Seed Priming and Coating by Nano-Scale Zinc Oxide Particles Improved Vegetative Growth, Yield and Quality of Fodder Maize (Zea mays)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of ZnONPs
2.2. Seed Treatments for Field Study
2.3. Zinc Source Seed Treatment Effect on Vegetative Growth Parameters of Fodder Maize
2.3.1. Vegetative, Photosynthetic, and Yield Parameters
2.3.2. Plant Nutrient Status
2.3.3. Plant Quality Parameters
2.3.4. Soil Nutrient and Microbiological Status
2.3.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of the Prepared ZnO NPs
3.2. Vegetative and Photosynthetic Parameters
3.3. Yield and Plant Nutrient Status
3.4. Plant Quality Parameters
3.5. Soil Nutrient Status and Microbial Parameters
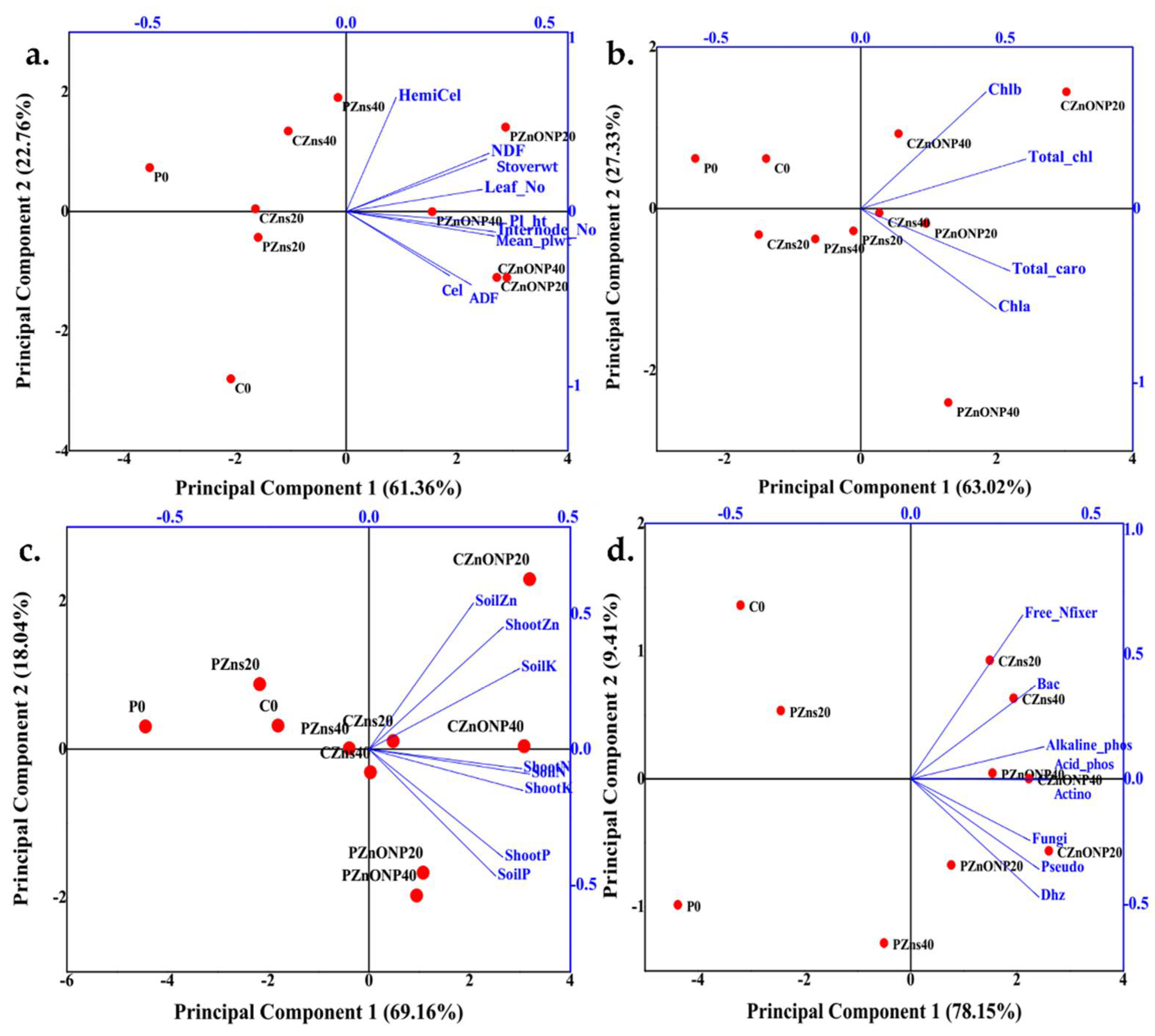
3.6. Principal Component Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tariq, A.; Anjum, S.A.; Randhawa, M.A.; Ullah, E.; Naeem, M.; Qamar, R.; Ashraf, U.; Nadeem, M. Influence of Zinc Nutrition on Growth and Yield Behaviour of Maize (Zea mays L.) Hybrids. Am. J. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacisalihoglu, G. Zinc (Zn): The last nutrient in the alphabet and shedding light on zn efficiency for the future of crop production under suboptimal zn. Plants 2020, 9, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Singh, M.; Kumar, R. Effect of nitrogen, phosphorus and zinc fertilization on yield and quality of kharif fodder—A review. Agric. Rev. 2015, 36, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Higgs, D. Response of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) cultivars to foliar application of zinc when grown in sand culture at low zinc. Sci. Hortic. 2002, 93, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsonev, T.; Lidon, F.J.C. Zinc in plants—An overview. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2012, 24, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada-Urbina, J.; Cruz-Alonso, A.; Santander-González, M.; Méndez-Albores, A.; Vázquez-Durán, A. Nanoscale Zinc Oxide Particles for Improving the Physiological and Sanitary Quality of a Mexican Landrace of Red Maize. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašev, N.; Kutáček, M. The effect of zinc on the biosynthesis of tryptophan, indol auxins and gibberellins in barley. Biol. Plant. 1966, 8, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganya, A.; Saravanan, A.; Manivannan, N. Role of Zinc Nutrition for Increasing Zinc Availability, Uptake, Yield, and Quality of Maize (Zea mays L.) Grains: An Overview. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2020, 51, 2001–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, A.H.; Swaraz, A.M.; Stangoulis, J. Zinc-deficiency resistance and biofortification in plants. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2014, 177, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joy, E.J.M.; Stein, A.J.; Young, S.D.; Ander, E.L.; Watts, M.J.; Broadley, M.R. Zinc-enriched fertilisers as a potential public health intervention in Africa. Plant. Soil 2015, 389, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengel, Z. Availability of Mn, Zn and Fe in the rhizosphere. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2015, 15, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangloff, W.J.; Westfall, D.G.; Peterson, G.A.; Mortvedt, J.J. Mobility of organic and inorganic zinc fertilizers in soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2006, 37, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloway, B.J. Soil factors associated with zinc deficiency in crops and humans. Environ. Geochem. Health 2009, 31, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, R.; Kalia, A.; Dhaliwal, S.S. Evaluation of Efficacy of ZnO Nanoparticles as Remedial Zinc Nanofertilizer for Rice. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2019, 19, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Amanzadeh, T.; Sabaghnia, N.; Dashti, S. Impact of foliar application of nano micronutrient fertilizers and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the growth and yield components of barley under supplemental irrigation. Acta Agric. Slov. 2016, 107, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaj Baddar, Z.; Unrine, J.M. Functionalized-ZnO-Nanoparticle Seed Treatments to Enhance Growth and Zn Content of Wheat (Triticum aestivum) Seedlings. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12166–12178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, M.E.; Britt, D.W.; Lara, L.M.; Cartwright, A.; Dos Santos, R.F.; Inoue, T.T.; Batista, M.A. Initial development of corn seedlings after seed priming with nanoscale synthetic zinc oxide. Agronomy 2020, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itroutwar, P.D.; Govindaraju, K.; Tamilselvan, S.; Kannan, M.; Raja, K.; Subramanian, K.S. Seaweed-Based Biogenic ZnO Nanoparticles for Improving Agro-morphological Characteristics of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant. Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Crosby, K.M.; Jifon, J.L.; Patil, B.S. Nanoparticle-Mediated Seed Priming Improves Germination, Growth, Yield, and Quality of Watermelons (Citrullus lanatus) at multi-locations in Texas. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Micronutrient application through seed treatments—A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2012, 12, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Sarkar, D.; Sankar, A.; Pal, S.; Singh, H.B.; Singh, R.K.; Bohra, J.S.; Rakshit, A. On-farm seed priming interventions in agronomic crops. Acta Agric. Slov. 2018, 111, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Usman, M.; Nadeem, F.; Rehman, H.U.; Wahid, A.; Basra, S.M.A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Seed priming in field crops: Potential benefits, adoption and challenges. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2019, 70, 731–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Singh, S. ZnO Nanoparticles Synthesis by Sol-Gel Method and Characterization. Indian J. Nanosci. 2016, 4, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.M.; Boardman, N. Studies on The Greening of Dark-Grown Bean Plants II. Development of Photochemical Activity. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1964, 17, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L.; Norvell, W.A. Development of a DTPA Soil Test for Zinc, Iron, Manganese, and Copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goering, H.K.; Van Soest, P.J. Forage Fiber Analyses (Apparatus, Reagents, Procedures, and Some Applications); Agriculture Research Service USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, S.; Cole, C.; Watanabe, F.; Dean, L. Estimation of Available Phosphorous by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Casida, L.E.; Klein, D.A.; Santoro, T. Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Sci. 1964, 98, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemingui, H.; Smiri, M.; Missaoui, T.; Hafiane, A. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induced Oxidative Stress and Changes in the Photosynthetic Apparatus in Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Panwar, S.; Kang, T.W.; Jeon, H.C.; Kumar, S.; Choubey, R.K. Effect of zinc oxide concentration in fluorescent ZnS:Mn/ZnO core-shell nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2014, 25, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakirov, M.I.; Semen’ko, M.P.; Korotchenkov, O.A. A simple sonochemical synthesis of nanosized ZnO from zinc acetate and sodium hydroxide. J. Nano Electron. Phys. 2018, 10, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturikova, H.; Krystofova, O.; Huska, D.; Adam, V. Zinc, zinc nanoparticles and plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 349, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, R. Effect of seed priming and foliar application with micronutrients on quality of forage corn (Zea mays). Environ. Exp. Biol. 2016, 14, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdieh, M.; Sangi, M.R.; Bamdad, F.; Ghanem, A. Effect of seed and foliar application of nano-zinc oxide, zinc chelate, and zinc sulphate rates on yield and growth of pinto bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) cultivars. J. Plant. Nutr. 2018, 41, 2401–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Faraz, A.; Yusuf, M.; Khan, S.T.; Hayat, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticle-mediated changes in photosynthetic efficiency and antioxidant system of tomato plants. Photosynthetica 2018, 56, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolenčík, M.; Ernst, D.; Komár, M.; Urík, M.; Šebesta, M.; Dobročka, E.; Černý, I.; Illa, R.; Kanike, R.; Qian, Y.; et al. Effect of foliar spray application of zinc oxide nanoparticles on quantitative, nutritional, and physiological parameters of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) under field conditions. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, D.M.; Osman, S.A.; Abd El-Aziz, M.E.; Abd Elwahed, M.S.A.; Shaaban, E.A. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the growth, genomic DNA, production and the quality of common dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 18, 101083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, T.; Kundu, S.; Rao, A.S. Zinc delivery to plants through seed coating with nano-zinc oxide particles. J. Plant. Nutr. 2016, 39, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, A.; Shahrajabian, M.H. The Effects of Fe, Mn and Zn Foliar Application on Yield, Ash and Protein Percentage of Forage Sorghum in Climatic Condition of Esfahan. Int. J. Biol. 2012, 4, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yu, S.; Chen, H. Organic acids exuded from roots increase the available potassium content in the rhizosphere soil: A rhizobag experiment in Nicotiana tabacum. HortScience 2019, 54, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Li, L.; Liang, J. Effects of Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria on the Growth, Photosynthesis, and Nutrient Uptake of Camellia oleifera Abel. Forests 2019, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, S.; Kafle, A. Comparative study of Azotobacter with or without other fertilizers on growth and yield of wheat in Western hills of Nepal. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2018, 16, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bageshwar, U.K.; Srivastava, M.; Pardha-Saradhi, P.; Paul, S.; Gothandapani, S.; Jaat, R.S.; Shankar, P.; Yadav, R.; Biswas, D.R.; Kumar, P.A.; et al. An environmentally friendly engineered Azotobacter strain that replaces a substantial amount of urea fertilizer while sustaining the same wheat yield. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Schimel, J.P.; Holdena, P.A. Identification of soil bacteria susceptible to TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6749–6758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raliya, R.; Tarafdar, J.C. ZnO Nanoparticle Biosynthesis and Its Effect on Phosphorous-Mobilizing Enzyme Secretion and Gum Contents in Clusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.). Agric. Res. 2013, 2, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raliya, R.; Saharan, V.; Dimkpa, C.; Biswas, P. Nanofertilizer for Precision and Sustainable Agriculture: Current State and Future Perspectives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6487–6503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimkpa, C.O.; White, J.C.; Elmer, W.H.; Gardea-Torresdey, J. Nanoparticle and ionic Zn promote nutrient loading of sorghum grain under low NPK fertilization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 8552–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, F.; Shi, Z.; Tong, R.; Shi, X. Bioavailability of Zn in ZnO nanoparticle-spiked soil and the implications to maize plants. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-González, J.; Ojeda-Barrios, D.; Hernández-Rodríguez, A.; González-Franco, A.C.; Robles-Hernández, L.; López-Ochoa, G.R. Zinc metalloenzymes in plants. Interciencia 2018, 43, 242–248. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Rakshit, R.; Bhowmik, A.; Mandal, N.; Das, A.; Adhikary, S. Nanoparticle-induced changes in resistance and resilience of sensitive microbial indicators towards heat stress in soil. Sustainability 2019, 11, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popović, V.; Ljubičić, N.; Kostić, M.; Radulović, M.; Blagojević, D.; Ugrenović, V.; Popović, D.; Ivošević, B. Genotype×Environment Interaction for Wheat Yield Traits Suitable for Selection in Different Seed Priming Conditions. Plants 2020, 9, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, Y.; Shah, G.A.; Rashid, M.I. ZnO nanoparticles and zeolite influence soil nutrient availability but do not affect herbage nitrogen uptake from biogas slurry. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
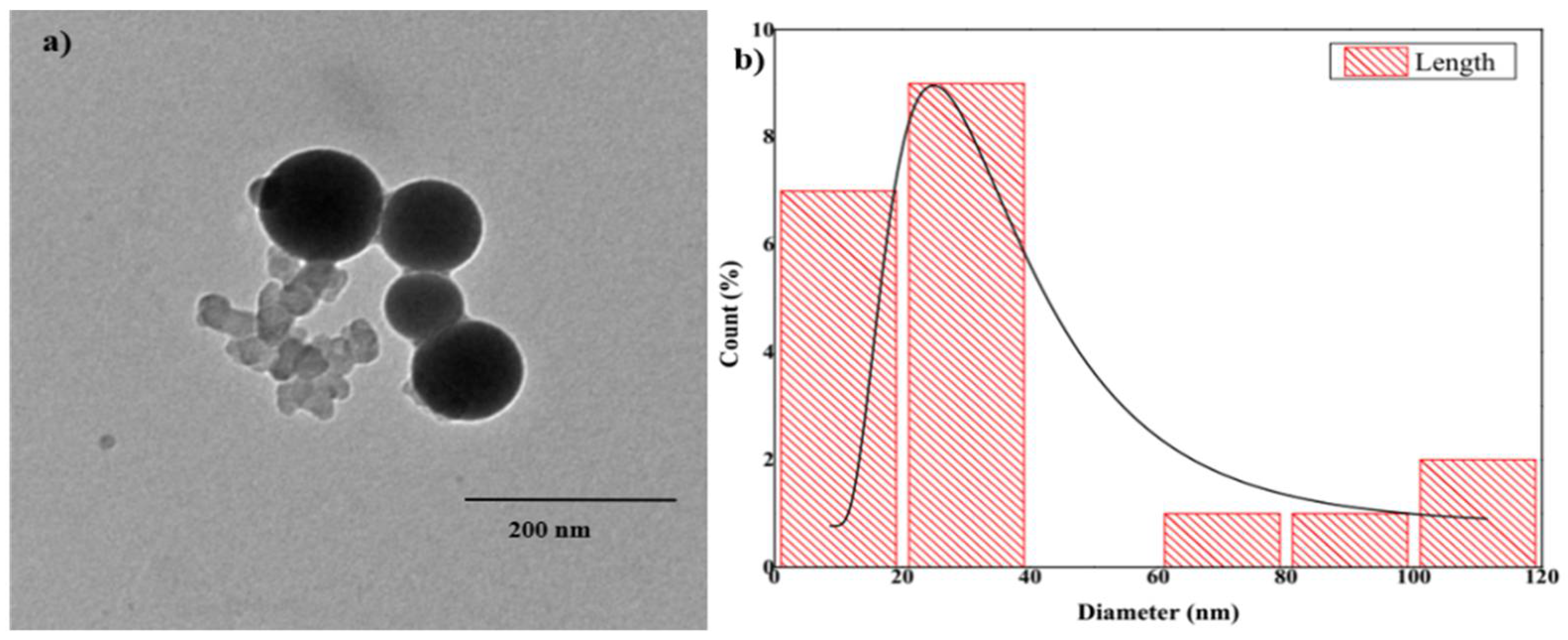
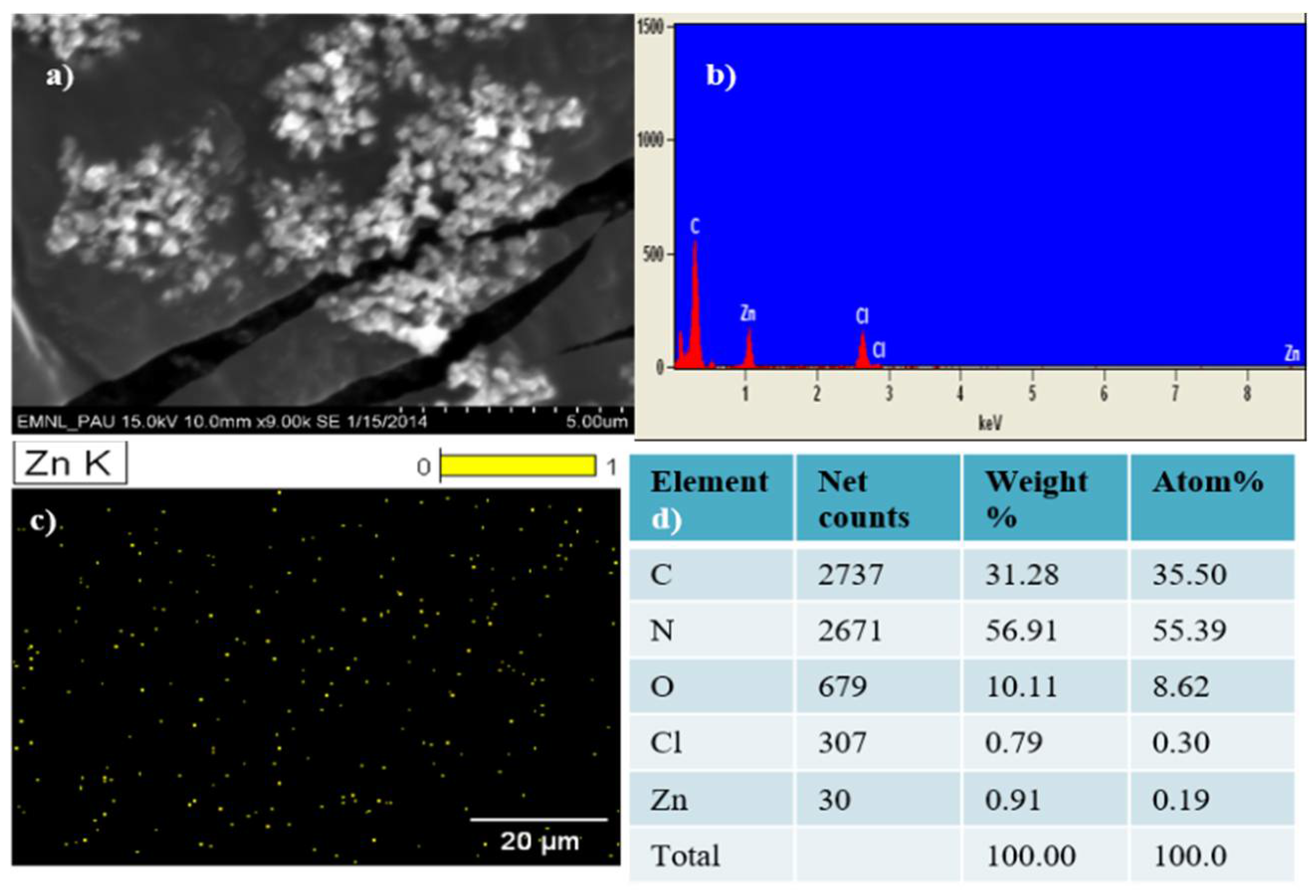

| Soil Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Type | Sandy loam |
| pH | 8.56 |
| EC (dS m−1) | 0.4 |
| OC (%) | 0.52 |
| Clay (%) | 12 |
| Sand (%) | 70 |
| Silt (%) | 18 |
| Treatments | No. of Plants | Plant Height (cm) | Leaf Number | No. of Internode | Total Stover Yield (Quintal ha−1) | Mean Fresh Shoot wt. (kg) | Mean Root Fresh wt. (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed Treatment | Priming | 34.0 a | 222.13 a | 10.0 b | 7.0 a | 37.02 a | 2.036 a | 290.67 b |
| Coating | 33.0 a | 224.20 a | 11.0 a | 8.0 a | 36.72 a | 2.108 a | 340.87 a | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 26.0 b | 210.00 c | 8.0 c | 7.00 c | 31.07 b | 1.810 c | 244.00 c |
| ZnSO4 20 | 29.0 b | 207.66 c | 10.0 b | 7.50 bc | 32.23 b | 1.860 bc | 246.67 c | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 37.0 a | 219.33 b | 11.0 b | 7.83 b | 38.58 a | 1.730 c | 280.33 c | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 38.0 a | 241.83 a | 12.0 a | 8.83 a | 43.45 a | 2.620 a | 437.50 a | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 37.0 a | 237.00 a | 12.0 a | 9.50 a | 39.02 a | 2.310 ab | 370.33 b | |
| Source of Variation | Chlorophyll Content (SPAD Readings) | Total Chlorophyll (mg g−1 Fresh Leaf Tissue) | Total Carotenoids (mg g−1 Fresh Leaf Tissue) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days after sowing (DAS) | 30 | 44.63 b | 8.59 b | 0.36 b |
| 60 | 46.70 a | 10.22 a | 0.57 a | |
| Seed treatment | Priming | 45.64 b | 9.05 b | 0.468 a |
| Coating | 49.14 a | 9.76 a | 0.464 a | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 44.60 c | 6.24 e | 0.443 bc |
| ZnSO4 20 | 44.85 c | 9.63 c | 0.463 b | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 48.02 ab | 8.83 d | 0.456 bc | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 47.84 ab | 11.67 a | 0.497 a | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 48.72 a | 10.66 b | 0.470 b | |
| Source of Variation | N (%) | K (%) | P (%) | Zn (mg kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant tissue | Shoot | 0.833 b | 6.707 b | 1.208 b | 3.27 b |
| Root | 1.186 a | 7.38 a | 1.229 a | 3.69 a | |
| Seed Treatment | Priming | 0.898 b | 6.586 b | 1.155 b | 1.60 b |
| Coating | 1.120 a | 8.130 a | 1.237 a | 3.77 a | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 0.703 e | 4.063 e | 1.076 e | 1.158 e |
| ZnSO4 20 | 0.923 d | 6.70 d | 1.157 d | 2.456 c | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 1.032 c | 7.94 c | 1.201 c | 2.412 d | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 1.137 b | 8.87 b | 1.250 b | 4.167 a | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 1.251 a | 9.20 a | 1.297 a | 3.275 b | |
| Source of Variation | NDF (%) | ADF (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Cellulose (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed Treatment | Priming | 62.42a | 38.22 b | 24.18 a | 29.00 b |
| Coating | 60.60 a | 40.20 a | 20.90 b | 30.33 a | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 57.30 e | 37.86 bc | 19.43 d | 28.80 b |
| ZnSO4 20 | 59.80 d | 38.45 b | 21.35 c | 28.61 b | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 62.05 c | 36.18 c | 25.71 a | 28.88 b | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 63.16 b | 42.41 a | 24.16 b | 30.76 a | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 65.23 a | 41.13 a | 22.03 c | 31.26 a | |
| Source of Variation | N (kg ha−1) | K (kg ha−1) | P (kg ha−1) | Zn (mg kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAS | 35 | 206.72 b | 198.98 b | 20.10 b | 2.36 b |
| 60 | 216.53a | 211.56 a | 24.08 a | 2.70 a | |
| Seed Treatment | Priming | 190.13 b | 199.54 b | 22.25 a | 2.60 a |
| Coating | 233.12 a | 211.01 a | 21.95 b | 2.46 b | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 152.80 e | 190.89 d | 13.47 e | 2.31 e |
| ZnSO4 20 | 191.05 d | 199.54 c | 18.62 d | 2.88 a | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 221.78 c | 207.38 b | 20.07 c | 2.61 a | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 240.96 b | 214.61 a | 27.25 b | 2.44 c | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 251.53 a | 213.94 a | 31.03 a | 2.40 d | |
| Source of Variation | Dehydrogenase Activity (μg TPF Formed/g Soil/h) | Phosphatase Activity (μg PNP/g of Soil) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acid | Alkaline | |||
| DAS | 35 | 1.2620 a | 0.9035 a | 0.8240 b |
| 60 | 1.2413 b | 0.8716 b | 1.0483 a | |
| Seed Treatment | Priming | 1.2323 b | 0.7886 b | 0.6660 b |
| Coating | 1.2710 a | 0.9865 a | 1.20633 a | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 0.7325 e | 0.5108 e | 0.5108 e |
| ZnSO4 20 | 1.1775 d | 0.8716 d | 0.8400 d | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 1.2366 c | 0.9430 c | 0.9225 c | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 1.5316 b | 1.0350 b | 1.1150 b | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 1.5800 a | 1.0775 a | 1.2925 a | |
| Source of Variation | Bacteria | Fungi | Pseudomonads | Actinobacteria | Non-Symbiotic N-Fixers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAS | 35 | 2.8760 b | 1.7333 b | 2.3070 b | 2.4063 b | 3.1266 a |
| 60 | 2.9265 a | 1.9368 a | 2.4166 a | 2.4883 a | 3.1363a | |
| Seed Treatment | Priming | 2.8281 b | 1.7856 b | 2.3556 b | 2.4080 b | 2.9723 b |
| Coating | 2.9744 a | 1.8845 a | 2.3680 a | 2.4866 a | 3.3006 a | |
| Zn source (mg L−1) | 0 | 2.6808 e | 1.7225 c | 2.2166 e | 2.3058 e | 2.5567 b |
| ZnSO4 20 | 2.9766 b | 1.7333 c | 2.2933 d | 2.4350 d | 3.1900 a | |
| ZnSO4 40 | 2.0166 d | 1.7822 b | 2.3508 c | 2.4608 c | 3.2033 a | |
| ZnONPs 20 | 2.9366 c | 1.9665 a | 2.4891 a | 2.4908 b | 3.3325 a | |
| ZnONPs 40 | 2.9954 a | 1.9708 a | 2.4591 b | 2.5441 a | 3.4000 a | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tondey, M.; Kalia, A.; Singh, A.; Dheri, G.S.; Taggar, M.S.; Nepovimova, E.; Krejcar, O.; Kuca, K. Seed Priming and Coating by Nano-Scale Zinc Oxide Particles Improved Vegetative Growth, Yield and Quality of Fodder Maize (Zea mays). Agronomy 2021, 11, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040729
Tondey M, Kalia A, Singh A, Dheri GS, Taggar MS, Nepovimova E, Krejcar O, Kuca K. Seed Priming and Coating by Nano-Scale Zinc Oxide Particles Improved Vegetative Growth, Yield and Quality of Fodder Maize (Zea mays). Agronomy. 2021; 11(4):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040729
Chicago/Turabian StyleTondey, Manisha, Anu Kalia, Alla Singh, Gurmeet Singh Dheri, Monica Sachdeva Taggar, Eugenie Nepovimova, Ondrej Krejcar, and Kamil Kuca. 2021. "Seed Priming and Coating by Nano-Scale Zinc Oxide Particles Improved Vegetative Growth, Yield and Quality of Fodder Maize (Zea mays)" Agronomy 11, no. 4: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040729
APA StyleTondey, M., Kalia, A., Singh, A., Dheri, G. S., Taggar, M. S., Nepovimova, E., Krejcar, O., & Kuca, K. (2021). Seed Priming and Coating by Nano-Scale Zinc Oxide Particles Improved Vegetative Growth, Yield and Quality of Fodder Maize (Zea mays). Agronomy, 11(4), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11040729









