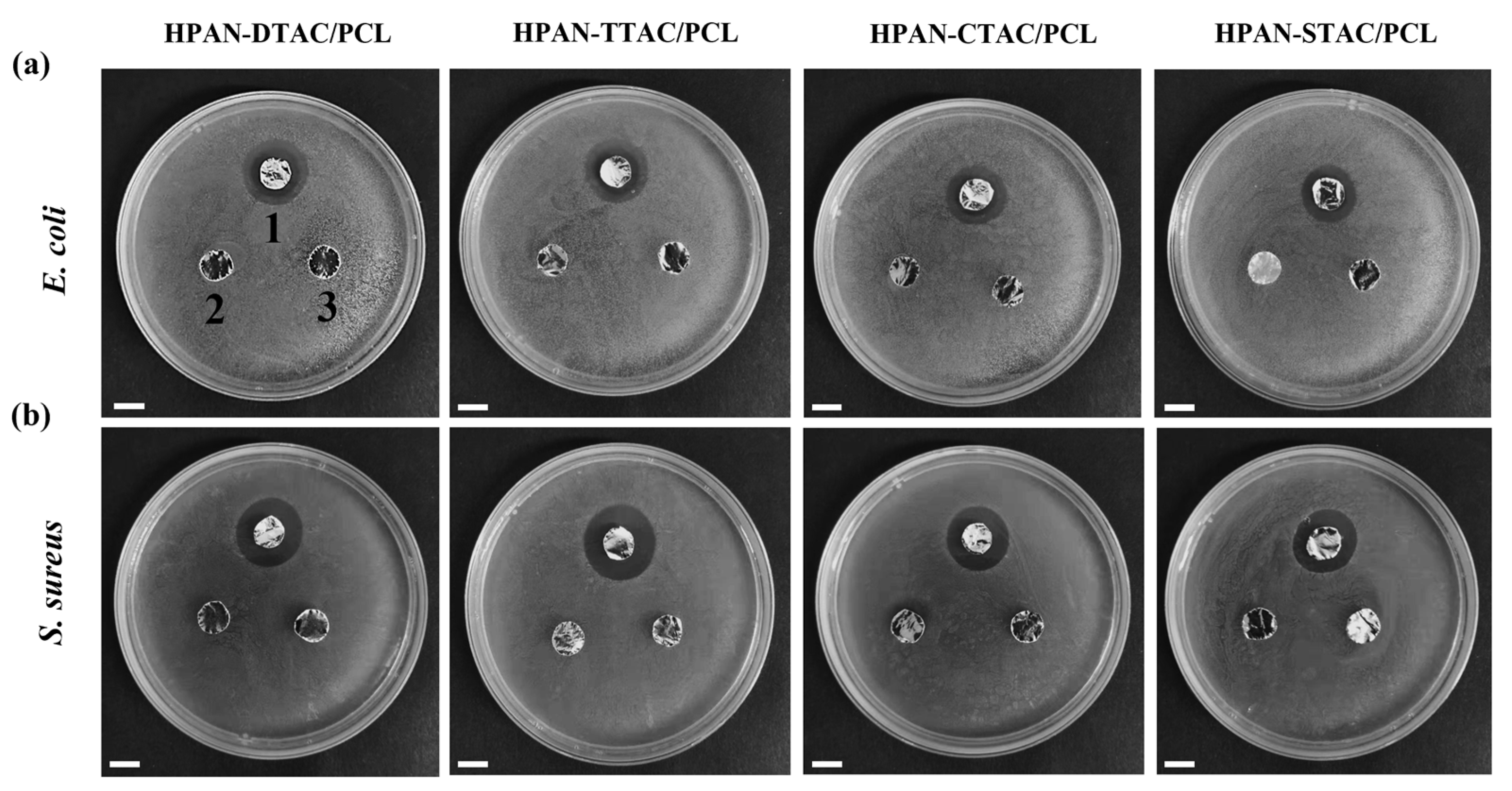
3.7. Antibacterial Activity of PESC/PCL NFs
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyake, M. Recent progress of the characterization of oppositely charged polymer/surfactant complex in dilution deposition system. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, D. Complexation of oppositely charged polyelectrolytes and surfactants in aqueous solutions. A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madinya, J.J.; Tjo, H.; Meng, X.; Ramírez Marrero, I.A.; Sing, C.E.; Perry, S.L. Surface Charge Density and Steric Repulsion in Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Coacervation. Macromolecules 2023, 11, 3973–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, X.; Martin, N.; Tian, L. Engineering the Coacervate Microdroplet Interface via Polyelectrolyte and Surfactant Complexation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 27447–27456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Brettmann, B. Intermolecular Interactions in Polyelectrolyte and Surfactant Complexes in Solution. Polymers 2019, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llamas, S.; Guzmán, E.; Ortega, F.; Baghdadli, N.; Cazeneuve, C.; Rubio, R.G.; Luengo, G.S. Adsorption of polyelectrolytes and polyelectrolytes-surfactant mixtures at surfaces: A physico-chemical approach to a cosmetic challenge. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 461–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhur, A.M.; Diaz, J.; Amin, S. Impact of polyelectrolyte-surfactant interactions on the rheology and wet lubrication performance of conditioning shampoo. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.; Turgeon, S.L. Protein/polysaccharide complexes and coacervates in food systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 167, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharipova, A.; Aidarova, S.; Grigoriev, D.; Mutalieva, B.; Madibekova, G.; Tleuova, A.; Miller, R. Polymer–surfactant complexes for microencapsulation of vitamin E and its release. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 137, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, U.K.; Brown, J.L.; Lapitsky, Y. Poly(allylamine)/tripolyphosphate coacervates enable high loading and multiple-month release of weakly amphiphilic anionic drugs: An in vitro study with ibuprofen. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 19409–19419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtič, J.; Kogej, K.; Baumgartner, S.; Smistad, G.; Kristl, J.; Hiorth, M. Development of Cetylpyridinium-Alginate Nanoparticles: A Binding and Formulation Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 511, 774–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homaeigohar, S.; Boccaccini, A.R. Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2020, 107, 25–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Kang, S.-X.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Yu, D.-G. Electrospun Functional Nanofiber Membrane for Antibiotic Removal in Water: Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wang, C.; Wei, Y. One-dimensional composite nanomaterials: Synthesis by electrospinning and their applications. Small 2009, 5, 2349–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donner, R.; Potirakis, S.; Balasis, G.; Eftaxias, K.; Kurths, J. Electrospun fiber-based strategies for controlling early innate immune cell responses: Towards immunomodulatory mesh designs that facilitate robust tissue repair. Phys. Chem. Earth 2023, 163, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassalah, M.E.; Cerdà, J.J.; Sintes, T.; Aschi, A.; Othman, T. Complex between cationic like-charged polyelectrolytes/surfactants systems. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 96, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durmaz, E.N.; Sahin, S.; Virga, E.; de Beer, S.; de Smet, L.C.P.M.; de Vos, W.M. Polyelectrolytes as Building Blocks for Next-Generation Membranes with Advanced Functionalities. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4347–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josef, E.; Guterman, R. Designing Solutions for Electrospinning of Poly(ionic liquid)s. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 5223–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Perry, S.L.; Schiffman, J.D. Complex Coacervation: Chemically Stable Fibers Electrospun from Aqueous Polyelectrolyte Solutions. ACS Macro Lett. 2017, 6, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Schiffman, J.D.; Perry, S.L. Electrospinning Cargo-Containing Polyelectrolyte Complex Fibers: Correlating Molecular Interactions to Complex Coacervate Phase Behavior and Fiber Formation. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 8821–8832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegel, C.; Kit, K.; McClements, D.; Weiss, J. Electrospinning of chitosan–poly(ethylene oxide) blend nanofibers in the presence of micellar surfactant solutions. Polymer 2009, 50, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Bowlin, G.L.; Mansfield, K.; Layman, J.; Simpson, D.G.; Sanders, E.H.; Wnek, G.E. Release of tetracycline hydrochloride from electrospun poly(ethylene-co-vinylacetate), poly(lactic acid), and a blend. J. Control. Release 2002, 81, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, M.B.; Kim, A.A. Silver nanoparticles decorated TiO2 nanoflakes for antibacterial properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 152, 110675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Quan, Z.; Qin, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, J. Functional nanofibers embedded into textiles for durable antibacterial properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 384, 123241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, H.; Sogame, Y.; Purevdorj, U.-E.; Ogata, M.; Tajima, K. Bacterial cellulose nanofibers modified with quaternary ammonium salts for antimicrobial applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 4854–4863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Geng, H.; Gong, M.; Ye, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Long-acting and broad-spectrum antimicrobial electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone)/gelatin micro/nanofibers for wound dressing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Long, H.; Yu, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, H. Hierarchical Surface Inspired by Geminized Cationic Amphiphilic Polymer Brushes for Super-Antibacterial and Self-Cleaning Properties. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 5213–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Q.; Wu, J.; Quan, Z.; Zhang, H.; Qin, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, J. Electrospun nanofibers of polyelectrolyte–surfactant complexes for antibacterial wound dressing application. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 10020–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.Y.; Kim, M.H.; Jeong, Y.G.; Yoon, Y.I.; Park, W.H. Effect of alkaline hydrolysis on cyclization reaction of PAN nanofibers. Mater. Des. 2017, 124, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.-L.; Chao, W.-C.; Hung, W.-S.; An, Q.; De Guzman, M.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R. Physicochemical effects of hydrolyzed asymmetric polyacrylonitrile membrane microstructure on dehydrating butanol. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 490, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, E.D. Polymer-surfactant interaction: Part II: Polymer and surfactant of opposite charge. In Interactions of Surfactants with Polymers and Proteins; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1986; Volume 19, pp. 301–329. [Google Scholar]
- Gradzielski, M.; Gradzielski, M. Polyelectrolyte–surfactant complexes as a formulation tool for drug delivery. Langmuir 2022, 38, 13330–13343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.F.; Schneider, G.F.; Whitesides, G.M. Effect of surfactant hydrophobicity on the pathway for unfolding of ubiquitin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 18739–18745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Holmberg, K.; Lindman, B. Cationic surfactants: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 375, 121335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberg, B. The hydrophobic effect. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 22, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, B.; Jin, H.; Chen, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, L. Intrinsically antibacterial thin film composite membranes with supramolecularly assembled lysozyme nanofilm as selective layer for molecular separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Pan, G.; Ge, Y.; Yang, X. Preparation of a low-protein-fouling and high-protein-retention membrane via novel pre-hydrolysis treatment of polyacrylonitrile (PAN). Membranes 2023, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, J.P.; Fontana, C.M. The thermal degradation of polyacrylonitrile. J. Polym. Sci. 1959, 39, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-A.; Qu, Z.; Meng, H.; Chen, B.; Wu, X.; Cui, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, K.; Shi, J.; Lu, M. Effect of polydopamine-modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the thermal stability and conductivity of UV-curable polyurethane/polysiloxane pressure-sensitive adhesives. Polymer 2021, 223, 123615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, Z.M.; Soleimani, M.; Ghasemi-Mobarakeh, L.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Sharifianjazi, F.; Esmaeilkhanian, A.; Khaksar, S. Control of drug release from cotton fabric by nanofibrous mat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 217, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, S.; Hashmi, M.; Kharaghani, D.; Khan, M.Q.; Saito, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Lee, J.; Kim, I.S. Antibacterial properties of in situ and surface functionalized impregnation of silver sulfadiazine in polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustine, R.; Dominic, E.A.; Reju, I.; Kaimal, B.; Kalarikkal, N.; Thomas, S. Electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)-based skin substitutes: In vivo evaluation of wound healing and the mechanism of cell proliferation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 1445–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy, O.E.; Ates, B.; Cerkez, I. Antibacterial polyacrylonitrile nanofibers produced by alkaline hydrolysis and chlorination. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 10013–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliścińska, E.; Gutarowska, B.; Brycki, B.; Krucińska, I. Electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers modified by quaternary ammonium salts. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Lan, L. Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030414
Qiu Q, Wang Z, Lan L. Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications. Polymers. 2024; 16(3):414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030414
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Qiaohua, Zhengkai Wang, and Liying Lan. 2024. "Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications" Polymers 16, no. 3: 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030414
APA StyleQiu, Q., Wang, Z., & Lan, L. (2024). Polyelectrolyte–Surfactant Complex Nanofibrous Membranes for Antibacterial Applications. Polymers, 16(3), 414. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16030414





