A Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (eMIP) to Determine Gallic Acid in Non-Alcoholic and Alcoholic Beverages
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. Modification of SPCs by eMIP and eNIP
2.3. Voltammetric and Amperometric Measurements
3. Results
3.1. SPC’s Working Electrode Modification by eMIP and Its Characterization
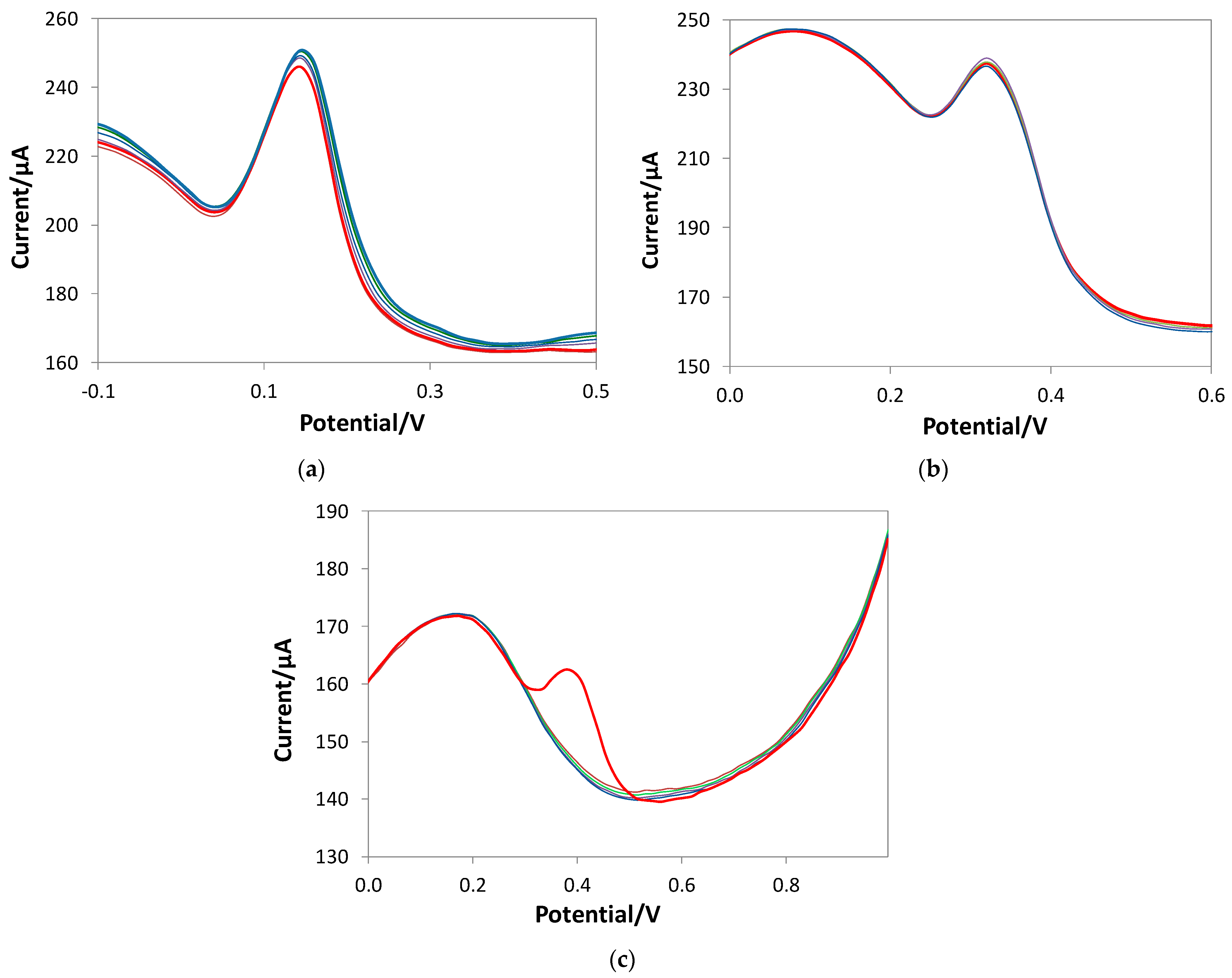
3.2. Characterization of the Gallic Acid Oxidation Reaction at the Bare and eMIP-Modified Electrodes
3.3. Quantitative Analysis of Gallic Acid by DPV
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brewer, M.S. Natural antioxidants: Sources, compounds, mechanisms of action, and potential applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roidoung, S.; Dolan, K.D.; Siddiq, M. Gallic acid as a protective antioxidant against anthocyanin degradation and color loss in vitamin-C fortified cranberry juice. Food Chem. 2016, 210, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Halquist, M.S.; Sweet, D.H. Simultaneous determination of gallic acid and gentisic acid in organic anion transporter expressing cells by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 937, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koçak, Ç.C.; Karabiberoğlu, Ş.U.; Dursun, Z. Highly sensitive determination of gallic acid on poly (l-Methionine)-carbon nanotube composite electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 853, 113552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, K.; Ning, Y.; Zhao, G. Effect of the structure of gallic acid and its derivatives on their interaction with plant ferritin. Food Chem. 2016, 213, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Węgiel, J.; Burnat, B.; Skrzypek, S. A graphene oxide modified carbon ceramic electrode for voltammetric determination of gallic acid. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 88, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.K.; Lafontaine, P.; Harnois, J. Gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of acids and phenols in distilled alcohol beverages. Application of anion-exchange disk extraction combined with in-vial elution and silylation. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 873, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Cheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.J. A validated solid-phase extraction HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of gallic acid, catechin and epicatechin in rhubarb decoction. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2012, 10, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.E.; Jiang, T.F.; Shi, Y.P. Determination of gallic acid and salidroside in Rhodiola and its preparation by capillary electrophoresis. J. Anal. Chem. 2006, 61, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrienko, S.G.; Medvedeva, O.M.; Ivanov, A.A.; Shpigun, O.A.; Zolotov, Y.A. Determination of gallic acid with 4-nitrobenzenediazonium tetrafluoroborate by diffuse reflectance spectrometry on polyurethane foam. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 469, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.A.; Li, H.; Lin, J.M. Enhancement of periodate-hydrogen peroxide chemiluminescence by nitrogen doped carbon dots and its application for the determination of pyrogallol and gallic acid. Talanta 2016, 153, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermis, N.; Zare, N.; Darabi, R.; Alizadeh, M.; Karimi, F.; Singh, J.; Shahidi, S.A.; Dragoi, E.N.; Camarada, M.B.; Baghayeri, M. Recent advantage in electrochemical monitoring of gallic acid and kojic acid: A new perspective in food science. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2023, 17, 3644–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Hu, T.; You, L.; Chen, W.; Jia, D.; Hu, N.; Qi, W. Electrochemical detection of gallic acid in green tea using molecularly imprinted polymers on TiO2@ CNTs nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2022, 17, 220426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, T.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.; Wang, G.; Feng, J.; Zhang, W. Facile potentiometric sensing of gallic acid in edible plants based on molecularly imprinted polymer. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2622–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, S.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Entezam, M.; Koosha, M.; Azimzadeh, M. An electrochemical nanosensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) for detection of gallic acid in fruit juices. Food Anal. Method 2016, 9, 2721–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, R.R.; Lakshmanakumar, M.; Arockia Jayalatha, J.B.B.; Rajan, K.S.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Fabrication of screen-printed electrodes: Opportunities and challenges. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 8951–9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renedo, O.D.; Alonso-Lomillo, M.A.; Martínez, M.A. Recent developments in the field of screen-printed electrodes and their related applications. Talanta 2007, 73, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, K.; Linares, A.V.; Bompart, M.; Bui, B.T.S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. In Topics in Current Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 325, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Beltran, A.; Borrull, F.; Marcé-Recasens, R.M.; Cormack, P. Molecularly-imprinted polymers: Useful sorbents for selective extractions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.; Andersson, H.; Andersson, L.I.; Ansell, R.J.; Kirsch, N.; Nicholls, I.A.; O’Mahony, J.; Whitcombe, M.J. Molecular imprinting science and technology: A survey of the literature for the years up to and including 2003. J. Mol. Recognit. 2006, 19, 106–180. [Google Scholar]
- Kupai, J.; Razali, M.; Buyuktiryaki, S.; Kecili, R.; Szekely, G. Long-term stability and reusability of molecularly imprinted polymers. Polym. Chem. 2016, 8, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhem, A.J.; Gentile, G.J.; Fidalgo de Cortalezzi, M.M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) in Sensors for Environmental and Biomedical Applications: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibl, N.; Haupt, K.; Gonzato, C.; Duma, L. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chemical Sensing: A Tutorial Review. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Pandey, I.; Srivastava, A.; Kumar, D.; Tiwari, M.P. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes-based pencil graphite electrode modified with an electrosynthesized molecularly imprinted nanofilm for electrochemical sensing of methionine enantiomers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 176, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral-Miranda, G.; Gidlund, M.; Sales, M.G.F. Backside-surface imprinting as a new strategy to generate specific plastic antibody materials. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 3087–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.; Sharma, S.; Dutra, R.A.; Noronha, J.P.; Cass, A.E.; Sales, M.G.F. Protein-responsive polymers for point-of-care detection of cardiac biomarker. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.P.G.; Silva, M.S.V.; Freitas, M.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for the point-of-care detection of a breast cancer biomarker (CA 15-3). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, P.; Costa-Rama, E.; Seguro, I.; Pacheco, J.G.; Nouws, H.P.A.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted polymer-based electrochemical sensors for environmental analysis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 172, 112719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.; Pacheco, J.; Rebelo, P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor prepared on a screen printed carbon electrode for naloxone detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguro, I.; Rebelo, P.; Pacheco, J.G.; Delerue-Matos, C. Electropolymerized, Molecularly Imprinted Polymer on a Screen-Printed Electrode—A Simple, Fast, and Disposable Voltammetric Sensor for Trazodone. Sensors 2022, 22, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.A.; Mounssef, B., Jr.; Carvalho, F.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Braga, A.A.; Aldous, L.; Gonçalves, L.M.; Quinaz, M.B. Methylone screening with electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymer on screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 316, 128133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, P.; Pacheco, J.G.; Voroshylova, I.V.; Melo, A.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.; Delerue-Matos, C. A simple electrochemical detection of atorvastatin based on disposable screen-printed carbon electrodes modified by molecularly imprinted polymer: Experiment and simulation. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1194, 339410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.M. Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polymers: Perceptions based on recent literature for soon-to-be world-class scientists. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2021, 25, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; Grinsven, B.v.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, C.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted thin film surfaces in sensing: Chances and challenges. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 161, 104855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavičius, S.; Morkvėnaitė-Vilkončienė, I.; Samukaitė-Bubnienė, U.; Ratautaitė, V.; Plikusienė, I.; Viter, R.; Ramanavičius, A. Electrochemically Deposited Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Sensors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Charge transfer and biocompatibility aspects in conducting polymer-based enzymatic biosensors and biofuel cells. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadki, S.; Schottland, P.; Brodie, N.; Sabouraud, G. The mechanisms of pyrrole electropolymerization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Burak, D.; Emregul, E.; Emregul, K.C. Copper–zinc alloy nanoparticle based enzyme-free superoxide radical sensing on a screen-printed electrode. Talanta 2015, 134, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Pesavento, M.; Merli, D.; Biesuz, R.; Alberti, G.; Marchetti, S.; Milanese, C. A MIP-based low-cost electrochemical sensor for 2-furaldehyde detection in beverages. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1142, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesavento, M.; D’Agostino, G.; Alberti, G.; Biesuz, R.; Merli, D. Voltammetric platform for detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene based on a molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundian, M.; Alizadeh, T.; Ganjali, M.R.; Rafiei, F. A new carbon paste electrode modified with MWCNTs and nano-structured molecularly imprinted polymer for ultratrace determination of trimipramine: The crucial effect of electrode components mixing on its performance. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magar, H.S.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; Mulchandani, A. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS): Principles, Construction, and Biosensing Applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, J.E.; Kinnamon, D.S.; Prasad, S. Randles Circuit Analysis Toward Investigating Interfacial Effects on Microchannel Electrodes. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2018, 2, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, Y.; Morali, U.; Erol, S.; Avci, H. Investigation of electrochemical behavior of potassium ferricyanide/ferrocyanide redox probes on screen printed carbon electrode through cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Turkish J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1895–1915. [Google Scholar]
- Milanesi, C.; Protti, S.; Chiodi, D.; Profumo, A.; Merli, D. Electrochemical characterization and voltammetric determination of aryl piperazine emerging as designer drugs. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 895, 115480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capucciati, A.; Burato, A.; Bersani, C.; Protti, S.; Profumo, A.; Merli, D. Electrochemical Behavior and Voltammetric Determination of Two Synthetic Aroyl Amides Opioids. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, D.; Lio, E.; Protti, S.; Coccia, R.; Profumo, A.; Alberti, G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-based voltammetric sensor for amino acids/indazole derivatives synthetic cannabinoids detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1288C, 342151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Yunhua, W.; Xiaobo, J.; Shengshui, H. Studies on electrochemical oxidation of azithromycin and its interactions with bovine serum albumin. Bioelectrochemistry 2004, 64, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Guidelli, R.; Compton, R.G.; Feliu, J.M.; Gileadi, E.; Lipkowski, J.; Schmickler, W.; Trasatti, S. Defining the transfer coefficient in electrochemistry: An assessment (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2014, 86, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, T.; Adams, R.N. Anodic Oxidation Studies of N,N-Dimethylaniline. I. Voltammetric and Spectroscopic Investigations at Platinum Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 2058–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, S.; Arantes, C.; Faria, V.; Souza, A.O.; Pimentel, M.; Barbosa, L.; Richter, M.; Munoz, A.A.; dos Santos, T.P. Electrochemistry of 5F-MDMB-PICA synthetic cannabinoid using a borondoped diamond electrode with short anodic-cathodic pretreatment: A simple screening method for application in forensic analysis. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 454, 142356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Lyu, Z.; Li, S.; Ruan, X.; Fei, M.; Zhou, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhu, W.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole nanotubes based electrochemical sensor for glyphosate detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 191, 113434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maouche, N.; Guergouri, M.; Gam-Derouich, S.; Jouini, M.; Nessark, B.; Chehimi, M.M. Molecularly imprinted polypyrrole films: Some key parameters for electrochemical picomolar detection of dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 685, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.A.; Hamnett, A. In situ spectroscopic investigations of the growth, electrochemical cycling and overoxidation of polypyrrole in aqueous solution. Electrochim. Acta 1991, 36, 1263–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, I.Y.; Szekeres, M.; Turcu, R.; Sáringer, S.; Illés, E.; Nesztor, D.; Tombácz, E. Mechanism of in situ surface polymerization of gallic acid in an environmental-inspired preparation of carboxylated core–shell magnetite nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15451–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, R.; Newair, E.F. Electrochemical behavior of antioxidants: I. Mechanistic study on electrochemical oxidation of gallic acid in aqueous solutions at glassy-carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 657, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahi, S.; Falahi, S.; Zarejousheghani, M.; Ehrlich, H.; Joseph, Y.; Rahimi, P. Electrochemical Sensing of Gallic Acid in Beverages Using a 3D Bio-Nanocomposite Based on Carbon Nanotubes/Spongin-Atacamite. Biosensors 2023, 13, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Calibration methods in instrumental analysis: Regression and correlation. In Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 6th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: Harlow Essex, UK, 2010; pp. 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, S.; Bosman, G.; du Toit, W.; Aleixandre-Tudo, J.L. White wine phenolics: Current methods of analysis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilasi, F.; La Torre, G.L.; Dugo, G.; Pellicanò, T.M. Contenuto di antiossidanti e tecniche colturali e di allevamento della vite. Enol.-Milano 2008, 44, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Dugo, G.; Giuffrida, D.; Magnisi, R.; Vilasi, F.; Pellicanò, T.M.; La Torre, G.L. Determinazione HPLC/MS di composti antiossidanti in vini siciliani da dessert. Enologo-Milano 2004, 40, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.K.; Lin, C.L.; Liang, Y.C.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Juan, I.M. Survey of catechins, gallic acid, and methylxanthines in green, oolong, pu-erh, and black teas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 3635–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

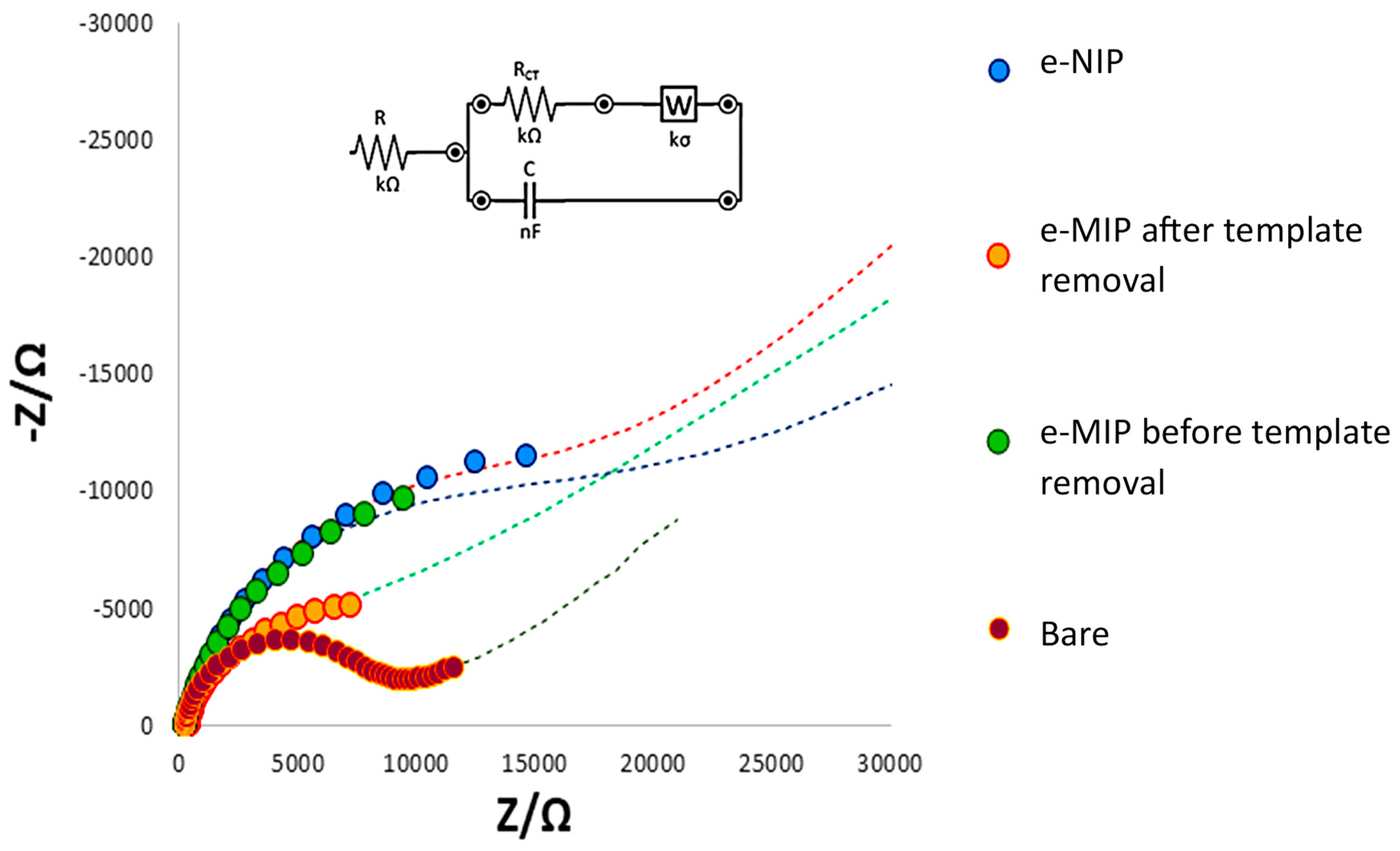
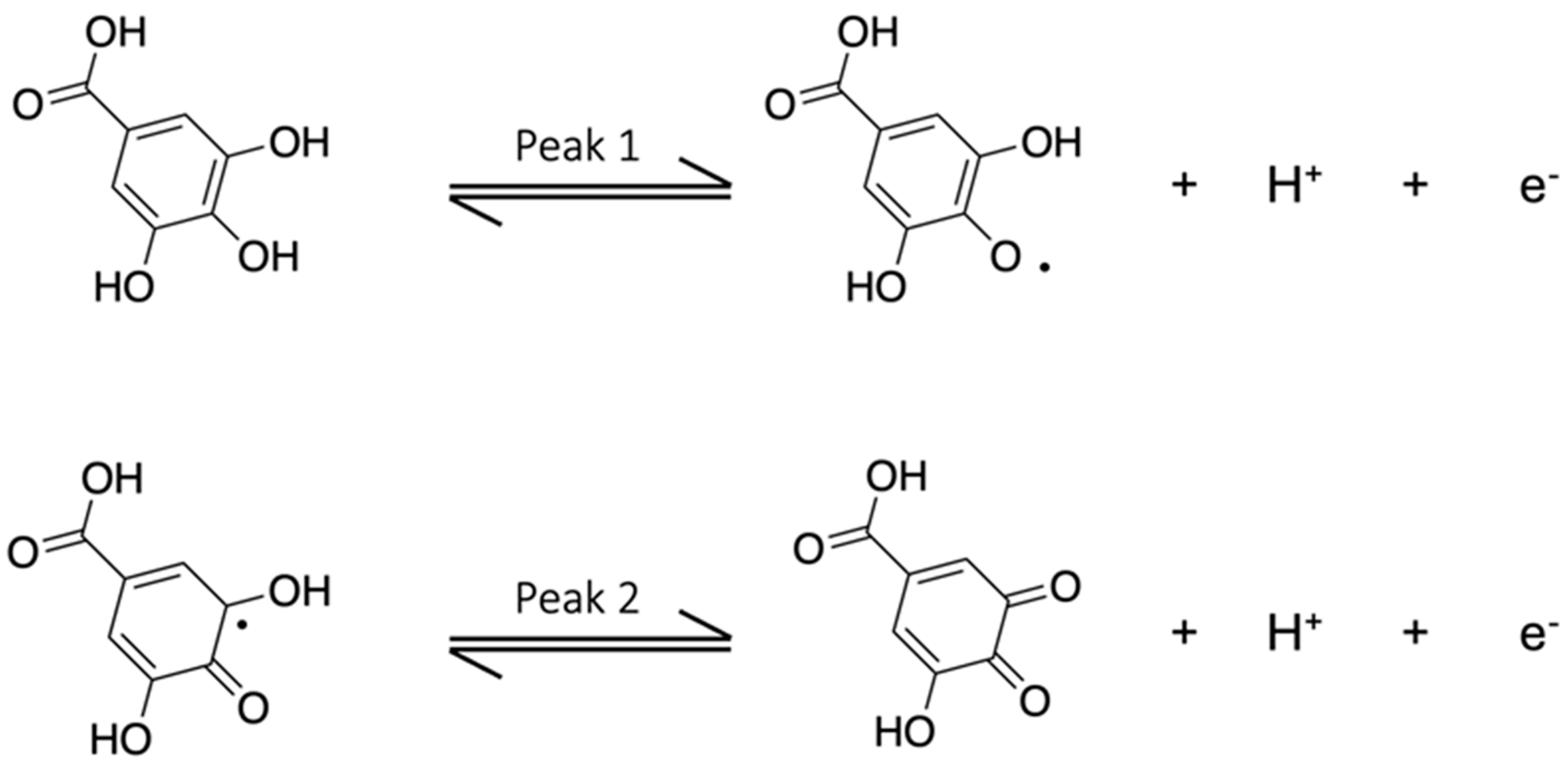
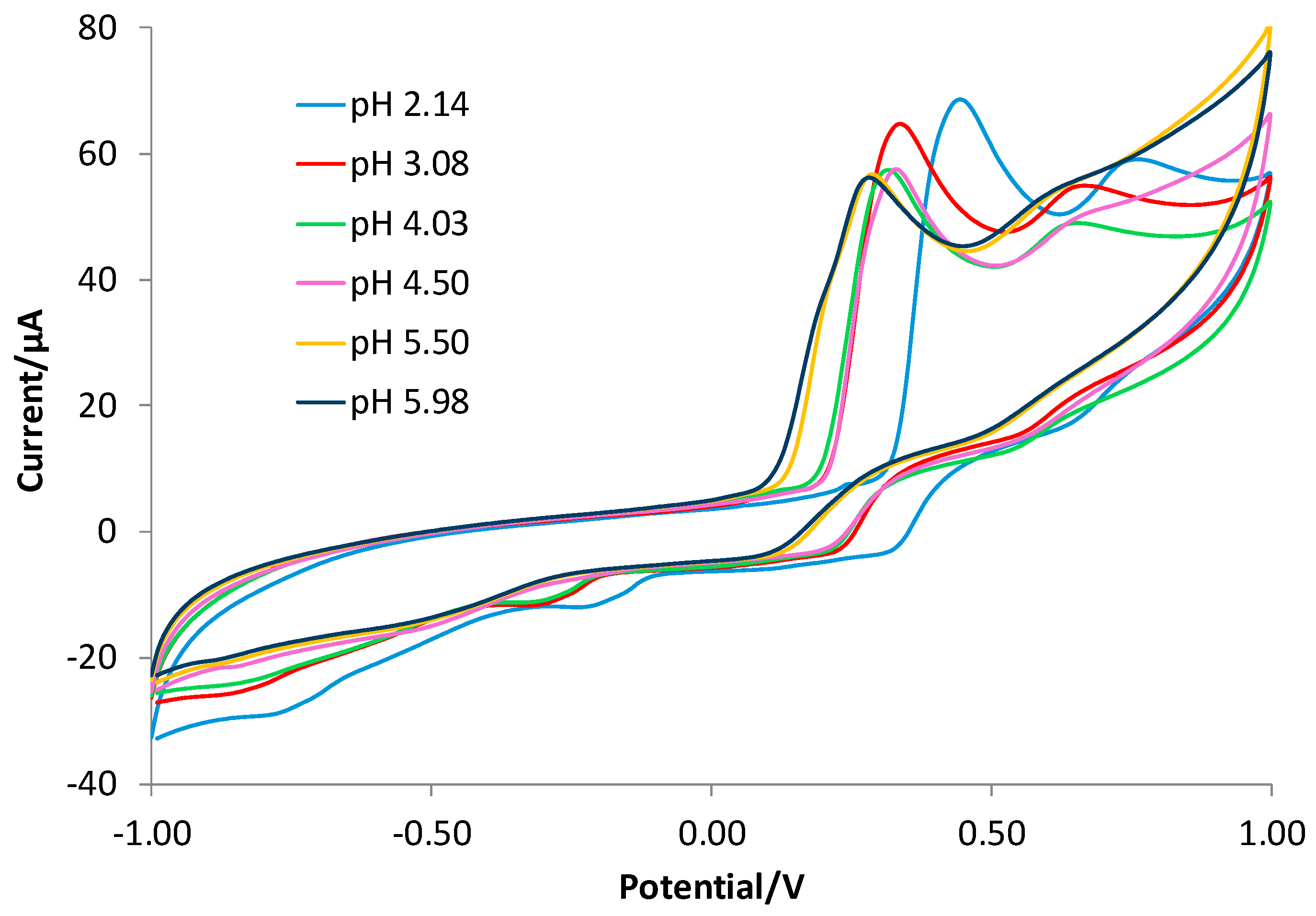
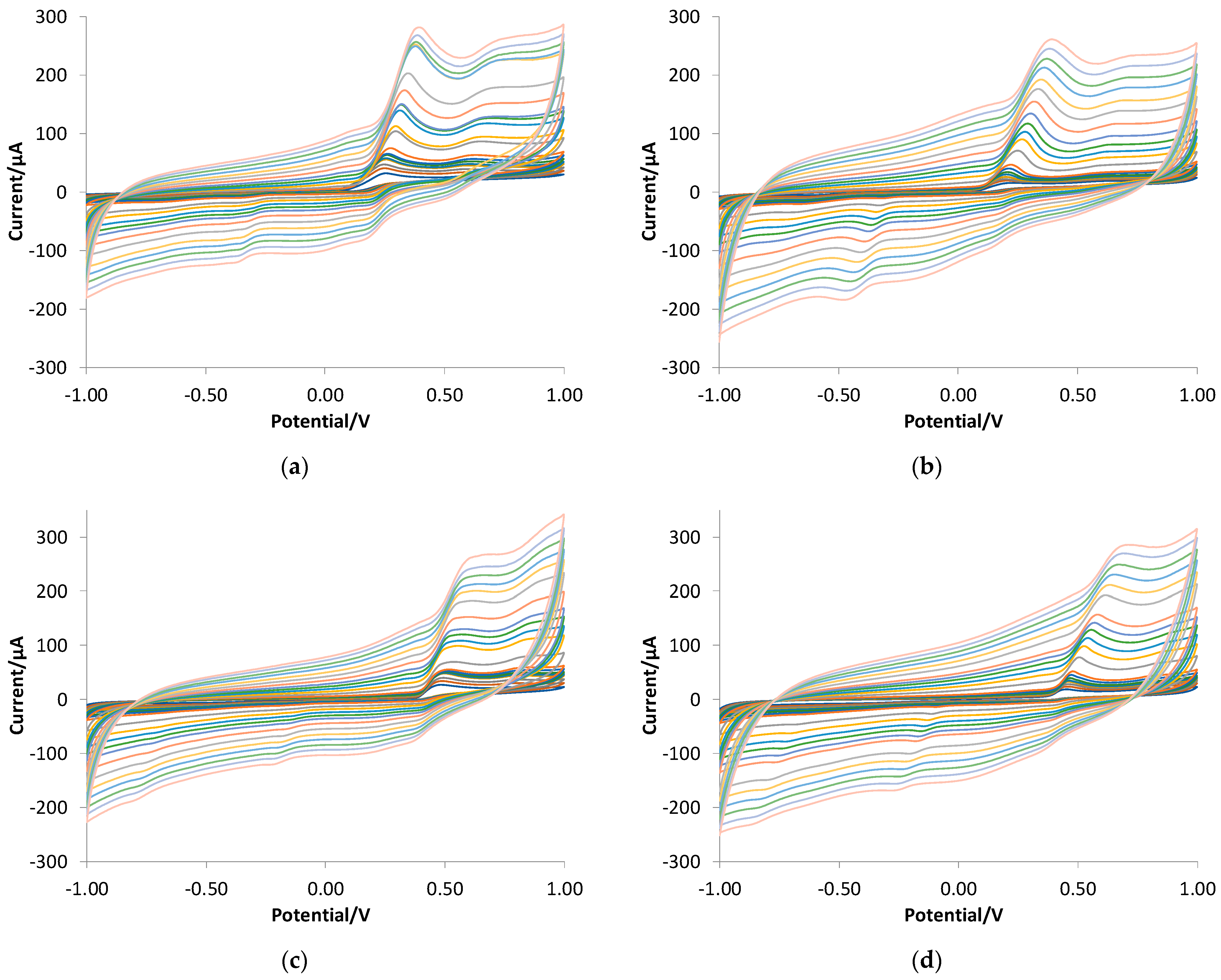




| Active Area (mm2) † | Capacitance (μF) | |
|---|---|---|
| bare electrode | 3.8 (2) | 0.7 (5) |
| eMIP-modified electrode | 2.4 (2) | 4.11 (3) |
| eNIP-modified electrode | 1.3 (1) | 1.49 (3) |
| R (kΩ) | RCT (kΩ) | C (µF) | W (kσ) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bare electrode | 0.29 | 6.5 | 3.8 | 4.0 |
| eMIP-modified electrode after template removal | 0.51 | 4.2 | 77.0 | 3.1 |
| eMIP-modified electrode before template removal | 0.70 | 10.0 | 15.4 | 0.2 |
| eNIP-modified electrode | 0.81 | 15.5 | 18.8 | 1.9 |
| αa (V) | E0′ (V) | D (cm2/s) | k0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| bare electrode (LiClO4 0.1M, gallic acid 2.5 mM) | 0.67 | 0.262 (4) | 7.4 (4) × 10−9 | 4.9 × 10−4 |
| eMIP-modified electrode (LiClO4 0.1M, gallic acid 2.5 mM) | 0.78 | 0.216 (6) | 4.7 (2) × 10−9 | 4.6 × 10−4 |
| bare electrode (LiClO4 0.1M, EtOH 20% gallic acid 2.5 mM) | 0.59 | 0.500 (3) | 2.9 (6) × 10−9 | 2.7 × 10−4 |
| eMIP-modified electrode (LiClO4 0.1M, EtOH 20% gallic acid 2.5 mM) | 0.79 | 0.493 (7) | 5.0 (2) × 10−9 | 4.7 × 10−4 |
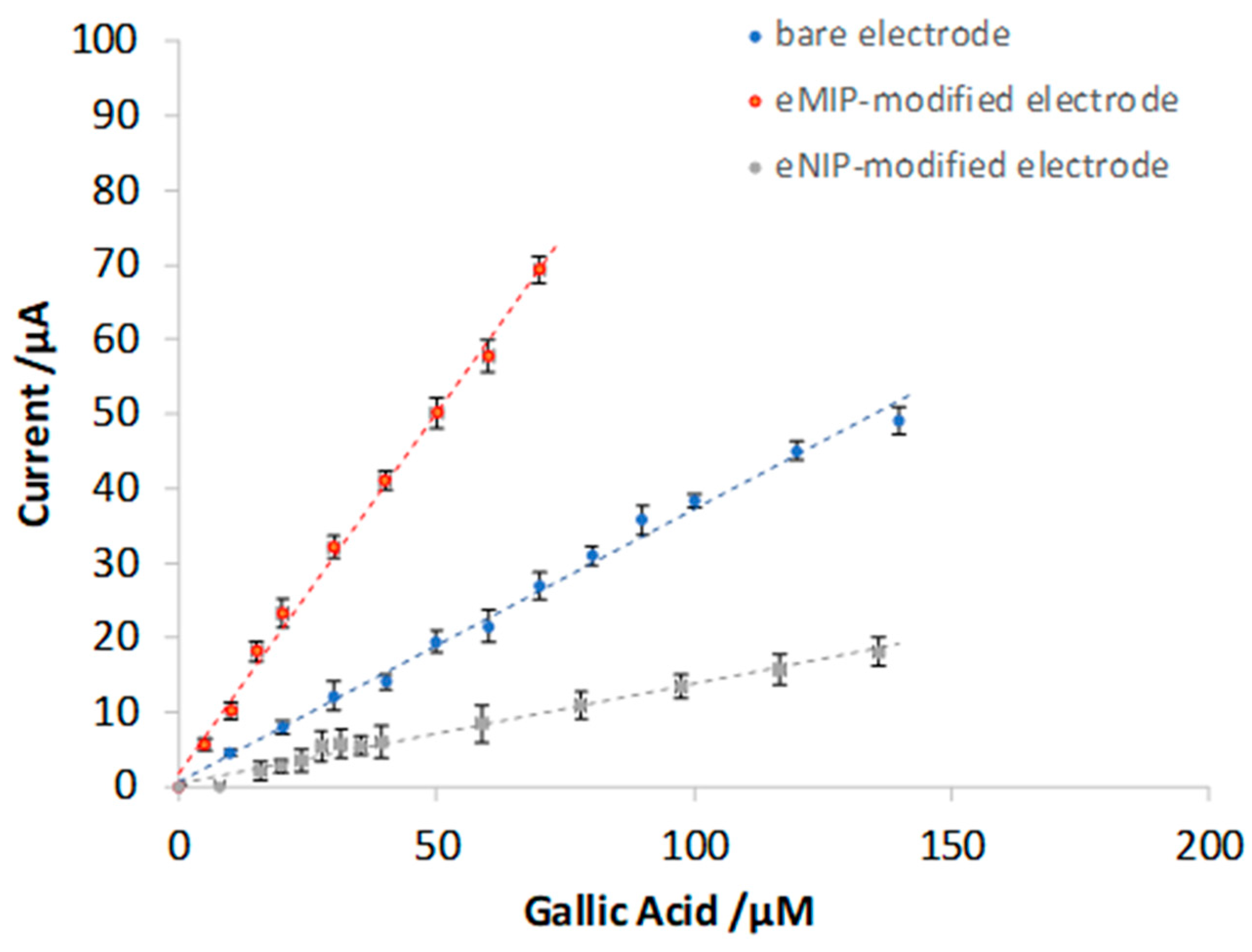
| Electrode | Slope (µA μM−1) | Intercept (µA) | R2 | LOD (µM) | LOQ (µM) | Linear Range (µM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare | 0.37 (1) | 0.7 (6) | 0.994 | 12 | 35 | 12–140 |
| eMIP | 0.97 (2) | 1.8 (8) | 0.996 | 5 | 16 | 5–70 |
| eNIP | 0.134 (5) | 0.4 (3) | 0.985 | 18 | 55 | 18–140 |
| Beverage | Gallic Acid mg L−1 | Total Polyphenols GAE, mg L−1 | Gallic Acid Mean Value, mg L−1 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| White wine | 14 (4) | 181.3 | 10 | [63] |
| Red wine | 145 (15) | 1285.1 | 7.76–172.01 | [64] |
| Rosè wine | 120 (13) | 1081.1 | 7.76–172.01 | [64] |
| Marsala | 17 (2) | 281 | 13 | [65] |
| Green tea | 138 (26) | 1535 | 104 | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zanoni, C.; Dallù, L.V.; Costa, C.; Cutaia, A.; Alberti, G. A Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (eMIP) to Determine Gallic Acid in Non-Alcoholic and Alcoholic Beverages. Polymers 2024, 16, 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081076
Zanoni C, Dallù LV, Costa C, Cutaia A, Alberti G. A Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (eMIP) to Determine Gallic Acid in Non-Alcoholic and Alcoholic Beverages. Polymers. 2024; 16(8):1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081076
Chicago/Turabian StyleZanoni, Camilla, Lucrezia Virginia Dallù, Clementina Costa, Alessandra Cutaia, and Giancarla Alberti. 2024. "A Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (eMIP) to Determine Gallic Acid in Non-Alcoholic and Alcoholic Beverages" Polymers 16, no. 8: 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081076
APA StyleZanoni, C., Dallù, L. V., Costa, C., Cutaia, A., & Alberti, G. (2024). A Screen-Printed Voltammetric Sensor Modified with Electropolymerized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (eMIP) to Determine Gallic Acid in Non-Alcoholic and Alcoholic Beverages. Polymers, 16(8), 1076. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16081076








