Development of Novel Cornstarch Hydrogel-Based Food Coolant and its Characterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.3. FTC of Hydrogels
2.4. Texture Determination
2.5. Melting Latent Heat
2.6. The Measurement of the Cooling Rate
2.7. Melting Curves
2.8. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Observation
2.9. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.10. Water Retention Measurement
2.11. Rehydration Capacity
2.12. Cooling Curve of Fresh Grapes and Blueberries
2.13. Surface Cleaning
2.14. Statistical Methods
3. Results
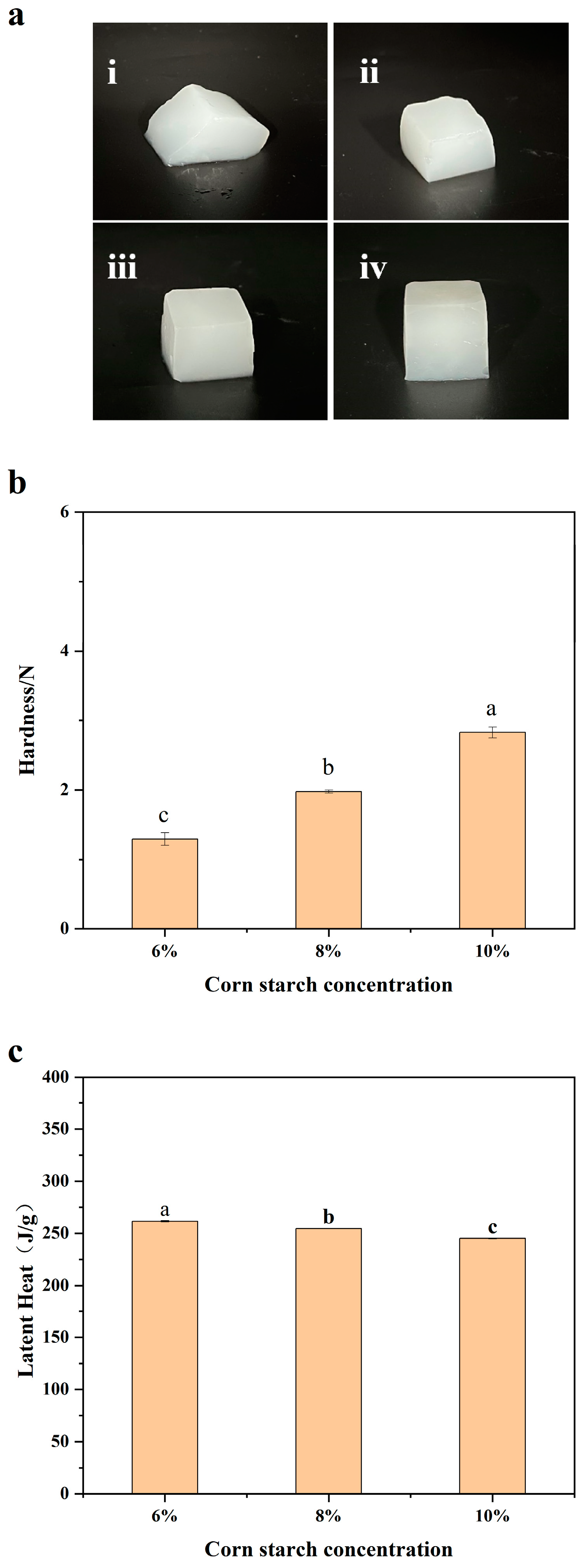
3.1. Determination of the Concentration
3.2. Temperature Profiles of Freezing and Melting Times
3.3. Properties of Hydrogels along FTCs
3.4. Water Retention, Rehydration, and Cooling Efficiency
3.5. Surface Cleaning of Cornstarch Hydrogel Ice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, C.; Sun, D.; García Martín, J.F.; Zhang, Z. Effects of different cooling methods on shelf-life of cooked jumbo plain sausages. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 54, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, G. Sustainable and Reusable Gelatin-Based Hydrogel “Jelly Ice Cubes” as Food Coolant. I: Feasibilities and Challenges. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 15357–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Rubina Gilani, S.; Iqbal Durani, A.; Naseem, S. Materials diversity of hydrogel: Synthesis, polymerization process and soil conditioning properties in agricultural field. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 33, 15–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh Kaith, B.; Rohit; Kumar, R. Psyllium Polysaccharide-Based hydrogels as smart Biomaterials: Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 53, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Wu, G.; Ao, N.; et al. Injectable andIn Situ-Formable Thiolated Chitosan-Coated Liposomal Hydrogels as Curcumin Carriers for Prevention of In Vivo Breast Cancer Recurrence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17936–17948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, M.A.; Bernardes, A.; De Azevêdo, E.R.; Guimarães, F.E.G.; Lowe, J.P.; Gale, E.M.; Polikarpov, I.; Scott, J.L.; Sharma, R.I. On the subtle tuneability of cellulose hydrogels: Implications for binding of biomolecules demonstrated for CBM 1. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3879–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AC Hernández-González, L.T.A.L. Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 229, 115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Wu, H.; Zheng, W.; Kan, D.; Cheng, R.; Yan, J.; Yu, C.; Sun, S. Biocompatible Iodine–Starch–Alginate Hydrogel for Tumor Photothermal Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 3654–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, H.; Irani, M.; Ahmad, Z. Starch-Based Hydrogels: Present Status and Applications. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 2013, 62, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yu, M.; Ji, N.; Dai, L.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Recent advances in the preparation, characterization, and food application of starch-based hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Copeland, L.; Niu, Q.; Wang, S. Starch Retrogradation: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2015, 14, 568–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichuwong, S.; Isono, N.; Jiang, H.; Mishima, T.; Hisamatsu, M. Freeze–thaw stability of starches from different botanical sources: Correlation with structural features. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 1275–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetapan, N.; Limparyoon, N.; Gamonpilas, C.; Methacanon, P.; Fuongfuchat, A. Effect of cryogenic freezing on textural properties and microstructure of rice flour/tapioca starch blend gel. J. Food Eng. 2015, 151, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, M.; Bayer, Ö.; Kırtıl, E.; Bayındırlı, A. Effect of freezing rate and storage on the texture and quality parameters of strawberry and green bean frozen in home type freezer. Int. J. Refrig. 2018, 88, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, E.; Kioupis, D.; Kakali, G.; Stoforos, N.G.; Mandala, I. Effect of starch concentration and resistant starch filler addition on the physical properties of starch hydrogels. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 5340–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, S.G. Some Studies on Starch Gelation. Starch-Stärke 1985, 37, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, P. Dynamic propagation of ice-water phase front in a supercooled water droplet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 152, 119468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z.; Pan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ai, Z. A Comparative Study of Different Freezing Methods on Water Distribution, Retrogradation, and Digestion Properties of Liangpi (Starch Gel Food). Starch-Stärke 2022, 74, 2100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.Y.; Chin, N.L.; Yusof, Y.A. Rheological and textural studies of fresh and freeze-thawed native sago starch–sugar gels. II. Comparisons with other starch sources and reheating effects. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Xu, M.; Gou, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, W. Effect of repeated freezing-thawing on structural, physicochemical and digestible properties of normal and waxy starch gels. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 2668–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varavinit, S.; Shobsngob, S.; Varanyanond, W.; Chinachoti, P.; Naivikul, O. Freezing and Thawing Conditions Affect the Gel Stability of Different Varieties of Rice Flour. Die Stärke 2002, 54, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hong, Y.; Gu, Z. Effect of NaCl addition on the freeze-thaw stability of tapioca starch gels. Starch-Stärke 2015, 67, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.Y.; Huang, T.; Bai, C.H.; Fu, Z. Influences of chitosan on freeze–thaw stability ofArenga pinnata starch. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muadklay, J.; Charoenrein, S. Effects of hydrocolloids and freezing rates on freeze–thaw stability of tapioca starch gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2008, 22, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Yang, R.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Chen, J.; Hu, X.; Wu, J. Improvement in freeze-thaw stability of rice starch gel by inulin and its mechanism. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenrein, S.; Tatirat, O.; Rengsutthi, K.; Thongngam, M. Effect of konjac glucomannan on syneresis, textural properties and the microstructure of frozen rice starch gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byars, J.A.; Singh, M.; Kenar, J.A. Effect of hydrocolloids on functional properties of navy bean starch. Starch-Stärke 2017, 69, 1600305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Wang, L.; Sun, G. Mechanisms and performances of physically and chemically crosslinked gelatin-based hydrogels as advanced sustainable and reusable “Jelly Ice Cube” coolants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 34087–34096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Sbodio, A.O.; Blanco Ulate, B.; Wang, L.; Sun, G. Novel Robust Reusable Microbial-Resistant and Compostable Protein-Based Cooling Media. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2201347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freschi, J.; Doran, L.; Malumba, P.; Blecker, C. Impact of freezing and thawing processes on wheat and potato starch gel syneresis. Starch-Stärke 2014, 66, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Starch retrogradation studied by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, C.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X. Sub-zero temperature preservation of fruits and vegetables: A review. J. Food Eng. 2020, 275, 109881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Ukwatta, R.H.; Xue, F.; Li, C. Development of Novel Cornstarch Hydrogel-Based Food Coolant and its Characterization. Polymers 2024, 16, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050569
Zheng Y, Ma Y, Ukwatta RH, Xue F, Li C. Development of Novel Cornstarch Hydrogel-Based Food Coolant and its Characterization. Polymers. 2024; 16(5):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050569
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Yalu, Yan Ma, Ruchika Hansanie Ukwatta, Feng Xue, and Chen Li. 2024. "Development of Novel Cornstarch Hydrogel-Based Food Coolant and its Characterization" Polymers 16, no. 5: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050569
APA StyleZheng, Y., Ma, Y., Ukwatta, R. H., Xue, F., & Li, C. (2024). Development of Novel Cornstarch Hydrogel-Based Food Coolant and its Characterization. Polymers, 16(5), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16050569






