Estimation of Synthetic Rubber Lifespan Based on Ozone Accelerated Aging Tests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Production
2.2. Ozone Exposure Test and Hardness Data Collection
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Life Time Calculation
3. Results
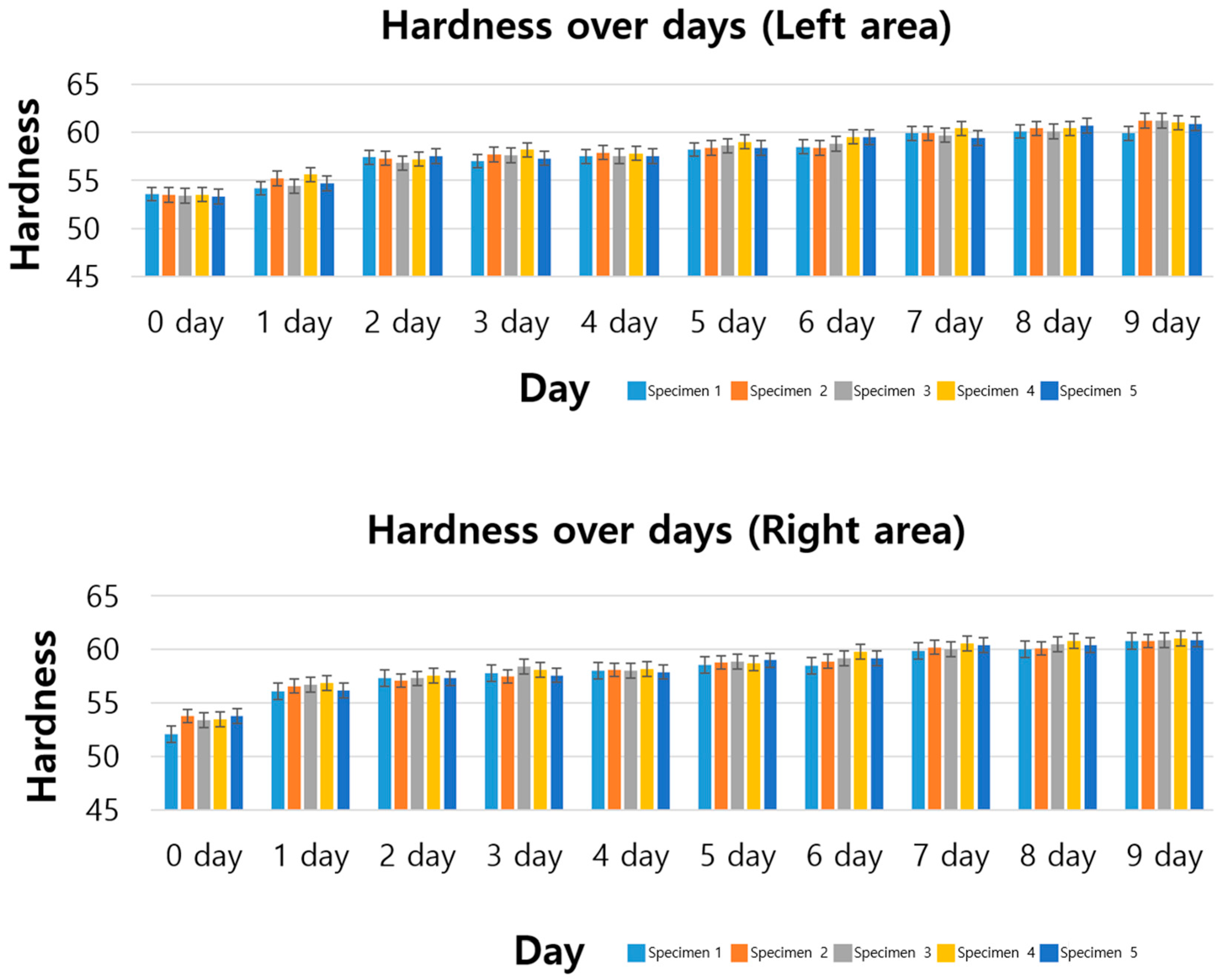
3.1. Standard Specimen Results for 9 Days
- Increase in hardness: In all specimens, hardness tended to increase as ozone exposure time increased;
- Model suitability: The coefficient of determination (R2) value is between 0.87 and 0.92, confirming that the linear regression model explains the hardness change data well;
- Pearson correlation coefficient evaluation: Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated to evaluate the linear relationship between ozone exposure time and hardness, and a positive correlation was found in all specimens. The values shown in the table are all between 0.94 and 0.96, showing a very high positive correlation. This indicates that there is a strong positive linear relationship between ozone exposure time and hardness change, meaning that as the exposure time increases, the hardness also steadily increases.
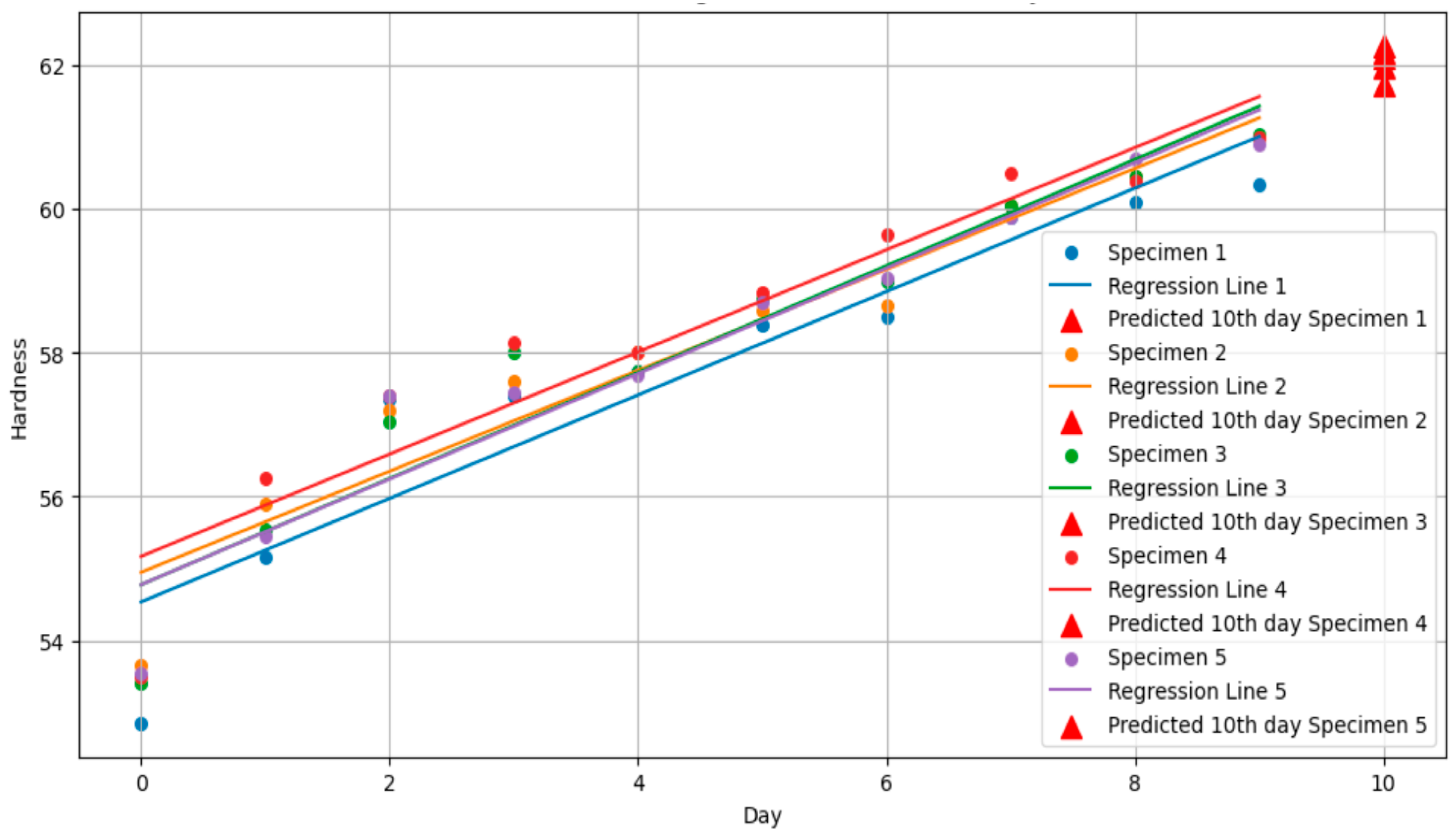
3.2. Standard Specimen Results for 10th Day
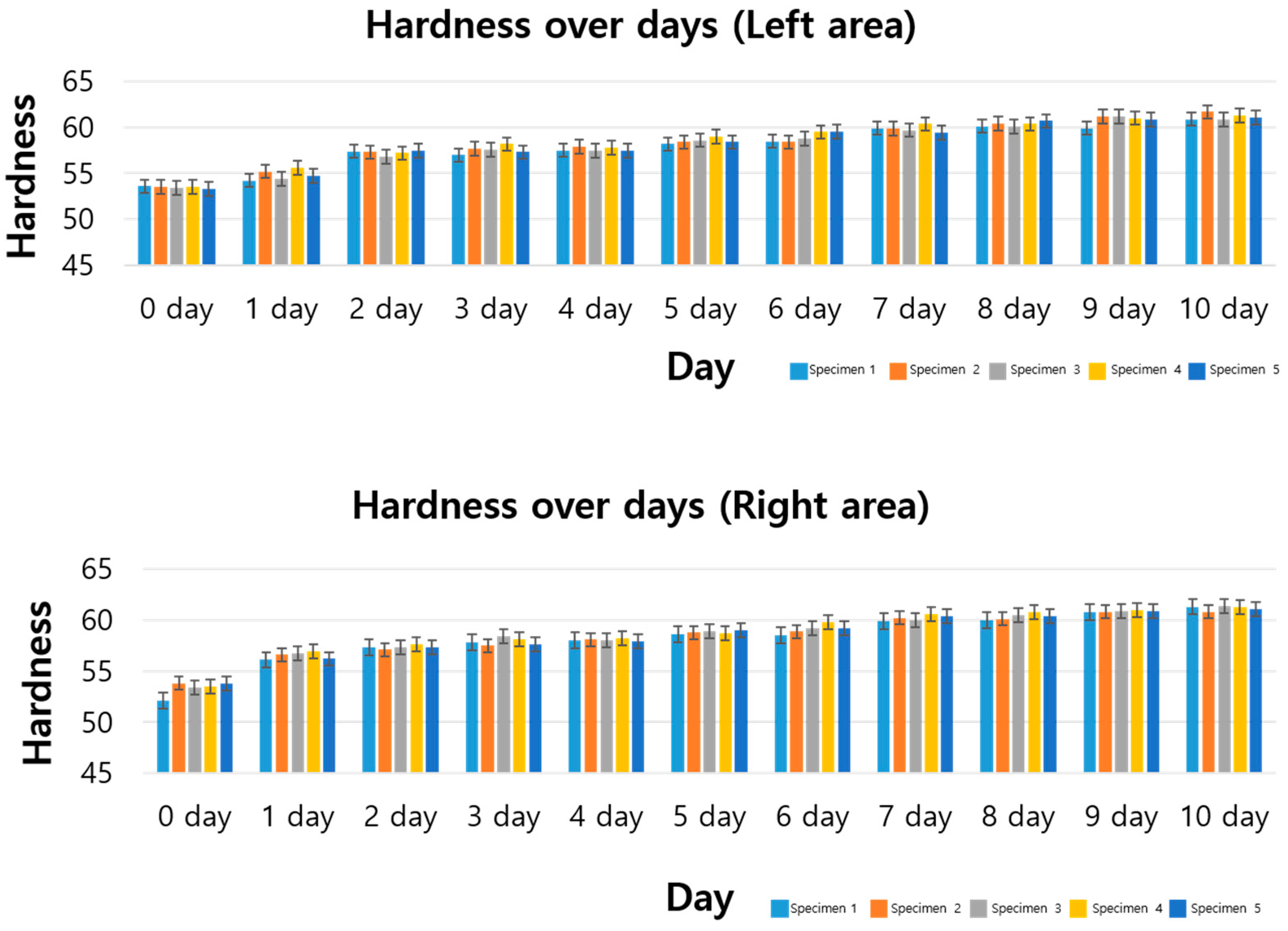
3.3. Standard Specimen Results for 16 Days
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Treib, C.; Loos, K.; Johlitz, M.; Lion, A. Ozone ageing: Experimental methods on pristine and protected natural rubber. Contin. Mech. Thermodyn. 2022, 34, 1563–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.G. Mechanism of exposure-cracking of rubbers. With a review of the influence of ozone. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1945, 18, 504–556. [Google Scholar]
- Poikelispää, M.; Shakun, A.; Sarlin, E. Nanodiamond—Carbon Black Hybrid Filler System for Demanding Applications of Natural Rubber—Butadiene Rubber Composite. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, J.; Ogawa, T.; Osawa, S.; Nakamura, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Minegishi, K. Ozone Deterioration of Nitrile Rubber Surface. J. Materials Life 1998, 10, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaruddin, S.; Muhr, A.H. Investigation of Ozone Cracking on Natural Rubber. J. Rubber Res. 2018, 21, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zheng, X.; Zhan, S.; Zhou, J.; Liao, S. Study on the ozone aging mechanism of Natural Rubber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 186, 109514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.H.; Yuan, X.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Hou, G.L. Natural Aging Life Prediction of Rubber Products Using Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm to Identify Acceleration Factor. Polymers 2022, 14, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.H.; Yuan, X.J.; Liu, G.Y.; Hou, G.L.; Zhang, Z. Storage Life Prediction of Rubber Products Based on Step Stress Accelerated Aging and Intelligent Algorithm. Polymers 2023, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, B.W.; Lee, J.M.; Park, S.; Seok, C.S. Study on the Aging Behavior of Natural Rubber/Butadiene Rubber (NR/BR) Blends Using a Parallel Spring Model. Polymers 2018, 10, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, G.J. Ozone Cracking and Protection of Rubber. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1970, 43, 1230–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.B.; Shi, W.K.; Chen, Z.Y. Natural environment degradation prediction of rubber and MPSO-based aging acceleration factor identification through the dispersion coefficient minimisation method. Polmer Test. 2019, 77, 105884. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, I.-S.; Lee, D.; Sohn, K.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Bae, J. Characterization on the Ozone Oxidation of Raw Natural Rubber Thin Film Using Image and FT-IR Analysis. Elastomers Compos. 2019, 54, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, M.; Fang, L.; Yu, H.; Rojruthai, P.; Sakdapipanich, J. Discoloration Mechanisms of Natural Rubber and Its Control. Polymers 2022, 14, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razumovskii, S.D.; Podmasteriev, V.V.; Zaikov, G.E. Kinetics and Mechanism of Stress Relaxation of Polyisoprene Vulcanizates Under Ozone Ageing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1988, 20, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Threadingham, D.; Obrecht, W.; Wieder, W.; Engehausen, R. Rubber, 3. Synthetic Rubbers, Introduction and Overview. Ullmann’s Encycl. Ind. Chem. 2021, 31, 597–622. [Google Scholar]
- Travaini, R.; Marangon-Jardim, C.; Colodette, J.L.; Morales-Otero, M.; Bolado-Rodríguez, S. Chapter 7—Ozonolysis. In Pretreatment of Biomass; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 105–135. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.M. Effect of Ozone on Rubbers: Countermeasures and Unsolved Problems. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1986, 15, 33–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS M 6518:2021; Physical Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber. KATS: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Devore, J.L. Probability and Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences, 8th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 508–510. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, J.L.; Nicewander, W.A. Thirteen Ways to Look at the Correlation Coefficient. Am. Stat. 1988, 42, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Bae, J.W.; Kim, J.S.; Hwang, T.J.; Park, S.D.; Park, S.H.; Yeo, T.M.; Kim, W.; Jo, N.J. Life-time Prediction of a Chloroprene Rubber (CR) O-Ring Using Intermittent Compression Stress Relaxation (CSR) and Time-Temperature Superposition (TTS) Principle. Macromol. Res. 2011, 19, 555–562. [Google Scholar]


| NR | CR | Carbon Black | CaCO3 | Others (Ca, Mg, Zn, etc.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48% | 48% | 10% | 25% | 17% |
| Specimen No. | Slope | Intercept | Coefficient of Determination (R2) | Pearson Correlation Coefficient (γ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.72 | 54.53 | 0.87 | 0.94 |
| 2 | 0.70 | 54.94 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| 3 | 0.74 | 54.77 | 0.92 | 0.96 |
| 4 | 0.71 | 55.17 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
| 5 | 0.73 | 54.77 | 0.93 | 0.96 |
| Specimen 1 | Specimen 2 | Specimen 3 | Specimen 4 | Specimen 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Predicted value | 61.74 | 61.98 | 62.18 | 62.28 | 62.12 |
| Actual value | 61.30 | 61.80 | 61.40 | 61.30 | 61.20 |
| Error (%) | 0.72 | 0.002 | 1.27 | 1.60 | 1.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, Y. Estimation of Synthetic Rubber Lifespan Based on Ozone Accelerated Aging Tests. Polymers 2025, 17, 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060819
Kim J, Kim Y, Cho Y. Estimation of Synthetic Rubber Lifespan Based on Ozone Accelerated Aging Tests. Polymers. 2025; 17(6):819. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060819
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jeongnam, Youngki Kim, and Youhee Cho. 2025. "Estimation of Synthetic Rubber Lifespan Based on Ozone Accelerated Aging Tests" Polymers 17, no. 6: 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060819
APA StyleKim, J., Kim, Y., & Cho, Y. (2025). Estimation of Synthetic Rubber Lifespan Based on Ozone Accelerated Aging Tests. Polymers, 17(6), 819. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17060819





