Optimization of Resin Composition for Zirconia Ceramic Digital Light Processing Additive Manufacturing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation and Characterization of Photosensitive Resin
2.3. Preparation of Zirconia Ceramic Slurry
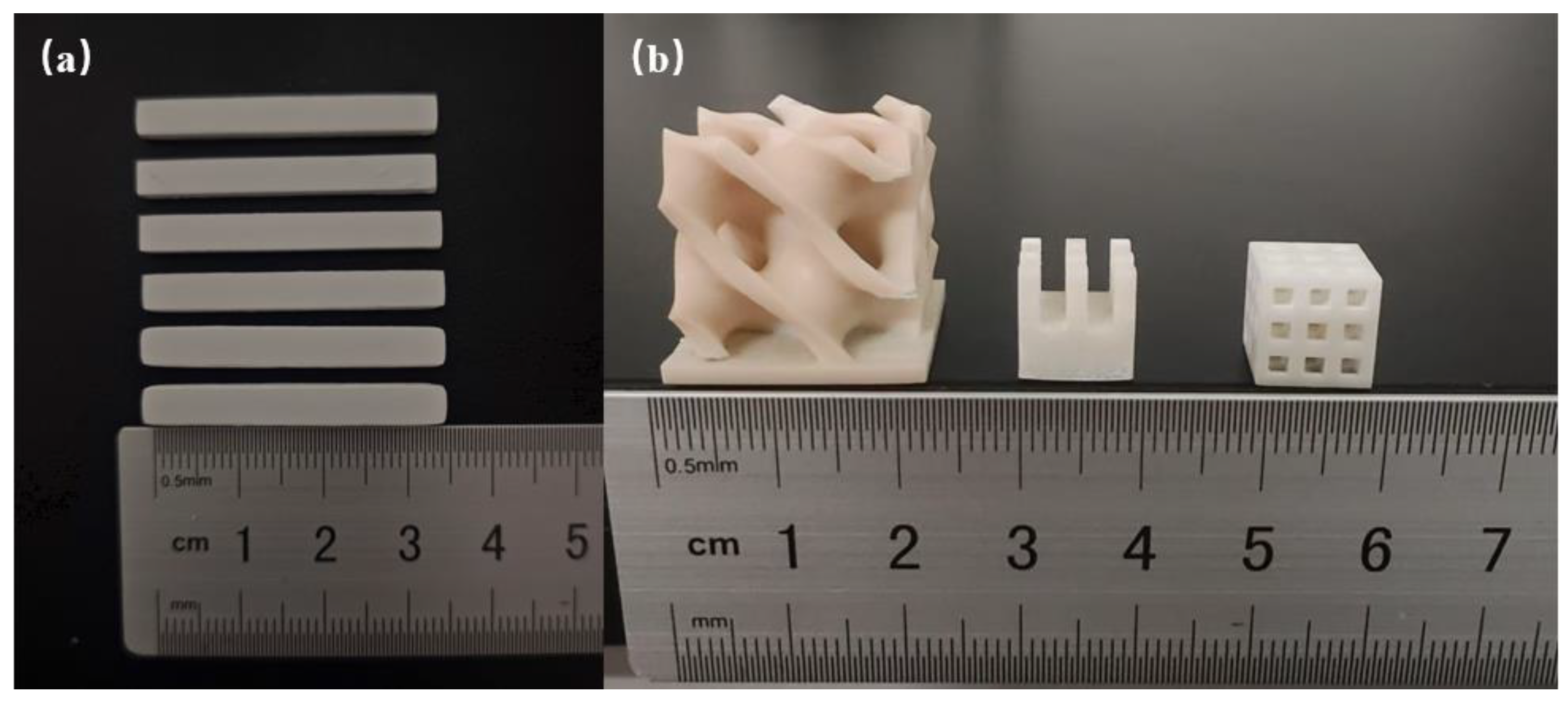
2.4. Ceramic Sample Fabrication
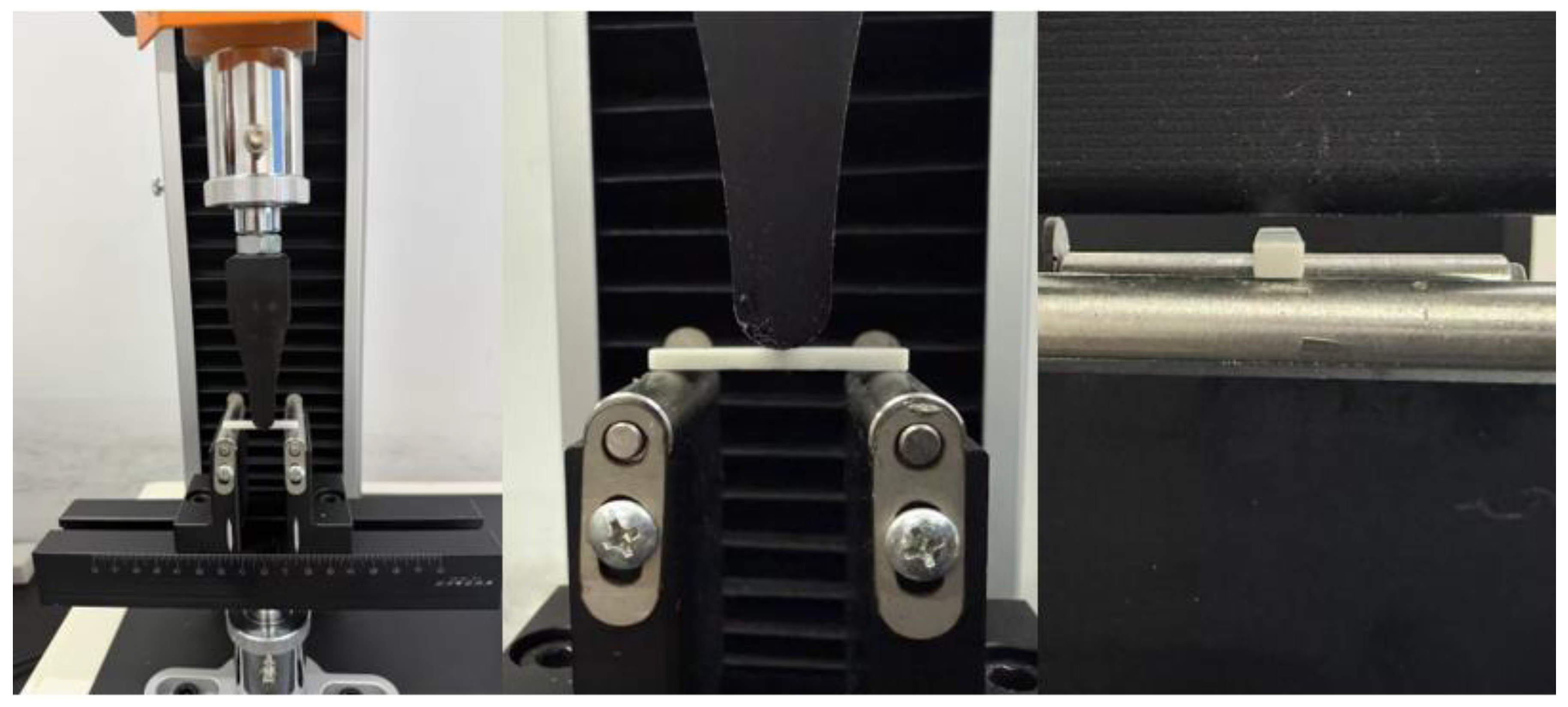
2.5. Mechanical Properties
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rheological Properties of Photosensitive Resin
3.2. Photocuring Performance of Photosensitive Resin
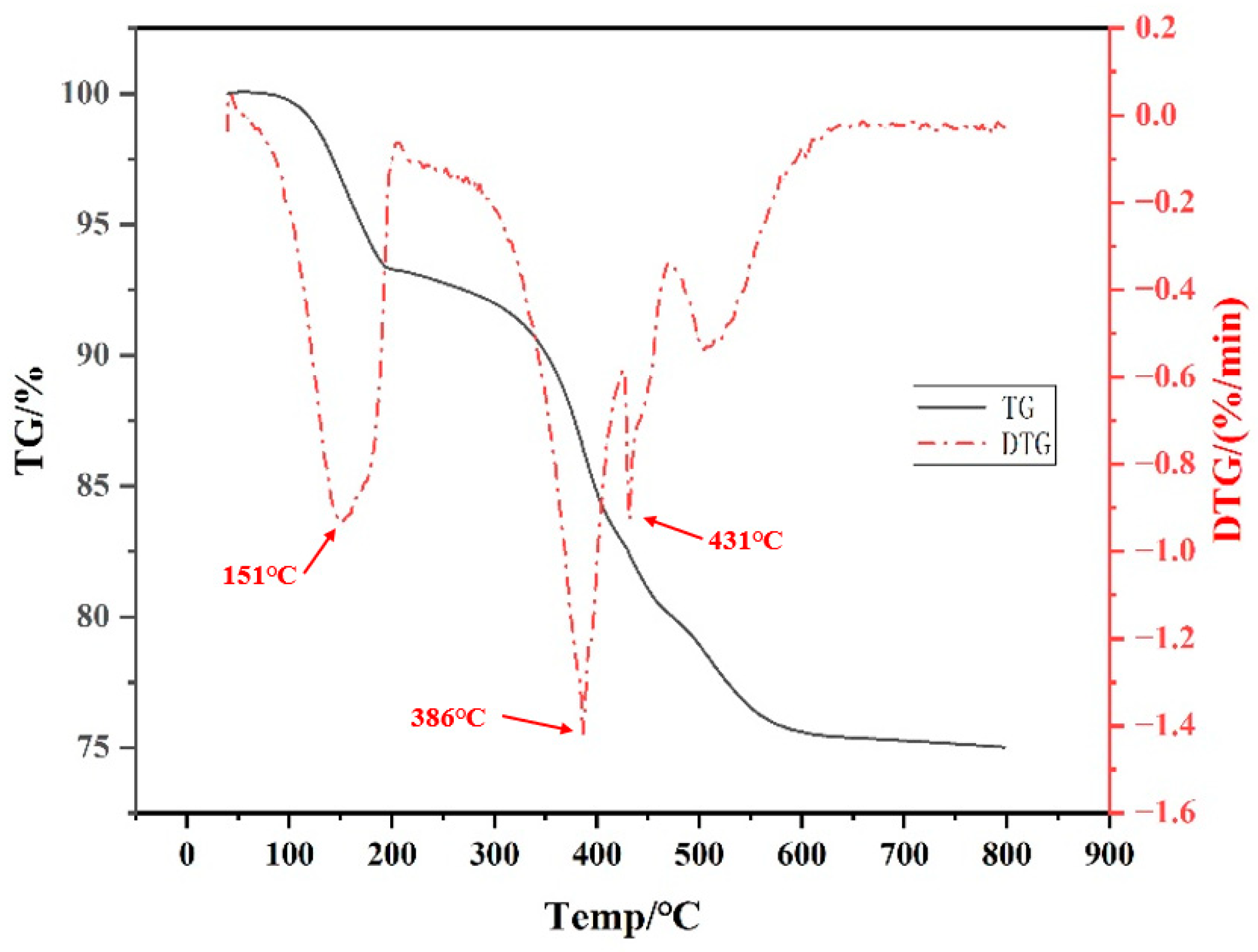
3.3. TG-DTG Analysis
3.4. Properties of Zirconia Ceramics
4. Conclusions
- Monomer impact: Two distinct monofunctional monomers, ACMO and HEMA, exhibit different effects on the photocuring behavior of photosensitive resin systems. Notably, after curing, the tensile strength of the resin with ACMO is higher than that of the resin with HEMA, while the bending strength of the resin with HEMA is significantly superior to that of the resin with ACMO.
- Photoinitiator impact: The content of the photoinitiator significantly influences the photocuring behavior. Initially, increasing the photoinitiator content led to a marked improvement in both tensile and bending strengths of the cured specimens. However, when the photoinitiator concentration exceeded 3%, further increases caused a decline in both tensile and bending strength.
- Ceramic slurry performance: A ceramic slurry with 56 vol% solid content was prepared using the photosensitive resin containing HEMA. After printing, debinding, and sintering, the bending strength of the resulting zirconia ceramic samples reached 766.85 MPa.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsui, K.; Hosoi, K.; Feng, B.; Yoshida, H.; Ikuhara, Y. Ultrahigh Toughness Zirconia Ceramics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 27, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.G.; Su, J.Z.; Geng, J.X.; Duan, L.Y.; He, W.B. Research Advances on Primary Machining Technologies of Zirconia Ceramics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 130, 23–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Preparation and Toughening Modification of Photosensitive Resins for Photocuring Rapid Prototyping. Master’s Thesis, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, W.M.; Liu, Y.F.; Jiang, X.F.; Dong, X.T.; Jun, J.; Baur, D.A.; Xu, J.J.; Pan, H.; Xu, X. Bionic Mechanical Design and 3D Printing of Novel Porous Ti6Al4V Implants for Biomedical Applications. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2019, 20, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarone, F.; Ruggiero, G.; Leone, R.; Breschi, L.; Leuci, S.; Sorrentino, R. Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate (ZLS) Mechanical and Biological Properties: A Literature Review. J. Dent. 2021, 109, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriella, A.C.; Ling, Y. Nano-Scale Mechanical Behavior of Pre-Crystallized Cad/Cam Zirconia-Reinforced Lithium Silicate Glass Ceramic. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 82, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, S.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, X. Design and Performance of Photosensitive Resin Slurry for Ceramic Photocuring 3D Printing. Plast. Technol. 2024, 52, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, G.; Ignazio, R.; Candido, F.P.; Annalisa, C. Current and Emerging Trends in Polymeric 3D Printed Microfluidic Devices. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 55, 102867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stampfl, J.; Martin, S.; Johannes, H.; Fritz, B. Lithography-Based Additive Manufacturing of Ceramics: Materials, Applications and Perspectives. MRS Commun. 2023, 13, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/ASTM 52900; Additive Manufacturing—General Principles—Fundamentals and Vocabulary. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Nie, G.L.; Li, Y.H.; Sheng, P.F.; Zuo, F.; Wu, H.L.; Liu, L.R.; Deng, X.; Bao, Y.W.; Wu, S.H. Microstructure Refinement-Homogenization and Flexural Strength Improvement of Al2O3 Ceramics Fabricated by DLP-Stereolithography Integrated with Chemical Precipitation Coating Process. J. Adv. Ceram. 2021, 10, 790–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.L.; An, X.L.; Liang, J.J.; Liu, Y.S.; Hu, K.H.; Lu, Z.G.; Yue, X.Y.; Li, J.G.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Sun, X.F. Balancing Flexural Strength and Porosity in DLP-3D Printing Al2O3 Cores for Hollow Turbine Blades. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.P.; Liu, W.; Wu, H.D.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, L.X.; He, F.P.; Chen, S.X.; Wu, S.H. Preparation of a Defect-Free Alumina Cutting Tool Via Additive Manufacturing Based on Stereolithography—Optimization of the Drying and Debinding Processes. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 11598–11602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, M.L.; Wu, H.D.; He, F.P.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.H. Cure Behavior of Colorful ZrO2 Suspensions During Digital Light Processing (DLP) Based Stereolithography Process. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 4921–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wu, H.D.; Tian, Z.; Li, Y.H.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, M.P.; Deng, X.; Xie, Z.P.; Wu, S.H. 3D Printing of Dense Structural Ceramic Microcomponents with Low Cost: Tailoring the Sintering Kinetics and the Microstructure Evolution. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 102, 2257–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Fu, H.; Xu, Z.F.; Liu, R.Z.; Jiang, P.; Shao, X.Y.; Shi, Y.S.; Yan, C.Z. Fabrication and Characterization of Carbon Fiber Reinforced SiC Ceramic Matrix Composites Based on 3D Printing Technology. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 38, 4604–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Chang, H.T.; Guo, X.T.; Liu, M.; Wei, Y.Q.; Huang, Z.R.; Yang, Y. Preparation of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced SiC Ceramics by Stereolithography and Secondary Silicon Infiltration. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 25159–25167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.J.; Yang, P.; Lin, L.F.; Li, Y.H.; Wu, S.H. Improving Cure Performance of Si3N4 Suspension with a High Refractive Index Resin for Stereolithography-Based Additive Manufacturing. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 12569–12577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, P.; Sheng, P.F.; Ou, J.; Ning, T.R.; Wu, S.H. Cure Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Si3N4 Ceramics with Bimodal Particle Size Distribution Prepared Using Digital Light Processing. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 12166–12172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, G.; Dou, R.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.B.; Li, H.Q.; Tan, H.H. Thermal Conductivities and Mechanical Properties of Aln Ceramics Fabricated by Three Dimensional Printing. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 3535–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.F.; Wu, H.D.; Li, Y.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Wu, S.H. Effect of Particle Size on Rheology, Curing Kinetics, and Corresponding Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic by Digital Light Processing (DLP)-Based Vat Photopolymerization. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2024, 44, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; David, W. Rosen and Brent Stucker. In Additive Manufacturing Technologies; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.X.; Zou, B.; Wang, X.F.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Q.H. Design, Manufacturing and Properties of Controllable Porosity of Ceramic Filters Based on SLA-3D Printing Technology. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, K.J.; Kong, J.H.; Fisher, J.G.; Park, S.W. Effect of the Volume Fraction of Zirconia Suspensions on the Microstructure and Physical Properties of Products Produced by Additive Manufacturing. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.W.; Li, Z.Y.; Li, J.J.; Liu, C.B.; Lao, C.S.; Fu, Y.L.; Liu, C.Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; He, Y. 3D Printing of Ceramics: A Review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2019, 39, 661–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloran, J.W. Ceramic Stereolithography: Additive Manufacturing for Ceramics by Photopolymerization. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2016, 46, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zeng, Y.; Li, P.R.; Chen, J.M. Fine Lattice Structural Titanium Dioxide Ceramic Produced by DLP 3D Printing. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 23007–23012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammel, E.C.; Ighodaro, O.L.R.; Okoli, O.I. Processing and Properties of Advanced Porous Ceramics: An Application Based Review. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 15351–15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, M.T.; Yue, X.Z.; Zhou, G.H.; Hu, S. Influence of Resin Composition on Rheology and Polymerization Kinetics of Alumina Ceramic Suspensions for Digital Light Processing (DLP) Additive Manufacturing. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 20456–20464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H. Development and Mechanical Property Study of Photosensitive Resin for Photocuring 3D Printing. Master’s Thesis, Hunan Institute of Science and Technology, Yueyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Yin, J.; Huang, H.; Huang, W.; Cai, M.; Xiang, H.; Liu, X. Kinetic Properties of Mixed Photocuring 3D Printing Resin Curing. Mater. Eng. 2019, 47, 143–150. [Google Scholar]
- Stansbury, J.W.; Idacavage, M.J. 3D Printing with Polymers: Challenges among Expanding Options and Opportunities. Dent. Mater. 2016, 32, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.J.; Zhang, X.C.; Xia, Z.; Han, P. Research Progress on UV-Curable Photosensitive Resin for 3D Printing: Composition, Toughening Modification, and Sustainable Development. Plast. Sci. Technol. 2024, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Komissarenko, D.; Sokolov, A.P.S.; Evstigneeva, A.D.; Slyusar, I.V.; Nartov, A.S.; Volkov, P.A.; Lyskov, N.V.; Evdokimov, P.V.; Putlayev, V.I.; Dosovitsky, A.E. DLP 3D Printing of Scandia-Stabilized Zirconia Ceramics. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.h.; Zhou, S.X.; Wu, J.F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.C. Relationship between the Adhesion Properties of UV-Curable Alumina Suspensions and the Functionalities and Structures of UV-Curable Acrylate Monomers for DLP-Based Ceramic Stereolithography. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 32699–32709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, E.; Lidström, O.; Johansson, J.; Lyckfeldt, O.; Adolfsson, O. Influence of Resin Composition on the Defect Formation in Alumina Manufactured by Stereolithography. Materials 2017, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komissarenko, D.; Roland, S.; Seeber, B.S.M.; Graule, T.; Blugan, G. DLP 3D Printing of High Strength Semi-Translucent Zirconia Ceramics with Relatively Low-Loaded UV-Curable Formulations. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 21008–21016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Wu, H.; Luo, X.; Liang, J.H.; Li, N.; Chen, S.G.; Long, Y. Investigating the Correlation and Composition of Organic Components in ZrO2-Based Slurry on Printability Improvement and Defect Suppression of Vat Photopolymerization. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaitai, F. Uniform Design and Uniform Design Tables; Beijing Science Press: Beijing, China, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 178; Plastics—Determination of Flexural Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001.
- ISO 527; Plastics—Determination of Tensile Properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- ISO 14704; Fine Ceramics (Advanced Ceramics, Advanced Technical Ceramics)—Test Method for Flexural Strength of Monolithic Ceramics at Room Temperature. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000.
- Hu, C.Q. Research on Photocuring Additive Manufacturing Process of Silicon Carbide Ceramics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chartier, T.; Chaput, C.; Doreau, F.; Loiseau, M. Stereolithography of Structural Complex Ceramic Parts. J. Mater. Sci. 2002, 37, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





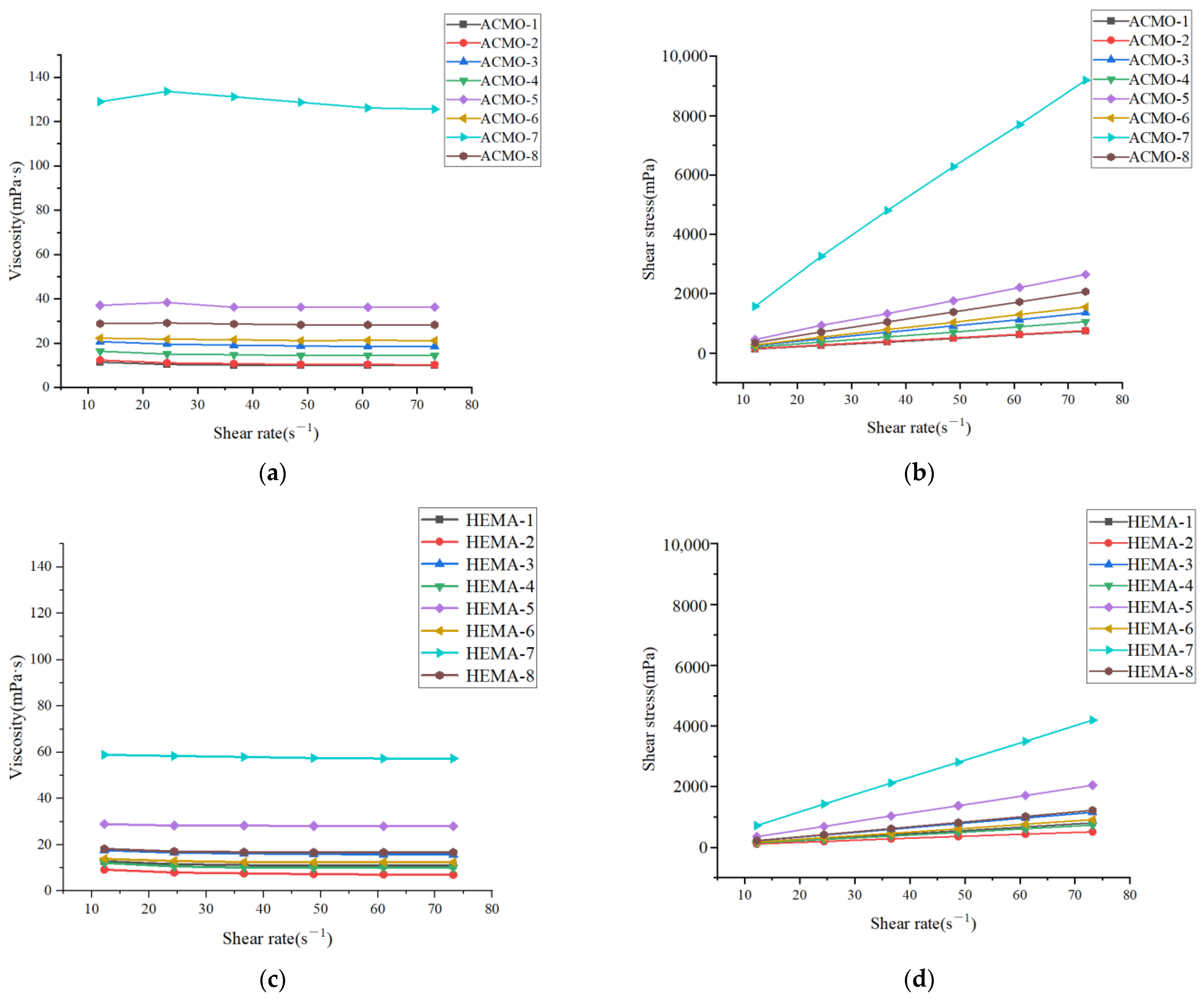
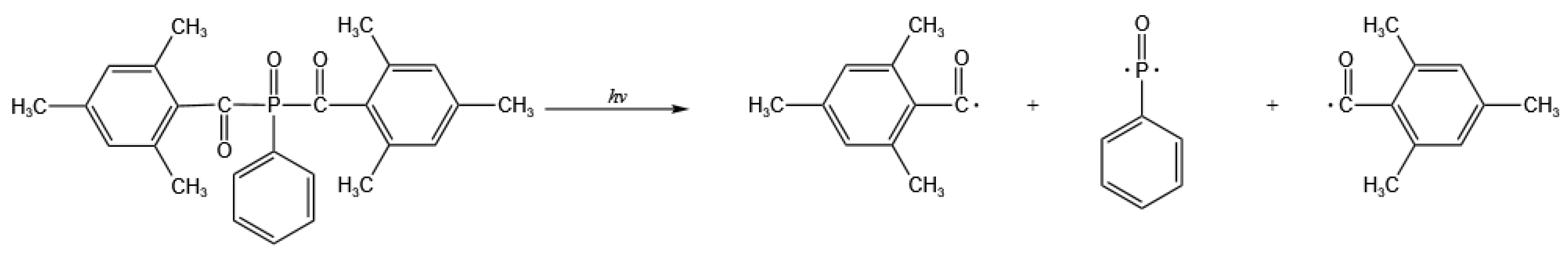
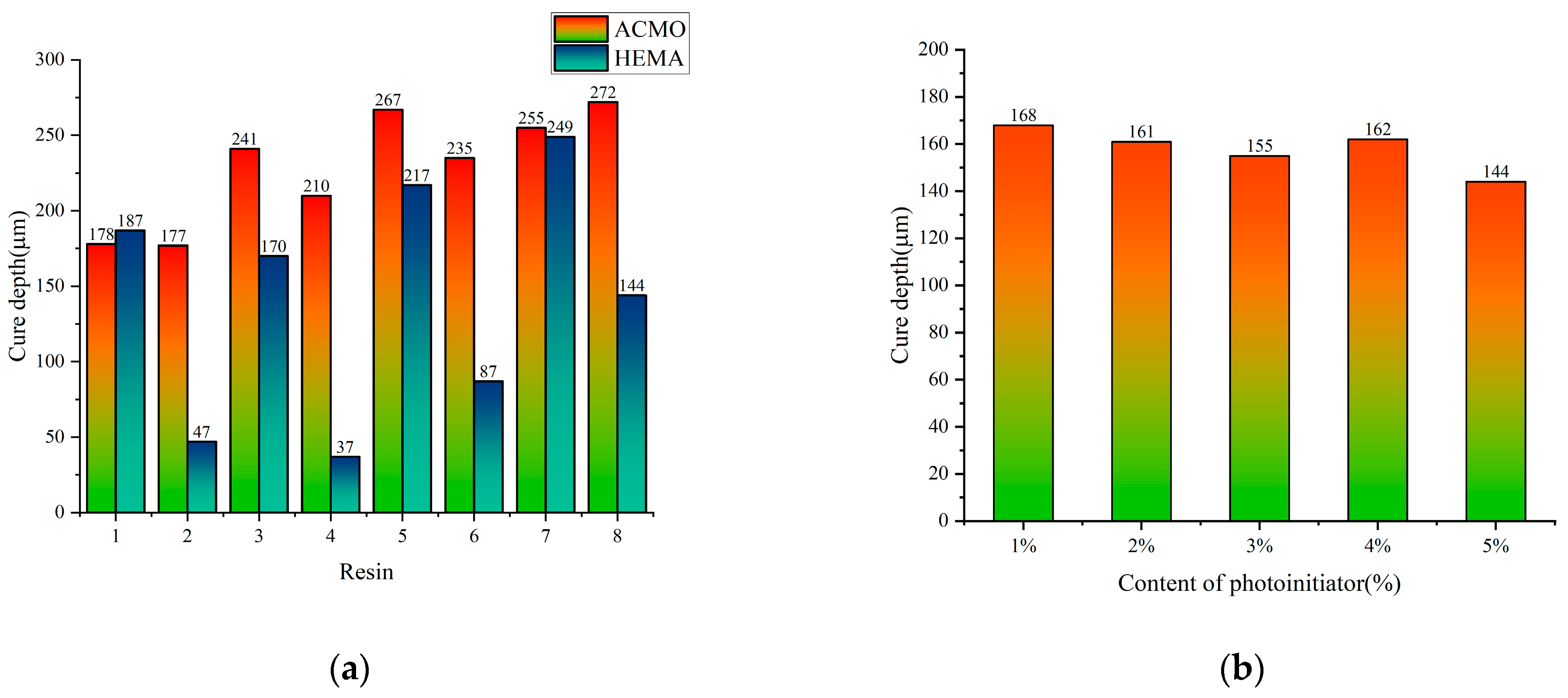

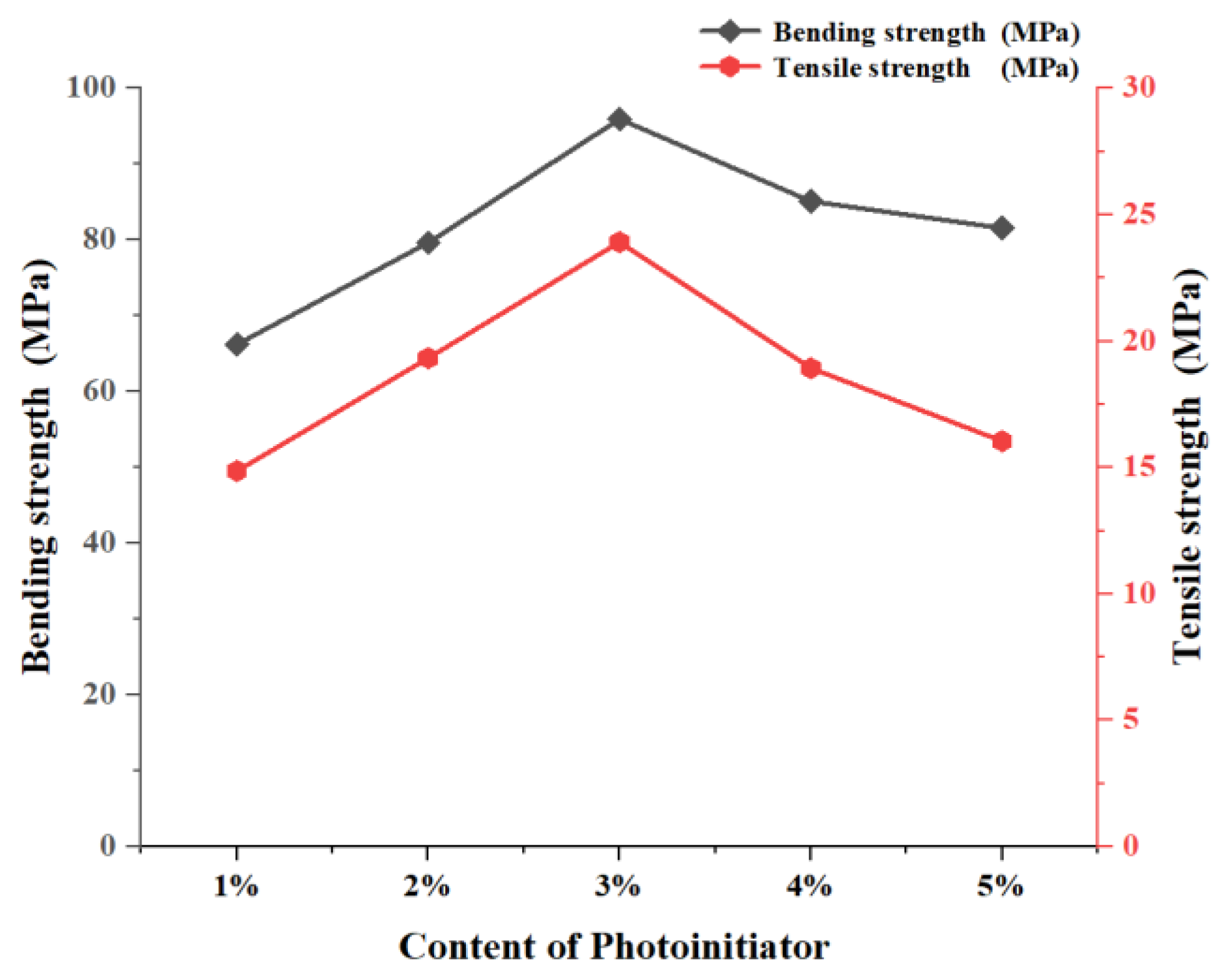

| Monomer Name | Abbreviation | Number of Functional Groups | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acryloyl morpholine | ACMO | 1 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Hydroxyethyl methacrylate | HEMA | 1 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Cyclic trimethylpropane formal acrylate | CTFA | 1 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 2-Phenoxyethyl acrylate | PHEA | 1 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| 1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate | HDDA | 2 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Polyethylene glycol (200) diacrylate | PEG200DA | 2 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| Polyethylene glycol (400) diacrylate | PEG400DA | 2 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| Polyethylene glycol (600) diacrylate | PEG600DA | 2 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| Tripropylene glycol diacrylate | TPGDA | 2 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| Diethylene glycol diacrylate | DEGDA | 2 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| Trimethylolpropane triacrylate | TMPTA | 3 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Di(trimethylolpropane) tetraacrylate | DiTMPTA | 3 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Ethoxylated pentaerythritol tetraacrylate | PPTTA | 4 | Shanghai Guangyi Chemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Pentaerythritol tetraacrylate | PETTA | 4 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| Dipentaerythritol hexaacrylate | DPHA | 6 | Guangzhou Lihou Trading Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China |
| No. | X1 HDDA (wt%) | X2 TMPTA (wt%) | X3 ACMO/HEMA (wt%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 75.0 | 14.1 | 10.9 |
| 2 | 56.7 | 2.7 | 40.6 |
| 3 | 44.1 | 38.4 | 17.5 |
| 4 | 33.9 | 12.4 | 53.7 |
| 5 | 25.0 | 60.9 | 14.1 |
| 6 | 17.1 | 25.9 | 57.0 |
| 7 | 9.9 | 84.5 | 5.6 |
| 8 | 3.2 | 42.4 | 54.5 |
| Name | Model/Grade | Specification | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotary Viscometer | NDJ-8Spro | Measuring range: 1 mPa·s—100,000 mPa·s | Shanghai Xiniulab Instruments Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China |
| Magnetic Stirrer | RCT-Basic | Rotational speed: 50–1500 rpm | IKA-Werke GmbH & Co. KG, Staufen im Breisgau, Germany |
| Planetary Ball Mill | BQM-1L | Rotational speed: 5–450 r/min | Changsha Miqi Instruments & Equipment Co., Ltd., Changsha, China |
| Micrometer | Q2LF0025 | Precision: 0.001 mm | Deqing Shengtaixin Electronic Technology Co., Ltd., Deqing, China |
| UV Radiometer | LS125 | Range: 0–20,000 mW/cm2 | Shenzhen Linshang Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China |
| Sintering Furnace | FMJ-05/17 | Maximum temperature: 1700 °C | Hefei Facerom Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd., Hefei, China |
| Debinding Furnace | FMJ-07/11 | Maximum temperature: 1100 °C | Hefei Facerom Intelligent Equipment Co., Ltd., Hefei, China |
| DLP Resin Printer | BLD-50-C1 | Printing precision: 50 μm | Qingdao Breuck 3D Additive Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China |
| DLP Ceramic Printer | BLD-25-C1 | Printing precision: 25 μm | Qingdao Breuck 3D Additive Manufacturing Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China |
| Digital Universal Testing Machine | WH-70 | Maximum Load: 5000 N | Ningbo Weiheng Testing Instruments Co., Ltd., Ningbo, China |
| Thermogravimetric Analyzer | TG209F3 | Heating and cooling rate: 0.001–200 K/min | Netzsch Instruments GmbH, Weimer, Germany |
| SEM Scanning Electron Microscope | SU8000 | Observation magnification: 30–500 K | Hitachi High-Technologies Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, N.; Xiao, M.; Qi, H.; Zhao, W.; Wu, J. Optimization of Resin Composition for Zirconia Ceramic Digital Light Processing Additive Manufacturing. Polymers 2025, 17, 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060797
Kuang N, Xiao M, Qi H, Zhao W, Wu J. Optimization of Resin Composition for Zirconia Ceramic Digital Light Processing Additive Manufacturing. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060797
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Ning, Minghui Xiao, Hao Qi, Wenjie Zhao, and Junfei Wu. 2025. "Optimization of Resin Composition for Zirconia Ceramic Digital Light Processing Additive Manufacturing" Polymers 17, no. 6: 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060797
APA StyleKuang, N., Xiao, M., Qi, H., Zhao, W., & Wu, J. (2025). Optimization of Resin Composition for Zirconia Ceramic Digital Light Processing Additive Manufacturing. Polymers, 17(6), 797. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060797






