Wheat Straw Biochar and NPK Fertilization Efficiency in Sandy Soil Reclamation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Experimental Setup
2.2. Water Content Measurements
2.3. Chemical Analysis of the Mixture after Experiment
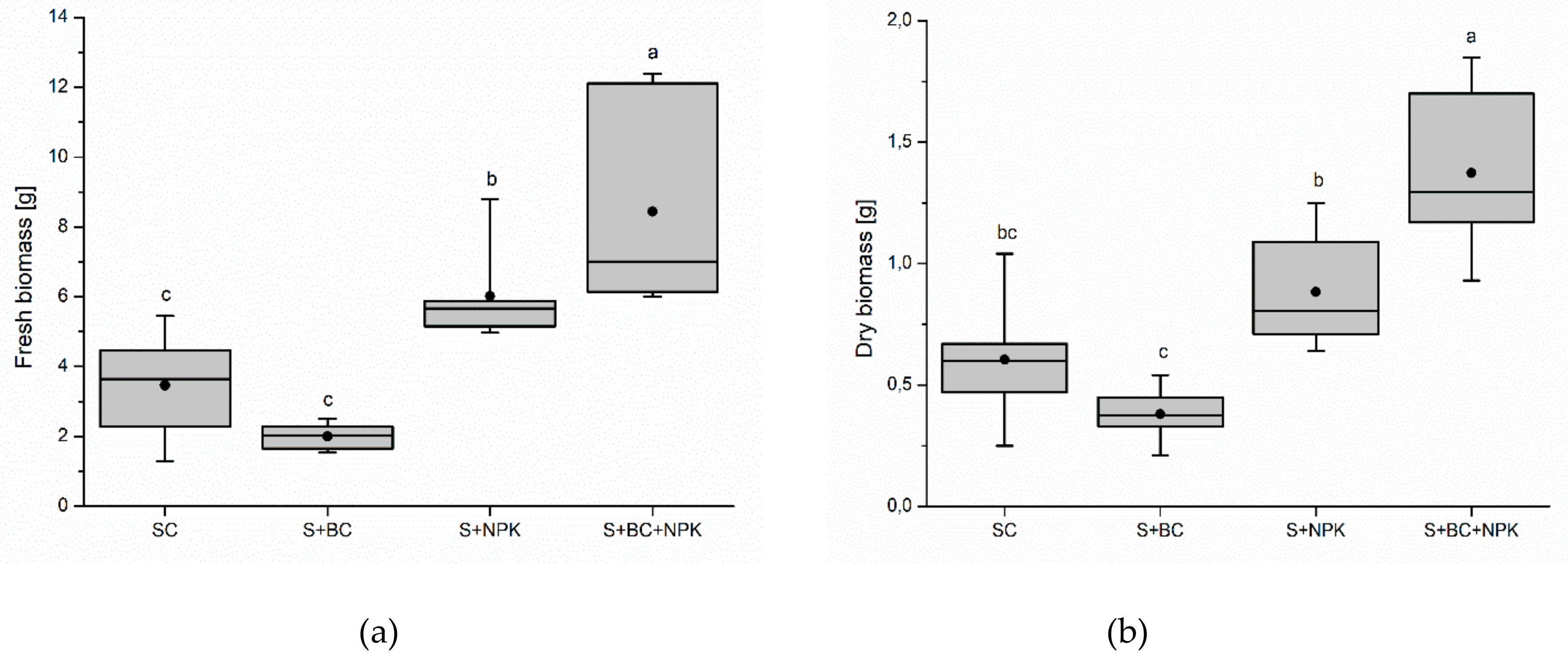
2.4. Plant Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yost, J.L.; Hartemink, A.E. Chapter Four - Soil organic carbon in sandy soils: A review. In Advances in Agronomy, 1st ed.; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press: Newark, DE, USA, 2019; pp. 217–230. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.; Reid, N.; Davies, I.; Grant, C. Adaptive restoration of sand-mined areas for biological conservation. J. Appl. Ecol. 2005, 42, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, T.; Wirth, S.; Ellmer, F. Microbial activity in a sandy arable soil is governed by the fertilization regime. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2004, 40, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cely, P.; Tarquis, A.M.; Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Méndez, A.; Gascó, G. Factors driving the carbon mineralization priming effect in a sandy loam soil amended with different types of biochar. Solid Earth 2014, 5, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mummey, D.L.; Stahl, P.D.; Buyer, J.S. Microbial biomarkers as an indicator of ecosystem recovery following surface mine reclamation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2002, 21, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Dale, B.E. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application on greenhouse gas emissions and economics of corn production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrzykowski, M.; Krzaklewski, W. Soil organic matter, C and N accumulation during natural succession and reclamation in an opencast sand quarry (southern Poland). Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2007, 53, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larney, F.J.; Angers, D.A. The role of organic amendments in soil reclamation: A review. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, L.; Moreno-Jiménez, E.; Gomez-Eyles, J.L.; Harris, E.; Robinson, B.; Sizmur, T. A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3269–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Zhu, W.; Kookana, R.; Katayama, A. Characteristics of biochar and its application in remediation of contaminated soil. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2013, 116, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellet, G.; Marchiol, L.; Delle Vedove, G.; Peressotti, A. Application of biochar on mine tailings: Effects and perspectives for land reclamation. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1262–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.N.; Peltz, C.D.; Stanton, M.; Rutherford, D.W.; Rostad, C.E. Biochar application to hardrock mine tailings: Soil quality, microbial activity, and toxic element sorption. Appl. Geochem. 2014, 43, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, R.; Blume, H.; Asio, V.; Spaargaren, O.; Schad, P. Guidelines for Soil Description, 4th ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the Uniterd Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; pp. 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- International Biochar Initiative. Available online: https://www.biochar-international.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/IBI_Biochar_Standards_V2.1_Final.pdf (accessed on 21 February 2020).
- Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Ćwieląg-Piasecka, I. Effect of Biochar Application on Heavy Metal Mobility in Soils Impacted by Copper Smelting Processes. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorich, E.G.; Carter, M.R.; Angers, D.A.; Drury, C.F. Using a sequential density and particle-size fractionation to evaluate carbon and nitrogen storage in the profile of tilled and no-till soils in eastern Canada. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 89, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabała, C.; Karczewska, A. Methods of soil and plant analysis. Available online: http://karnet.up.wroc.pl/~kabala/Analizy2017v8.pdf, (accessed on 5 February 2020).
- Masud, M.M.; Li, J.Y.; Xu, R.K. Use of alkaline slag and crop residue biochars to promote base saturation and reduce acidity of an acidic ultisol. Pedosphere 2014, 24, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeatt, J.H.; Ross, A.B.; Williams, P.T.; Forster, P.M.; Nahil, M.A.; Singh, S. Characteristics of biochars from crop residues: Potential for carbon sequestration and soil amendment. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 146, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medyńska-Juraszek, A. Biochar as a soil amendment. Soil Sci. Annu. 2016, 67, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boersma, M.; Wrobel-Tobiszewska, A.; Murphy, L.; Eyles, A. Impact of biochar application on the productivity of a temperate vegetable cropping system. N. Zeal. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2017, 45, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, J.M.; Busscher, W.J.; Laird, D.L.; Ahmedna, M.; Watts, D.W.; Niandou, M.A.S. Impact of biochar amendment on fertility of a southeastern coastal plain soil. Soil Sci. 2009, 174, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, K.Y.; Van Zwieten, L.; Meszaros, I.; Downie, A.; Joseph, S. Agronomic values of greenwaste biochar as a soil amendment. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, M.; Tzortzakis, N.; McDaniel, N. Chemical characterization of biochar and assessment of the nutrient dynamics by means of preliminary plant growth tests. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barak, P.; Jobe, B.O.; Krueger, A.R.; Peterson, L.A.; Laird, D.A. Effects of long-term soil acidification due to nitrogen fertilizer inputs in Wisconsin. Plant Soil 1997, 197, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintala, R.; Mollinedo, J.; Schumacher, T.E.; Malo, D.D.; Julson, J.L. Effect of biochar on chemical properties of acidic soil. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2014, 60, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, G.E. Chapter 9 – Management Strategies for Organic Vegetable Fertility. In Safety and Practice for Organic Food; Biswas, D., Micallef, S.A., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; pp. 193–212. [Google Scholar]
- Šimanský, V.; Klimaj, A. How does biochar and biochar with nitrogen fertilization influence soil reaction? J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohara, H.; Dodla, S.; Wang, J.J.; Darapuneni, M.; Acharya, B.S.; Magdi, S.; Pavuluri, K. Influence of poultry litter and biochar on soil water dynamics and nutrient leaching from a very fine sandy loam soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhu, K.; Mattila, T.; Bergström, I.; Regina, K. Biochar addition to agricultural soil increased CH4 uptake and water holding capacity - Results from a short-term pilot field study. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Peters, A.; Trinks, S.; Schonsky, H.; Facklam, M.; Wessolek, G. Impact of biochar and hydrochar addition on water retention and water repellency of sandy soil. Geoderma 2013, 202–203, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.E.; Holthusen, D.; Horn, R. Changes in microstructural behaviour and hydraulic functions of biochar amended soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, P.; Krull, E.; Butler, G.; Herbert, A.; Solaiman, Z. Effect of banded biochar on dryland wheat production and fertiliser use in south-western Australia: An agronomic and economic perspective. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2010, 48, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Herbert, S.; Xing, B. Impacts of adding biochar on nitrogen retention and bioavailability in agricultural soil. Geoderma 2013, 206, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micks, P.; Aber, J.D.; Boone, R.D.; Davidson, E.A. Short-term soil respiration and nitrogen immobilization response to nitrogen applications in control and nitrogen-enriched temperate forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 196, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spokas, K.A. Review of the stability of biochar in soils: Predictability of O:C molar ratios. Carbon Manag. 2010, 1, 289–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota - A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bista, P.; Ghimire, R.; Machado, S.; Pritchett, L. Biochar Effects on Soil Properties and Wheat Biomass vary with Fertility Management. Agronomy 2019, 9, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Biochar | |
| Substrate | wheat straw |
| Pyrolysis temperature | 550 °C |
| Pyrolysis time | 30 sec. |
| pH | 9.5 |
| Surface area | 230 m2g−1 |
| Ash content | 30% |
| TOC * | 65% |
| TN | 1.12% |
| Sandy substrate | |
| Texture | loose sand (93% sand, 6% silt, 1% clay) |
| pH (water) | 6.99 |
| EC | 2.60 µS cm−1 |
| CEC | 1.02 cmol (+) kg−1 |
| pH | TOC % | TN % | CEC cmol (+) kg−1 | C:N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 7.04 (0.08) c | 0.12 (0.04) c | 0.008 (0.004) cd | 1.08 (0.30) ab | 12:1 |
| S + BC | 7.35 (0.07) a | 0.27 (0.06) b | 0.020 (0.005) b | 1.22 (0.20) a | 14:1 |
| S + NPK | 7.22 (0.13) b | 0.10 (0.04) c | 0.013 (0.003) d | 0.84 (0.12) b | 10:1 |
| S + BC + NPK | 7.33 (0.07) ab | 0.45 (0.10) a | 0.041 (0.002) a | 1.05 (0.34) ab | 11:1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bednik, M.; Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Dudek, M.; Kloc, S.; Kręt, A.; Łabaz, B.; Waroszewski, J. Wheat Straw Biochar and NPK Fertilization Efficiency in Sandy Soil Reclamation. Agronomy 2020, 10, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040496
Bednik M, Medyńska-Juraszek A, Dudek M, Kloc S, Kręt A, Łabaz B, Waroszewski J. Wheat Straw Biochar and NPK Fertilization Efficiency in Sandy Soil Reclamation. Agronomy. 2020; 10(4):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040496
Chicago/Turabian StyleBednik, Magdalena, Agnieszka Medyńska-Juraszek, Michał Dudek, Szymon Kloc, Agata Kręt, Beata Łabaz, and Jarosław Waroszewski. 2020. "Wheat Straw Biochar and NPK Fertilization Efficiency in Sandy Soil Reclamation" Agronomy 10, no. 4: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040496
APA StyleBednik, M., Medyńska-Juraszek, A., Dudek, M., Kloc, S., Kręt, A., Łabaz, B., & Waroszewski, J. (2020). Wheat Straw Biochar and NPK Fertilization Efficiency in Sandy Soil Reclamation. Agronomy, 10(4), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10040496






