Surface-Driven Phase Segregation in Conducting Polymer Thin Films Enables High Selectivity and Storage Stability of Chemiresistive Sensors in Humid Air
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of EDOT-HFIP and EDOT-Cn
2.3. Fabrication of the Chemiresistive Sensor
2.4. Materials and Interface Characterization
2.5. Evaluation of Chemiresistive Sensors
2.6. Calculation of the Selectivity Coefficient
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of P(EDOT-HFIP-Co-EDOT-Cn)s
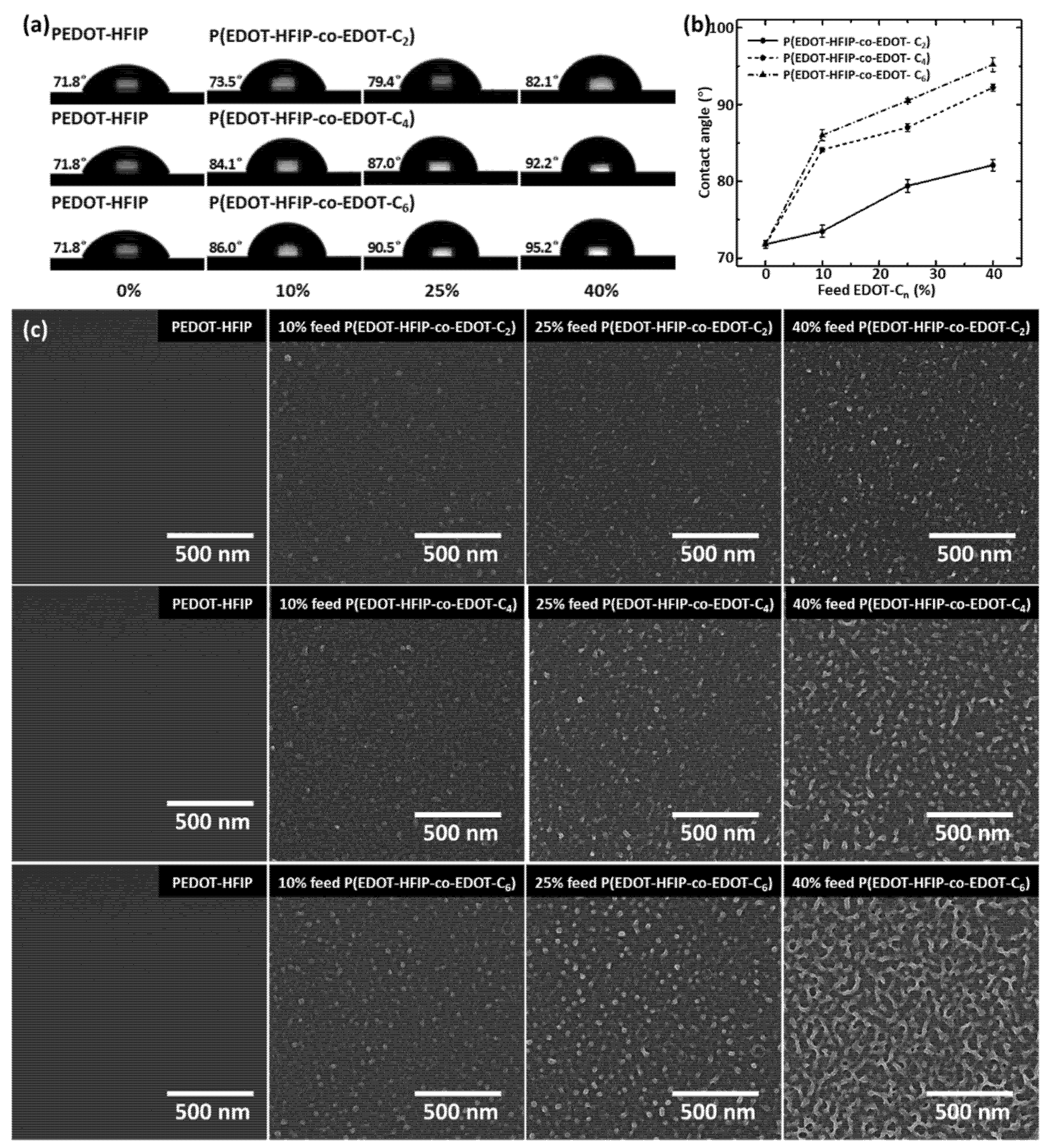
3.2. Surface-Driven Nano-Assembly and Phase Segregation
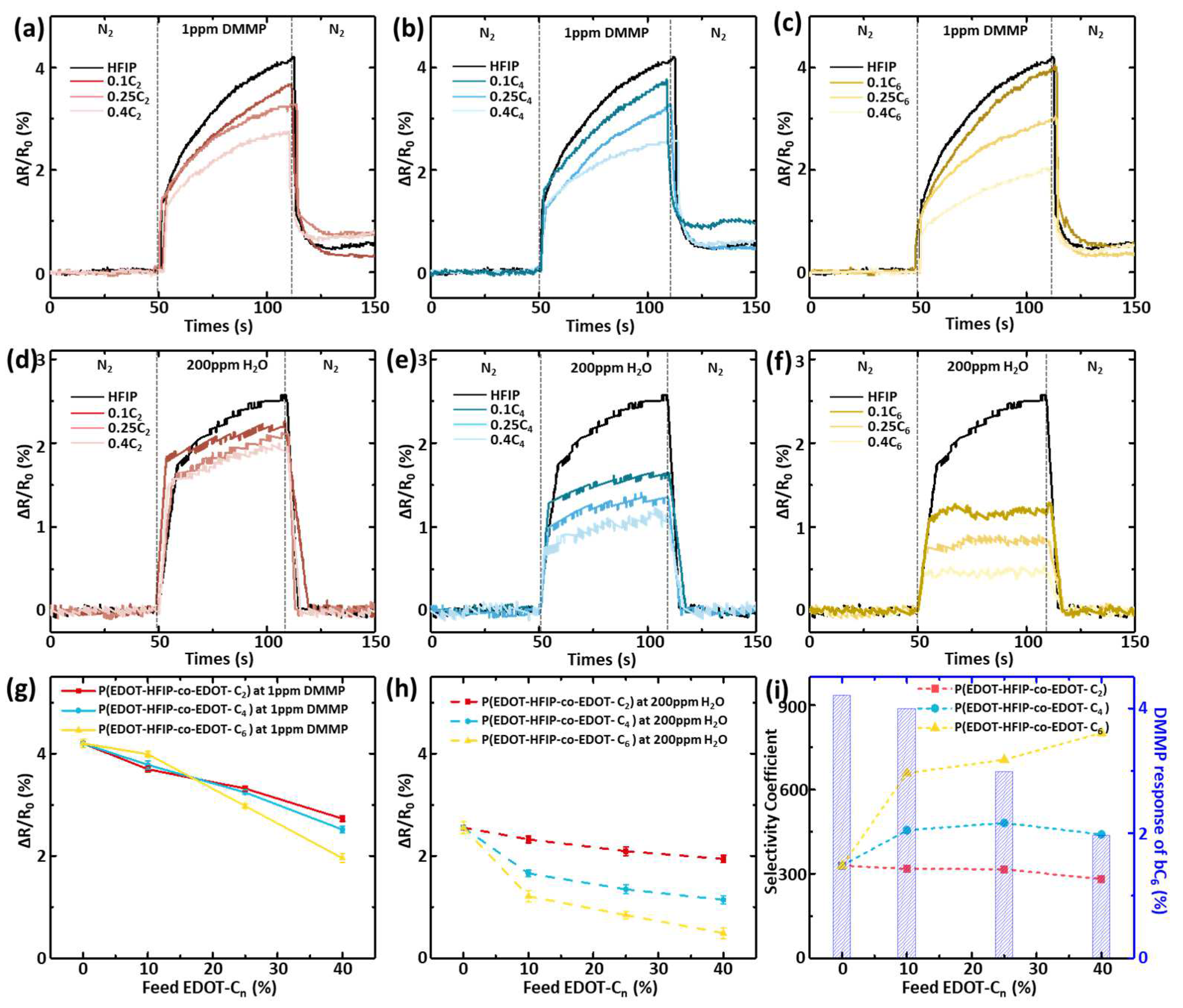
3.3. Specific Sensing and Water Resistance of P(EDOT-HFIP-Co-EDOT-Cn) Sensors
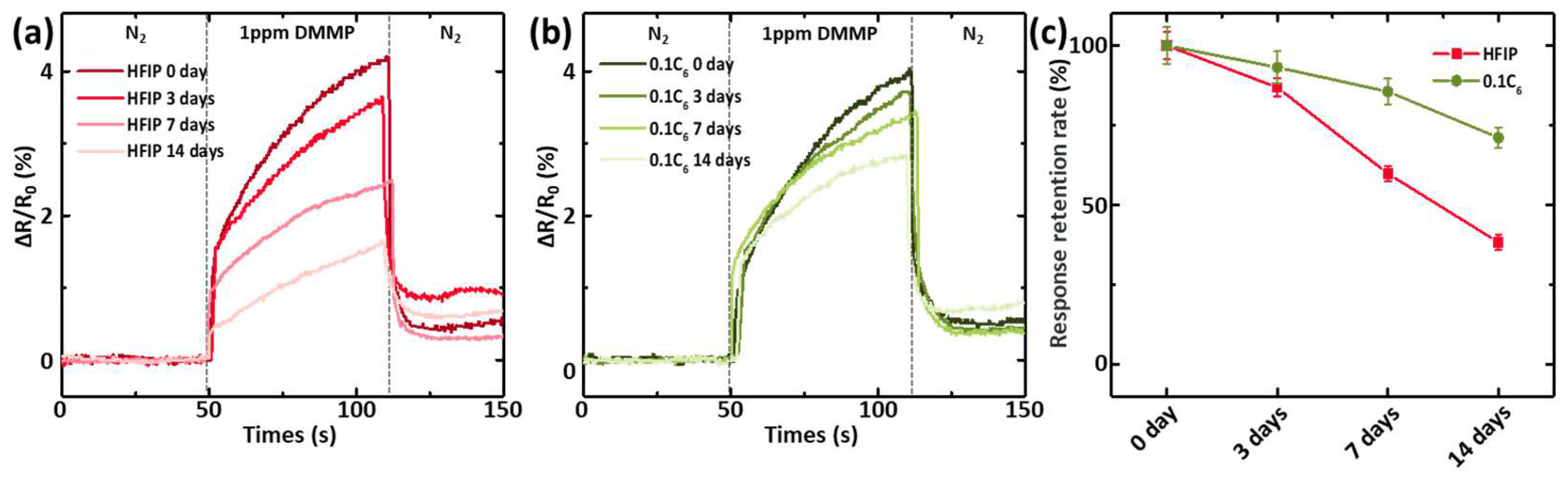
3.4. Shelf Storage Stability of P(EDOT-HFIP-Co-EDOT-Cn) Sensors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallero, D.A. Fundamentals of Air Pollution—Fifth Edition; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Qin, M.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J. Progress of sensitive materials in chemiresistive sensors for detecting chemical warfare agent simulants: A review. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2023, 42, 20220052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, P.; Ghaemi, A. Chemiresistor gas sensors: Design, Challenges, and Strategies: A comprehensive review. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 154999–155046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, L.A.; Deo, V.V.; Shinde, M.D.; Bari, A.R.; Kaushik, M.P. Sensing of 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide (2-CEES)—A CWA simulant—Using pure and platinum doped nanostructured CdSnO3 thin films prepared from ultrasonic spray pyrolysis technique. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fei, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. The synergistic effects of oxygen vacancy engineering and surface gold decoration on commercial SnO2 for ppb-level DMMP sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Duan, G.; Cheng, Z.; Xu, L.; Li, T.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Cai, W. Janus gas: Reversible redox transition of Sarin enables its selective detection by an ethanol modified nanoporous SnO2 chemiresistor. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8193–8196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Li, K.; Ren, X.; Yan, W.; Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. A highly selective gas sensor based on the WO3/WS2 van der Waals heterojunction for the 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide (2-CEES) sensing application. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. Opt. Electron. Devices 2021, 9, 17496–17503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Cho, S.; Song, M.-J.; Lee, W. Highly sensitive gas sensor based on Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles for detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate as a chemical warfare agent simulant. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Jiang, M.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Zeng, M.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, N.; Su, Y.; Yang, Z. Room temperature DMMP gas sensing based on cobalt phthalocyanine derivative/graphene quantum dot hybrid materials. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 14805–14813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, M.; Liu, W.; Dong, L.; Chen, D.; Peng, C. Gas sensors based on assembled porous graphene multilayer frameworks for DMMP detection. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. Opt. Electron. Devices 2019, 7, 9248–9256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Wang, Y.; Chai, J.; Gao, R.; Yang, Z.; Kong, E.S.-W.; Zhang, Y. Gas sensor based on p-phenylenediamine reduced graphene oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 163, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-T.; Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, C.Y. Graphene chemiresistors modified with functionalized triphenylene for highly sensitive and selective detection of dimethyl methylphosphonate. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33976–33980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederoder, M.S.; Nallon, E.C.; Weiss, M.; McGraw, S.K.; Schnee, V.P.; Bright, C.J.; Polcha, M.P.; Paffenroth, R.; Uzarski, J.R. Graphene Nanoplatelet-Polymer Chemiresistive Sensor Arrays for the Detection and Discrimination of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Han, H.; Jang, J.; Cho, S. Fabrication and Optimization of Conductive Paper Based on Screen-Printed Polyaniline/Graphene Patterns for Nerve Agent Detection. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 5586–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saetia, K.; Schnorr, J.M.; Mannarino, M.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Rutledge, G.C.; Swager, T.M.; Hammond, P.T. Spray-Layer-by-Layer Carbon Nanotube/Electrospun Fiber Electrodes for Flexible Chemiresistive Sensor Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhang, Y.; Sonkusale, S.R.; Wang, M.L.; Dokmeci, M.R. SWNT based nanosensors for wireless detection of explosives and chemical warfare agents. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Meng, F.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Liu, J. Novel pyrenehexafluoroisopropanol derivative-decorated single-walled carbon nanotubes for detection of nerve agents by strong hydrogen-bonding interaction. Analyst 2010, 135, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gu, H.; Swager, T.M. Carbon nanotube/polythiophene chemiresistive sensors for chemical warfare agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5392–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Kim, J.; Song, M.-J.; Lee, W.; Noh, J.S. Nano-composite sensors composed of single-walled carbon nanotubes and polyaniline for the detection of a nerve agent simulant gas. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Xia, Y. Carbon nanomaterials-based electrochemical aptasensors. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.C.; Ang, B.C.; Haseeb, A.S.M.A.; Baharuddin, A.A.; Wong, Y.H. Review—Conducting polymers as chemiresistive gas sensing materials: A review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 37503–37518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Weng, J.; Geng, Z.; Pan, Q.; Pei, X.; He, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Wei, R.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Solution-processed wafer-scale nanoassembly of conducting polymers enables selective ultratrace nerve agent detection at low power. Nano Res. 2022, 16, 5653–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grate, J.W.; Klusty, M.; Barger, W.R.; Snow, W. Role of selective sorption in chemiresistor sensors for organophosphorus detection. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 1927–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, M.K.; Sumita, M.; Labuta, J.; Payne, D.T.; Hill, J.P.; Yamauchi, Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kataura, H.; Koga, K.; et al. Selective Detection of Toxic C1 Chemicals Using a Hydroxylamine-Based Chemiresistive Sensor Array. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiggemann, L.; Ballen, S.C.; Bocalon, C.M.; Graboski, A.M.; Manzoli, A.; Steffens, J.; Valduga, E.; Steffens, C. Electronic nose system based on polyaniline films sensor array with different dopants for discrimination of artificial aromas. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. 2017, 43, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, R.J.; Farajikhah, S.; Oveissi, F.; Dehghani, F.; Naficy, S. Chemiresistive Sensor Arrays for Gas/Volatile Organic Compounds Monitoring: A Review. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 25, 2200830–2200851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.A.; Luo, S.C.; Zhu, B.; Chen, C.; Yamashita, Y.; Yu, H.H. Molecular or Nanoscale Structures? The Deciding Factor of Surface Properties on Functionalized Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Nanorod Arrays. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3212–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, J.; Wu, W.; Qian, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Geng, Z.; Zhu, B. Surface-Driven Phase Segregation in Conducting Polymer Thin Films Enables High Selectivity and Storage Stability of Chemiresistive Sensors in Humid Air. Polymers 2025, 17, 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070979
Weng J, Wu W, Qian M, Zhang J, Zhang S, Geng Z, Zhu B. Surface-Driven Phase Segregation in Conducting Polymer Thin Films Enables High Selectivity and Storage Stability of Chemiresistive Sensors in Humid Air. Polymers. 2025; 17(7):979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070979
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Jianan, Wei Wu, Minghao Qian, Jiarui Zhang, Shuhua Zhang, Zhi Geng, and Bo Zhu. 2025. "Surface-Driven Phase Segregation in Conducting Polymer Thin Films Enables High Selectivity and Storage Stability of Chemiresistive Sensors in Humid Air" Polymers 17, no. 7: 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070979
APA StyleWeng, J., Wu, W., Qian, M., Zhang, J., Zhang, S., Geng, Z., & Zhu, B. (2025). Surface-Driven Phase Segregation in Conducting Polymer Thin Films Enables High Selectivity and Storage Stability of Chemiresistive Sensors in Humid Air. Polymers, 17(7), 979. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17070979





