Natural Variation in Fatty Acid Composition of Diverse World Soybean Germplasms Grown in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Field Experiments
2.3. Fatty Acid Extraction and Determination
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
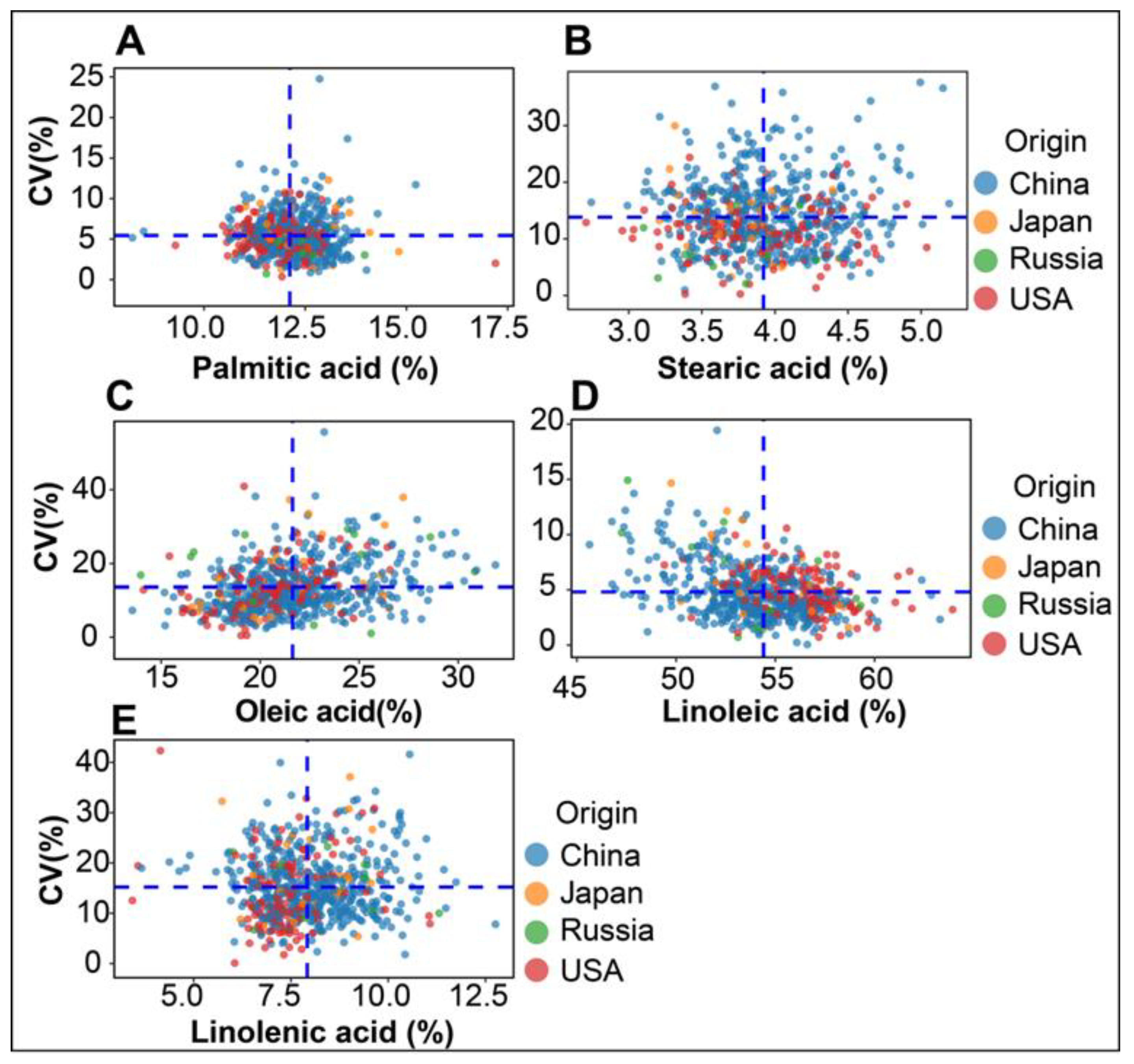
3.1. Variation in Seed Fatty Acid Composition in Soybean Accessions
3.2. Effect of Germplasm Origins on Variation in Seed Fatty Acid Composition
3.3. Effect of Maturity Group on Seed Fatty Acid Composition
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Seed Fatty Acids
3.5. Stability of Soybean Fatty Acids across Different Environments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PA | palmitic acid |
| SA | stearic acid |
| OA | oleic acid |
| LA | linoleic acid |
| LNA | linolenic acid |
| CNSGB | Chinese National Soybean Gene Bank |
| MG | maturity group |
| GC | gas chromatography |
References
- SoyStats a Reference Guide to Important Soybean Facts and Figures. American Soybean Association. 2018. Available online: http://soystats.com/ (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Gale, F.; Valdes, C.; Ash, M. Interdependence of China, United States, and Brazil in Soybean Trade. In New York: U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Economic Research Service (ERS) Report; USDA, Southwest: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mensink, R.P.; Zock, P.L.; Kester, A.D.M.; Katan, M.B. Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins: A meta-analysis of 60 controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1146–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siri-Tarino, P.W.; Sun, Q.; Hu, F.B.; Krauss, R.M. Saturated fat, carbohydrate, and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neff, W.E.; List, G.R. Oxidative stability of natural and randomized high-palmitic-and high-stearic-acid oils from genetically modified soybean varieties. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999, 76, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Wu, J.H.Y.; Appel, L.J.; Creager, M.A.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Miller, M.; Rimm, E.B.; Rudel, L.L.; Robinson, J.G. Dietary fats and cardiovascular disease: A presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2017, 136, e1–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehr, W.R. Breeding for modified fatty acid composition in soybean. Crop Sci. 2007, 47, S-72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, S.K.; Psota, T.L.; Harris, W.S.; Kris-Etherton, P.M. n−3 fatty acid dietary recommendations and food sources to achieve essentiality and cardiovascular benefits. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1526S–1535S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalon, S. Omega-3 fatty acids and monoamine neurotransmission. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2006, 75, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, T.E.; Cahoon, E.B. Soybean oil: Genetic approaches for modification of functionality and total content. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1030–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Z.; Bachleda, N.; Pham, A.T.; Bilyeu, K.; Shannon, G.; Nguyen, H.; Li, Z. High-throughput and functional SNP detection assays for oleic and linolenic acids in soybean. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.-T.; Shannon, J.G.; Bilyeu, K.D. Combinations of mutant FAD2 and FAD3 genes to produce high oleic acid and low linolenic acid soybean oil. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachleda, N.; Grey, T.; Li, Z. Effects of high oleic acid soybean on seed yield, protein and oil contents, and seed germination revealed by near-isogeneic lines. Plant Breed. 2017, 136, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebetzke, G.J.; Burton, J.W.; Carter, T.E.; Wilson, R.F. Changes in agronomic and seed characteristics with selection for reduced palmitic acid content in soybean. Crop Sci. 1998, 38, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.C.; Bergman, J.W.; Flynn, C.R. Oil and meal characteristics of core and non-core safflower accessions from the USDA collection. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1999, 46, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Martinez, J.; Del Rio, M.; De Haro, A. Survey of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) germplasm for variants in fatty acid composition and other seed characters. Euphytica 1993, 69, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffman, F.D.; Pinson, S.; Bergman, C. Genetic diversity for lipid content and fatty acid profile in rice bran. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2003, 80, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzinis, S.; Marburger, D.; Gaska, J.; Diallo, T.; Lauer, J.; Conley, S. Corn and soybean yield response to tillage, rotation, and nematicide seed treatment. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 1704–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, T.E.; Nelson, R.L.; Sneller, C.H.; Cui, Z.; Boerma, H.R.; Specht, J.E.; Carter, T.; Nelson, R.; Sneller, C.; Cui, Z. Genetic Diversity in Soybean. In Soybeans: Improvement, Production and Use, 3rd ed.; Boerma, H., Specht, J., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 2004; pp. 303–450. [Google Scholar]
- Wee, C.D.; Hashiguchi, M.; Anai, T.; Suzuki, A.; Akashi, R. Fatty acid composition and distribution in wild soybean (Glycine soja) seeds collected in Japan. Asian J. Plant Sci. 2017, 16, 52–64. [Google Scholar]
- La, T.; Large, E.; Taliercio, E.; Song, Q.; Gillman, J.D.; Xu, D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Shannon, G.; Scaboo, A. Characterization of select wild soybean accessions in the USDA germplasm collection for seed composition and agronomic traits. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.; Jiang, H.; Feng, L.; Qu, Y.; Teng, W.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, H.; Han, Y.; Li, W. Genome-wide association and transcriptional studies reveal novel genes for unsaturated fatty acid synthesis in a panel of soybean accessions. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uzun, B.; Arslan, Ç.; Furat, Ş. Variation in fatty acid compositions, oil content and oil yield in a germplasm collection of sesame (Sesamum indicum L.). J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2008, 85, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, Y.; Majidi, M.M.; Goli, S.A.H.; Rashidi, F. Oil content and fatty acids composition in Brassica species. Int. J. Food Prop. 2015, 18, 2145–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurasiak-Popowska, D.; Ryńska, B.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Analysis of distribution of selected bioactive compounds in Camelina sativa from seeds to pomace and oil. Agronomy 2019, 9, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Bella, S.; Tuttolomondo, T.; Lazzeri, L.; Matteo, R.; Leto, C.; Licata, M. An agronomic evaluation of new safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) germplasm for seed and oil yields under Mediterranean climate conditions. Agronomy 2019, 9, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medic, J.; Atkinson, C.; Hurburgh, C.R., Jr. Current knowledge in soybean composition. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.R.; Seo, M.J.; Lee, Y.Y.; Park, C.H. Selection of useful germplasm based on the variation analysis of growth and seed quality of soybean germplasms grown at two different latitudes. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.Y.; Piao, X.M.; Choi, Y.M.; Lee, G.A.; Chung, J.W.; Lee, J.R.; Jung, Y.; Park, H.J.; Lee, M.C. Evaluation of genetic diversity and comparison of biochemical traits of soybean (Glycine max L.) Germplasm collections. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2014, 1, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.D.; Bilyeu, K.D.; Shannon, J.G. Genetics and breeding for modified fatty acid profile in soybean seed oil. J. Crop Sci. Biotech. 2007, 10, 201–210. [Google Scholar]
- Grieshop, C.M.; Fahey, G.C. Comparison of quality characteristics of soybeans from Brazil, China, and the United States. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 2669–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Ren, H.; Qi, Y.; Li, C.; Cao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, Z.; Gai, J. Genetic variation of world soybean maturity date and geographic distribution of maturity groups. Breed. Sci. 2017, 67, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Xing, L.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Jackson, S.A. A platform for soybean molecular breeding: The utilization of core collections for food security. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 83, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Li, Y.; Guan, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Chang, R. Establishment, representative testing and research progress of soybean core collection and mini core collection. Acta Agron. Sin. 2009, 35, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Reif, J.C.; Ma, Y.; Hong, H.; Liu, Z.; Chang, R.; Qiu, L. Targeted association mapping demonstrating the complex molecular genetics of fatty acid formation in soybean. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, R.P.; Song, W.W.; Sun, S.; Wu, C.X.; Wang, H.J.; Han, T.F. Comparison of soybean yield and yield-related traits of agri-technology demonstration counties in different regions of China. Soybean Sci. 2012, 31, 557–567. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Sun, S.; Ibrahim, S.E.; Xu, Z.; Wu, H.; Hu, X.; Jia, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, S.; et al. Standard Cultivar Selection and Digital Quantification for Precise Classification of Maturity Groups in Soybean. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 1997–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nelson, R.L.; Amdor, P.J.; Orf, J.H.; Lambert, J.W.; Cavins, J.F.; Kleiman, R.; Laviolette, F.A.; Athow, K.L. Evaluation of the USDA Soybean Germplasm Collection: Maturity Groups 000 to IV; Technical Bulletins 157020; United States Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1987; 267p.
- Zhang, J.; Ge, Y.; Han, F.; Li, B.; Yan, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, L. Isoflavone content of soybean cultivars from maturity group 0 to VI grown in northern and southern China. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, S.; Li, B.; Yu, F.; Han, F.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Analysis of additive and epistatic quantitative trait loci underlying fatty acid concentrations in soybean seeds across multiple environments. Euphytica 2015, 206, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SAS Institute. The SAS system for Windows, Release 9.2; SAS Inst. Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, P.; Song, W.; Yang, X.; Sun, S.; Zhou, X.; Yang, R.; Li, N.; Hou, W.; Wu, C.; Han, T. Regional distribution of protein and oil compositions of soybean cultivars in China. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Yang, R.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, B.; Tian, S.; Liu, X.; Han, T. Analyzing the effects of climate factors on soybean protein, oil contents, and composition by extensive and high-density sampling in China. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 4121–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liang, X.; Wang, L.; Lu, X.; Huang, J.; Cao, J.; Li, H.; Gu, D. Effect of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on endothelial function: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, E.M.; Piovesan, N.D.; de Barros, E.G.; Moreira, M.A. Low linolenic soybeans for biodiesel: Characteristics, performance and advantages. Fuel 2013, 104, 861–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Bhusal, S.J.; Song, Q.; Cregan, P.B.; Yen, Y.; Brown, M.; Jiang, G. Genome-wide scan for seed composition provides insights into soybean quality improvement and the impacts of domestication and breeding. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fehr, W.R.; Welke, G.A.; Hammond, E.G.; Duvick, D.N.; Cianzio, S.R. Inheritance of reduced linolenic acid content in soybean genotypes A16 and A17. Crop Sci. 1992, 32, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.L.; Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Florez-Palacios, L.; Zeng, A.; Wang, X.; Bowen, R.A.; Miller, A.; Berry, H. Genetic analysis of sugar composition and its relationship with protein, oil, and fiber in soybean. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 2413–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graef, G.; LaVallee, B.J.; Tenopir, P.; Tat, M.; Schweiger, B.; Kinney, A.J.; Van Gerpen, J.H.; Clemente, T.E. A high-oleic-acid and low-palmitic-acid soybean: Agronomic performance and evaluation as a feedstock for biodiesel. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2009, 7, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourtzinis, S.; Gaspar, A.P.; Naeve, S.L.; Conley, S.P. Planting date, maturity, and temperature effects on soybean seed yield and composition. Agron. J. 2017, 109, 2040–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dardanelli, J.L.; Balzarini, M.; Martínez, M.J.; Cuniberti, M.; Resnik, S.; Ramunda, S.F.; Herrero, R.; Baigorri, H. Soybean maturity groups, environments, and their interaction define mega-environments for seed composition in Argentina. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, Y.; Bajjalieh, N.; Archontoulis, S.; Casteel, S.; Davidson, D.; Kovács, P.; Naeve, S.; Ciampitti, I.A. Spatial characterization of soybean yield and quality (amino acids, oil, and protein) for United States. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldflus, F.; Ceccantini, M.; Santos, W. Amino acid content of soybean samples collected in different Brazilian states: Harvest 2003/2004. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2006, 8, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, S.; Chen, P.; Longer, D.E.; Hou, A.; Shi, A.; Ishibashi, T.; Zhang, B.; Brye, K.R. Planting date and irrigation effects on seed quality of early-maturing soybean in the Mid-South USA. J. New Seeds 2008, 9, 212–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, Y.; Purcell, L.C.; Salmeron, M.; Naeve, S.; Casteel, S.N.; Kovács, P.; Archontoulis, S.; Licht, M.; Below, F.; Kandel, H.; et al. Assessing variation in us soybean seed composition (protein and oil). Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellaloui, N.; Smith, J.R.; Ray, J.D.; Gillen, A.M. Effect of maturity on seed composition in the early soybean production system as measured on near-isogenic soybean lines. Crop Sci. 2009, 49, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, S.M.; Kinoshita, T.; Anai, T.; Takagi, Y. Combining ability in loci for high oleic and low linolenic acids in soybean. Crop Sci. 2001, 41, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Jung, S.; Moore, K.; Powell, G.; Ainsworth, C.; Abbott, A. High-oleate peanut mutants result from a MITE insertion into the FAD2 gene. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 1492–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.; Taware, S.P.; Oak, M.D.; Tamhankar, S.A.; Rao, V.S. Improvement of oil quality in soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merrill] by mutation breeding. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Yang, X.; Sun, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Jia, H.; Man, W.; Fu, L.; Song, W.; Wu, C. Temporal–spatial characterization of seed proteins and oil in widely grown soybean cultivars across a century of breeding in China. Crop Sci. 2017, 57, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, C.; Xu, R.; Lu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wei, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, H. Stability of growth periods traits for soybean cultivars across multiple locations. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulai, M.S.; Sallah, P.Y.K.; Safo-Kantanka, O. Maize grain yield stability analysis in full season lowland maize in Ghana. Int. J. Agric. Biol 2007, 9, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Temesgen, T.; Keneni, G.; Sefera, T.; Jarso, M. Yield stability and relationships among stability parameters in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) genotypes. Crop J. 2015, 3, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemingway, J.; Eskandari, M.; Rajcan, I. Genetic and environmental effects on fatty acid composition in soybeans with potential use in the automotive industry. Crop Sci. 2015, 55, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, F.M.; Jia, G.; Xiao, J.; Duguid, S.D.; Rashid, K.Y.; Booker, H.M.; Cloutier, S. Genetic variability of 27 traits in a core collection of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Hwang, Y.S.; Kim, S.T.; Yoon, W.B.; Han, W.Y.; Kang, I.K.; Choung, M.G. Seed coat color and seed weight contribute differential responses of targeted metabolites in soybean seeds. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Cho, E.G.; Baek, H.J. DNA profiling and genetic diversity of Korean soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) landraces by SSR markers. Euphytica 2009, 165, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terhaag, M.M.; Almeida, M.B.; de Benassi, M.T. Soymilk plain beverages: Correlation between acceptability and physical and chemical characteristics. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 33, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suppavorasatit, I.; Lee, S.; Cadwallader, K.R. Effect of enzymatic protein deamidation on protein solubility and flavor binding properties of soymilk. J. Food Sci. 2013, 78, C1–C7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, B.; Han, F.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.; Sun, J. Evaluation of the chemical quality traits of soybean seeds, as related to sensory attributes of soymilk. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Component | Mean a | SD | CV (%) | Min (%) | Max (%) | Skew | Kur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palmitic acid | 12.12 | 0.78 | 6.44 | 8.23 | 17.20 | 0.24 | 4.09 |
| Stearic acid | 3.92 | 0.41 | 10.36 | 2.71 | 5.19 | 0.23 | −0.11 |
| Oleic acid | 21.63 | 2.94 | 13.60 | 13.55 | 31.88 | 0.48 | 0.36 |
| Linoleic acid | 54.41 | 2.76 | 5.07 | 45.64 | 63.93 | −0.21 | 0.51 |
| Linolenic acid | 7.93 | 1.22 | 15.34 | 3.43 | 12.76 | 0.28 | 0.94 |
| Fatty Acid | ID Number | Name | Mean a | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Palmitic acid | - | YZY2004-15-W90 | 8.23 | China |
| WDD01709 | T309 | 17.20 | USA | |
| Stearic acid | WDD00405 | Yellow marvel | 2.71 | USA |
| ZDD00294 | Qingdou | 5.19 | China | |
| Oleic acid | ZDD09581 | DLHD | 13.55 | China |
| ZDD02925 | DLFB | 31.88 | China | |
| Linoleic acid | ZDD02925 | DLFB | 45.64 | China |
| WDD03084 | S01-9391 | 63.93 | USA | |
| Linolenic acid | WDD01482 | C1640 | 3.43 | USA |
| ZDD03739 | PXDZHC | 12.76 | China |
| MG | Palmitic Acid | Stearic Acid | Oleic Acid | Linoleic Acid | Linolenic Acid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Mean a | 12.33 a | 3.92 b | 22.63 a | 53.77 ef | 7.31 d |
| Range | 10.27–15.33 | 2.24–5.5 | 13.3–46 | 34.55–63.36 | 4.3–13.67 | |
| I | Mean | 12.20 ab | 4.16 a | 22.99 a | 53.30 f | 7.35 d |
| Range | 9.91–14.67 | 2.80–41.02 | 10.64–63.93 | 38.88–63.93 | 4.08–12.90 | |
| II | Mean | 12.01 c | 3.94 b | 21.34 b | 55.02 bc | 7.51 d |
| Range | 9.8–15.56 | 2.21–5.91 | 12.6–35.49 | 44.18–66.75 | 2.94–11.89 | |
| III | Mean | 12.07 c | 4 b | 21.89 b | 54.21 de | 7.89 c |
| Range | 9.61–17.48 | 2.37–6.39 | 13.03–42.48 | 38.77–62.43 | 3.94–14.91 | |
| IV | Mean | 12.15 bc | 3.93 b | 21.48 d | 54.15 de | 8.30 b |
| Range | 9.97–15.00 | 2.49–6.57 | 14.08–32.78 | 43.48–61.71 | 5.05–12.58 | |
| V | Mean | 12.09 bc | 3.79 c | 21.18 d | 54.70 cd | 8.25 b |
| Range | 9.77–14.71 | 2.37–6.48 | 13.62–37.98 | 42.93–61.74 | 4.65–13.37 | |
| VI | Mean | 12.08 bc | 3.69 cd | 19.88 c | 55.47 ab | 8.88 a |
| Range | 7.93–16.71 | 2.61–5.49 | 11.95–33.50 | 44.67–66.90 | 3.68–13.91 | |
| VII | Mean | 11.75 d | 3.79 c | 19.73 c | 56.20 a | 8.54 ab |
| Range | 9.72–18.44 | 2.62–6.08 | 13.63–28.85 | 48.80–62.31 | 5.04–13.95 |
| Fatty Acid | ID Number | Name | Mean a | CV (%) | Origin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher palmitic acid (PA) | WDD01709 | T309 | 17.20 | 2.03 | USA |
| WDD01215 | Saikai 20 | 14.81 | 3.45 | Japan | |
| ZDD24126 | gongdou10 | 14.01 | 1.18 | China | |
| WDD02708 | PSB313 | 13.97 | 3.05 | Russia | |
| Higher stearic acid (SA) | WDD02225 | L72-920 | 5.04 | 8.48 | USA |
| - | Laidou24 | 5.01 | 12.57 | China | |
| - | HLT2-Heihe13 | 4.72 | 6.39 | China | |
| Z13-633-1 | Z13-633-1 | 4.81 | 12.82 | China | |
| Higher oleic acid (OA) | ZDD11235 | SQDDD | 28.47 | 9.98 | China |
| ZDD06021 | Qingpidou | 28.14 | 4.93 | China | |
| ZDD12746 | SCQPD | 27.31 | 4.67 | China | |
| WDD02995 | PI 468903 | 27.27 | 6.58 | USA | |
| Higher linoleic acid (LA) | WDD03084 | S01-9391 | 63.93 | 3.20 | USA |
| ZDD03222 | RNPDS | 63.30 | 2.32 | China | |
| - | YZY2004-15-15W83 | 62.86 | 4.51 | China | |
| WDD00713 | Dorchsoy | 61.88 | 3.30 | USA | |
| WDD01488 | CX1038-14 | 61.04 | 3.86 | USA | |
| WDD01618 | Camp | 60.10 | 1.55 | USA | |
| Lower linoleic acid (LA) | ZDD04382 | DYBHSBD | 47.36 | 4.55 | China |
| ZDD06450 | YGZHD | 47.71 | 4.59 | China | |
| ZDD07088 | LQDD | 48.24 | 4.40 | China | |
| ZDD06021 | Qingpidou | 48.29 | 3.51 | China | |
| Higher linolenic acid (LNA) | ZDD03739 | PXDZHC | 12.76 | 7.82 | China |
| ZDD16816 | CSHD | 11.48 | 11.02 | China | |
| PI84751 | G1593|2017 | 11.32 | 10.68 | USA | |
| WDD02708 | PSB313 | 11.31 | 10.00 | Russia | |
| PI43848913 | G1592|2017 | 11.07 | 7.90 | USA | |
| WDD01674 | T116H | 11.05 | 9.47 | USA | |
| Lower linolenic acid (LNA) | WDD01482 | C1640 | 3.43 | 12.53 | USA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelghany, A.M.; Zhang, S.; Azam, M.; Shaibu, A.S.; Feng, Y.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hong, H.; Li, B.; et al. Natural Variation in Fatty Acid Composition of Diverse World Soybean Germplasms Grown in China. Agronomy 2020, 10, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010024
Abdelghany AM, Zhang S, Azam M, Shaibu AS, Feng Y, Qi J, Li Y, Tian Y, Hong H, Li B, et al. Natural Variation in Fatty Acid Composition of Diverse World Soybean Germplasms Grown in China. Agronomy. 2020; 10(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelghany, Ahmed M., Shengrui Zhang, Muhammad Azam, Abdulwahab S. Shaibu, Yue Feng, Jie Qi, Yanfei Li, Yu Tian, Huilong Hong, Bin Li, and et al. 2020. "Natural Variation in Fatty Acid Composition of Diverse World Soybean Germplasms Grown in China" Agronomy 10, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010024
APA StyleAbdelghany, A. M., Zhang, S., Azam, M., Shaibu, A. S., Feng, Y., Qi, J., Li, Y., Tian, Y., Hong, H., Li, B., & Sun, J. (2020). Natural Variation in Fatty Acid Composition of Diverse World Soybean Germplasms Grown in China. Agronomy, 10(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10010024









