Characterization of Novel Castor Oil-Based Polyurethane Polymer Electrolytes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Castor Oil-Based Polyol and Polymer Electrolytes Preparation
2.3. Analytical Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy


3.2. Room Temperature Conductivity

3.3. Temperature Dependent Conductivity

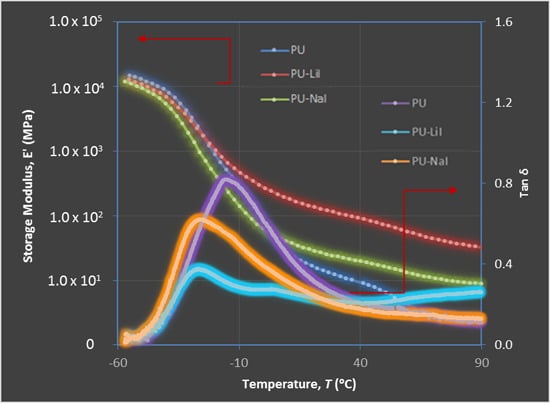
3.4. Dynamic Mechanical Analysis

3.5. Electrochemical Studies

3.6. Transference Number Measurement

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fonseca, C.P.; Rosa, D.S.; Gaboardi, F.; Neves, S. Development of a biodegradable polymer electrolyte for rechargeable batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 155, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.S.; Bhat, D.K. Polyvinyl alcohol-polystyrene sulphonic acid blend electrolyte for supercapacitor application. Phys. B 2009, 404, 1143–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, K.V.; Shikha, G. Natural polymer-based electrolytes for electrochemical devices: Review. Ionics 2011, 17, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, M.A.R.; Metzger, J.O.; Schubert, U.S. Plant oil renewable resources as green alternatives in polymer science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1788–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cateto, C.A.; Barreiro, M.F.; Rodrigues, A.E. Monitoring of lignin-based polyurethane synthesis by FTIR-ATR. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2008, 27, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Han, C.-H.; Sung, Y.-M.; Sekhon, S.S.; Kim, K.-J. Gel electrolyte based on UV-cured polyurethane for dye-sensitized solar cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2011, 11, S158–S162. [Google Scholar]
- Rashmi, B.J.; Rusu, D.; Prashantha, K.; Lacrampe, M.F.; Krawczak, P. Development of water-blown bio-based thermoplastic polyurethane foams using bio-derived chain extender. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J.; Głowińska, E. Chemical modifications of natural oils and examples of their usage for polyurethane synthesis. J. Elastom. Plast. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Cao, Q.; Liao, H. Investigation of a hyperbranched polyurethane as a solid-state phase change material. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bil, M.; Ryszkowska, J.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Effect of polyurethane composition and the fabrication process on scaffold properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, S. Dependence of fungal biodegradation of PEG/castor oil-based polyurethane elastomers on the hard-segment structure. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, G.R.; da Silva-Cunha, A., Jr.; Vieira, L.C.; Silva, L.M.; Ayres, E.; Oréfice, R.L.; Fialho, S.L.; Saliba, J.B.; Behar-Cohen, F. Montmorillonite clay based polyurethane nanocomposite as substrate for retinal pigment epithelial cell growth. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, S. Effect of the long chain extender on the properties of linear and castor oil cross-linked PEG-based polyurethane elastomers. J. Mater. Sci. 2011, 46, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J.; Kacprzyk, M. Thermal analysis and static strength of polyurethanes obtained from glycolysates. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2008, 93, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J. Synthesis and investigation of glycolysates and obtained polyurethane elastomers. J. Elastom. Plast. 2010, 42, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, P.; Vasudevan, T.; Gopalan, A.; Lee, K.-P. Preparation and properties of new cross-linked polyurethane acrylate electrolytes for lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, Y.J.; Chen, R.J.; Chen, S. Preparation and characterization of a mixing soft-segment waterborne polyurethane polymer electrolyte. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009, 20, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavall, R.L.; Ferrari, S.; Tomasi, C.; Marzantowicz, M.; Quartarone, E.; Fagnoni, M.; Mustarelli, P.; Saladino, M.L. MCM-41 silica effect on gel polymer electrolytes based on thermoplastic polyurethane. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 60, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leszkowski, K.; Haponiuk, J.; Datta, J. Preparation and properties of ion conductive polyurethane materials. Przem. Chem. 2012, 91, 1999–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Su’ait, M.S.; Ahmad, A.; Badri, K.H.; Mohamed, N.S.; Rahman, M.Y.A.; Azanza Ricardo, C.L.; Scardi, P. The potential of polyurethane bio-based solid polymer electrolyte for photoelectrochemical cell application. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 3005–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Min, K. Solid polymer electrolytes of blends of polyurethane and polyether modified polysiloxane and their ionic conductivity. Polymer 2010, 51, 2621–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, P.; Gopalan, A.; Vasudevan, T.; Lee, K.-P. Evaluation of a cross-linked polyurethane acrylate as polymer electrolyte for lithium batteries. Mater. Res. Bull. 2006, 41, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, Z.S. Polyurethanes from vegetable oils. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 109–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, M.A.G.; Armenta, J.L.R.; Martínez, A.M.M.; Muñiz, R.; Vazquez, N.A.R.; Rojas, E.T. Interpenetrating polymer networks based on castor oil polyurethane/cellulose derivatives and polyacrylic acid. Lat. Am. Appl. Res. 2009, 39, 131–136. [Google Scholar]
- Somani, K.P.; Kansara, S.S.; Patel, N.K.; Rakshit, A.K. Castor oil based polyurethane adhesives for wood-to-wood bonding. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2003, 23, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, K.K.; Chattopadhyay, D.K.; Raju, K.V.S.N. Synthesis and characterization of hyperbranched polyurethane-urea coatings. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Karak, N. Castor oil-based hyperbranched polyurethanes as advanced surface coating materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, D.L.; Lampman, G.M.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.R. Introduction to Spectroscopy,, 4th ed.; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.-C.; Chen, H.-H.; Wen, T.-C.; Digar, M.; Gopalan, A. Morphology and ionic conductivity of thermoplastic polyurethane electrolytes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Heumen, J.D.; Stevens, J.R. The role of lithium salts in the conductivity and phase morphology of a thermoplastic polyurethane. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 4268–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.-C.; Du, Y.-L.; Digar, M. Compositional effect on the morphology and ionic conductivity of thermoplastic polyurethane based electrolytes. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-H.; Lin, W.-C.; Liu, F.-J. Waterborne polyurethane single-ion electrolyte from aliphatic diisocyanate and various molecular length of polyethylene glycol. Express Polym. Lett. 2007, 1, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.C.; Barbosa, P.C.; Silva, M.M.; Smith, M.J. Electrochemical and thermal properties of polymer electrolytes based on poly(epichlorohydrin-co-ethylene oxide-co-ally glycidyl ether). Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, P.-H.; Choi, M.-G.; Jo, N.J.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, J.-O. Effect of salt concentration on the glass transition temperature and ionic conductivity of poly(ethylene glycol)-polyurethane/LiClO4 complexes. Macromol. Res. 2004, 12, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Lee, J.Y.; Geng, J.; Jung, H.-T.; Park, J.-K. Effect of cation size on solid polymer electrolyte based dye-sensitized solar cells. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3276–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavall, R.L.; Ferrari, S.; Tomasi, C.; Marzantowicz, M.; Quartarone, E.; Magistris, A.; Mustarelli, P.; Lazzaroni, S.; Fagnoni, M. Novel polymer electrolytes based on thermoplastic polyurethane and ionic liquid/lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide/propylene carbonate salt system. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5761–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wang, S.W.; Moore, R.B.; Colby, R.H.; Long, T.E. Polyurethanes containing an imidazolium diol-based ionic-liquid chain extender for incorporation of ionic-liquid electrolytes. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2013, 214, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Tatsumisago, M.; Wakihara, M.; Iwakura, C.; Kohjiya, S.; Tanaka, I. Solid State Ionics for Batteries; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Baskaran, R.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Kuwata, N.; Kawamura, J.; Hattori, T. Conductivity and thermal studies of blend polymer electrolytes based on PVAC-PMMA. Solid State Ion. 2006, 177, 2679–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.V.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Rao, V.V.R.N. Conductivity and discharge characteristics of polyblend (PVP + PVA + KIO3) electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2003, 114, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, X.; Tang, X. The effects of salt concentration on ion state and conductivity in comb cross-linked polymer electrolytes. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 3007–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, M.A.S.A.; Alloin, F.; Sanchez, J.-Y.; Dufresne, A. Cross-linked nanocomposite polymer electrolytes reinforced with cellulose whiskers. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 4839–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appetecchi, G.B.; Croce, F.; Scrosati, B. High-performance electrolyte membranes for plastic lithium batteries. J. Power Sources 1997, 66, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, M.; Kumar, A.; Deka, H.; Karak, N. Ionic transport studies in hyperbranched polyurethane/clay nanocomposite gel polymer electrolytes. Ionics 2011, 18, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, T.; Reddy, M.J.; Ramalingaiah, S.; Subba Rao, U.V. Ion-conducting polymer electrolyte based on polyethylene oxide/complexed with NaNO3 salt-application as an electrochemical cell. J. Power Sources 1999, 79, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibrahim, S.; Ahmad, A.; Mohamed, N.S. Characterization of Novel Castor Oil-Based Polyurethane Polymer Electrolytes. Polymers 2015, 7, 747-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7040747
Ibrahim S, Ahmad A, Mohamed NS. Characterization of Novel Castor Oil-Based Polyurethane Polymer Electrolytes. Polymers. 2015; 7(4):747-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbrahim, Salmiah, Azizan Ahmad, and Nor Sabirin Mohamed. 2015. "Characterization of Novel Castor Oil-Based Polyurethane Polymer Electrolytes" Polymers 7, no. 4: 747-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7040747
APA StyleIbrahim, S., Ahmad, A., & Mohamed, N. S. (2015). Characterization of Novel Castor Oil-Based Polyurethane Polymer Electrolytes. Polymers, 7(4), 747-759. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym7040747