Abstract
Ground beetles (Carabidae) are beneficial insects providing ecosystem services by regulating insect pests and weed seeds. Despite several studies conducted on ground beetles worldwide, there is a lack of knowledge on how these insects are affected by differently managed organic systems (e.g., tillage-based versus grazed-based) compared to that of chemical-based no-tillage conventional cropping systems. In a 5-year (2013–2017) study, we assessed the ground beetle communities in cover crops and winter wheat (Triticum aestivium L.) in Montana, USA, with three contrasting cropping systems: a chemically managed no-tillage, a tillage-based organic, and a livestock-integrated organic with reduced tillage. The first three years (i.e., 2013–2015) corresponded to the transition to organic period, while the last two (i.e., 2016–2017) were conducted in United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) organic-certified tillage-based and livestock-integrated organic systems. The experiment was designed with three management systems across three blocks as the whole plot variable and 5-year rotation of crop phases as the subplot variable. Using pitfall traps, we sampled ground beetles across all cover crop and winter wheat subplots for five years (n = 450). The data were analyzed using mixed effects models and PERMANOVA and visualized with non-metric multidimensional scaling ordination. Our study indicated that organically managed farms, whether tilled or grazed, enhance activity density, species richness, diversity, and evenness of ground beetles in the dryland row crop productions. Also, irrespective of farming system, cover crops supported higher species richness, diversity, and evenness of ground beetles than winter wheat. The ground beetle communities were mostly similar during the transition to organic period. However, during the established organic phase, cropping systems acted as contrasting ecological filters and beetle communities became dissimilar. Cover cropping affected ground beetle communities positively not only in organically managed systems but also in chemical-based conventional systems. Our study provides evidence supporting the adoption of ecologically-based cropping systems such as crop-livestock integration, organic farming, and cover cropping to enhance beneficial insects and their pest-regulation services.
1. Introduction
Industrialized crop production relies heavily on the use of off-farm chemical and mechanical inputs to control pest populations, maintain soil fertility, and prepare fields for planting. While these intensive management practices may secure yields, they are major drivers of declines in local and regional biodiversity, soil erosion, selection of pesticide resistance, greenhouse gas emissions, and eutrophication [1,2]. These negative consequences of modern industrialized agriculture have spawned interest in the development of ecologically-based cropping, an approach to food, fiber, and bioenergy production that relies on augmenting ecological processes to provide the functions necessary for sustained production, thus helping to reduce excessive use of off-farm inputs [3,4]. Examples of ecologically-based management practices include integrated crop-livestock production, crop rotations, conservation biological control, and cover cropping [1,4].
Cover cropping is one of the most widely used ecologically-based management practices as it can help increase soil organic matter, reduce soil erosion, improve soil nutrient retention [5], suppress weeds, and fix nitrogen if a legume is included [6]. In addition to these agronomic benefits, cover crops may also provide several auxiliary ecosystem services including provisioning of food and habitat to beneficial organisms and sequestering carbon [6,7]. However, being non-marketable plants, cover crops do not produce any direct revenue but add extra establishment, maintenance, and termination costs and challenges [8]. For example, to prevent interference with subsequent cash crops, cover crops need to be terminated before they compromise future nutrient or moisture content [9,10] or produce seeds. Currently, the two most common methods of cover crop termination are chemical fallowing with herbicides and tillage [11] but both methods have drawbacks. For example, herbicide applications can have negative impacts including non-target effects on native plants and beneficial insects and increase the selective pressure towards the selection of herbicide-resistant biotypes [12,13]. Similarly, tillage reduces soil carbon and nutrient, releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, and accelerate soil erosion [14,15].
Recent research has evaluated the potential of integrating livestock into crop production to terminate cover crops and manage weeds [16,17]. Livestock grazing for cover crop termination may provide alternative revenue sources to producers [11,17], enhance provisioning of food and ecosystem services [18], and avoid many of the detrimental effects of chemically- or mechanically-based farm management approaches. However, the current adoption of integrated crop-livestock system is limited due to its potential effects on the associated biodiversity and soil structure, a reluctance by growers to increase the complexity of their production enterprise, and lack of information regarding its economic feasibility [8,19].
Cover crop composition and termination methods, whether it is through herbicides, tillage, or grazing, could act as distinct ecological filters of insect communities, selectively favoring some taxa while excluding others [20]. Ground beetles are one of the most widespread, abundant, and speciose groups of insects. Because most ground beetles are generalist predators of a variety of crop pests including aphids, fly maggots, grubs, and slugs [21,22], and most species in the Harpalini and Zabrini tribes are seed predators, they help regulate insect pest and weed populations [23,24]. Thus, cover crop management practices may shift community composition and increase abundance of these beneficial insects that enhance conservation biological control of weeds and insect pests [25,26].
Globally, very few studies have evaluated the impacts of crop-livestock integration on ground beetle community structure in agroecosystems (but see [17]). Furthermore, there is a dearth of information regarding the impacts of differently managed agricultural management systems that use contrasting weed control and cover crop termination strategies on ground beetle community dynamics in the Northern Great Plains, USA, an important region for the production of organic and conventional small grain, pulse, and oilseed crops [10,27], where tilled organic and no-till conventional farming are predominantly adopted. Additionally, while limited research has been carried out on the effects of transition to organic system on associated biodiversity (but see [28,29]), to our knowledge no information exists on how an integrated crop-livestock organic production and cover cropping affect the ground beetle communities during both transition to and established organic phases. Hence, to fill these knowledge gaps, we conducted an experimental study at Fort Ellis, MT, USA for five years (2013–2017) to compare ground beetle community structure in cover crops and winter wheat among three contrasting agricultural management systems: chemical-based conventional no-till, tilled organic, and integrated-crop-livestock organic production with reduced tillage. Targeted grazing was used to terminate cover crops and manage weeds during pre-seeding and post-harvest. This study encompassed five years with two temporal periods in the organic systems: the three years of transition phase and the first two years of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) organic certified phase. We hypothesized that because conventional no-till, tilled organic, and integrated crop-livestock organic cropping systems use different farm inputs and management, they act as distinct ecological filters affecting the ground beetle communities differently. Also, based on previous studies [29,30,31], we expected that both organic systems and cover cropping, compared to conventional and cereal cropping, would enhance ground beetle abundance and diversity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Cropping History
This experiment was conducted at the Fort Ellis Research and Extension Center, Montana State University Bozeman Montana, USA (45.85° N, 111.82° W; Altitude 1468 m) between 2013 and 2017. The 30-year mean annual precipitation for Fort Ellis is 518 mm and the mean annual maximum and minimum temperatures are 13.6 °C and −0.9 °C, respectively (Supplementary Table S1). The site is underlain with Blackmore silt loam (fine-silty, mixed, superactive, frigid Typic Agruistoll) [32].
Prior to 2004, the study site was planted with perennial grasses (Bromus inermis L., Thinopyrum intermedium (Host) Barkworth and D.R. Dewey, and Poa compressa L.). Between 2004 and 2009, the experimental site followed either continuous spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), or spring wheat-fallow, or winter wheat-fallow crop rotation. From 2009 to 2012, the study site followed either a continuous alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) or a three-year crop rotation consisting of spring wheat in the first year followed by pea (Pisum sativum L.), and hay barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in the second and third years, respectively [16,33]. In the spring of 2012, the entire experimental site was planted with glyphosate tolerant rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and treated with herbicide. The rapeseed was tilled to a depth of 15 cm in July 2012 and planted in September 2012 following the experimental design described below.
2.2. Experimental Design
Our experiment followed a split-plot design, with cropping management systems as the whole plot variable and crop phases as the subplot variable. We assigned each whole plot randomly to one of three management systems: conventional no-tillage row crop production, tilled organic row crop production, and integrated crop-livestock organic row crop production. The conventional no-tillage used herbicides, while the tilled organic used tillage to terminate cover crops and control weeds (Supplementary Table S2). In grazed organic system, sheep (Ovis aries L.) were used to eliminate or reduce tillage intensity, terminate cover crops, and manage weeds. Both tilled and grazed organic systems received the USDA organic certification on July 11, 2015 making that year’s crop harvest eligible for the organic label. Thus, this study comprises the three years of transition to organic period (July 2012 to July 2015) and the first two years (2016–2017) of the established organic systems. The agronomic management details are provided in Supplementary Table S2.
Each subplot (13 m × 90 m each), separated by a 1 m fallow strip, was assigned randomly to one of the five crops in the 2012–2013 growing season and then followed a 5-year rotation of crop phases sequentially as (Yr1) safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) under sown with yellow sweet clover [Melilotus officianalis (L.) Lam], (Yr2) yellow sweet clover cover crop, (Yr3) winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), (Yr4) lentils (Lens culinaris Medik), and (Yr5) winter wheat. Due to logistics, we compared the impacts of cropping systems beginning with the yellow sweet clover cover crop (Yr2) and winter wheat (Yr3) phases in all five years (2013–2017). Austrian winter pea (Pisum sativum subsp. arvense.) was planted in fall 2012 for the first year (2013) of the experiment because of the biennial nature of yellow sweet clover which would have required a previous year of seeding (Supplementary Table S2).
2.3. Ground Beetle Community Sampling
We estimated ground beetle activity density and community structure using pitfall traps, the most common method of sampling for ground dwelling insects [34]. In the center of one half of each subplot, we placed four pitfall traps arranged in a 2 m × 2 m rhombus pattern (Supplementary Figure S1). To construct the pitfall traps, we dug 10 cm × 12 cm holes using a post-hole auger, placed two stacked 0.5 L plastic cups (Solo Cup Co, Lake Forest, IL, USA) flush with the soil surface, and filled approximately 25% of the top cup with a propylene glycol-based antifreeze as a killing agent (Arctic Ban Antifreeze, Camco Manufacturing, Greensboro, NC, USA). The traps were open for a 48-h interval in every month from early spring (May) to late summer (September) for five consecutive years (2013–2017). We transferred all ground beetles caught in the pitfall traps from each subplot (n = 450) to plastic bags (Whirl-Pak®, Nasco Inc., Fort Atkinson, WI, USA), cleaned in the lab, preserved in 70% ethyl alcohol, and identified to species following Lindroth [35]. The few ground beetles that we could not positively identify to species (<1% of the sample) were identified to genus and recorded as morpho-species. Nomenclature follows Bousquet [36].
2.4. Data Analysis
Metrics of ground beetle community structure included abundance (measured as activity density), species richness, α-diversity, and evenness. We calculated abundance as the number of individual sampled, species richness (S) as the total number of species present, and α-diversity as Simpson’s Diversity Index (1-D) in each subplot:
where pi is proportion of individuals of ith species in a community and S is the total number of species in that community [37,38]. Similarly, species evenness (J′) was calculated using Pielou’s evenness [39]:
where H′ is the Shannon–Wiener diversity index, Hmax = log(S), and S is the total number of species or species richness. The Shannon–Wiener diversity index is calculated as where pi is the proportion of each species [40].
We compared these metrics of ground beetle diversity among cropping systems, between crop phases, and through time using linear and generalized linear mixed effects models with a random intercept for year and block. Cropping system, crop phase, and sampling year were treated as fixed effects and block, year, and month were treated as random effects with month nested within year. Residuals were examined for homogeneity of variance and qq-plots were used to check for normality. The R packages ‘lme4′ and ‘lmerTest’ were used for analysis [41,42]. The standard lmerTest provides p-values for type III analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the models in lme4 via Satterthwaite’s approximation of degrees of freedom method. Estimated marginal means and post-hoc tests were made using the R package “emmeans” [43].
Temporal differences in community structure of ground beetles across cropping systems and crop phases were assessed using non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination and permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) on a Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix. Pairwise dissimilarity was computed using the Bray–Curtis index:
where BCjk is the dissimilarity between communities j and k, aij and aik are the abundances of species i in sites j and k, respectively, and S is the combined total number of species in beetle communities [44,45]. To assess whether beetle communities were different among cropping systems and between crop phases across the five years of this study, we performed “adonis” test of PERMANOVA. Finally, we identified indicator species for cropping systems and crop phases using “IndVal” [46], a procedure to detect key species in a particular site based on their relative abundance (specificity) and relative frequency (fidelity) [47]. Indicator species analysis was performed to one-way (i.e., each system alone) and two-way combinations (i.e., systems paired) of farming systems. All statistical analyses were performed using R 3.2.4 [48]. Multivariate analyses and ordination graphics were conducted using vegan [49] packages of R. We produced all other graphics using the “ggplot2” and “sciplot” packages in R.
3. Results
We collected a total of 2929 beetle specimens over the five-year study period, representing 71 species; 1544 specimens and 60 species occurred in cover crop subplots, and 1385 specimens and 48 species were occurred in winter wheat subplots. Among the 60 beetle species that were sampled in cover crops, 20 (315 specimens) were collected in the conventional no-till system, 47 (674 specimens) in the tilled organic, and 42 (555 specimens) in the reduced-till grazed organic (Supplementary Table S3). Similarly, among the 48 beetle species that were sampled in winter wheat, 20 (168 specimens) were collected in the conventional no-till system, 34 (437 specimens) in the tilled organic, and 31 (780 specimens) in the reduced-till grazed organic (Supplementary Table S4).
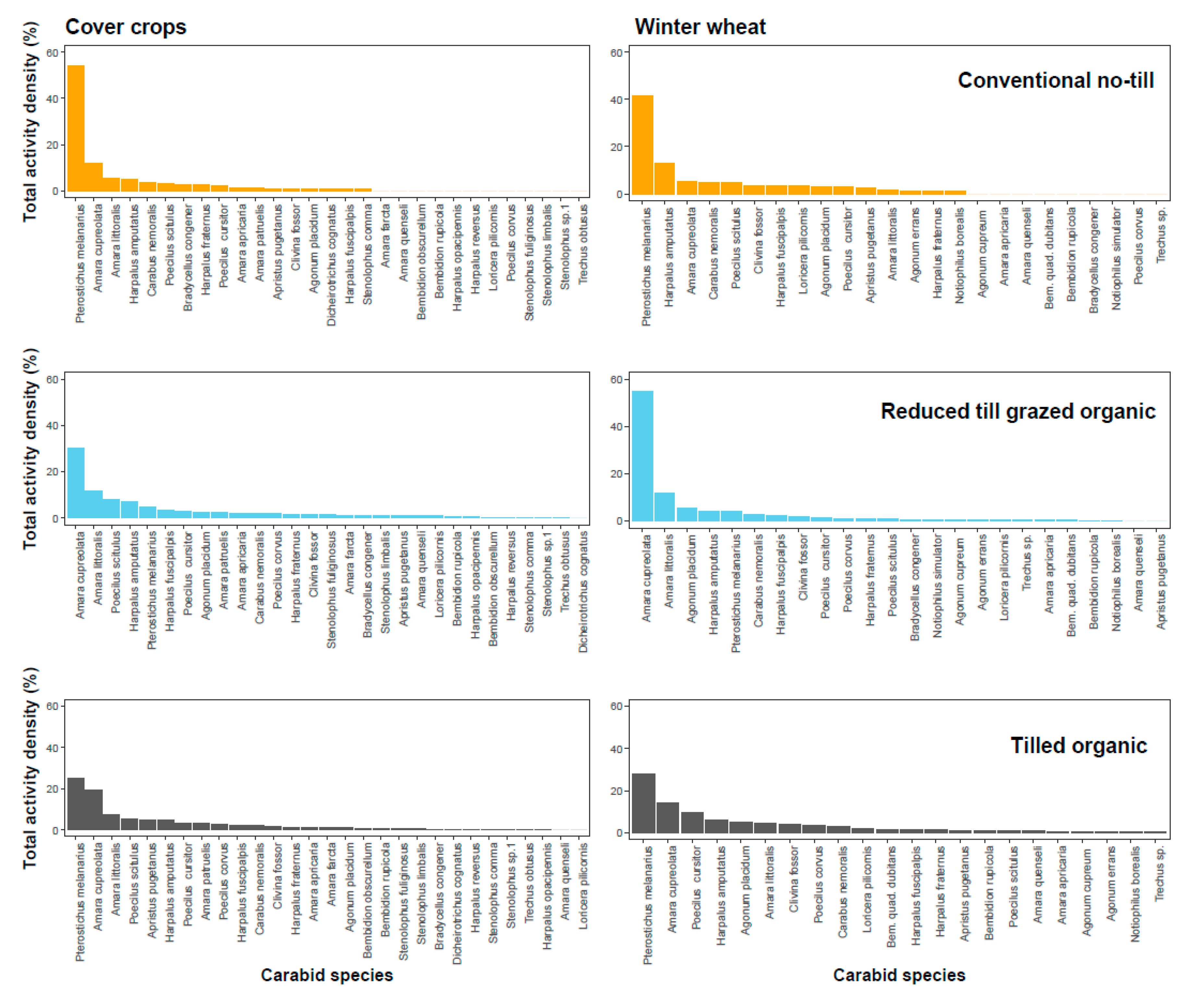
In cover crops, the five most abundant beetle species sampled represented about 80% of the total capture in the conventional no-till system, 62% in tilled organic system, and 62% in reduced-till grazed organic system (Figure 1; Supplementary Table S3). Similarly, in winter wheat, the five most abundant beetle species sampled represented about 70% of the total capture in the conventional no-till system, 63% in the tilled organic system, and 80% in the reduced-till grazed organic system (Figure 1; Supplementary Table S4)
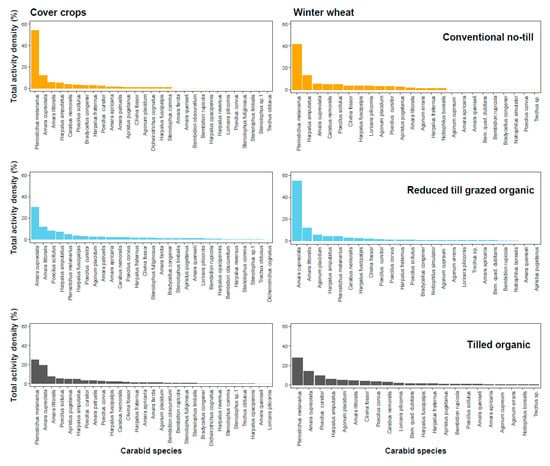
Figure 1.
Percent distribution (evenness) of activity density of ground beetles in cover crops (left panel) and winter wheat (right panel) across three cropping systems (first row: conventional no-till, second row: reduced-till grazed organic, third row: tilled organic). Overall, cover crops and organic systems, compared to winter wheat and conventional no-till system, helped to increase evenness of beetle species (see Table 1 and text for details).
The effects of cropping system on activity density, diversity, and evenness, depended on year (Year × System; Table 1), but the overall trend was that these impacts were lower during the transition to organic period when compared to established organic systems (Table 1; Figure 2). The effects of crops on activity density, richness, diversity, and evenness of ground beetles also depended on year (Year × Crop) (Table 1). Overall, cover crop subplots had greater beetle richness, diversity, and evenness, but not activity density, than winter wheat subplots (Table 1; Figure 1 and Figure 2; p < 0.01 in all cases). The effects of crops and cropping system on activity density, richness, diversity, and evenness did not depend on year (Year × Crop × System; Table 1).

Table 1.
Type III analysis of variance with Satterthwaite’s method for ground beetle activity density, species diversity, species richness, and species evenness among conventional no-till, reduced-till grazed organic, and tilled organic systems across five years from Fort Ellis Experiment Center, Bozeman, MT. Significant p-values (p ≤ 0.05) are bolded. See supplementary table (Supplementary Table S-I) for the post-hoc test results. DF = Degrees of freedom.
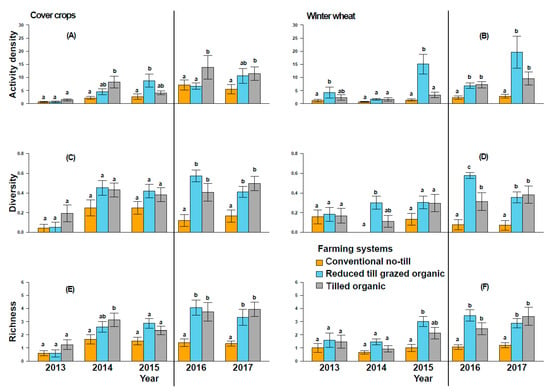
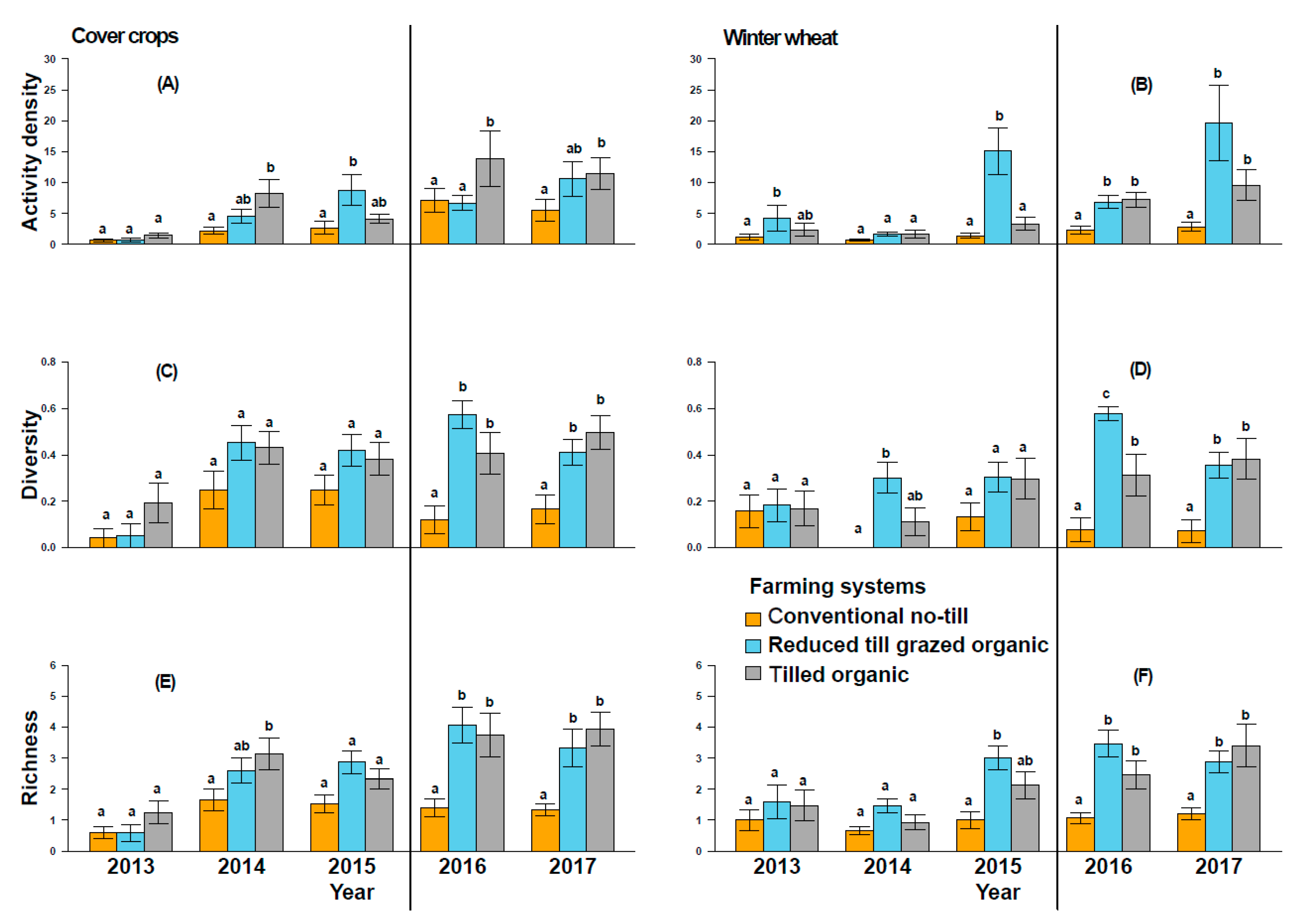
Figure 2.
Ground beetle activity density/sampling (A,B), species diversity (C,D), and species richness (E,F) in cover crops and winter wheat, across conventional no-till, reduced-till grazed organic, and tilled organic systems. Error bars represent the standard errors of the mean, while letters above bars indicate significant differences between systems at p < 0.05 within each year. Vertical black lines separate the transition to organic (to the left) and organic certification (to the right) phases.
In both cover crops and winter wheat subplots, the mean ground beetle activity density, diversity, and richness were greater in tilled and reduced-till grazed organic than in conventional no-till, but generally the organic systems were not different from each other (Table 1; Figure 2). In cover crop subplots, the activity density was not different among cropping systems in the years 2013, 2016, and 2017 (Supplementary Table S3 and S-I; Figure 2). Interestingly, beetle species richness and diversity were similar among cropping systems during transition to organic period (2013–2015), and these metrics were larger in established organic systems in 2016 and 2017 than in conventional no-till systems (Figure 2). Similarly, in winter wheat subplots, reduced-till grazed organic had greater beetle activity density in 2015, 2016, and 2017 and tilled organic had greater activity density in 2016 and 2017 than in conventional no-till (Figure 2). Beetle richness and diversity were similar among systems during the transition to organic period (2013–2015), but greater in organic systems in 2016 and 2017 than in the conventional no-till after the organic certification was achieved (Figure 2).
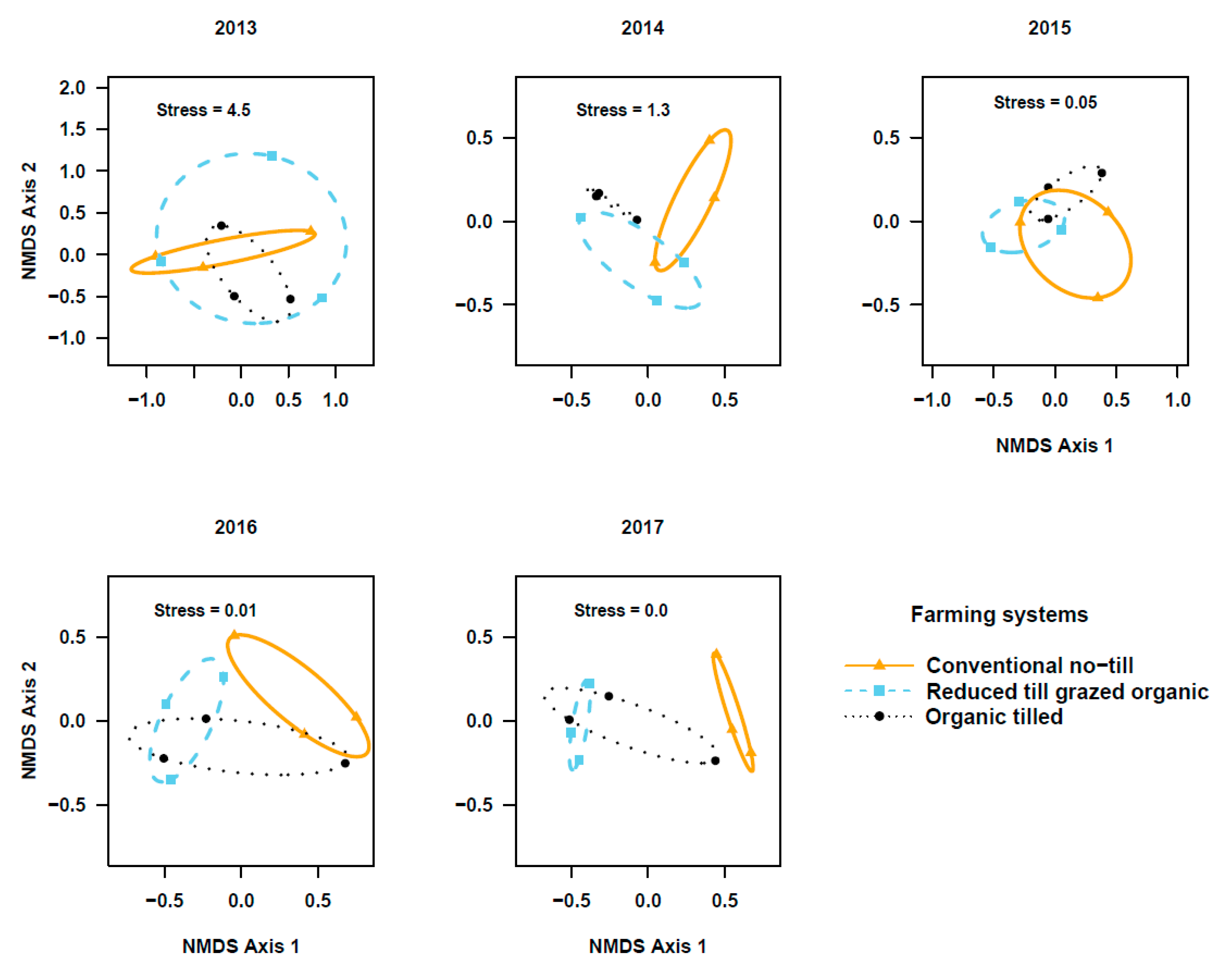
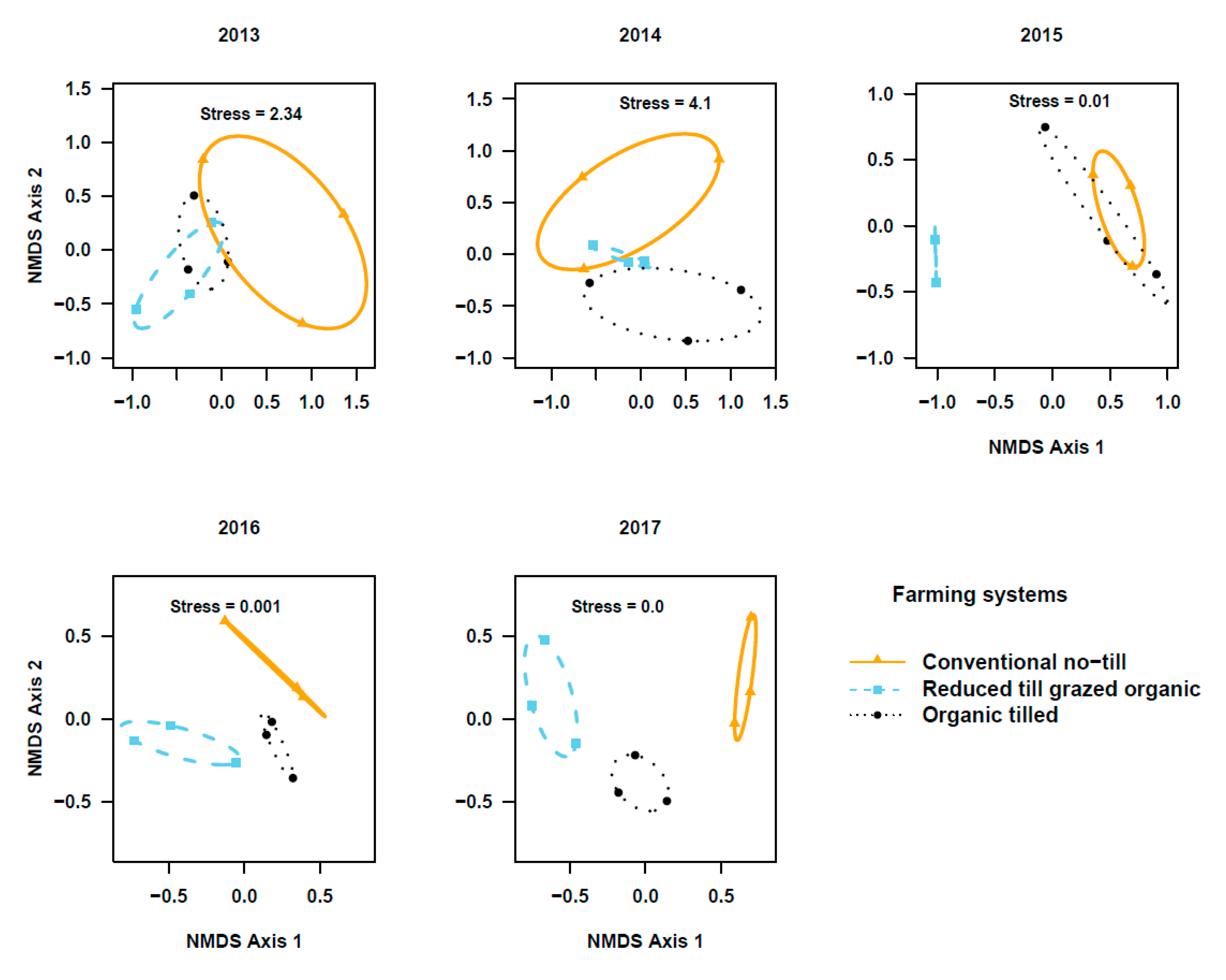
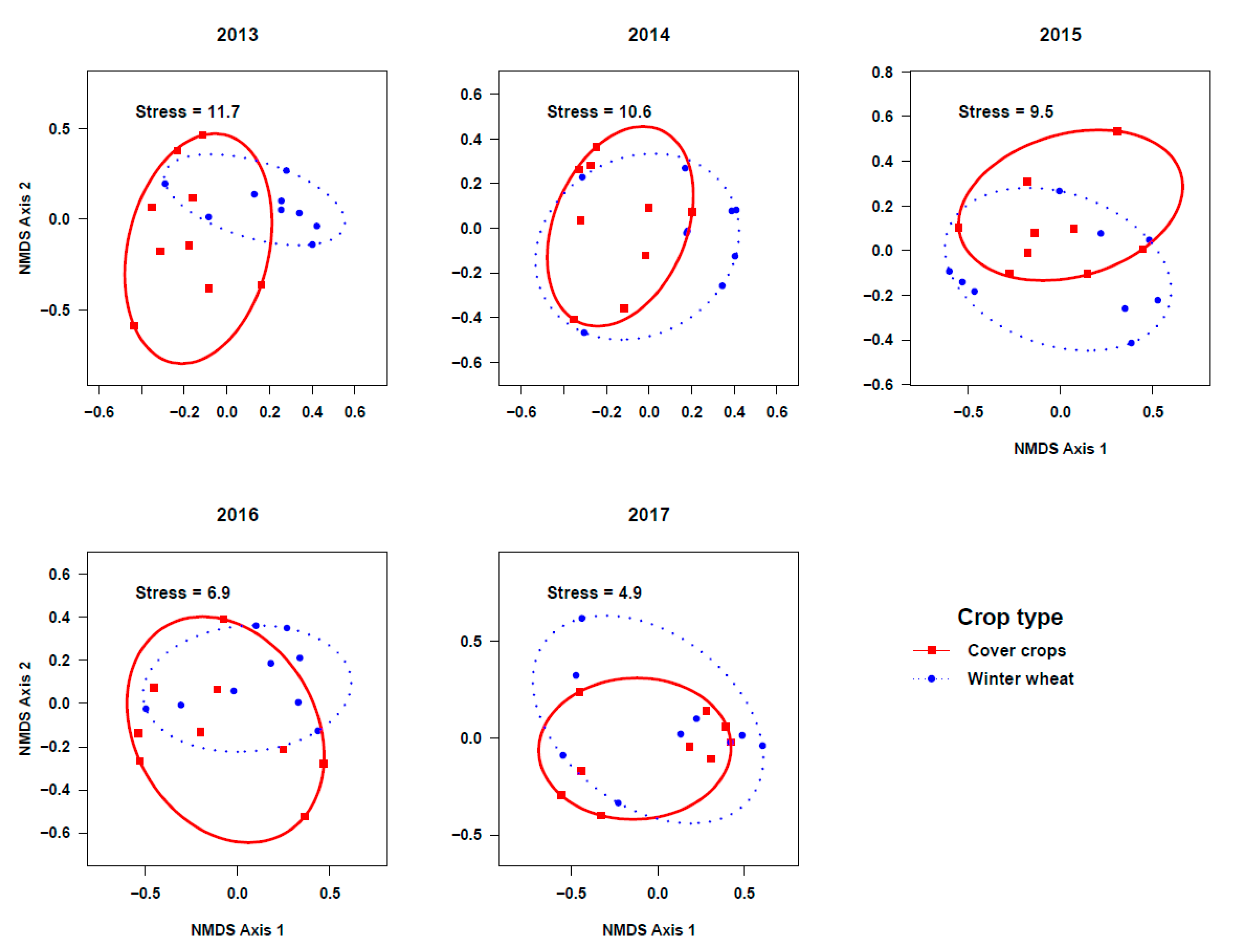
The PERMANOVA based on activity density and species composition indicated that the community composition of ground beetle in the two studied crops did not differ among cropping systems during transition to organic period (Cover crops: Figure 3; Pseudo-F2, 6 = 0.83; r2 = 0.22; p = 0.66 in 2013, Pseudo-F2,6 = 1.7; r2 = 0.36; p = 0.07 in 2014, and Pseudo-F2, 6 = 1.1; r2 = 0.27; p = 0.35 in 2015. Winter wheat: Figure 4; Pseudo-F2, 6 = 1.56; r2 = 0.34; p = 0.13 in 2013, Pseudo-F2, 6 = 0.88; r2 = 0.23; p = 0.67 in 2014, and Pseudo-F2, 6 = 2.9; r2 = 0.49; p = 0.03 in 2015). However, beetle communities in the reduced-till grazed and tilled organic systems were different from that of the chemical-based conventional no-till, particularly in the fifth year in cover crops (Figure 3; Pseudo-F2, 6 = 1.6, r2 = 0.35; p = 0.11 in 2016 and Pseudo-F2, 6 = 3.8; r2 = 0.56; p = 0.06 in 2017) and third-fifth year in winter wheat (Figure 4, Pseudo-F2, 6 = 3.5; r2 = 0.54; p = 0.009 in 2016, and Pseudo- F2, 6 = 5.2, r2 = 0.63; p = 0.005 in 2017). Indicator species analysis on beetle community matrix of five years’ data showed that Apristus pugetanus was indicative of tilled organic system, but no species was indicative of either conventional no-till or reduced-till grazed organic systems alone (Supplementary Table S5). However, when the systems were paired, P. melanarius was indicative of conventional no-till and tilled organic whereas A. placidum, A. cupreolata, A. littoralis, Clivina fossor, Harpalus fuscipalpis, Poecilus corvus, and P. cursitor were indicative of both organic systems, but no species was indicative of conventional no-till and reduced-till grazed organic systems (Supplementary Table S5).
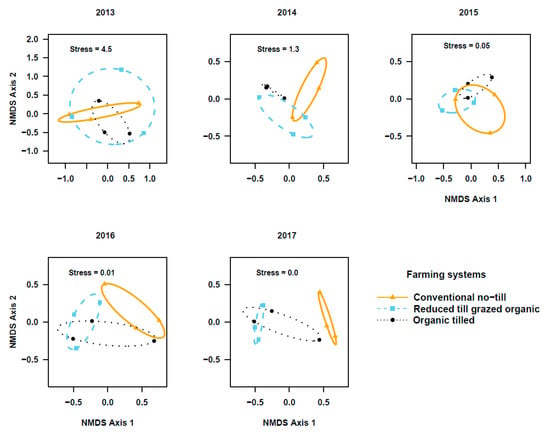
Figure 3.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination of ground beetle communities in cover crop plots among three cropping systems (stress values at k = 3). Note the gradual shifts in beetle communities among cropping systems across five years (2013–2017) of study.
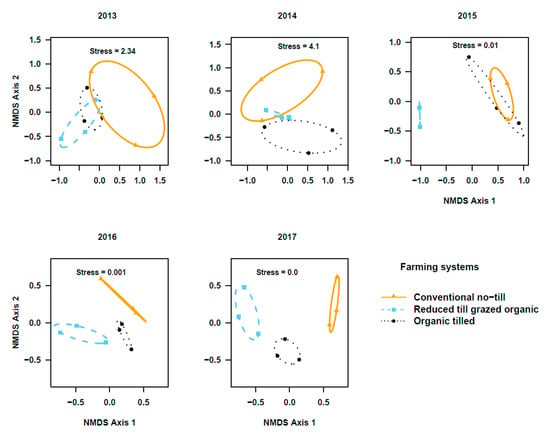
Figure 4.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination of ground beetle communities in winter wheat plots among three cropping systems (stress values at k = 3). Note the distinct shifts in beetle communities among cropping systems across the five years (2013–2017) of study.
As opposed to the impact of cropping systems, the ground beetle community composition was different between crop types during the initial two years of our study, marginally different during the third and fourth years, and similar during the final year (Figure 5; Pseudo-F1,16 = 2.9; r2 = 0.15; p = 0.004 in 2013, Pseudo-F1,16 = 2.3; r2 = 0.13; p = 0.01 in 2014, Pseudo-F1,16 = 1.23; r2 = 0.07; p = 0.28 in 2015, Pseudo-F1,16 = 2.09; r2 = 0.12; p = 0.07 in 2016, and Pseudo-F1,16 = 0.82; r2 = 0.05; p = 0.51 in 2017). Indicator species analysis on beetle community matrix of five years’ data showed that Amara apricaria, A. patruelis, Apristus pugetanus, Bradycellus congener, and P. scitulus were indicative of cover crops whereas only Loricera pilicornis was indicative of the winter wheat crop (Supplementary Table S5).
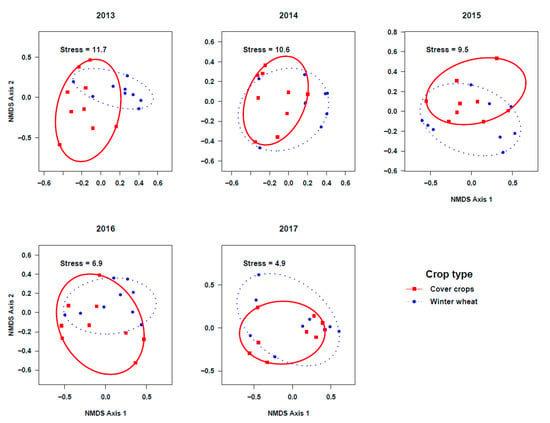
Figure 5.
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) ordination of ground beetle communities in cover crops and winter wheat plots across five years (stress values at k = 3). Compared to the initial years, the beetle communities were more similar during the final years. Year 1 (2013) was seeded to pea, but Year 2–5 (2014–2017) were seeded to yellow sweet clover, as cover crops.
4. Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparing the effects of tilled and reduced-till grazed transition to organic and established organic systems with a chemical-based no-till conventional system on ground beetle communities. With the goal of minimizing the negative effects of tillage, we used sheep to reduce tillage intensity, terminate cover crops, and manage weeds. Our study indicated that organically managed diversified systems, particularly with livestock integration, enhance ground beetle communities in the dryland crop production systems. Specifically, we observed the highest ground beetle activity density, species richness, species diversity, and species evenness in the reduced-till grazed organic, intermediate in tilled organic, and the lowest in no-till conventional systems. Also, we observed greater species richness and diversity of ground beetles in cover crop phases than in winter wheat. Hence, our study highlights the advantages of adopting ecologically-based agriculture such as organic cropping, integrated livestock, and cover cropping to enhance beneficial insects such as ground beetles that potentially provide ecosystem services of pest regulation.
Consistent with the previous studies conducted in the region [17,50,51], ground beetle communities in our study site were dominated by a small subset of species from the commonly occurring genera in the Northern Hemisphere such as Agonum, Amara, Carabus, Harpalus, and Pterostichus. In agreement with previous studies [51,52], but in contradiction to other studies [53,54], we found a greater activity density, richness, and diversity of ground beetles in established organic systems compared to those in no-till conventional, suggesting that in the semi-arid Northern Great Plains organic cropping systems provides diverse and suitable habitat conditions [55]. The divergence of the beetle communities after three years of initiating this study indicates that the three studied cropping systems acted as distinct ecological filters. A study done by Rivers et al. [56] also found an increase in ground beetle activity density and richness during their 3-year transition to organic experiment. However, previous studies were done either only for a short and transition to organic period [29,54,57] or in the established organic phase [30,58], which may not be representative of the temporal changes occurring during both transition to and established organic phases.
In accordance with previous studies [59], ground beetle species were more evenly distributed in organically managed crops than in no-till conventional ones, which were dominated by a few species including P. melanarius, A. cupreolata, and H. amputatus. In addition to these three and other omnivorous species (e.g., Agonum placidum, Amara cupreolata), organic systems also had predominantly granivorous species such as H. herbivagus, A. idahona, and A. quenseli and carnivorous species such as Bembidion quadrimaculatum, C. fossor, and, P. corvus [23] that were either rare or absent in the conventional system. Hence, the enhancement of species evenness in organic cropping has the potential for increasing biological control of pests [60], including mealworms, cricket, aphids, fly maggots, grubs, slugs, and lepidopteran eggs [21,59]. In addition to consuming insect pests [61], many ground beetle species are known to consume substantial amounts of weed seeds [62,63], having the potential to help regulate weed population [64,65]. As such, the increase of natural enemies observed in organic cropping systems [66,67] could help design ecologically-based insect pests and weeds management programs [68].
The ecology of many of the ground beetle species sampled in this study is largely unknown. Previous studies have shown that large bodied ground beetle species such as P. melanarius prefer undisturbed ground such as reduced- or no-till systems [54,69,70]. We observed P. melanarius to be associated with both conventional no-till and tilled organic systems, but less so with reduced-till grazed organic crops, suggesting that this species might prefer habitats that has no animal manures. Similarly, small-sized beetles such as Amara and Bembidion are known to be associated with tilled systems [54,70], which is not consistent with our results that small-bodied beetles were abundant in both till and reduced till organic systems. For example, while Apristus pugetanus has been reported in dry sand or gravel near banks [35], in our study it was strongly associated with reduced-till grazed organic, suggesting its affinity to animal manure and urine. Agonum placidum, Amara cupreolata, A. littoralis, C. fossor, P. corvus, and P. cursitor were sampled in the two studied organic systems and were rare in the conventional system. These species occur in cultivated soil with weedy vegetation [35], and the associations we observed could be due to the weedier characteristics of organic systems in Montana [51,71,72].
Previous studies showed that increased soil disturbance due to tillage reduces ground beetle habitat suitability [53,64] and increase the beetle mortality [73]. In accordance, the greater beetle activity density and richness observed in the reduced-till grazed organic system than in the tilled organic suggests that soil disturbance creates a less favorable environment for the overall beetle communities. In contrast with these observations, Hatten et al. [69] indicated that crop residues in no-till conventional fields may impede carabid movement, but tillage in organic fields reduces crop residues and facilitates beetle activity density. Additionally, Jowett et al. [74] found insignificant effects of tillage on ground beetle communities.
Consistent with previous studies [31,57,75], our study showed that cover crops support greater species richness and diversity of ground beetles than winter wheat, which could have positive effects on weed seed and insect pest regulations. Interestingly, as opposed to the effects shown by cropping systems, the ground beetle communities were different between crop phases during the initial two years of this study, but they were similar during the final three years. The exact reason of the similarity in established phases is unknown, but based on previous studies [29,56,76,77], cover crops, which were followed by winter wheat in our rotation scheme, could have legacy effects in affecting ground beetle communities in the subsequent crops. Cover crops provide ecosystem services such as soil erosion control, water-quality regulation, accumulation of soil organic matter, increase soil microbial biomass, increase in subsequent crop yield, colonization of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, and weed suppression [78,79], but the research on effects of cover crops on insect pests, natural enemies, and biological control were lacking [80]. Hence, while cover crops can help organic and conventional growers improve soil fertility and suppress weeds [79,81], our study shows that they can also play an important role in supporting ground beetles in semi-arid agroecosystems.
Our study found that A. apricaria, A. patruelis, Apristus pugetanus, Bradycellus congener, and Poecilus scitulus were indicative of cover crops, but ecological drivers of these associations are, to our understanding, unknown. Only one species, Loricera pilicornis, was indicative of wheat subplots. Previous studies have found that L. pilicornis prefers shade and soils rich in organic matter [36], and that it primarily consumes Collembola in cereal fields [22]. A previous study has shown a significantly lower Collembola in cover crops compared to control treatment plots [75] so, it is possible that the wheat subplots had more Collembola, than cover crops subplots but assessing underground arthropods was beyond the scope of our study.
5. Conclusions
Management practices such as tillage, cover cropping, crop rotation, and pesticides alter habitat suitability for ground beetles [82,83]. Our study suggests that, by enhancing generalist predators like ground beetles, ecologically-based farming such as diversified organic systems with integrated livestock and cover crops, can enhance conservation biological control and, ultimately, help to avoid chemical-based pest control tactics. Integrated crop–livestock systems can be a viable option not only to terminate cover crops, reduce soil erosion, and increase economic benefits to the producers [84,85], but, as shown in this study, to support beneficial insects. However, the benefits of integration of livestock into cropping systems may come with the cost of increased weed pressure [16], requiring more effective weed management practices. With the benefits of cover cropping in increasing soil health, suppressing weeds [79], and supporting beneficial insects, either a close collaboration of ranchers and growers for the grazing lease to terminate cover crops [84] or a local integration of cropping with livestock systems [18] could provide new approaches to increase the sustainability of the agricultural industry.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4395/10/8/1210/s1: Figure S1: Experimental design showing three blocks (i.e., reps), plots (i.e., farming systems), and split plots (i.e., crops) at Fort Ellis Experimental center, Bozeman, MT. Table S1: Precipitation and temperature data for Fort Ellis Research and Extension Center in Bozeman, MT, USA. Table S2: Agronomic management details in cover crops and winter wheat across conventional no-till, reduced-till grazed organic, and tilled organic between 2013 to 2017 at Fort Ellis Research and Extension Center in Bozeman, MT, USA. Table S3: List of ground beetle species collected from Fort Ellis Experimental center, Bozeman, MT, 2013–2017 from cover crops across three farming management. Table S4: List of ground beetle species collected from Fort Ellis Experimental center, Bozeman, MT, 2013 - 2017 from winter wheat across three farming management. Table S5: Indicator ground beetle species and their indicator values across farming systems and crop types between 2013 and 2017. Only the species with P < 0.05 are listed. Table S-I. Raw table output from the posthoc test by emmeans for farming systems and crops across five years (2013–2017) for ground beetle abundance, richness, diversity, and evenness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.A. & F.D.M.; Writing-original draft, S.A.; Data collection, analysis, and interpretation: S.A.; Resources, F.D.M; Writing-Review & Editing, S.A. and F.D.M.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the United States Department of Agriculture National Institute of Food and Agriculture [grant numbers MONB00314 and MONB00128].
Acknowledgments
We thank S. McKenzie for his support in beetle identification, and J. Barroso, S. Johnson, N. Ranabhat, M. Nixon, A. Thornton, S. Leuthold, A. Thorson, K. Crisps, C. Larson, L Vinola, and W. Holmes for their assistance in the field and laboratory. C. Barbour and L. Lin at Montana State University-Statistical Consulting and Research Services are thankful for providing statistical helps.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hole, D.G.; Perkins, A.J.; Wilson, J.D.; Alexander, I.H.; Grice, P.V.; Evans, A.D. Does organic farming benefit biodiversity? Biol. Conserv. 2005, 122, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Adhikari, A.; Weaver, D.K.; Bekkerman, A.; Menalled, F.D. Impacts of agricultural management systems on biodiversity and ecosystem services in highly simplified dryland landscapes. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremen, C.; Iles, A.; Bacon, C. Diversified farming systems: An agroecological, systems-based alternative to modern industrial agriculutre. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonitto, C.; David, M.B.; Drinkwater, L.E. Replacing bare fallows with cover crops in fertilizer-intensive cropping systems: A meta-analysis of crop yield and N dynamics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 112, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheaffer, C.C.; Seguin, P. Forage legumes for sustainable cropping systems. J. Crop Prod. 2003, 8, 187–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K.; Baligar, V.C.; Bailey, B.A. Role of cover crops in improving soil and row crop productivity. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36, 2733–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, J.C.; Faulkner, D.B. Use of cover crops with integrated crop-livestock production systems. In Cover Crops for Clean Water; Hargrove, W.L., Ed.; Soil and Water Conservation Society: Ankeny, IA, USA, 1991; pp. 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Snapp, S.S.; Swinton, S.M.; Labarta, R.; Mutch, D.; Black, J.R.; Leep, R.; Nyiraneza, J.; O’Neil, K. Evaluating cover crops for benefits, costs and performance within cropping system niches. Agron. J. 2005, 97, 322–332. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, P.R.; Lighthiser, E.J.; Jones, C.A.; Holmes, J.A.; Rick, T.L.; Wraith, J.M. Pea green manure management affects organic winter wheat yield and quality in semiarid Montana. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2011, 91, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiessen Martens, J.; Entz, M. Integrating green manure and grazing systems: A review. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2011, 91, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, J.F.; Bohnenblust, E.; Goslee, S.; Mortensen, D.; Tooker, J. Herbicide drift can affect plant and arthropod communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 185, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszyk, D.; Pfleeger, T.; Lee, E.H.; Plocher, M. Glyphosate and dicamba herbicide tank mixture effects on native plant and non-genetically engineered soybean seedlings. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1014–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, R. Tillage effects on soil degradation, soil resilience, soil quality, and sustainability. Soil Tillage Res. 1993, 27, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, R.T.; Easter, M.; Paustian, K.; Swan, A.; Williams, S. Impacts of periodic tillage on soil C stocks: A synthesis. Soil Tillage Res. 2007, 95, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, Z.J.; Menalled, F.D.; Sainju, U.M.; Lenssen, A.W.; Hatfield, P.G. Integrating sheep grazing into cereal-based crop rotations: Spring wheat yields and weed communities. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, S.C.; Goosey, H.B.; O’Neill, K.M.; Menalled, F.D. Impact of integrated sheep grazing for cover crop termination on weed and ground beetle (Coleoptera:Carabidae) communities. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 218, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, G.; Franzluebbers, A.; de Faccio Carvalho, P.C.; Dedieu, B. Integrated crop-livestock systems: Strategies to achieve synergy between agricultural production and environmental quality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 190, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Tozer, P.; Abrecht, D. Livestock in no-till cropping systems—A story of trade-offs. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2012, 52, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, J.L.; Cleland, E.E.; Suding, K.N.; Zavaleta, E.S. Restoration through reassembly: Plant traits and invasion resistance. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larochelle, A. The food of carabid beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae, including Cicindelidae). In Fabreries Supplement; Association des entomologistes amateurs du Québec: Varennes, France, 1990; Volume 5, pp. 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sunderland, K.D. The Diet of some predatory arthropods in cereal crops. J. Appl. Ecol. 1975, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaines, H.R.; Gratton, C. Seed predation increases with ground beetle diversity in a Wisconsin (USA) potato agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 137, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honek, A.; Martinkova, Z.; Jarosik, V. Ground beetles (carabidae) as seed predators. EJE 2013, 100, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, P. Agroecosystems and conservation biological control. In Conservation Biological Control; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 39–54. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, D.A.; Wratten, S.D.; Gurr, G.M. Habitat management to conserve natural enemies of arthropod pests in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 175–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, A.M.; Tanaka, D.L.; Miller, P.R.; Brandt, S.A.; Nielsen, D.C.; Lafond, G.P.; Riveland, N.R. Oilseed crops for semiarid cropping systems in the Northern Great Plains. Agron. J. 2002, 94, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonason, D.; Andersson, G.K.S.; Öckinger, E.; Rundlöf, M.; Smith, H.G.; Bengtsson, J. Assessing the effect of the time since transition to organic farming on plants and butterflies. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, R.; Pisani-Gareau, T.; Smith, R.G.; Mullen, C.; Barbercheck, M. Cover crop and tillage intensities alter ground-dwelling arthropod communities during the transition to organic production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2016, 31, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgio, G.; Campanelli, G.; Leteo, F.; Ramilli, F.; Depalo, L.; Fabbri, R.; Sgolastra, F. Ecological sustainability of an organic four-year vegetable rotation system: Carabids and other soil arthropods as bioindicators. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2015, 39, 295–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommaggio, D.; Peretti, E.; Burgio, G. The effect of cover plants management on soil invertebrate fauna in vineyard in Northern Italy. BioControl 2018, 63, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Lenssen, A.W.; Goosey, H.B.; Snyder, E.; Hatfield, P.G. Sheep grazing in a wheat–fallow system affects dryland soil properties and grain yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsotti, J.L.; Sainju, U.M.; Lenssen, A.W.; Montagne, C.; Hatfield, P.G. Crop yields and soil organic matter responses to sheep grazing in US Northern Great Plains. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 134, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.R.; Matthews, I.M. A review of extensive variation in the design of pitfall traps and a proposal for a standard pitfall trap design for monitoring ground-active arthropod biodiversity. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 3953–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindroth, C.H. The ground beetles (Carabidae, excl. Cicindelinae) of Canada and Alaska, Part 1–6; Entomologiska Siillskapet: Lund, Sweden, 1969; pp. 1–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, Y. Catalogue of Geadephaga (Coleoptera, Adephaga) of America, North of Mexico. Zookeys 2012, 245, 1–1722. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Partitioning diversity into independent alpha and beta components. Ecology 2007, 88, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pielou, E.C. Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 10, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution and measurement of specis diversity. Taxon 1972, 21, 213–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.M.; Walker, S.C. Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, A.; Brockhoff, P.B.; Christensen, R.H.B. lmerTest Package: Tests in Linear Mixed Effects Models. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 82, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenth, R.; Singmann, H.; Love, J.; Buerkner, P.; Herve, M. Package “Emmeans”:Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. 2019. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/emmeans.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 325–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCune, B.; Grace, J.B.; Urban, D.L. Analysis of Ecological Communities; MjM Software Design: Gleneden Beach, OR, USA, 2002; Volume 3–12, pp. 1–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cáceres, M.; Legendre, P. Associations between species and groups of sites: Indices and statistical inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species assemblages and indicator species: The need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. The R Manuals. 2016. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/manuals.html (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Oksanen, J. CRAN—Package Vegan. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Goosey, H.B.; Mckenzie, S.C.; Rolston, M.G.; O’Neill, K.M.; Menalled, F.D. Impacts of contrasting alfalfa production systems on the drivers of carabid beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae) community dynamics. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 1052–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Menalled, F.D. Impacts of dryland farm management systems on weeds and ground beetles (Carabidae) in the Northern Great Plains. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoudi, E.A.; Plantegenest, M.; Aviron, S.; Pétillon, J. Local vs. landscape characteristics differentially shape emerging and circulating assemblages of carabid beetles in agroecosystems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 270–271, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menalled, F.D.; Smith, R.G.; Dauer, J.T.; Fox, T.B. Impact of agricultural management on carabid communities and weed seed predation. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 118, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalonde, O.; Légèe, A.; Stevenson, F.C.; Roy, M.; Vanasse, A. Carabid beetle communities after 18 years of conservation tillage and crop rotation in a cool humid climate. Can. Entomol. 2012, 144, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, E.M.; Kennedy, C.M.; Kremen, C.; Batáry, P.; Berendse, F.; Bommarco, R.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Carvalheiro, L.G.; Snyder, W.E.; Williams, N.M.; et al. A global synthesis of the effects of diversified farming systems on arthropod diversity within fields and across agricultural landscapes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 4946–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, A.; Mullen, C.; Wallace, J.; Barbercheck, M. Cover crop-based reduced tillage system influences Carabidae (Coleoptera) activity, diversity and trophic group during transition to organic production. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2017, 32, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivers, A.; Voortman, C.; Barbercheck, M. Cover crops support arthropod predator activity with variable effects on crop damage during transition to organic management. Biol. Control 2020, 151, 104377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depalo, L.; Burgio, G.; Magagnoli, S.; Sommaggio, D.; Montemurro, F.; Canali, S.; Masetti, A. Influence of Cover Crop Termination on Ground Dwelling Arthropods in Organic Vegetable Systems. Insects 2020, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, D.W.; Northfield, T.D.; Strand, M.R.; Snyder, W.E. Organic agriculture promotes evenness and natural pest control. Nature 2010, 466, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, W.E. Give predators a complement: Conserving natural enemy biodiversity to improve biocontrol. Biol. Control 2019, 135, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menalled, F.D.; Lee, J.C.; Landis, D.A. Manipulating carabid beetle abundance alters prey removal rates in corn fields. BioControl 1999, 43, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frei, B.; Guenay, Y.; Bohan, D.A.; Traugott, M.; Wallinger, C. Molecular analysis indicates high levels of carabid weed seed consumption in cereal fields across Central Europe. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonne, B.; Bohan, D.A.; Petit, S. Key carabid species drive spring weed seed predation of Viola arvensis. Biol. Control 2020, 141, 104148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.S.; Dosdall, L.M.; Spence, J.R.; Willenborg, C.J. Depth of seed burial and gender influence weed seed predation by three species of ground beetle (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Weed Sci. 2015, 63, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Trichard, A.; Biju-Duval, L.; McLaughlin, B.; Bohan, D.A. Interactions between conservation agricultural practice and landscape composition promote weed seed predation by invertebrates. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, M.P.D.; Wright, D.J.; Leather, S.R. The effects of farming system and fertilisers on pests and natural enemies: A synthesis of current research. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Seipel, T.; Menalled, F.D.; Weaver, D.K. Farming system and wheat cultivar affect infestation of and parasitism on Cephus cinctus in the Northern Great Plains. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 2480–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S. Adopting Diversified Organic Farming to Increase Ecosystem Services|Organic Farmer. Available online: http://organicfarmermag.com/2019/09/adopting-diversified-organic-farming-to-increase-ecosystem-services/ (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Hatten, T.D.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Labonte, J.R.; Guy, S.O.; Eigenbrode, S.D. Effects of tillage on the activity density and biological diversity of carabid beetles in spring and winter crops. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, M.D.; Luff, M.L.; Leifert, C. Crop, field boundary, productivity and disturbance influences on ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae) in the agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 165, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Burkle, L.A.; O’Neill, K.M.; Weaver, D.K.; Menalled, F.D. Dryland organic farming increases floral resources and bee colony success in highly simplified agricultural landscapes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2019, 270–271, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.; Burkle, L.A.; O’Neill, K.M.; Weaver, D.K.; Delphia, C.M.; Menalled, F.D. Dryland organic farming partially offsets negative effects of highly simplified agricultural landscapes on forbs, bees, and bee–flower networks. Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blubaugh, C.K.; Kaplan, I. Tillage compromises weed seed predator activity across developmental stages. Biol. Control 2015, 81, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jowett, K.; Milne, A.E.; Garrett, D.; Potts, S.G.; Senapathi, D.; Storkey, J. Above- and below-ground assessment of carabid community responses to crop type and tillage. Agric. For. Entomol. 2020, 12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pedro, L.; Perera-Fernández, L.G.; López-Gallego, E.; Pérez-Marcos, M.; Sanchez, J.A. The effect of cover crops on the biodiversity and abundance of ground-dwelling arthropods in a Mediterranean pear orchard. Agronomy 2020, 10, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.; Ott, D.; Götze, P.; Koch, H.; Scherber, C. Crop identity and memory effects on aboveground arthropods in a long-term crop rotation experiment. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 7307–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.S.P.; Sanderson, R.A.; Eyre, M.D. Soil tillage reduces arthropod biodiversity and has lag effects within organic and conventional crop rotations. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, E.G.; Ray, S.; Lemmon, M.E.; Luthe, D.S.; Kaye, J.P. Cover crop species affect mycorrhizae-mediated nutrient uptake and pest resistance in maize. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesbah, A.; Nilahyane, A.; Ghimire, B.; Beck, L.; Ghimire, R. Efficacy of cover crops on weed suppression, wheat yield, and water conservation in winter wheat–sorghum–fallow. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 1745–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, E.G. Can agricultural practices that mitigate or improve crop resilience to climate change also manage crop pests? Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017, 23, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittwer, R.A.; Dorn, B.; Jossi, W.; Van Der Heijden, M.G.A. Cover crops support ecological intensification of arable cropping systems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41911. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.C.; Menalled, F.D.; Landis, D.A. Refuge habitats modify impact of insecticide disturbance on carabid beetle communities. J. Appl. Ecol. 2001, 38, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.J.; Ryan, M.R.; Curran, W.S.; Barbercheck, M.E.; Mortensen, D.A. Cover crops and disturbance influence activity-density of weed seed predators Amara aenea and Harpalus pensylvanicus (Coleoptera: Carabidae). Weed Sci. 2011, 59, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, S.C.; Goosey, H.B.; O’Neill, K.M.; Menalled, F.D. Integration of sheep grazing for cover crop termination into market gardens: Agronomic consequences of an ecologically based management strategy. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2017, 32, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sieverding, H.; Lai, L.; Thandiwe, N.; Wienhold, B.; Redfearn, D.; Archer, D.; Ussiri, D.; Faust, D.; Landblom, D.; et al. Facilitating crop–livestock reintegration in the northern great plains. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2141–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).