Preparation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Various Polymerylated Divalent Metal-Doped MF2O4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn) Ferrites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
Characterization
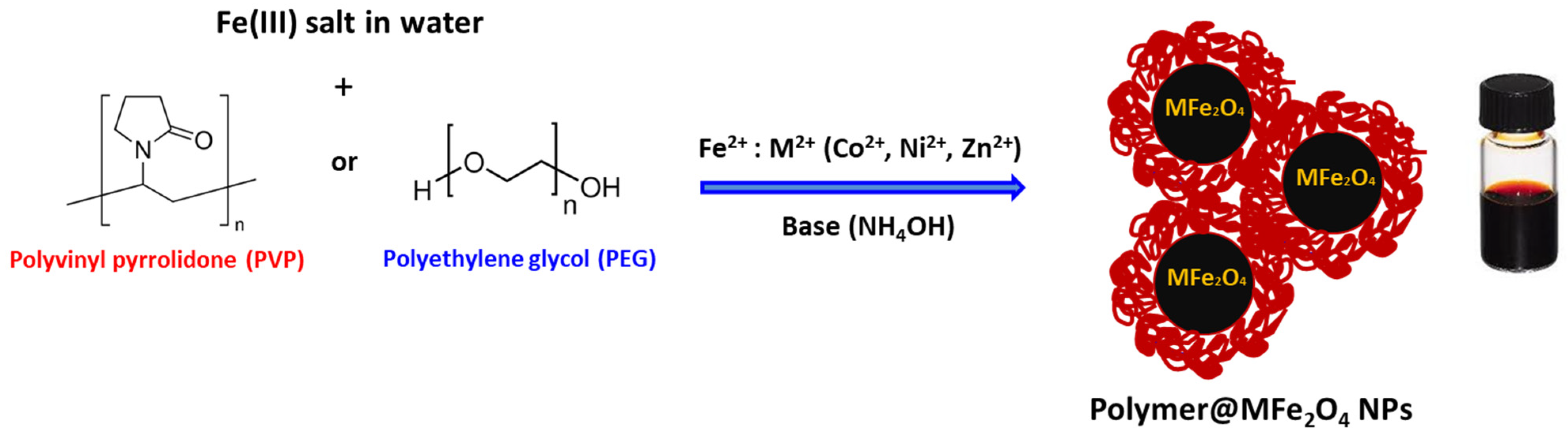
2.2. Preparation of Polymer-Coated MFe2O4 NPs
2.3. Antibacterial Inhibition Experiments
2.4. Cell Viability and Proliferation Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Polymer-Coated Ferrites
3.2. Magnetic Properties
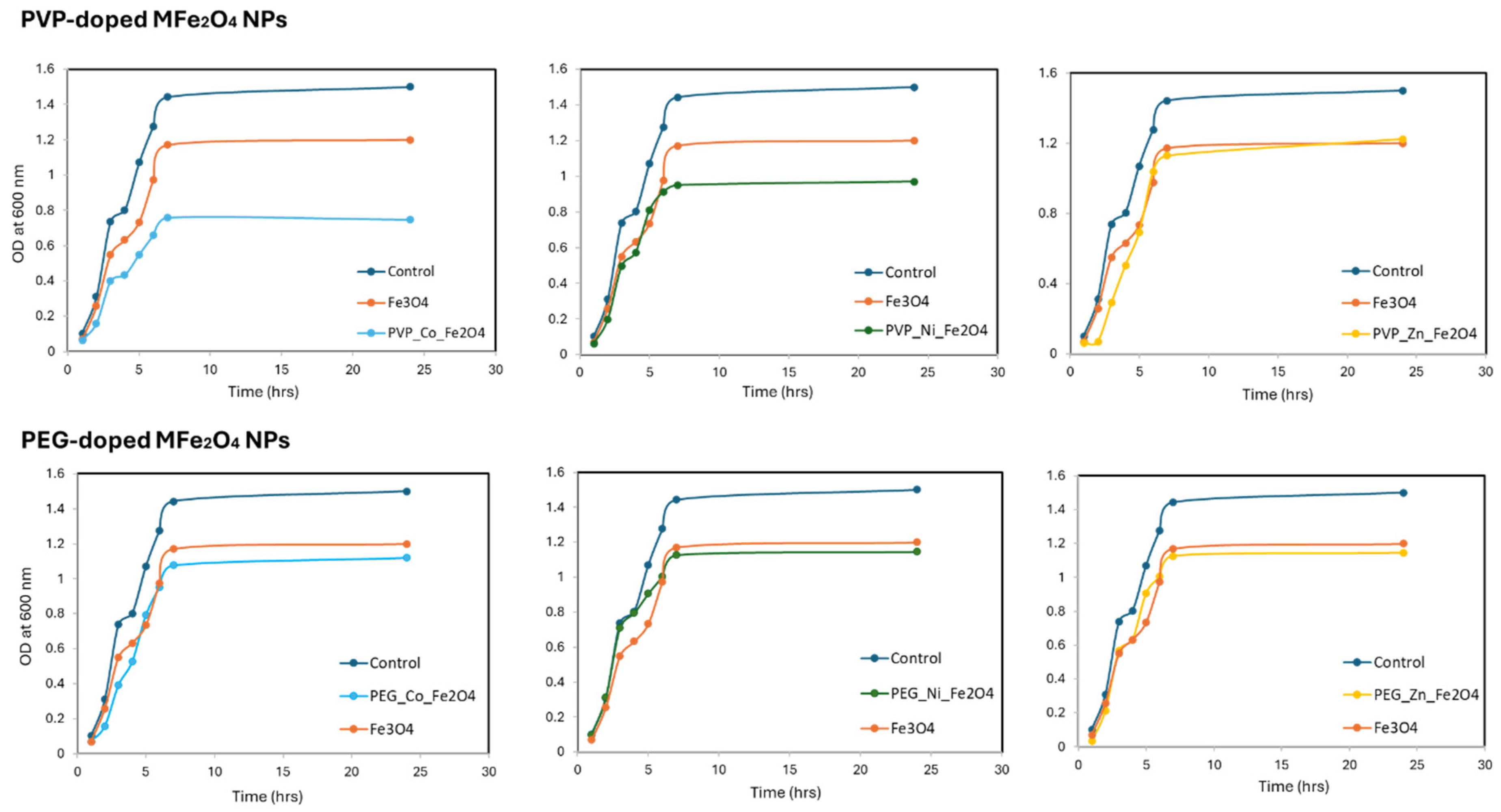
3.3. Antibacterial Activity
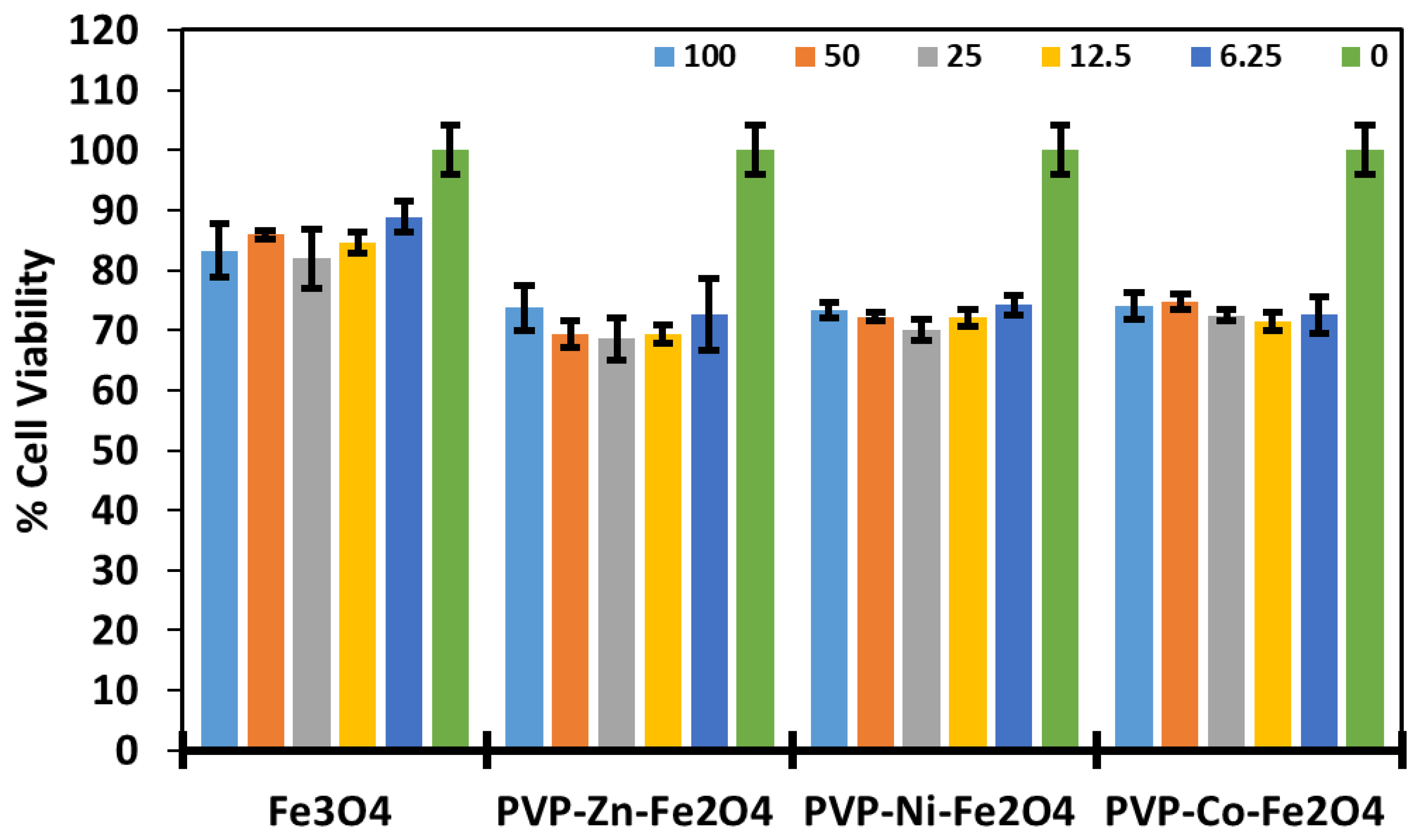
3.4. Cytotoxicity and Safety Profiles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baker, R.E.; Mahmud, A.S.; Miller, I.F.; Rajeev, M.; Rasambainarivo, F.; Rice, B.L.; Takahashi, S.; Tatem, A.J.; Wagner, C.E.; Wang, L.F.; et al. Infectious disease in an era of global change. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, M.; Saïd, N.; Ojcius, D.M. The book reopened on infectious diseases. Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban-Chmiel, R.; Marek, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Wieczorek, K.; Dec, M.; Nowaczek, A.; Osek, J. Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria-A Review. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanini-Salinas, J.; Andrades-Lagos, J.; Mella-Raipan, J.; Vasquez-Velasquez, D. Novel Classes of Antibacterial Drugs in Clinical Development, a Hope in a Post-antibiotic Era. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 1188–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Korilis, A.; Cojocaru, M.; Berzosa, M.; Gamazo, C.; Andrade, N.J.; Ciuffi, K.J. Comparison of antibacterial activity and cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver-loaded montmorillonite and saponite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 240, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, N.; Durán, M.; de Jesus, M.B.; Seabra, A.B.; Fávaro, W.J.; Nakazato, G. Silver nanoparticles: A new view on mechanistic aspects on antimicrobial activity. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.A.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.; Reynolds, E.C.; Pantarat, N.; Biswas, D.P.; O’Connor, A.J. Low cytotoxic trace element selenium nanoparticles and their differential antimicrobial properties against S. aureus and E. coli. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 045101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.S.G.G.; Ramalho, P.S.F.; Viana, A.T.; Lopes, A.R.; Gonçalves, A.G.; Nunes, O.C.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Soares, O.S.G.P. Feasibility of using magnetic nanoparticles in water disinfection. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 288, 112410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Saei, A.A.; Walker, E.D.; Conley, B.; Omidi, Y.; Lee, K.B.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanotechnology for Targeted Detection and Removal of Bacteria: Opportunities and Challenges. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Gruden, C.; Huang, X. Magnetic Glyco-nanoparticles: A Unique Tool for Rapid Pathogen Detection, Decontamination, and Strain Differentiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 13392–13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhang, J.; Jia, H.; Guo, X.; Yue, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Yue, T. Synthesis of silver/Fe3O4@chitosan@polyvinyl alcohol magnetic nanoparticles as an antibacterial agent for accelerating wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 221, 1404–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Brahim, J.S. Saussurea costus extract as bio mediator in synthesis iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) and their antimicrobial ability. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf, E.M.; Hassan, A.; Al-Salmi, F.A.; Albalwe, F.M.; Albalawi, H.M.R.; Darwish, D.B.; Fayad, E. Synergistic antibacterial activity of compact silver/magnetite core-shell nanoparticles core shell against Gram-negative foodborne pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, M.; Thiesen, B.; Wust, P.; Jordan, A. Magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia for prostate cancer. Int. J. Hyperth. 2010, 26, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Boubbou, K. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as drug carriers: Clinical relevance. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, P.V.; Rao, K.S.; Kumar, K.R.; Kapusetti, G.; Choppadandi, M.; Kiran, J.N.; Rao, K.H. A study of uncoated and coated nickel-zinc ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 266, 124546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samavati, A.; Ismail, A.F. Antibacterial properties of copper-substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. Particuology 2017, 30, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasnim, N.T.; Ferdous, N.; Rumon, M.M.H.; Shakil, M.S. The Promise of Metal-Doped Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Antimicrobial Agent. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekha, K.; Nirmala, M.; Nair, M.G.; Anukaliani, A. Structural, optical, photocatalytic and antibacterial activity of zinc oxide and manganese doped zinc oxide nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2010, 405, 3180–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczak, K.; Kosmalska, D.; Kaczor, D.; Raszkowska-Kaczor, A.; Wedderburn, L.; Malinowski, R. Bactericidal and Fungistatic Properties of LDPE Modified with a Biocide Containing Metal Nanoparticles. Materials 2021, 14, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, S.J.; Mahmood, W.M. Review on magnetic spinel ferrite (MFe2O4) nanoparticles: From synthesis to application. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana Acharyulu, N.P.; Sohan, A.; Banoth, P.; Chintalapati, S.; Doshi, S.; Reddy, V.; Santhosh, C.; Grace, A.N.; De Los Santos Valladares, L.; Kollu, P. Effect of the Graphene- Ni/NiFe2O4 Composite on Bacterial Inhibition Mediated by Protein Degradation. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 30794–30800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbu, P. Chemical synthesis of NiFe2O4/NG/cellulose nanocomposite and its antibacterial potential against bacterial pathogens. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022, 69, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfei, S.; Schito, G.C.; Schito, A.M.; Zuccari, G. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Antibacterial Oxidative Therapies: Available Methods to Generate ROS and a Novel Option Proposal. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, A.K.; Sen Yadav, B.; Singh, J.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, N. Antibacterial activity of PANI coated CoFe2O4 nanocomposite for gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheidari, D.; Mehrdad, M.; Maleki, S.; Hosseini, S. Synthesis and potent antimicrobial activity of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles under visible light. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghniaz, R.; Rabbani, A.; Vajhadin, F.; Khan, T.; Kousar, R.; Khan, A.R.; Montazerian, H.; Iqbal, J.; Libanori, A.; Kim, H.-J.; et al. Anti-bacterial and wound healing-promoting effects of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, R.; Ahmed, M.K.; Uskoković, V. Magnetic, microstructural and photoactivated antibacterial features of nanostructured Co–Zn ferrites of different chemical and phase compositions. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 856, 157013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Lemine, O.M.; Algessair, S.; Madkhali, N.; Al-Najar, B.; AlMatri, E.; Ali, R.; Henini, M. Preparation and characterization of various PVPylated divalent metal-doped ferrite nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 15664–15679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Boubbou, K. Acid-Stabilized Iron-Based Metal Oxide Colloidal Nanoparticles, and Methods Thereof. U.S. Patent, US10629339B2, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- El-Boubbou, K.; Lemine, O.M.; Ali, R.; Huwaizi, S.M.; Al-Humaid, S.; AlKushi, A. Evaluating magnetic and thermal effects of various Polymerylated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for combined chemo-hyperthermia. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 5489–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Sarkar, K. Effect of iron oxide and gold nanoparticles on bacterial growth leading towards biological application. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Maashani, M.S.; Khalaf, K.A.; Gismelseed, A.M.; Al-Omari, I.A. The structural and magnetic properties of the nano-CoFe2O4 ferrite prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 817, 152786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaoud, A.; Lemine, O.M.; Ihzaz, N.; El Mir, L.; Alrub, S.A.; El-Boubbou, K. Magneto-thermal properties of Co-doped maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia applications. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2022, 639, 413993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, A.; Sharma, M.; Sahu, N.K. Assessing magnetic and inductive thermal properties of various surfactants functionalised Fe3O4 nanoparticles for hyperthermia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, S.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.-X.J.; Yu, J.C.; Leung, K.C.-F. Facile synthesis of size-controllable monodispersed ferrite nanospheres. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5086–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choa, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.H. Comparison of the Magnetic Properties for the Surface-Modified Magnetite Nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2874–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antarnusa, G.; Suharyadi, E. A synthesis of polyethylene glycol (PEG)-coated magnetite Fe3O4 nanoparticles and their characteristics for enhancement of biosensor. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 056103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, K.; Mumtaz, A.; Hasanain, S.K.; Ceylan, A. Synthesis and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite (CoFe2O4) nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 308, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, A.; Geleta, D.D.; Krishnamoorthi, C.; Lee, J. Synthesis, characterization and magnetic hyperthermia properties of nearly monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 28035–28041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vara Prasad, B.B.V.S.; Ramesh, K.V.; Srinivas, A. Structural and Magnetic Studies of Nano-crystalline Ferrites MFe2O4 (M = Zn, Ni, Cu, and Co) Synthesized Via Citrate Gel Autocombustion Method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2017, 30, 3523–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, Q.; Gao, M. Preparation of water-soluble magnetite nanocrystals from hydrated ferric salts in 2-pyrrolidone: Mechanism leading to Fe3O4. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Bao, H.; Gao, M. One-Pot Reaction to Synthesize Water-Soluble Magnetite Nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 1391–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebniya, S.; Sharifi, I.; Saeri, M.R.; Doostmohammadi, A. Study of Cation Distribution and Magnetic Properties of MFe2O4 (M = Fe, Co, Zn, Mn, and Cu) Nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 2022, 35, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P, L.R.; Seetharaman, D. Investigation of thermal stability, structure, magnetic and dielectric properties of solvothermally synthesised SnFe2O4. Open Ceram. 2022, 9, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanigaram, M.; Kodam, U.; Noh, J.-S.; Nam, Y.-W. Cation distribution in MFe2O4 (M = Ni, Co): X-ray diffraction, electron spectroscopy, Raman, and magnetization studies. J. Phys. Chem. Solid. 2022, 171, 111036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Rana, A.; Yadav, M.S.; Pant, R.P. Size-induced effect on nano-crystalline CoFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2008, 320, 1729–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, S.; Li, G. Growth Kinetics, Cation Occupancy, and Magnetic Properties of Multimetal Oxide Nanoparticles: A Case Study on Spinel NiFe2O4. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 19467–19477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunpratub, S.; Phokha, S.; Kidkhunthod, P.; Chanlek, N.; Chindaprasirt, P. The effect of cation distribution on the magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 nanoparticles. Results Phys. 2021, 24, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, R.; De, M.; Tewari, H.S.; Ghoshal, S.K. Structural and magnetic properties of tailored NiFe2O4 nanostructures synthesized using auto-combustion method. Results Phys. 2020, 16, 102916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Lee, N.; Kim, H.; An, K.; Park, Y.I.; Choi, Y.; Shin, K.; Lee, Y.; Kwon, S.G.; Na, H.B.; et al. Large-Scale Synthesis of Uniform and Extremely Small-Sized Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for High-Resolution T1 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Contrast Agents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12624–12631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, F.; MacRenaris, K.W.; Waters, E.A.; Liang, T.; Schultz-Sikma, E.A.; Eckermann, A.L.; Meade, T.J. Ultrasmall, Water-Soluble Magnetite Nanoparticles with High Relaxivity for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20855–20860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; von Maltzahn, G.; Zhang, L.; Schwartz, M.P.; Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Magnetic iron oxide nanoworms for tumor targeting and imaging. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemine, O.M.; Algessair, S.; Madkhali, N.; Al-Najar, B.; El-Boubbou, K. Assessing the Heat Generation and Self-Heating Mechanism of Superparamagnetic Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia Application: The Effects of Concentration, Frequency, and Magnetic Field. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska-Krochmal, B.; Dudek-Wicher, R. The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance. Pathogens 2021, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial activity of metals: Mechanisms, molecular targets and applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdal Dayem, A.; Hossain, M.K.; Lee, S.B.; Kim, K.; Saha, S.K.; Yang, G.M.; Choi, H.Y.; Cho, S.G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in the Biological Activities of Metallic Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezealigo, U.S.; Ezealigo, B.N.; Aisida, S.O.; Ezema, F.I. Iron oxide nanoparticles in biological systems: Antibacterial and toxicology perspective. JCIS Open 2021, 4, 100027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovita, C.; Florea, A.; Scorus, L.; Pall, E.; Dudric, R.; Moldovan, A.I.; Stiufiuc, R.; Tetean, R.; Lucaciu, C.M. Hyperthermia, Cytotoxicity, and Cellular Uptake Properties of Manganese and Zinc Ferrite Magnetic Nanoparticles Synthesized by a Polyol-Mediated Process. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
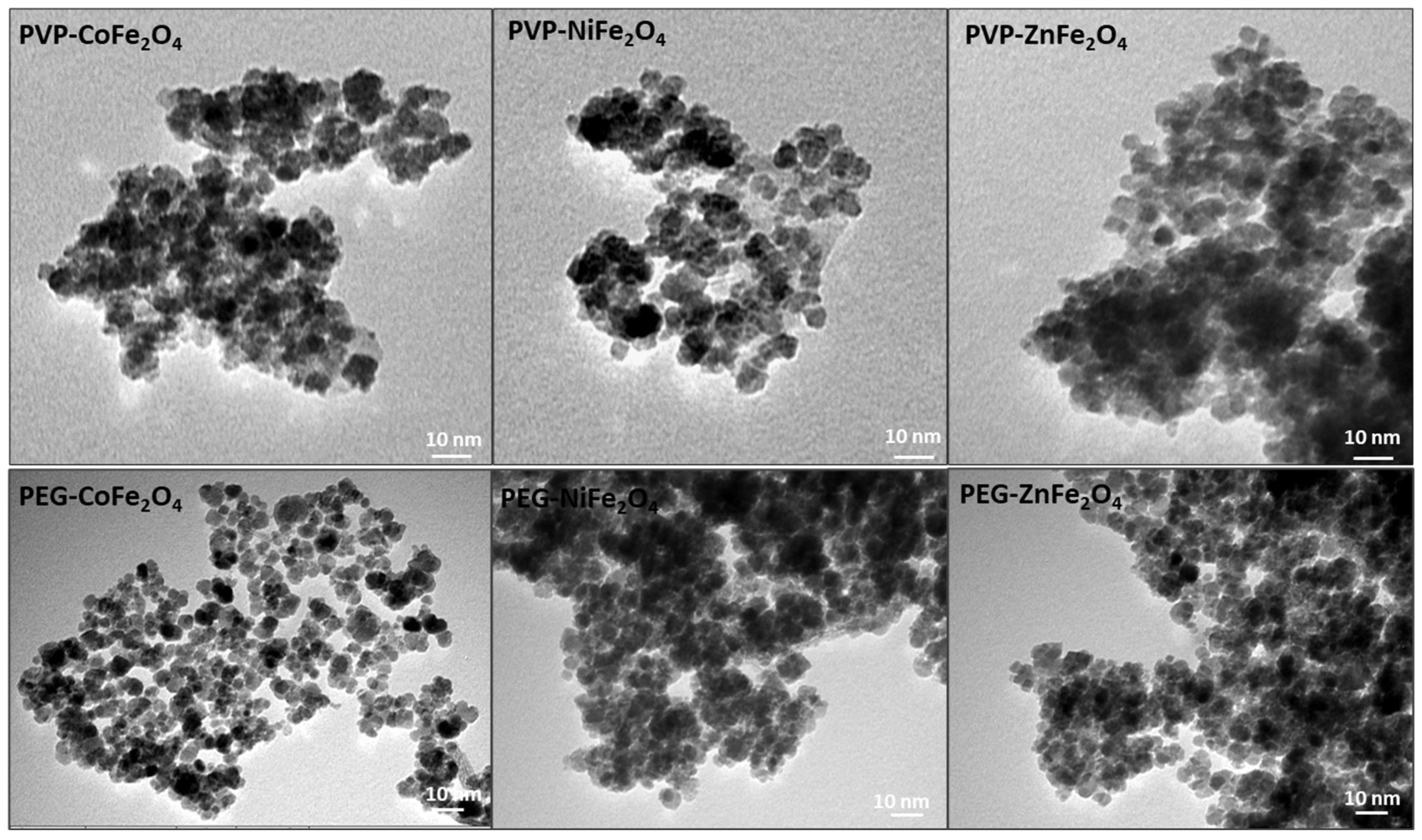

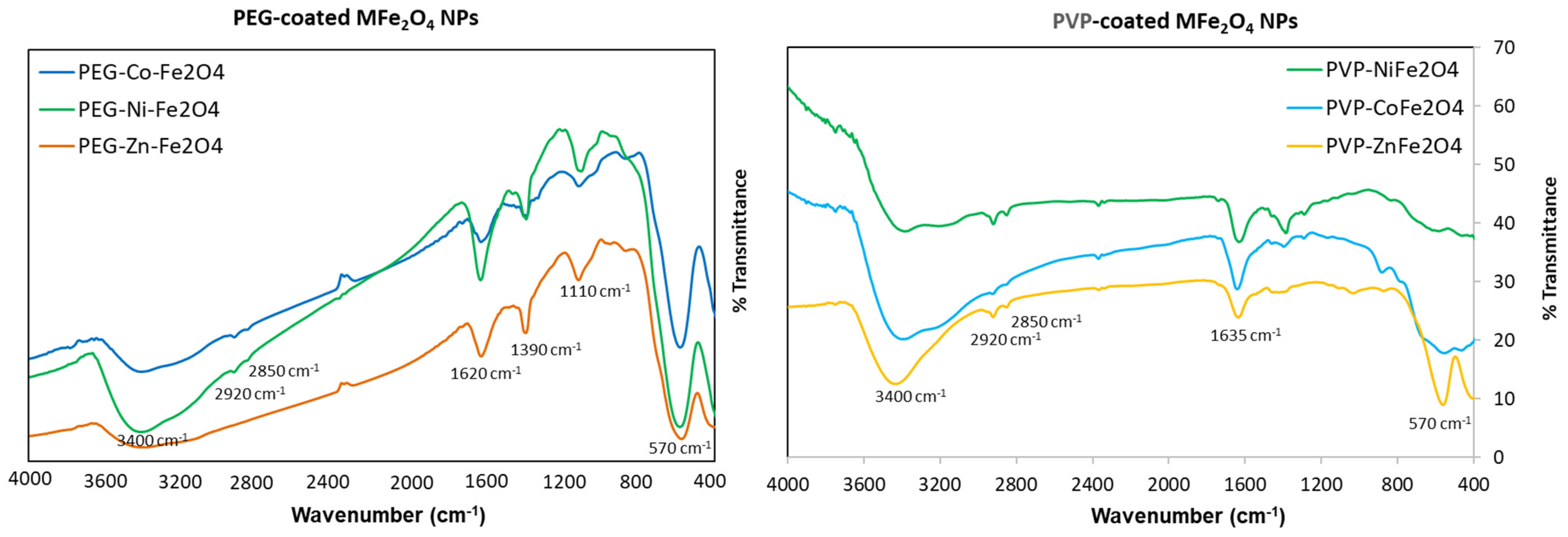


| Sample | Phase Composition (%) | Crystallite Size (nm) | Microstrain (%) | Lattice Parameters (Å) | Fit Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG-CoFe2O4 | CoFe2O4 100 | 10.37 | 0.350 | a = b = c = 8.369 α = β = γ = 90° | Rwp = 38.99% Re = 20.20% Rp = 28.20% S = 1.0646 χ2 = 1.1334 |
| PEG-NiFe2O4 | NiFe2O4 100 | 11.90 | 0.140 | a = b = c = 8.379 α = β = γ = 90° | Rwp = 40.47% Re = 36.71% Rp = 29.85% S = 1.1010 χ2 = 1.2122 |
| PEG-ZnFe2O4 | ZnFe2O4 100 | 7.80 | 0.330 | a = b = c = 8.404 α = β = γ = 90° | Rwp = 46.81% Re = 45.38% Rp = 36.63% S = 1.0302 χ2 = 1.0614 |
| PVP-CoFe2O4 | CoFe2O4 100 | 7.20 | 0.506 | a = b = c = 8.431 α = β = γ =90° | Rwp = 37.39% Re = 36.29% Rp = 27.02% S = 1.0288 χ2 = 1.0584 |
| PVP-NiFe2O4 | NiFe2O4 100 | 13.79 | 0.228 | a = b = c = 8.383 α = β = γ =90° | Rwp = 40.92% Re = 37.56% Rp = 30.47% S = 1.0878 χ2 = 1.1833 |
| PVP-ZnFe2O4 | ZnFe2O4 100 | 8.07 | 0.410 | a = b = c = 8.407 α = β = γ = 90° | Rwp = 42.49% Re = 39.74% Rp = 31.98% S = 1.0678 χ2 = 1.1401 |
| Sample | Experimental | Law of Saturation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hc | Mr | Ms | Mr/Ms | Ms | Keff | |
| (Oe) | (emu/g) | (emu/g) | (emu/g) | (erg/cm3) | ||
| PEG-CoFe2O4 | 0.810 | 14.91 | 65.87 | 0.226 | 68.06 ± 0.24996 | 2.02 × 105 |
| PEG-NiFe2O4 | 1.331 | 10.19 | 52.56 | 0.194 | 53.24 ± 0.02422 | 1.04 × 105 |
| PEG-ZnFe2O4 | 1.064 | 14.14 | 37.75 | 0.375 | 38.66 ± 0.03468 | 1.21 × 105 |
| PVP-CoFe2O4 | 0.687 | 16.37 | 47.29 | 0.346 | 50.12 ± 0.11923 | 2.07 × 105 |
| PVP-NiFe2O4 | 0.921 | 9.416 | 58.38 | 0.161 | 60.58 ± 0.37308 | 1.95 × 105 |
| PVP-ZnFe2O4 | 0.225 | 27.77 | 20.94 | 1.326 | 23.31 ± 0.19074 | 1.29 × 105 |
| MNPs Concentration (µg/mL) | Bacterial Growth % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP-Co | PEG-Co | PVP-Zn | PEG-Zn | PVP-Ni | PEG-Ni | Fe3O4 | |
| 1000 | 0.00 | 8.00 | 0.00 | 62.43 | 0.00 | 30.68 | 0.00 |
| 500 | 0.00 | 13.23 | 54.87 | 65.05 | 24.96 | 60.74 | 57.68 |
| 250 | 0.00 | 46.73 | 70.79 | 86.91 | 32.48 | 84.13 | 79.50 |
| 125 | 35.00 | 93.50 | 80.66 | 96.61 | 65.05 | 94.57 | 81.82 |
| 62.5 | 65.44 | 95.00 | 90.69 | 95.35 | 80.95 | 95.10 | 84.78 |
| 31.3 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 86.77 | 100.00 | 98.07 |
| 15.6 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 98.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlMatri, E.; Madkhali, N.; Mustafa, S.; Lemine, O.M.; Algessair, S.; Mustafa, A.; Ali, R.; El-Boubbou, K. Preparation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Various Polymerylated Divalent Metal-Doped MF2O4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn) Ferrites. Polymers 2025, 17, 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091171
AlMatri E, Madkhali N, Mustafa S, Lemine OM, Algessair S, Mustafa A, Ali R, El-Boubbou K. Preparation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Various Polymerylated Divalent Metal-Doped MF2O4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn) Ferrites. Polymers. 2025; 17(9):1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091171
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlMatri, Enas, Nawal Madkhali, Sakina Mustafa, O. M. Lemine, Saja Algessair, Alia Mustafa, Rizwan Ali, and Kheireddine El-Boubbou. 2025. "Preparation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Various Polymerylated Divalent Metal-Doped MF2O4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn) Ferrites" Polymers 17, no. 9: 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091171
APA StyleAlMatri, E., Madkhali, N., Mustafa, S., Lemine, O. M., Algessair, S., Mustafa, A., Ali, R., & El-Boubbou, K. (2025). Preparation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity of Various Polymerylated Divalent Metal-Doped MF2O4 (M = Ni, Co, Zn) Ferrites. Polymers, 17(9), 1171. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17091171







