Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
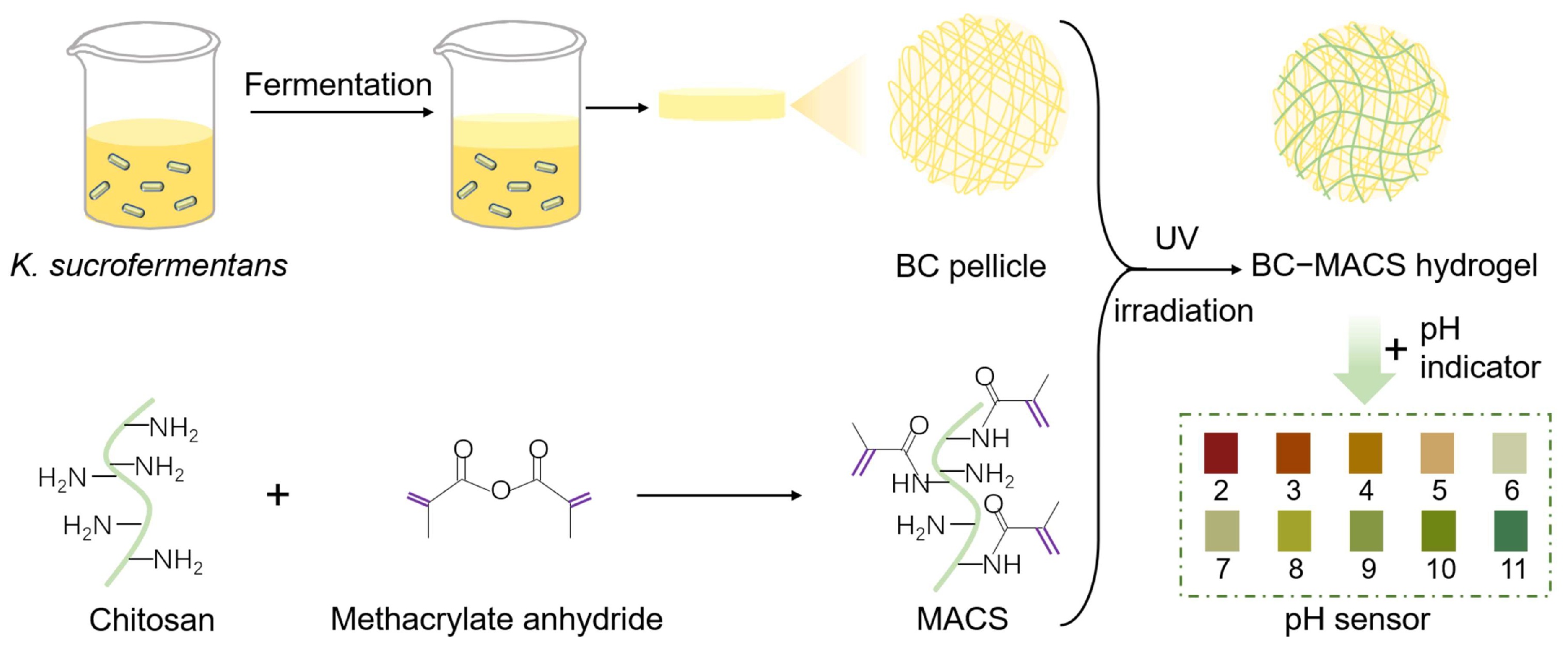
2.2. Synthesis of MACS and BC
2.2.1. Synthesis of MACS
2.2.2. Synthesis of BC Pellicles
2.3. Preparation of MACS and BC-MACS Hydrogels
2.4. Characterization of BC-MACS Hydrogel
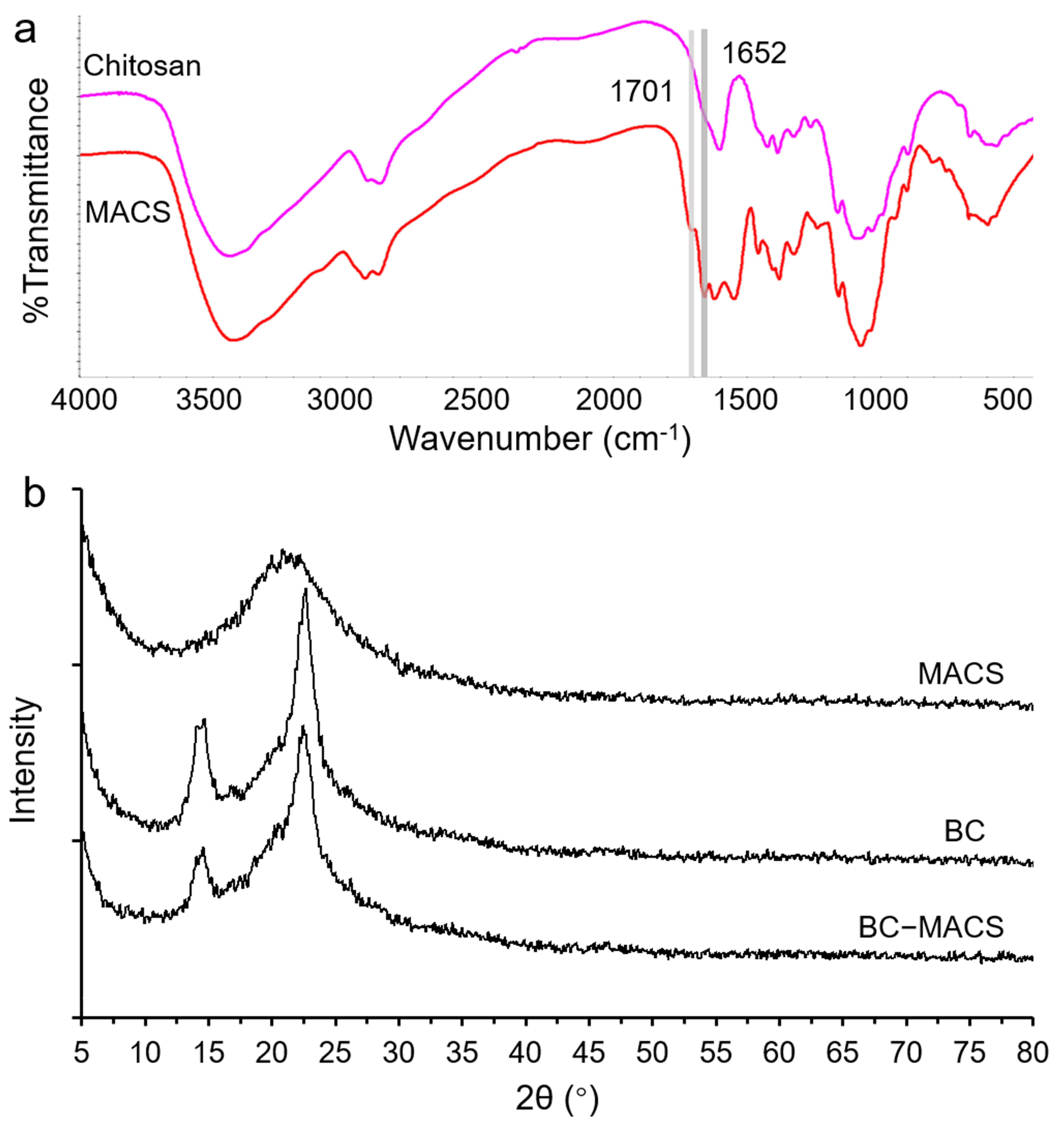
2.4.1. FTIR Analysis
2.4.2. XRD Analysis
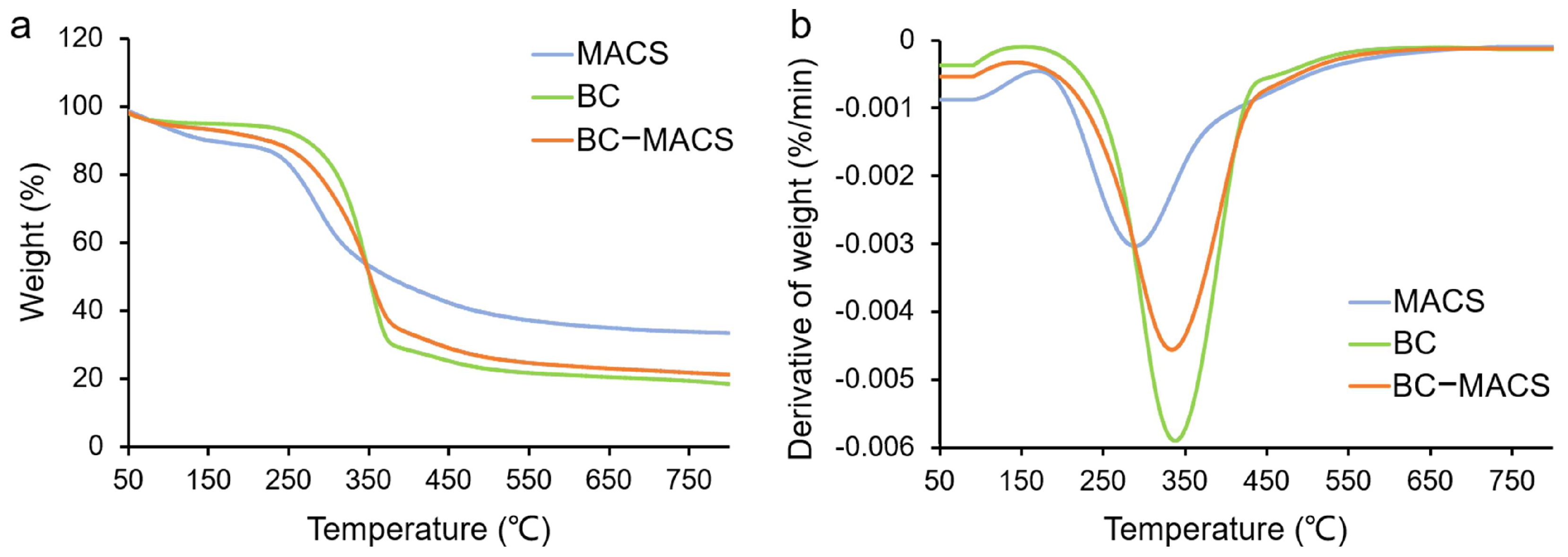
2.4.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
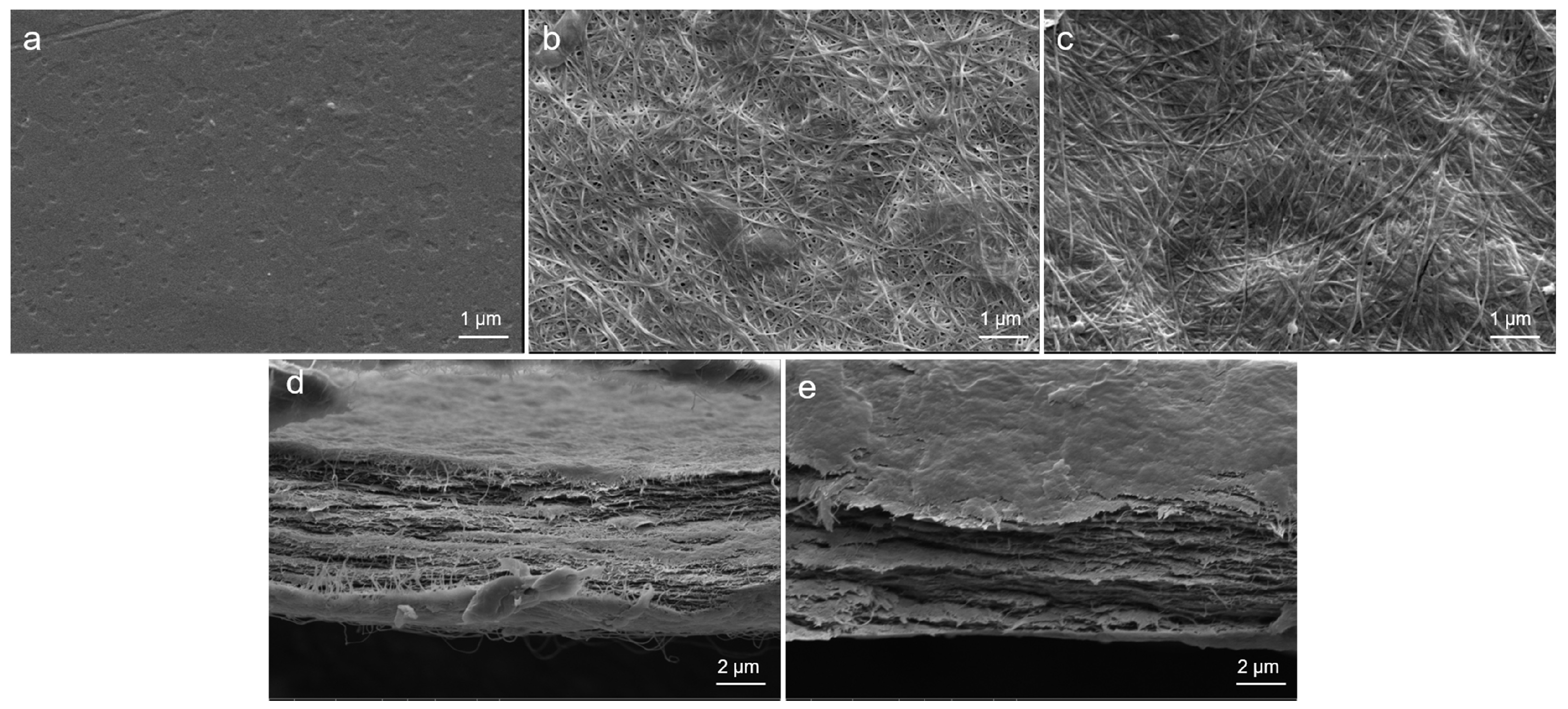
2.4.4. SEM
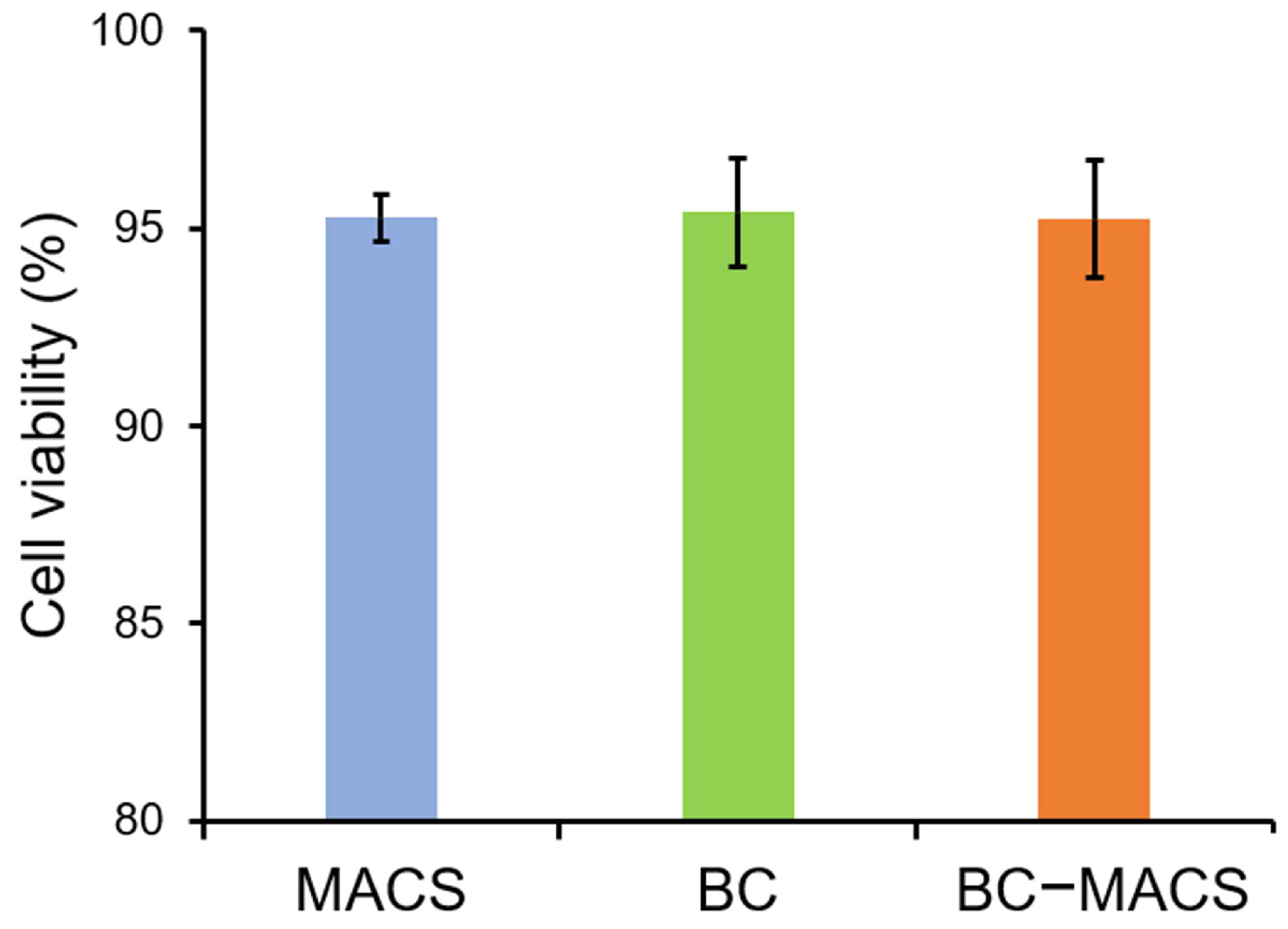
2.4.5. Cytocompatibility
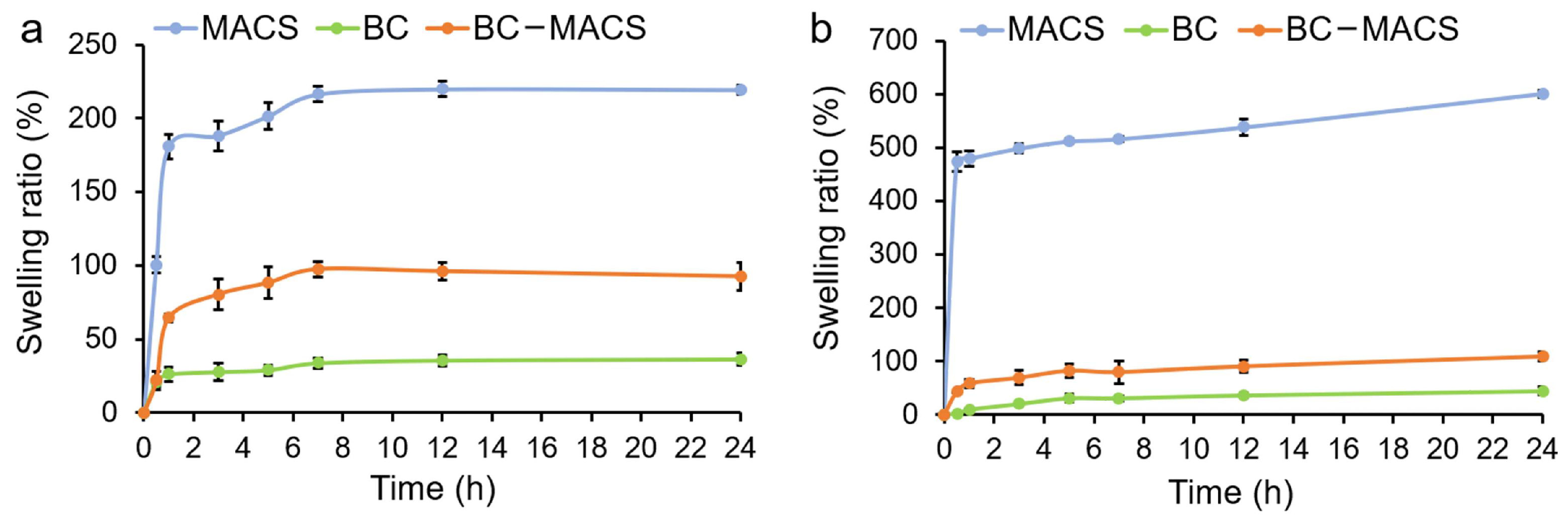
2.5. Swelling Behavior
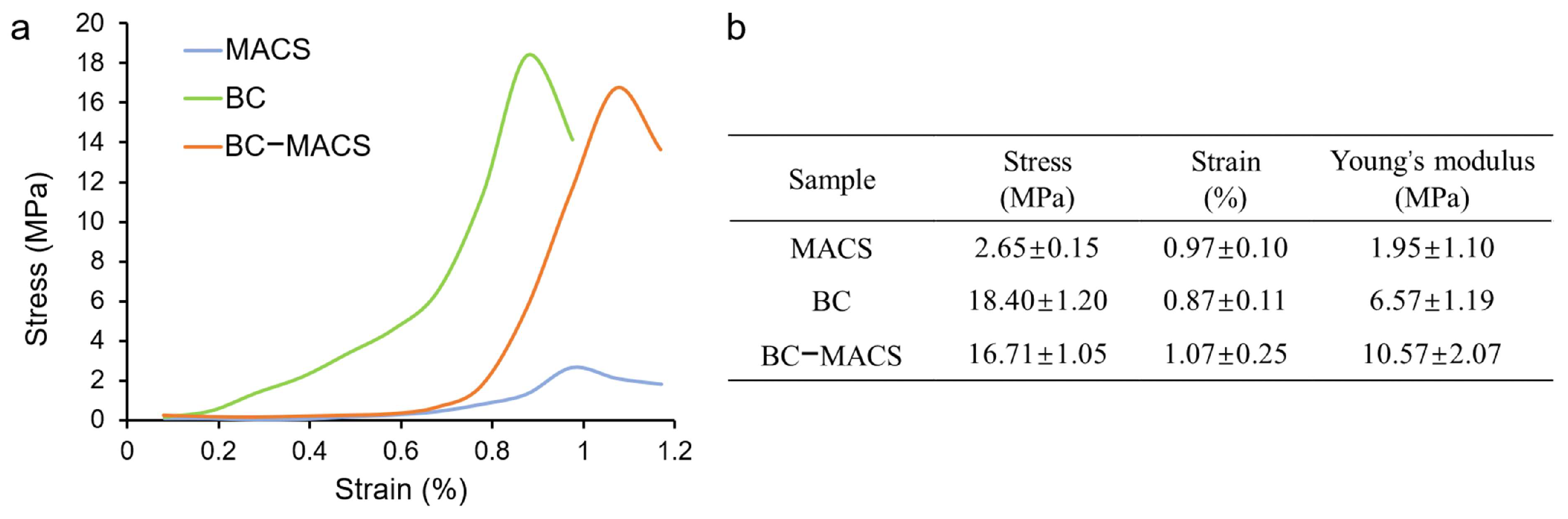
2.6. Mechanical Properties
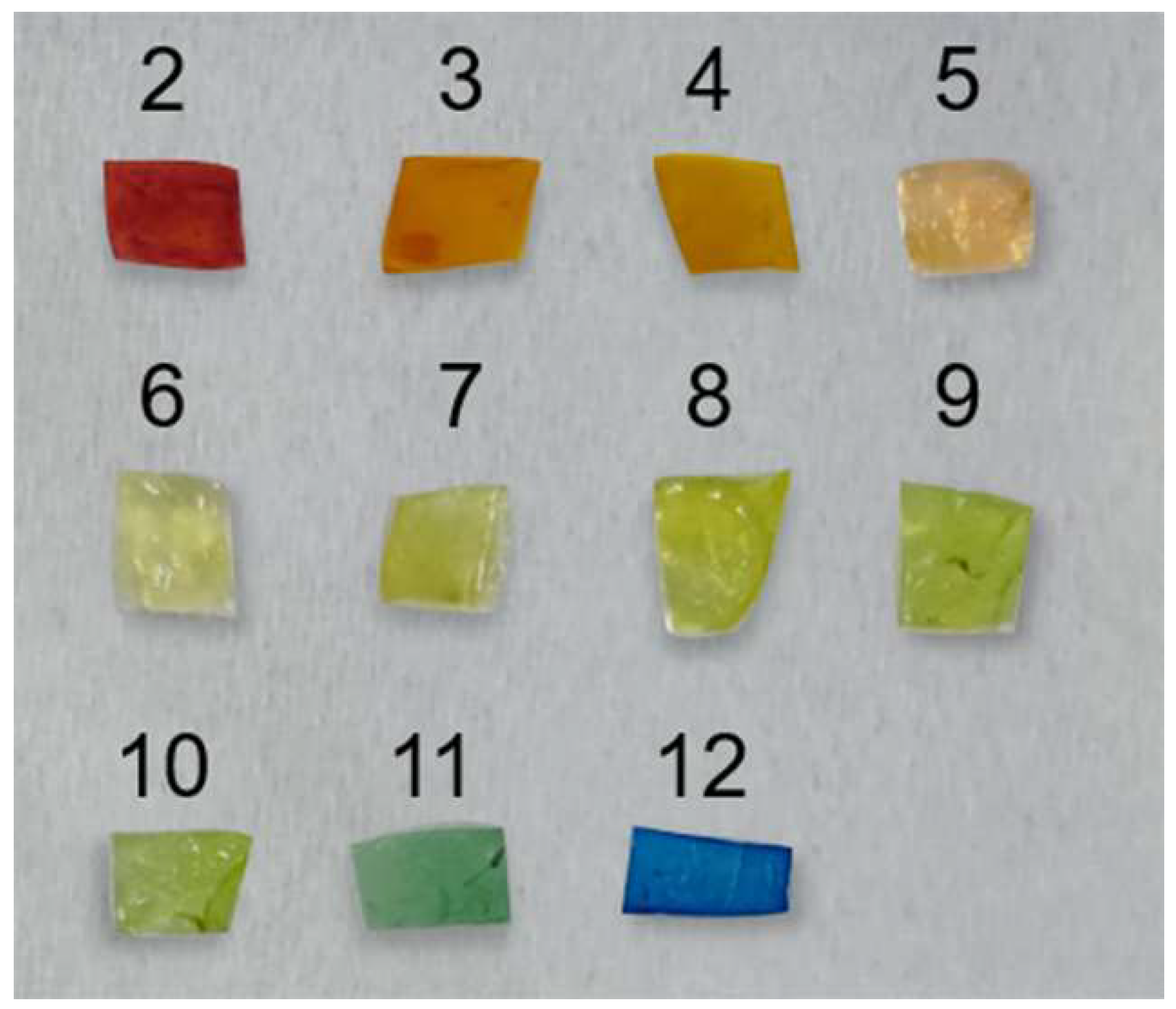
2.7. Preparation of BC-MACS pH Sensor
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of BC-MACS Hydrogel
3.2. Swelling Behavior
3.3. Mechanical Properties
3.4. BC-MACS-Based Colorimetric pH Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Avolio, R.; Grozdanov, A.; Avella, M.; Barton, J.; Cocca, M.; De Falco, F.; Dimitrov, A.T.; Errico, M.E.; Fanjul-Bolado, P.; Gentile, G.; et al. Review of pH sensing materials from macro- to nano-scale: Recent developments and examples of seawater applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 979–1021. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Li, J.; Ma, N.; Ma, X.; Gao, M. Bacterial cellulose hydrogel for sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 461, 142062. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Wang, T.; Liu, G.; Liu, H.; Xie, X.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, C.; He, Y.; Xu, F. Materials with tunable optical properties for wearable epidermal sensing in health monitoring. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2109055. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Su, R.; Teng, L.; Tian, Q.; Han, F.; Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Xie, R.; Li, G.; Liu, X.; et al. Recent advances in flexible and wearable sensors for monitoring chemical molecules. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1653–1669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vivaldi, F.; Santalucia, D.; Poma, N.; Bonini, A.; Salvo, P.; Del Noce, L.; Melai, B.; Kirchhain, A.; Kolivoška, V.; Sokolova, R.; et al. A voltammetric pH sensor for food and biological matrices. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 322, 128650. [Google Scholar]
- Waimin, J.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Heredia-Rivera, U.; Kerr, N.A.; Nejati, S.; Gallina, N.L.F.; Bhunia, A.K.; Rahimi, R. Low-Cost nonreversible electronic-free wireless pH sensor for spoilage detection in packaged meat products. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 45752–45764. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, E.M.; Sandoval, S.; Erten, A.; Takeshita, Y.; Kummel, A.C.; Martz, T.R. Solid state sensor for simultaneous measurement of total alkalinity and pH of seawater. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pourjavaher, S.; Almasi, H.; Meshkini, S.; Pirsa, S.; Parandi, E. Development of a colorimetric pH indicator based on bacterial cellulose nanofibers and red cabbage (Brassica oleraceae) extract. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 156, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Wells, N.; Yusufu, D.; Mills, A. Colourimetric plastic film indicator for the detection of the volatile basic nitrogen compounds associated with fish spoilage. Talanta 2019, 194, 830–836. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, C.M.; Maciel, V.B.V.; Mendonça, M.E.D.; Franco, T.T. Chitosan biobased and intelligent films: Monitoring pH variations. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 83–89. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, S.; Chen, X.J.S.; Chemical, A.B. A visual pH sensing film using natural dyes from Bauhinia blakeana Dunn. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 198, 268–273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Holmes, M. Novel colorimetric films based on starch/polyvinyl alcohol incorporated with roselle anthocyanins for fish freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 308–317. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, V.A., Jr.; de Arruda, I.N.Q.; Stefani, R. Active chitosan/PVA films with anthocyanins from Brassica oleraceae (Red Cabbage) as Time–Temperature Indicators for application in intelligent food packaging. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 180–188. [Google Scholar]
- Rukchon, C.; Nopwinyuwong, A.; Trevanich, S.; Jinkarn, T.; Suppakul, P. Development of a food spoilage indicator for monitoring freshness of skinless chicken breast. Talanta 2014, 130, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khattak, W.A.; Park, J.K. Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: A multipurpose advanced material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Li, J.; Bao, Z.; Hu, M.; Nian, R.; Feng, D.; An, D.; Li, X.; Xian, M.; Zhang, H. A natural in situ fabrication method of functional bacterial cellulose using a microorganism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 437. [Google Scholar]
- Siripongpreda, T.; Somchob, B.; Rodthongkum, N.; Hoven, V.P. Bacterial cellulose-based re-swellable hydrogel: Facile preparation and its potential application as colorimetric sensor of sweat pH and glucose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117506. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi, M.; Tajik, H.; Almasi, H.; Forough, M.; Ezati, P.J. A novel pH-sensing indicator based on bacterial cellulose nanofibers and black carrot anthocyanins for monitoring fish freshness. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115030. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Han, J.; Sun, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X.; Jia, Z. An intelligent colorimetric film based on complex anthocyanins and bacterial cellulose nanofibers for tilapia freshness detection in an actual cold chain. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Hiekkataipale, P.; Malm, J.; Karppinen, M.; Ikkala, O.; Ras, R.H.A. Inorganic hollow nanotube aerogels by atomic layer deposition onto native nanocellulose templates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Osi, A.R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Fu, J.; Müller-Buschbaum, P.; Zhong, Q. Three-Dimensional-printable thermo/photo-cross-linked methacrylated chitosan–gelatin hydrogel composites for tissue engineering. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 22902–22913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Bratlie, K.M. pH sensitive methacrylated chitosan hydrogels with tunable physical and chemical properties. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Yin, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Photocrosslinked methacrylated chitosan-based nanofibrous scaffolds as potential skin substitute. Cellulose 2017, 24, 4253–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Wang, K.; Yang, D.; Nie, J. Photopolymerization of methacrylated chitosan/PNIPAAm hybrid dual-sensitive hydrogels as carrier for drug delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2009, 44, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.M.; Lau, W.M.; Khutoryanskiy, V. Methacrylated chitosan as a polymer with enhanced mucoadhesive properties for transmucosal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Li, N.; Jian, X. Apatite formation induced by chitosan/gelatin hydrogel coating anchored on poly(aryl ether nitrile ketone) substrates to promote osteoblastic differentiation. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, 2100262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hakkarainen, M.; Grützmacher, H.; Chiappone, A.; Sangermano, M. Photocrosslinked chitosan hydrogels reinforced with chitosan-derived nano-graphene oxide. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2019, 220, 1900174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, A.; Lu, B.; Zhang, T.; Kong, M. Dual cure (thermal/photo) composite hydrogel derived from chitosan/collagen for in situ 3D bioprinting. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Du, H.; Chai, N.; Sha, Z.; Geng, M.; Zhou, X.; He, C. Tannic acid-reinforced methacrylated chitosan/methacrylated silk fibroin hydrogels with multifunctionality for accelerating wound healing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; Rai, K.; Zhang, M.; Nian, R.; Bao, Z.; et al. High-Strength collagen-based composite films regulated by water-soluble recombinant spider silk proteins and water annealing. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 3341–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, I.M.S.; Silva, R.R.; Pacheco, G.; Lustri, W.R.; Tercjak, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Júnior, J.R.S.; Azevedo, F.H.C.; Figuêredo, G.S.; Vega, M.L.; et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of bacterial cellulose–copper oxide nanocomposites and evaluation of their antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima Fontes, M.; Meneguin, A.B.; Tercjak, A.; Gutierrez, J.; Cury, B.S.F.; dos Santos, A.M.; Ribeiro, S.J.L.; Barud, H.S. Effect of in situ modification of bacterial cellulose with carboxymethylcellulose on its nano/microstructure and methotrexate release properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Ji, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jia, Z.; Yang, X. Preparation and characterization of intelligent packaging film for visual inspection of tilapia fillets freshness using cyanidin and bacterial cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.; Dong, S.; Shen, J.; Dong, J. Improved thermal and mechanical properties of bacterial cellulose with the introduction of collagen. Cellulose 2017, 24, 3777–3787. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Zhang, X.-L.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Wu, Z.-L. Removal of color from textile dyeing wastewater by foam separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Promphet, N.; Rattanawaleedirojn, P.; Siralertmukul, K.; Soatthiyanon, N.; Potiyaraj, P.; Thanawattano, C.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Rodthongkum, N. Non-Invasive textile based colorimetric sensor for the simultaneous detection of sweat pH and lactate. Talanta 2019, 192, 424–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. Bacterial cellulose incorporating multicolor fluorescent probes for visual acidity detection in paper-based cultural relics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 60902–60911. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bao, Z.; Liu, J.; Bi, Y.; Zhao, G. Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring. Polymers 2025, 17, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914
Bao Z, Liu J, Bi Y, Zhao G. Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914
Chicago/Turabian StyleBao, Zixian, Jiezheng Liu, Yujia Bi, and Guang Zhao. 2025. "Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring" Polymers 17, no. 7: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914
APA StyleBao, Z., Liu, J., Bi, Y., & Zhao, G. (2025). Smart Bacterial Cellulose–Methylacrylated Chitosan Composite Hydrogel: Multifunctional Characterization for Real-Time pH Monitoring. Polymers, 17(7), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070914








